Alexithymia, Dissociation, and Family Functioning in a Sample of Online Gamblers: A Moderated Mediation Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
- exploring the differences in the analysed variables, based on gambling severity in online regular gamblers, to provide a better understanding of the characteristics related to problematic online gambling; and
- investigating the relationship between alexithymia, dissociation, and family functioning in contributing to problem gambling among online gamblers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants, Procedure and Ethics
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS)
2.2.2. Twenty-Items Toronto Alexithymia Scale (TAS-20)
2.2.3. Dissociative Experience Scale-II (DES-II)
2.2.4. Family Adaptability and Cohesion Evaluation Scales-IV (FACES IV)
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gainsbury, S.M. Online gambling addiction: The relationship between internet gambling and disordered gambling. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2015, 2, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Petry, N.M.; Blanco, C.; Auriacombe, M.; Borges, G.; Bucholz, K.; Crowley, T.J.; Grant, B.F.; Hasin, D.S.; O’Brien, C. An overview of and rationale for changes proposed for pathological gambling in DSM-5. J. Gambl. Stud. 2014, 30, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, A.; Griffiths, M.D. Motivating and inhibiting factors in online gambling behaviour: A grounded theory study. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2012, 10, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reith, G. Beyond addiction or compulsion: The continuing role of environment in the case of pathological gambling. Addiction 2012, 107, 1736–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuss, D.; Griffiths, M.D. Internet gambling behavior. In Encyclopedia of Cyber Behavior; Yan, Z., Ed.; IGI Global: Hershey PA, USA, 2012; pp. 735–753. [Google Scholar]
- Canale, N.; Griffiths, M.D.; Vieno, A.; Siciliano, V.; Molinaro, S. Impact of Internet gambling on problem gambling among adolescents in Italy: Findings from a large-scale nationally representative survey. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 57, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaii, S.S.H.; Kamaly, A.; Esfahani, M. Meta-analysis of individual and environmental factors that influence people’s addiction tendencies. Int. J. High Risk. Behav. Addict. 2012, 1, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caretti, V.; Gori, A.; Craparo, G.; Giannini, M.; Iraci-Sareri, G.; Schimmenti, A. A new measure for assessing substance-related and addictive disorders: The addictive behavior questionnaire (ABQ). J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.M.; Jones, S.A.; Kliamovich, D.; Harman, G.; Nagel, B.J. Identifying early risk factors for addiction later in life: A review of prospective longitudinal studies. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2020, 7, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lussier, I.D.; Derevensky, J.; Gupta, R.; Vitaro, F. Risk, compensatory, protective, and vulnerability factors related to youth gambling problems. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2014, 28, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.J. Recent developments in alexithymia theory and research. Can. J. Psychiat. 2000, 45, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morie, K.P.; Yip, S.W.; Nich, C.; Hunkele, K.; Carroll, K.M.; Potenza, M.N. Alexithymia and addiction: A review and preliminary data suggesting neurobiological links to reward/loss processing. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2016, 3, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gori, A.; Craparo, G.; Caretti, V.; Giannini, M.; Iraci-Sareri, G.; Bruschi, A.; Janiri, L.; Ponti, L.; Tani, F. Impulsivity, alexithymia and dissociation among pathological gamblers in different therapeutic settings: A multisample comparison study. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 246, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gori, A.; Topino, E.; Craparo, G.; Bagnoli, I.; Caretti, V.; Schimmenti, A. A Comprehensive Model for Gambling Behaviors: Assessment of the Factors that can Contribute to the Vulnerability and Maintenance of Gambling Disorder. J. Gambl. Stud. 2021. Online first. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, V.V.; Lugo, R.G.; Sütterlin, S. The somatic marker theory in the context of addiction: Contributions to understanding development and maintenance. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2015, 8, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khantzian, E.J. The self-medication hypothesis of addictive disorders: Focus on heroin and cocaine dependence. In The Cocaine Crisis; Allen, D.F., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Di Trani, M.; Renzi, A.; Vari, C.; Zavattini, G.C.; Solano, L. Gambling disorder and affect regulation: The role of alexithymia and attachment style. J. Gambl. Stud. 2017, 33, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogier, G.; Velotti, P. Conceptualizing gambling disorder with the process model of emotion regulation. J. Behav. Addict. 2018, 7, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, D.; Verrocchio, M.C.; Porcelli, P. Gambling problems and alexithymia: A systematic review. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogier, G.; Capone, A.; Velotti, P. Emotion regulation strategies and dissociation in Gambling Disorder. Int. Gambl. Stud. 2021. Online first. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogier, G.; Beomonte Zobel, S.; Marini, A.; Camponeschi, J.; Velotti, P. Gambling disorder and dissociative features: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2021, 35, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperatori, C.; Innamorati, M.; Bersani, F.S.; Imbimbo, F.; Pompili, M.; Contardi, A.; Farina, B. The association among childhood trauma, pathological dissociation and gambling severity in casino gamblers. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 2017, 24, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, L.D. Normative dissociation. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2006, 29, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewenstein, R.J. Dissociation debates: Everything you know is wrong. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartmill, T.; Slatter, T.; Wilkie, B. The role of anxiety and dissociation in young Australian gamblers. J. Gambl. Stud. 2015, 31, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, M.J.; Graydon, C.; Harrigan, K.A.; Wojtowicz, L.; Siu, V.; Fugelsang, J.A. The allure of multi-line games in modern slot machines. Addiction 2014, 109, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, J.; Delfabbro, P.; Denson, L.A. Psychological vulnerability and problem gambling: An application of Durand Jacobs’ general theory of addictions to electronic gaming machine playing in Australia. J. Gambl. Stud. 2012, 28, 665–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D.; Russell, C.S.; Sprenkle, D.H. Circumplex Model: Systemic Assessment and Treatment of Families; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tafà, M.; Baiocco, R. Addictive behavior and family functioning during adolescence. Am. J. Fam. Ther. 2009, 37, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafà, M.; Cimino, S.; Ballarotto, G.; Bracaglia, F.; Bottone, C.; Cerniglia, L. Female adolescents with eating disorders, parental psychopathological risk and family functioning. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2017, 26, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzo, G.; Cascio, V.L.; Pace, U. The role of individual and relational characteristics on alcohol consumption among Italian adolescents: A discriminant function analysis. Child Indic. Res. 2013, 6, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, M.; Chong, S.A.; Satghare, P.; Browning, C.J.; Thomas, S. Gambling and family: A two-way relationship. J. Behav. Addict. 2017, 6, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleczka, P.; Braun, B.; Grüne, B.; Bühringer, G.; Kraus, L. Family functioning and gambling problems in young adulthood: The role of the concordance of values. Addict. Res. Theory 2018, 26, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolini, D.; Leonardi, C.; Visani, E.; Rodofili, G. The gambling disorder: Family styles and cognitive dimensions. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Kourgiantakis, T.; Saint-Jacques, M.C.; Tremblay, J. Problem gambling and families: A systematic review. J. Soc. Work Pract. Addict. 2013, 13, 353–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesieur, H.R.; Blume, S.B. The South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS): A new instrument for the identification of pathological gamblers. Am. J. Psychiatry 1987, 144, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreschi, C.; Gander, S. Versione Italiana del South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS) di H.R. In Giocati Dal Gioco. Quando il Divertimento Diventa una Malattia: Il Gioco D’azzardo Patologico; Guerreschi, C., Ed.; San Paolo Edizioni: Milan, Italy, 2002; pp. 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Bagby, R.M.; Parker, J.D.; Taylor, G.J. The twenty-item Toronto Alexithymia Scale-I. Item selection and cross-validation of the factor structure. J. Psychosom. Res. 1994, 38, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagby, R.M.; Taylor, G.J.; Parker, J.D. The twenty-item Toronto Alexithymia Scale-II. Convergent, discriminant, and concurrent validity. J. Psychosom. Res. 1994, 38, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, C.; Taylor, G.; Parker, J.; Bressi, S.; Brambilla, V.; Aguglia, E.; Allegranti, I.; Bongiorno, A.; Gilberti, F.; Bucca, M.; et al. Cross validation of the factor structure of the 20-item Toronto Alexithymia Scale: An Italian multicenter study. J. Psychosom. Res. 1996, 41, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, E.B.; Putnam, F.W. An update on the Dissociative Experiences Scale. Dissociation Prog. Dissociative Disord. 1994, 6, 16–27. [Google Scholar]
- Schimmenti, A. Dissociative experiences and dissociative minds: Exploring a nomological network of dissociative functioning. J. Trauma Dissociation 2016, 17, 338–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D. FACES IV and the circumplex model: Validation study. J. Marital Fam. Ther. 2011, 37, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiocco, R.; Cacioppo, M.; Laghi, F.; Tafà, M. Factorial and construct validity of FACES IV among Italian adolescents. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2013, 22, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis Second Edition: A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wayne, S.J.; Lemmon, G.; Hoobler, J.M.; Cheung, G.W.; Wilson, M.S. The ripple effect: A spillover model of the detrimental impact of work–family conflict on job success. J. Organ. Behav. 2017, 38, 876–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes-Balog, K.E.; Hemphill, S.A. Relationships between online gambling, mental health, and substance use: A review. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2012, 15, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, N.A.; Merkouris, S.S.; Greenwood, C.J.; Oldenhof, E.; Toumbourou, J.W.; Youssef, G.J. Early risk and protective factors for problem gambling: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2017, 51, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgerton, J.D.; Keough, M.T.; Roberts, L.W. Co-development of problem gambling and depression symptoms in emerging adults: A parallel-process latent class growth model. J. Gambl. Stud. 2018, 34, 949–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerniglia, L.; Cimino, S.; Tafà, M.; Marzilli, E.; Ballarotto, G.; Bracaglia, F. Family profiles in eating disorders: Family functioning and psychopathology. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2017, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jozefiak, T.; Greger, H.K.; Koot, H.M.; Klöckner, C.A.; Wallander, J.L. The role of family functioning and self-esteem in the quality of life of adolescents referred for psychiatric services: A 3-year follow-up. Qual. Life Res. 2019, 28, 2443–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacioppo, M.; Barni, D.; Correale, C.; Mangialavori, S.; Danioni, F.; Gori, A. Do attachment styles and family functioning predict adolescents’ problematic internet use? A relative weight analysis. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2019, 28, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimeno, M.V.; Ricarte, J.J.; Toledano, A.; Mangialavori, S.; Cacioppo, M.; Ros, L. Role of Attachment and Family Functioning in Problematic Smartphone Use in Young Adults. J. Fam. Issues 2021. Online first. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnaire, C.; Phan, O. Relationships between parental attitudes, family functioning and Internet gaming disorder in adolescents attending school. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 255, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, G.; Picone, F.; van Holst, R.J.; Bolloni, C.; Scardina, S.; Cannizzaro, C. Alterations in the emotional regulation process in gambling addiction: The role of anger and alexithymia. J. Gambl. Stud. 2017, 33, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnaire, C.; Barrault, S.; Aïte, A.; Cassotti, M.; Moutier, S.; Varescon, I. Relationship between pathological gambling, alexithymia, and gambling type. Am. J. Addict. 2017, 26, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craparo, G.; Magnano, P.; Zapparrata, M.V.; Gori, A.; Costanzo, G.; Pace, U.; Pellerone, M. Coping, attachment style and resilience: The mediating role of alexithymia. Mediterr. J. Clin. Psychol. 2018, 6, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerone, M.; Cascio, M.I.; Costanzo, G.; Gori, A.; Pace, U.; Craparo, G. Alexithymia and psychological symptomatology: Research conducted on a non-clinical group of Italian adolescents. Int. J. Cult. Ment. Health 2017, 10, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craparo, G.; Gori, A.; Dell’Aera, S.; Costanzo, G.; Fasciano, S.; Tomasello, A.; Vicario, C.M. Impaired emotion recognition is linked to alexithymia in heroin addicts. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craparo, G.; Ardino, V.; Gori, A.; Caretti, V. The relationships between early trauma, dissociation, and alexithymia in alcohol addiction. Psychiatry Investig. 2014, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, A.; Sharma, P. Association of Internet addiction and alexithymia-A scoping review. Addict. Behav. 2018, 81, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, P.; Segrist, D.J. Difficulty identifying feelings, distress tolerance and compulsive buying: Analyzing the associations to inform therapeutic strategies. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2012, 10, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, P.; Gambarini, A. Exercise addiction and alexithymia. J. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 2015, 3, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lyssenko, L.; Schmahl, C.; Bockhacker, L.; Vonderlin, R.; Bohus, M.; Kleindienst, N. Dissociation in psychiatric disorders: A meta-analysis of studies using the dissociative experiences scale. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craparo, G. The role of dissociation, affect dysregulation, and developmental trauma in sexual addiction. Clin. Neuropsychiatry 2014, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musetti, A.; Terrone, G.; Schimmenti, A. An exploratory study on problematic Internet use predictors: Which role for attachment and dissociation. Clin. Neuropsychiatry 2018, 15, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Schluter, M.G.; Hodgins, D.C. Dissociative experiences in gambling disorder. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2019, 6, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, A.; Jauregui, P.; Macía, L.; Martín-Pérez, C. Alexithymia and Emotion Regulation Strategies in Adolescent Gamblers with and Without At-Risk Profiles. J. Gambl. Stud. 2021. Online first. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, L.; Derevensky, J.L.; Gupta, R. Youth gambling problems: Examining risk and protective factors. Int. Gambl. Stud. 2008, 8, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shead, N.W.; Derevensky, J.L.; Fong, T.W.; Gupta, R. Characteristics of Internet gamblers among a sample of students at a large, public university in Southwestern United States. J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 2012, 53, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszczynski, A.; Nower, L. A pathways model of problem and pathological gambling. Addiction 2002, 97, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirni, D.; Garufo, E.; Di Falco, L.; Lavanco, G. The Playing Brain. The Impact of Video Games on Cognition and Behavior in Pediatric Age at the Time of Lockdown: A Systematic Review. Pediatr. Rep. 2021, 13, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gori, A.; Topino, E.; Pucci, C.; Griffiths, M.D. The Relationship between Alexithymia, Dysmorphic Concern, and Exercise Addiction: The Moderating Effect of Self-Esteem. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, A.; Arcioni, A.; Topino, E.; Craparo, G.; Lauro Grotto, R. Development of a New Measure for Assessing Mentalizing: The Multidimensional Mentalizing Questionnaire (MMQ). J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmenti, A.; Sideli, L.; La Marca, L.; Gori, A.; Terrone, G. Reliability, validity, and factor structure of the maladaptive daydreaming scale (MDS–16) in an Italian sample. J. Pers. Assess. 2020, 102, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černis, E.; Evans, R.; Ehlers, A.; Freeman, D. Dissociation in relation to other mental health conditions: An exploration using network analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 136, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirni, D.; Beadle, J.N.; Paradiso, S. An initial study of alexithymia and its relationship with cognitive abilities among mild cognitive impairment, mild Alzheimer’s disease, and healthy volunteers. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2018, 206, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogrodniczuk, J.S.; Kealy, D.; Hadjinpsvlou, G.A.; Cameron, K. Therapeutic Issues. In Alexithymia: Advances in Research, Theory, and Clinical Practice; Luminet, O., Bagby, R.M., Taylor, G.J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 190–206. [Google Scholar]
- Steele, K.; van der Hart, O. Treating dissociation. In Treating Complex Traumatic Stress Disorders: An Evidence-Based Guide; Courtois, C.A., Ford, J.D., Eds.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 145–165. [Google Scholar]
- Rodda, S.N.; Dowling, N.A.; Thomas, A.C.; Bagot, K.L.; Lubman, D.I. Treatment for family members of people experiencing gambling problems: Family members want both gambler-focused and family-focused options. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2020, 18, 1318–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | M ± SD | n | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 28.8 ± 10.59 | |||
| Sex | ||||
| Females | 33 | 17.1 | ||
| Males | 160 | 82.9 | ||
| Marital Status | ||||
| Single | 152 | 78.8 | ||
| Married | 20 | 10.4 | ||
| Cohabiting | 17 | 8.8 | ||
| Separated | 1 | .5 | ||
| Divorced | 2 | 1.0 | ||
| Widowed | 1 | .5 | ||
| Education | ||||
| Middle School Diploma | 19 | 9.8 | ||
| High School Diploma | 106 | 54.9 | ||
| University Degree | 48 | 24.9 | ||
| Master’s Degree | 10 | 5.2 | ||
| Post-Lauream Specialization | 10 | 5.2 | ||
| Occupation | ||||
| Student | 42 | 21.8 | ||
| Working Student | 43 | 22.3 | ||
| Employee | 73 | 37.8 | ||
| Freelance | 5 | 2.6 | ||
| Entrepreneur | 2 | 1.0 | ||
| Artisan | 13 | 6.7 | ||
| Unemployed | 14 | 7.3 | ||
| Retired | 1 | .5 | ||
| Severity of gambling-related problems (SOGS) | ||||
| Absence Of Gambling Disease | 110 | 57.0 | ||
| At Risk For Gambling Disease | 33 | 17.1 | ||
| Problematic Gambling | 50 | 25.9 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. SOGS | 1 | ||||||||
| 2. DES-II | 0.330 ** | 1 | |||||||
| 3. TAS20 | 0.284 ** | 0.351 ** | 1 | ||||||
| 4. FACES-IV (1) | −0.241 ** | −0.323 ** | −0.141 | 1 | |||||
| 5. FACES-IV (2) | −0.130 | −0.186 ** | −0.059 | 0.839 ** | 1 | ||||
| 6. FACES-IV (3) | 0.115 | 0.347 ** | 0.265 ** | −0.199 ** | −0.079 | 1 | |||
| 7. FACES-IV (4) | 0.180 * | 0.359 ** | 0.303 ** | −0.006 | 0.105 | 0.445 ** | 1 | ||
| 8. FACES-IV (5) | −0.025 | 0.174 * | 0.290 ** | 0.374 ** | 0.505 ** | 0.398 ** | 0.536 ** | 1 | |
| 9. FACES-IV (6) | 0.087 | 0.304 ** | 0.248 ** | −0.024 | 0.095 | 0.607 ** | 0.512 ** | 0.377 ** | 1 |
| M | 3.306 | 33.811 | 49.181 | 22.72 | 21.813 | 17.725 | 15.399 | 18.197 | 16.798 |
| SD | 4.217 | 15.483 | 11.325 | 6.589 | 5.813 | 5.191 | 4.688 | 4.664 | 4.554 |
| Absence | At Risk | Problematic | F | p | ηp2 | Scheffé Post Hoc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |||||
| (N = 110) | (N = 33) | (N = 50) | ||||||||
| Cohesion | 24.227 | 6.010 | 21.000 | 6.955 | 20.540 | 6.801 | 7.171 | <0.001 | 0.070 | P < A, R |
| Flexibility | 22.645 | 5.734 | 20.152 | 6.893 | 21.080 | 4.927 | 2.931 | 0.056 | 0.030 | - |
| Disengaged | 17.245 | 4.530 | 16.879 | 5.754 | 19.340 | 5.889 | 3.411 | 0.035 | 0.035 | - |
| Enmeshed | 14.736 | 4.323 | 15.424 | 4.596 | 16.840 | 5.258 | 3.553 | 0.031 | 0.036 | - |
| Rigid | 18.255 | 4.069 | 17.939 | 5.645 | 18.240 | 5.247 | 0.060 | 0.942 | 0.001 | - |
| Chaotic | 16.536 | 3.960 | 15.848 | 4.487 | 18.000 | 5.566 | 2.687 | 0.071 | 0.028 | - |
| Absence | At Risk | Problematic | F | p | Scheffé Post Hoc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 110) | (N = 33) | (N = 50) | |||||||
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | ||||
| Alexithyima | 47.036 | 10.932 | 47.182 | 10.463 | 55.220 | 10.725 | 10.549 | <0.001 | P > A, R |
| Dissociation | 30.497 | 13.916 | 33.636 | 14.133 | 41.224 | 17.242 | 8.935 | <0.001 | P > A |
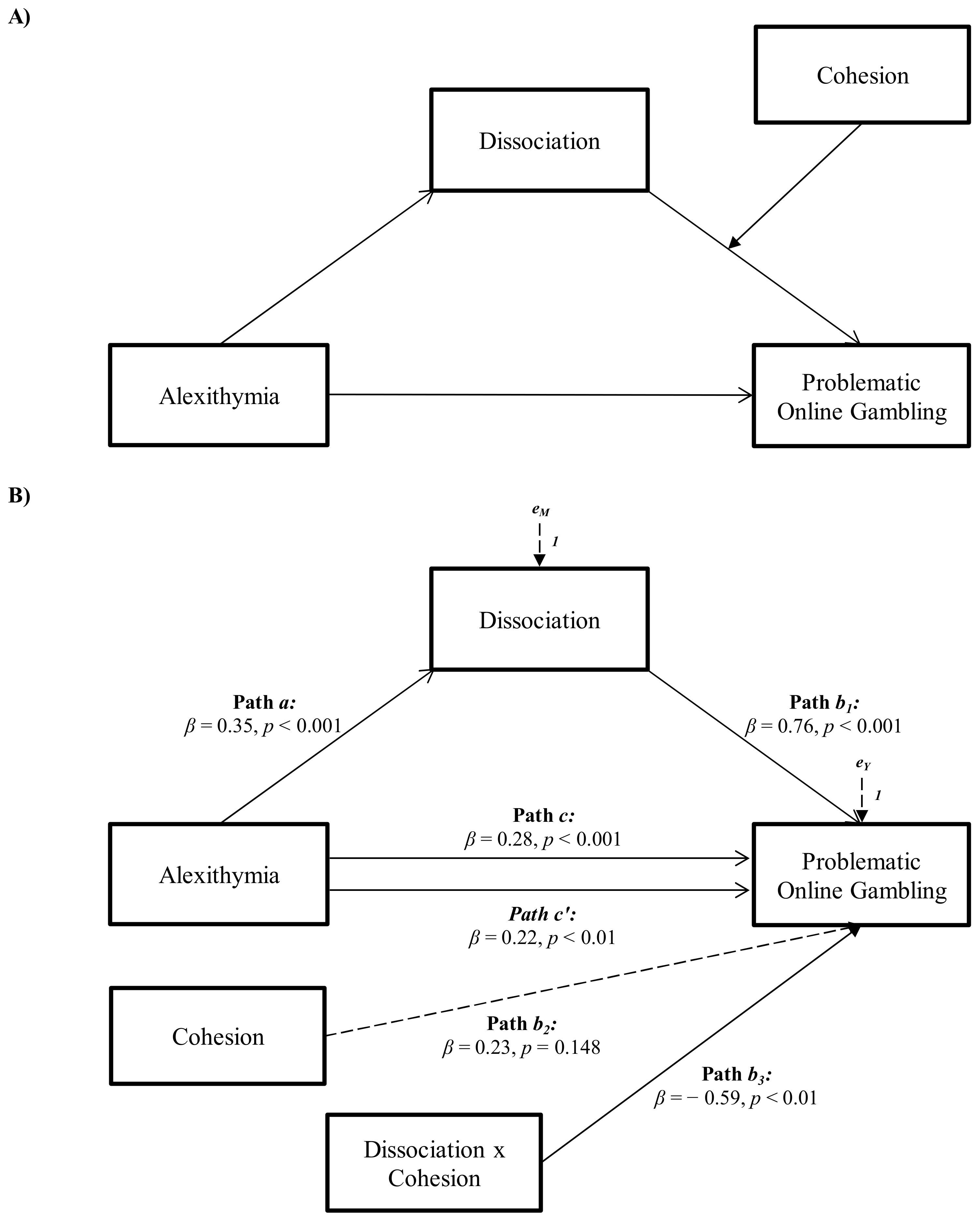
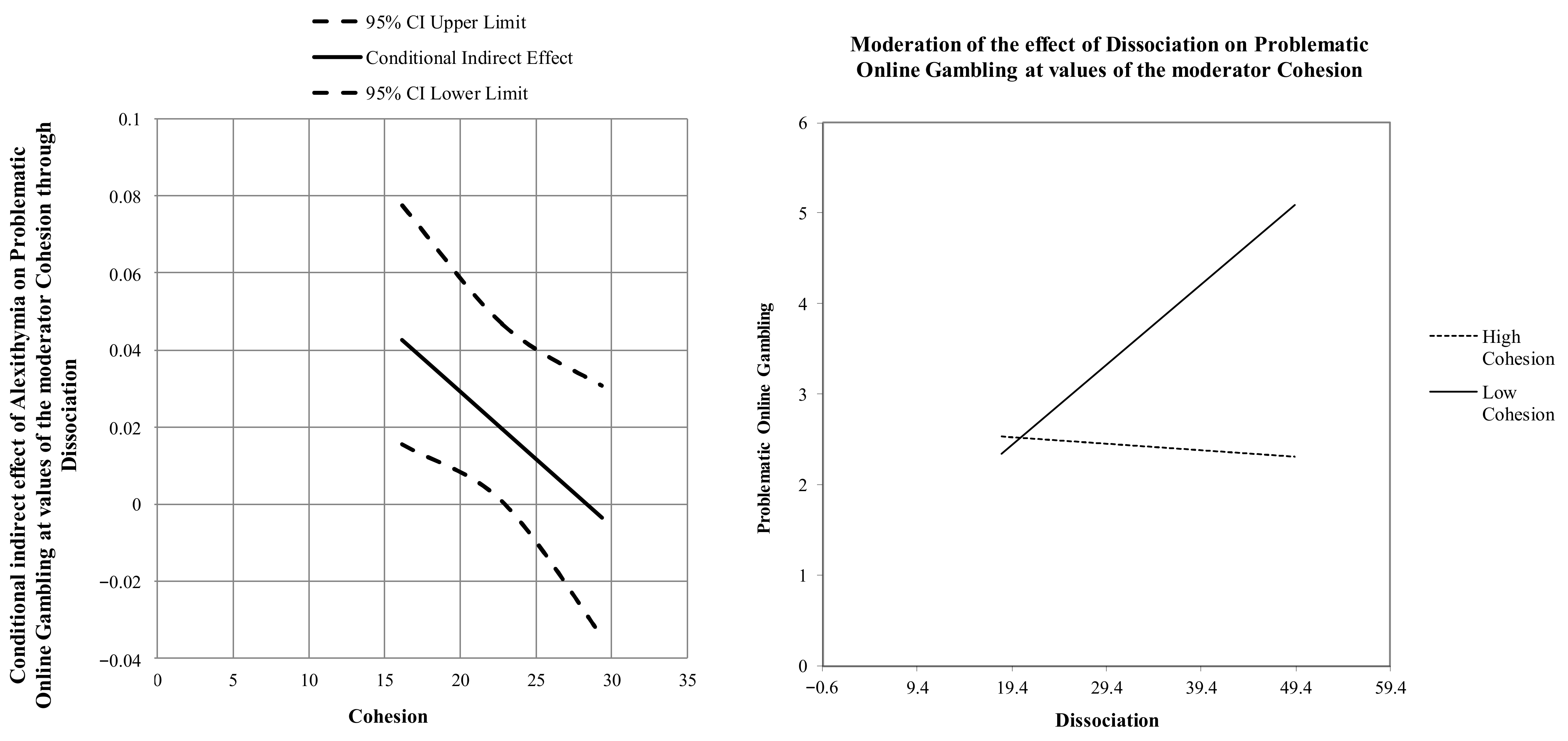
| Antecedent | Consequent | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | Y | ||||||||||
| Coeff. | SE | p | 95% CI | Coeff. | SE | p | 95% CI | Test(s) of Highest Order Unconditional Interaction(s) | |||
| X | a | 0.048 | 0.099 | <0.001 | [0.2971; 0.6625] | c′ | 0.083 | 0.027 | 0.002 | [0.0306; 0.1356] | |
| M | - | - | - | - | b1 | 0.206 | 0.060 | <0.001 | [0.0885; 0.3238] | ||
| W | - | - | - | - | b2 | 0.148 | 0.102 | 0.148 | [−0.0532; 0.3496] | ||
| M × W | - | - | - | - | b3 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.010 | [−0.0128; −0.0018] | ΔR2 = 0.030 F (1, 188) = 6.861, p < 0.01 | |
| constant | iM | 1.021 | 0.467 | 0.031 | [0.9920; 19.4307] | iY | −5.765 | 2.814 | 0.042 | [−11.3152; −0.2144] | |
| R2 = 0.123 F (1, 191) = 26.838, p < 0.001 | R2 = 0.190 F(4, 188) = 10.987, p < 0.001 | ||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Topino, E.; Gori, A.; Cacioppo, M. Alexithymia, Dissociation, and Family Functioning in a Sample of Online Gamblers: A Moderated Mediation Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413291
Topino E, Gori A, Cacioppo M. Alexithymia, Dissociation, and Family Functioning in a Sample of Online Gamblers: A Moderated Mediation Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(24):13291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413291
Chicago/Turabian StyleTopino, Eleonora, Alessio Gori, and Marco Cacioppo. 2021. "Alexithymia, Dissociation, and Family Functioning in a Sample of Online Gamblers: A Moderated Mediation Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 24: 13291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413291
APA StyleTopino, E., Gori, A., & Cacioppo, M. (2021). Alexithymia, Dissociation, and Family Functioning in a Sample of Online Gamblers: A Moderated Mediation Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(24), 13291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413291







