Comorbidity Prevalence in Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Predominantly Hispanic U.S.–Mexico Border Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parker, E.D.; Lin, J.; Mahoney, T.; Ume, N.; Yang, G.; Gabbay, R.A.; ElSayed, N.A.; Bannuru, R.R. Economic Costs of Diabetes in the U.S. in 2022. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. National Diabetes Statistics Report. 15 May 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/index.html (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- CDC. The Surprising Truth About Prediabetes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 15 May 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/prevention-type-2/truth-about-prediabetes.html (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Cai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, J.H.; Mai, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y. Association between prediabetes and risk of all cause mortality and cardiovascular disease: Updated meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 370, m2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutie, P.M.; Pomares-Millan, H.; Atabaki-Pasdar, N.; Jordan, N.; Adams, R.; Daly, N.L.; Tajes, J.F.; Giordano, G.N.; Franks, P.W. An investigation of causal relationships between prediabetes and vascular complications. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, M.R.; Rawlings, A.M.; Pankow, J.S.; Tcheugui, J.B.E.; Coresh, J.; Sharrett, A.R.; Selvin, E. Risk of Progression to Diabetes Among Older Adults With Prediabetes. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, S.; Neuenschwander, M.; Barbaresko, J.; Lang, A.; Maalmi, H.; Rathmann, W.; Roden, M.; Herder, C. Prediabetes and risk of mortality, diabetes-related complications and comorbidities: Umbrella review of meta-analyses of prospective studies. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.L.; Kalyani, R.R.; Golden, S.; Stearns, S.C.; Wruck, L.; Yeh, H.C.; Coresh, J.; Selvin, E. Diabetes and Prediabetes and Risk of Hospitalization: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.P.; Cheng, T.Y.D.; Tsai, S.P.; Hsu, H.L.; Wang, S.L. Increased Mortality Risks of Pre-Diabetes (Impaired Fasting Glucose) in Taiwan. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2756–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowska, M.; Zghebi, S.S.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Buchan, I.; Chew-Graham, C.; Holt, T.; Mallen, C.; Van Marwijk, H.; Peek, N.; Perera-Salazar, R.; et al. The comorbidity burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Patterns, clusters and predictions from a large English primary care cohort. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.K.; Bullard, K.M.; Saydah, S.; Imperatore, G.; Gregg, E.W. Cardiovascular and renal burdens of prediabetes in the USA: Analysis of data from serial cross-sectional surveys, 1988–2014. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilat-Tsanani, S.; Margalit, A.; Golan, L.N. Occurrence of comorbidities in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients and their impact after 11 years’ follow-up. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglay, K.; Hannachi, H.; Howie, P.J.; Xu, J.; Li, X.; Engel, S.S.; Moore, L.M.; Rajpathak, S. Prevalence and co-prevalence of comorbidities among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2016, 32, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safieddine, B.; Sperlich, S.; Epping, J.; Lange, K.; Geyer, S. Development of comorbidities in type 2 diabetes between 2005 and 2017 using German claims data. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagami, T.; the DECODA Study Group. Hyperglycaemia and mortality from all causes and from cardiovascular disease in five populations of Asian origin. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saydah, S.H.; Loria, C.M.; Eberhardt, M.S.; Brancati, F.L. Subclinical States of Glucose Intolerance and Risk of Death in the U.S. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veugen, M.G.J.; Onete, V.G.; Henry, R.M.A.; Rocca, H.-P.B.-L.; Koster, A.; Dagnelie, P.C.; Schaper, N.C.; Sep, S.J.S.; van der Kallen, C.J.H.; van Boxtel, M.P.J.; et al. Health burden in type 2 diabetes and prediabetes in The Maastricht Study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranfar, N.; Smith, T.C. When Should “Pre” Carry as Much Weight in the Diabetes Comorbidity Debate? Insights from a Population-Based Survey. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2018, 15, E36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. ICD-10-CM. 7 June 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/icd/icd-10-cm/index.html (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Diabetes, Now What? Available online: https://pdnhf.org/health-articles/diabetes-now-what (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Hackl, C.M.; Lee, W.C.; Sallam, H.S.; Jneid, H.; Campbell, K.M.; Serag, H. Racial Disparities in Selected Complications and Comorbidities among People with Type 2 Diabetes. Healthcare 2024, 12, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanakis, E.K.; Golden, S.H. Race/Ethnic Difference in Diabetes and Diabetic Complications. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2013, 13, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sidell, M.A.; Arterburn, D.; Daley, M.F.; Desai, J.; Fitzpatrick, S.L.; Horberg, M.A.; Koebnick, C.; McCormick, E.; Oshiro, C.; et al. Racial/Ethnic Disparities in the Prevalence of Diabetes and Prediabetes by BMI: Patient Outcomes Research To Advance Learning (PORTAL) Multisite Cohort of Adults in the U.S. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. Akaike, H. A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification. In Selected Papers of Hirotugu Akaike; Parzen, E., Tanabe, K., Kitagawa, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaviz, K.I.; Weber, M.B.; Suvada, K.; Gujral, U.P.; Wei, J.; Merchant, R.; Dharanendra, S.; Haw, J.S.; Narayan, K.V.; Ali, M.K. Interventions for Reversing Prediabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2022, 62, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, S.H.; Maruthur, N.; Mathioudakis, N.; Spanakis, E.; Rubin, D.; Zilbermint, M.; Hill-Briggs, F. The Case for Diabetes Population Health Improvement: Evidence-Based Programming for Population Outcomes in Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2017, 17, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malin, S.K.; Gerber, R.; Chipkin, S.R.; Braun, B. Independent and combined effects of exercise training and metformin on insulin sensitivity in individuals with prediabetes. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.-R.; Li, G.-W.; Hu, Y.-H.; Yang, W.-Y.; An, Z.-X.; Hu, Z.-X.; Lin, J.; Xiao, J.-Z.; Cao, H.-B.; Liu, P.-A.; et al. Effects of diet and exercise in preventing NIDDM in people with impaired glucose tolerance. The Da Qing IGT and Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Snehalatha, C.; Mary, S.; Mukesh, B.; Bhaskar, A.D.; Vijay, V.; Indian Diabetes Prevention Programme (IDPP). The Indian Diabetes Prevention Programme shows that lifestyle modification and metformin prevent type 2 diabetes in Asian Indian subjects with impaired glucose tolerance (IDPP-1). Diabetologia 2006, 49, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruss, S.M.; Nhim, K.; Gregg, E.; Bell, M.; Luman, E.; Albright, A. Public Health Approaches to Type 2 Diabetes Prevention: The US National Diabetes Prevention Program and Beyond. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, R.F.; Wing, R.R.; Edelstein, S.L.; Lachin, J.M.; Bray, G.A.; Delahanty, L.; Hoskin, M.; Kriska, A.M.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Pi-Sunyer, X.; et al. Effect of weight loss with lifestyle intervention on risk of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2102–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, A.; Shi, L.; Nasrollahzadeh, A.A.; Narayanan, H.; Chen, L. Comparing the Lifestyle Interventions for Prediabetes: An Integrated Microsimulation and Population Simulation Model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.M.M.; Chua, Z.J.Y.; Tan, J.C.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Z.; Zhao, Y. From Pre-Diabetes to Diabetes: Diagnosis, Treatments and Translational Research. Medicina 2019, 55, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | No. (Column %) | |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis of Prediabetes (n = 12,071) | Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes (n = 88,724) | |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 4415 (36.6) | 40,176 (45.3) |
| Female | 7618 (63.1) | 48,196 (54.3) |
| Unknown | 38 (0.3) | 352 (0.4) |
| Age decade | ||
| <29 | 652 (5.4) | 1986 (2.2) |
| 30–39 | 1031 (8.5) | 4442 (5.0) |
| 40–49 | 2036 (16.9) | 9727 (11.0) |
| 40–59 | 3145 (26.1) | 17,468 (19.7) |
| 60–69 | 3066 (24.4) | 24,510 (27.6) |
| 70–79 | 1446 (12.0) | 18,961 (21.4) |
| 80–89 | 576 (4.8) | 9472 (10.7) |
| >90 | 119 (1.0) | 2158 (2.4) |
| Race | ||
| African American or Black | 16 (0.1) | 199 (0.2) |
| Asian | 15 (01) | 89 (0.1) |
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 3 (0.02) | 58 (0.1) |
| Pacific Islander | 40 (0.3) | 276 (0.3) |
| White | 7705 (63.8) | 57,240 (64.5) |
| Other | 3213 (26.6) | 11,005 (12.4) |
| Unknown | 1079 (8.9) | 19,857 (22.4) |
| Ethnicity | ||
| Hispanic | 8482 (70.3) | 61,498 (69.3) |
| Non-Hispanic | 3589 (29.7) | 27,226 (30.7) |
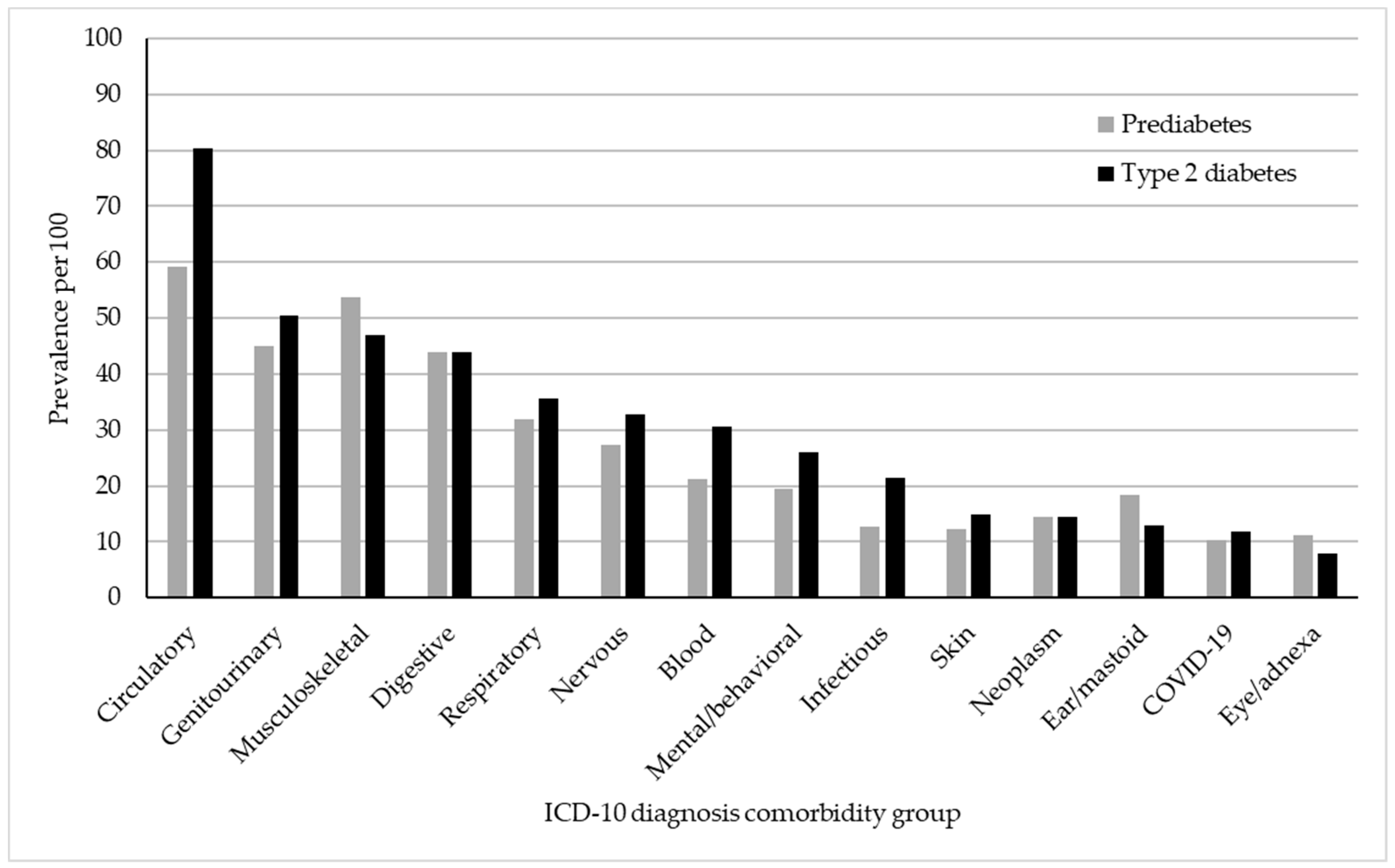
| Prevalence per 100 | Prevalence Difference per 100 (95% CI) | Prevalence Ratio (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prediabetes | Type 2 Diabetes | Unadjusted Model | Adjusted Model (Age, Gender, and Ethnicity) | Unadjusted Model | Adjusted Model (Age, Gender, and Ethnicity) | |
| Diseases of the circulatory system | 59.1 | 80.4 | −21.3 *** (−22.3, −20.4) | −14.6 *** (−15.7, −13.7) | 0.73 *** (0.72, 0.75) | 0.82 *** (0.81, 0.84) |
| Diseases of the genitourinary system | 44.9 | 50.5 | −5.6 *** (−6.6, −4.7) | −1.3 ** (−2.3, −0.4) | 0.89 *** (0.87, 0.91) | 0.97 * (0.96, 0.99) |
| Diseases of the musculoskeletal and connective tissue | 53.8 | 47.0 | 6.8 *** (5.8, 7.7) | 8.5 *** (7.5, 9.4) | 1.14 *** (1.12, 1.16) | 1.19 *** (1.17, 1.21) |
| Diseases of the digestive system | 44.0 | 44.0 | −0.01 (−1.0, −0.9) | 1.1 * (0.1, 2.0) | 1.00 (0.99, 1.02) | 1.02 * (1.00, 1.05) |
| Diseases of the respiratory system | 32.0 | 35.7 | −3.7 *** (−4.6, −2.8) | −2.1 *** (−3.0, −1.2) | 0.90 *** (0.87, 0.92) | 0.94 *** (0.92, 0.97) |
| Diseases of the nervous system | 27.4 | 32.8 | −5.4 *** (−6.3, −4.6) | −3.2 *** (−4.1, −2.4) | 0.83 *** (0.81, 0.86) | 0.91 *** (0.88, 0.94) |
| Diseases of the blood | 21.2 | 30.5 | −9.28 *** (−10.1, −8.5) | −6.7 *** (−7.4, −5.9) | 0.70 *** (0.67, 0.72) | 0.77 *** (0.75, 0.80) |
| Mental and behavioral illnesses | 19.5 | 26.1 | −6.6 *** (−7.4, −5.9) | −7.2 *** (−8.0, −6.5) | 0.75 *** (0.72, 0.78) | 0.72 *** (0.69, 0.75) |
| Infectious and parasitic diseases | 12.8 | 21.5 | −8.6 *** (−9.3, −8.0) | −7.5 *** (−8.2, −6.9) | 0.60 *** (0.57, 0.63) | 0.63 *** (0.60, 0.66) |
| Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue | 12.2 | 14.8 | −2.6 *** (−3.2, −2.0) | −2.5 *** (−3.1, −1.8) | 0.82 *** (0.78, 0.87) | 0.82 *** (0.78, 0.86) |
| Neoplasms | 14.4 | 14.5 | −0.1 (−0.8, 0.6) | 1.7 (1.0, 2.3) | 0.99 (0.95, 1.04) | 1.12 *** (1.06, 1.17) |
| Diseases of the ear and mastoid process | 18.4 | 12.9 | 5.4 *** (4.7, 6.2) | 6.1 *** (5.3, 6.8) | 1.42 *** (1.36, 1.48) | 1.54 *** (1.47, 1.60) |
| COVID-19 and post-COVID-19 | 10.2 | 11.9 | −1.7 *** (−2.3, 1.1) | −1.6 ** (−2.2, −1.0) | 0.86 *** (0.81, 91) | 0.86 *** (0.81, 0.91) |
| Diseases of the eye and adnexa | 11.1 | 7.8 | 3.3 *** (2.7, 3.9) | 3.5 *** (2.9, 4.1) | 1.42 *** (1.34, 1.50) | 1.52 *** (1.43, 1.61) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noriega, R.X.; Nañez, J.J.; Hartmann, E.F.; Beard, J.D.; Sloan-Aagard, C.D.; Thacker, E.L. Comorbidity Prevalence in Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Predominantly Hispanic U.S.–Mexico Border Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050673
Noriega RX, Nañez JJ, Hartmann EF, Beard JD, Sloan-Aagard CD, Thacker EL. Comorbidity Prevalence in Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Predominantly Hispanic U.S.–Mexico Border Population. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(5):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050673
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoriega, Ricardo X., Juan J. Nañez, Emily F. Hartmann, John D. Beard, Chantel D. Sloan-Aagard, and Evan L. Thacker. 2025. "Comorbidity Prevalence in Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Predominantly Hispanic U.S.–Mexico Border Population" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 5: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050673
APA StyleNoriega, R. X., Nañez, J. J., Hartmann, E. F., Beard, J. D., Sloan-Aagard, C. D., & Thacker, E. L. (2025). Comorbidity Prevalence in Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Predominantly Hispanic U.S.–Mexico Border Population. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(5), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050673







