Effects of Brain Breaks Video Intervention of Decisional Balance among Malaysians with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
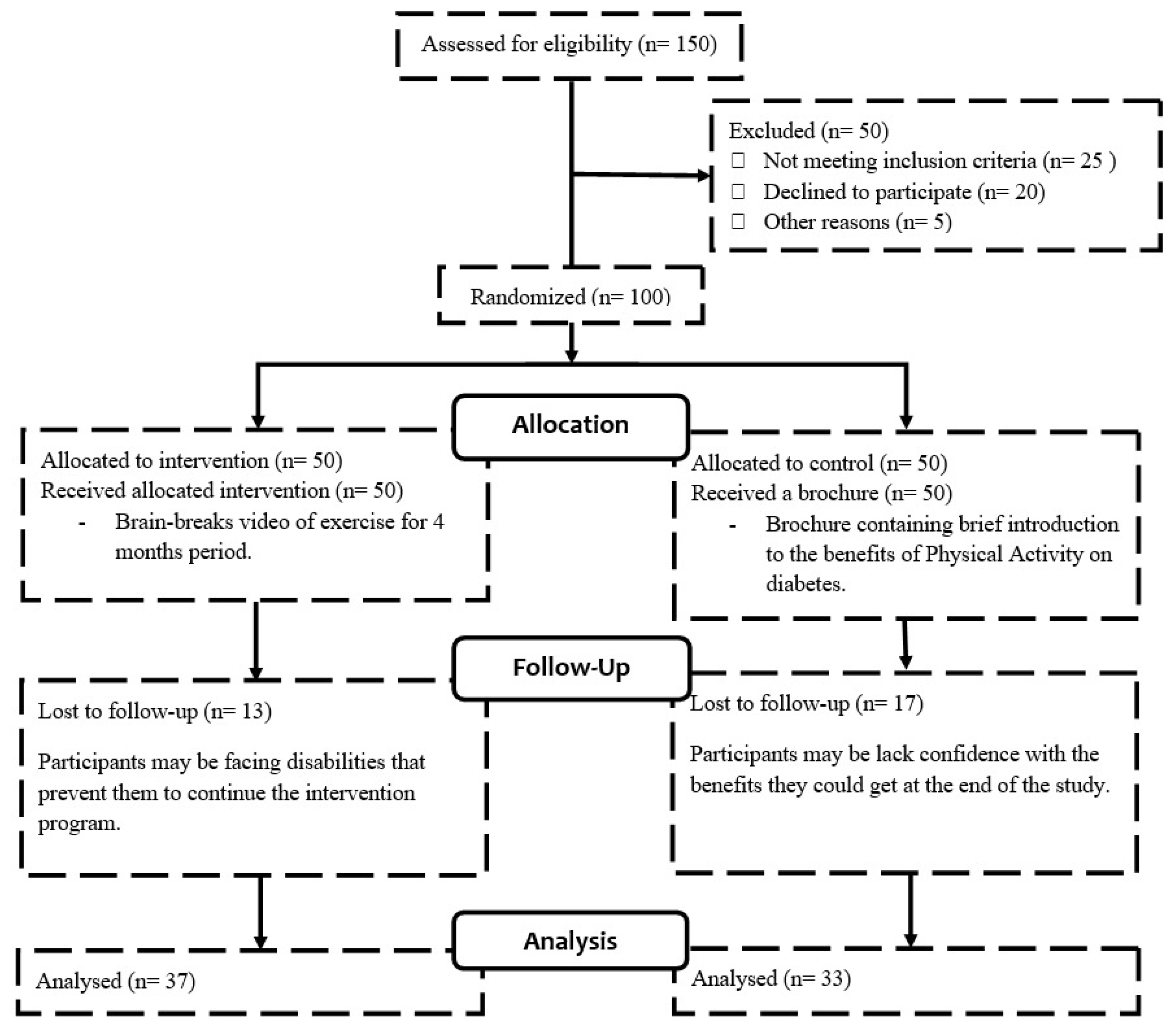
2.1. Study Design, Recruitment, and Sampling
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Sample Size Determination
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Results of RM MANOVA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. What Is Diabetes. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/diabetes.html (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Diabetes. Available online: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/data/en/world/ (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- Holman, N.; Young, B.; Gadsby, R. Current prevalence of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes in adults and children in the UK. Diabet. Med. 2015, 32, 1119–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khardori, R. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/117853-overview (accessed on 24 December 2020).
- Mustaffa, B. Diabetes epidemic in Malaysia. Med. J. Malays. 2004, 59, 295–296. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, R.S.; Brown, A.; Ebrahim, S.; Jolliffe, J.; Noorani, H.; Rees, K.; Skidmore, B.; Stone, J.A.; Thompson, D.R.; Oldridge, N. Exercise-based rehabilitation for patients with coronary heart disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Med. 2004, 116, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, B.M.; Neilson, H.K.; Friedenreich, C.M. Physical activity and breast cancer prevention. In Physical Activity and Cancer, 1st ed.; Kerry, S.C., Christine, M.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; Volume 1, pp. 13–42. [Google Scholar]
- Church, T.S.; Blair, S.N.; Cocreham, S.; Johannsen, N.; Johnson, W.; Kramer, K.; Mikus, C.R.; Myers, V.; Nauta, M.; Rodarte, R.Q.; et al. Effects of aerobic and resistance training on hemoglobin A1c levels in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2010, 304, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigal, R.J.; Kenny, G.P. Combined aerobic and resistance exercise for patients with type 2 diabetes. JAMA 2010, 304, 2298–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-López, A.; Babio, N.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Amor, A.J.; Fitó, M.; Estruch, R.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Fiol, M.; et al. Mediterranean diet, retinopathy, nephropathy, and microvascular diabetes complications: A post hoc analysis of a randomized trial. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 2134–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotnikoff, R.C.; Blanchard, C.; Hotz, S.B.; Rhodes, R. Validation of the decisional balance scales in the exercise domain from the transtheoretical model: A longitudinal test. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2001, 5, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, P.; Romain, A.-J.; Trouillet, R.; Gernigon, C.; Nigg, C.; Ninot, G. Validation of the TTM processes of change measure for physical activity in an adult French sample. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2014, 21, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, S.; Farmanbar, R.; Njafi, F.; Ghiasvand, A.M.; Dehghankar, L. Decisional balance and self-efficacy of physical activity among the elderly in Rasht in 2013 based on the transtheoretical model. Electron. Physician 2017, 9, 4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Interactive Youth Physical Education Training System. Available online: http://www.hopsports.com (accessed on 14 August 2018).
- Balasekaran, G.; Ibrahim, A.A.B.; Cheo, N.Y.; Wang, P.K.; Kuan, G.; Popeska, B.; Chin, M.-K.; Mok, M.M.C.; Edginton, C.R.; Culpan, I.; et al. Using Brain-Breaks® as a technology tool to increase attitude towards physical activity among students in Singapore. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, G.; Rizal, H.; Hajar, M.S.; Chin, M.K.; Mok, M.M.C. Bright sports, physical activity investments that work: Implementing brain breaks in Malaysia primary schools. Br. J. Sports Med. 2019, 53, 905–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajar, M.S.; Rizal, H.; Kueh, Y.C.; Muhamad, A.S.; Kuan, G. The effects of Brain Breaks on motives of participation in physical activity among primary school children in Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popeska, B.; Jovanova-Mitkovska, S.; Chin, M.-K.; Edginton, C.R.; Mok, M.M.C.; Gontarev, S. Implementation of brain breaks® in the classroom and effects on attitudes toward physical activity in a Macedonian school setting. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizal, H.; Hajar, M.S.; Muhamad, A.S.; Kueh, Y.C.; Kuan, G. The effect of brain breaks® on physical activity behavior among primary school children: A transtheoretical perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; He, S.; Zhou, Y.; Popeska, B.; Kuan, G.; Chen, L.; Chin, M.K.; Mok, M.M.C.; Edginton, C.R.; Culpan, I.; et al. Implementation of brain breaks in the classroom and its effects on attitude towards physical activity in Chinese school setting. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidrus, A.; Kueh, Y.C.; Norsaádah, B.; Chang, Y.K.; Hung, T.M.; Naing, N.N.; Kuan, G. Effects of brain breaks videos on the motives for the physical activity of Malaysians with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K. An overview of randomization techniques: An unbiased assessment of outcome in clinical research. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2011, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shin, W. How to do random allocation (randomization). Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2014, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, G.; Sabo, A.; Sawang, S.; Kueh, Y.C. Factorial validity, measurement and structure invariance of the Malay language decisional balance scale in exercise across gender. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988; p. 286. [Google Scholar]
- Moeini, B.; Rahimi, M.; Hazaveie, S.; Allahverdi Pour, H.; Moghim Beigi, A.; Mohammadfam, I. Effect of education based on trans-theoretical model on promoting physical activity and increasing physical work capacity. Iran. J. Mil. Med. 2010, 12, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Shtaynberger, J.; Krebs, P. Associations between decisional balance and health behaviors among adult cancer survivors. J. Cancer Educ. 2016, 31, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S. Using Multivariate Statistics, 3rd ed.; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 481–498. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.Y. Statistical notes for clinical researchers: A one-way repeated measures ANOVA for data with repeated observations. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2015, 40, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Intervention | Control | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequencies | Percentage | Median (IQR) | Mean (SD) | Frequencies | Percentage | Median (IQR) | Mean (SD) | ||
| Gender | 0.208 a | ||||||||
| Male | 18 | 48.6% | 21 | 63.6% | |||||
| Female | 19 | 51.4% | 12 | 36.4% | |||||
| Age | 56.00 (10.00) | 63.00 (8.00) | <0.001 c | ||||||
| Ethnicity | 0.242 b | ||||||||
| Malay | 34 | 91.9% | 29 | 87.9% | |||||
| Chinese | 3 | 8.1% | 1 | 3.0% | |||||
| Indian | 0 | 0% | 1 | 3.0% | |||||
| Others | 0 | 0% | 2 | 6.1% | |||||
| HbA1c (n = 65) | 80.11 (3.74) | 76.23 (4.26) | 0.529 d | ||||||
| BMI | 28.06 (5.90) | 26.59 (6.19) | 0.902 c | ||||||
| Comparison | Intervention Group | Control Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pros | Cons | Pros | Cons | |||||
| MD (95% CI) | p-Value | MD (95% CI) | p-Value | MD (95% CI) | p-Value | MD (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Pre-1st month | −1.19 (−1.68, −0.70) | <0.001 | 0.51 (0.14, 0.89) | 0.002 | 0.27 (0.002, 0.54) | 0.048 | −0.27 (−0.60, 0.06) | 0.176 |
| Pre-2nd month | −1.95 (−2.60, −1.29) | <0.001 | 1.27 (0.65, 1.89) | <0.001 | 0.27 (0.002, 0.54) | 0.048 | −0.55 (−1.00, −0.09) | 0.010 |
| Pre-3rd month | −2.78 (−3.80, −1.77) | <0.001 | 2.22 (1.21, 3.23) | <0.001 | 0.73 (0.11, 1.35) | 0.012 | −0.97 (−1.52, −0.42) | <0.001 |
| Pre vs. Post intervention | −4.10 (−5.40, −2.81) | <0.001 | 3.68 (2.10, 5.25) | <0.001 | 0.97 (0.10, 1.84) | 0.019 | −1.55 (−2.27, −0.83) | <0.001 |
| 1st month–2nd month | −0.76 (−1.05, −0.46) | <0.001 | 0.76 (0.33, 1.18) | <0.001 | - | - | −0.27 (−0.57, 0.03) | 0.102 |
| 1st month–3rd month | −1.60 (−2.28, −0.91) | <0.001 | 1.70 (0.90, 2.50) | <0.001 | 0.46 (−0.06, 0.96) | 0.113 | −0.70 (−1.14, −0.25) | <0.001 |
| 1st month–Post | −2.92 (−3.88, −1.96) | <0.001 | 3.16 (1.81, 4.51) | <0.001 | 0.70 (−0.003, 1.40) | 0.052 | −1.27 (−1.85, −0.70) | <0.001 |
| 2nd month–3rd month | −0.84 (−1.36, −0.31) | <0.001 | 0.95 (0.42, 1.48) | <0.001 | 0.46 (−0.06, 0.96) | 0.113 | −0.42 (−0.69, −0.16) | <0.001 |
| 2nd month-Post | −2.16 (−2.94, −1.38) | <0.001 | 2.41 (1.35, 3.46) | <0.001 | 0.70 (−0.003, 1.40) | 0.052 | −1.00 (−1.46, −0.55) | <0.001 |
| 3rd month-Post | −1.32 (−1.76, −0.89) | <0.001 | 1.46 (0.75, 2.17) | <0.001 | 0.24 (−0.17, 0.66) | 0.882 | −0.58 (−1.03, −0.12) | 0.006 |
| Comparison (Intervention and Control Groups) | Mean Difference (95% CI) | F (df) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pros | 4.01 (2.63, 5.40) | 33.447 (1, 68) | <0.001 |
| Cons | −2.04 (−3.52, −0.55,) | 7.489 (1, 68) | 0.008 |
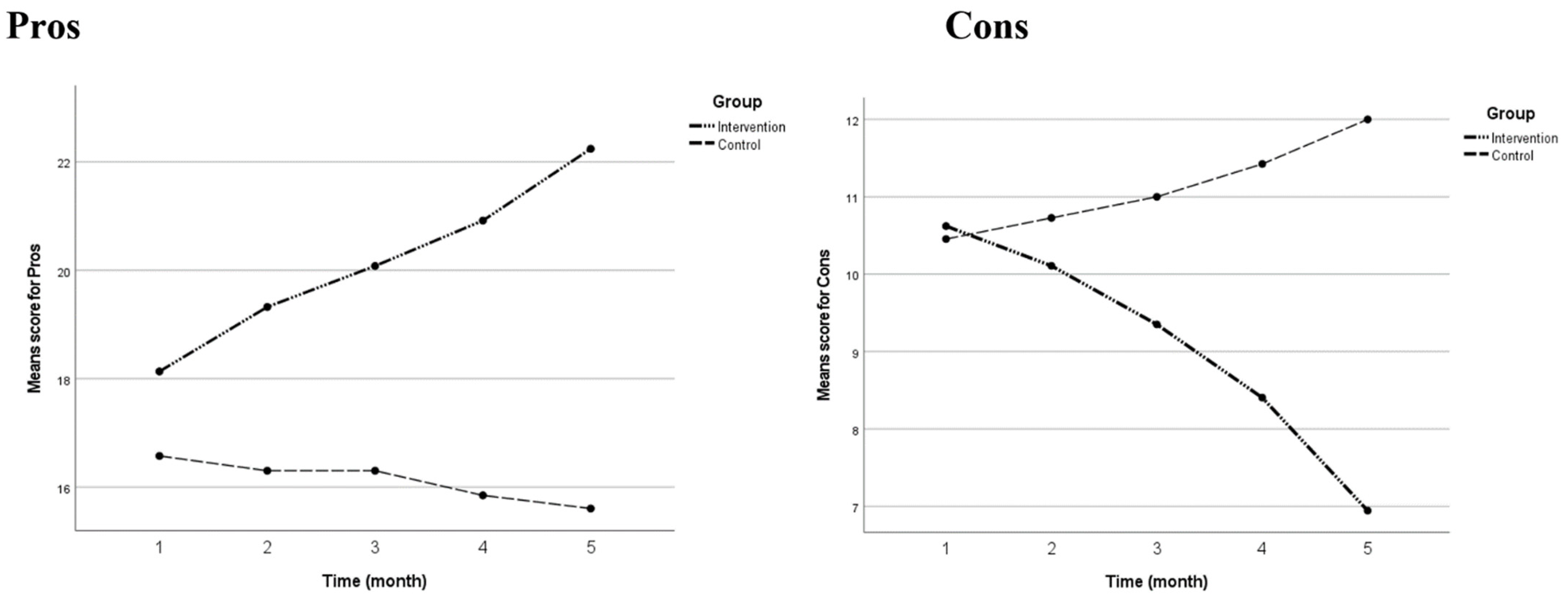
| Factor | Time | Group | Mean (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pros | Pre-intervention | Intervention | 18.14 (16.95, 19.32) | 0.075 |
| Control | 16.58 (15.32, 17.83) | |||
| 1st month | Intervention | 19.32 (18.27, 20.38) | <0.001 | |
| Control | 16.30 (15.19, 17.42) | |||
| 2nd month | Intervention | 20.08 (19.06, 21.11) | <0.001 | |
| Control | 16.30 (15.22, 17.39) | |||
| 3rd month | Intervention | 20.92 (20.06, 21.78) | <0.001 | |
| Control | 15.85 (14.94, 16.76) | |||
| Post-intervention | Intervention | 22.24 (21.46, 23.03) | <0.001 | |
| Control | 15.61 (14.77, 16.44) | |||
| Cons | Pre-intervention | Intervention | 10.62 (9.32, 11.92) | 0.861 |
| Control | 10.46 (9.08, 11.83) | |||
| 1st month | Intervention | 10.11 (8.92, 11.30) | 0.478 | |
| Control | 10.73 (9.47, 11.99) | |||
| 2nd month | Intervention | 9.35 (8.29, 10.42) | 0.038 | |
| Control | 11.00 (9.87, 12.13) | |||
| 3rd month | Intervention | 8.41 (7.48, 9.33) | <0.001 | |
| Control | 11.42 (10.45, 12.40) | |||
| Post-intervention | Intervention | 6.95 (6.18, 7.72) | <0.001 | |
| Control | 12.00 (11.19, 12.82) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hidrus, A.; Kueh, Y.C.; Norsa’adah, B.; Chang, Y.-K.; Kuan, G. Effects of Brain Breaks Video Intervention of Decisional Balance among Malaysians with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18178972
Hidrus A, Kueh YC, Norsa’adah B, Chang Y-K, Kuan G. Effects of Brain Breaks Video Intervention of Decisional Balance among Malaysians with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomised Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(17):8972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18178972
Chicago/Turabian StyleHidrus, Aizuddin, Yee Cheng Kueh, Bachok Norsa’adah, Yu-Kai Chang, and Garry Kuan. 2021. "Effects of Brain Breaks Video Intervention of Decisional Balance among Malaysians with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomised Controlled Trial" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 17: 8972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18178972
APA StyleHidrus, A., Kueh, Y. C., Norsa’adah, B., Chang, Y.-K., & Kuan, G. (2021). Effects of Brain Breaks Video Intervention of Decisional Balance among Malaysians with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomised Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(17), 8972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18178972







