Influence of a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill on the Surrounding Environment: Landfill Vegetation as a Potential Risk of Allergenic Pollen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Vegetation Study and Plant Analysis
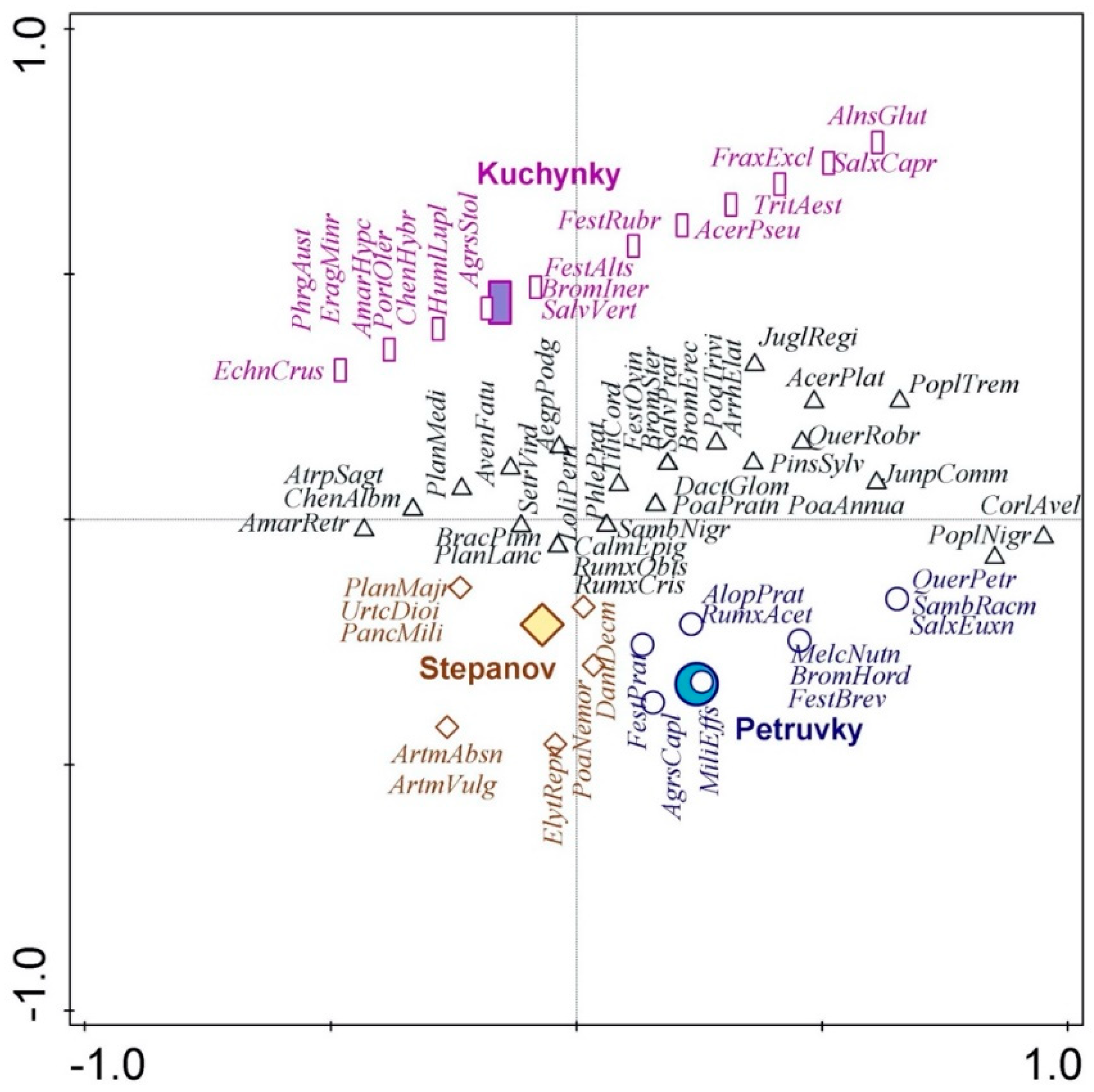
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Bourn, M.; Robinson, R.; Innocenti, F.; Scheutz, C. Regulating landfills using measured methane emissions: An English perspective. Waste Manag. 2019, 85, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansel, B.; Inanloo, B. Odor impact zones around landfills: Delineation based on atmospheric conditions and land use characteristics. Waste Manag. 2019, 88, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koda, E.; Sieczka, A.; Osiński, P. Ammonium concentration and migration in groundwater in the vicinity of waste management site located in the neighborhood of protected areas of Warsaw, Poland. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaverková, M.D. Landfill Impacts on the Environment—Review. Geosciences 2019, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.C.; Fujiwara, T.; Houng, H.J.; Sun, C.H.; Li, W.Y.; Kuo, Y.W. Management of landfill reclamation with regard to biodiversity preservation, global warming mitigation and landfill mining: Experiences from the Asia–Pacific region. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 104, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Joo, G.J. Importance of closed landfills as green space in space in urbanized areas: Ecological assessment using carabid beetles. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 10, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Qin, T.; Liu, F.; Liu, S.; Dong, B.; Wang, J.; Nie, H. Eects of Slope Ecological Restoration on Runo and Its Response to Climate Change. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, E.; Pachuta, K.; Osiński, P. Potential of Plant Applications in the Initial Stage of the Landfill Reclamation Process. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 22, 1731–1739. [Google Scholar]
- Salt, M.; Yuen, S.T.S.; Ashwath, N.; Sun, J.; Benaud, P.; Zhu, G.X.; Jaksa, M.B.; Ghadiri, H.; Greenway, M.; Fourie, A.B. Phytocapping of Landfills. In Solid Waste Landfilling: Concepts, Processes, Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 677–688. [Google Scholar]
- Cossu, R.; Garbo, F. Landfill Covers: Principles and Design. In Solid Waste Landfilling. Concepts, Processes, Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 649–676. [Google Scholar]
- Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.S.; Thangarajan, R.; Jena, U.; Das, K.C.; Wang, H.; Naidu, R. Biomass Energy from Revegetation of Landfill Sites. In Bioremediation and Bioeconomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, I.R.; Greenway, M.; Robertson, S. Use of phytocaps in remediation of closed landfills—Correct selection of soil materials. Land Contam. Reclam. 2004, 12, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaparrotta, A.; Verini, M.; Consilvio, N.P.; Cingolani, A.; Rapino, D.; Attanasi, M.; Cerasa, M.; Di Pillo, S.; Chiarelli, F. Sensitization to timothy grass pollen allergenic molecules in children. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2013, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, M.P.; Alcázar, P.; Hernández-Ceballos, M.A.; Galán, C. Mismatch in aeroallergens and airborne grass pollen concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Morte, J.; Rojo, J.; Rivero, R.; Fernández-González, F.; Pérez-Badia, R. Standardised index for measuring atmospheric grass-pollen emission. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogawski, P.; Grewling, Ł.; Nowak, M.; Smith, M.; Jackowiak, B. Trends in atmospheric concentrations of weed pollen in the context of recent climate warming in Poznań (Western Poland). Int. J. Biometeorol. 2014, 58, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buters, J.; Prank, M.; Sofiev, M.; Pusch, G.; Albertini, R.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Antunes, C.; Behrendt, H.; Berger, U.; Brandao, R.; et al. Variation of the group 5 grass pollen allergen content of airborne pollen in relation to geographic location and time in season. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza, P.I.; Speziale, K.L.; Lambertucci, S.A. Rubbish dumps as invasive plant epicentres. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 2277–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canova, C.; Heinrich, J.; Anto, J.M.; Leynaert, B.; Smith, M.; Kuenzli, N.; Zock, J.P.; Janson, C.; Cerveri, I.; de Marco, R.; et al. The influence of sensitisation to pollens and moulds on seasonal variations in asthma attacks. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 42, 935–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiou, C.; Isukapalli, S.; Georgopoulos, P. A mechanistic modeling system for estimating large-scale emissions and transport of pollen and co-allergens. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2260–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Harrison, R. The effects of meteorological factors on atmospheric bioaerosol concentrations e a review. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 326, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuparinen, A. Mechanistic models for wind dispersal. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofiev, M.; Siljamo, P.; Ranta, H.; Rantio-Lehtimäki, A. Towards numerical forecasting of long-range air transport of birch pollen: Theoretical considerations and a feasibility study. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2006, 50, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranta, H.; Kubin, E.; Siljamo, P.; Sofiev, M. Long distance pollen transport cause problems for determining the timing of birch pollen season in Fenno-scandia by using phenological observations. Grana 2006, 45, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjøth, C.; Sommer, J.; Stach, A.; Smith, M.; Brandt, J. The long-range transport of birch Betula pollen from Poland and Germany causes significant pre-season concentrations in Denmark. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Mozo, H. Poaceae pollen as the leading aeroallergen worldwide: A review. Allergy 2017, 72, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holgate, S.T.; Thomas, M. Chapter 7—Asthma. In Middleton’s Allergy Essentials, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 151–204. [Google Scholar]
- Radauer, C.; Breiteneder, H. Pollen allergens are restricted to few protein families and show distinct patterns of species distribution. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichovníková, V.; Šťastná, M.; Kotovicová, J.; Vaverková, M.D.; Adamcová, D. The Influence of the Solid Waste Landfill Existence on the Environmental and Economic Situation of Petrůvky Village (Czechia). Eur. Countrys. 2015, 4, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gworek, B.; Hajduk, A.; Koda, E.; Grochowalski, A.; Jeske, A. Influence of a municipal waste landfill on the spatial distribution of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDDs/Fs) in the natural environment. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaverková, M.D.; Elbl, J.; Radziemska, M.; Adamcová, D.; Kintl, A.; Baláková, L.; Bartoň, S.; Hladký, J.; Kynický, J.; Brtnický, M. Environmental risk assessment and consequences of MSW disposal. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintner, I.; Klug, B. Can vegetation indicate landfill cover features? Fuel Energy Abstr. 2011, 206, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaverková, M.D.; Winkler, J.; Adamcová, D.; Raziemska, M.; Uldrjan, D.; Zloch, J. Municipal solid waste landfill—Vegetation succession in an area transformed by human impact. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 129, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danihelka, J.; Chrtek, J.; Kaplan, Z. Checklist of vascular plants of the Czech Republic. Preslia 2012, 84, 647–811. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Botany and Zoology Faculty of Science Masaryk University. Database of the Czech Flora and Vegetation. 2018. Available online: https://pladias.cz/en/ (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Pollen Information Service. Meditorial+. 2018. Available online: http://www.pylovasluzba.cz/ (accessed on 2 July 2019).
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination (Version 5.0); Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ČSN 83 8035 (838025) Landfilling of Waste—Landfill Closure and Reclamation, Setting Guidelines for the Establishment and Treatment of Grass Stands on the Landfill Body. 2019. Available online: http://www.technicke-normy-csn.cz/838035-csn-83-8035_4_52116.html (accessed on 2 July 2019).
- Vaverková, M.D.; Adamcová, D. Case study of landfill reclamation at Czech landfill site. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2018, 17, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breza-Boruta, B. Bioaerosols of the municipal waste landfill site as a source of microbiological air pollution and health hazard. Ecol. Chem. Eng. 2012, 19, 851–862. [Google Scholar]
- Breza-Boruta, B. The assessment of airborne bacterial and fungal contamination emitted by a municipal landfill site in Northern Poland. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Sun, P.; Lin, B.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Ma, R.; Xiang, M.; Li, H.; Guo, S. Effects of ambient air pollution from municipal solid waste landfill on children’s non-specific immunity and respiratory health. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormi, T.; Ali, N.B.H.; Abichou, T.; Green, R. Estimation of landfill methane emissions using stochastic search methods. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gębicki, J.; Dymerski, T.; Namieśnik, J. Investigation of Air Quality beside a Municipal Landfill: The Fate of Malodour Compounds as a Model VOC. Environments 2017, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, W.; Wang, H.; Huang, O.; Gao, X. Odor impact assessment of trace sulfur compounds from working faces of landfills in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 220, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, R.N.; Hemming, D.; Burgess, P.; Lyndsay, D.; Osborne, N.J.; Skjøth, C.A.; Thomas, S.; Vardoulakis, S. Mapping allergenic pollen vegetation in UK to study environmental exposure and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, A.N.; Hellings, P.W.; Rotiroti, G.; Scadding, G.K. Allergic rhinitis. Lancet 2012, 378, 2112–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjøth, C.A.; Sikoparija, B.; Jager, S. EAN-Network Pollen sources. In Allergenic Pollen: A Review of the Production, Release, Distribution and Health Impacts; Sofiev, M., Bergmann, K.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 9–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sofiev, M.; Bergmann, K.C. (Eds.) Chapter 5. In Allergenic Pollen: A Review of the Production, Release, Distribution and Health Impacts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 127–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ramtek, D.S. Reclamation and Remediation of Solid Waste through Bio-chemical Process. In Bioremediation Technology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 285–314. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, D.; Maiti, S.K. Ecorestoration of Waste Dump by the Establishment of Grass-Legume Cover. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2014, 3, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Matiti, S.K.; Matiti, D. Ecological restoration of waste dumps by topsoil blanketing, coir-matting and seeding with grass–legume mixture. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 77, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Chen, R.; Coo, J.L.; Liu, J.; Ni, J.J.; Chen, Y.M.; Zhan, T.L.T.; Guo, H.W.; Lu, B.W. A novel vegetated three-layer landfill cover system using recycled construction wastes without geomembranes. Can. Geotech. J. 2019, 56, 1863–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, E. Restoration of landfill sites for ecological diversity. Waste Manag. Res. 1999, 17, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.L.; Tarrant, S.; McCollin, D.; Ollerton, J. The conservation value of restored landfill sites in the East Midlands, UK for supporting bird communities. Biodivers. Conserv. 2011, 20, 1879–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaverková, M.D.; Radziemska, M.; Bartoň, S.; Cerdà, A.; Koda, E. The use of vegetation as a natural strategy for landfill restoration. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3674–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.C.; Chu, L.M. Identifying suitable tree species for evapotranspiration covers of landfills in humid regions using seedlings. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 38, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruczek, A.; Puc, M.; Wolskiki, T. Airborne pollen from allergenic herbaceous plants in urban and rural areas of Western Pomerania, NW Poland. Grana 2017, 56, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, J.K.; White, M.P.; Huang, J.; Ng, S.; Hui, Y.; Leung, C.; Tse, L.A.; Fung, F.; Elliott, L.R.; Depledge, M.H.; et al. Urban blue space and health and wellbeing in Hong Kong: Results from a survey of older adults. Health Place 2019, 55, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woon, K.S.; Lo, I.M.C. An integrated life cycle costing and human health impact analysis of municipal solid waste management options in Hong Kong using modified eco-efficiency indicator. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 107, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.P.; Thakur, I.S. An integrated approach to study the risk from landfill soil of Delhi: Chemical analyses, in vitro assays and human risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 143, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
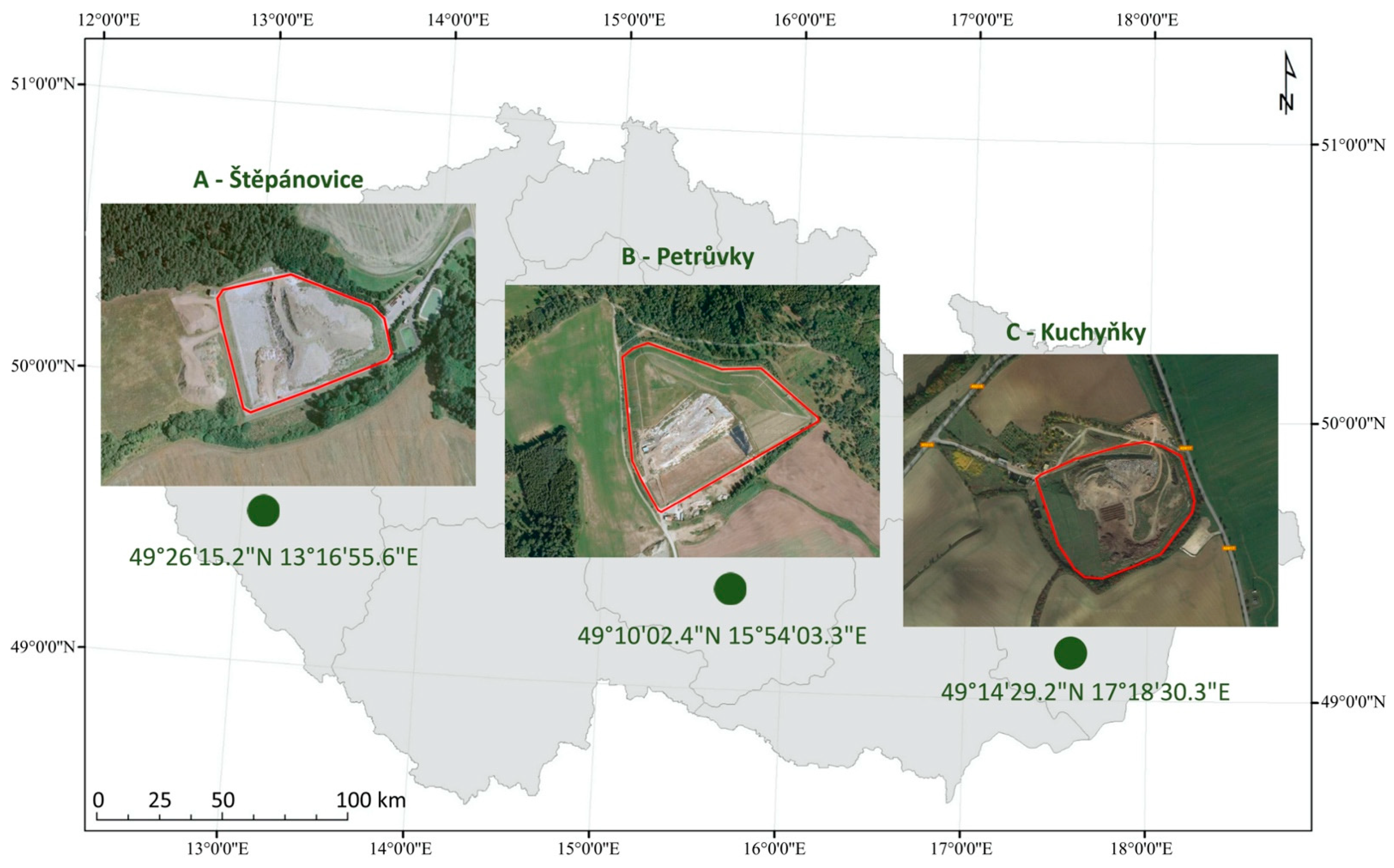

| Monitored Sites | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Kuchyňky (C) | Petrůvky (B) | Štěpánovice (A) | |
| Altitude (m a.s.l.) | 270–285 | 550–650 | 450 |
| Basin of River | Morava | Morava | Vltava |
| Type of landscape in the landfill surroundings | Intensively used agricultural landscape | Extensively used agricultural landscape | Landscape dominated by forests |
| Potential natural vegetation | Floodplain forests | Herb-rich beech forests | Acidophilous beech-fir-birch and pine oak forests |
| Blooming Time and Significance of Pollen as Allergen | Monitored Sites | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kuchyňky (C) | Petrůvky (B) | Štěpánovice (A) | ||
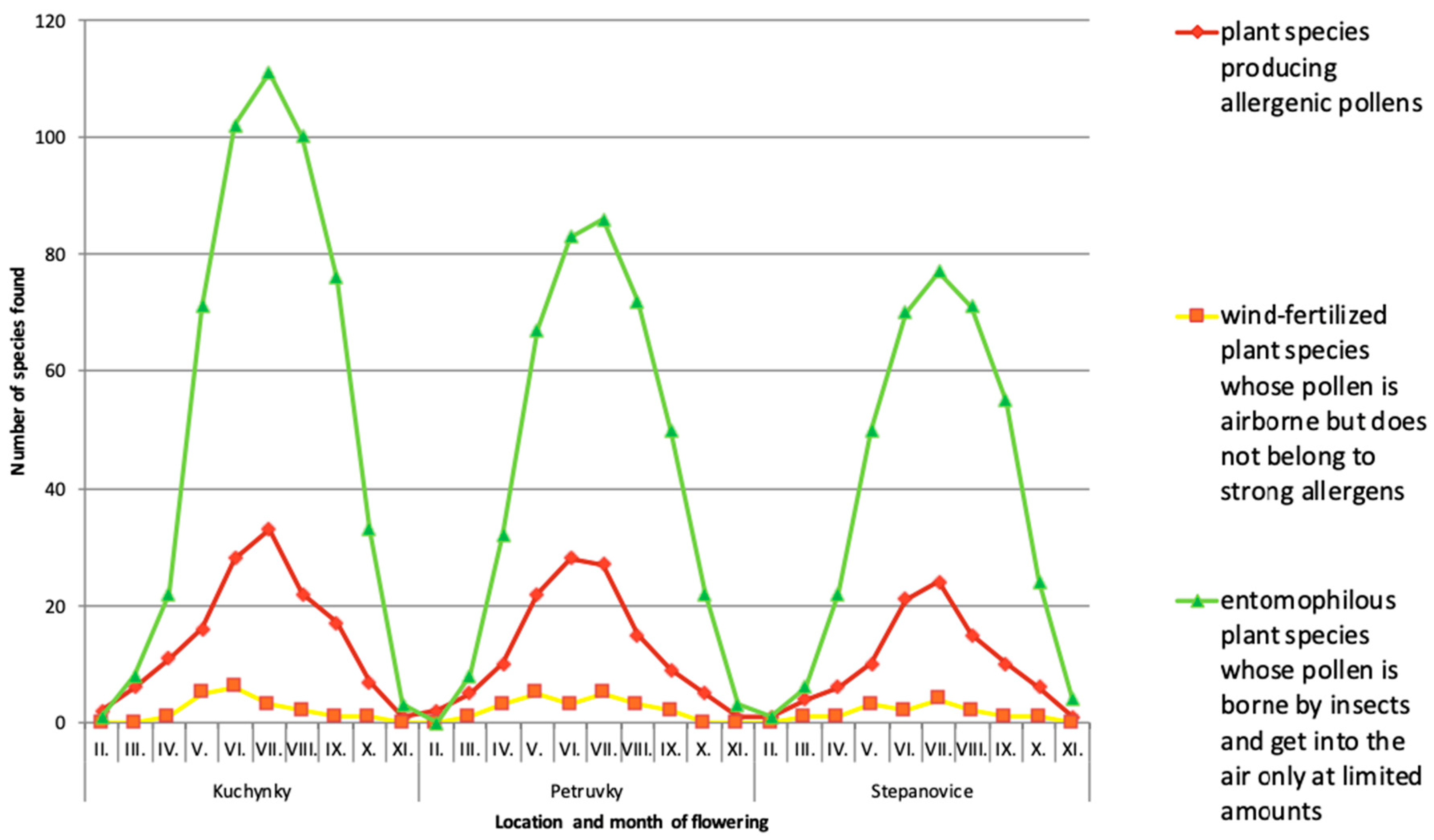
| Total | 192 | 162 | 127 | |
| Number of plant species flowering in selected months | February (II) | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| March (III) | 13 | 13 | 9 | |
| April (IV) | 32 | 43 | 27 | |
| May (V) | 92 | 93 | 62 | |
| June (VI) | 136 | 112 | 91 | |
| July (VII) | 148 | 117 | 105 | |
| August (VIII) | 125 | 89 | 88 | |
| September (IX) | 94 | 60 | 66 | |
| October (X) | 41 | 26 | 33 | |
| Plant species | Plant species producing allergenic pollen | 45 | 40 | 29 |
| Wind-fertilized plant species not belonging to strong allergens | 7 | 9 | 5 | |
| Entomophilous plant species whose pollen gets into the air only at limited extent | 139 | 112 | 92 | |
| Plant species with no pollen production (cryptogams) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
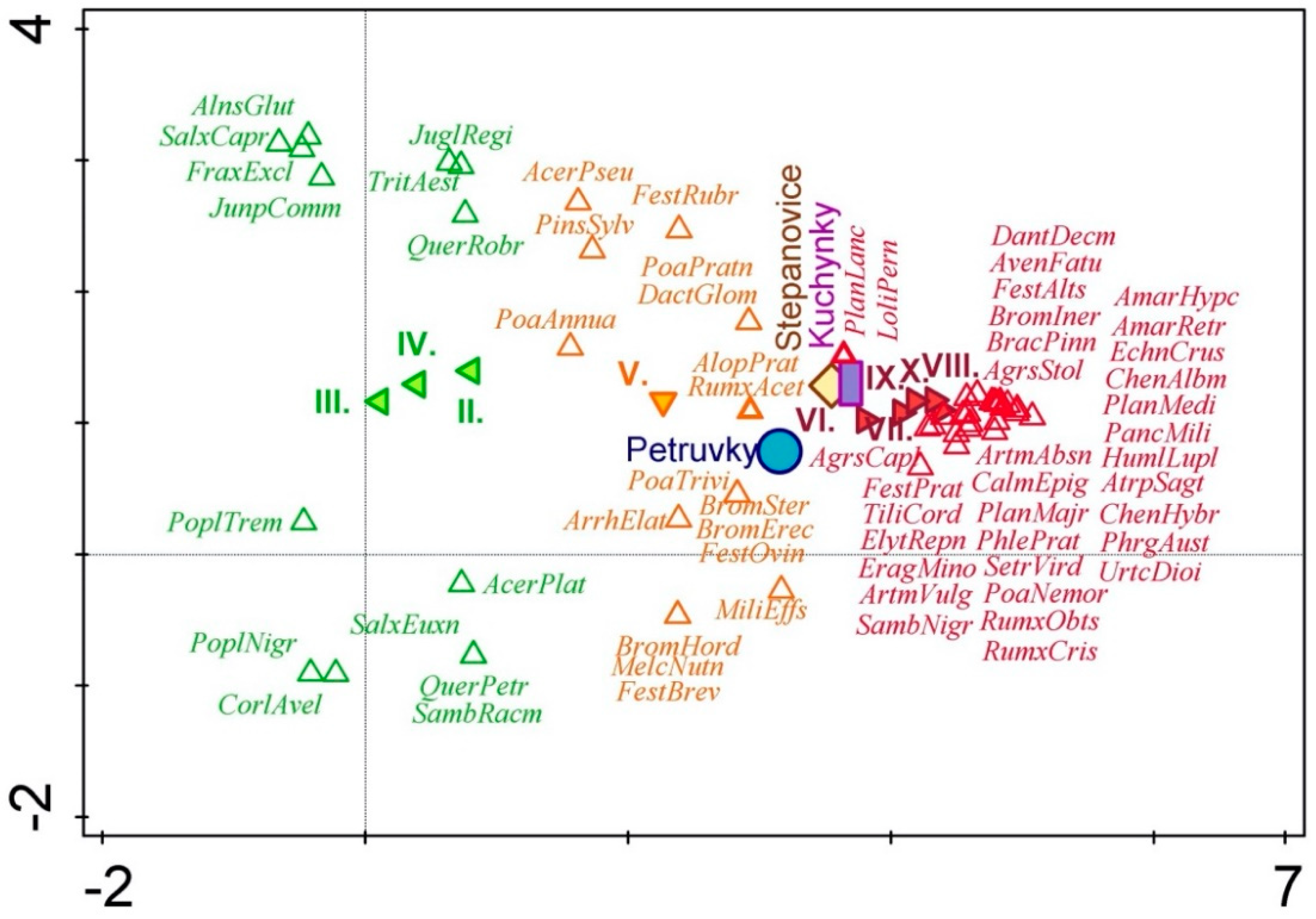
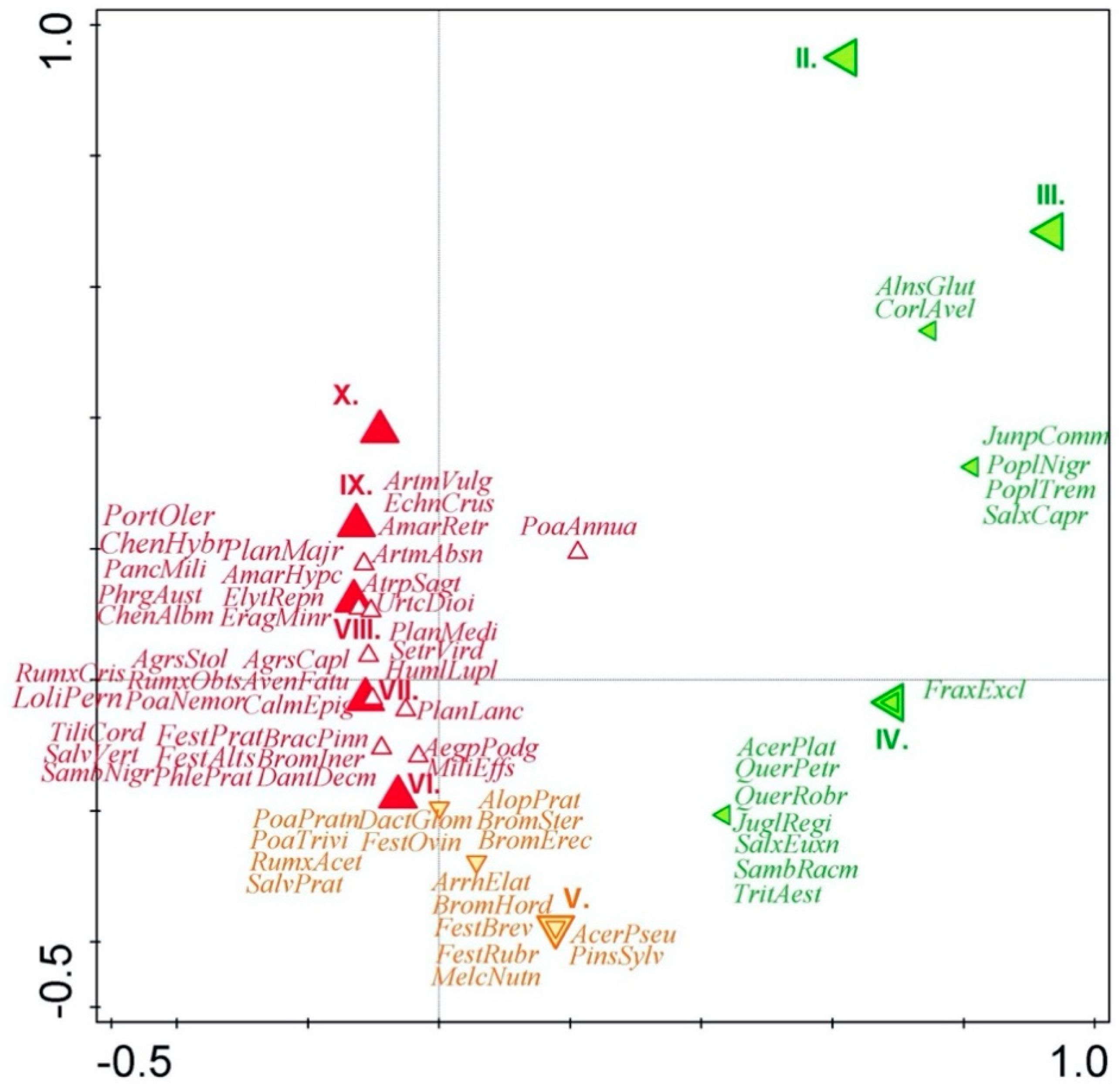
| Factors | Explained Variation (%) | Statistical Significance (p-Value) | Pseudo F |
|---|---|---|---|
| Month of blooming | 22.6 | 0.001 | 2.0 |
| Landfill locality | 23.0 | 0.001 | 3.6 |
| Year of evaluation | 6.0 | 0.2 | 8.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaverková, M.D.; Adamcová, D.; Winkler, J.; Koda, E.; Červenková, J.; Podlasek, A. Influence of a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill on the Surrounding Environment: Landfill Vegetation as a Potential Risk of Allergenic Pollen. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245064
Vaverková MD, Adamcová D, Winkler J, Koda E, Červenková J, Podlasek A. Influence of a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill on the Surrounding Environment: Landfill Vegetation as a Potential Risk of Allergenic Pollen. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(24):5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245064
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaverková, Magdalena Daria, Dana Adamcová, Jan Winkler, Eugeniusz Koda, Jana Červenková, and Anna Podlasek. 2019. "Influence of a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill on the Surrounding Environment: Landfill Vegetation as a Potential Risk of Allergenic Pollen" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 24: 5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245064
APA StyleVaverková, M. D., Adamcová, D., Winkler, J., Koda, E., Červenková, J., & Podlasek, A. (2019). Influence of a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill on the Surrounding Environment: Landfill Vegetation as a Potential Risk of Allergenic Pollen. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(24), 5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245064










