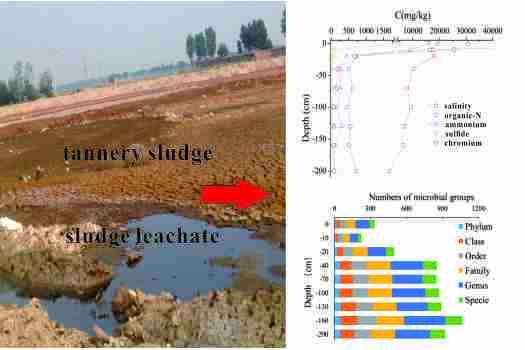
Soil Pollution Characteristics and Microbial Responses in a Vertical Profile with Long-Term Tannery Sludge Contamination in Hebei, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
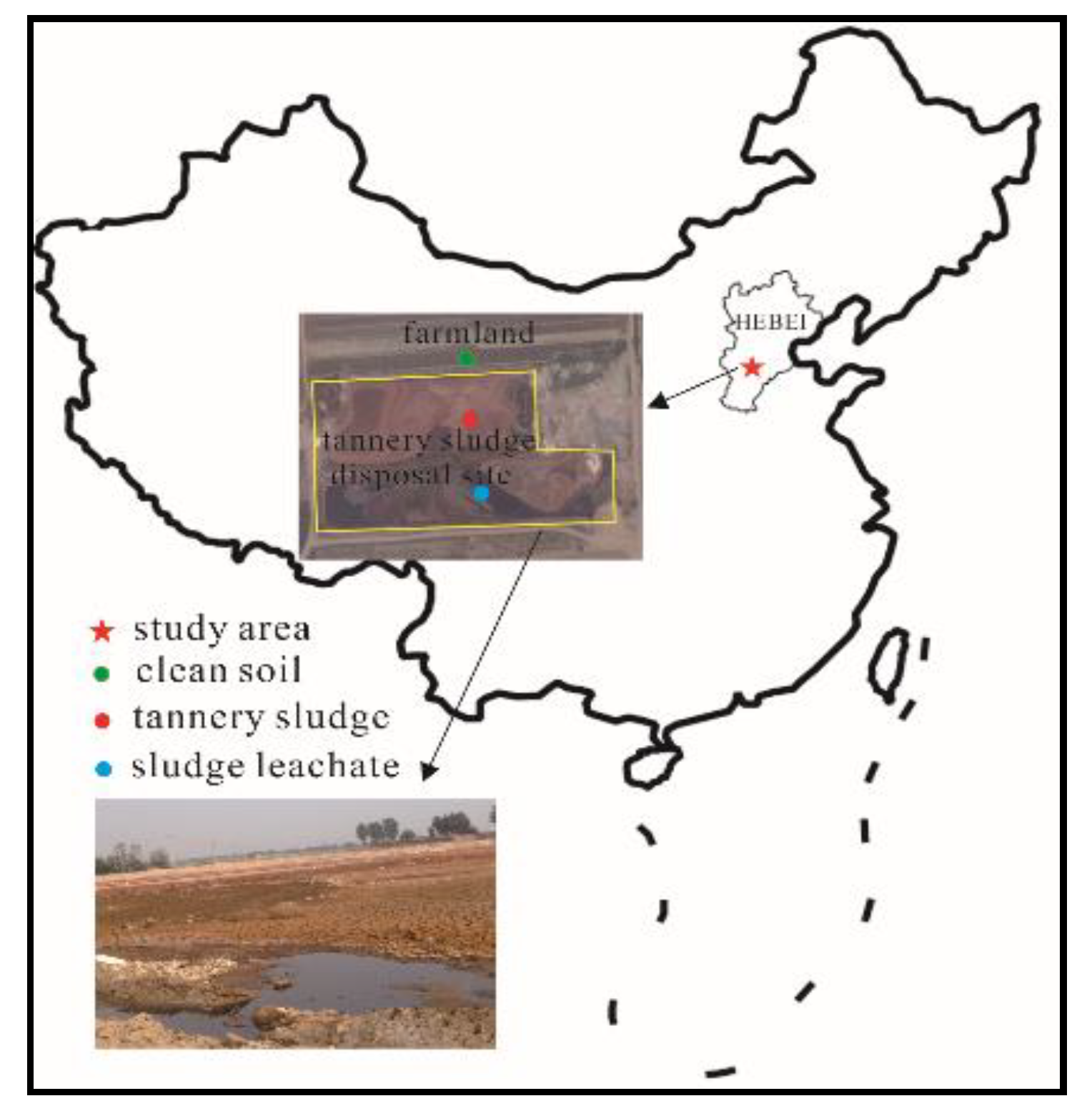
2.1. Field Survey and Sampling
2.2. Chemical Analysis of Tannery Sludge and Soils
2.3. Microbiological Test Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Tannery Sludge
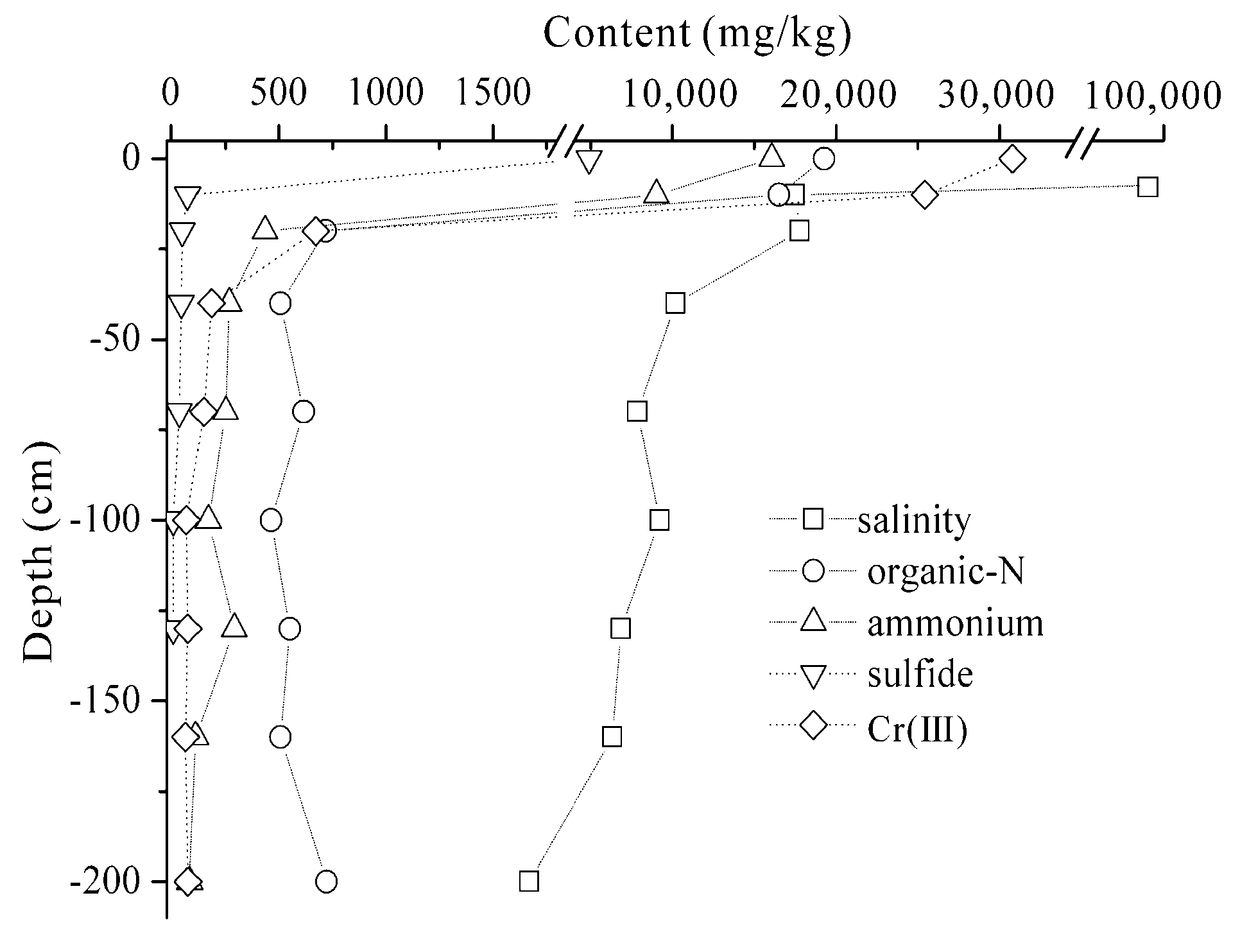
3.2. Effects of the Tannery Sludge on Soil Physicochemical Properties in the Vertical Profile
3.2.1. The Vertical Distribution Characteristics of Contaminates
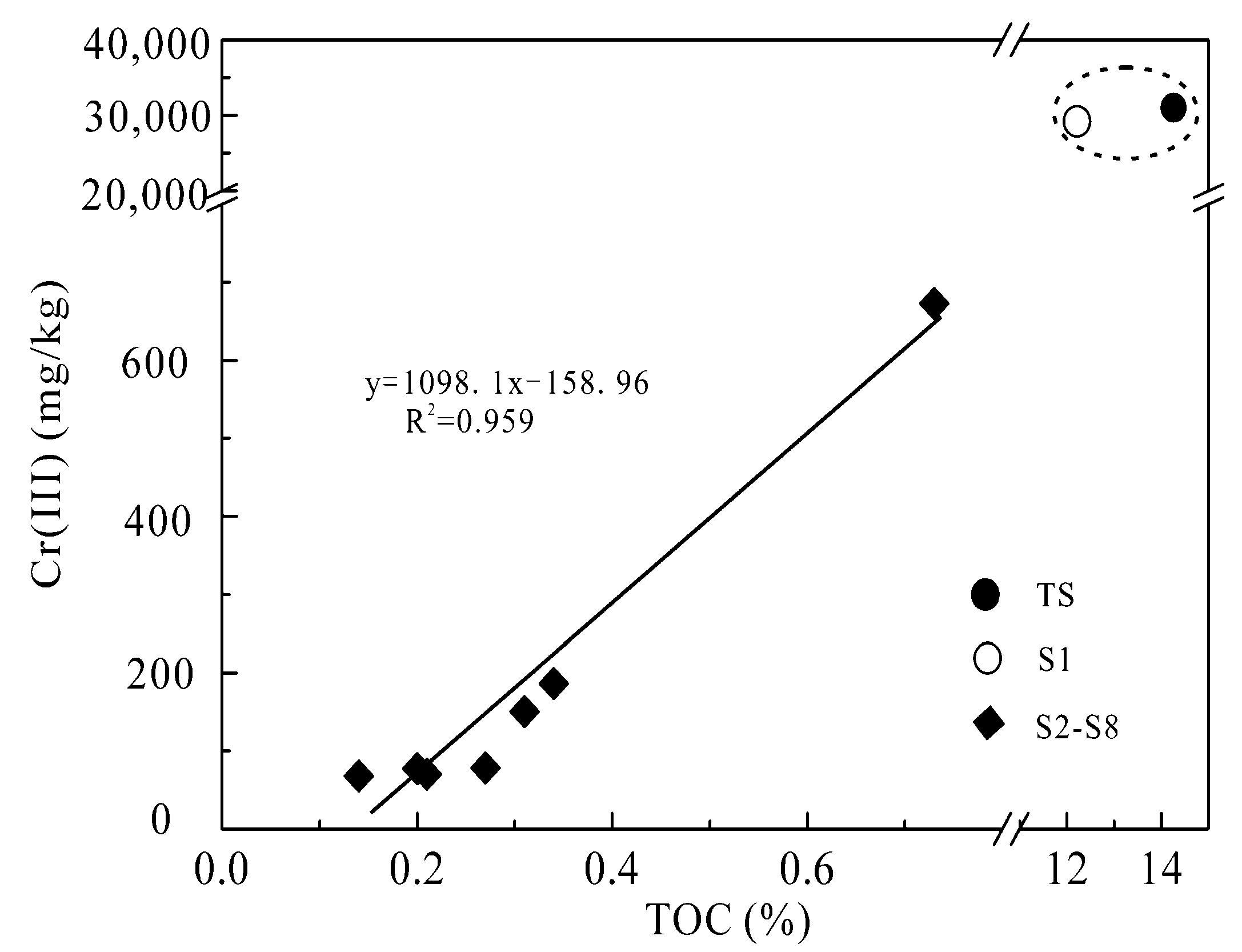
3.2.2. The Correlation between Cr(III) and Total Organic Carbon (TOC)
3.3. Effects of Tannery Sludge on the Soil Microbial Communities in the Vertical Profile
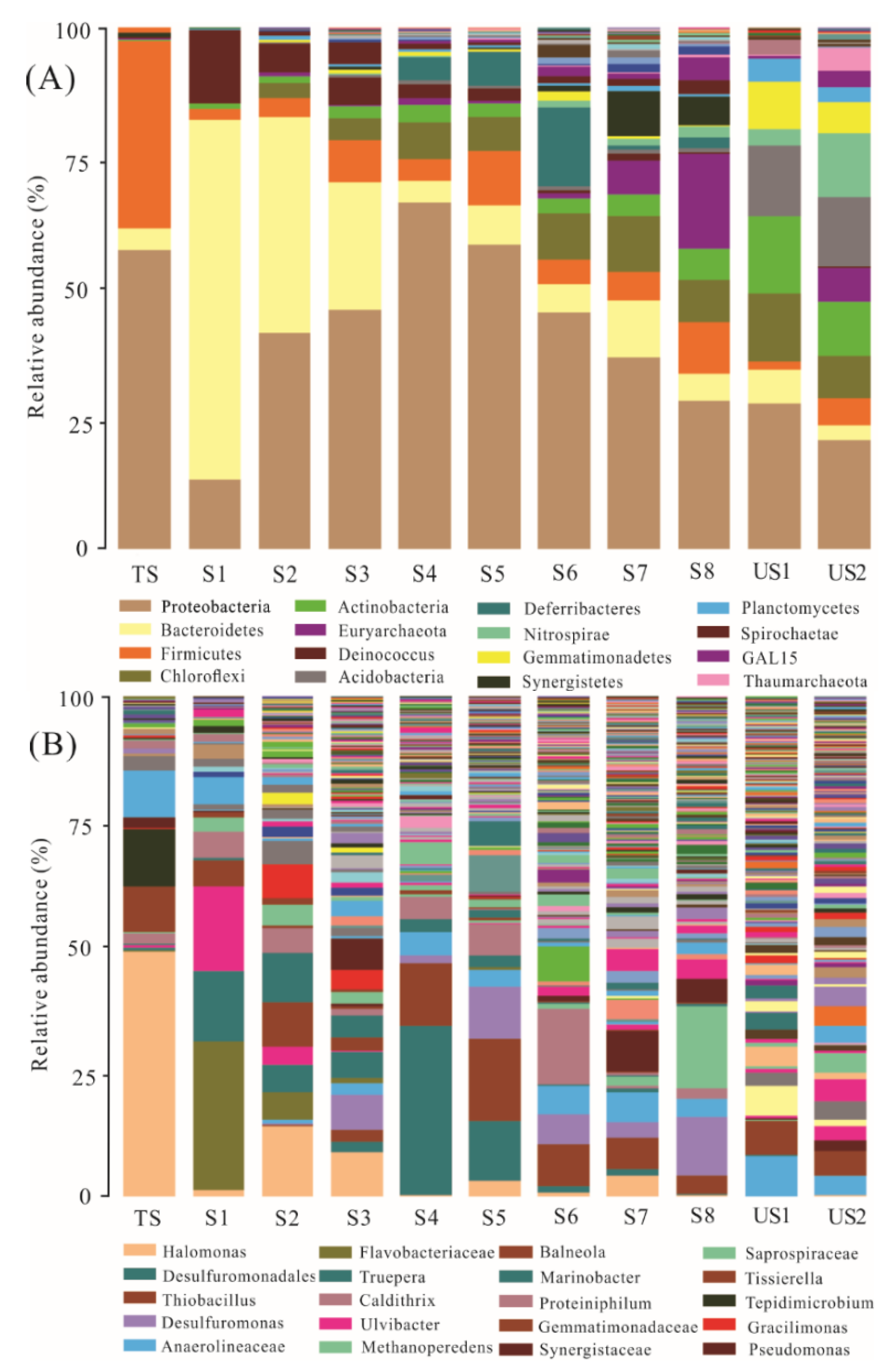
3.3.1. Changes in Soil Microbial Abundance and Diversity
3.3.2. Clustering of Soil Samples Based Microbial Communities
3.3.3. Responses of Soil Microorganisms to the Contaminant Factors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, J.; Gou, M.; Tang, Y.Q.; Li, G.Y.; Sun, Z.Y.; Kida, K. Effective bioleaching of chromium in tannery sludge with an enriched sulfur-oxidizing bacterial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zhou, J.; Hua, L.; Cheng, F.; Zhou, L.; Qiao, X. Chromium recovery from tannery sludge by bioleaching and its reuse in tanning process. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 142, 2752–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; He, S.; Shan, C.; Ye, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Pan, B. Chromium speciation in tannery effluent after alkaline precipitation. Isolation and characterization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 316, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Zhou, L. Supplementation of inorganic phosphate enhancing the removal efficiency of tannery sludge-borne Cr through bioleaching. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5295–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantazopoulou, E.; Zouboulis, A. Chemical toxicity and ecotoxicity evaluation of tannery sludge stabilized with ladle furnace slag. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 216, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, D.; Chi, Y.; Dong, J.; Fu, C.; Wang, F.; Ni, M. Supercritical water oxidation of tannery sludge: Stabilization of chromium and destruction of organics. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Hu, B.X.; Qi, Z.; Yang, H. Evaluating equilibrium and non-equilibrium transport of ammonium in a loam soil column. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolińska, A.; Stępniewska, Z.; Włosek, R. The influence of old leather tannery district on chromium contamination of soils, water and plants. Nat. Sci. 2013, 22, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, A.S.; Martines, A.M.; Nogueira, M.A.; Fagotti, D.S.L.; Oliveira, A.G.; Bini, D.; Sousa, J.P.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N. Changes in the genetic structure of bacteria and microbial activity in an agricultural soil amended with tannery sludge. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.M.; Zhou, X.B.; Shi, X.J. Impact of Cr3+ pollution on microbial characteristics in purple paddy soil. Protein Exp. Purif. 2012, 82, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Aceves, M.B.; Santos, H.E.; Berber, J.D.R.; Mota, J.L.O.; Vázquez, R.R. Distribution and mobility of Cr in tannery waste amended semi-arid soils under simulated rainfall. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotnik, B.; Zuliani, T.; Ščančar, J.; Milačič, R. Inhibition of the nitrification process in activated sludge by trivalent and hexavalent chromium, and partitioning of hexavalent chromium between sludge compartments. Chemosphere 2014, 105, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Bao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xie, S.; Huang, J. Vertical distribution of microbial communities in soils contaminated by chromium and perfluoroalkyl substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, J.; Castañeda, C. Changes in soil salinity in the habitats of five halophytes after 20 years. Catena 2013, 109, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeomans, J.C.; Bremner, J.M. A rapid and precise method for routine determination of organic carbon in soil 1. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1988, 19, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, D.A.; David, M.B.; Gentry, L.E.; Starks, K.M.; Cooke, R.A. Effectiveness of constructed wetlands in reducing nitrogen and phosphorus export from agricultural tile drainage. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1262–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Li, Y.S.; Wen, Y.; Fei, Y.H. Response of soil microbial communities to roxarsone pollution along a concentration gradient. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2017, 52, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonthiphand, P.; Hall, M.W.; Neufeld, J.D. Biogeography of anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing (anammox) bacteria. Front. Microb. Immunol. 2014, 5, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerappa, A.M.; Vishweswaraiah, S.; Lingaiah, K.; Murthy, M.; Suresh, R.V.; Manjegowda, D.S.; Ramachandra, N.B. Global spectrum of copy number variations reveals genome organizational plasticity and proposes new migration routes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.K.; Han, Z.T.; Zhang, W.; Song, L.; Li, H. Synthesis of zeolite-supported microscale zero-valent iron for the removal of Cr6+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 169, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martines, A.M.; Nogueira, M.A.; Santos, C.A.; Nakatani, A.S.; Andrade, C.A.; Coscione, A.R.; Cantarella, H.; Sousa, J.P.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N. Ammonia volatilization in soil treated with tannery sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4690–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebien, D.O.P.; Bortolon, L.; Tedesco, M.J.; Bissani, C.A.; Camargo, F.A.O. Environmental factors affecting chromium-manganese oxidation-reduction reactions in soil. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijonen, I.; Hartikainen, H. Oxidation mechanisms and chemical bioavailability of chromium in agricultural soil-pH as the master variable. Appl. Geochem. 2016, 74, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, J.P.; Persson, I.; Oromieh, A.G.; van Schaik, J.W.J.; Sjöstedt, C.; Dan, B.K.; Kleja, D.B. Chromium(III) complexation to natural organic matter: Mechanisms and modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, C.; Parikh, R.Y.; Vaishnav, T.; Shouche, Y.S.; Madamwar, D. Tracking the influence of long-term chromium pollution on soil bacterial community structures by comparative analyses of 16S rRNA gene phylotypes. Res. Microbiol. 2009, 160, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.G.; Hu, Y.T.; Yin, Z.; Hu, Y.H.; Zhong, H. Microbial diversity of chromium contaminated soils and characterization of six chromium-removing bacteria. Environ. Manag. 2016, 57, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, M.E.M.; Arayes, M.A.; Sabry, S.A. Hexavalent chromium reduction by chromate-resistant haloalkaliphilic Halomonas sp. M-Cr newly isolated from tannery effluent. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2014, 28, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, C.; Schleicher, A.; Collins, M.D.; Andreesen, J.R. Tissierella creatinophila sp. nov. a gram-positive, anaerobic, non-spore-forming, creatinine-fermenting organism. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alauzet, C.; Marchandin, H.; Courtin, P.; Mory, F.; Lemée, L.; Pons, J.L.; Chapot-Chartier, M.P.; Lozniewski, A.; Jumas-Bilak, E. Multilocus analysis reveals diversity in the genus Tissierella: Description of Tissierella carlieri sp. nov. in the new class Tissierellia classis nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 37, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.D.; Lawson, P.A.; Collins, M.D.; Falsen, E.; Tanner, R.S. Cloacibacterium normanense gen. nov. sp. nov. a novel bacterium in the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from municipal wastewater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.H.; Lim, J.S.; Khan, M.A.; Kim, B.S.; Choi, D.Y.; Lee, E.Y.; Ahn, H.K. High-throughput nucleotide sequence analysis of diverse bacterial communities in leachates of decomposing pig carcasses. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2015, 38, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | Depth/cm | Moisture/% | pH | Salinity /mg/kg | TOC/wt% | Total Cr/mg/kg | Cr(Ⅲ)/mg/kg | Total Nitrogen/mg/kg | Ammonium/mg/kg | Organic-N/mg/kg | Sulfide/mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS 1 | surface | 64.1 | 7.67 | 99,000 | 14.3 | 30,970 | 30,800 | 33,080 | 16,080 | 16,500 | 4910 |
| S1 2 | 0~20 | 48.3 | 7.94 | 17,500 | 12.2 | 25,500 | 25,427 | 28,390 | 9010 | 19,271 | 75 |
| S2 2 | 20~40 | 17.9 | 8.37 | 17,800 | 0.73 | 672.61 | 672 | 1224 | 435 | 719 | 52 |
| S3 2 | 40~60 | 18.1 | 8.12 | 10,200 | 0.34 | 186.46 | 184 | 816 | 268 | 507 | 47 |
| S4 2 | 60~80 | 21.1 | 8.39 | 7860 | 0.31 | 150.61 | 150 | 900 | 252 | 616 | 38 |
| S5 2 | 80~100 | 18.5 | 8.31 | 9220 | 0.21 | 70.39 | 69.8 | 654 | 171 | 463 | <10 |
| S6 2 | 120~150 | 19.5 | 8.06 | 6850 | 0.20 | 77.27 | 76.6 | 864 | 292 | 551 | <10 |
| S7 2 | 150~180 | 21.5 | 8.42 | 6330 | 0.14 | 67.76 | 67.2 | 630 | 113 | 508 | <10 |
| S8 2 | 180~200 | 18.9 | 8.20 | 1670 | 0.27 | 78.12 | 77.5 | 817 | 85 | 723 | <10 |
| US1 3 | 0~20 | 14.4 | 8.30 | 1480 | 0.23 | 70 | 69.86 | 1210 | <20 | 1178 | <10 |
| US2 3 | 120~150 | 16.8 | 8.01 | 717 | 0.14 | 67.2 | 66.58 | 154 | <20 | 152 | <10 |
| Samples | Depth/cm | Exchangeable/mg/kg | Carbonate/mg/kg | Fe/Mn Oxides /mg/kg | Strong Organic/mg/kg | Residual/mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tannery sludge | 0 | 153 | 229 | 21,700 | 3860 | 2880 |
| S1 | 10 | 11.2 | 124 | 18,100 | 7580 | 3110 |
| S2 | 20 | 2.5 | 6.7 | 141.6 | 117.2 | 353.2 |
| S3 | 40 | <0.5 | 1.3 | 40.7 | 29.4 | 121.8 |
| Contaminant | Halomonas | Anaeroli-neaceae | Flavobacte-riaceae | Ulvibacter | Tissierella | Tepidimicr-obium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| salinity | 0.972 ** | −0.579 * | 0.003 | 0.021 | 0.997 ** | 0.982 ** |
| TOC | 0.667 * | −0.676 * | 0.578 * | 0.587 * | 0.788 ** | 0.732 * |
| Cr | 0.676 * | −0.667 * | 0.563 * | 0.572 * | 0.796 ** | 0.743 * |
| ammonium | 0.799 ** | −0.643 * | 0.388 | 0.400 | 0.900** | 0.863 ** |
| organic-N | 0.524 | −0.649 * | 0.707 * | 0.714 * | 0.662 * | 0.598 * |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, X.; Li, C.; Wang, P.; Huang, G.; Li, Z.; Han, Z. Soil Pollution Characteristics and Microbial Responses in a Vertical Profile with Long-Term Tannery Sludge Contamination in Hebei, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16040563
Kong X, Li C, Wang P, Huang G, Li Z, Han Z. Soil Pollution Characteristics and Microbial Responses in a Vertical Profile with Long-Term Tannery Sludge Contamination in Hebei, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(4):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16040563
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Xiangke, Chunhui Li, Ping Wang, Guoxin Huang, Zhitao Li, and Zhantao Han. 2019. "Soil Pollution Characteristics and Microbial Responses in a Vertical Profile with Long-Term Tannery Sludge Contamination in Hebei, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 4: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16040563
APA StyleKong, X., Li, C., Wang, P., Huang, G., Li, Z., & Han, Z. (2019). Soil Pollution Characteristics and Microbial Responses in a Vertical Profile with Long-Term Tannery Sludge Contamination in Hebei, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(4), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16040563