Effect of Red Arch-Support Insoles on Subjective Comfort and Movement Biomechanics in Various Landing Heights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Foot Insole Conditions
2.3. Test Procedure
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Joint Angle Variables
3.2. Ground Reaction Force Variables
3.3. Joint Moment Variables
3.4. Subjective Comfort Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, R.A.; Barton, R.A. Psychology: Red enhances human performance in contests. Nature 2005, 435, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenless, I.; Eynon, M.; Thelwell, R. Color of soccer goalkeepers’ uniforms influences the outcome of penalty kicks. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2013, 117, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenless, I.; Leyland, A.; Thelwell, R.; Filby, W. Soccer penalty takers’ uniform colour and pre-penalty kick gaze affect the impressions formed of them by opposing goalkeepers. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feltman, R.; Elliot, A.J. The influence of red on perceptions of relative dominance and threat in a competitive context. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2011, 13, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedemann, D.; Burt, D.M.; Hill, R.A.; Barton, R.A. Red clothing increases perceived dominance, aggression and anger. Biol. Lett. 2015, 11, 20150166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attrill, M.J.; Gresty, K.A.; Hill, R.A.; Barton, R.A. Red shirt colour is associated with long-term team success in English football. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, A.J.; Aarts, H. Perception of the color red enhances the force and velocity of motor output. Emotion 2011, 11, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreiskaemper, D.; Strauss, B.; Hagemann, N.; Busch, D. Influence of red jersey color on physical parameters in combat sports. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2013, 35, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.K.; Kam, K.; Qu, Y.; Capio, C.M. Influence of shoe colour on perceived and actual jumping performance. Footwear Sci. 2017, 9, S3–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Abdelkrim, N.; El Fazaa, S.; El Ati, J. Time-motion analysis and physiological data of elite under-19-year-old basketball players during competition. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, B.M. Biomechanics of Sport Shoes; Topline Printing Inc.: Calgary, Alberta, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cumps, E.; Verhagen, E.; Meeusen, R. Prospective epidemiological study of basketball injuries during one competitive season: Ankle sprains and overuse knee injuries. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2007, 6, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dick, R.; Hertel, J.; Agel, J.; Grossman, J.; Marshall, S.W. Descriptive epidemiology of collegiate men’s basketball injuries: National Collegiate Athletic Association Injury surveillance system, 1988–1989 through 2003–2004. J. Athl. Train. 2007, 42, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bressel, E.; Cronin, J. The landing phase of a jump strategies to minimize injuries. J. Phys. Educ. Recreat. Dance 2005, 76, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Lin, C.F.; Garrett, W.E. Lower extremity biomechanics during the landing of a stop-jump task. Clin. Biomech. 2006, 21, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arastoo, A.A.; Aghdam, E.M.; Habibi, A.H.; Zahednejad, S. Kinetic factors of vertical jumping for heading a ball in flexible flatfooted amateur soccer players with and without insole adoption. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2014, 38, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, C.; Bleakley, C.; Delahunt, E.; Holden, S. Treatment and prevention of acute and recurrent ankle sprain: An overview of systematic reviews with meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports. Med. 2017, 51, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Preston, J.J.; Queen, R.M.; Byram, I.R.; Hardaker, W.M.; Gross, M.T.; Davis, J.M.; Taft, T.N.; Garrett, W.E. Effects of wearing foot orthosis with medial arch support on the fifth metatarsal loading and ankle inversion angle in selected basketball tasks. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2007, 37, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, W.L.; Raedeke, S.G.; Williams, D.S. The relationship between the use of foot orthoses and knee ligament injury in female collegiate basketball players. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2008, 98, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, W.L.; Williams, D.S.; Durland, A.; Adams, B.; O’Brien, K. Foot orthotic devices decrease transverse plane motion during landing from a forward vertical jump in healthy females. J. Appl. Biomech. 2009, 25, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, K.W.; van der Wees, P.J.; Rowe, B.H.; de Bie, R.; van Mechelen, W.; Verhagen, E. Interventions for preventing ankle ligament injuries (Protocol). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losito, J.M. Basketball and Volleyball. In Athletic Footwear and Orthoses in Sports Medicine; Werd, M.B., Knight, E.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, D.M. Prefabricated insoles and modifications in sports medicine. In Athletic Footwear and Orthoses in Sports Medicine; Werd, M.B., Knight, E.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, M.; Tlberio, D.; Baird, J.L.; Trojian, T.H.; Anderson, J.M.; Kraemer, W.J.; Maresh, C.M. Knee valgus during drop jumps in national collegiate athletic association division I female athletes. Am. J. Sports Med. 2008, 36, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillman, M.D.; Chiumento, A.B.; Trimble, M.H.; Bauer, J.A.; Cauraugh, J.H.; Kaminski, T.W.; Hass, C.J. Tibiofemoral rotation in landing: The influence of medially and laterally posted orthotics. Phys. Ther. Sport 2003, 4, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.; Jones, R.; Harwood, C.; Mitchell, S.; Rothberg, S. Human perceptions of sports equipment under playing conditions. J. Sports Sci. 2001, 19, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, M.; Trudeau, M.B.; Nigg, S.R.; Nigg, B.M. Increased athletic performance in lighter basketball shoes: Shoe or psychology effect? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Z.Y.; Au, I.P.; Zhang, J.; Ferber, R.; Shum, G.; An, W.W.; Cheung, R.T. Effects of deceptive footwear condition on subjective comfort and running biomechanics. Transl. Sports Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.; Blanch, P.; Chapman, A.R.; McPoil, T.G.; Vicenzino, B. Foot orthoses and gait: A systematic review and meta-analysis of literature pertaining to potential mechanisms. Br. J. Sports Med. 2010, 44, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinchington, M.; Ball, K.; Naughton, G. Relation between lower limb comfort and performance in elite footballers. Phys. Ther. Sport. 2012, 13, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinchington, M.; Ball, K.; Naughton, G. Effects of footwear on comfort and injury in professional rugby league. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keis, O.; Cheun, C.C. Donning red underwear to play Mahjong: Superstitious beliefs and problem gambling among Chinese Mahjong players in Macau. Gambl. Res. J. Natl. Assoc. Gambl. Stud. 2010, 22, 18–33. [Google Scholar]
- Law, J.C.L.; Wong, T.W.L.; Chan, D.C.L.; Lam, W.K. Effects of shoe top visual patterns on shoe wears’ width perception and dynamic stability. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2018, 125, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, M.; Denegar, C.R.; Horn, E.; MacDougall, B.; Rahl, M.; Sheehan, J.; Kraemer, W.J. A 5o medial wedge reduces frontal but not saggital plane motion during jump landing in highly trained women athletes. J. Sports Med. 2010, 1, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- FIBA. Key Numbers. Federation Internationale de Basketball Amateur. Available online: http://www.fiba.basketball/Mid-termActivityReport2017.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2020).
- Stojanovic, E.; Stojiljkovic, N.; Scanlan, A.T.; Dalbo, V.J.; Berkelmans, D.M.; Milanovic, Z. The activity demands and physiological responses encountered during basketball match-play: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2017, 48, 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.K.; Kan, W.H.; Chia, J.S.; Kong, P.W. Effect of shoe modifications on biomechanical changes in basketball: A systematic review. Sports Biomech. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nin, D.Z.; Lam, W.K.; Kong, P.W. Effect of body mass and midsole hardness on kinetic and perceptual variables during basketball landing manoeuvres. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, Z.; Woo, J.; Liebenberg, J.; Park, S.K.; Ryu, J.; Lam, W.K. Kinetics and perception of basketball landing in various heights and footwear cushioning. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Clowers, K.; Kohstall, C.; Yu, Y.J. Effects of various midsole densities of basketball shoes on impact attenuation during landing activities. J. Appl. Biomech. 2005, 21, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rubio, M.A.; Picazo-Tadeo, A.J.; Gonzalez-Gomez, F. Does a red shirt improve sporting performance? Evidence from Spanish football. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2011, 18, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, M.; Sutter, M. Shirt colour and team performance in football. In Myths and Facts about Football: The Economics and Psychology of the World’s Greatest Sport; Andersson, P., Ayton, P., Schmidt, C., Eds.; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh, P.R.; Rodgers, M.M. The arch index: A useful measure from footprints. J. Biomech. 1987, 20, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marey, H.; Semary, N.; Mandour, S. Ishihara electronic color blindness test: An evaluation study. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 3, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.K.; Liu, H.; Wu, G.Q.; Liu, Z.L.; Sun, W. Effect of shoe wearing time and midsole hardness on ground reaction forces, ankle stability and perceived comfort in basketball landing. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporta, J.W.; Brown, L.E.; Coburn, J.W.; Galpin, A.J.; Tufano, J.J.; Cazas, V.L. Effects of different footwear on vertical jump and landing parameters. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beedie, C.J.; Coleman, D.; Foad, A.J. Positive and negative placebo effects resulting from the deceptive administration of an ergogenic aid. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2007, 17, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.K.; Sterzing, T.; Cheung, J.T.M. Reliability of a basketball specific testing protocol for footwear fit and comfort perception. Footwear Sci. 2011, 3, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, G.W.K.; Park, E.J.; Lee, K.K.; Cheung, J.T. Shoe collar height effect on athletic performance, ankle joint kinematics and kinetics during unanticipated maximum-effort side-cutting performance. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 1738–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wu, Z.; Lam, W.K. Collar height and heel counter-stiffness for ankle stability and athletic performance in basketball. Res. Sports Med. 2017, 25, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Kong, P.W.; Chong, L.J.Y.; Lam, W.K. Foot orthoses alter lower limb biomechanics but not jump performance in basketball players with and without flat feet. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2019, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeow, C.; Lee, P.V.; Goh, J.C. Regression relationships of landing height with ground reaction forces, knee flexion angles, angular velocities and joint powers during double-leg landing. Knee 2009, 16, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, H.; Galinsky, A.D. Enclothed cognition. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2012, 48, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Kakihana, W.; Nakagawa, T.; Mitomi, H.; Hikita, A.; Suzuki, R.; Akai, M.; Iwaya, T.; Nakamura, K.; Fukui, N. Addition of an arch-support improves the biomechanical effect of a laterally wedged insole. Gait Posture 2009, 29, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wortley, M.; Slivernail, J.F.; Carson, D.; Paquette, M.R. Do ankle braces provide similar effects on ankle biomechanical variables in subjects with and without chronic ankle instability during landing? J. Sport Health Sci. 2012, 1, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacoff, A.; Nigg, B.M.; Reinschmidt, C.; van der Bogert, A.J.; Lundberg, A. Tibiocalcaneal kinematics of barefoot versus shod running. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Stergiou, P.; Worobets, J.; Nigg, B.; Stefanyshyn, D. Improved footwear comfort reduces oxygen consumption during running. Footwear Sci. 2009, 1, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, A.J.; Maier, M.A. Color Psychology: Effects of perceiving color on psychological functioning in humans. Ann. Rev. Psychol. 2014, 65, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmond, A.C.; Keenan, A.M.; Landorf, K.B. Contoured, prefabricated foot orthoses demonstrate comparable mechanical properties to contoured, customised foot orthoses: A plantar pressure study. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2009, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

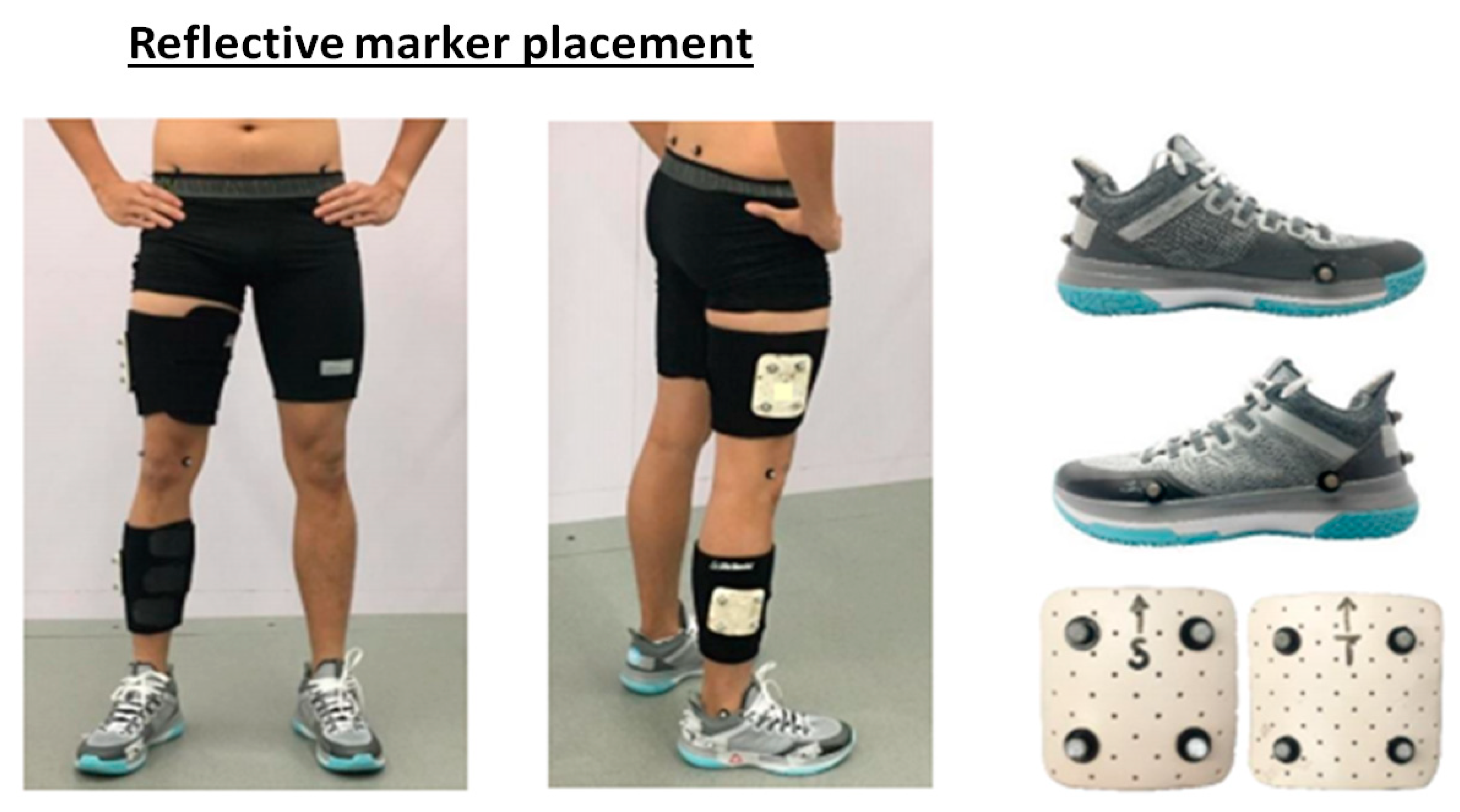
| Variable | Insole (I) | HxI | H | I | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (H) | Red–AS | White–AS | White–Flat | p | p | p | |
| Ankle joint (°) | |||||||
| Plantarflexion at touch down | Low | 12.3 (7.6) | 10.6 (10.4) | 14.0 (8.8) | 0.168 | 0.136 | 0.395 |
| High | 12.4 (8.3) | 13.9 (9.1) | 14.1 (8.6) | ||||
| Eversion at touch down | Low | 4.9 (4.1) | 5.0 (5.5) | 4.4 (4.5) | 0.125 | <0.001 | 0.803 |
| High | 4.4 (4.0) | 3.4 (5.1) | 4.2 (4.8) | ||||
| Peak dorsiflexion | Low | 28.6 (6.4) | 29.2 (8.4) | 28.0 (6.6) | 0.299 | 0.168 | 0.842 |
| High | 29.7 (5.8) | 28.8 (8.3) | 29.5 (7.4) | ||||
| Peak eversion | Low | 3.6 (3.0) | 2.6 (4.0) | 3.5 (3.7) | 0.754 | 0.001 | 0.204 |
| High | 2.9 (3.1) | 1.8 (3.9) | 2.8 (3.9) | ||||
| RoM-sagittal | Low | 39.2 (7.8) | 38.5 (7.3) | 38.9 (7.6) | 0.517 | <0.001 | 0.816 |
| High | 42.4 (7.2) | 42.5 (6.9) | 43.4 (6.9) | ||||
| RoM-coronal | Low | 8.6 (2.5) | 9.2 (3.8) | 8.3 (2.6) | 0.166 | 0.135 | 0.827 |
| High | 9.4 (2.7) | 9.1 (2.3) | 9.4 (2.6) | ||||
| Knee joint (°) | |||||||
| Flexion at touch down | Low | 20.4 (5.5) | 20.5 (5.8) | 21.2 (5.0) | 0.648 | <0.001 | 0.540 |
| High | 23.7 (4.9) | 23.6 (6.5) | 25.0 (6.1) | ||||
| Peak flexion | Low | 86.0 (13.9) | 83.9 (17.7) | 85.3 (15.3) | 0.499 | <0.001 | 0.567 |
| High | 93.8 (14.5) | 91.0 (18.1) | 94.1 (15.6) | ||||
| RoM-sagittal | Low | 83.8 (14.5) | 81.1 (19.8) | 82.5 (18.7) | 0.472 | <0.001 | 0.469 |
| High | 92.5 (16.3) | 87.9 (20.3) | 90.6 (17.9) | ||||
| Variable | Insole (I) | HxI | H | I | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (H) | Red–AS | White–AS | White–Flat | p | p | p | |
| GRF (BW) | |||||||
| Forefoot peak vGRF | Low | 1.11 (0.60) | 1.10 (0.28) | 1.06 (0.32) | 0.859 | <0.001 | 0.533 |
| High | 1.42 (0.36) | 1.37 (0.37) | 1.32 (0.36) | ||||
| Rearfoot peak vGRF | Low | 3.51 (0.60) | 3.63 (0.75) | 3.55 (0.75) | 0.710 | <0.001 | 0.642 |
| High | 4.05 (0.63) | 4.12 (0.82) | 4.01 (0.73) | ||||
| Rearfoot max LR (BW/s) | Low | 467.10 (190.11) | 453.50 (195.70) | 433.97 (177.36) | 0.110 | <0.001 | 0.37 |
| High | 593.43 (231.34) | 500.30 (171.31) | 534.66 (230.58) | ||||
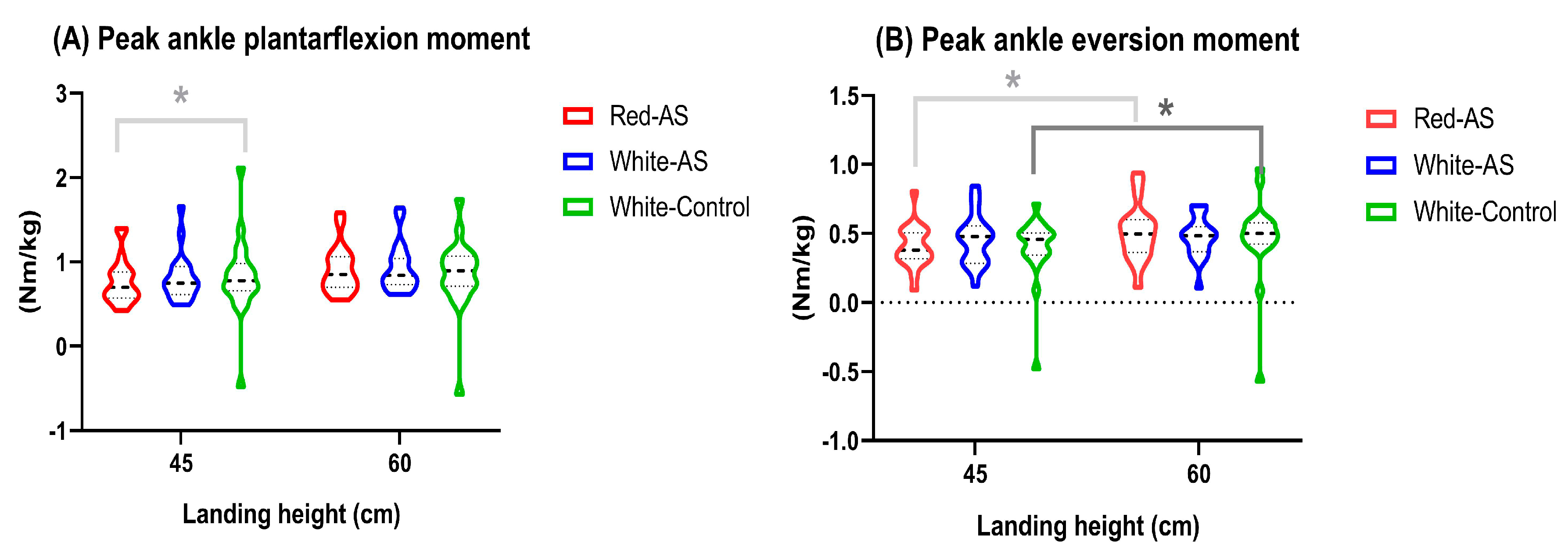
| Joint moment (Nm/kg) | |||||||
| Peak plantarflexion moment | Low | 0.77 (0.27) | 0.81 (0.28) | 0.89 (0.38) | 0.005 | <0.001 | 0.034 |
| High | 0.91 (0.28) | 0.93 (0.29) | 0.93 (0.30) | ||||
| Peak ankle eversion moment | Low | 0.40 (0.16) | 0.46 (0.18) | 0.44 (0.14) | 0.032 | <0.001 | 0.733 |
| High | 0.51 (0.21) | 0.47 (0.15) | 0.52 (0.18) | ||||
| Peak knee extension moment | Low | 2.06 (0.60) | 2.13 (0.68) | 2.06 (0.61) | 0.152 | <0.001 | 0.910 |
| High | 2.66 (0.82) | 2.50 (0.81) | 2.63 (0.82) | ||||
| Comfort perception | |||||||
| Forefoot comfort perception | Low | 9.46 (2.58) | 7.14 (2.17) | 7.34 (2.62) | 0.233 | 0.437 | <0.001 |
| High | 8.83 (2.51) | 7.43 (2.42) | 7.07 (2.72) | ||||
| Rearfoot comfort perception | Low | 9.71 (2.56) | 8.75 (2.53) | 7.02 (1.97) | 0.127 | 0.481 | <0.001 |
| High | 9.33 (2.83) | 8.12 (2.77) | 7.42 (3.04) | ||||
| Stability perception | Low | 9.65 (2.38) | 9.41 (2.46) | 8.87 (2.56) | 0.656 | 0.544 | 0.142 |
| High | 9.70 (2.42) | 9.05 (2.59) | 8.72 (2.22) | ||||
| Overall comfort perception | Low | 9.76 (2.18) | 8.88 (2.69) | 7.64 (2.14) | 0.362 | 0.192 | 0.005 |
| High | 9.53 (2.47) | 8.16 (2.46) | 7.68 (2.32) | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Lam, W.-K.; Cheung, C.-H.; Leung, A.K.-L. Effect of Red Arch-Support Insoles on Subjective Comfort and Movement Biomechanics in Various Landing Heights. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072476
Wang Y, Lam W-K, Cheung C-H, Leung AK-L. Effect of Red Arch-Support Insoles on Subjective Comfort and Movement Biomechanics in Various Landing Heights. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(7):2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072476
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yi, Wing-Kai Lam, Cheuk-Hei Cheung, and Aaron Kam-Lun Leung. 2020. "Effect of Red Arch-Support Insoles on Subjective Comfort and Movement Biomechanics in Various Landing Heights" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 7: 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072476
APA StyleWang, Y., Lam, W.-K., Cheung, C.-H., & Leung, A. K.-L. (2020). Effect of Red Arch-Support Insoles on Subjective Comfort and Movement Biomechanics in Various Landing Heights. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(7), 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072476





