Forecasting the Status of Municipal Waste in Smart Bins Using Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Study
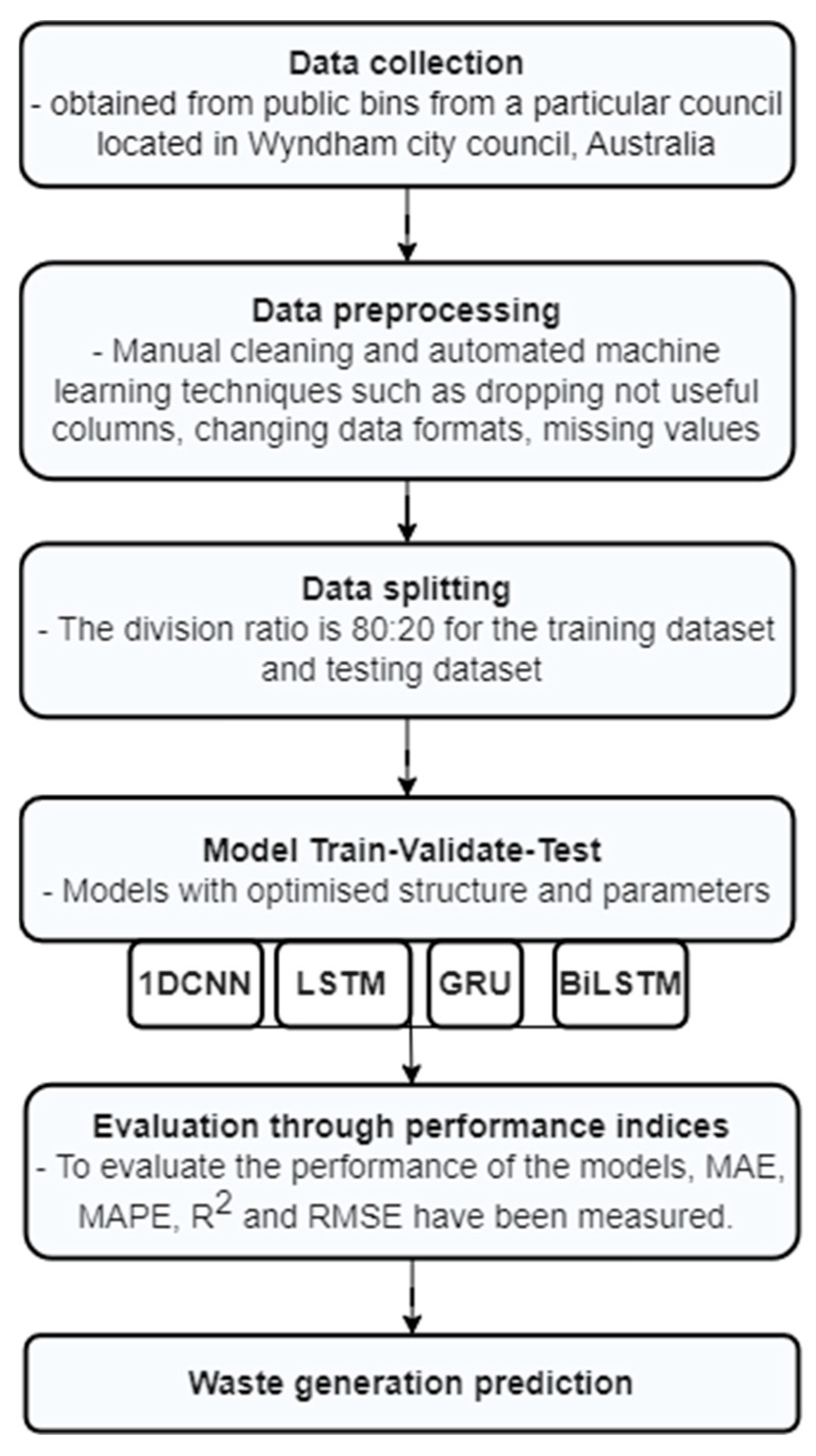
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Deep Learning Models
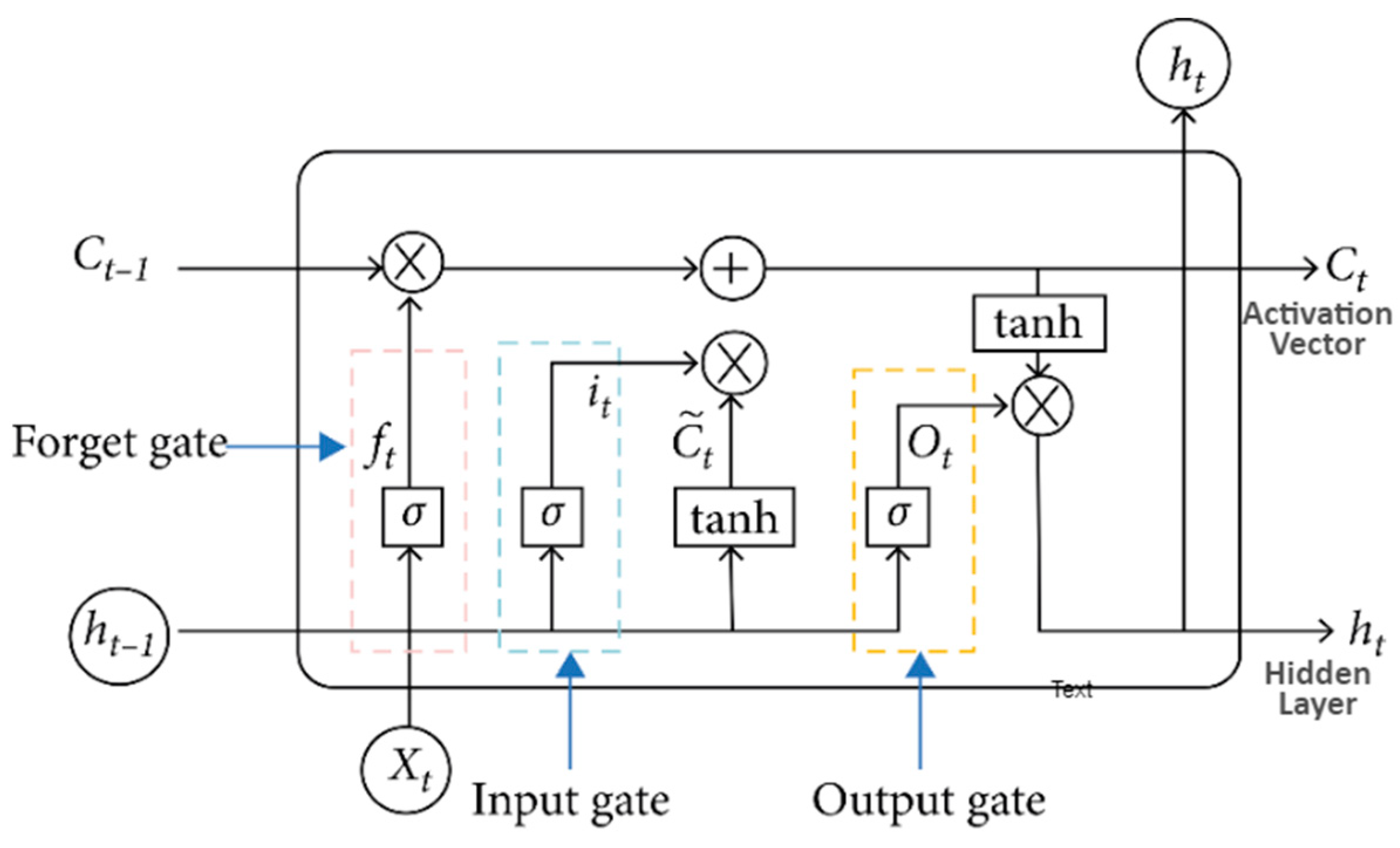
3.1.1. LSTM Model
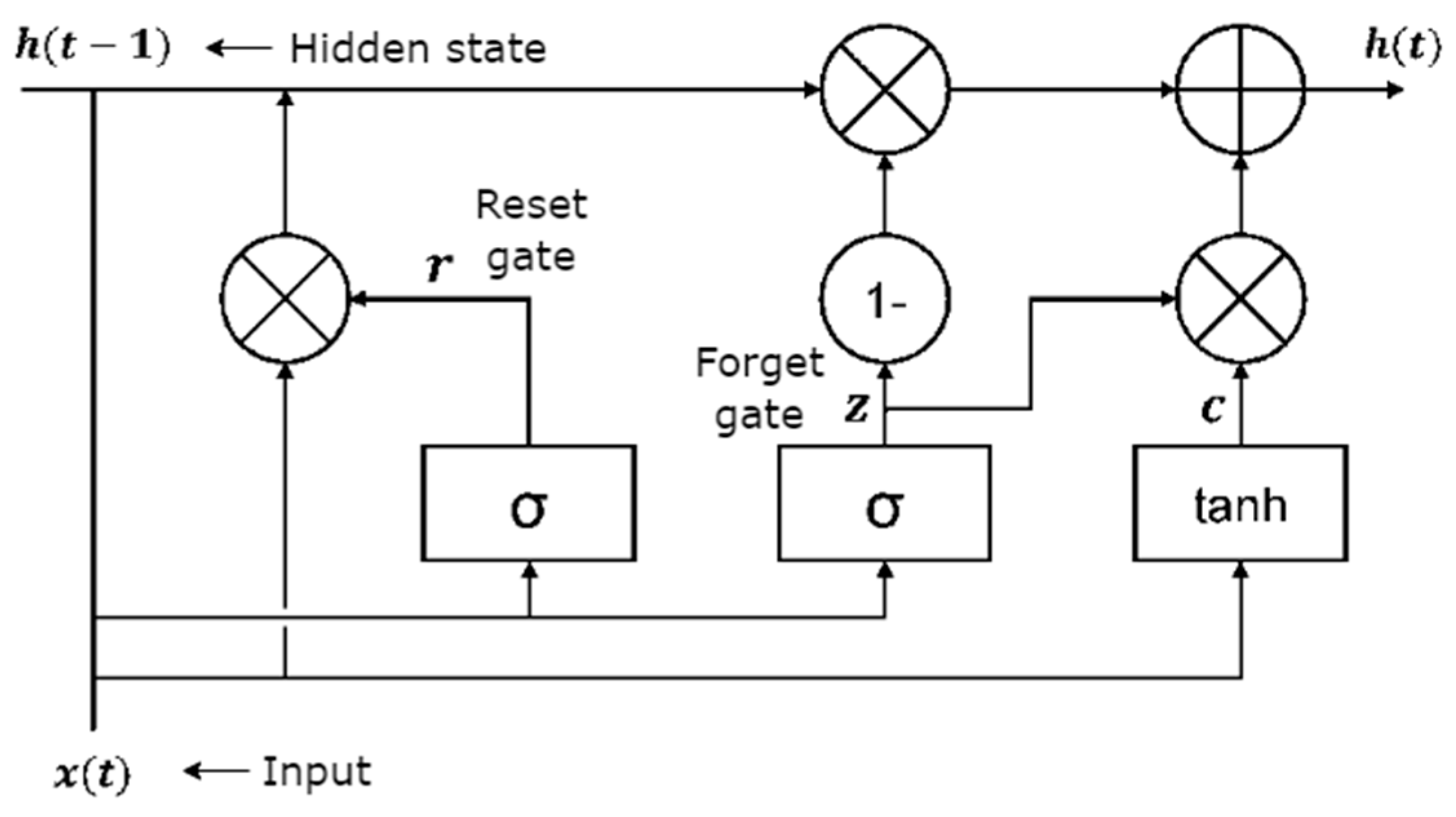
3.1.2. GRU Model
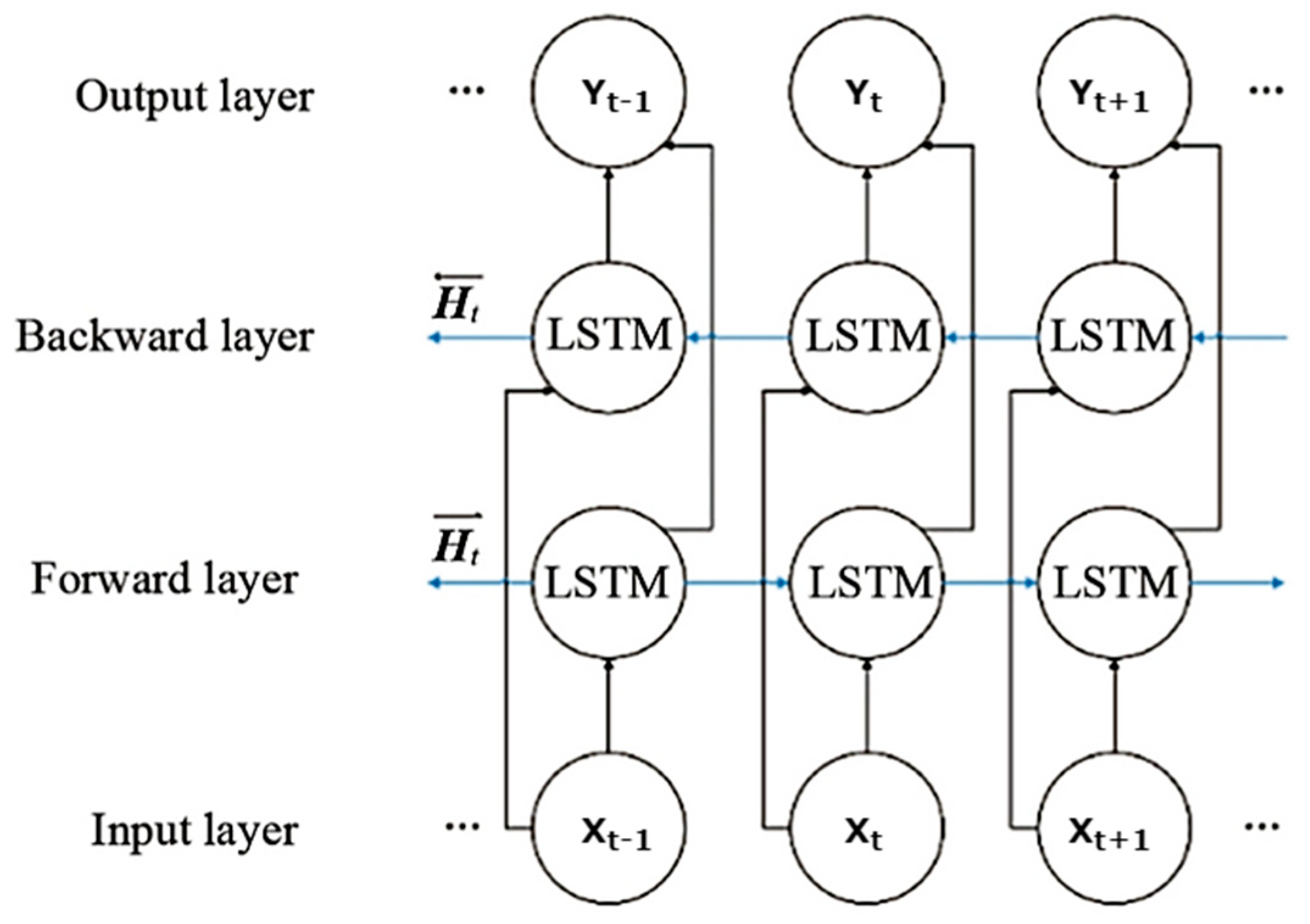
3.1.3. Bidirectional LSTM Model
3.2. Performance Indices
3.3. Data Description
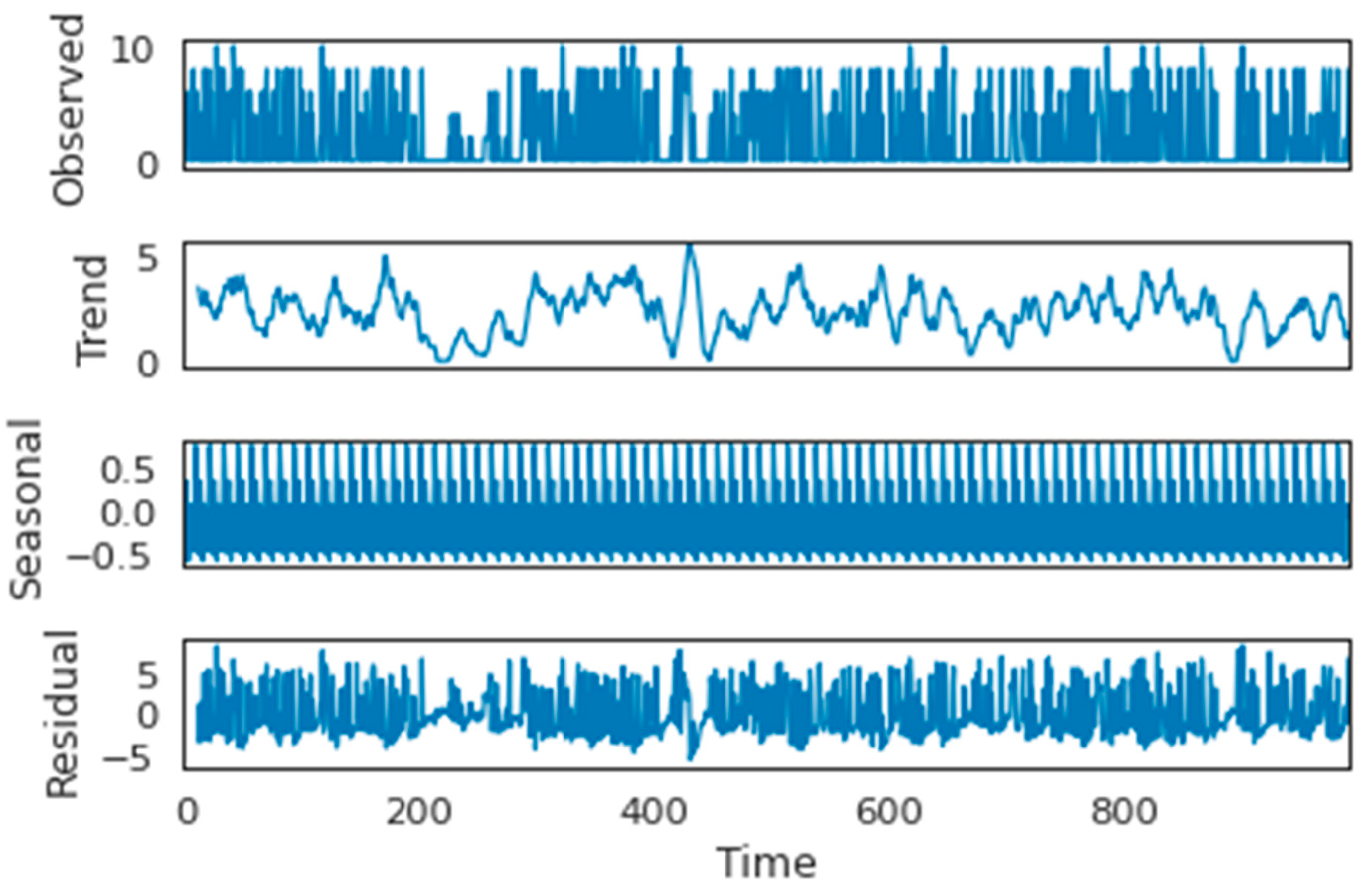
3.4. Data Exploration
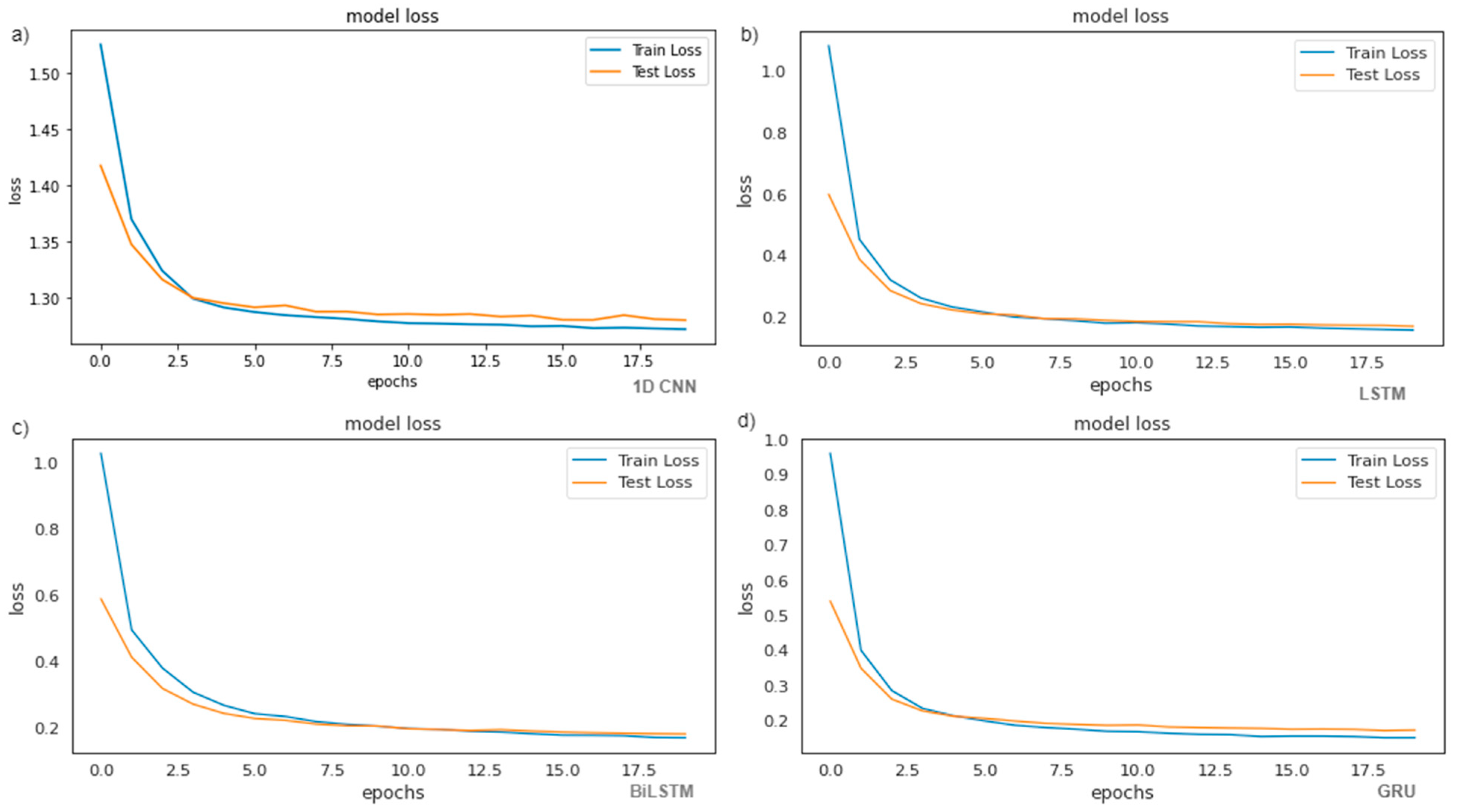
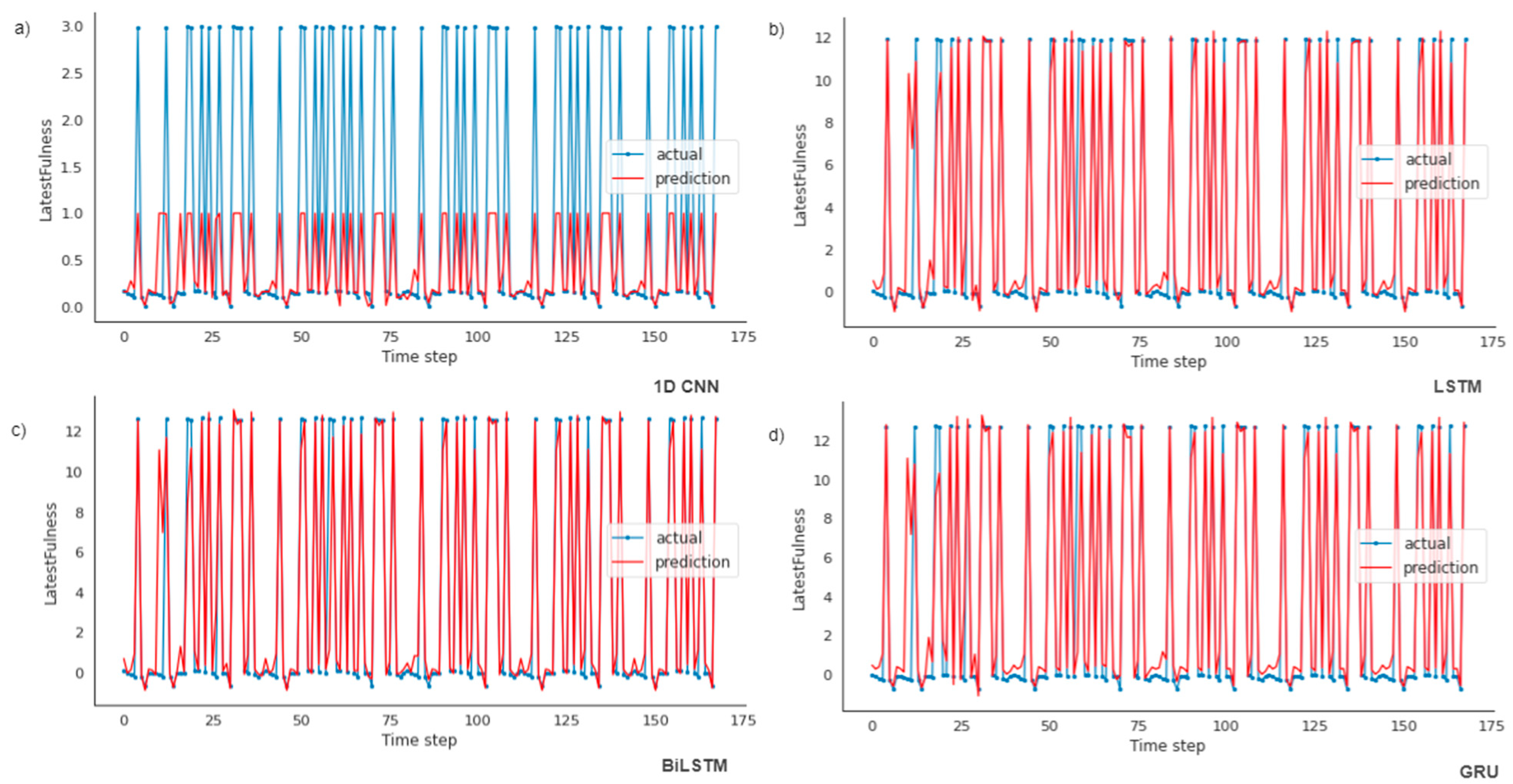
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sosunova, I.; Porras, J. IoT-Enabled Smart Waste Management Systems for Smart Cities: A Systematic Review. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 73326–73363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Anjum, R.; Raza, S.T.; Ahmed Bazai, N.; Ihtisham, M. Technologies for Municipal Solid Waste Management: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andeobu, L.; Wibowo, S.; Grandhi, S. A Systematic Review of E-waste Generation and Environmental Management of Asia Pacific Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Zhou, C.; Chi, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G. Estimating Physical Composition of Municipal Solid Waste in China by Applying Artificial Neural Network Method. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9609–9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, T. Estimation of Municipal Solid Waste Amount Based on One-Dimension C N Network and Long Short-Term Memory with Attention Mechanism Model: A Case Study of Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Joshi, S.; Kannan, D.; Govindan, K.; Singh, R.; Purohit, H. Internet of Things (IoT) Adoption Barriers of Smart cities’ Waste Management: An Indian Context. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassim, M.S.; Coskuner, G.; Zontul, M. Comparative Performance Analysis of Support Vector Regression and Artificial Neural Network for Prediction of Municipal Solid Waste Generation. Waste Manage. Res. 2022, 40, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Zhao, Y.; Kuo, J.-H.; Deng, H.; Cui, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, C.; Gao, X.; Zhou, T.; et al. Toward smarter management and recovery of municipal solid waste: A critical review on deep learning approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 346, 130943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, F.; Addante, A.S.; Valenzano, B.; Scannicchio, G. Variables Influencing per Capita Production, Separate Collection, and Costs of Municipal Solid Waste in the Apulia Region (Italy): An Experience of Deep Learning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Draz, U.; Ali, T.; Tariq, S.; Irfan, M.; Glowacz, A.; Antonino Daviu, J.A.; Yasin, S.; Rahman, S. Waste Management and Prediction of Air Pollutants Using IoT and Machine Learning Approach. Energies 2020, 13, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I.; Alam, G.; Jamal, A.; Shaik, F. Recent Advances in Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Solid Waste Management: A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, R.; Ryan, P. Big Data Analytics in Australian Local Government. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.; Ryan, P. Visualization and Waste Collection Route Heuristics of Smart Bins Data using Python Big Data Analytics. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Software Engineering and Information Management, Yokohama, Japan, 16–18 January 2021; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Wang, W.; Chaudhry, N.; Geng, Y. Hospital Waste Management in Developing Countries: A Mini Review. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolis, V.; Capón-García, E.; Weder, O.; Hungerbühler, K. New Classification of Chemical Hazardous Liquid Waste for the Estimation of its Energy Recovery Potential based on Existing Measurements. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferronato, N.; Torretta, V. Waste Mismanagement in Developing Countries: A Review of Global Issues. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettiarachchi, H.; Meegoda, J.N.; Ryu, S. Organic Waste Buyback as a Viable Method to Enhance Sustainable Municipal Solid Waste Management in Developing Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.W.; Islam, R.; Hasan, A.; Bithi, N.I.; Hasan, M.M.; Rahman, M.M. Intelligent Waste Management System Using Deep Learning with IoT. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 2072–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookkaiah, S.S.; Thangavelu, G.; Hebbar, R.; Haldar, N.; Singh, H. Design and Development of Smart Internet of Things–based Solid Waste Management System Using Computer Vision. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 64871–64885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, P.; Pamuła, T. Application of Deep Learning Object Classifier to Improve E-waste Collection Planning. Waste Manag. 2020, 109, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latha, C.J.; Kalaiselvi, K.; Ramanarayan, S.; Srivel, R.; Vani, S.; Sairam, T. Dynamic Convolutional Neural Network based E-waste Management and Optimized Collection Planning. Concurr. Computat. Pract. Exper. 2022, 34, e6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andeobu, L.; Wibowo, S.; Grandhi, S. Artificial Intelligence Applications for Sustainable Solid Waste Management Practices in Australia: A Systematic Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Ge, Z. Deep Learning for Industrial KPI Prediction: When Ensemble Learning Meets Semi-supervised Data. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, V.K.; Hersam, M.C. Neuromorphic Nanoelectronic Materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, P.; Aziz, F.; Newaz, M.T.; Sher, W.; Simon, L. The Classification of Construction Waste Material Using a Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Shree, V.; Hiremath, L.; Rajendran, S. The Use of Modern Technology in Smart Waste Management and Recycling: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. In Recent Advances in Computational Intelligence; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh Khoa, T.; Phuc, C.H.; Lam, P.D.; Nhu, L.M.B.; Trong, N.M.; Phuong, N.T.H.; Dung, N.V.; Tan-Y, N.; Nguyen, H.N.; Duc, D.N.M. Waste Management System Using IoT-Based Machine Learning in University. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2020, 2020, 6138637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, J.K.S.; Yepes, D.O.; Rodrigo-Ilarri, J.; Cassiraga, E. Predictive Analysis of Urban Waste Generation for the City of Bogotá, Colombia, Through the Implementation of Decision Trees-Based Machine Learning, Support Vector Machines and Artificial Neural Networks. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Wu, F.; Dai, S.; He, S.; Wu, B. Detection of Long-Term Effect in Forecasting Municipal Solid Waste Using a Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, W.; Ye, H. Accurate Workload Prediction for Edge Data Centers: Savitzky-Golay filter, CNN and BiLSTM with Attention Mechanism. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 13027–13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Tang, J.; He, Z.-Y.; Tan, J.; Li, C. A Novel Displacement Orediction Method Using Gated Recurrent Unit Model with Time Series Analysis in the Erdaohe landslide. Nat. Hazards 2021, 105, 783–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Bae, S.; Cha, G.; Yoo, J. Aggregated Electric Vehicle Fast-Charging Power Demand Analysis and Forecast Based on LSTM Neural Network. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhay, L.; Reyad, M.A.H.; Suy, R.; Islam, M.R.; Mian, M.M. Municipal Solid Waste Generation in China: Influencing F Analysis and Multi-Model Forecasting. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; El Hanandeh, A. Forecasting Municipal Solid Waste Generation Using Artificial Intelligence Modelling Approaches. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, H.L.; Bolingbroke, D.; Ng, K.T.W.; Fallah, B. Assessment of Waste Characteristics and their Impact on GIS Vehicle Collection Route Optimization Using ANN Waste Forecasts. Waste Manag. 2019, 88, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Houdt, G.; Mosquera, C.; Nápoles, G. A Review on the Long Short-Term Memory Model. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 5929–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherstinsky, A. Fundamentals of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2020, 404, 132306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning Phrase Representations U RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Jing, H.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Q. Gated Recurrent Unit Based Recurrent Neural Network for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Nonlinear Deterioration Process. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 185, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, R.; Salem, F.M. Gate-Variants of Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 60th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Boston, MA, USA, 6–9 August 2017; pp. 1597–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, N.; Brown, J. An EEMD-BiLSTM Algorithm Integrated with Boruta Random Forest Optimiser for Significant Wave Height Forecasting along Coastal Areas of Queensland, Australia. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K.K. Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Warrens, M.J.; Jurman, G. The Coefficient of Determination R-squared is More I than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in Regression Analysis Evaluation. Peer J. Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyndham City Council Waste Data. Available online: https://data.gov.au/search?organisation=Wyndham+City+Council (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Carneiro, T.; Da Nóbrega, R.V.M.; Nepomuceno, T.; Bian, G.-B.; De Albuquerque, V.H.C.; Reboucas Filho, P.P. Performance Analysis of Google Colaboratory as a Tool for Accelerating Deep Learning Applications. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 61677–61685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaswi, N.K. Understanding and working with Keras. In Deep Learning with Applications Using Python; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Application | Region | Dataset | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waste generation using ANN | Logan City, Australia | Waste generation (July 1996 to June 2014) | 18-year period historical dataset did not use the smart bin data | Abbasi and El Hanandeh [34] |
| Predicting waste amount using LSTM | Suzhou, China | 730 data (January 2018 to December 2019) | Time series dataset from a historical record for five different districts. The data is as a whole amount the waste for a district on a particular day. | Niu et al. [29] |
| Predicting waste amount using Attention, 1D CNN, LSTM and 1D CLA | Shanghai, China | January 1990 to December 2018 | Considered 24 socioeconomic factors and the historical dataset did not use the smart bin data | Lin et al. [5] |
| Forecasting waste generation ANN, Linear regression | Shanghai, China | Date from 2000 to 2016 | Contemplated eight socio-economic-factors with the historical dataset not using the smart bin data | Chhay et al. [33] |
| Predicting waste generation | Melbourne, Australia | Date from 2010 to 2020 | Multiple socioeconomic factors data are available for conducting further research including the smart bin | Watson and Ryan [12,13] |
| ANN | Austin, USA | Weekly collected garbage (2004–2018) | Predicting the garbage generation using weekly amount of collected garbage | Vu et al. [35] |
| S. No. | Attribute | Attribute Information |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Type | Points |
| 2 | Coordinates0 | Geographical position Latitude |
| 3 | Coordinates1 | Geographical position Longitude |
| 4 | LatestFullness | Numeric 0 to 10 |
| 5 | Reason | Fullness and Not_Ready |
| 6 | SerialNumber | Numeric number |
| 7 | Description | Details about the points |
| 8 | Position | Centre |
| 9 | AgeThreshold | Numeric 0 to 10 |
| 10 | FullnessThreshold | Numeric 6 or 8 |
| 11 | Timestamp | Date |
| Layer | Output Shape | Parameters | Parameter Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Parameter | Trainable Parameter | Non-Trainable Parameter | |||
| 1D CNN | (None, 1, 200) | 6200 | 6401 | 6401 | 0 |
| GlobalMaxPooling1D | (None, 200) | 0 | |||
| Dense | (None, 1) | 201 | |||
| LSTM | (None, 100) | 52,400 | 52,501 | 52,501 | 0 |
| Dropout | (None, 100) | 0 | |||
| Dense | (None, 1) | 101 | |||
| GRU | (None, 100) | 39,600 | 39,701 | 39,701 | 0 |
| Dropout | (None, 100) | 0 | |||
| Dense | (None, 1) | 101 | |||
| BiLSTM | (None, 200) | 104,800 | 105,001 | 105,001 | 0 |
| Dropout | (None, 200) | 0 | |||
| Dense | (None, 1) | 201 | |||
| Model | MAE | MAPE | RMSE | R2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test | |
| 1D CNN | 0.667 | 0.677 | 3.170 | 3.678 | 1.128 | 1.132 | 0.274 | 0.269 |
| LSTM | 0.602 | 0.705 | 1.855 | 2.198 | 1.579 | 1.798 | 0.925 | 0.903 |
| GRU | 0.698 | 0.811 | 2.427 | 2.787 | 1.694 | 1.937 | 0.921 | 0.897 |
| BiLSTM | 0.638 | 0.747 | 7.951 | 8.911 | 1.543 | 1.774 | 0.925 | 0.901 |
| Purpose | Models | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waste generation | ANFIS | MAE: 0.001, MAPE: 3.39 × 10−6 RMSE: 0.002, R2: 0.99 | Abbasi and El Hanandeh [34] |
| ANN | MAE: 335.03, MAPE: 0.07 RMSE: 498.43, R2: 0.83 | ||
| Estimating waste amount | LSTM | MAPE: 63.66, RMSE: 659.58, R2: 0.96 | Niu et al. [29] |
| Predicting waste amount | LSTM | R2: 0.90 | Lin et al. [5] |
| Attention | R2: 0.78 | ||
| CNN | R2: 0.86 | ||
| Predicting waste generation | ANN | MAE: 228.53, MAPE: 0.0143 RMSE: 450.84, R2: 0.931 | Chhay et al. [33] |
| Estimating waste generation | 1D CNN | MAE: 0.667, MAPE: 3.170, | The proposed models |
| RMSE: 1.128, R2: 0.274 | |||
| LSTM | MAE: 0.602, MAPE: 1.855, | ||
| RMSE: 1.579, R2: 0.925 | |||
| GRU | MAE: 0.698, MAPE: 2.427, | ||
| RMSE: 1.694, R2: 0.921 | |||
| BiLSTM | MAE: 0.638, MAPE: 7.951, | ||
| RMSE: 1.543, R2: 0.925 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, S.; Mubarak, S.; Du, J.T.; Wibowo, S. Forecasting the Status of Municipal Waste in Smart Bins Using Deep Learning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416798
Ahmed S, Mubarak S, Du JT, Wibowo S. Forecasting the Status of Municipal Waste in Smart Bins Using Deep Learning. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(24):16798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416798
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Sabbir, Sameera Mubarak, Jia Tina Du, and Santoso Wibowo. 2022. "Forecasting the Status of Municipal Waste in Smart Bins Using Deep Learning" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 24: 16798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416798
APA StyleAhmed, S., Mubarak, S., Du, J. T., & Wibowo, S. (2022). Forecasting the Status of Municipal Waste in Smart Bins Using Deep Learning. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(24), 16798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416798







