Comparison of Pollution Levels, Biomagnification Capacity, and Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Nearshore and Offshore Regions of the South China Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Collection and Preparation
2.2. Heavy Metals Analysis
2.3. Pollution Evaluation for Seawater and Fish
2.4. C, N Isotope and TL Analysis for Biological Samples
2.5. Human Health Risk Assessment
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. HM Levels and Contamination in Seawater
3.2. HM Levels and Contamination in Fish
3.3. Geographical Differences of δ13C, δ15N, and TL
3.4. Biomagnification, Biodilution, and Correlations of HMs
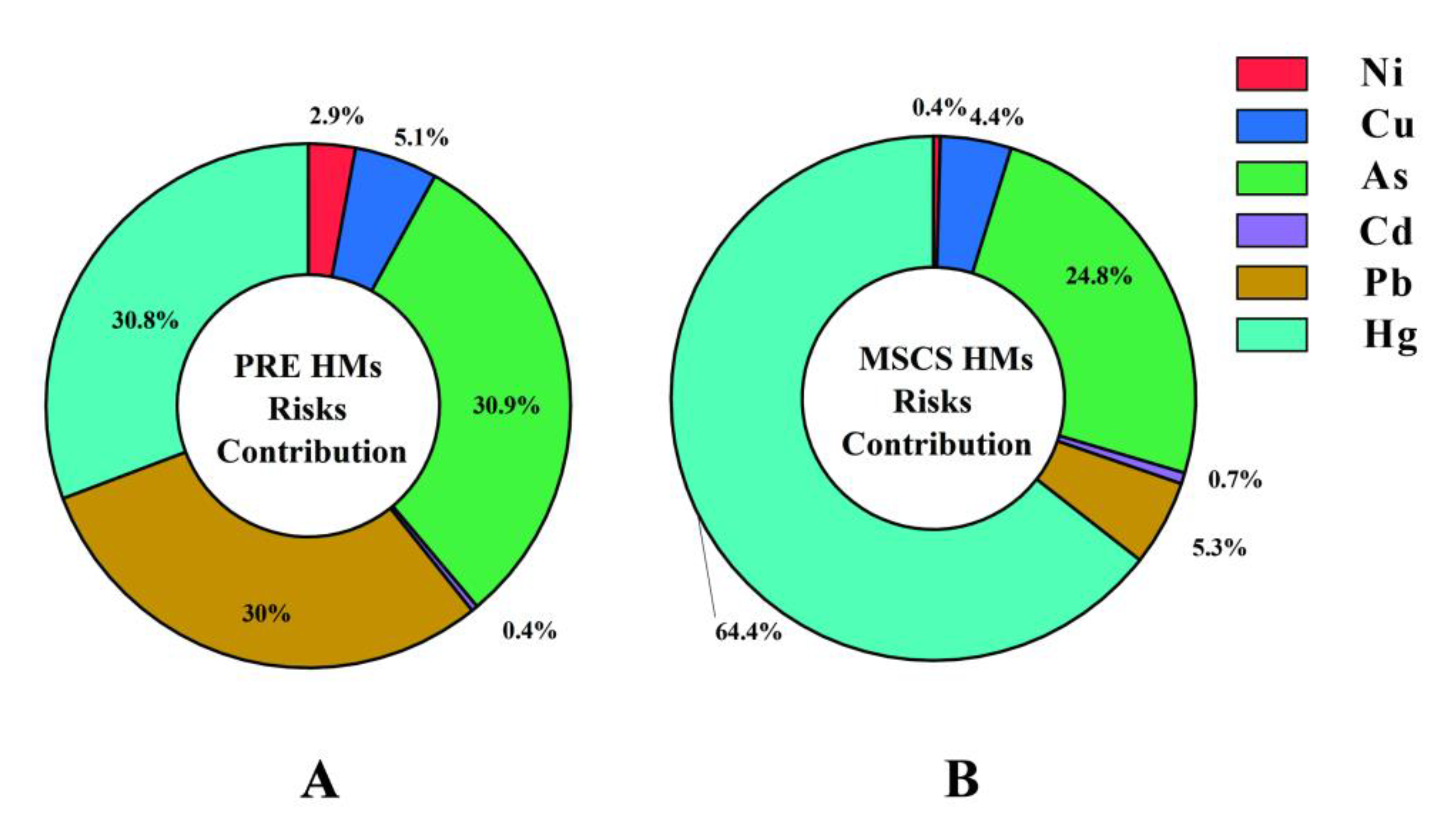
3.5. HMs Health Risks of Marine Fish
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asante, K.A.; Agusa, T.; Mochizuki, H.; Ramu, K.; Inoue, S.; Kubodera, T.; Takahashi, S.; Subramanian, A.; Tanabe, S. Trace elements and stable isotopes (δ13C and δ15N) in shallow and deep-water organisms from the East China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego, J.; Morales, J.A.; Torre, M.L.; Grande, J.A. Geochemical characteristics of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of the Tinto and Odiel river estuary. Environ. Geol. 2002, 41, 785–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, C.; Song, Z.; Chen, M.; Ding, L.; Liang, X.; Bi, X.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Zheng, W. Heavy metal in rice and vegetable and human exposure near a large Pb/Zn smelter in central China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Ding, Z.; Peng, J.; Jin, M.; Wang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Yue, W. Heavy metals in wild marine fish from South China Sea: Levels, tissue- and species-specific accumulation and potential risk to humans. Ecotoxicology 2015, 2, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirak, A.; Yilmaz, F.; Tuna, A.L.; Ozdemir, N. Heavy metals in water, sediment and tissues of Leuciscus cephalus from a stream in southwestern Turkey. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Bi, X.; Ning, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, P. Profiles, source identification and health risks of potentially toxic metals in pyrotechnic-related road dust during Chinese New Year. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, L.; Dou, S. Trophic transfer, biomagnification and risk assessments of four common heavy metals in the food web of Laizhou Bay, the Bohai Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Carranza, M.; Sepulveda-Lozada, A.; Dias-Ferreira, C.; Geissen, V. Distribution and bioconcentration of heavy metals in a tropical aquatic food web: A case study of a tropical estuarine lagoon in SE Mexico. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.G.; Wanjari, U.R.; Renu, K.; Vellingiri, B.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V. Heavy metal and metalloid-induced reproductive toxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 92, 103859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Peng, B.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, L.; Sun, J.; Peng, G.; Bai, X. Human health risk assessment of toxic heavy metal and metalloid intake via consumption of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) from rice-crayfish co-culture fields in China. Food Control 2021, 128, 108181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Long, M.L.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, Q.Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J. Food chain transfer of cadmium and lead to cattle in a lead-zinc smelter in Guizhou, China. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 3078–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Analyzing trophic transfer of heavy metals for food webs in the newly-formed wetlands of the Yellow River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Yu, S.; Cheng, H.; Hong, Y.; Feng, X. Mercury pollution in fish from South China Sea: Levels, species-specific accumulation, and possible sources. Environ. Res. 2014, 131, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, H.M.; Leung, A.O.W.; Wang, H.S.; Ma, K.K.; Liang, Y.; Ho, K.C.; Cheung, F.T.; Yung, K.K.L. Assessment of heavy metals/metalloid (As, Pb, Cd, Ni, Zn, Cr, Cu, Mn) concentrations in edible fish species tissue in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundiran, M.; Adewoye, S.; Ayandiran, T.; Dahunsi, S. Heavy metal, proximate and microbial profile of some selected commercial marine fish collected from two markets in south western Nigeria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Xiaona, H.; Wei, M. Distribution and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in aquatic organisms of different trophic levels and potential health risk assessment from Taihu lake, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 81, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W. The three ‘B’ of fish mercury in China: Bioaccumulation, biodynamics and biotransformation. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, L.S.; Pestana, I.A.; Almeida, M.G.; Nery, A.F.C.; Bastos, W.R.; Souza, C.M.M. Mercury biomagnification in an ichthyic food chain of an amazon floodplain lake (Puruzinho Lake): Influence of seasonality and food chain modeling. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhao, L.L.; Xu, H.Z.; Zhang, X.M. Spatial and seasonal characteristics of dissolved heavy metals in the surface seawater of the Yellow River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pan, X.; Chen, Q.; Huang, B. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in marine fish to the population in Zhejiang, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, M.S.; Saito, L.; Peacock, M. Anthropogenic impacts on mercury concentrations and nitrogen and carbon isotope ratios in fish muscle tissue of the Truckee River watershed, Nevada, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 347, 282–294. [Google Scholar]
- Tadiso, T.M.; Borgstrøm, R.; Rosseland, B.O. Mercury concentrations are low in commercial fish species of Lake Ziway, Ethiopia, but stable isotope data indicated biomagnification. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.G.; Wang, W.X. Linking mercury, carbon, and nitrogen stable isotopes in Tibetan biota: Implications for using mercury stable isotopes as source tracers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polak-Juszczak, L. Bioaccumulation of mercury in the trophic chain of flatfish from the Baltic Sea. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 585–591. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Schartup, A.T.; Valberg, A.P.; Ewald, J.D.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Yin, R.; Balcom, P.H.; Sunderland, E.M. Environmental origins of methylmercury accumulated in subarctic estuarine fish indicated by mercury stable isotopes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11559–11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Yang, Q.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Mu, Y. Analysis on the relationship between fisheries economic growth and marine environmental pollution in China's coastal regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, G.; Xu, W.; Li, X.; Yao, H.; Liang, P.; Li, J.; Sommar, J.; Yin, R.; et al. Mercury in the marine boundary layer and seawater of the South China Sea: Concentrations, sea/air flux, and implication for land outflow. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D06303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Feng, X.B.; Yin, R.S.; Zhu, W.; Li, Z. Mercury distributions and mercury isotope signatures in sediments of Dongjiang River, the Pearl River Delta. China. Chem. Geol. 2011, 287, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Jiang, W.; Li, F.; Pan, Y.; Wang, C.; Tian, H. Occurrence, partition, and risk of seven heavy metals in sediments, seawater, and organisms from the eastern sea area of Shandong Peninsula, Yellow Sea, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, B.; Qin, C.; Yin, R.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Point, D.; Maurice, L.; Sonke, J.E.; Zhang, L.; et al. Compound-specific stable isotope analysis provides new insights for tracking human monomethylmercury exposure sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12493–12503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Method 1631. Revision E, Mercury in Water by Oxidation, Purge and Trap, and Cold Vapor Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- GB 3097-1997; Sea Water Quality Standard. Administration of quality supervision, inspection and quarantine of the People’s Republic of China). Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 1997.
- GB 18421-2001; Marine Biological Quality. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2001.
- Liu, Y.; Kuang, W.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Lin, C.; Lin, H. Distribution, source and risk assessment of heavy metals in the seawater, sediments, and organisms of the Daya Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoof, R.A.; Yost, L.J.; Eickhoff, J.; Crecelius, E.A.; Cragin, D.W.; Meacher, D.M.; Menzel, D.B. A market basket survey of inorganic arsenic in food. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kumar, K.S.; Shin, K.H. Applicability of stable C and N isotope analysis in inferring the geographical origin and authentication of commercial fish (Mackerel, Yellow Croaker and Pollock). Food Chem. 2015, 172, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botto, F.; Gaitán, E.; Mianzan, H.; Acha, M.; Giberto, D.; Schiariti, A.; Lribarne, O. Origin of resources and trophic pathways in a large SW Atlantic estuary: An evaluation using stable isotopes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hull, P.; Rifkin, E.; Bouwer, E.J. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification of mercury and selenium in the Sarasota Bay ecosystem. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Wu, Q.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Ning, Y.; Xie, S.; Huang, W.; Bi, X. Enrichment of trace elements in red swamp crayfish: Influences of region and production method, and human health risk assessment. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NBS. China Statistical Yearbook 2019; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, W.X. The distribution and speciation of trace metalsin surface sediments from the Pearl River estuary and the Daya Bay, southern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Chen, J.; Gao, L.; Liang, Z.; Li, S.; Li, R.; Jin, G.; Shimizu, Y.; Onodera, S.I.; Saito, M.; et al. 210Pb dating to investigate the historical variations and identification of different sources of heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Liu, L.; Wei, R.; Sun, K. Heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk assessment in a typical mariculture area in western Guangdong. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; He, H.; Xia, Z.; Gan, H.; Xue, Q.; Cui, Z.; Chen, J. Heavy metals and Pb isotopes in a marine sediment core record environmental changes and anthropogenic activities in the Pearl River Delta over a century. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 151934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H. Distribution, sources, and fluxes of heavy metals in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 30, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Maavara, T.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Raymond, P. Rivers as the largest source of mercury to coastal oceans worldwide. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budko, D.F.; Demina, L.L.; Lisitzin, A.P. The heavy metal partitioning in the particle flux of the subarctic White Sea (Northwestern Russia). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 249, 107063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ni, Z.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, X. Atmospheric deposition of trace elements to Daya Bay, South China Sea: Fluxes and sources. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Tang, C.; Yi, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in fish and accumulation patterns in food web in the upper Yangtze River, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdoba-Tovar, L.; Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Barón, P.R.; Díez, S. Drivers of biomagnification of Hg, As and Se in aquatic food webs: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B. Food web structure on Georges Bank from stable C, N, and S isotopic compositions. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Fry, B. Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1987, 18, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, S.; Zhou, C.; Yuan, Z.; Da, C. Distribution of heavy metals, stable isotope ratios (δ13C and δ15N) and risk assessment of fish from the Yellow River Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.G.; Ning, J.J.; Ke, C.L.; Huang, H.H. Bioaccessibility and human health implications of heavy metals in different trophic level marine organisms: A case study of the South China Sea. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, K.A.; Agusa, T.; Kubota, R.; Mochizuki, H.; Ramu, K.; Nishida, S.; Ohta, S.; Yeh, H.; Subramanian, A.; Tanabe, S. Trace elements and stable isotope ratios (δ13C and δ15N) in fish from deep-waters of the Sulu Sea and the Celebes Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Xu, J. Decreased trophic position as a function of increasing body size of a benthic omnivorous fish from the largest freshwater lake in China. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2011, 91, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Gu, X.; Zeng, Q.; Zhou, L.; Sun, M. Food web structure of a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China) assessed by stable isotope analysis. Hydrobiologia 2012, 683, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shan, B.; Yu, W.; Li, H.; Sun, D. Heavy metal pollution and stable isotope ratios (δ13C and δ15N) in marine organisms from the Northern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Oki, T.; Kanae, S.; Mouri, G.; Kodama, K.; Komori, D.; Seto, S. Integrated biogeochemical modelling of nitrogen load from anthropogenic and natural sources in Japan. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 2325–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Harrison, P.J. Nitrogen over enrichment in subtropical Pearl River estuarine coastal waters: Possible causes and consequences. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.; Norstrom, R.; Hobson, K.; Muir, D.; Backus, S.; Fisk, A. Mercury and other trace elements in a pelagic Arctic marine food web (Northwater Polynya, Baffin Bay). Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 351–352, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayden, M.G.; Arsenault, L.M.; Kidd, K.A.; O’Driscoll, N.J.; Mallory, M.L. Mercury bioaccumulation and biomagnification in a small Arctic polynya ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 509–510, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, W.X. Size-dependence of the potential for metal biomagnification in early life stages of marine fishes. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, G.; Santoro, M.; Cottignoli, S.; Fabbri, M.; Carpene, E.; Isani, G. Metal distribution and metallothionein in loggerhead (Caretta caretta) and green (Chelonia mydas) sea turtles. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buekers, J.; Redeker, E.S.; Smolders, E. Lead toxicity to wildlife: Derivation of a critical blood concentration for wildlife monitoring based on literature data. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3431–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Ji, C.; Shan, X.; Li, F. Evaluation on the biomagnification or biodilution of trace metals in global marine food webs by meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 113856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, S.; De Broyer, C.; Zauke, G.P. Significance and interspecific variability of accumulated trace metal concentrations in Antarctic benthic crustaceans. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2008, 93, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.G.; Lin, Q.; Wang, X.H.; Du, F.Y.; Yu, Z.L.; Huang, H.H. Heavy metal concentrations in wild fishes captured from the South China Sea and associated health risks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 96, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carocci, A.; Rovito, N.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Genchi, G. Mercury toxicity and neurodegenerative effects. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 229, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Onsanit, S.; Ke, C.H.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, K.J.; Wang, W.X. Trace elements in two marine fish cultured in fish cages in Fujian province, China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, W.X. Large-scale spatial and interspecies differences in trace elements and stable isotopes in marine wild fish from Chinese waters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215–216, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| n | Ni | Cu | As | Cd | Pb | Hg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seawater | |||||||
| PRE | 8 | 4.36 ± 2.37 | 8.18 ± 1.42 | 4.50 ± 2.39 | 0.27 ± 0.61 | 0.20 ± 0.43 | 5.81 ± 3.32 |
| MSCS | 6 | 1.45 ± 0.12 | 1.24 ± 0.23 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 1.27 ± 0.39 |
| Fish | |||||||
| Scoliodon laticaudus | 6 | 2.30 ± 1.95 | 7.55 ± 5.30 | 6.16 ± 3.29 | 7.35 ± 16.60 | 0.94 ± 1.23 | 0.37 ± 0.17 |
| Coilia mystus | 4 | 3.07 ± 2.85 | 4.15 ± 1.91 | 3.44 ± 0.78 | 18.43 ± 21.25 | 2.93 ± 2.26 | 0.04 ± 0.08 |
| Konosirus punctatus | 2 | 0.83 ± 0.22 | 4.15 ± 1.96 | 5.56 ± 0.46 | 30.13 ± 41.64 | 1.56 ± 1.41 | 0.04 ± 0.02 |
| Thryssa kammalensis | 2 | 0.80 ± 0.29 | 6.09 ± 3.23 | 3.16 ± 0.00 | 2.00 ± 1.75 | 2.17 ± 0.68 | 0.07 ± 0.00 |
| Pennahia argentata | 3 | 0.73 ± 0.58 | 6.70 ± 3.43 | 2.77 ± 2.30 | 1.68 ± 1.80 | 0.14 ± 0.20 | 0.13 ± 0.12 |
| Sardina | 7 | 0.53 ± 0.37 | 3.07 ± 1.51 | 2.36 ± 1.40 | 7.80 ± 13.33 | 0.39 ± 0.59 | 0.09 ± 0.05 |
| Harpadon nehereus | 1 | 6.21 | 27.36 | 33.91 | 1.02 | 2.55 | 0.10 |
| Collichthys niveatus | 1 | 0.71 | 5.20 | 1.57 | 58.15 | 1.94 | 0.05 |
| Acanthopagrus schlegelii | 2 | 3.46 ± 1.81 | 2.11 ± 0.47 | 0.90 ± 0.81 | 1.14 ± 0.78 | 1.91 ± 2.70 | 0.10 ± 0.08 |
| Total of the PRE | 28 | 1.75 ± 1.93 | 5.74 ± 5.39 | 4.65 ± 6.23 | 10.83 ± 18.84 | 1.30 ± 1.50 | 0.14 ± 0.13 |
| Caranx ignobilis | 3 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 24.10 ± 5.64 | 3.59 ± 0.62 | 13.09 ± 12.43 | 0.49 ± 0.13 | 0.59 ± 0.33 |
| Acanthopagrus schlegelii | 2 | 0.44 ± 0.10 | 20.41 ± 0.94 | 5.94 ± 0.41 | 163.51 ± 153.88 | 0.49 ± 0.13 | 0.59 ± 0.33 |
| Pampus chinensis | 2 | 0.38 ± 0.09 | 8.12 ± 2.74 | 7.43 ± 0.09 | 2.39 ± 1.90 | 0.45 ± 0.07 | 0.27 ± 0.00 |
| Pennahia argentata | 2 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 83.50 ± 25.64 | 15.85 ± 0.27 | 120.35 ± 55.51 | 0.47 ± 0.00 | 0.31 ± 0.06 |
| Pomadasys maculatus | 1 | 0.64 | 48.58 | 17.47 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.236 |
| Trichiurus lepturus | 3 | 0.26 ± 0.05 | 14.98 ± 15.18 | 3.60 ± 0.57 | 161.12 ± 51.56 | 0.36 ± 0.07 | 1.37 ± 0.18 |
| Pentapus | 5 | 0.77 ± 0.25 | 5.24 ± 2.60 | 14.08 ± 5.78 | 2.57 ± 4.05 | 0.97 ± 0.40 | 0.25 ± 0.13 |
| Cephalopholis | 4 | 2.33 ± 2.62 | 2.32 ± 0.84 | 13.45 ± 4.31 | 32.04 ± 54.40 | 1.44 ± 1.38 | 0.27 ± 0.17 |
| Priacanthus | 2 | 0.78 ± 0.40 | 4.91 ± 1.96 | 4.36 ± 0.26 | 2.57 ± 4.05 | 0.97 ± 0.40 | 0.25 ± 0.13 |
| Neoniphon | 1 | 1.15 | 15.22 | 16.68 | 1.66 | 0.99 | 1.05 |
| Epinephelus | 5 | 0.86 ± 0.32 | 6.58 ± 5.02 | 8.35 ± 3.58 | 25.63 ± 39.51 | 0.66 ± 0.25 | 0.57 ± 0.16 |
| Balistapus | 2 | 0.44 ± 0.12 | 12.23 ± 5.44 | 45.39 ± 39.66 | 9.65 ± 12.66 | 0.94 ± 0.20 | 0.29 ± 0.13 |
| Sebastiscus | 3 | 0.98 ± 0.20 | 4.23 ± 2.33 | 9.23 ± 5.35 | 7.20 ± 5.31 | 0.68 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.13 |
| Decapterus maruadsi | 2 | 0.34 ± 0.07 | 17.74 ± 10.63 | 4.03 ± 0.86 | 20.31 ± 8.79 | 0.35 ± 0.05 | 0.23 ± 0.04 |
| Thunnini | 2 | 0.53 ± 0.18 | 11.31 ± 0.13 | 8.03 ± 0.13 | 69.38 ± 28.37 | 0.58 ± 0.22 | 1.49 ± 0.44 |
| Ilisha elongata Bennett | 2 | 0.56 ± 0.02 | 20.70 ± 0.55 | 2.78 ± 0.04 | 3.26 ± 3.46 | 0.60 ± 0.15 | 0.20 ± 0.01 |
| Scomberomorus niphonius | 3 | 0.33 ± 0.10 | 28.74 ± 9.62 | 20.20 ± 27.28 | 16.24 ± 17.45 | 0.46 ± 0.28 | 0.92 ± 0.75 |
| Apogonidae | 2 | 1.12 ± 0.30 | 7.79 ± 7.98 | 13.35 ± 7.25 | 22.40 ± 30.67 | 1.32 ± 0.97 | 0.80 ± 0.36 |
| Myripristis berndti | 1 | 0.74 | 1.89 | 29.04 | 0.85 | 0.75 | 2.13 |
| Hemibarbus | 2 | 1.32 ± 0.60 | 3.41 ± 0.67 | 13.66 ± 9.65 | 5.66 ± 0.41 | 0.61 ± 0.19 | 0.36 ± 0.11 |
| Lethrinus haematopterus | 3 | 0.82 ± 0.24 | 2.83 ± 2.29 | 8.88 ± 3.03 | 13.00 ± 21.01 | 0.67 ± 0.13 | 0.45 ± 0.10 |
| Variola | 1 | 0.78 | 11.52 | 12.16 | 0.78 | 1.20 | 0.20 |
| Upeneus | 1 | 0.94 | 4.40 | 22.50 | 14.30 | 0.55 | 0.27 |
| Mullidae | 1 | 0.40 | 14.16 | 10.66 | 0.61 | 0.52 | 0.47 |
| Ariussinensis Lacepede | 1 | 0.49 | 6.13 | 13.00 | 0.53 | 0.40 | 0.41 |
| Total of MSCS | 56 | 0.78 ± 0.82 | 13.8 ± 17.3 | 11.9 ± 11.7 | 31.3 ± 56.9 | 0.71 ± 0.490 | 0.570 ± 0.468 |
| Ni | Cu | As | Cd | Pb | Hg | CPI/ΣTHQ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SFPIs | |||||||
| PRE | 0.87 | 1.64 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 3.32 |
| MSCS | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.56 |
| SFPIf | |||||||
| PRE | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.47 |
| MSCS | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.73 |
| EDI | |||||||
| PRE | 4.61 × 10−4 | 1.64 × 10−3 | 1.48× 10−3 | 3.16 × 10−6 | 3.59 × 10−4 | 2.46 × 10−5 | - |
| MSCS | 1.83 × 10−4 | 3.84 × 10−3 | 3.26 × 10−3 | 1.50 × 10−5 | 1.74 × 10−4 | 1.41 × 10−4 | - |
| THQ | |||||||
| PRE | 2.31 × 10−2 | 4.10 × 10−2 | 2.47 × 10−1 | 3.16 × 10−3 | 2.40 × 10−1 | 2.46 × 10−1 | 1.05 × 100 |
| MSCS | 9.17 × 10−3 | 9.60 × 10−2 | 5.44 × 10−1 | 1.50 × 10−2 | 1.16 × 10−1 | 1.44 × 100 | 2.74 × 100 |
| Ni | Cu | As | Cd | Pb | Hg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRE | ||||||
| Slope | 0.25 | 0.11 | 0.07 | −0.16 | −0.27 | 0.33 |
| Intercept | −0.75 | 0.29 | 0.25 | −2.18 | 0.18 | −2.02 |
| BF | 1.78 | 1.29 | 1.17 | 0.69 | 0.54 | 2.14 |
| R | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.39 |
| p | 0.25 | 0.44 | 0.74 | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.04 * |
| MSCS | ||||||
| Slope | −0.25 | 0.43 | −0.08 | 0.29 | −0.16 | 0.40 |
| Intercept | 0.57 | −0.41 | 1.19 | −3.16 | 0.28 | −1.61 |
| BF | 0.56 | 2.69 | 0.83 | 1.95 | 0.69 | 2.51 |
| R | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.43 | 0.66 |
| p | <0.01 * | <0.01 * | 0.32 | 0.18 | <0.01 * | <0.01 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Sun, K.; Liu, J.; Wei, N.; Zhao, X. Comparison of Pollution Levels, Biomagnification Capacity, and Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Nearshore and Offshore Regions of the South China Sea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912248
Yang S, Sun K, Liu J, Wei N, Zhao X. Comparison of Pollution Levels, Biomagnification Capacity, and Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Nearshore and Offshore Regions of the South China Sea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912248
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shaochen, Kaifeng Sun, Jinling Liu, Nan Wei, and Xing Zhao. 2022. "Comparison of Pollution Levels, Biomagnification Capacity, and Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Nearshore and Offshore Regions of the South China Sea" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912248
APA StyleYang, S., Sun, K., Liu, J., Wei, N., & Zhao, X. (2022). Comparison of Pollution Levels, Biomagnification Capacity, and Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Nearshore and Offshore Regions of the South China Sea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912248






