Association between Reproductive Factors and Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Diagnostic Criteria
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristic of the Participants
3.2. Association between Menopausal Status and T2DM
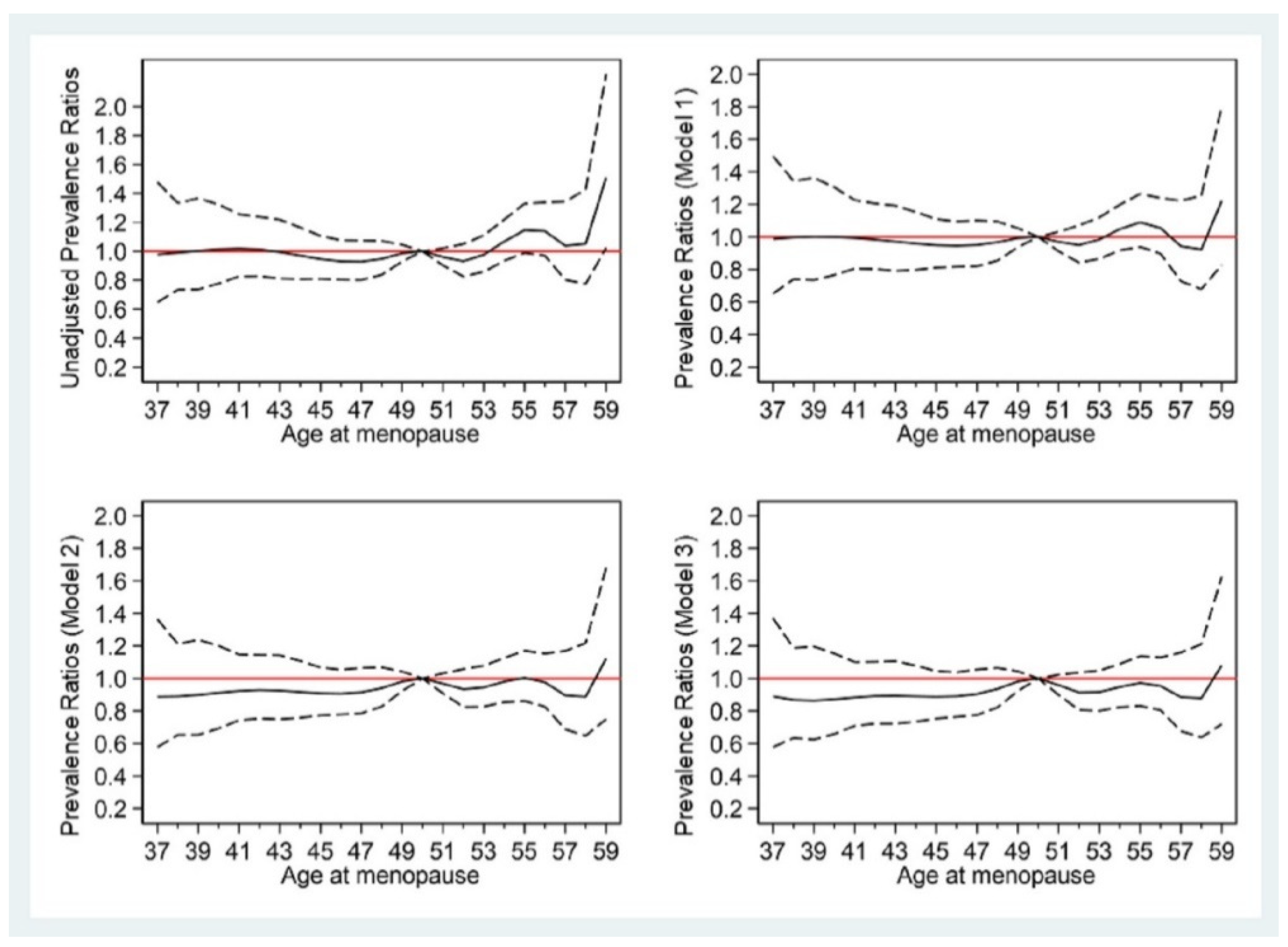
3.3. Association between Age at Menopause and T2DM
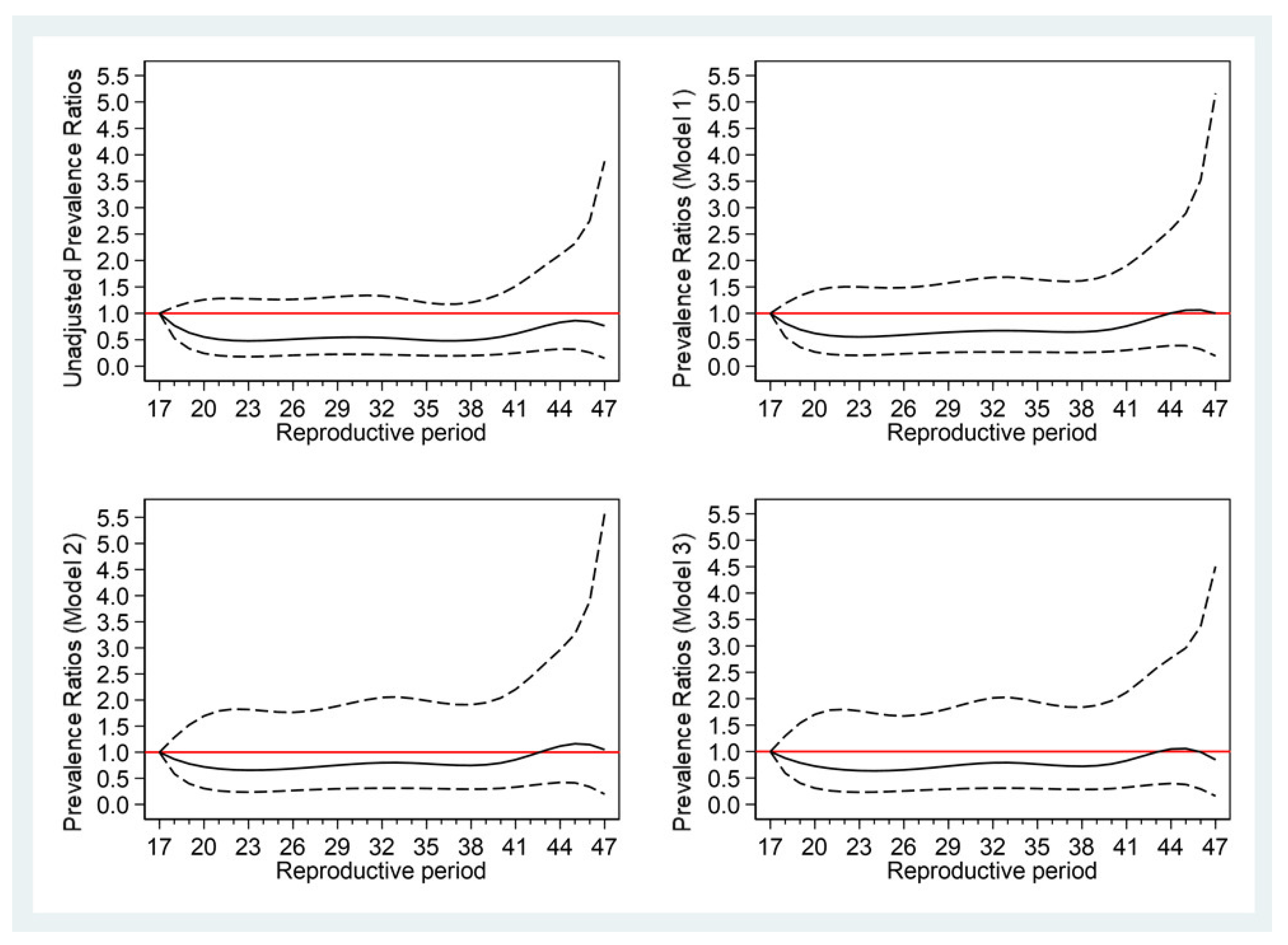
3.4. Association between Reproductive Period and T2DM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statemen
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association. Introduction: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaboration NCDRF. Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: A pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF). IDF Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014, 37 (Suppl. S1), S81–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paneni, F.; Beckman, J.A.; Creager, M.A.; Cosentino, F. Diabetes and vascular disease: Pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: Part I. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbudi, A.; Rahmadika, N.; Tjahjadi, A.I.; Ruslami, R. Type 2 Diabetes and its Impact on the Immune System. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2020, 16, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalamandris, S.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Oikonomou, E.; Papamikroulis, G.A.; Vogiatzi, G.; Papaioannou, S.; Deftereos, S.; Tousoulis, D. The Role of Inflammation in Diabetes: Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. Eur. Cardiol. 2019, 14, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, R.; Karuranga, S.; Malanda, B.; Saeedi, P.; Basit, A.; Besancon, S.; Bommer, C.; Bommer, C.; Esteghamati, A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional estimates and projections of diabetes-related health expenditure: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goodman, N.F.; Cobin, R.H.; Ginzburg, S.B.; Katz, I.A.; Woode, D.E.; Camacho, P.M.; Manson, J.E.; Petak, S.M. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for the diagnosis and treatment of menopause. Endocr. Pract. 2011, 17 (Suppl. S6), 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACOG. Practice Bulletin No. 141: Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 123, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, H.D. Menopause. Lancet 2008, 371, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, S.; Henderson, V.W.; Siseles, N.; Tan, D.; Villaseca, P. Age of menopause and impact of climacteric symptoms by geographical region. Climacteric 2010, 13, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Tang, X.; Li, N.; Wu, Y.Q.; Wang, J.W.; Li, J.R.; Zhang, Z.X.; Dou, H.D.; Liu, J.J.; Yu, L.P.; et al. Menopause with cardiovascular disease and its risk factors among rural Chinese women in Beijing: A population-based study. Maturitas 2012, 72, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuenkel, C.A.; Davis, S.R.; Gompel, A.; Lumsden, M.A.; Murad, M.H.; Pinkerton, J.V.; Santen, R.J. Treatment of Symptoms of the Menopause: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3975–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; Mao, Z.; Yang, X.; Fan, M.; Han, S.; Li, L. Effect of the Age at Menarche and Menopause Status Interaction on Type 2 Diabetes: The Henan Rural Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e139–e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Pham, N.M.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Nguyen, V.Q.; La, Q.N.; Lee, A.H. Menopausal status and type 2 diabetes: A nationwide epidemiological survey in Vietnam. Public Health 2016, 138, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wen, J.; Pan, X.; Su, J.; Du, W.; Pan, E.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, N.; Sheng, H.; Liu, C.; et al. Age at menarche and age at natural menopause as predictors of glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Song, L.; Li, H.; Liu, B.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Y. Association between earlier age at natural menopause and risk of diabetes in middle-aged and older Chinese women: The Dongfeng-Tongji cohort study. Diabetes Metab. 2017, 43, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heianza, Y.; Arase, Y.; Kodama, S.; Hsieh, S.D.; Tsuji, H.; Saito, K.; Shimano, H.; Hara, S.; Sone, H. Effect of postmenopausal status and age at menopause on type 2 diabetes and prediabetes in Japanese individuals: Toranomon Hospital Health Management Center Study 17 (TOPICS 17). Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 4007–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, C.; Li, Q.; Tian, G.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Yin, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; et al. Association of age at menopause and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies. Prim. Care Diabetes 2019, 13, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, J.S.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Onland-Moret, N.C.; Sharp, S.J.; Ong, K.K.; Khaw, K.T.; Ardanaz, E.; Amiano, P.; Boeing, H.; Chirlaque, M.D.; et al. Age at menopause, reproductive life span, and type 2 diabetes risk: Results from the EPIC-InterAct study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ley, S.H.; Li, Y.; Tobias, D.K.; Manson, J.E.; Rosner, B.; Hu, F.B.; Rexrode, K.M. Duration of Reproductive Life Span, Age at Menarche, and Age at Menopause Are Associated With Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Women. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tramunt, B.; Smati, S.; Grandgeorge, N.; Lenfant, F.; Arnal, J.; Montagner, A.; Gourdy, P. Sex differences in metabolic regulation and diabetes susceptibility. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, B.; Wang, R.; Zhu, M.; Shao, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, F.; Wang, W.; et al. Cohort profile: Protocol and baseline survey for the Shanghai Suburban Adult Cohort and Biobank (SSACB) study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, T.; Borghi, C.; Charchar, F.; Khan, N.; Poulter, N.; Prabhakaran, D.; Ramirez, A.; Schlaich, M.; Stergiou, G.; Tomaszewski, M.; et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension global hypertension practice guidelines. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 982–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint Committee for Guideline Revision. 2016 Chinese guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia in adults. J. Geriatr. Cardiol 2018, 15, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Mu, Y.; Zou, X.; Zou, D.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Tao, L.; Guo, X. Gender Differences in the Association between Serum Uric Acid and Prediabetes: A Six-Year Longitudinal Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, H.A.; Park, J.K.; Park, S.A.; Lee, J.S. Age, menopause, and cardiovascular risk factors among korean middle-aged women: The 2005 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Womens Health 2010, 19, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mi, J.; Shan, X.Y.; Wang, Q.J.; Ge, K.Y. Is China facing an obesity epidemic and the consequences? The trends in obesity and chronic disease in China. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrell, F.E., Jr. Regression Modeling Strategies: With Applications to Linear Models, Logistic and Ordinal Regression, and Survival Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Muka, T.; Asllanaj, E.; Avazverdi, N.; Jaspers, L.; Stringa, N.; Milic, J.; Ligthart, S.; Ikram, M.A.; Laven, J.S.; Kavousi, M.; et al. Age at natural menopause and risk of type 2 diabetes: A prospective cohort study. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Hu, R.Y.; Wang, H.; Gong, W.W.; Wang, C.M.; Xie, K.X.; Chen, Z.M.; Guo, Y.; Yu, M.; Li, L.M. Age at natural menopause and risk of diabetes in adult women: Findings from the China Kadoorie Biobank study in the Zhejiang area. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karvonen-Gutierrez, C.A.; Park, S.K.; Kim, C. Diabetes and Menopause. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, F.R.; Ruth, K.S.; Thompson, D.J.; Lunetta, K.L.; Pervjakova, N.; Chasman, D.I.; Stolk, L.; Finucane, H.K.; Sulem, P.; Bulik-Sullivan, B.; et al. Large-scale genomic analyses link reproductive aging to hypothalamic signaling, breast cancer susceptibility and BRCA1-mediated DNA repair. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, J.L. The Menopausal Transition. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 44, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vryonidou, A.; Paschou, S.A.; Muscogiuri, G.; Orio, F.; Goulis, D.G. Mechanisms in Endocrinology: Metabolic syndrome through the female life cycle. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 173, R153–R163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stampfer, M.J.; Colditz, G.A.; Willett, W.C.; Manson, J.E.; Rosner, B.; Speizer, F.E.; Hennekens, C.H. Postmenopausal estrogen therapy and cardiovascular disease. Ten-year follow-up from the nurses’ health study. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, I. Estradiol-induced changes in lipoprotein lipase, eating, and body weight in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1981, 240, E533–E538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeaib, N.; Peeyananjarassri, K.; Liabsuetrakul, T.; Buhachat, R.; Myriokefalitaki, E. Hormone replacement therapy after surgery for epithelial ovarian cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 1, CD012559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermehl, T.L.; Parkinson, K.C.; Hubbard, G.B.; Ikeno, Y.; Engelmeyer, J.I.; Schumacher, B.; Mason, J.B. Extension of longevity and reduction of inflammation is ovarian-dependent, but germ cell-independent in post-reproductive female mice. Geroscience 2019, 41, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaMonte, M.J.; Manson, J.E.; Chomistek, A.K.; Larson, J.C.; Lewis, C.E.; Bea, J.W.; Johnson, K.C.; Li, W.; Klein, L.; LaCroix, A.Z.; et al. Physical Activity and Incidence of Heart Failure in Postmenopausal Women. JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seals, D.R.; Nagy, E.E.; Moreau, K.L. Aerobic exercise training and vascular function with ageing in healthy men and women. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 4901–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhu, M.; Liu, X.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, Q. Sleep quality of Shanghai residents: Population-based cross-sectional study. Qual. Life Res. 2020, 29, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Manson, J.E.; Urrutia, R.P.; Hendryx, M.; LeBlanc, E.S.; Margolis, K.L. Risk of Diabetes After Hysterectomy With or Without Oophorectomy in Postmenopausal Women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 185, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Brown, W.C.; Cai, Q.; Krust, A.; Chambon, P.; McGuinness, O.P.; Stafford, J.M. Estrogen treatment after ovariectomy protects against fatty liver and may improve pathway-selective insulin resistance. Diabetes 2013, 62, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, F.; Tao, M.; Teng, Y.; Shao, H.; Li, C.; Mills, E. Knowledge and attitude towards menopause and hormone replacement therapy in Chinese women. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2015, 79, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Menopausal Status | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Menopause | Post-Menopause Age | ||||
| (n = 5775) | ≤44 (n = 1682) | 45–50 (n = 6554) | >50 (n = 6117) | ||
| Age | <0.001 | ||||
| ≤55 | 5650 (97.8%) | 446 (26.5%) | 1916 (29.2%) | 1403 (22.9%) | |
| 56–60 | 101 (1.7%) | 351 (20.9%) | 1389 (21.2%) | 1561 (25.5%) | |
| 61–65 | 24 (0.4%) | 368 (21.9%) | 1519 (23.2%) | 1602 (26.2%) | |
| >65 | 0 | 517 (30.7%) | 1730 (26.4%) | 1551 (25.4%) | |
| Marital status | <0.001 | ||||
| Married | 5423 (93.9%) | 1496 (88.9%) | 5980 (91.2%) | 5542 (90.6%) | |
| Unmarried/Divorced/Widowed | 352 (6.1%) | 186 (11.1%) | 574 (8.8%) | 575 (9.4%) | |
| Pregnancies (times) | <0.001 | ||||
| 0 | 253 (4.4%) | 14 (0.8%) | 38 (0.6%) | 16 (0.3%) | |
| 1 | 1704 (29.5%) | 226 (13.4%) | 1088 (16.6%) | 944 (15.4%) | |
| 2 | 2085 (36.1%) | 665 (39.5%) | 2610 (39.8%) | 2569 (42.0%) | |
| ≥3 | 1733 (30.0%) | 777 (46.2%) | 2818 (43.0%) | 2588 (42.3%) | |
| Age at menarche (years) | <0.001 | ||||
| ≤15 | 3980 (68.9%) | 602 (35.8%) | 2470 (37.7%) | 2014 (32.9%) | |
| 16–18 | 1709 (29.6%) | 837 (49.8%) | 3222 (49.2%) | 3330 (54.4%) | |
| >18 | 86 (1.5%) | 243 (14.4%) | 862 (13.2%) | 773 (12.6%) | |
| Reproductive period (years) | <0.001 | ||||
| 17–31 | N/A | 1697 (97.0%) | 1968 (29.0%) | 53 (0.8%) | |
| 32–34 | N/A | 53 (3.0%) | 2890 (42.5%) | 776 (12.3%) | |
| 35–36 | N/A | 0 | 1720 (25.3%) | 1996 (31.5%) | |
| 37–47 | N/A | 0 | 215 (3.2%) | 3504 (55.4%) | |
| Education | <0.001 | ||||
| Primary or below | 932 (16.1%) | 1184 (70.4%) | 4209 (64.2%) | 3949 (64.6%) | |
| Secondary or vocational | 3606 (62.4%) | 489 (29.1%) | 2304 (35.2%) | 2144 (35.0%) | |
| University or college | 1237 (21.4%) | 9 (0.5%) | 41 (0.6%) | 24 (0.4%) | |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | <0.001 | ||||
| <24 | 3743 (64.8%) | 755 (44.9%) | 3111 (47.5%) | 2721 (44.5%) | |
| 24–27.9 | 1515 (26.2%) | 679 (40.4%) | 2549 (38.9%) | 2502 (40.9%) | |
| ≥28 | 517 (9.0%) | 248 (14.7%) | 894 (13.6%) | 894 (14.6%) | |
| Smoking | 0.063 | ||||
| Never | 5750 (99.6%) | 1678 (99.8%) | 6541 (99.8%) | 6106 (99.8%) | |
| Former | 6 (0.1%) | 2 (0.1%) | 1 (<1%) | 3 (<1%) | |
| Current | 19 (0.3%) | 2 (0.1%) | 12 (0.2%) | 8 (0.1%) | |
| Alcohol | 0.063 | ||||
| No | 5719 (99.0%) | 1671 (99.3%) | 6516 (99.4%) | 6077 (99.3%) | |
| Yes | 56 (1.0%) | 11 (0.7%) | 38 (0.6%) | 40 (0.7%) | |
| Exercise | 0.019 | ||||
| No | 3854 (66.7%) | 1156 (68.7%) | 4546 (69.4%) | 4170 (68.2%) | |
| Yes | 1921 (33.3%) | 526 (31.3%) | 2008 (30.6%) | 1947 (31.8%) | |
| T2DM | 231 (4.0%) | 288 (17.1%) | 1140 (17.4%) | 1093 (17.9%) | <0.001 |
| Family history of T2DM | 765 (13.2%) | 229 (13.6%) | 775 (11.8%) | 786 (12.8%) | 0.058 |
| Hypertension | 1395 (24.2%) | 1004 (59.7%) | 3755 (57.3%) | 3766 (61.6%) | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 793 (13.7%) | 515 (30.6%) | 1855 (28.3%) | 1791 (29.3%) | <0.001 |
| Menopause | <0.001 | ||||
| Natural | — | 1258 (74.8%) | 6217 (94.9%) | 5988 (97.9%) | |
| Surgical | — | 424 (25.2%) | 337 (5.1%) | 129 (2.1%) | |
| Characteristics | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR (95% CI) | p | PR (95% CI) | p | PR (95% CI) | p | |
| Premenopausal women (n = 5775) | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - |
| Postmenopausal women (all) (n = 14,390) | 3.12 (2.65,3.67) | <0.001 | 2.83 (2.39,3.34) | <0.001 | 2.12 (1.79,2.51) | <0.001 |
| Postmenopausal women (natural) (n = 13,463) | 3.07 (2.60,3.61) | <0.001 | 2.81 (2.37,3.33) | <0.001 | 2.10 (1.77,2.50) | <0.001 |
| Postmenopausal women (surgical or other cause) (n = 890) | 3.64 (2.90,4.57) | <0.001 | 3.00 (2.37,3.79) | <0.001 | 2.27 (1.79,2.88) | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR (95% CI) | p | PR (95% CI) | p | PR (95% CI) | p | |
| Premenopausal women | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - |
| Age at menopause (postmenopausal women) | ||||||
| ≤44 years | 3.00 (2.45,3.68) | <0.001 | 2.64 (2.14,3.25) | <0.001 | 1.94 (1.57,2.40) | <0.001 |
| 45–50 years | 3.13 (2.64,3.71) | <0.001 | 2.89 (2.43,3.44) | <0.001 | 2.19 (1.83,2.61) | <0.001 |
| >50 years | 3.15 (2.65,3.74) | <0.001 | 2.81 (2.35,3.35) | <0.001 | 2.09 (1.74,2.50) | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR (95% CI) | p | PR (95% CI) | p | PR (95% CI) | p | |
| Age at menopause | ||||||
| ≤44 | 0.96 (0.83,1.11) | 0.572 | 0.91 (0.79,1.06) | 0.230 | 0.89 (0.77,1.03) | 0.126 |
| 45–50 | 1 | . | 1 | . | 1 | . |
| >50 | 1.01 (0.92,1.10) | 0.891 | 0.98 (0.89,1.07) | 0.624 | 0.96 (0.87,1.06) | 0.428 |
| Per 1-year increase | 1.01 (1.00,1.02) | 0.184 | 1.00 (0.99,1.01) | 0.555 | 1.00 (0.99,1.01) | 0.618 |
| Reproductive period (years) | ||||||
| 17–31 | 1 | . | 1 | . | 1 | . |
| 32–34 | 1.09 (0.97,1.24) | 0.154 | 1.11 (0.98,1.26) | 0.106 | 1.11 (0.98,1.27) | 0.101 |
| 35–36 | 0.97 (0.88,1.06) | 0.621 | 0.97 (0.88,1.08) | 0.665 | 0.97 (0.88,1.08) | 0.712 |
| 37–47 | 1.06 (0.94,1.20) | 0.356 | 1.03 (0.90,1.18) | 0.678 | 1.02 (0.89,1.17) | 0.772 |
| Per 1-year increase | 1.01 (1.00,1.02) | 0.284 | 1.00 (0.99,1.01) | 0.534 | 1.00 (0.99,1.01) | 0.594 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zaid, M.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Tong, X.; et al. Association between Reproductive Factors and Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19021019
Yu Y, Li J, Jiang Y, Zaid M, Zhao Q, Wang N, Liu X, Qiu Y, Zhu J, Tong X, et al. Association between Reproductive Factors and Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(2):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19021019
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yuting, Jing Li, Yonggen Jiang, Maryam Zaid, Qi Zhao, Na Wang, Xing Liu, Yun Qiu, Junjie Zhu, Xin Tong, and et al. 2022. "Association between Reproductive Factors and Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 2: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19021019
APA StyleYu, Y., Li, J., Jiang, Y., Zaid, M., Zhao, Q., Wang, N., Liu, X., Qiu, Y., Zhu, J., Tong, X., Cui, S., Wu, Y., Yu, J., & Zhao, G. (2022). Association between Reproductive Factors and Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(2), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19021019






