Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Hospitalizations in the Pisan Longitudinal Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
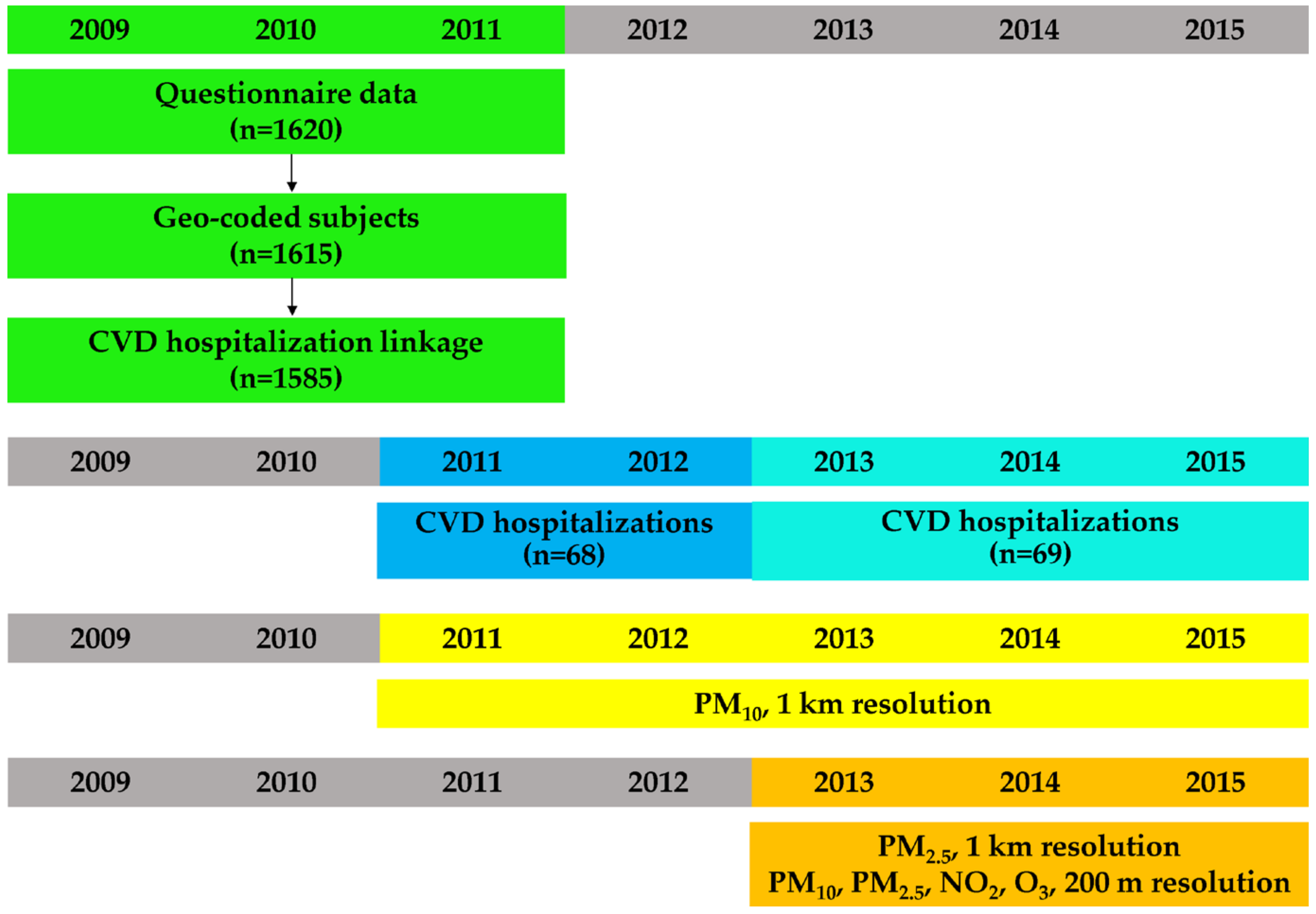
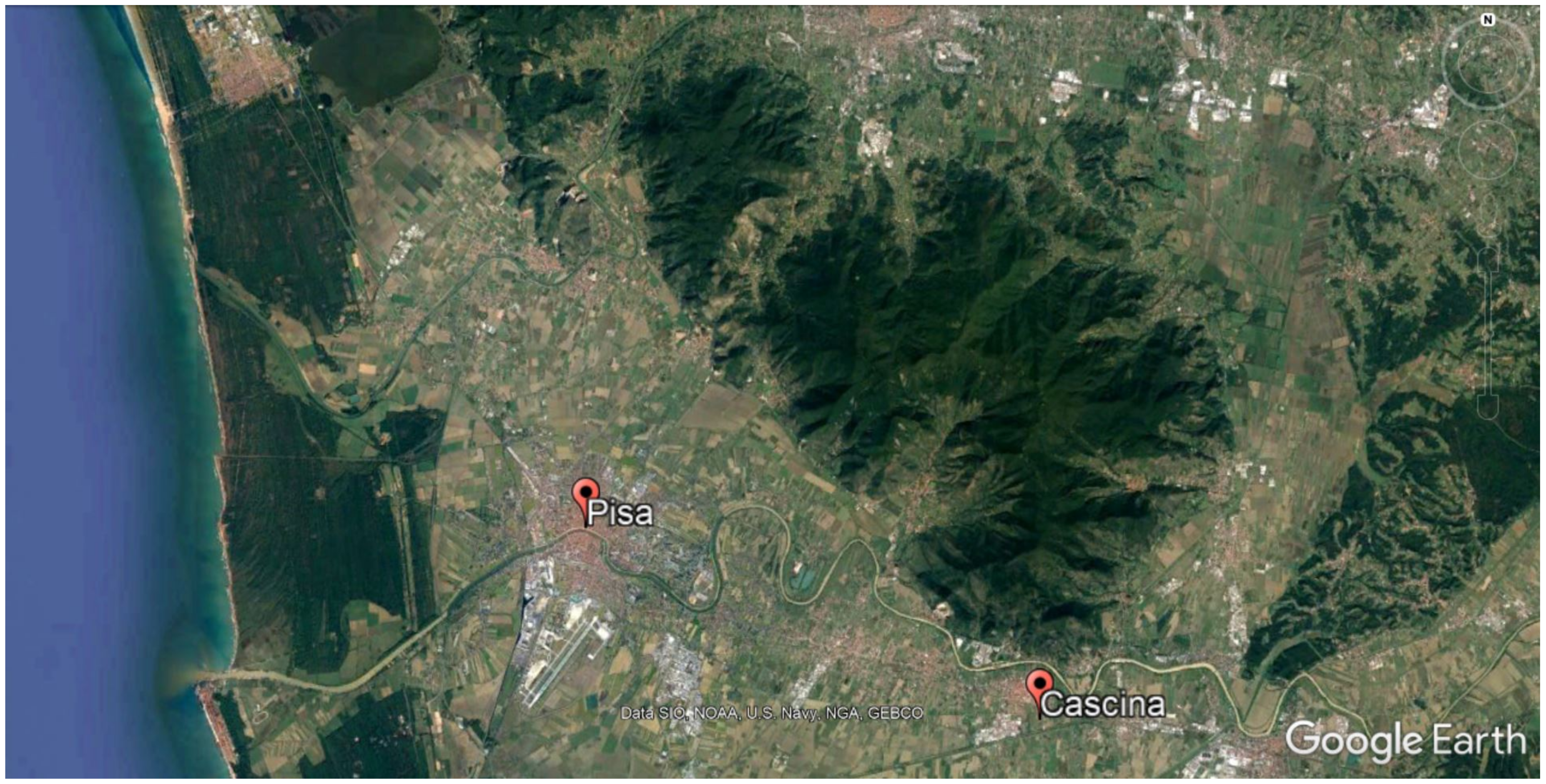
2.1. Study Design and Area
2.2. Questionnaire Data
2.3. Cardiovascular Hospitalizations
2.4. PM10, and PM2.5, 1 km Resolution
2.5. PM10, PM2.5, NO2 and O3, 200 m Resolution
2.6. Time-Varying Confounders
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
Acute Effects of Air Pollutants on CVD Hospitalizations
4. Discussion
4.1. Acute Effects of PM on CVD Hospitalizations
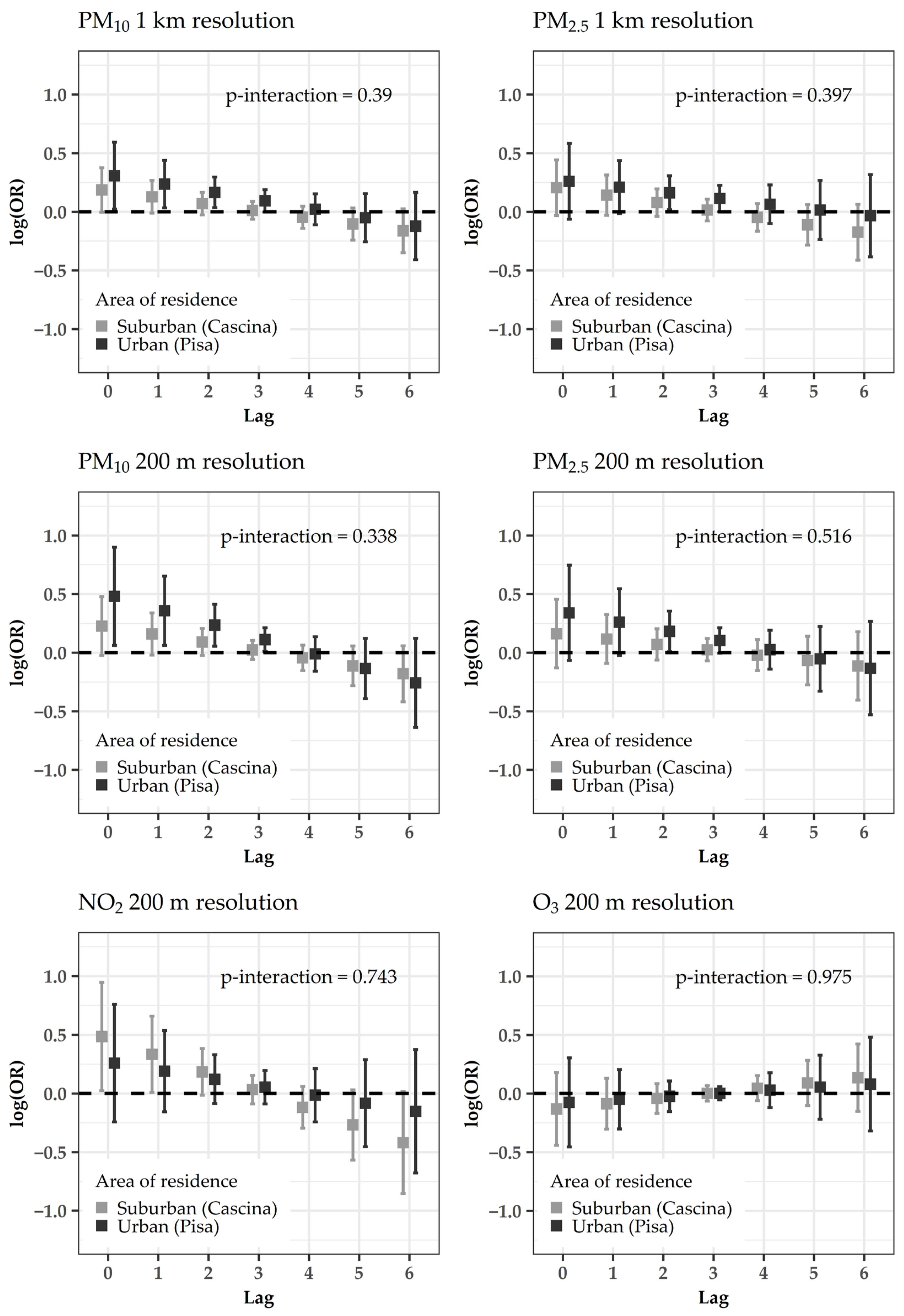
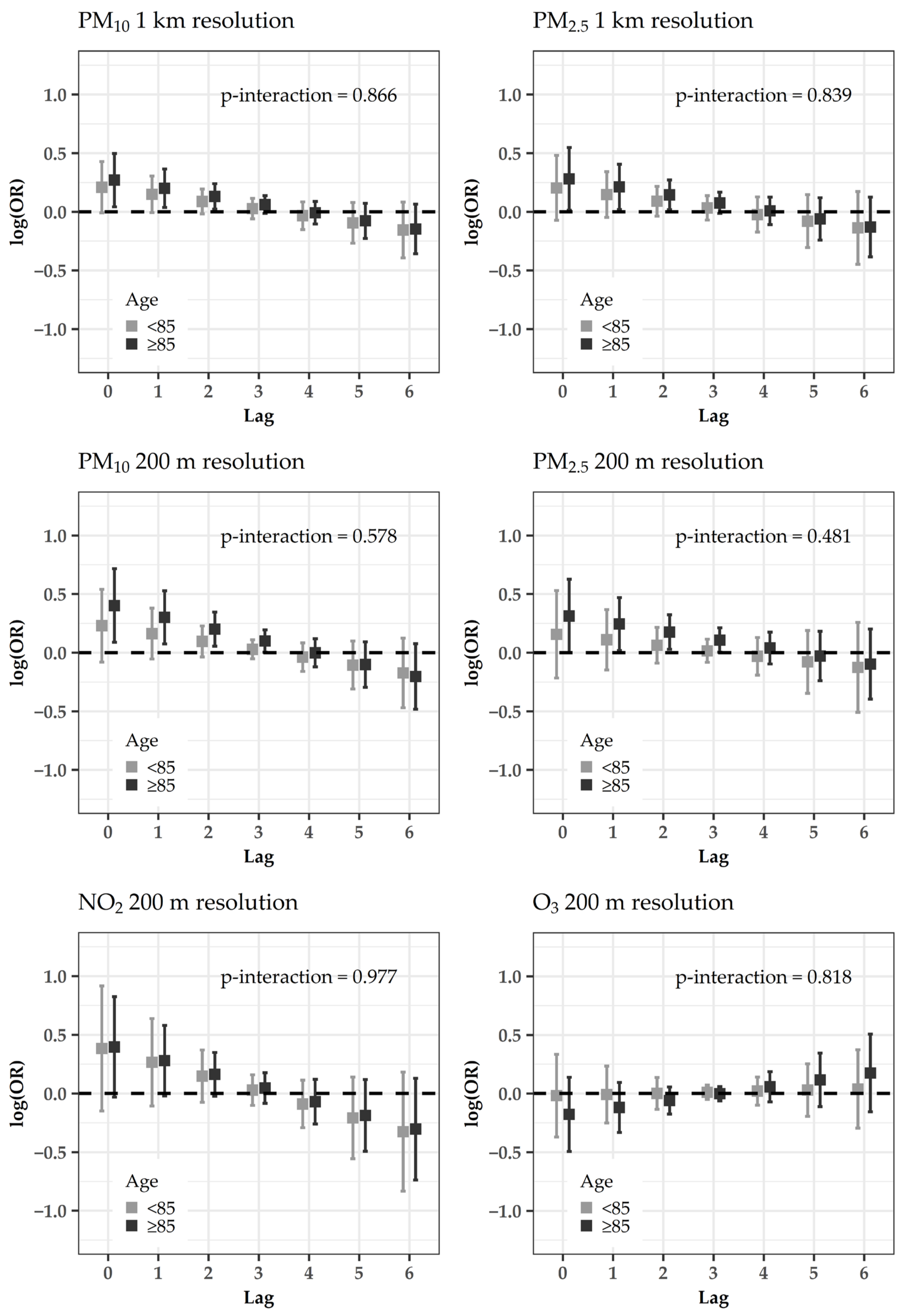
4.2. Subanalyses
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thurston, G.D.; Kipen, H.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Balmes, J.; Brook, R.D.; Cromar, K.; De Matteis, S.; Forastiere, F.; Forsberg, B.; Frampton, M.W.; et al. A Joint ERS/ATS Policy Statement: What Constitutes an Adverse Health Effect of Air Pollution? An Analytical Framework. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1600419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüss-Üstün, A.; Wolf, J.; Corvalán, C.; Bos, R.; Neira, M. Preventing Disease through Healthy Environments: A Global Assessment of the Burden of Disease from Environmental Risks; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. EPA. Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Particulate Matter (Final Report, Dec 2019); EPA/600/R-19/188; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Kloog, I.; Nordio, F.; Zanobetti, A.; Coull, B.A.; Koutrakis, P.; Schwartz, J.D. Short Term Effects of Particle Exposure on Hospital Admissions in the Mid-Atlantic States: A Population Estimate. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buszman, P.E.; Derbisz, K.; Kwasiborski, P.; Chrząszcz, P.; Mularska, M.; Baron, D.; Sobieszek, A.; Mendyk, A.; Skoczylas, P.; Cisowski, M.; et al. Impact of Air Pollution on Hospital Patients Admitted with ST-and Non-ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction in Heavily Polluted Cities within the European Union. Cardiol. J. 2018, 27, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzinger, S.; Schneider, A.; Breitner, S.; Stafoggia, M.; Erzen, I.; Dostal, M.; Pastorkova, A.; Bastian, S.; Cyrys, J.; Zscheppang, A.; et al. Ultrafine and Fine Particles and Hospital Admissions in Central Europe. Results from the UFIREG Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafoggia, M.; Samoli, E.; Alessandrini, E.; Cadum, E.; Ostro, B.; Berti, G.; Faustini, A.; Jacquemin, B.; Linares, C.; Pascal, M.; et al. Short-Term Associations between Fine and Coarse Particulate Matter and Hospitalizations in Southern Europe: Results from the MED-PARTICLES Project. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Si, Y.; Song, J.; Cao, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; et al. Association between Ambient Fine Particulate Pollution and Hospital Admissions for Cause Specific Cardiovascular Disease: Time Series Study in 184 Major Chinese Cities. BMJ 2019, 367, l6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.-Y.; Cheung, S.-M.; Chen, F.-C.; Wu, K.-H.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Chuang, P.-C.; Cheng, F.-J. Short-Term Effects of Ambient Air Pollution on ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Events: Are There Potentially Susceptible Groups? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhung, N.T.T.; Schindler, C.; Chau, N.Q.; Hanh, P.T.; Dien, T.M.; Thanh, N.T.N.; Künzli, N. Exposure to Air Pollution and Risk of Hospitalization for Cardiovascular Diseases amongst Vietnamese Adults: Case-Crossover Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.M.; Forti, M.C.; De Freitas, C.U.; Nascimento, F.P.; Junger, W.L.; Gouveia, N. Effects of Particulate Matter and Its Chemical Constituents on Elderly Hospital Admissions Due to Circulatory and Respiratory Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Di, Q.; Sofer, T.; Awad, Y.A.; Schwartz, J. Inverse Probability Weighted Distributed Lag Effects of Short-Term Exposure to PM2.5 and Ozone on CVD Hospitalizations in New England Medicare Participants-Exploring the Causal Effects. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakenhoff, T.B.; Van Smeden, M.; Visseren, F.L.; Groenwold, R.H. Random Measurement Error: Why Worry? An Example of Cardiovascular Risk Factors. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandini, M.; Scarinzi, C.; Bande, S.; Berti, G.; Carna, P.; Ciancarella, L.; Costa, G.; Demaria, M.; Ghigo, S.; Piersanti, A.; et al. Long Term Effect of Air Pollution on Incident Hospital Admissions: Results from the Italian Longitudinal Study within LIFE MED HISS Project. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafoggia, M.; Bellander, T.; Bucci, S.; Davoli, M.; De Hoogh, K.; De’Donato, F.; Gariazzo, C.; Lyapustin, A.; Michelozzi, P.; Renzi, M.; et al. Estimation of Daily PM10 and PM2.5 Concentrations in Italy, 2013–2015, Using a Spatiotemporal Land-Use Random-Forest Model. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinaccio, A.; Scortichini, M.; Gariazzo, C.; Leva, A.; Bonafede, M.; De’Donato, F.K.; Stafoggia, M.; Viegi, G.; Michelozzi, P.; Carla, A.; et al. Nationwide Epidemiological Study for Estimating the Effect of Extreme Outdoor Temperature on Occupational Injuries in Italy. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasola, S.; Maio, S.; Baldacci, S.; La Grutta, S.; Ferrante, G.; Forastiere, F.; Stafoggia, M.; Gariazzo, C.; Viegi, G. Effects of Particulate Matter on the Incidence of Respiratory Diseases in the Pisan Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariazzo, C.; Carlino, G.; Silibello, C.; Renzi, M.; Finardi, S.; Pepe, N.; Radice, P.; Forastiere, F.; Michelozzi, P.; Viegi, G.; et al. A Multi-City Air Pollution Population Exposure Study: Combined Use of Chemical-Transport and Random-Forest Models with Dynamic Population Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, S.; Baldacci, S.; Carrozzi, L.; Pistelli, F.; Angino, A.; Simoni, M.; Sarno, G.; Cerrai, S.; Martini, F.; Fresta, M.; et al. Respiratory Symptoms/Diseases Prevalence Is Still Increasing: A 25-Yr Population Study. Respir. Med. 2016, 110, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, S.; Baldacci, S.; Carrozzi, L.; Pistelli, F.; Simoni, M.; Angino, A.; La Grutta, S.; Muggeo, V.; Viegi, G. 18-Yr Cumulative Incidence of Respiratory/Allergic Symptoms/Diseases and Risk Factors in the Pisa Epidemiological Study. Respir. Med. 2019, 158, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuvolone, D.; Balzi, D.; Chini, M.; Scala, D.; Giovannini, F.; Barchielli, A. Short-Term Association between Ambient Air Pollution and Risk of Hospitalization for Acute Myocardial Infarction: Results of the Cardiovascular Risk and Air Pollution in Tuscany (RISCAT) Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 174, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMCA II Web Site. Available online: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/chafea_pdb/health/projects/2005121/summary (accessed on 31 July 2020).
- Stafoggia, M.; Schwartz, J.; Badaloni, C.; Bellander, T.; Alessandrini, E.; Cattani, G.; De’Donato, F.; Gaeta, A.; Leone, G.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. Estimation of Daily PM10 Concentrations in Italy (2006–2012) Using Finely Resolved Satellite Data, Land Use Variables and Meteorology. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, D.P.; et al. The ERA-Interim Reanalysis: Configuration and Performance of the Data Assimilation System. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclure, M. The Case-Crossover Design: A Method for Studying Transient Effects on the Risk of Acute Events. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1991, 133, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carracedo-Martínez, E.; Taracido, M.; Tobias, A.; Saez, M.; Figueiras, A. Case-Crossover Analysis of Air Pollution Health Effects: A Systematic Review of Methodology and Application. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J. Is There Harvesting in the Association of Airborne Particles with Daily Deaths and Hospital Admissions? Epidemiology 2001, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solimini, A.G.; Renzi, M. Association between Air Pollution and Emergency Room Visits for Atrial Fibrillation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collart, P.; Dubourg, D.; Levêque, A.; Sierra, N.B.; Coppieters, Y. Short-Term Effects of Nitrogen Dioxide on Hospital Admissions for Cardiovascular Disease in Wallonia, Belgium. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 255, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariazzo, C.; Carlino, G.; Silibello, C.; Tinarelli, G.; Renzi, M.; Finardi, S.; Pepe, N.; Barbero, D.; Radice, P.; Marinaccio, A.; et al. Impact of Different Exposure Models and Spatial Resolution on the Long-Term Effects of Air Pollution. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Regional Office. Review of Evidence on Health Aspects of Air Pollution–REVIHAAP Project: Final Technical Report; WHO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Saifipour, A.; Azhari, A.; Pourmoghaddas, A.; Hosseini, S.M.; Jafari-Koshki, T.; Rahimi, M.; Nasri, A.; Shishehforoush, M.; Lahijanzadeh, A.; Sadeghian, B.; et al. Association between Ambient Air Pollution and Hospitalization Caused by Atrial Fibrillation. ARYA Atheroscler. 2019, 15, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Milojevic, A.; Wilkinson, P.; Armstrong, B.; Bhaskaran, K.; Smeeth, L.; Hajat, S. Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on a Range of Cardiovascular Events in England and Wales: Case-Crossover Analysis of the MINAP Database, Hospital Admissions and Mortality. Heart 2014, 100, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarinzi, C.; Alessandrini, E.R.; Chiusolo, M.; Galassi, C.; Baldini, M.; Serinelli, M.; Pandolfi, P.; Bruni, A.; Biggeri, A.; De Togni, A.; et al. Inquinamento Atmosferico e Ricoveri Ospedalieri Urgenti in 25 Città Italiane: Risultati Del Progetto EpiAir2. Epidemiol. Prev. 2013, 37, 230–241. [Google Scholar]
- Montresor-López, J.A.; Yanosky, J.D.; Mittleman, M.A.; Sapkota, A.; He, X.; Hibbert, J.D.; Wirth, M.D.; Puett, R.C. Short-Term Exposure to Ambient Ozone and Stroke Hospital Admission: A Case-Crossover Analysis. J. Exp. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuvolone, D.; Balzi, D.; Pepe, P.; Chini, M.; Scala, D.; Giovannini, F.; Cipriani, F.; Barchielli, A. Ozone Short-Term Exposure and Acute Coronary Events: A Multicities Study in Tuscany (Italy). Environ. Res. 2013, 126, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, A.; Bellander, T.; Bero-Bedada, G.; Dahlquist, M.; Hollenberg, J.; Jonsson, M.; Lind, T.; Rosenqvist, M.; Svensson, L.; Ljungman, P.L. Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in Stockholm. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.C.; Pereira, L.A.; Lin, C.A.; Santos, U.P.; Prioli, G.; Luiz, O.d.C.; Saldiva, P.H.; Braga, A.L.F. The Effects of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Diseases: Lag Structures. Rev. Saude Publica 2006, 40, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, M.A.; Ebisu, K.; Dominici, F.; Wang, Y.; Peng, R.D.; Bell, M.L. Airborne Fine Particles and Risk of Hospital Admissions for Understudied Populations: Effects by Urbanicity and Short-Term Cumulative Exposures in 708 US Counties. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, M.A.; Khaheshi, I.; Sharifi, A.; Yousefi, N.; Naderian, M.; Namazi, M.H.; Safi, M.; Vakili, H.; Saadat, H.; Parsa, S.A.; et al. The Association between Exposure to Air Pollutants Including PM10, PM2.5, Ozone, Carbon Monoxide, Sulfur Dioxide, and Nitrogen Dioxide Concentration and the Relative Risk of Developing STEMI: A Case-Crossover Design. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, T.; Li, X.; Wang, G. Ambient Air Pollution and Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, X.; Juan, J.; Song, J.; Cao, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, M.; Hu, Y. Ambient Particulate Matter Concentrations and Hospital Admissions in 26 of China’s Largest Cities: A Case–Crossover Study. Epidemiology 2018, 29, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumake, K.L.; Sacks, J.D.; Lee, J.S.; Johns, D.O. Susceptibility of Older Adults to Health Effects Induced by Ambient Air Pollutants Regulated by the European Union and the United States. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 25, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clougherty, J.E. A Growing Role for Gender Analysis in Air Pollution Epidemiology. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A. Environmental Determinants of Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulka, C.M.; Daviglus, M.L.; Persky, V.W.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Lash, J.P.; Elfassy, T.; Lee, D.J.; Ramos, A.R.; Tarraf, W.; Argos, M. Association of Occupational Exposures with Cardiovascular Disease among US Hispanics/Latinos. Heart 2019, 105, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, M.; Baldacci, S.; Maio, S.; Cerrai, S.; Sarno, G.; Viegi, G. Adverse Effects of Outdoor Pollution in the Elderly. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Simoni, M.; Jaakkola, M.; Carrozzi, L.; Baldacci, S.; Di Pede, F.; Viegi, G. Indoor Air Pollution and Respiratory Health in the Elderly. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 21, 15s–20s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hospitalization Characteristics | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| Disease group (ICD-9 code) | |
| Hypertensive disease (401–405) | 1 (1) |
| Ischemic heart disease (410–414) | 32 (23) |
| Diseases of pulmonary circulation (415–417) | 9 (7) |
| Other forms of heart disease (420–429) | 55 (40) |
| Cerebrovascular disease (430–438) | 27 (20) |
| Diseases of arteries, arterioles, and capillaries (440–449) | 8 (6) |
| Diseases of veins and lymphatics, and other diseases of circulatory system (451–459) | 5 (4) |
| Year | |
| 2011 | 30 (22) |
| 2012 | 38 (28) |
| 2013 | 26 (19) |
| 2014 | 16 (12) |
| 2015 | 27 (20) |
| Area of residence | |
| Urban (Pisa) | 55 (40) |
| Suburban (Cascina) | 82 (60) |
| Age class | |
| <85 years | 87 (64) |
| ≥85 years | 50 (36) |
| Gender | |
| Female | 69 (50) |
| Male | 68 (50) |
| Smoking status | |
| Non-smoker | 67 (49) |
| Ever smoker | 70 (51) |
| Occupational exposure | |
| Not exposed | 73 (53) |
| Exposed | 64 (47) |
| Pre-existent cardiovascular/respiratory diseases | |
| No | 77 (56) |
| Yes | 60 (44) |
| Pollutants | Mean | SD | Median | 25th Percentile | 75th Percentile | IQR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011–2015 (n = 411 1) | ||||||
| PM10, 1 km | 26.2 | 11.7 | 23.3 | 18.3 | 30.1 | 11.8 |
| 2013–2015 (n = 207 2) | ||||||
| PM10, 1 km | 25.9 | 13.0 | 22.2 | 16.9 | 29.7 | 12.8 |
| PM2.5, 1 km | 17.4 | 11.3 | 13.0 | 10.2 | 19.5 | 9.3 |
| PM10, 200 m | 24.9 | 11.0 | 22.1 | 18.1 | 26.9 | 8.8 |
| PM2.5, 200 m | 16.0 | 9.2 | 12.9 | 10.2 | 17.5 | 7.3 |
| NO2, 200 m | 26.7 | 10.9 | 24.4 | 18.5 | 32.4 | 13.9 |
| O3, 200 m | 47.1 | 19.3 | 48.5 | 32.5 | 62.7 | 30.2 |
| Pollutants | Day 0 | Day −7 | Day +7 | Δ(0,−7) | p-Value 1 | Δ(0,+7) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011–2015 (n = 137) | |||||||
| PM10, 1 km | 27.6 (12.7) | 25.9 (11.8) | 25.5 (10.3) | 1.7 (14.0) | 0.149 | 2.1 (11.4) | 0.030 |
| 2013–2015 (n = 69) | |||||||
| PM10, 1 km | 28.5 (14.8) | 24.4 (12.3) | 25.0 (11.5) | 4.1 (15.8) | 0.033 | 3.5 (12.0) | 0.021 |
| PM2.5, 1 km | 18.9 (12.4) | 16.8 (11.0) | 16.7 (10.2) | 2.1 (13.0) | 0.181 | 2.2 (9.2) | 0.051 |
| PM10, 200 m | 26.5 (11.3) | 23.9 (11.7) | 24.5 (9.9) | 2.6 (11.8) | 0.073 | 2.0 (9.0) | 0.070 |
| PM2.5, 200 m | 17.1 (10.1) | 15.7 (9.3) | 15.6 (8.2) | 1.4 (9.9) | 0.231 | 1.5 (8.1) | 0.123 |
| NO2, 200 m | 27.5 (11.3) | 26.1 (10.8) | 26.8 (10.8) | 1.4 (6.8) | 0.096 | 0.7 (6.0) | 0.311 |
| O3, 200 m | 46.6 (19.4) | 47.7 (19.7) | 46.3 (19.1) | −1.1 (8.4) | 0.269 | 0.3 (8.5) | 0.781 |
| Lags | 2011–2015 n = 137 | 2013–2015 n = 69 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM10, 1 km | PM10, 1 km | PM2.5, 1 km | PM10, 200 m | PM2.5, 200 m | NO2, 200 m | O3, 200 m | |
| Lag 0 | 1.137 (1.023, 1.264) | 1.268 (1.085, 1.483) | 1.273 (1.053, 1.540) | 1.365 (1.103, 1.690) | 1.264 (1.006, 1.589) | 1.477 (1.058, 2.061) | 0.896 (0.710, 1.130) |
| Lag 1 | 1.099 (1.017, 1.188) | 1.190 (1.063, 1.332) | 1.197 (1.045, 1.372) | 1.255 (1.078, 1.461) | 1.193 (1.015, 1.401) | 1.313 (1.040, 1.658) | 0.930 (0.794, 1.089) |
| Lag 2 | 1.062 (1.006, 1.121) | 1.116 (1.036, 1.203) | 1.126 (1.029, 1.231) | 1.154 (1.049, 1.270) | 1.125 (1.016, 1.245) | 1.167 (1.012, 1.346) | 0.965 (0.885, 1.054) |
| Lag 3 | 1.027 (0.984, 1.071) | 1.047 (0.990, 1.108) | 1.059 (0.989, 1.133) | 1.061 (0.998, 1.129) | 1.061 (0.989, 1.139) | 1.038 (0.947, 1.137) | 1.002 (0.961, 1.046) |
| Lag 4 | 0.992 (0.942, 1.044) | 0.982 (0.913, 1.058) | 0.995 (0.908, 1.091) | 0.976 (0.897, 1.061) | 1.001 (0.905, 1.107) | 0.922 (0.804, 1.058) | 1.041 (0.954, 1.135) |
| Lag 5 | 0.959 (0.890, 1.033) | 0.922 (0.825, 1.030) | 0.936 (0.815, 1.075) | 0.897 (0.782, 1.029) | 0.945 (0.805, 1.109) | 0.820 (0.654, 1.029) | 1.081 (0.923, 1.265) |
| Lag 6 | 0.927 (0.837, 1.026) | 0.865 (0.741, 1.009) | 0.880 (0.726, 1.068) | 0.825 (0.677, 1.006) | 0.891 (0.710, 1.118) | 0.729 (0.526, 1.011) | 1.122 (0.890, 1.415) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fasola, S.; Maio, S.; Baldacci, S.; La Grutta, S.; Ferrante, G.; Forastiere, F.; Stafoggia, M.; Gariazzo, C.; Silibello, C.; Carlino, G.; et al. Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Hospitalizations in the Pisan Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031164
Fasola S, Maio S, Baldacci S, La Grutta S, Ferrante G, Forastiere F, Stafoggia M, Gariazzo C, Silibello C, Carlino G, et al. Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Hospitalizations in the Pisan Longitudinal Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(3):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031164
Chicago/Turabian StyleFasola, Salvatore, Sara Maio, Sandra Baldacci, Stefania La Grutta, Giuliana Ferrante, Francesco Forastiere, Massimo Stafoggia, Claudio Gariazzo, Camillo Silibello, Giuseppe Carlino, and et al. 2021. "Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Hospitalizations in the Pisan Longitudinal Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 3: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031164
APA StyleFasola, S., Maio, S., Baldacci, S., La Grutta, S., Ferrante, G., Forastiere, F., Stafoggia, M., Gariazzo, C., Silibello, C., Carlino, G., Viegi, G., & on behalf of the BEEP Collaborative Group. (2021). Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Hospitalizations in the Pisan Longitudinal Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031164








