Design Features in Multiple Generations of Electronic Cigarette Atomizers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electronic Cigarette Selection
2.2. Dissections of EC Atomizer Components
3. Results
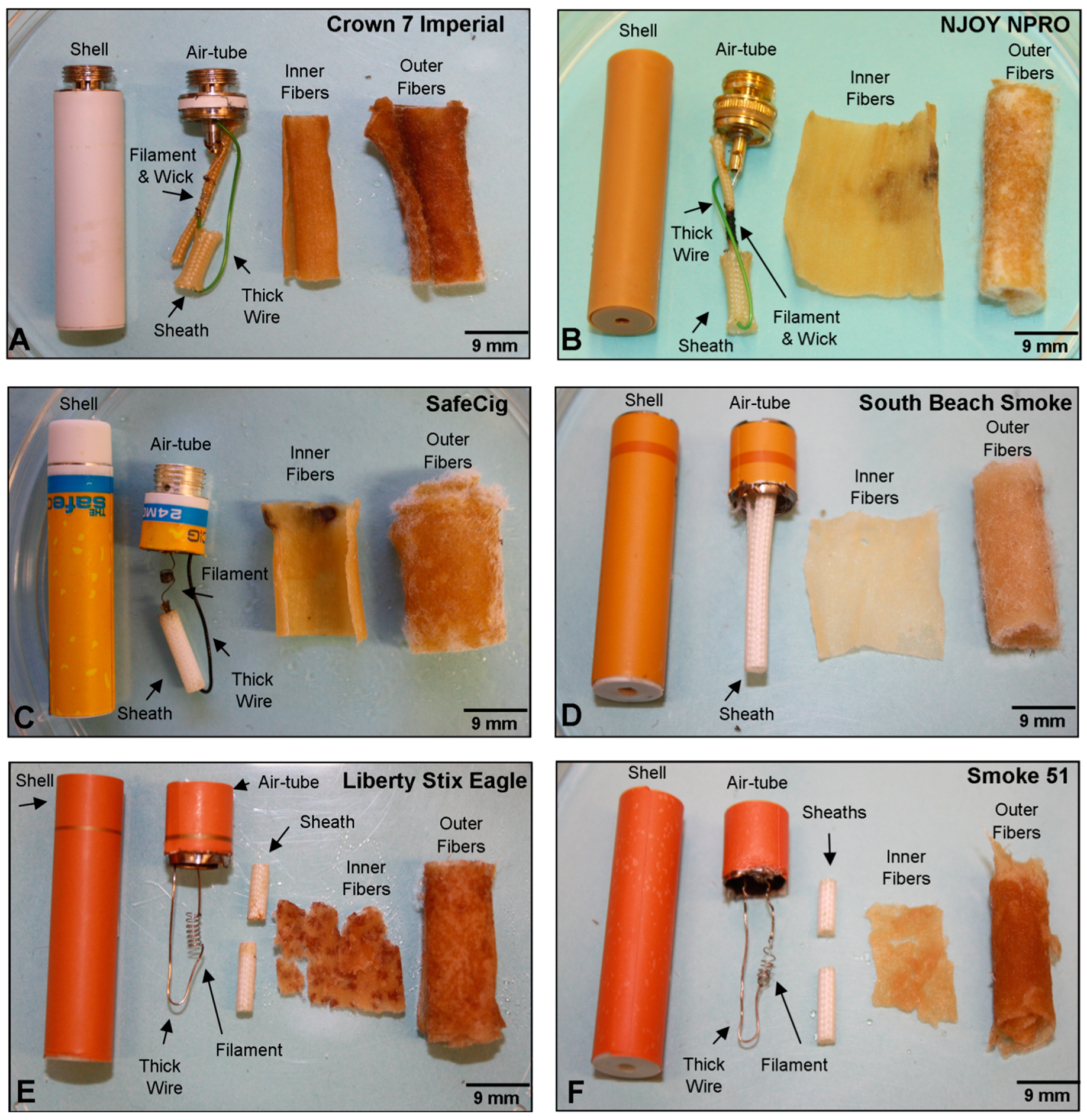
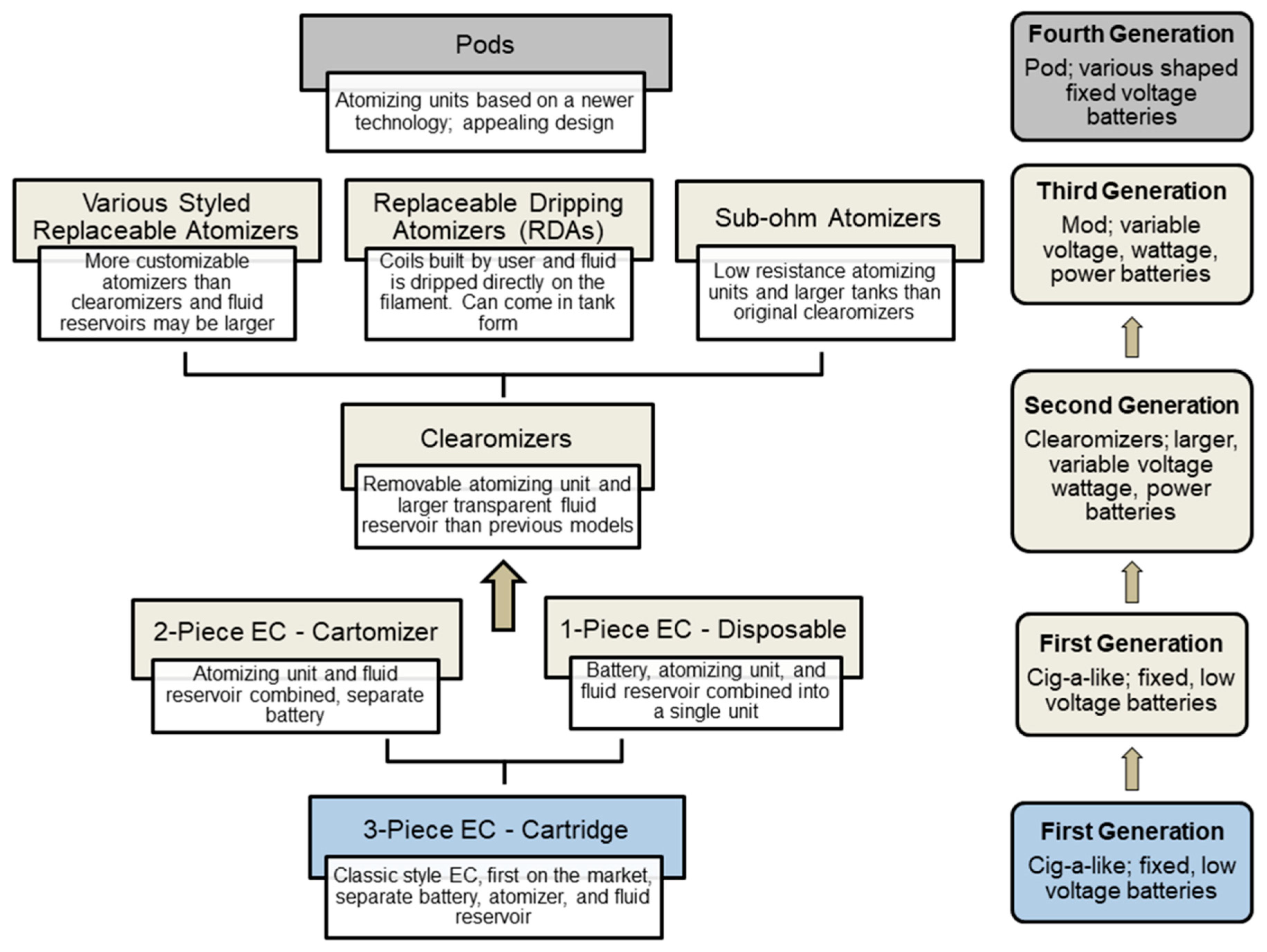
3.1. Design and Anatomy of Cig-a-Like Style ECs
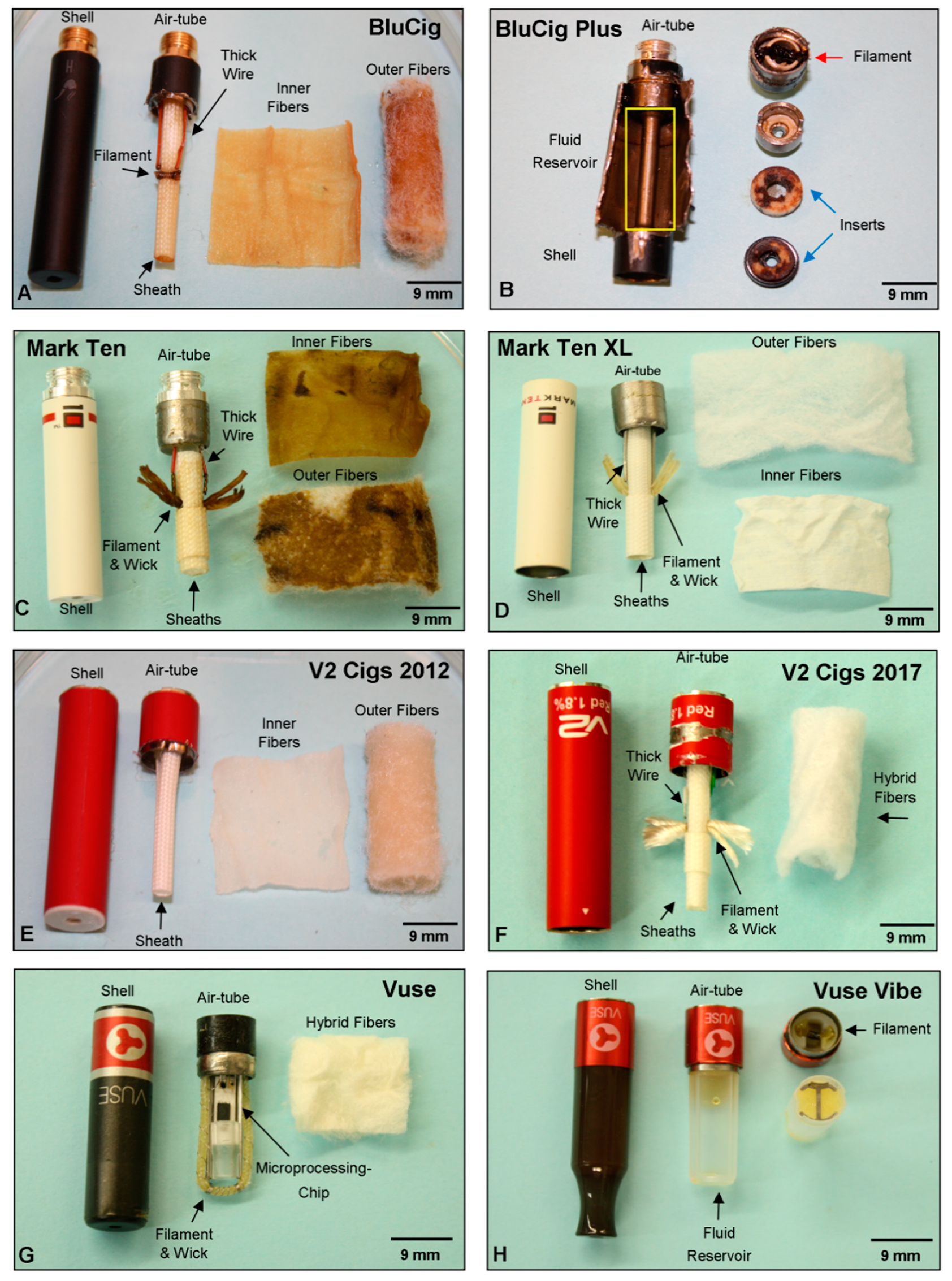
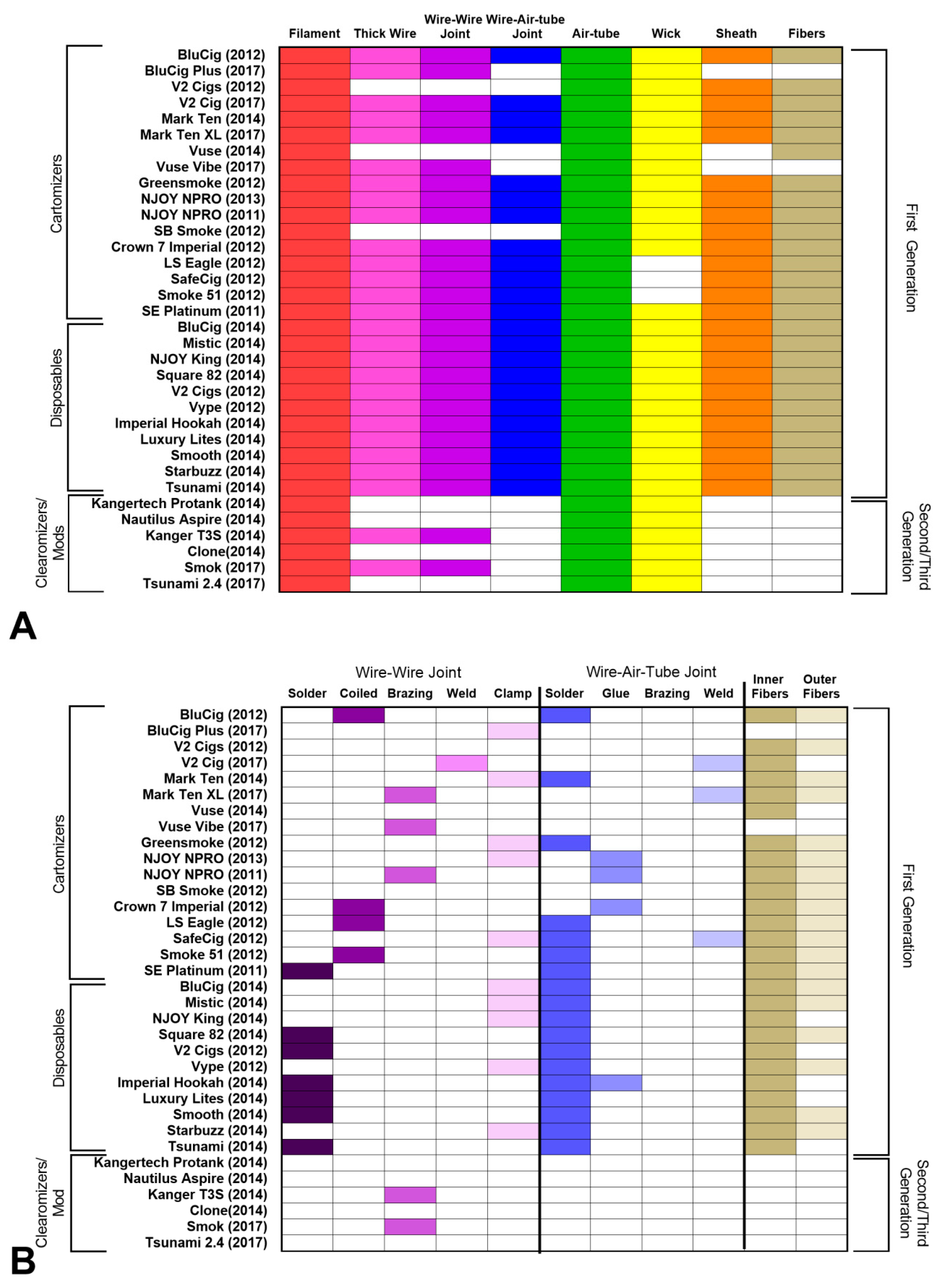
3.2. Evaluation of Atomizing Unit Design across Cartomizer Generations
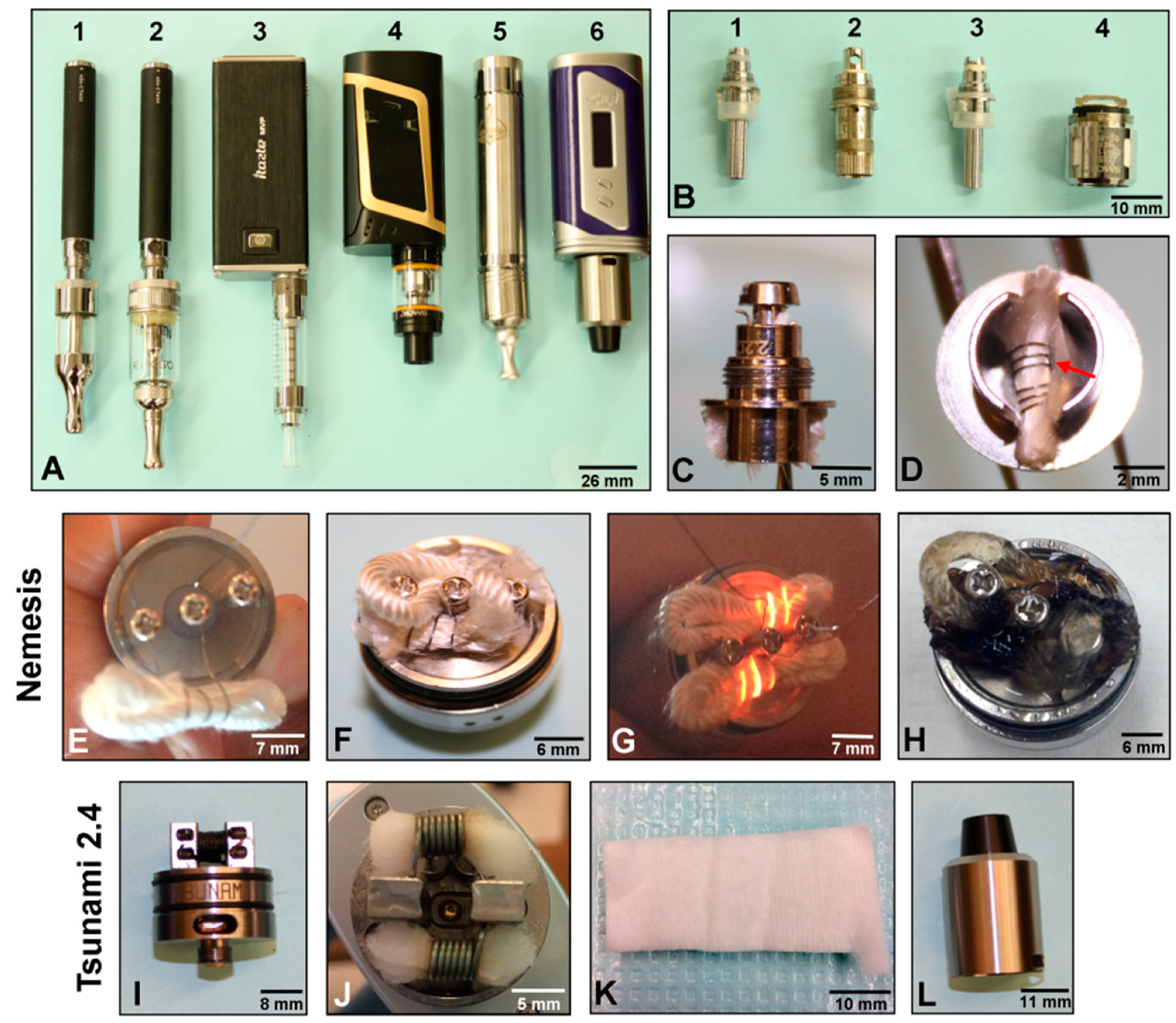
3.3. Design and Anatomy of Second Generation Clearomizer and Third Generation Mod-Style ECs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banga, B. Global E-Cigarette and T-Vapor Market to Reach $86.43 Billion by 2025, Reports BIS Research. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/global-e-cigarette-and-t-vapor-market-to-reach-8643-billion-by-2025-reports-bis-research-675808803.html (accessed on 7 February 2019).
- Breland, A.; Soule, E.; Lopez, A.; Ram, C.; El-hellani, A.; Eissenberg, T. Electronic cigarettes: What are they and what do they do? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1394, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T. 4 Facts You Need to Know About E-Cigarettes. Available online: https://www.verywellmind.com/facts-about-e-cigarettes-2825261 (accessed on 23 January 2019).
- Stratton, K.; Kwan, L.Y.; Eaton, D.L.; Health, P.; Practice, P.H.; Division, M. Public Health Consequences of E-Cigarettes; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-309-46834-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gaur, S.; Agnihotri, R. Health Effects of Trace Metals in Electronic Cigarette Aerosols—A Systematic Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 188, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peace, M.R.; Mulder, H.A.; Baird, T.R.; Butler, K.E. Evaluation of Nicotine and the Components of e-Liquids Generated from e-Cigarette Aerosols. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2018, 42, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.; Bozhilov, K.; Ghai, S.; Talbot, P. Elements including metals in the atomizer and aerosol of disposable electronic cigarettes and electronic hookahs. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, R.P.; Luo, W.; Pankow, J.F.; Strongin, R.M.; Peyton, D. Hidden Formaldehyde in E-Cigarette Aerosols. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talih, S.; Balhas, Z.; Eissenberg, T.; Salman, R.; Karaoghlanian, N.; Hellani, A.E.; Baalbaki, R.; Saliba, N.; Shihadeh, A. Effects of user puff topography, device voltage, and liquid nicotine concentration on electronic cigarette nicotine yield: Measurements and model predictions. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2015, 17, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talih, S.; Balhas, Z.; Salman, R.; Karaoghlanian, N.; Shihadeh, A. “Direct dripping”: A high-temperature, high- formaldehyde emission electronic cigarette use method. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2016, 18, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahl, V.; Lin, S.; Xu, N.; Davis, B.; Wang, Y.; Talbot, P. Comparison of electronic cigarette refill fluid cytotoxicity using embryonic and adult models. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 34, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, R.Z.; Davis, B.; Wang, Y.; Bahl, V.; Lin, S.; Talbot, P. Toxicology in Vitro Identification of toxicants in cinnamon-flavored electronic cigarette refill fluids. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, R.Z.; Luo, W.; McWhirter, K.J.; Pankow, J.F.; Talbot, P. Analytical and toxicological evaluation of flavor chemicals in electronic cigarette refill fluids. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, R.Z.; Wang, Y.; Talbot, P. Comparing the cytotoxicity of electronic cigarette fluids, aerosols and solvents. Tob. Control 2017, 27, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, P.W.; Pawlak, E.A.; Lackey, J.T.; Keating, J.E.; Reeber, S.L.; Glish, G.L.; Jaspers, I. Flavored e-cigarette liquids and cinnamaldehyde impair respiratory innate immune cell function. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L278–L292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillman, I.G.; Kistler, K.A.; Stewart, E.W.; Paolantonio, A.R. Effect of variable power levels on the yield of total aerosol mass and formation of aldehydes in e-cigarette aerosols. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 75, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsalinos, K.E.; Spyrou, A.; Tsimopoulou, K.; Stefopoulos, C.; Romagna, G.; Voudris, V. Nicotine absorption from electronic cigarette use: Comparison between first and new-generation devices. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, R.Z.; Hua, M.; Talbot, P. Puffing Topography and Nicotine Intake of Electronic Cigarette Users. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.J.; Hensel, E.C.; Morabito, P.N.; Roundtree, K.A. Electronic Cigarette Topography in the Natural Environment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; To, A.; Bozhilov, K.; Talbot, P. Strategies to Reduce Tin and Other Metals in Electronic Cigarette Aerosol. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Bozhilov, K.N.; Talbot, P. Analysis of the elements and metals in multiple generations of electronic cigarette atomizers. Environ. Res. 2019, 175, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, P.T.; Eissenberg, T. Automated dripping devices for vapers: RDTAs, bottomfeeders, squonk mods and dripboxes. Tob. Control 2018, 27, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protano, C.; Avino, P.; Manigrasso, M.; Vivaldi, V.; Perna, F.; Valeriani, F.; Vitali, M. Environmental Electronic Vape Exposure from Four Different Generations of Electronic Cigarettes: Airborne Particulate Matter Levels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Duan, Z.; Kwok, J.; Binns, S.; Vera, L.E.; Kim, Y.; Szczypka, G.; Emery, S.L. Vaping versus JUULing: How the extraordinary growth and marketing of JUUL transformed the US retail e-cigarette market. Tob. Control 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trtchounian, A.; Talbot, P. Electronic nicotine delivery systems: Is there a need for regulation? Tob. Control 2011, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Ghai, S.; Talbot, P. Disposable Electronic Cigarettes and Electronic Hookahs: Evaluation of Performance. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2014, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grana, R.; Benowitz, N.; Glantz, S. A E-cigarettes: A scientific review. Circulation 2014, 129, 1972–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Omaiye, E.; Luo, W.; McWhirter, K.; Pankow, J.F.; Talbot, P. Identification of Cytotoxic Flavor Chemicals in Top-Selling Electronic Cigarette Refill Fluids. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Disposable Electronic Cigarette. US Patent 2014/0311506 A1, 21 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grana, R.; Benowitz, N.L.; Glantz, S. A Background Paper on E-Cigarettes (Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems); World Health Organization Tobacco Free Initiative: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/13p2b72n (accessed on 19 April 2019).
- Hess, C.A.; Olmedo, P.; Navas-Acien, A.; Goessler, W.; Cohen, J.E.; Rule, A.M. E-cigarettes as a source of toxic and potentially carcinogenic metals. Environ. Res. 2017, 152, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, P.; Goessler, W.; Tanda, S.; Grau-Perez, M.; Jarmul, S.; Aherrera, A.; Chen, R.; Hilpert, M.; Cohen, J.E.; Navas-Acien, A.; et al. Metal Concentrations in e-Cigarette Liquid and Aerosol Samples: The Contribution of Metallic Coils. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 027010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, L. The Basics of Vaping—Types of E-Cig Atomizers and Vape Tanks. Available online: https://ecigarettereviewed.com/types-of-atomizer (accessed on 5 February 2019).
- Omaiye, E.E.; Mcwhirter, K.J.; Luo, W.; Pankow, J.F.; Talbot, P. High-Nicotine Electronic Cigarette Products: Toxicity of JUUL Fluids and Aerosols Correlates Strongly with Nicotine and Some Flavor Chemical Concentrations. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavuluru, R.; Han, S.; Hahn, E.J. On the popularity of the USB flash drive-shaped electronic cigarette Juul. Tob. Control 2019, 28, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Villarreal, A.; Bozhilov, K.; Lin, S.; Talbot, P. Metal and silicate particles including nanoparticles are present in electronic cigarette cartomizer fluid and aerosol. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Talbot, P. Variability among electronic cigarettes in the pressure drop, airflow rate, and aerosol production. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2011, 13, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Villarreal, A.; Davis, B.; Talbot, P. Comparison of the performance of cartomizer style electronic cigarettes from major tobacco and independent manufacturers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goniewicz, M.L.; Knysak, J.; Gawron, M.; Kosmider, L.; Sobczak, A.; Kurek, J.; Prokopowicz, A.; Jablonska-Czapla, M.; Rosik-Dulewska, C.; Havel, C.; et al. Levels of selected carcinogens and toxicants in vapour from electronic cigarettes. Tob. Control 2014, 23, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyarah, R.; Long, G.A. Comparison of select analytes in aerosol from e-cigarettes with smoke from conventional cigarettes and with ambient air. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 70, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goniewicz, M.L.; Kuma, T.; Gawron, M.; Knysak, J.; Kosmider, L. Nicotine levels in electronic cigarettes. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2013, 15, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Helen, G.; Ross, K.; Dempsey, D.; Havel, C.; Jacob, P., III; Benowitz, N.L. Nicotine Delivery and Vaping Behavior During ad Libitum E- cigarette Access Gideon. Tob. Regul. Sci. 2016, 2, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajek, P.; Przulj, D.; Phillips, A.; Anderson, R.; Mcrobbie, H. Nicotine delivery to users from cigarettes and from different types of e-cigarettes. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2017, 234, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan-sarin, S.; Morean, M.; Kong, G.; Bold, K.W. E-Cigarettes and “Dripping” Among High-School Youth NIH. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20163224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poklis, J.L.; Mulder, H.A.; Halquist, M.S.; Wolf, C.E.; Poklis, A.; Peace, M.R. The Blue Lotus Flower (Nymphea caerulea) Resin Used in a New Type of Electronic Cigarette, the Re-Buildable Dripping Atomizer. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2018, 49, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.; Llados, F.; Diamond, G.; Chappell, L.L. Toxicological Profile for Tin and Tin Compounds; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2005; p. 302.
- Abadin, H.; Ashizawa, A.; Stevens, Y.-W.; Llados, F.; Diamond, G.; Sage, G.; Citra, M.; Quinones, A.; Bosch, S.J.; Swarts, S.G. Toxicological Profile for Lead; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007.
- Dunworth, J. Electronic Cigarette Batteries: The Ultimate Beginners Guide. Available online: https://www.ecigarettedirect.co.uk/ashtray-blog/2014/04/electronic-cigarette-batteries-guide.html#comments (accessed on 2 February 2019).
- Kosmider, L.; Sobczak, A.; Fik, M.; Knysak, J.; Zaciera, M.; Kurek, J.; Goniewicz, M.L. Carbonyl compounds in electronic cigarette vapors: Effects of nicotine solvent and battery output voltage. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2014, 16, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, P.A.; Karpinski, C.D.; Brown, J.E.; Luo, W.; Pankow, J.F. Flavour chemicals in electronic cigarette fluids. Tob. Control 2016, 25, e10–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlet, V.; Farsalinos, K.; Augsburger, M.; Thomas, A.; Etter, J.F. Toxicity assessment of refill liquids for electronic cigarettes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 4796–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Williams, M.; Talbot, P. Design Features in Multiple Generations of Electronic Cigarette Atomizers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162904
Williams M, Talbot P. Design Features in Multiple Generations of Electronic Cigarette Atomizers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(16):2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162904
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilliams, Monique, and Prue Talbot. 2019. "Design Features in Multiple Generations of Electronic Cigarette Atomizers" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 16: 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162904
APA StyleWilliams, M., & Talbot, P. (2019). Design Features in Multiple Generations of Electronic Cigarette Atomizers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(16), 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162904




