A Systematic Review of the Guidelines and Delphi Study for the Multifactorial Fall Risk Assessment of Community-Dwelling Elderly
Abstract
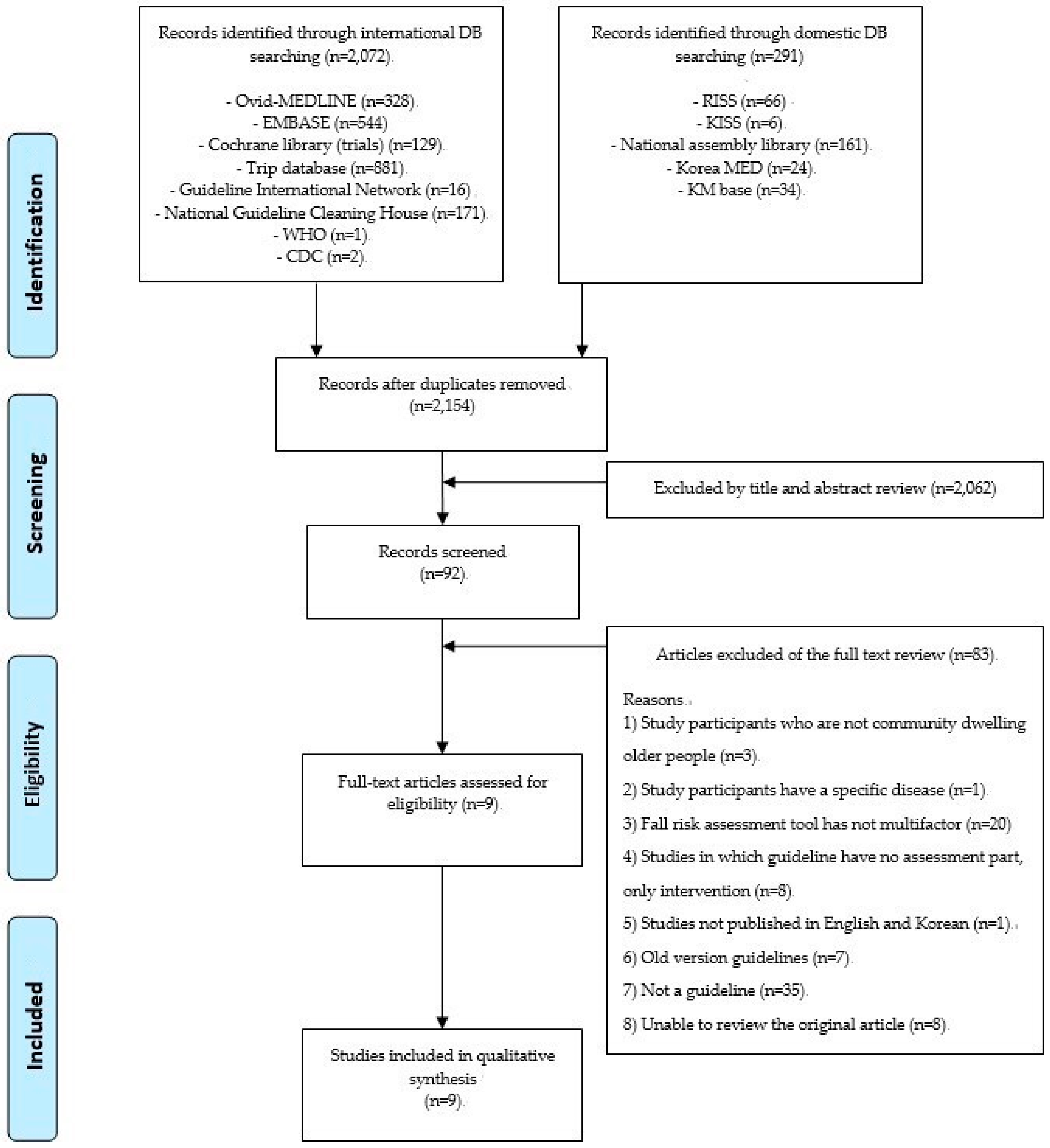
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Review
2.2. Delphi Study
3. Results
3.1. Systematic Review and an Initial List of Potential Standards
3.2. Delphi Study to Identify and Prioritize Standards
3.2.1. Open Round
3.2.2. Consensus in Scoring Rounds
4. Discussion
4.1. Items Excluded from this Multifactorial Assessment Instrument
4.2. Additional Items in This Multifactorial Assessment Instrument
4.3. Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrer, A.; Formiga, F.; Sanz, H.; de Vries, O.J.; Badia, T.; Pujol, R. Multifactorial assessment and targeted intervention to reduce falls among the oldest-old: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.; Hector, M. Effectiveness of intervention programs in preventing falls: A systematic review of recent 10 years and meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2012, 13, 188.e113–188.e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, E.; Kakara, R.J.M.; Report, M.W. Deaths from falls among persons aged ≥ 65 Years—United States, 2007–2016. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burns, E.R.; Stevens, J.A.; Lee, R.J. The direct costs of fatal and non-fatal falls among older adults—United States. J. Safety Res. 2016, 58, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.C.; Chon, J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, S.D.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.A.; Han, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, B.Y. The association between fall history and physical performance tests in the community-dwelling elderly: A cross-sectional analysis. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 41, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sertel, M.; Demirci, C.S.; Sakizli, E.; Bezgin, S. Determination of cut-off values of tinetti performance oriented mobility assessment and fall risk questionnaire in older adults individuals with cognitive impairment. J. Turgut Ozal Med. Cent. 2019, 26, 204–208. [Google Scholar]
- Payette, M.-C.; Belanger, C.; Léveillé, V.; Grenier, S. Fall-related psychological concerns and anxiety among community-dwelling older adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maghfouri, B.; Mehraban, A.H.; Taghizade, G.; Aminian, G.; Jafari, H.J.M.R. Validity and reliability of persion version of home falls and accident screening tool in Iranian elderly. J. Mod. Rehabil. 2012, 5, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Keglovits, M.; Clemson, L.; Hu, Y.L.; Nguyen, A.; Neff, A.J.; Mandelbaum, C.; Hudson, M.; Williams, R.; Silianoff, T.; Stark, S. A scoping review of fall hazards in the homes of older adults and development of a framework for assessment and intervention. Aust. Occup. Ther. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callis, N. Falls prevention: Identification of predictive fall risk factors. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2016, 29, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, E.; Straus, S.; Holroyd-Leduc, J. Risk factors for falls in the elderly. In Medication-Related Falls in Older People; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Wood, D.A. Primary prevention of ischaemic heart disease: Populations, individuals, and health professionals. Lancet 2019, 394, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, S.K. Delirium—A framework to improve acute care for older persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2018, 66, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaeyen, E.; Coussement, J.; Leysens, G.; Van der Elst, E.; Delbaere, K.; Cambier, D.; Denhaerynck, K.; Goemaere, S.; Wertelaers, A.; Dobbels, F.J. Characteristics and effectiveness of fall prevention programs in nursing homes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, P.; Klenk, J.; Cattelani, L.; Bandinelli, S.; Ferrucci, L.; Rapp, K.; Chiari, L.; Rothenbacher, D. Predictive performance of a fall risk assessment tool for community-dwelling older people (FRAT-up) in 4 European cohorts. J. Am. Med Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Falls in Older People: Assessing Risk and Prevention; NICE: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Panel on Prevention of Falls in Older Persons, American Geriatrics Society; British Geriatrics Society. Summary of the updated American Geriatrics Society/British Geriatrics Society clinical practice guideline for prevention of falls in older persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2011, 59, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bristol Community Health. Multi Factorial Falls Risk Assessment Tool. Available online: https://briscomhealth.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/V10_Multifactorial_Falls_Risk_Assessment_tool.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Medicine, I.O. Clinical Practice Guidelines We Can. Trust; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B.; et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, I.R.; Grant, R.C.; Feldman, B.M.; Pencharz, P.B.; Ling, S.C.; Moore, A.M.; Wales, P.W. Defining consensus: A systematic review recommends methodologic criteria for reporting of Delphi studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 67, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, E.; Duffield, C.; Jacob, D. A protocol for the development of a critical thinking assessment tool for nurses using a Delphi technique. J. Adv. Nurs. 2017, 73, 1982–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirguis-Blake, J.M.; Michael, Y.L.; Perdue, L.A.; Coppola, E.L.; Beil, T.L. Falls prevention in community-dwelling older adults: Interventions. JAMA 2013, 309, 1406–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Commission on Safety Quality in Health Care. Preventing Falls and Harm from Falls in Older People. Best Practice Guidelines for Australian Community Care. Available online: https://doi.org/www.safetyandquality.gov.au/our-work/falls-prevention/falls-prevention-community (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Avin, K.G.; Hanke, T.A.; Kirk-Sanchez, N.; McDonough, C.M.; Shubert, T.E.; Hardage, J.; Hartley, G. Management of falls in community-dwelling older adults: Clinical guidance statement from the Academy of geriatric physical therapy of the american physical therapy association. Phys. Ther. 2015, 95, 815–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeMier, M. Falls Among Older Adults: Strategies for Prevention; Washington State Department of Health: Seattle, WA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Laffoy, M. Strategy to Prevent Falls and Fractures in Ireland’s Ageing Population Summary, Conclusions and Recomendations; Health Service Executive: Dubin, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Preventing Falls: A Guide to Implementing Effective Community-Based Fall Prevention Programs; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Agency of Canada. Seniors’ Falls in Canada: Second Report. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/content/dam/phac-aspc/migration/phac-aspc/seniors-aines/publications/public/injury-blessure/seniors_falls-chutes_aines/assets/pdf/seniors_falls-chutes_aines-eng.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Scott, V.; Peck, S.; Kendall, P. Prevention of Falls and Injuries among the Elderly: A Special Report from the Office of the Provincial Health Officer; Provincial Health Officer: Victoria BC, Canada, 2004. Available online: https://www.health.gov.bc.ca/library/publications/year/2004/falls.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Todd, C.; Skelton, D. What are the Main Risk Factors for Falls among Older People and what are the Most Effective Interventions to Prevent these Falls. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0018/74700/E82552.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Rahn, D. Transformational teamwork: Exploring the impact of nursing teamwork on nurse-sensitive quality indicators. J. Nurs. Care Qual. 2016, 31, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Willett, W.C.; Staehelin, H.B.; Bazemore, M.G.; Zee, R.Y.; Wong, J.B. Effect of vitamin D on falls: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2004, 291, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lips, P.; Bouillon, R.; Van Schoor, N.M.; Vanderschueren, D.; Verschueren, S.; Kuchuk, N.; Milisen, K.; Boonen, S. Reducing fracture risk with calcium and vitamin D. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2010, 73, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolland, M.J.; Grey, A.; Gamble, G.D.; Reid, I.R. Vitamin D supplementation and falls: A trial sequential meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfon, M.; Phan, O.; Teta, D. Vitamin D: A review on its effects on muscle strength, the risk of fall, and frailty. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 953241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoang, P.D.; Cameron, M.H.; Gandevia, S.C.; Lord, S.R. Neuropsychological, balance, and mobility risk factors for falls in people with multiple sclerosis: A prospective cohort study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodakowski, J.; Becker, A.M.; Golias, K.W. Activity-based goals generated by older adults with mild cognitive impairment. OTJR Occup. Particip. Health 2018, 38, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, M.W.; Chyun, D.A.; Skolnick, A.H.; Alexander, K.P.; Forman, D.E.; Kitzman, D.W.; Maurer, M.S.; McClurken, J.B.; Resnick, B.M.; Shen, W.K. Knowledge gaps in cardiovascular care of the older adult population: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, and American Geriatrics Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 2419–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshida, T.; Yamazaki, H.; Kato, H. Vitamin D and calcium are required during denosumab treatment in osteoporosis with rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leveille, S.; Hausdorff, J.; Dong, Z.; Milberg, W.; McLean, R.; van der Leeuw, G. Does attention mediate the relationship between chronic pain and falls in older adults? Innov. Aging 2018, 2, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kachroo, S.; Kawabata, H.; Colilla, S.; Shi, L.; Zhao, Y.; Mukherjee, J.; Iloeje, U.; Fonseca, V. Association between hypoglycemia and fall-related events in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Analysis of a US commercial database. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2015, 21, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, S.; Conner, C.; Aagren, M.; Ruiz, K.; Bouchard, J. Association between hypoglycaemic events and fall-related fractures in Medicare-covered patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlie, H.D.; Garwood, C.L. Diabetes medications related to an increased risk of falls and fall-related morbidity in the elderly. Ann. Pharm. 2010, 44, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, B.; West, E.; Patchay, S.; Schofield, P. Is there a relationship between pain and psychological concerns related to falling in community dwelling older adults? A systematic review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2014, 36, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabre, J.M.; Ellis, R.; Kosma, M.; Wood, R.H. Falls risk factors and a compendium of falls risk screening instruments. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2010, 33, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieringa, S.; Dreesens, D.; Forland, F.; Hulshof, C.; Lukersmith, S.; Macbeth, F.; Shaw, B.; van Vliet, A.; Zuiderent-Jerak, T. Different knowledge, different styles of reasoning: A challenge for guideline development. BMJ Evid. Based Med. 2018, 23, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, M.A.; Hill, K.D.; Blackberry, I.; Day, L.M.; Dharmage, S.C. The reliability and predictive accuracy of the falls risk for older people in the community assessment (FROP-Com) tool. Age Ageing 2008, 37, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| No. | First Author or Publisher (Year) | Country | Age (Years) | Sex | Person Who Performed the Assessment | Factors | Items |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CDC (2015) | No restrictions | Aged 65 years and over | No restrictions | Health care providers | Biological risk factors | Muscle weakness or balance problems Medication side effects and/or interactions Chronic health conditions such as arthritis and stroke Vision changes and vision loss Loss of sensation in feet |
| Behavioral risk factors | Inactivity Risky behaviors such as standing on a chair in place of a step stool Alcohol use | ||||||
| Environmental risk factors | Clutter and tripping hazards Poor lighting Lack of stair railings Lack of grab bars inside and outside the tub or shower Poorly designed public spaces | ||||||
| 2 | Avin. K.G. (2015) | No restrictions | Aged 65 years and over | No restrictions | Physical therapist | Medication review with emphasis on polypharmacy and psychoactive drugs | |
| Medical history with an emphasis on new or unmanaged risk factors | Osteoporosis Depression Cardiac disease, including signs or symptoms of cardioinhibitory carotid sinus hypersensitivity | ||||||
| Body functions and structure, activity and participation, environmental factors, and personal factors | Strength Balance Gait Activities of daily living Footwear Environmental hazards Cognition Neurological function Cardiac function, including postural hypotension Vision Urinary incontinence | ||||||
| 3 | Canada PHAC (2014) | Canada | Aged 65 years and over | No restrictions | N/I | Biological or intrinsic risk factors | Acute illness Balance and gait deficits Chronic conditions and disabilities Cognitive impairments Low vision Muscle weakness and reduced physical fitness |
| Behavioral risk factors | Assistive devices Excessive alcohol Fear of falling Footwear and clothing History of previous falls Inadequate diet Medications Risk-taking behavior Vitamin D | ||||||
| Social and economic risk factors | Social networks Socio–economic status: | ||||||
| Environmental risk factors | Factors in the community Factors in the living environment Weather and climate | ||||||
| 4 | ACSQHC (2009) | Australia | Aged 65 years and over | No restrictions | Health professionals, and all members of the health care team | Intrinsic risk factors | Increased age History of falls Chronic medical conditions (e.g., stroke, Parkinson’s disease, arthritis) Multiple medications and specific types (e.g., psychoactive drugs) Impaired balance and mobility Reduced muscle strength Sensory problems (e.g., impaired vision, peripheral neuropathy) Dizziness Impaired cognition Incontinence Depression Low levels of physical activity Slow reaction time Fear of falling Being female |
| Extrinsic risk factors | Inappropriate footwear (high heels and slippers) Inappropriate spectacles Hazards inside and outside the home | ||||||
| 5 | BC, Ministry of Health (2004) | British Columbia | Aged 65 years and over | No restrictions | Community health workers, home care nurses, and other senior service providers | Biological/medical risk factors | Advanced age Gender Chronic and acute illness Physical disability Muscle weakness and diminished physical fitness Vision changes Cognitive impairments |
| Behavioral risk factors | Risk-taking behaviors Medication use Inattention Alcohol use Inappropriate footwear Handbags Inadequate diet/exercise Fear of falling | ||||||
| Environmental risk factors | Home hazards Community hazards Institutional hazards | ||||||
| Social and economic risk factors | |||||||
| 6 | WHO (2004) | No restrictions | Aged 65 years and over | No restrictions | Emergency department medical staff, health authorities, primary health care teams, | Intrinsic risk factors | A history of falls, age, gender (women), living alone, ethnicity, medicines, medical conditions (circulatory disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, depression, and arthritis, chronic disease burden, thyroid dysfunction, dizziness, depression, and incontinence), impaired mobility and gait, sedentary behavior, psychological status, nutritional deficiencies, impaired cognition, visual impairments, foot problems |
| Extrinsic risk factors | Environmental hazards (poor lighting, slippery floors, uneven surfaces, etc.) Footwear and clothing Inappropriate walking aids or assistive devices | ||||||
| 7 | Washington State Department of Health (2002) | No restrictions | Aged 65 years and over | No restrictions | A nurse or other health professional trained to conduct tests | Demographic characteristics of people who fall | Age (65 years or older) Gender (female) Race (White) |
| Causes of falls | Chronic health problems Physical and functional impairments Alcohol and medication use Hazards in the home | ||||||
| 8 | HSE (2008) | Ireland | Aged 65 years and over | No restrictions | N/I | Intrinsic risk factors | Muscle weakness History of falls Gait and balance deficits Visual deficits Arthritis Depression Cognitive impairment Age > 80 years Urinary incontinence Orthostatic or postprandial hypotension Dizziness Fear of falling Limited activity (institutional setting) Hearing (institutional setting) |
| Extrinsic risk factors | Use of assistive devices Impaired ADL High level of activity (community setting) Medication | ||||||
| Environmental risk factors | Environmental hazards Home hazards | ||||||
| 9 | USPSTF (2018) | United States of America | Aged 65 years and over | No restrictions | Clinicians (usually nursing staff) | Biological factors | Age Physical function Mobility limitation |
| Behavioral factor | A history of falls |
| Guideline Development Group | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domain | CDC | Avin et al. | Canada PHAC | ACSQHC | BC, Ministry of Health | WHO | Washington State Department of Health | HSE | USPSTF | Mean (Range), % |
| 1. Scope and Purpose | 83.3 | 100 | 83.3 | 100.0 | 83.3 | 44.4 | 83.3 | 83.3 | 85.7 | 83.0 (44.4–100.0) |
| 2. Stakeholder Involvement | 77.8 | 77.8 | 44.4 | 66.7 | 50.0 | 55.6 | 55.6 | 44.4 | 85.7 | 62.0 (44.4–85.7) |
| 3. Rigor of Development | 29.2 | 81.3 | 27.1 | 85.4 | 25.0 | 37.5 | 25.0 | 45.8 | 82.1 | 48.7 (25.0–85.4) |
| 4. Clarity of Presentation | 88.9 | 50.0 | 44.4 | 88.9 | 61.1 | 33.3 | 55.6 | 44.4 | 81.0 | 60.8 (33.3–88.9) |
| 5. Applicability | 50.0 | 0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 75.0 | 25.0 | 28.6 | 36.5 (0–75.0) |
| 6. Editorial Independence | 33.3 | 83.3 | 0 | 83.3 | 33.3 | 33.3 | 50.0 | 0 | 78.6 | 43.9 (0–83.3) |
| Overall Outcome of Guideline Development | 66.7 | 66.7 | 66.7 | 100.0 | 66.7 | 66.7 | 66.7 | 66.7 | 73.8 | 71.2 (66.7–100.0) |
| Factors | Behavioral Factor | Biological Factor | Environmental Factor | General Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Items | Multiple medication use Excess alcohol intake Lack of exercise Inadequate diet History of previous falls Fear of falling Inappropriate footwear Use of assistive devices | Sex (Female) Increased age Impaired ADL Low vision History of disease Musculoskeletal function Mobility/balance/gait deficits Neurological function Cognitive capacity Cardiac function Cardiovascular drugs Psychoactive drugs Vitamin D deficiency Incontinence Hypotension Dizziness Medication side effect | Indoor environment Outdoor environment Social network | Low income Living alone |
| Factors | Items | 2nd Round | 3rd Round | Judgment | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Necessity | Applicability | Necessity | Applicability | |||||||||||||||
| CVR | DoCs | DoCv | CV | CVR | DoCs | DoCv | CV | CVR | DoCs | DoCv | CV | CVR | DoCs | DoCv | CV | |||
| General Characteristics | Sex (female) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included |
| Increased age | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included | |
| Living alone | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included | |
| Low income | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.16 | 0.80 | 0.50 * | 0.50 | 0.16 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.11 | Included (after discussion) | |
| Behavior Factor | Inadequate diet | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.16 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.10 | Included |
| History of previous falls | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.06 | Included | |
| Fear of falling | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | Included | |
| Lack of exercise | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.12 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.11 | Included | |
| Vitamin D deficiency | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 0.60 * | 1.00 * | 0.23 | Excluded | |||||||||
| Excess alcohol intake | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | Included | |
| Disease History | Stroke | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included |
| Dementia | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included | |
| Parkinson’s | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included | |
| Dizziness | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included | |
| Cardiovascular | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.19 | Included | |
| Hypotension | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included | |
| Respiratory | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included | |
| Peripheral neuropathy | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | Included | |
| Diabetes | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 0.15 | Included | |
| Chronic pain | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.06 | Included | |
| Arthritis | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included | |
| Osteoporosis | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included | |
| Incontinence | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.17 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 0.63 * | 0.21 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.11 | Included (After discussion) | |
| Medication History | Psychoactive drugs | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | Included |
| Cardiovascular drugs | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included | |
| Multiple medication use | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.17 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 0.09 | Included | |
| Medication side effects | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.63 * | 0.25 * | 1.13 * | 0.47 | Excluded | |||||||||
| Physical Function | Low vision | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included |
| Mobility/balance/gait deficits | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | Included | |
| Impaired ADL | 1.00 | 0.90 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 0.25 | 0.10 | Included | |
| Musculoskeletal function | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 0.09 | Included | |
| Cardiac function | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 1.00 | 0.58 * | 1.00 * | 0.24 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.19 | Included (After discussion) | |
| Neurological function | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | Included | |
| Inappropriate footwear | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | Included | |
| Use of assistive devices | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Included | |
| Cognitive Function | Cognitive capacity | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.93 | 0.60 * | 1.00 * | 0.15 | Excluded | ||||||||
| Environmental Factor | Indoor environment | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.01 | 0.03 | Included |
| Outdoor environment | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.04 | 0.08 | Included | |
| Social network | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.15 | Included | |
| Factors | Items | Contents of Question | Options | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General characteristics | Sex (female) | Sex (female) | Male | Female | ||
| Increased age | Age | Age | ||||
| Living alone | Residential type | Alone | Together | |||
| Low income | Health insurance | Medical insurance | Medicaid 1 | Medicaid 2 | ||
| Behavior factor | Inadequate diet | Number of meals/day | 3 times of meal/day | 2 times of meal/day | 1 time of meal/day | Poor, irregular |
| History of previous falls | Experience of falls | Yes (experienced) | No (inexperienced) | |||
| Details of fall experience | Time | Place | Number of falls | Extent of damage | ||
| Fear of falling | Going out alone | Feeling no fear | Feeling like usual | Feeling a little fear | Feeling a lot of fear | |
| Cooking alone | Feeling no fear | Feeling like usual | Feeling a little fear | Feeling a lot of fear | ||
| Activities in the bathroom | Feeling no fear | Feeling like usual | Feeling a little fear | Feeling a lot of fear | ||
| Getting out of bed alone | Feeling no fear | Feeling like usual | Feeling a little fear | Feeling a lot of fear | ||
| Walking for exercise | Feeling no fear | Feeling like usual | Feeling a little fear | Feeling a lot of fear | ||
| Going out on a slippery road (snow, rain, frozen road) | Feeling no fear | Feeling like usual | Feeling a little fear | Feeling a lot of fear | ||
| Visiting friends or relatives alone | Feeling no fear | Feeling like usual | Feeling a little fear | Feeling a lot of fear | ||
| Lowering things on the head | Feeling no fear | Feeling like usual | Feeling a little fear | Feeling a lot of fear | ||
| Going to crowded places | Feeling no fear | Feeling like usual | Feeling a little fear | Feeling a lot of fear | ||
| Going up and down the stairs | Feeling no fear | Feeling like usual | Feeling a little fear | Feeling a lot of fear | ||
| Bending over and grabbing objects | Feeling no fear | Feeling like usual | Feeling a little fear | Feeling a lot of fear | ||
| Lack of exercise | Times of exercise/day | None | < 30 min | 30 min–1 h | 1–2 h | |
| > 2 h | ||||||
| Excess alcohol intake | Alcohol intake | Yes | No | Stop drinking | ||
| Details of alcohol intake | Kind of alcoholic drink | Average drinking quantity | A period of drinking | |||
| Disease history | Stroke | Having a disease | Yes | No | ||
| Dementia | Having a disease | Yes | No | |||
| Parkinson’s | Having a disease | Yes | No | |||
| Dizziness | Having a disease | Yes | No | |||
| Cardiovascular | Having a disease | Yes | No | |||
| Hypotension | Having a disease | Yes | No | |||
| Respiratory | Having a disease | Yes | No | |||
| Peripheral neuropathy | Having a disease | Yes | No | |||
| Diabetes | Having a disease | Yes | No | |||
| Chronic pain | Having a disease | Yes | No | |||
| Arthritis | Having a disease | Yes | No | |||
| Osteoporosis | Having a disease | Yes | No | |||
| Incontinence | Having a disease | Yes | No | |||
| Medication history | Psychoactive drugs | Taking sedative drugs | Yes | No | ||
| - Diazepam | Yes | No | ||||
| - Etizolam | Yes | No | ||||
| - Clonazepam | Yes | No | ||||
| - Lorazepam | Yes | No | ||||
| - Alprazolam | Yes | No | ||||
| Taking haloperidol | Yes | No | ||||
| Taking sleeping drugs | ||||||
| - Zolpidem | Yes | No | ||||
| Taking antiemetic drugs | Yes | No | ||||
| Taking antidepressants | ||||||
| - TCAs | Yes | No | ||||
| - SSRIs | Yes | No | ||||
| Cardiovascular drugs | Taking loop diuretics | Yes | No | |||
| Taking antiarrhythmic drugs | Yes | No | ||||
| Taking digoxin | Yes | No | ||||
| Taking oral hypoglycemic/insulin | Yes | No | ||||
| Taking calcium channel blockers | Yes | No | ||||
| Multiple medication use | Total number of medication | ≤ 3 | 4 | 5 | ≥ 6 | |
| Physical function | Low vision | Eyesight | Left eyesight | Right eyesight | Unknown | |
| Wearing glasses | Yes | No | ||||
| Diabetic retinopathy | Yes | No | ||||
| Ophthalmologic disease | Yes | No | ||||
| Mobility/balance/gait deficits | 30 s chair stand test below-average score based on age and gender | Age; 60–64 | Men: <14 | Women: <12 | ||
| - Average score | Age; 65–69 | Men: <12 | Women: <11 | |||
| Age; 70–74 | Men: <12 | Women: <10 | ||||
| Age; 75–79 | Men: <11 | Women: <10 | ||||
| Age; 80–84 | Men: <10 | Women: <9 | ||||
| 4-step balance test within 10 s | Yes | No | ||||
| - Standing upright | ||||||
| - Standing aside | ||||||
| - Tandem gait | ||||||
| - Standing on one leg | ||||||
| Taking TUG test more than 12 s | Yes | No | ||||
| Impaired ADL | Bathing | Dependence | Partial dependence | Independence | ||
| Dressing | Dependence | Partial dependence | Independence | |||
| Using the toilet | Dependence | Partial dependence | Independence | |||
| Transferring | Dependence | Partial dependence | Independence | |||
| Continence | Dependence | Partial dependence | Independence | |||
| Feeding | Dependence | Partial dependence | Independence | |||
| Musculoskeletal function | Restriction of ROM | |||||
| - Upper limbs | Yes | No | ||||
| - Lower limbs | Yes | No | ||||
| - Hip joint | Yes | No | ||||
| - Knee joint | Yes | No | ||||
| - Ankle joint | Yes | No | ||||
| Cardiac function | Heart rate | Heart rate (/min) | ||||
| Arrhythmia | Yes | No | ||||
| - Result of EKG | ||||||
| Postural hypotension | Yes | No | ||||
| Standing position (BP/HR) | Supine position (BP/HR) | Standing position (BP/HR) | ||||
| Neurological function | Disease history | |||||
| - CVA | Yes | No | ||||
| - Epilepsy or seizure | Yes | No | ||||
| - Walk-related diseases | Yes | No | ||||
| - Peripheral neuropathy | Yes | No | ||||
| - Peripheral vertigo | Yes | No | ||||
| Inappropriate footwear | Toe deformities/ulcer | Yes | No | |||
| Use of assistive devices | Walking assistance device | Yes | No | |||
| Power train (e.g., wheelchair) | Yes | No | ||||
| Environmental factor | Indoor environment | Risk factors in the living room and bedroom | ||||
| - Brightness of light | Brightness | Normal | Darkness | Lux | ||
| - Bare and telephone wire | Yes | No | ||||
| - Carpet | Yes | No | ||||
| - Slipperiness | Yes | No | ||||
| - Height of threshold | High | Medium | Low | None | ||
| - Height of bed | High | Medium | Low | None | ||
| Risk factors of bathroom | ||||||
| - Brightness of light | Brightness | Normal | Darkness | Lux | ||
| - Slipperiness | Yes | No | ||||
| - Nonslip mat | Yes | No | ||||
| - Height of threshold | High | Medium | Low | None | ||
| - Safety rail of shower booth | Yes | No | ||||
| Outdoor environment | Risk factors of outdoor environment | |||||
| - Brightness of light | Brightness | Normal | Darkness | Lux | ||
| - Access road | Slipperiness | The steep slope of a footpath | Broken sidewalk block | No elevator | ||
| - Height of stairs | High | Medium | Low | Damaged stairs | ||
| None | ||||||
| - Safety rail | Yes | No | ||||
| Social network | Support of community | Yes | No |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Lee, W.; Lee, S.H. A Systematic Review of the Guidelines and Delphi Study for the Multifactorial Fall Risk Assessment of Community-Dwelling Elderly. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176097
Kim J, Lee W, Lee SH. A Systematic Review of the Guidelines and Delphi Study for the Multifactorial Fall Risk Assessment of Community-Dwelling Elderly. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(17):6097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176097
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jieun, Worlsook Lee, and Seon Heui Lee. 2020. "A Systematic Review of the Guidelines and Delphi Study for the Multifactorial Fall Risk Assessment of Community-Dwelling Elderly" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 17: 6097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176097
APA StyleKim, J., Lee, W., & Lee, S. H. (2020). A Systematic Review of the Guidelines and Delphi Study for the Multifactorial Fall Risk Assessment of Community-Dwelling Elderly. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(17), 6097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176097





