The Positive Relationship between Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity and Bone Mineral Content Is Not Mediated by Free Leptin Index in Prepubertal Children: The PANIC Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
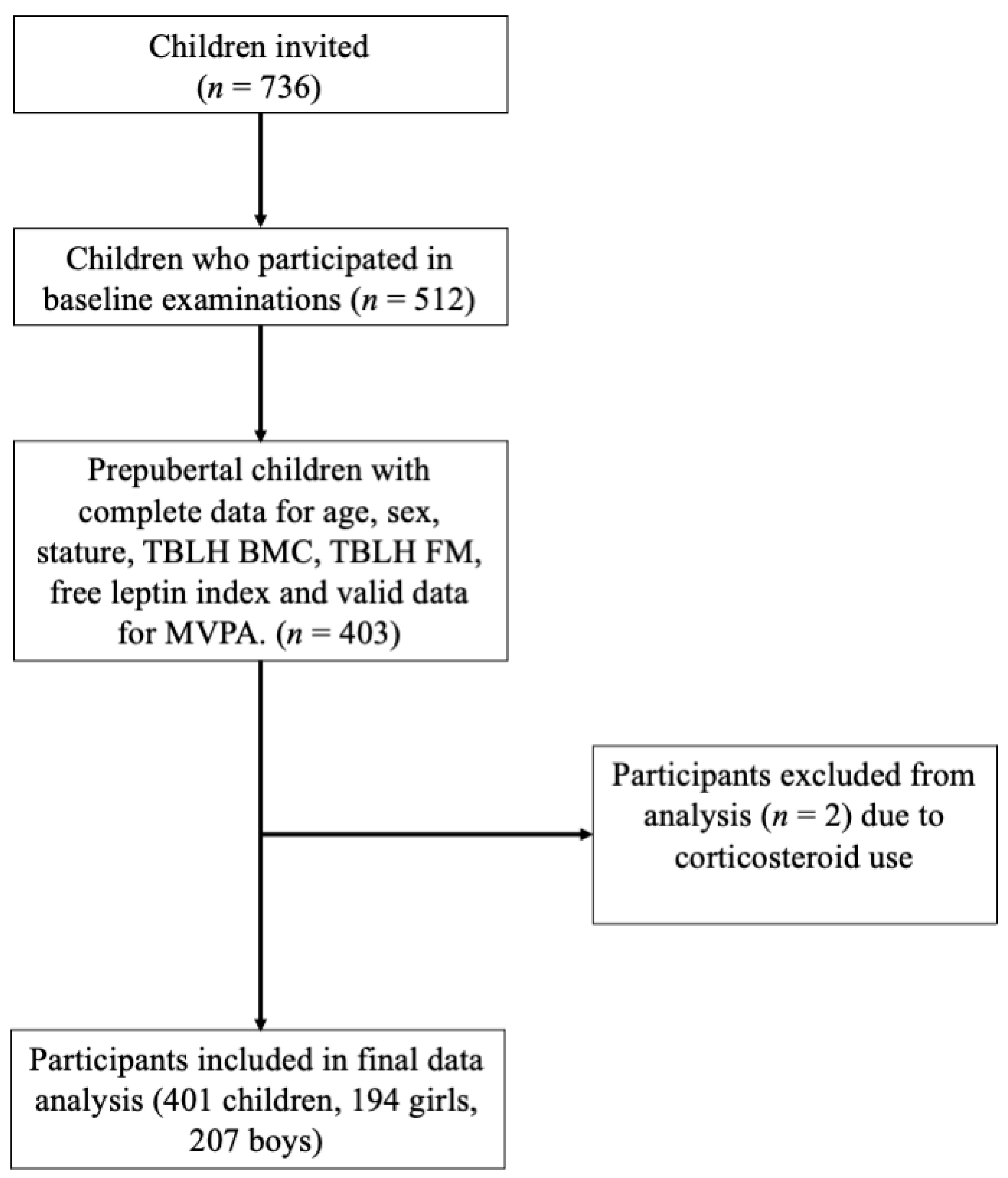
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Protocol
2.2. Assessment of General Health and Pubertal Status
2.3. Anthropometry
2.4. Assessment of Bone Mineral Content and Body Composition
2.5. Assessment of Physical Activity
2.6. Assessment of Free Leptin Index
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Children
3.2. Associations between Mediator, Dependent and Independent Variables
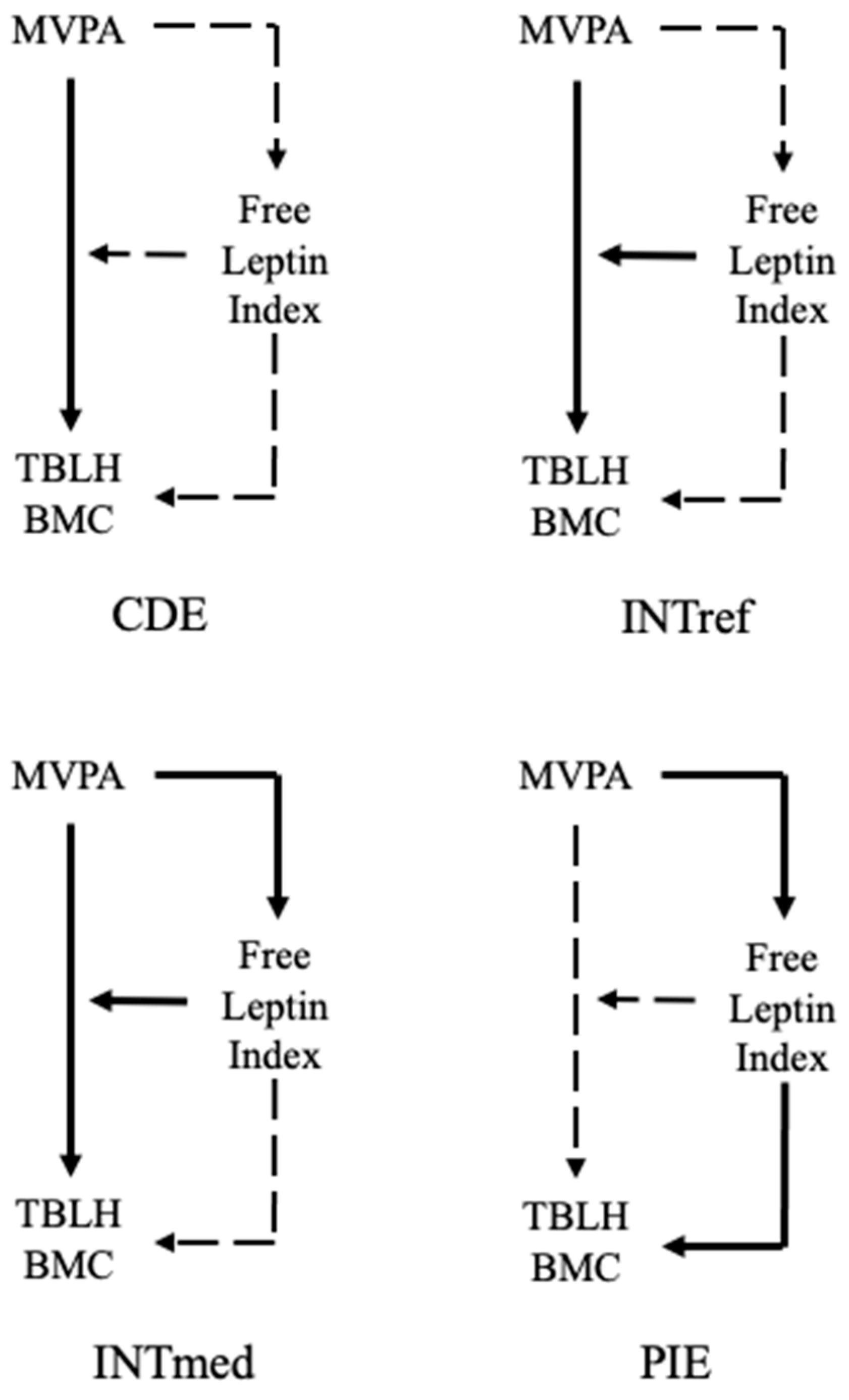
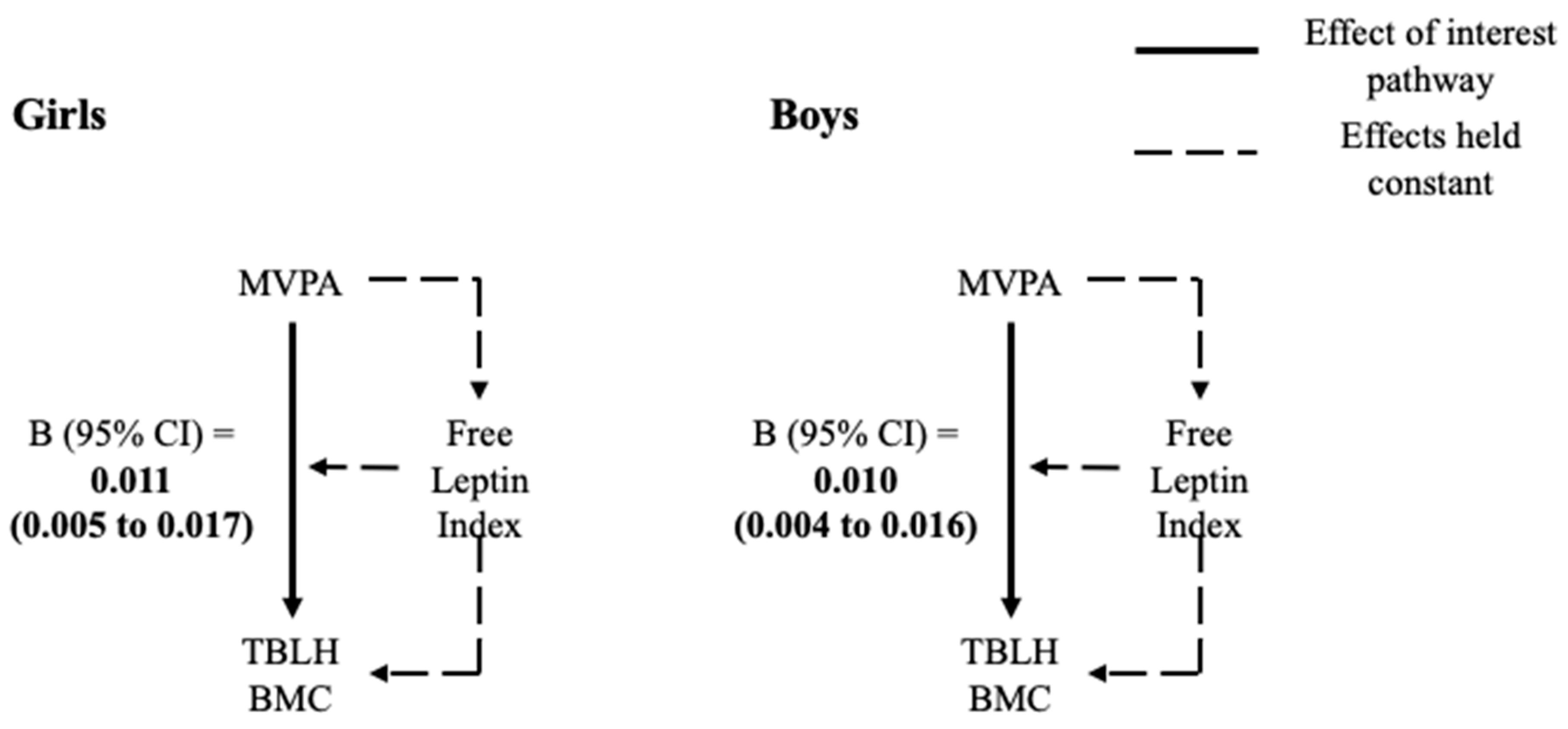
3.3. 4-Way Decomposition
4. Discussion
4.1. Free Leptin Index and Bone Mineral Content
4.2. MVPA and Free Leptin Index
4.3. MVPA, Free Leptin Index and Bone Mineral Content
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frost, H.M. Bone’s mechanostat: A 2003 update. Anat. Rec. Part A Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 2003, 275A, 1081–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, C.M.; Gordon, C.M.; Janz, K.F.; Kalkwarf, H.J.; Lappe, J.M.; Lewis, R.; O’Karma, M.; Wallace, T.C.; Zemel, B.S. The National Osteoporosis Foundation’s position statement on peak bone mass development and lifestyle factors: A systematic review and implementation recommendations. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 1281–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Specker, B.; Thiex, N.W.; Sudhagoni, R.G. Does Exercise Influence Pediatric Bone? A Systematic Review. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 3658–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, A.M.; Vlachopoulos, D.; Barker, A.R.; Moore, S.A.; Soininen, S.; Haapala, E.A.; Väistö, J.; Westgate, K.; Brage, S.; Mahonen, A.; et al. The independent and interactive associations of physical activity intensity and vitamin D status with bone mineral density in prepubertal children: The PANIC Study. Osteoporos. Int. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaitkeviciute, D.; Latt, E.; Maestu, J.; Jurimae, T.; Saar, M.; Purge, P.; Maasalu, K.; Jurimae, J. Longitudinal associations between bone and adipose tissue biochemical markers with bone mineralization in boys during puberty. BMC Pediatr. 2016, 16, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, R.R.; Chu, H.; Castracane, V.D. Leptin and Exercise. Exp. Biol. Med. 2002, 227, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzoli, R.; Bianchi, M.L.; Garabedian, M.; McKay, H.A.; Moreno, L.A. Maximizing bone mineral mass gain during growth for the prevention of fractures in the adolescents and the elderly. Bone 2010, 46, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedewa, M.V.; Hathaway, E.D.; Ward-Ritacco, C.L.; Williams, T.D.; Dobbs, W.C. The Effect of Chronic Exercise Training on Leptin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 1437–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soininen, S.; Sidoroff, V.; Lindi, V.; Mahonen, A.; Kröger, L.; Kröger, H.; Jääskeläinen, J.; Atalay, M.; Laaksonen, D.E.; Laitinen, T.; et al. Body fat mass, lean body mass and associated biomarkers as determinants of bone mineral density in children 6–8years of age—The Physical Activity and Nutrition in Children (PANIC) study. Bone 2018, 108, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romon, M.; Lafay, L.; Bresson, J.L.; Oppert, J.M.; Borys, J.M.; Kettaneh, A.; Charles, M.A. Relationships between physical activity and plasma leptin levels in healthy children: The Fleurbaix-Laventie Ville Sante II Study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004, 28, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, B.S.; Jeffery, A.N.; Hosking, J.; Voss, L.D.; Sattar, N.; Wilkin, T.J. Objectively Measured Physical Activity and Its Association With Adiponectin and Other Novel Metabolic Markers. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, S.P.; Högler, W.; Blades, B.; Baur, L.A.; Peat, J.; Lee, J.; Cowell, C.T. Relation between hormones and body composition, including bone, in prepubertal children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderWeele, T.J. A unification of mediation and interaction: A 4-way decomposition. Epidemiology 2014, 25, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.M. Normal growth and techniques of growth assessment. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1986, 15, 411–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saari, A.; Sankilampi, U.; Hannila, M.-L.; Kiviniemi, V.; Kesseli, K.; Dunkel, L. New Finnish growth references for children and adolescents aged 0 to 20 years: Length/height-for-age, weight-for-length/height, and body mass index-for-age. Ann. Med. 2011, 43, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, T.J.; Lobstein, T. Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut-offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkovitz, L.A.; Henwood, M.J. Pediatric DXA: Technique and interpretation. Pediatr. Radiol. 2007, 37, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworski, M.; Pludowski, P. Precision errors, least significant change, and monitoring time interval in pediatric measurements of bone mineral density, body composition, and mechanostat parameters by GE lunar prodigy. J. Clin. Densitom. 2013, 16, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wren, T.A.; Liu, X.; Pitukcheewanont, P.; Gilsanz, V. Bone acquisition in healthy children and adolescents: Comparisons of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and computed tomography measures. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 1925–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Heaney, R.P. Bone mineral content, not bone mineral density, is the correct bone measure for growth studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 350–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, M.B.; Shults, J.; Elliott, D.M.; Stallings, V.A.; Zemel, B.S. Interpretation of whole body dual energy X-ray absorptiometry measures in children: Comparison with peripheral quantitative computed tomography. Bone 2004, 34, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corder, K.; Brage, S.; Mattocks, C.; Ness, A.; Riddoch, C.; Wareham, N.J.; Ekelund, U. Comparison of two methods to assess PAEE during six activities in children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 2180–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brage, S.; Brage, N.; Franks, P.W.; Ekelund, U.; Wareham, N.J. Reliability and validity of the combined heart rate and movement sensor Actiheart. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowlands, A.V.; Pilgrim, E.L.; Eston, R.G. Patterns of habitual activity across weekdays and weekend days in 9–11-year-old children. Prev. Med. 2008, 46, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegle, O.; Fallert, S.V.; MacKay, D.J.; Brage, S. Gaussian process robust regression for noisy heart rate data. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintu, N.; Tompuri, T.; Viitasalo, A.; Soininen, S.; Laitinen, T.; Savonen, K.; Lindi, V.; Lakka, T.A. Cardiovascular fitness and haemodynamic responses to maximal cycle ergometer exercise test in children 6-8 years of age. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brage, S.; Brage, N.; Franks, P.W.; Ekelund, U.; Wong, M.Y.; Andersen, L.B.; Froberg, K.; Wareham, N.J. Branched equation modeling of simultaneous accelerometry and heart rate monitoring improves estimate of directly measured physical activity energy expenditure. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 96, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collings, P.J.; Westgate, K.; Väistö, J.; Wijndaele, K.; Atkin, A.J.; Haapala, E.A.; Lintu, N.; Laitinen, T.; Ekelund, U.; Brage, S.; et al. Cross-Sectional Associations of Objectively-Measured Physical Activity and Sedentary Time with Body Composition and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Mid-Childhood: The PANIC Study. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janz, K.F.; Rao, S.; Baumann, H.J.; Schultz, J.L. Measuring children’s vertical ground reaction forces with accelerometry during walking, running, and jumping: The Iowa Bone Development Study. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2003, 15, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, N.C.; Cole, Z.A.; Crozier, S.R.; Kim, M.; Ntani, G.; Goodfellow, L.; Robinson, S.M.; Inskip, H.M.; Godfrey, K.M.; Dennison, E.M.; et al. Physical activity, calcium intake and childhood bone mineral: A population-based cross-sectional study. Osteoporos. Int. 2012, 23, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corder, K.; Brage, S.; Wareham, N.J.; Ekelund, U. Comparison of PAEE from combined and separate heart rate and movement models in children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Carson, V.; Chaput, J.P. Introduction to the Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for Children and Youth: An Integration of Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour, and Sleep. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, iii–iv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brage, S.; Westgate, K.; Wijndaele, K.; Godinho, J.; Griffin, S.; Wareham, N. Evaluation of a method for minimizing diurnal information bias in objective sensor data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Ambulatory Monitoring of Physical Activity and Movement, Amherst, MA, USA, 17–19 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kratzsch, J.; Lammert, A.; Bottner, A.; Seidel, B.; Mueller, G.; Thiery, J.; Hebebrand, J.; Kiess, W. Circulating soluble leptin receptor and free leptin index during childhood, puberty, and adolescence. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 4587–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discacciati, A.; Bellavia, A.; Lee, J.J.; Mazumdar, M.; Valeri, L. Med4way: A Stata command to investigate mediating and interactive mechanisms using the four-way effect decomposition. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 48, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J. Regression Diagnostics; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.L.; Ong, K.K.; Dunger, D.B. Childhood obesity and the timing of puberty. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausten-Thomsen, U.; Christiansen, M.; Louise Hedley, P.; Esmann Fonvig, C.; Stjernholm, T.; Pedersen, O.; Hansen, T.; Holm, J.-C. Reference values for serum leptin in healthy non-obese children and adolescents. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2016, 76, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitri, P.; Wales, J.K.; Bishop, N. Adipokines, bone-derived factors and bone turnover in obese children; evidence for altered fat-bone signalling resulting in reduced bone mass. Bone 2011, 48, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Ortega, F.B.; Artero, E.G.; Labayen, I.; Vicente-Rodriguez, G.; Huybrechts, I.; Moreno, L.A.; Manios, Y.; Béghin, L.; Polito, A.; et al. Physical Activity, Fitness, and Serum Leptin Concentrations in Adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2012, 160, 598–603.e592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, P.E.; Gill, M.S.; Hall, C.M.; Tillmann, V.; Whatmore, A.J.; Price, D.A. Serum leptin through childhood and adolescence. Clin. Endocrinol. 1997, 46, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutin, B.; Ramsey, L.; Barbeau, P.; Cannady, W.; Ferguson, M.; Litaker, M.; Owens, S. Plasma leptin concentrations in obese children: Changes during 4-mo periods with and without physical training. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migueles, J.H.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Löf, M.; Esteban-Cornejo, I.; Molina-Garcia, P.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Rodriguez-Ayllon, M.; Garcia-Marmol, E.; Ekelund, U.; et al. Comparability of published cut-points for the assessment of physical activity: Implications for data harmonization. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderwall, C.; Randall Clark, R.; Eickhoff, J.; Carrel, A.L. BMI is a poor predictor of adiposity in young overweight and obese children. BMC Pediatr. 2017, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, J.H.; Steer, C.D.; Mattocks, C.G.; Riddoch, C.; Ness, A.R. Habitual Levels of Physical Activity Influence Bone Mass in 11-Year-Old Children From the United Kingdom: Findings From a Large Population-Based Cohort. J. Bone Min. Res. 2007, 22, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janz, K.F.; Burns, T.L.; Torner, J.C.; Levy, S.M.; Paulos, R.; Willing, M.C.; Warren, J.J. Physical activity and bone measures in young children: The Iowa bone development study. Pediatrics 2001, 107, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Society for Clinical Densitometry. 2019 ISCD Official Positions-Pediatric. Available online: https://www.iscd.org/official-positions/2019-iscd-official-positions-pediatric/ (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Binkley, T.L.; Berry, R.; Specker, B.L. Methods for measurement of pediatric bone. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2008, 9, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total | Girls | Boys | p Value for Sex Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 401 | n = 194 | n = 207 | ||
| Mean (SD)/ Median (IQR) | Mean (SD)/ Median (IQR) | Mean (SD)/ Median (IQR) | ||
| Age (years) | 7.65 (0.39) | 7.61 (0.37) | 7.68 (0.40) | 0.105 |
| Body height (cm) | 128.65 (5.63) | 127.46 (5.56) | 129.77 (5.49) | <0.001 |
| IOTF definition | ||||
| % (cases) normal weight | 88.8 (356) | 88.7 (172) | 88.9 (184) | 0.970 |
| % (cases) overweight | 8.0 (32) | 8.2 (16) | 7.7 (16) | |
| % (cases) obese | 3.2 (13) | 3.1 (6) | 3.4 (7) | |
| MVPA recommendations (>4 METs) | ||||
| % (cases) ≥ 60 min/day | 78.6 (315) | 72.7 (141) | 84.1 (174) | 0.006 |
| % (cases) < 60 min/day | 21.4 (86) | 27.3 (53) | 15.9 (33) | |
| TBLH BMC (g) | 670.78 (132.51) | 645.47 (126.12) | 694.49 (134.26) | <0.001 |
| TBLH fat mass (kg) | 4.34 (2.96 to 6.19) | 4.73 (3.55 to 6.67) | 3.79 (2.42 to 5.83) | <0.001 |
| Plasma leptin (ng/mL) | 3.70 (2.70 to 5.75) | 4.25 (3.20 to 6.60) | 3.10 (2.40 to 4.70) | <0.001 |
| Free leptin index | 8.82 (5.84 to 16.14) | 10.63 (7.35 to 19.22) | 6.87 (5.11 to 12.82) | <0.001 |
| MVPA (mins/day spent > 0.75 m/s2) | 130.08 (42.47) | 121.30 (36.82) | 138.31 (45.73) | <0.001 |
| Free Leptin Index | TBLH BMC (g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r/p-Value | Result | r/p-Value | Result | |
| MVPA (> 4 METs) | ||||
| Girls | 0.044/0.542 | 0.229/0.001 | ||
| No relationship between free leptin index and MVPA, controlled for age, body height and TBLH fat mass | Weak positive relationship between BMC and MVPA, controlled for age, body height and TBLH fat mass | |||
| Boys | −0.094/0.182 | 0.238/0.001 | ||
| All | −0.055/0.277 | 0.261/ < 0.001 | ||
| Free Leptin Index | ||||
| Girls | – | −0.147/0.043 | ||
| Weak negative relationship between BMC and free leptin index, controlled for age, body height and TBLH fat mass | ||||
| Boys | – | −0.227/0.001 | ||
| All | – | −0.227/ < 0.001 | ||
| Girls (n = 194) | Boys (n = 207) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (95% CI) | p-value | β (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Free Leptin Index | ||||
| TE | 0.0110 (0.0048 to 0.0171) | <0.001 | 0.0104 (0.0043 to 0.0164) | 0.001 |
| CDE | 0.0113 (0.0052 to 0.0173) | <0.001 | 0.0095 (0.0035 to 0.0155) | 0.002 |
| INTref | 0.0000 (−0.0003 to 0.0004) | 0.811 | 0.0000 (−0.0004 to 0.0004) | 0.938 |
| INTmed | −0.0000 (−0.0004 to 0.0002) | 0.570 | −0.0000 (−0.0002 to 0.0002) | 0.938 |
| PIE | −0.0003 (−0.0011 to 0.0006) | 0.556 | 0.0008 (−0.0005 to 0.0022) | 0.214 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Constable, A.M.; Porter, J.E.; Benger, D.; Vlachopoulos, D.; Barker, A.R.; Moore, S.A.; Soininen, S.; Haapala, E.A.; Westgate, K.; Brage, S.; et al. The Positive Relationship between Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity and Bone Mineral Content Is Not Mediated by Free Leptin Index in Prepubertal Children: The PANIC Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105365
Constable AM, Porter JE, Benger D, Vlachopoulos D, Barker AR, Moore SA, Soininen S, Haapala EA, Westgate K, Brage S, et al. The Positive Relationship between Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity and Bone Mineral Content Is Not Mediated by Free Leptin Index in Prepubertal Children: The PANIC Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(10):5365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105365
Chicago/Turabian StyleConstable, Annie M., Josie E. Porter, Danielle Benger, Dimitris Vlachopoulos, Alan R. Barker, Sarah A. Moore, Sonja Soininen, Eero A. Haapala, Kate Westgate, Soren Brage, and et al. 2021. "The Positive Relationship between Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity and Bone Mineral Content Is Not Mediated by Free Leptin Index in Prepubertal Children: The PANIC Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 10: 5365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105365
APA StyleConstable, A. M., Porter, J. E., Benger, D., Vlachopoulos, D., Barker, A. R., Moore, S. A., Soininen, S., Haapala, E. A., Westgate, K., Brage, S., Agostinete, R. R., Fernandes, R. A., & Lakka, T. A. (2021). The Positive Relationship between Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity and Bone Mineral Content Is Not Mediated by Free Leptin Index in Prepubertal Children: The PANIC Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(10), 5365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105365







