Benefits of Cycling Wheelchair Training for Elderly with Physical Disability: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
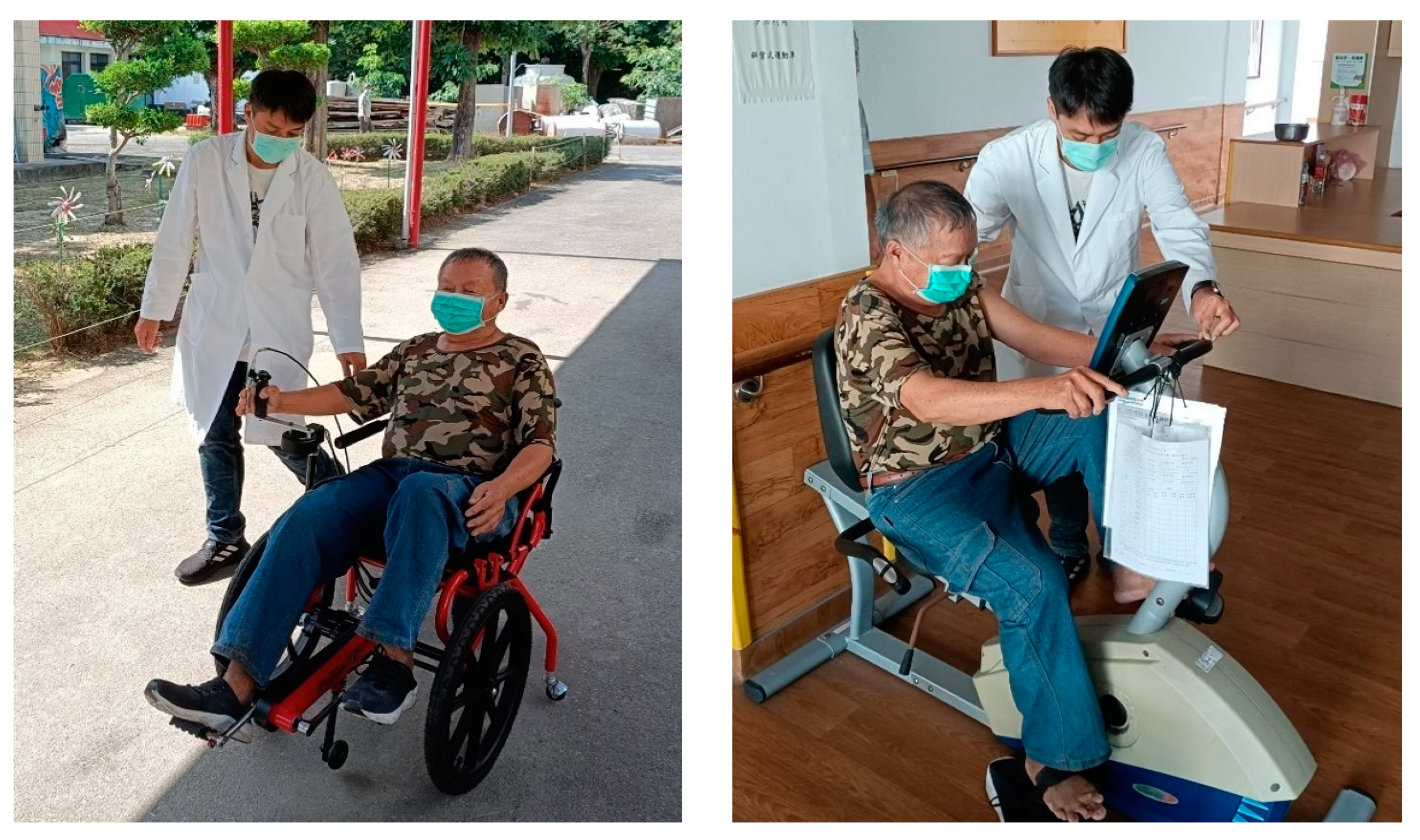
2.2. Study Protocol
2.3. Outcome Measures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Basic Demographics
3.2. SF-12
3.3. MMSE
3.4. Aero Bike Test
3.5. Physiological Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, S.; Merghani, A.; Mont, L. Exercise and the heart: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seals, D.R.; Nagy, E.E.; Moreau, K.L. Aerobic exercise training and vascular function with ageing in healthy men and women. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 4901–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSouza, C.A.; Shapiro, L.F.; Clevenger, C.M.; Dinenno, F.A.; Monahan, K.D.; Tanaka, H.; Seals, D.R. Regular aerobic exercise prevents and restores age-related declines in endothelium-dependent vasodilation in healthy men. Circulation 2000, 102, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, J.R. Effects of physical activity on children’s executive function: Contributions of experimental research on aerobic exercise. Dev. Rev. 2010, 30, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.J.; Blumenthal, J.A.; Hoffman, B.M.; Cooper, H.; Strauman, T.A.; Welsh-Bohmer, K.; Browndyke, J.N.; Sherwood, A. Aerobic exercise and neurocognitive performance: A meta-analytic review of randomized controlled trials. Psychosom. Med. 2010, 72, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Sato, F.; Choi, J.B.; Watada, H.; Niwa, M.; Kinoshita, J.; Ooka, A.; Kumashiro, N.; Igarashi, Y.; et al. Effects of Diet and Exercise on Muscle and Liver Intracellular Lipid Contents and Insulin Sensitivity in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 3191–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J. Cardiology patient pages. Exercise and cardiovascular health. Circulation 2003, 107, e2–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.G.; Furlini, G.; Zati, A.; Letizia Mauro, G. The Effectiveness of Physical Exercise on Bone Density in Osteoporotic Patients. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4840531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandolesi, L.; Polverino, A.; Montuori, S.; Foti, F.; Ferraioli, G.; Sorrentino, P.; Sorrentino, G. Effects of Physical Exercise on Cognitive Functioning and Wellbeing: Biological and Psychological Benefits. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojman, P.; Gehl, J.; Christensen, J.F.; Pedersen, B.K. Molecular Mechanisms Linking Exercise to Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruning, R.S.; Sturek, M. Benefits of exercise training on coronary blood flow in coronary artery disease patients. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 57, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wołoszyn, N.; Grzegorczyk, J.; Wiśniowska-Szurlej, A.; Kilian, J.; Kwolek, A. Psychophysical Health Factors and Its Correlations in Elderly Wheelchair Users Who Live in Nursing Homes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, C.; Struckmeyer, L.; Kazem-Zadeh, M.; Campbell, N.; Ahrentzen, S.; Classen, S. A Social-Ecological Approach to Identify Facilitators and Barriers of Home Modifications. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, L.; de Sire, A.; Folli, A.; Turco, A.; Moalli, S.; Ammendolia, A.; Maconi, A.; Invernizzi, M. Environmental Factors in the Rehabilitation Framework: Role of the One Health Approach to Improve the Complex Management of Disability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, M.; Ibañez, J.; Gorostiaga, E.; Garrues, M.; Zúñiga, A.; Antón, A.; Larrión, J.L.; Häkkinen, K. Maximal strength and power characteristics in isometric and dynamic actions of the upper and lower extremities in middle-aged and older men. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1999, 167, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calbet, J.A.; Holmberg, H.C.; Rosdahl, H.; van Hall, G.; Jensen-Urstad, M.; Saltin, B. Why do arms extract less oxygen than legs during exercise? Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 289, R1448–R1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.D.; Nawaz, S.; Wilkinson, C.H.; Saxton, J.M.; Pockley, A.G.; Wood, R.F. Influence of upper- and lower-limb exercise training on cardiovascular function and walking distances in patients with intermittent claudication. J. Vasc. Surg. 2000, 31, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-Vidotti, H.G.; Mendes, R.G.; Simões, R.P.; Castello-Simões, V.; Catai, A.M.; Borghi-Silva, A. Cardiac autonomic responses during upper versus lower limb resistance exercise in healthy elderly men. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2014, 18, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyward, O.W.; Vegter, R.J.K.; de Groot, S.; van der Woude, L.H.V. Shoulder complaints in wheelchair athletes: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozingo, J.D.; Akbari-Shandiz, M.; Murthy, N.S.; Van Straaten, M.G.; Schueler, B.A.; Holmes, D.R., 3rd; McCollough, C.H.; Zhao, K.D. Shoulder mechanical impingement risk associated with manual wheelchair tasks in individuals with spinal cord injury. Clin. Biomech. 2020, 71, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liampas, A.; Neophytou, P.; Sokratous, M.; Varrassi, G.; Ioannou, C.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Zis, P. Musculoskeletal Pain Due to Wheelchair Use: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, K.; Sato, M.; Handa, Y. Increase of muscle activities in hemiplegic lower extremity during driving a cycling wheelchair. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2009, 219, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxton, J.M.; Zwierska, I.; Blagojevic, M.; Choksy, S.A.; Nawaz, S.; Pockley, A.G. Upper-versus lower-limb aerobic exercise training on health-related quality of life in patients with symptomatic peripheral arterial disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 53, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellapen, T.J.; Hammill, H.V.; Swanepoel, M.; Strydom, G.L. The health benefits and constraints of exercise therapy for wheelchair users: A clinical commentary. Afr. J. Disabil. 2017, 6, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viosca, E.; Martínez, J.L.; Almagro, P.L.; Gracia, A.; González, C. Proposal and Validation of a New Functional Ambulation Classification Scale for Clinical Use. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, A.; Kofler, M.; Quirbach, E.; Matzak, H.; Fröhlich, K.; Saltuari, L. Prospective, Blinded, Randomized Crossover Study of Gait Rehabilitation in Stroke Patients Using the Lokomat Gait Orthosis. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2007, 21, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, I.T.; Lee, W.J.; Lin, S.Y.; Chang, S.T.; Kao, C.L.; Cheng, Y.Y. Therapeutic Effects of Exercise Training on Elderly Patients With Dementia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 101, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.; Kosinski, M.; Keller, S. SF-12: How to Score the SF-12 Physical and Mental Health Summary Scales. 1998. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242636950_SF-12_How_to_Score_the_SF-12_Physical_and_Mental_Health_Summary_Scales (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Ware, J., Jr.; Kosinski, M.; Keller, S.D. A 12-Item Short-Form Health Survey: Construction of scales and preliminary tests of reliability and validity. Med. Care 1996, 34, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, D.W.; Standish, T.I. A guide to the standardized Mini-Mental State Examination. Int. Psychogeriatr. 1997, 9 (Suppl. S1), 87–94; discussion 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, J.; Powers, S.K.; Dodd, S. A time-saving incremental cycle ergometer protocol to determine peak oxygen consumption. Br. J. Sport. Med. 1987, 21, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.W.; Wang, D. The Reliability and Validity of Short Form-12 Health Survey Version 2 for Chinese Older Adults. Iran. J. Public Health 2019, 48, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carcaillon, L.; Amieva, H.; Auriacombe, S.; Helmer, C.; Dartigues, J.F. A subtest of the MMSE as a valid test of episodic memory? Comparison with the Free and Cued Reminding Test. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2009, 27, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejeski, W.J.; Mihalko, S.L. Physical Activity and Quality of Life in Older Adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2001, 56, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anokye, N.K.; Trueman, P.; Green, C.; Pavey, T.G.; Taylor, R.S. Physical activity and health related quality of life. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, D.L.; Hammond, C.C.; Reifsteck, E.J.; Jehu, C.M.; Williams, R.A.; Adams, M.M.; Lange, E.H.; Becofsky, K.; Rodriguez, E.; Shang, Y.T. Physical activity and quality of life. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2013, 46 (Suppl. S1), S28–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, A.; Ramos-Díaz, E.; Axpe-Saez, I. The Role of Resilience and Psychological Well-Being in School Engagement and Perceived Academic Performance: An Exploratory Model to Improve Academic Achievement. In Health and Academic Achievement; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.H.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, S.U.; Jung, S.H.; Lee, S.Y. Association between exercise type and quality of life in a community-dwelling older people: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Arribas, M.J.; Fernández-Serrano, M.; Royuela, A.; Kovacs, F.M.; Gallego-Izquierdo, T.; Ramos-Sánchez, M.; Llorca-Palomera, R.; Pardo-Hervás, P.; Martín-Pariente, O.S. Minimal Clinically Important Difference in Quality of Life for Patients With Low Back Pain. Spine 2017, 42, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, N.D.; Weir, D.; Holland, J.; Gerrand, C.; Deehan, D.J. Meaningful changes in the Short Form 12 physical and mental summary scores after total knee arthroplasty. Knee 2019, 26, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, F.J.; Kuipers, H. The relation between power output, oxygen uptake and heart rate in male athletes. Int. J. Sport. Med. 1994, 15, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, F.; Vernillo, G.; de Morree, H.M.; Bonomi, A.G.; La Torre, A.; Kubis, H.P.; Veicsteinas, A. Estimation of maximal oxygen uptake via submaximal exercise testing in sports, clinical, and home settings. Sport. Med. 2013, 43, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannetta, D.; de Almeida Azevedo, R.; Ingram, C.P.; Keir, D.A.; Murias, J.M. Evaluating the suitability of supra-PO(peak) verification trials after ramp-incremental exercise to confirm the attainment of maximum O(2) uptake. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2020, 319, R315–R322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, A.; Yajima, T.; Adachi, H.; Shimizu, N.; Kano, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Niwa, A.; Marumo, F.; Hiroe, M. Evaluation of exercise capacity using submaximal exercise at a constant work rate in patients with cardiovascular disease. Circulation 1995, 91, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.C.; Nielson, K.A.; Antuono, P.; Lyons, J.A.; Hanson, R.J.; Butts, A.M.; Hantke, N.C.; Verber, M.D. Semantic memory functional MRI and cognitive function after exercise intervention in mild cognitive impairment. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 37, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.; Lord, S.R. Effects of group exercise on cognitive functioning and mood in older women. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 1997, 21, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandel José Pacheco Lopes, F.; Camila Rosa de, O.; Maria Gabriela Valle, G. Effects of karate-dô training in older adults cognition: Randomized controlled trial. J. Phys. Educ. 2019, 30, e-3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, K.; Kropf, S.; Darius, S.; Emmermacher, P.; Böckelmann, I. Comparing the effectiveness of karate and fitness training on cognitive functioning in older adults—A randomized controlled trial. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016, 5, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehfeld, K.; Lüders, A.; Hökelmann, A.; Lessmann, V.; Kaufmann, J.; Brigadski, T.; Müller, P.; Müller, N.G. Dance training is superior to repetitive physical exercise in inducing brain plasticity in the elderly. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophins: Roles in neuronal development and function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 677–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nystoriak, M.A.; Bhatnagar, A. Cardiovascular Effects and Benefits of Exercise. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, R.; Amir, M.; Pakhare, A.; Rathi, P.; Chaudhary, L. Age Related Changes in Autonomic Functions. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, CC11–CC15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 10th ed.; Riebe, D., Ehrman, J., Liguori, G., Magal, M., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
| Before Training | After Training | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome Measure | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| GH | 40.00 | 22.50 | 51.88 | 19.10 | <0.001 * |
| PF | 41.25 | 31.80 | 48.75 | 30.98 | 0.003 * |
| RP | 38.75 | 40.01 | 76.25 | 39.20 | <0.001 * |
| BP | 65.00 | 20.25 | 73.13 | 15.39 | <0.001 * |
| RE | 91.25 | 22.32 | 97.50 | 11.04 | 0.025 * |
| VT | 57.50 | 18.22 | 65.50 | 16.32 | <0.001 * |
| MH | 76.50 | 11.22 | 83.00 | 8.53 | <0.001 * |
| SF | 58.75 | 20.84 | 67.50 | 20.57 | <0.001 * |
| PCS-12 | 33.60 | 12.20 | 40.46 | 10.26 | <0.001 * |
| MCS-12 | 54.60 | 4.54 | 56.55 | 2.72 | 0.001 * |
| Before Training | After Training | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome Measure | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Orientation | 6.25 | 2.01 | 6.40 | 1.95 | 0.465 |
| Registration | 2.90 | 0.38 | 2.78 | 0.53 | 0.16 |
| Attention/Calculation | 3.35 | 1.89 | 3.60 | 1.89 | 0.018 * |
| Short term memory | 1.9 | 0.92 | 2.18 | 0.78 | 0.041 * |
| Comprehension/Behavior | 5.05 | 1.26 | 4.93 | 1.36 | 0.132 |
| Total score | 23.95 | 5.56 | 24.10 | 5.65 | 0.527 |
| Before Training | After Training | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bike Resistance Levels | Work Load (W) | Number | Percentage | Number | Percentage |
| 1 | 51 | 16 | 40.0 | 9 | 22.5 |
| 2 | 68 | 19 | 47.5 | 7 | 17.5 |
| 3 | 78 | 4 | 10.0 | 16 | 40.0 |
| 4 | 90 | 1 | 2.5 | 7 | 17.5 |
| 5 | 104 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2.5 |
| Total | 40 | 100.0 | 40 | 100.0 | |
| Before Training | After Training | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome Measure | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Work load(W) | 62.75 | 10.63 | 72.93 | 14.25 | <0.001 * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.48 | 3.42 | 23.53 | 3.49 | 0.104 |
| Resting HR(beats) | 76.59 | 8.04 | 75.62 | 8.98 | 0.793 |
| SBP(mmHg) | 126.97 | 11.54 | 126.90 | 11.87 | 0.931 |
| DBP(mmHg) | 69.17 | 9.35 | 71.03 | 12.35 | 0.411 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, J.C.-M.; Fu, P.-K.; Cheng, Y.-Y. Benefits of Cycling Wheelchair Training for Elderly with Physical Disability: A Prospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416773
Fu JC-M, Fu P-K, Cheng Y-Y. Benefits of Cycling Wheelchair Training for Elderly with Physical Disability: A Prospective Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(24):16773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416773
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Jimmy Chun-Ming, Pin-Kuei Fu, and Yuan-Yang Cheng. 2022. "Benefits of Cycling Wheelchair Training for Elderly with Physical Disability: A Prospective Cohort Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 24: 16773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416773
APA StyleFu, J. C.-M., Fu, P.-K., & Cheng, Y.-Y. (2022). Benefits of Cycling Wheelchair Training for Elderly with Physical Disability: A Prospective Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(24), 16773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416773







