Influence of Contoured Insoles with Different Materials on Kinematics and Kinetics Changes in Diabetic Elderly during Gait
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.4. Kinematics and Kinetics Data Acquisition
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Insole Materials on Kinematics
3.2. Effects of Insole Materials on Kinetics
3.3. Effects of Insole Materials on Offloading PPP Values
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Federation, I.D. Diabetes around World in 2021. Secondary Diabetes around World in 2021. 2021. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chang, T.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, X. Global Trends and Research Hotspots of Exercise for Intervening Diabetes: A Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allet, L.; Armand, S.; Golay, A.; Monnin, D.; De Bie, R.; de Bruin, E.D. Gait characteristics of diabetic patients: A systematic review. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2008, 24, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mettelinge, T.R.; Delbaere, K.; Calders, P.; Gysel, T.; Van Den Noortgate, N.; Cambier, D. The impact of peripheral neuropathy and cognitive decrements on gait in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, I.C.; Hamamoto, A.N.; Tonicelli, L.M.; Watari, R.; Ortega, N.R.; Sartor, C.D. Abnormalities of plantar pressure distribution in early, intermediate, and late stages of diabetic neuropathy. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomozzi, C.; D’ambrogi, E.; Uccioli, L.; Macellari, V. Does the thickening of Achilles tendon and plantar fascia contribute to the alteration of diabetic foot loading? Clin. Biomech. 2005, 20, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Saltzman, C.; Yack, H.J. Ankle ROM and stiffness measured at rest and during gait in individuals with and without diabetic sensory neuropathy. Gait Posture 2006, 24, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, I.; Hamamoto, A.; Gomes, A.; Onodera, A.; Hirata, R.P.; Hennig, E. Role of ankle mobility in foot rollover during gait in individuals with diabetic neuropathy. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazari, A.; Maiya, A.G.; Shivashankara, K.; Agouris, I.; Monteiro, A.; Jadhav, R.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, C.S.; Mayya, S.S. Kinetics and kinematics of diabetic foot in type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, M.; Crowther, R.; Lazzarini, P.; Sangla, K.; Cunningham, M.; Buttner, P.; Golledge, J. Biomechanical characteristics of peripheral diabetic neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of findings from the gait cycle, muscle activity and dynamic barefoot plantar pressure. Clin. Biomech. 2013, 28, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, H.B.; Lord, S.R.; St George, R.; Fitzpatrick, R.C. Walking stability and sensorimotor function in older people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, I.C.; Picon, A.P.; Macedo, D.O.; Butugan, M.K.; Watari, R.; Sartor, C.D. Alterations in the lower limb joint moments precede the peripheral neuropathy diagnosis in diabetes patients. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2015, 17, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, U.; Riley, D.R.; Jugdey, R.S.; Azmi, S.; Rajbhandari, S.; D’Août, K.; Malik, R.A. Diabetic neuropathy and gait: A review. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frykberg, R.G.; Lavery, L.A.; Pham, H.; Harvey, C.; Harkless, L.; Veves, A. Role of neuropathy and high foot pressures in diabetic foot ulceration. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deursen, R. Mechanical loading and off-loading of the plantar surface of the diabetic foot. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, S87–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, P.R.; Bus, S.A. Off-loading the diabetic foot for ulcer prevention and healing. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2010, 100, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel, J.S.; Najafi, B. Diabetic foot biomechanics and gait dysfunction. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allet, L.; Armand, S.; De Bie, R.; Golay, A.; Monnin, D.; Aminian, K.; Staal, J.; de Bruin, E.D. The gait and balance of patients with diabetes can be improved: A randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Netten, J.J.; Raspovic, A.; Lavery, L.A.; Monteiro-Soares, M.; Rasmussen, A.; Sacco, I.C.; Bus, S.A. Prevention of foot ulcers in the at-risk patient with diabetes: A systematic review. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yick, K.L.; Tse, C. Textiles and other materials for orthopaedic footwear insoles. In Handbook of Footwear Design and Manufacture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 341–371. [Google Scholar]
- Mündermann, A.; Nigg, B.M.; Humble, R.N.; Stefanyshyn, D.J. Consistent immediate effects of foot orthoses on comfort and lower extremity kinematics, kinetics, and muscle activity. J. Appl. Biomech. 2004, 20, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shurr, D.G.; Michael, J.W.; Cook, T.M. Prosthetics and Orthotics; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, O.; Cerny, K.; Rojek, L.; Herbert, K.; Turner, R.; Waistell, S. The effects of Plastazote® and Aliplast®/Plastazote® orthoses on plantar pressures in elderly persons with diabetic neuropathy. JPO J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2004, 16, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusardi, M.M.; Nielsen, C.C.; Emery, M.J.; Bowers, D.M.; Vaughan, V.G. Orthotics and Prosthetics in Rehabilitation, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Saraswathy, G.; Gopalakrishna, G.; Das, B.; Radhakrishnan, G.; Pal, S. Development of polyurethane-based sheets by phase inversion method for therapeutic footwear applications: Synthesis, fabrication, and characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 2387–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.W.; Ng, E.Y. Preliminary investigation on the reduction of plantar loading pressure with different insole materials (SRP–Slow Recovery Poron®, P–Poron®, PPF–Poron®+ Plastazote, firm and PPS–Poron®+ Plastazote, soft). The Foot 2010, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frowen, P.; O’Donnell, M.; Burrow, J.G. Neale’s Disorders of the Foot; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bus, S.A.; Ulbrecht, J.S.; Cavanagh, P.R. Pressure relief and load redistribution by custom-made insoles in diabetic patients with neuropathy and foot deformity. Clin. Biomech. 2004, 19, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guldemond, N.; Leffers, P.; Schaper, N.; Sanders, A.; Nieman, F.; Willems, P.; Walenkamp, G. The effects of insole configurations on forefoot plantar pressure and walking convenience in diabetic patients with neuropathic feet. Clin. Biomech. 2007, 22, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arts, M.; De Haart, M.; Waaijman, R.; Dahmen, R.; Berendsen, H.; Nollet, F.; Bus, S. Data-driven directions for effective footwear provision for the high-risk diabetic foot. Diabet. Med. 2015, 32, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.Q.; Li, P.L.; Yick, K.-L.; Li, N.-W.; Jiao, J. Effects of contoured insoles with different materials on plantar pressure offloading in diabetic elderly during gait. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collings, R.; Freeman, J.; Latour, J.M.; Paton, J. Footwear and insole design features for offloading the diabetic at risk foot—A systematic review and meta-analyses. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2021, 4, e00132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amemiya, A.; Noguchi, H.; Oe, M.; Ohashi, Y.; Ueki, K.; Kadowaki, T.; Mori, T.; Sanada, H. Elevated plantar pressure in diabetic patients and its relationship with their gait features. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawacha, Z.; Guarneri, G.; Cristoferi, G.; Guiotto, A.; Avogaro, A.; Cobelli, C. Integrated kinematics–kinetics–plantar pressure data analysis: A useful tool for characterizing diabetic foot biomechanics. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspovic, A. Gait characteristics of people with diabetes-related peripheral neuropathy, with and without a history of ulceration. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, F.; Bonaventura, A.; Vecchiè, A.; Casula, M.; Liberale, L.; Dallegri, F.; Montecucco, F. Impact of Endocrine Disorders on Blood Pressure. Endocrinol. Syst. Dis. 2021, 29–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, M.; Maganaris, C.N.; Deschamps, K.; Verschueren, S.M.; Bowling, F.L.; Boulton, A.J.; Reeves, N.D. Altered Achilles tendon function during walking in people with diabetic neuropathy: Implications for metabolic energy saving. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 124, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddas, R.; Ju, K.L.; Belanger, T.; Lieberman, I.H. The use of gait analysis in the assessment of patients afflicted with spinal disorders. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Mei, Q.; Gu, Y. Plantar loading reflects ulceration risks of diabetic foot with toe deformation. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 326493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawacha, Z.; Gabriella, G.; Cristoferi, G.; Guiotto, A.; Avogaro, A.; Cobelli, C. Diabetic gait and posture abnormalities: A biomechanical investigation through three dimensional gait analysis. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švehlík, M.; Zwick, E.B.; Steinwender, G.; Linhart, W.E.; Schwingenschuh, P.; Katschnig, P.; Ott, E.; Enzinger, C. Gait analysis in patients with Parkinson’s disease off dopaminergic therapy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprile, I.; Galli, M.; Pitocco, D.; Di Sipio, E.; Simbolotti, C.; Germanotta, M.; Bordieri, C.; Padua, L.; Ferrarin, M. Does first ray amputation in diabetic patients influence gait and quality of life? J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018, 57, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.A.; Onodera, A.N.; Otuzi, M.E.; Pripas, D.; Mezzarane, R.A.; Sacco, I.C.N. Electromyography and kinematic changes of gait cycle at different cadences in diabetic neuropathic individuals. Muscle Nerve 2011, 44, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.-u.; Stenholm, S.; Chia, C.W.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L. Gait pattern alterations in older adults associated with type 2 diabetes in the absence of peripheral neuropathy—Results from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Gait Posture 2011, 34, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.D. Gait Alterations and Plantar Pressure in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Preliminary Study; Brigham Young University: Provo, UT, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, W.-T.; Yick, K.-L.; Lau, N.; Tse, L.-T.; Ng, S.-P.; Yip, J. Effects of slipper features and properties on walking and sit-to-stand tasks of older women. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2017, 25, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eng, J.J.; Pierrynowski, M.R. The effect of soft foot orthotics on three-dimensional lower-limb kinematics during walking and running. Phys. Ther. 1994, 74, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goske, S.; Erdemir, A.; Petre, M.; Budhabhatti, S.; Cavanagh, P.R. Reduction of plantar heel pressures: Insole design using finite element analysis. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 2363–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
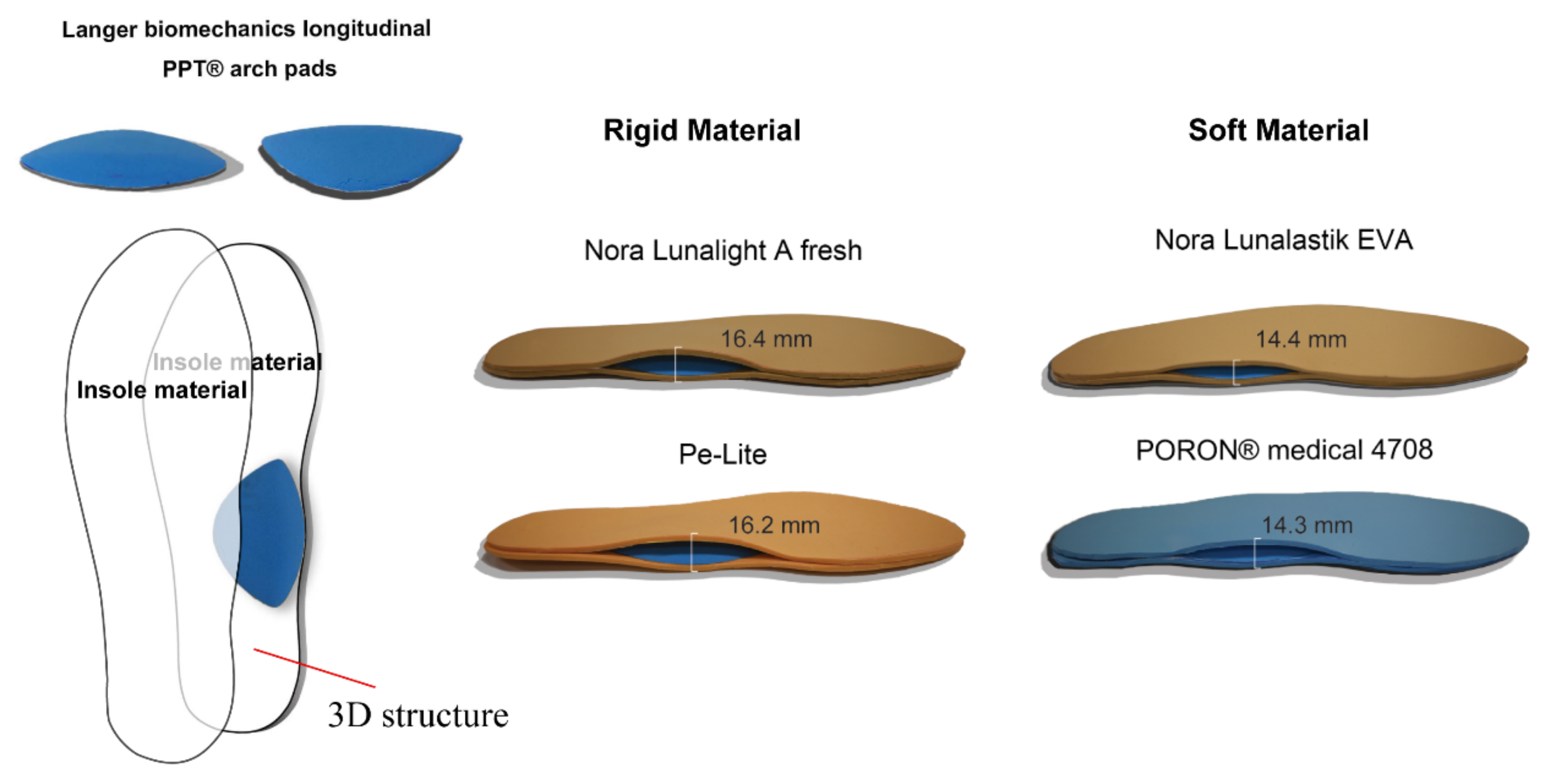


| Insole Material (2-Layer) | A | B | C | D | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness(mm) | Under 0 kPa | 8.20 | 8.00 | 6.20 | 6.05 | 8.20 |
| Under 50 kPa | 8.20 | 7.95 | 6.01 | 5.71 | 7.05 | |
| Under 150 kPa | 8.18 | 7.88 | 5.48 | 4.58 | 5.53 | |
| Under 200 kPa | 8.16 | 7.79 | 5.04 | 3.51 | 4.48 | |
| Density (g/cm3) | 0.35 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.20 | ||
| Hardness | Rigid 58 shore A | Rigid 30 shore A | Soft 25 shore A | Soft 18 shore A | ||
| Parameter | Barefoot | PORON® Medical 4708 | Pe-Lite | Nora Lunalight A Fresh | Nora Lunalastik EVA | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Soft) | (Rigid) | (Rigid) | (Soft) | ||||
| Ankle angle (degree) | |||||||
| Max dorsiflexion | 13.93 (5.0) | 16.08 (3.8) | 15.54 (4.7) | 17.80 (5.0) | 18.60 (10.5) | 0.630 | 0.021 |
| Max plantarflexion | −7.32 (5.9) | −15.11 (12.8) | −14.05 (10.6) | −11.28 (7.4) | −11.73 (14.3) | 0.069 | 0.129 |
| ROM over gait cycle | 21.25 (6.5) | 31.19 (13.1) # | 29.60 (11.0) # | 29.08 (10.7) # | 30.32 (13.3) # | 0.001 | 0.341 |
| Knee angle (degree) | |||||||
| Max flexion | 45.51 (15.2) | 47.50 (18.7) | 48.91 (15.8) | 44.47 (17.0) | 49.79 (17.0) # | 0.027 | 0.147 |
| Max extension | 2.30 (6.9) | 1.97 (7.3) | 1.85 (9.0) | 1.52 (8.3) | 1.61 (8.4) | 0.760 | 0.017 |
| ROM over gait cycle | 44.47 (11.5) | 47.57 (13.5) | 47.75 (13.1) | 44.00 (13.5) | 48.93 (13.3) | 0.044 | 0.135 |
| Hip angle (degree) | |||||||
| Max flexion | 22.60 (8.3) | 21.98 (9.1) | 21.20 (7.7) | 24.75 (13.1) | 22.59 (7.3) | 0.191 | 0.078 |
| Max extension | −13.47 (6.8) | −15.14 (7.3) | −14.11 (9.6) | −14.75 (11.6) | −14.72 (9.1) | 0.771 | 0.015 |
| ROM over gait cycle | 36.07 (8.0) | 37.12 (8.4) | 35.98 (10.0) | 39.50 (8.2) | 37.31 (8.5) | 0.231 | 0.070 |
| Parameter | Barefoot | PORON® Medical 4708 | Pe-Lite | Nora Lunalight A Fresh | Nora Lunalastik EVA | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ankle moment (Nm/kg) | |||||||
| Max plantarflexion | 1.25 (0.3) | 1.22 (0.4) | 1.14 (0.4) | 1.10 (0.4) | 1.19 (0.4) | 0.112 | 1.829 |
| Max dorsiflexion in loading response | −0.04 (0.1) | 0.01 (0.1) | 0.02 (0.1) | 0.02 (0.1) | −0.04 (0.1) | 0.021 | 0.127 |
| Ankle power (W/kg) | |||||||
| Max generation | 1.02 (0.4) | 1.12 (0.5) | 1.15 (0.6) | 1.16 (0.6) | 1.27 (0.8) | 0.317 | 0.054 |
| Max absorption | −0.38 (0.3) | −0.58 (0.5) | −0.60 (0.7) | −0.53 (0.5) | −0.70 (1.0) | 0.111 | 0.103 |
| Knee moment (Nm/kg) | |||||||
| Max extension | 0.19 (0.2) | 0.12 (0.1) | 0.12 (0.1) | 0.16 (0.2) | 0.12 (0.1) | 0.115 | 0.098 |
| Max flexion | −0.36 (0.2) | −0.44 (0.2) # | −0.43 (0.2) | −0.41 (0.3) | −0.43 (0.3) | 0.022 | 0.126 |
| Knee power (W/kg) | |||||||
| Max generation in single support | 0.62 (0.7) | 0.35 (0.3) | 0.45 (0.4) | 0.35 (0.3) | 0.47 (0.5) | 0.160 | 0.085 |
| Max absorption during stance | −1.09 (0.8) | −0.61 (0.5) | −0.71 (0.8) | −0.59 (0.3) | −0.70 (0.4) | 0.046 | 0.142 |
| Hip moment (Nm/kg) | |||||||
| Max extension | 0.55 (0.3) | 0.46 (0.2) | 0.48 (0.4) | 0.45 (0.2) | 0.43 (0.3) | 0.253 | 0.063 |
| Max flexion | −0.60 (0.3) | −0.43 (0.3) # | −0.45 (0.3) | −0.44 (0.3) # | −0.45 (0.3) # | 0.006 | 0.187 |
| Hip power (W/kg) | |||||||
| Max generation during preswing | 1.00 (0.5) | 0.92 (0.5) | 1.01 (0.8) | 0.86 (0.4) | 0.95 (0.5) | 0.569 | 0.030 |
| Max absorption during stance | −0.63 (0.4) | −0.66 (0.5) | −0.71 (0.8) | −0.61 (0.5) | −0.73 (0.5) | 0.751 | 0.022 |
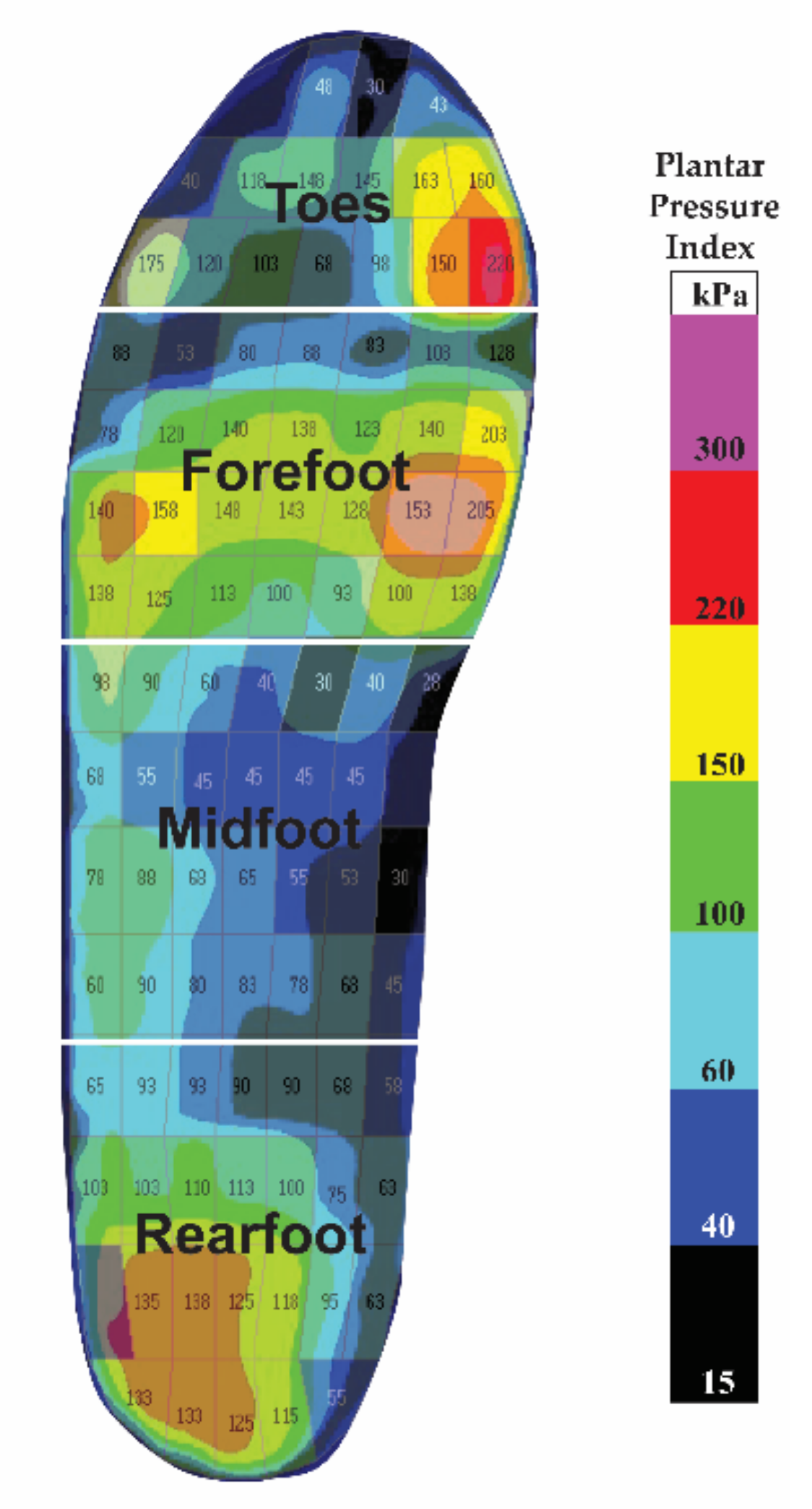
| Plantar Region | Gait Phase | Barefoot | PORON® Medical 4708 | Pe-Lite | Nora Lunalight A Fresh | Nora Lunalastik EVA | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toes | Stance | 243.87 (107.3) | 227.90 (61.7) | 265.37 (48.6) | 243.23 (54.7) | 312.69 (81.7) # | 0.002 | 0.248 |
| Swing | 56.10 (65.8) | 38.22 (14.5) | 40.90 (25.5) | 50.60 (55.1) | 41.55 (18.9) | 0.491 | 0.036 | |
| Forefoot | Stance | 350.50 (82.03) | 180.04 (40.9) ** | 229.39 (67.3) ** | 249.79 (85.7) ** | 199.03 (46.7) ** | <0.001 | 0.705 |
| Swing | 41.86 (12.1) | 33.91 (12.8) | 31.66 (10.9) | 46.30 (38.0) | 36.31 (19.9) | 0.172 | 0.084 | |
| Midfoot | Stance | 142.34 (58.6) | 103.30 (27.5) | 131.72 (37.9) | 128.05 (33.6) | 106.10 (30.6) | 0.009 | 0.191 |
| Swing | 26.79 (10.3) | 29.13 (9.0) | 29.05 (5.6) | 34.33 (17.4) | 31.43 (12.5) | 0.253 | 0.066 | |
| Rearfoot | Stance | 303.48 (68.7) | 161.48 (19.6) ** | 201.71 (27.6) ** | 220.44 (32.0) ** | 176.11 (16.4) ** | <0.001 | 0.738 |
| Swing | 144.29 (50.5) | 61.19 (21.0) ** | 67.50 (21.5) ** | 81.91 (40.2) # | 68.69 (25.6) ** | <0.001 | 0.559 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Q.-Q.; Li, P.-L.; Yick, K.-L.; Jiao, J.; Liu, Q.-L. Influence of Contoured Insoles with Different Materials on Kinematics and Kinetics Changes in Diabetic Elderly during Gait. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912502
Shi Q-Q, Li P-L, Yick K-L, Jiao J, Liu Q-L. Influence of Contoured Insoles with Different Materials on Kinematics and Kinetics Changes in Diabetic Elderly during Gait. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912502
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Qiu-Qiong, Pui-Ling Li, Kit-Lun Yick, Jiao Jiao, and Qi-Long Liu. 2022. "Influence of Contoured Insoles with Different Materials on Kinematics and Kinetics Changes in Diabetic Elderly during Gait" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912502
APA StyleShi, Q.-Q., Li, P.-L., Yick, K.-L., Jiao, J., & Liu, Q.-L. (2022). Influence of Contoured Insoles with Different Materials on Kinematics and Kinetics Changes in Diabetic Elderly during Gait. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912502





