Distribution of the Soil PAHs and Health Risk Influenced by Coal Usage Processes in Taiyuan City, Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
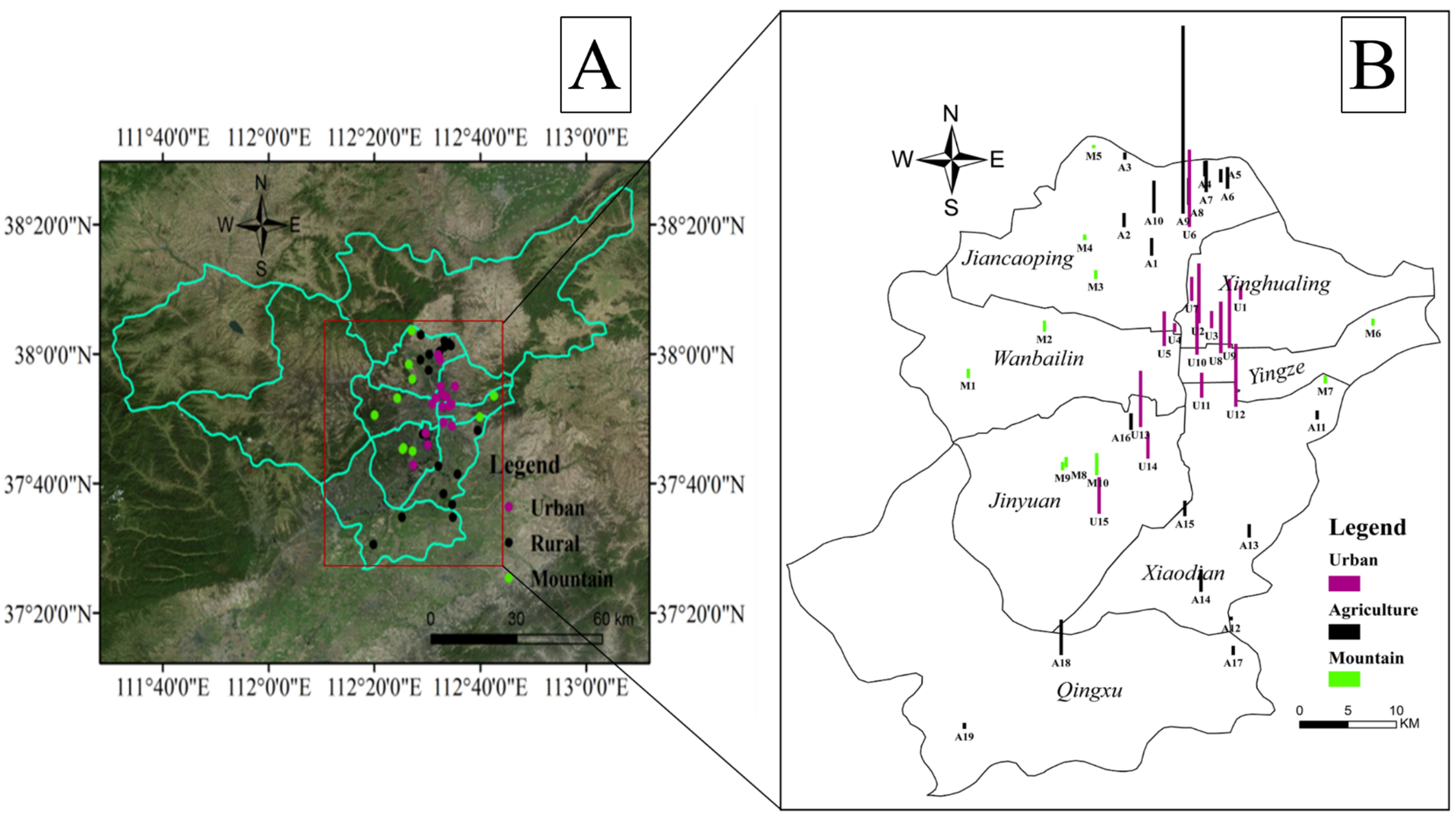
2.1. Study Region and Soil Sampling
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.3. Quality Assurance/Quality Control
2.4. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF)
2.5. BaP Toxic Equivalent Concentration
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
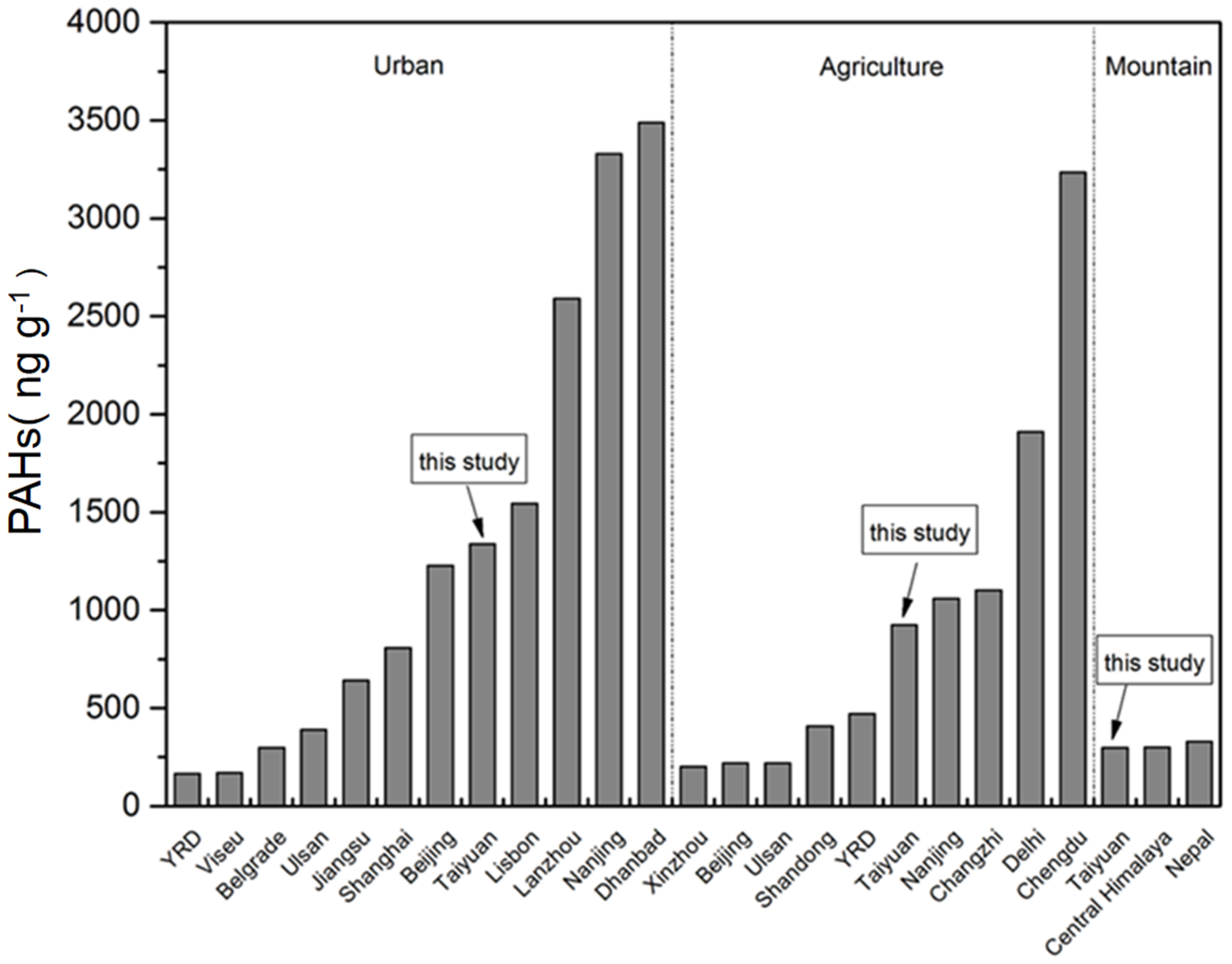
3.1. PAHs Levels
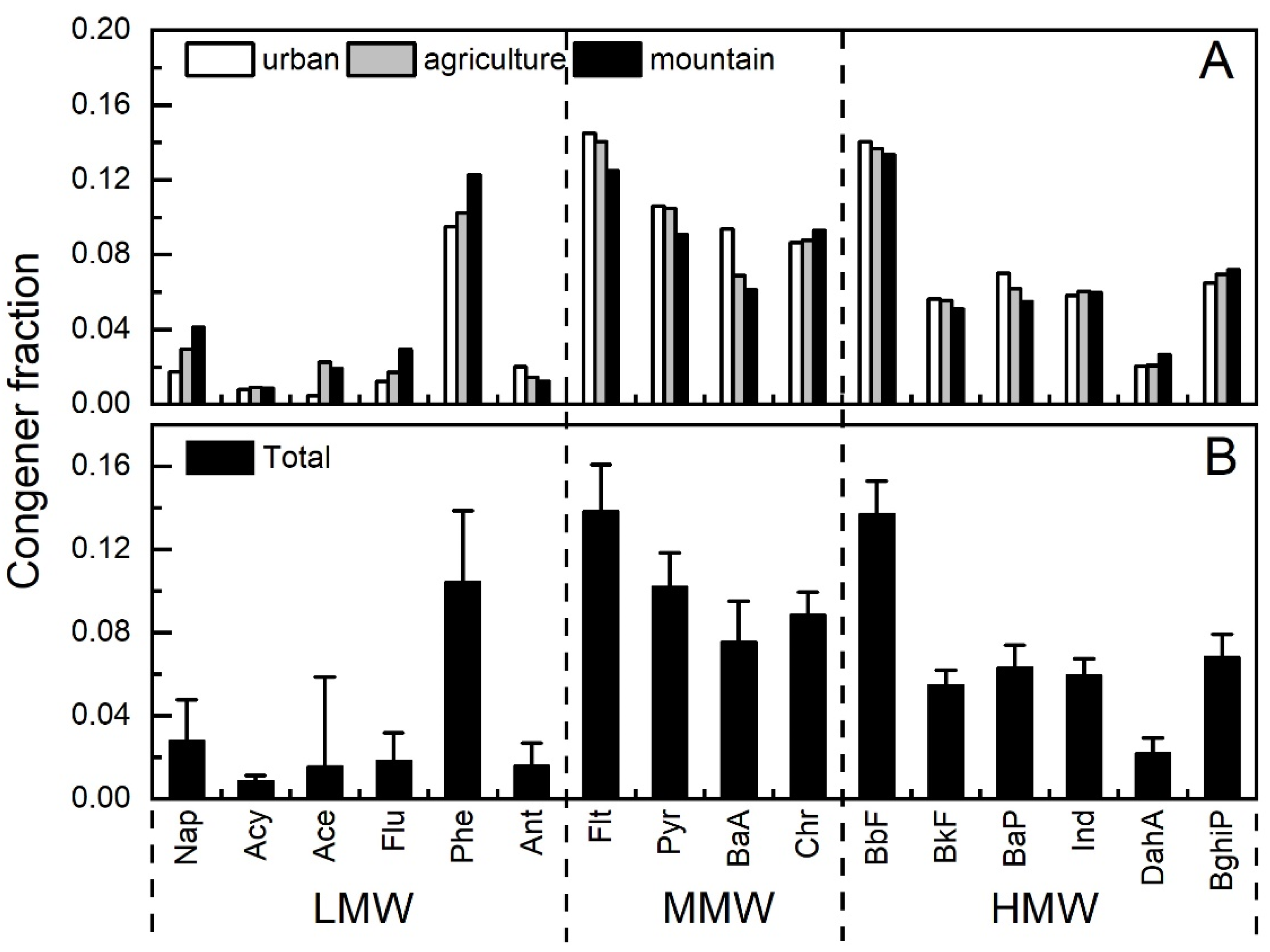
3.2. Compositional Profiles of PAHs
3.3. Spatial Distribution of PAHs
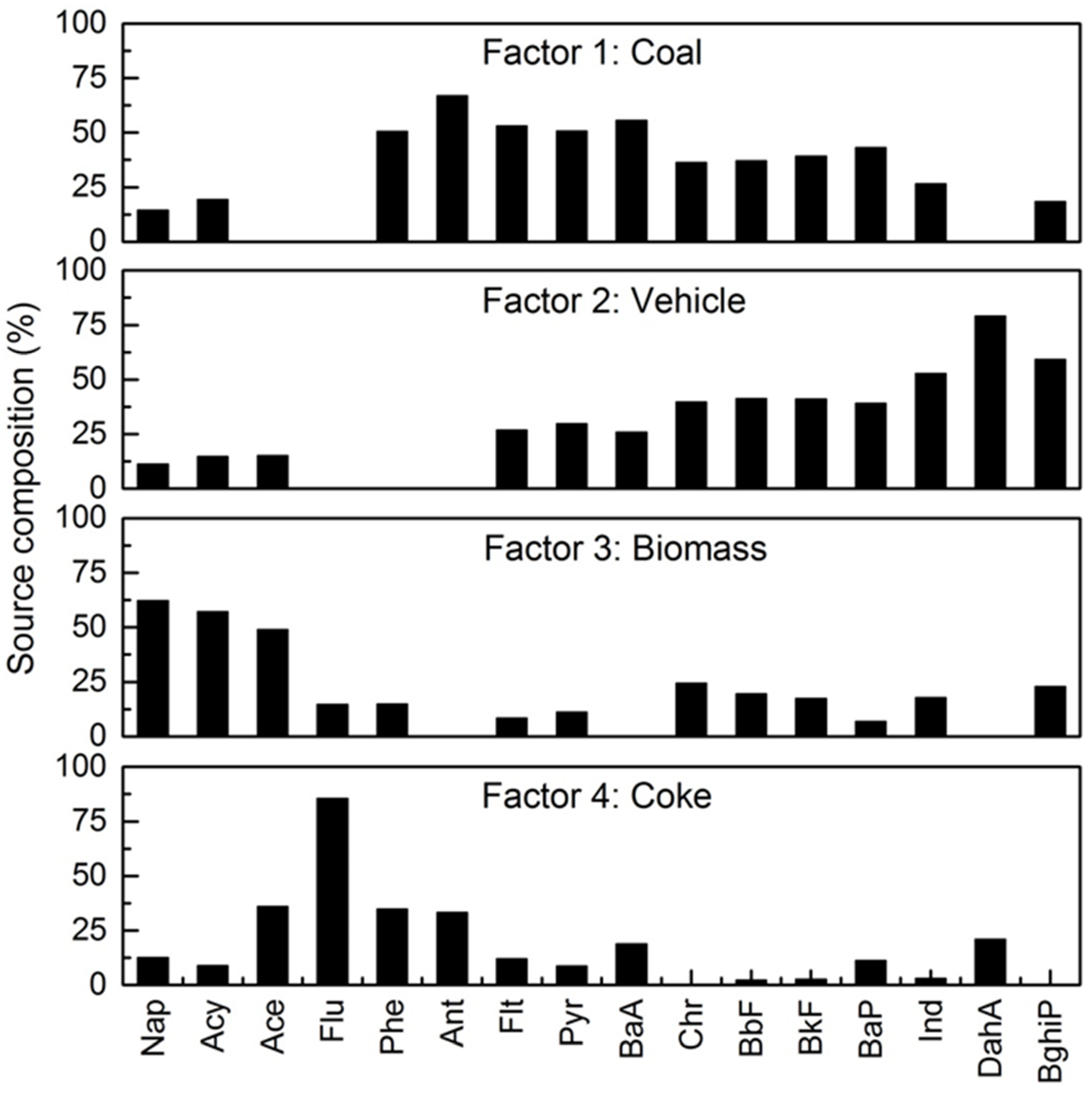
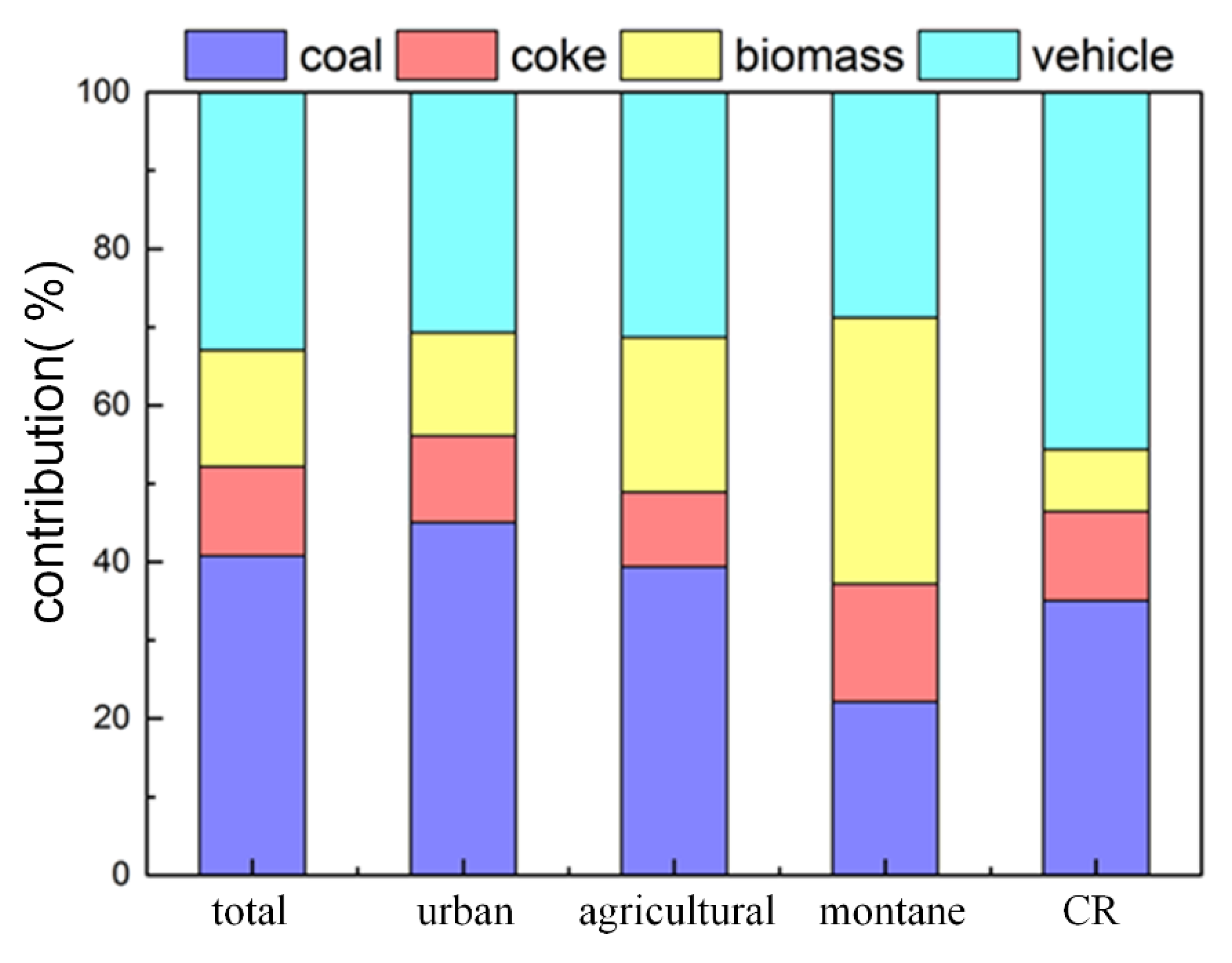
3.4. Source Identification by PMF
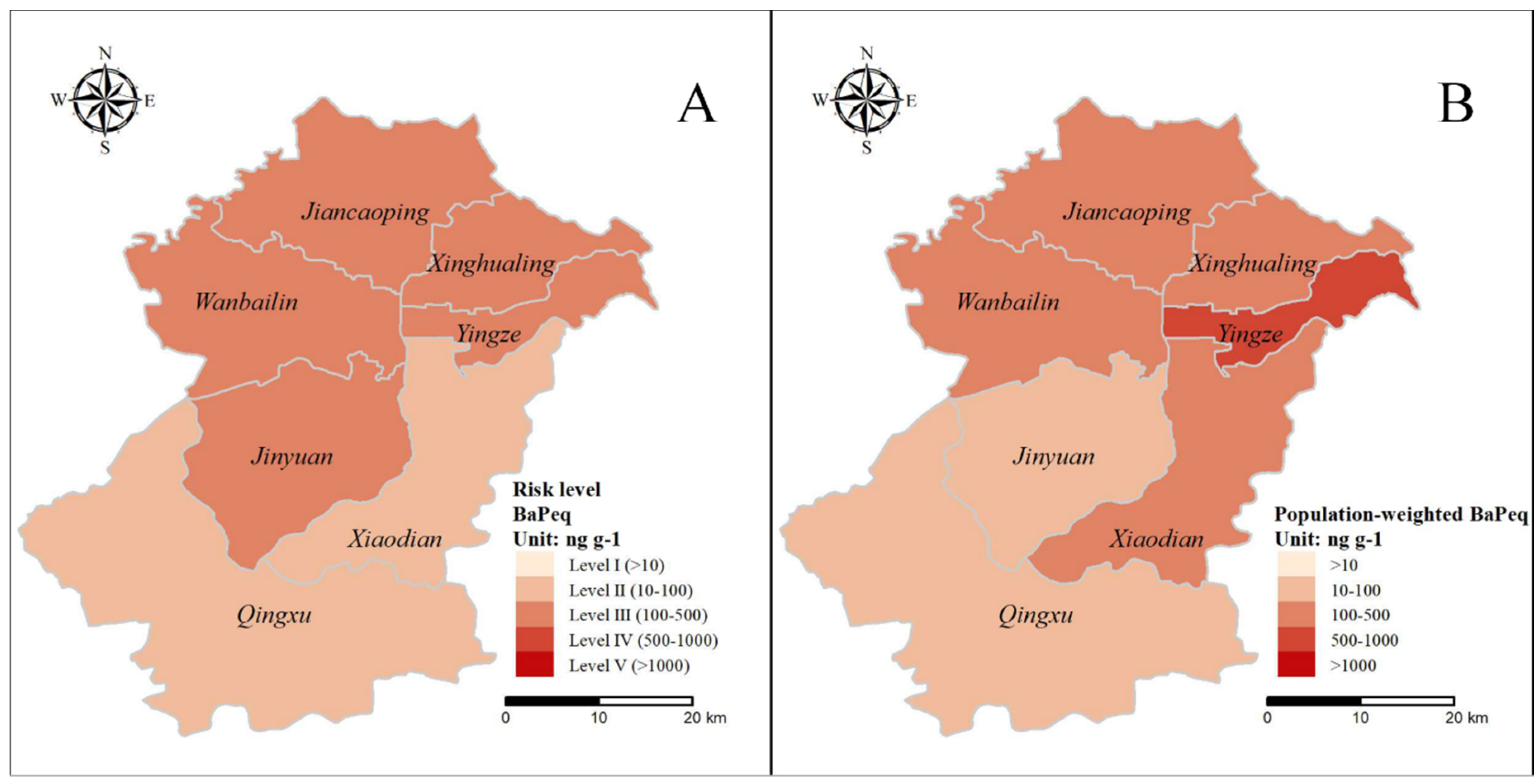
3.5. Human Health Risk Assessments of PAHs in Soils
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MEP (Ministry of Environmental Protection, China); MLR (Ministry of Land and Resources, China). Bulletin of National Soil Survey; 2014. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/foot/site1/20140417/782bcb88840814ba158d01.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2020).
- Jiang, Y.; Yves, U.J.; Sun, H.; Hu, X.; Zhan, H.; Wu, Y. Distribution, compositional pattern and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soils of an industrial city, Lanzhou, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, T.; Khillare, P.S.; Shridhar, V.; Ray, S. Pattern, sources and toxic potential of PAHs in the agricultural soils of Delhi, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, D.; Bradlow, L.; Ms, W.; Woodruff, T.; Hoel, D.; Anton-Culver, H. Medical Hypothesis: Xenoestrogens as Preventable Causes of Breast Cancer. Environ. Health Perspect. 1993, 101, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; He, Q.; Guo, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Shao, M.; Wang, Y. Source apportionment and toxicity of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by PMF: Quantifying the influence of coal usage in Taiyuan, China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 193, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, L.; Cao, R.; Gao, B.; Yan, Y.; He, Q. A wintertime study of PM 2.5 -bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Taiyuan during 2009–2013: Assessment of pollution control strategy in a typical basin region. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.; Cheng, M.; Guo, L.; Liu, M.; Chen, L. Particle dry deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and its risk assessment in a typical coal-polluted and basin city, northern China. Atmosp. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, W.; Tao, S. Emission of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Y. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contamination in surface soil of China: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Niu, J.; Guo, W.; An, X.; Long, Z. Ecological and health risk-based characterization of agricultural soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the vicinity of a chemical plant in China. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 461. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.T.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.K.; Lei, B.L.; Sun, Y.F.; Zhou, J.; Wu, M.H. Occurrence, sources and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban (Pudong) and suburban soils from Shanghai in China. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Shen, G.; Tao, S.; Hong, J.; Chen, Y.; Xue, M.; Li, T.; Su, S.; Shen, H.; Fu, X.; et al. Characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in agricultural soils at a typical coke production base in Shanxi, China. Chemosphere 2015, 127, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Guo, W.; Niu, J.; An, X.; Zhao, L. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in agricultural soils around the industrial city of Changzhi, China: Characteristics, spatial distribution, hotspots, sources, and potential risks. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Fang, D. Gridded Field Observations of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soils From a Typical County in Shanxi Province, China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 68, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, H.; Shangguan, Y.; Cheng, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, X.; Huo, X.; Zhao, X. Occurrence, sources, and potential human health risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in agricultural soils of the coal production area surrounding Xinzhou, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 108, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, S.; Zhou, S.L.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Shi, Y. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from urban to rural areas in Nanjing: Concentration, source, spatial distribution, and potential human health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527–528, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Smith, D.J.T.; Luhana, L. Source Apportionment of Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Collected from an Urban Location in Birmingham, U.K. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, R.K.; Baker, J.E. Source Apportionment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Urban Atmosphere: A Comparison of Three Methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcik, M.F.; Eisenreich, S.J.; Lioy, P.J. Source apportionment and source/sink relationships of PAHs in the coastal atmosphere of Chicago and Lake Michigan. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 5071–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Duan, Y.H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Tao, S. Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface soil in Tianjin, China. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X. PAH contamination in Beijing’s topsoil: A unique indicator of the megacity’s evolving energy consumption and overall environmental quality. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nisbet, I.C.; LaGoy, P.K. Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 1992, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tao, S.; Shen, H.; Ma, J. Inhalation exposure to ambient polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and lung cancer risk of Chinese population. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21063–21067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bureau, T.S. Taiyuan Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, H.O.; Choi, S.D. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils from a multi-industrial city, South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crnković, D.; Ristić, M.; Jovanović, A.; Antonović, D. Levels of PAHs in the soils of Belgrade and its environs. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 125, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachada, A.; Pato, P.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Silva, E.F.D.; Duarte, A.C. Levels, sources and potential human health risks of organic pollutants in urban soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 430, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Wang, M.; Chen, W. Spatial Analysis of PAHs in Soils along an Urban–Suburban–Rural Gradient: Scale effect, distribution patterns, diffusion and influencing factors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Chao, S.; Qiao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Fan, X. Urbanization-related changes in soil PAHs and potential health risks of emission sources in a township in Southern Jiangsu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 575, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Di, W.; Wang, X.L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Li, X.D.; Sun, J.T.; Zhu, L.Z.; Shen, H.Z.; Shu, T. Spatial distribution, emission source and health risk of parent PAHs and derivatives in surface soils from the Yangtze River Delta, eastern China. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, S.; Sinha, A.; Tarafdar, A. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) concentration levels, pattern, source identification and soil toxicity assessment in urban traffic soil of Dhanbad, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545–546, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ling, W.; Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Kang, F.; Gao, Y. Contamination and health risk assessment of PAHs in soils and crops in industrial areas of the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, C.; Cheng, Q.; Wu, J.; Zeng, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, X.; Ma, D.; Ge, W. Contamination, source identification, and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the soils of vegetable greenhouses in Shandong, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, X.; Qi, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Odhiambo, J.O. Spatial distribution and source diagnosis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from Chengdu Economic Region, Sichuan Province, western China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 110, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Luo, W.; Gao, J.; Xu, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Romesh, K.Y.; Giesy, J.P.; Kang, S.; De, B.J. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from the Central-Himalaya region: Distribution, sources, and risks to humans and wildlife. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 556, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliszewska-Kordybach, B. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in agricultural soils in Poland: Preliminary proposals for criteria to evaluate the level of soil contamination. Appl. Geochem. 1996, 11, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, P.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X. Urban fractionation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from Dalian soils. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2011, 10, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Tong, F.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, B. Distribution and Source Apportionment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Forest Soils from Urban to Rural Areas in the Pearl River Delta of Southern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2642–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xia, X.; Yang, L.; Shen, M.; Liu, R. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soils of different land uses in Beijing, China: Distribution, sources and their correlation with the city’s urbanization history. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.T.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Wu, M.H.; Yu, G. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban soils of the megacity Shanghai: Occurrence, source apportionment and potential human health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla, V.M.; Jurado, E.; Dachs, J.; Sweetman, A.J.; Jones, K.C. The maximum reservoir capacity of soils for persistent organic pollutants: Implications for global cycling. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 134, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, N.R.; Scheff, P.A.; Holsen, T.M. PAH source fingerprints for coke ovens, diesel and, gasoline engines, highway tunnels, and wood combustion emissions. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, X.; Jiang, Z.; He, S.; Qian, K. Occurrence and source apportionment of PAHs in highly vulnerable karst system. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Hu, X.X.; Lu, B.; Tao, S.; Wang, R. Estimation of annual emission and distribution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Taiyuan. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, G.; He, Q.; Wang, X. Characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rainwater in Taiyuan. Environ. Chem. 2014, 33, 2144–2151. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wania, F.; Westgate, J.N. On the mechanism of mountain cold-trapping of organic chemicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9092–9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compounds | Urban Soils | Agricultural Soils | Montane Soils | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | |
| Nap | 8.35 | 38.67 | 19.53 | 9.53 | 9.29 | 31.26 | 14.65 | 5.55 | 6.13 | 17.97 | 11.18 | 3.92 |
| Acy | 1.94 | 23.58 | 11.00 | 6.87 | 1.42 | 55.89 | 7.70 | 11.94 | 1.08 | 3.88 | 2.36 | 0.90 |
| Ace | 1.84 | 13.24 | 5.61 | 3.39 | 1.48 | 71.11 | 7.97 | 15.73 | 0.71 | 15.53 | 5.20 | 4.08 |
| Flu | 6.26 | 42.40 | 14.72 | 9.21 | 3.83 | 30.16 | 9.36 | 5.92 | 3.94 | 14.48 | 7.97 | 3.50 |
| Phe | 24.44 | 324.52 | 128.31 | 80.13 | 18.61 | 510.73 | 81.29 | 107.66 | 17.17 | 80.96 | 35.75 | 18.62 |
| Ant | 3.74 | 149.62 | 30.41 | 36.35 | 3.65 | 77.97 | 12.21 | 16.86 | 1.49 | 8.44 | 3.53 | 1.82 |
| Flt | 37.85 | 424.45 | 200.46 | 120.64 | 9.31 | 1090.25 | 143.94 | 236.50 | 9.24 | 99.04 | 38.38 | 23.46 |
| Pyr | 33.15 | 308.48 | 144.02 | 83.56 | 6.32 | 816.54 | 107.35 | 177.14 | 6.87 | 65.52 | 27.38 | 15.14 |
| BaA c | 24.04 | 256.24 | 131.24 | 78.95 | 4.19 | 597.21 | 73.07 | 129.90 | 5.07 | 45.99 | 18.72 | 11.21 |
| Chr c | 24.79 | 209.74 | 113.31 | 55.82 | 8.70 | 521.56 | 78.88 | 111.03 | 6.65 | 73.05 | 28.71 | 17.52 |
| BbF c | 37.64 | 350.47 | 185.73 | 93.52 | 12.79 | 896.81 | 127.58 | 191.56 | 11.44 | 106.22 | 41.03 | 25.56 |
| BkF c | 16.43 | 156.38 | 75.64 | 40.84 | 4.00 | 392.74 | 53.61 | 84.34 | 4.01 | 36.56 | 15.39 | 8.61 |
| BaP c | 20.72 | 158.04 | 94.03 | 49.65 | 3.72 | 543.43 | 65.57 | 118.01 | 5.49 | 41.04 | 16.60 | 9.64 |
| Ind c | 18.06 | 144.87 | 76.29 | 38.45 | 4.94 | 414.53 | 57.12 | 88.76 | 7.31 | 38.31 | 17.23 | 8.24 |
| DahA c | 9.83 | 45.64 | 25.89 | 12.66 | 1.66 | 168.64 | 20.85 | 36.55 | 4.68 | 14.45 | 7.14 | 3.07 |
| BghiP | 24.81 | 148.13 | 82.42 | 38.77 | 6.85 | 431.22 | 62.89 | 91.82 | 8.28 | 44.00 | 20.74 | 9.65 |
| ∑7cPAHs | 151.98 | 1285.07 | 702.12 | 362.94 | 39.99 | 3534.92 | 476.69 | 759.33 | 44.81 | 355.62 | 144.81 | 82.96 |
| ∑16PAHs | 294.36 | 2540.64 | 1338.60 | 709.18 | 132.82 | 6594.63 | 924.05 | 1410.44 | 104.78 | 695.26 | 297.30 | 157.11 |
| PAHs | TEFs | Urban | Agricultural | Montane |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Acy | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Ace | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Flu | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Phe | 0.001 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.04 |
| Ant | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.12 | 0.04 |
| Flt | 0.001 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.04 |
| Pyr | 0.001 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.03 |
| BaA | 0.1 | 13.12 | 7.31 | 1.87 |
| Chr | 0.01 | 1.13 | 0.79 | 0.29 |
| BbF | 0.1 | 18.57 | 12.76 | 4.10 |
| BkF | 0.1 | 7.56 | 5.36 | 1.54 |
| BaP | 1 | 94.03 | 65.57 | 16.60 |
| Ind | 0.1 | 7.63 | 5.71 | 1.72 |
| DahA | 1 | 25.89 | 20.85 | 7.14 |
| BghiP | 0.01 | 0.82 | 0.63 | 0.21 |
| Total | - | 169.59 | 119.48 | 33.63 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Cheng, M.; Cui, Y.; He, Q.; Guo, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, X. Distribution of the Soil PAHs and Health Risk Influenced by Coal Usage Processes in Taiyuan City, Northern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176319
Li R, Cheng M, Cui Y, He Q, Guo X, Chen L, Wang X. Distribution of the Soil PAHs and Health Risk Influenced by Coal Usage Processes in Taiyuan City, Northern China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(17):6319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176319
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Rongjie, Mingchao Cheng, Yang Cui, Qiusheng He, Xiaofang Guo, Laiguo Chen, and Xinming Wang. 2020. "Distribution of the Soil PAHs and Health Risk Influenced by Coal Usage Processes in Taiyuan City, Northern China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 17: 6319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176319






