Agronomic Management and Rice Varieties Controlling Cd Bioaccumulation in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Description of Field Experimental Plots
2.1.1. Methods for Soil and Plant Sampling
2.1.2. Test Area Background
2.2. Rice Varieties and Stabilization Agents
2.2.1. Rice Varieties Used for the Screening Test
2.2.2. Low Cd Rice Varieties Used for Remediation
2.3. Rice Variety Screening Experiment Design
2.4. Soil Remediation Experiments with a Combination of Low Cd Accumulating Rice Variety and Applications of Stabilization Agents
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
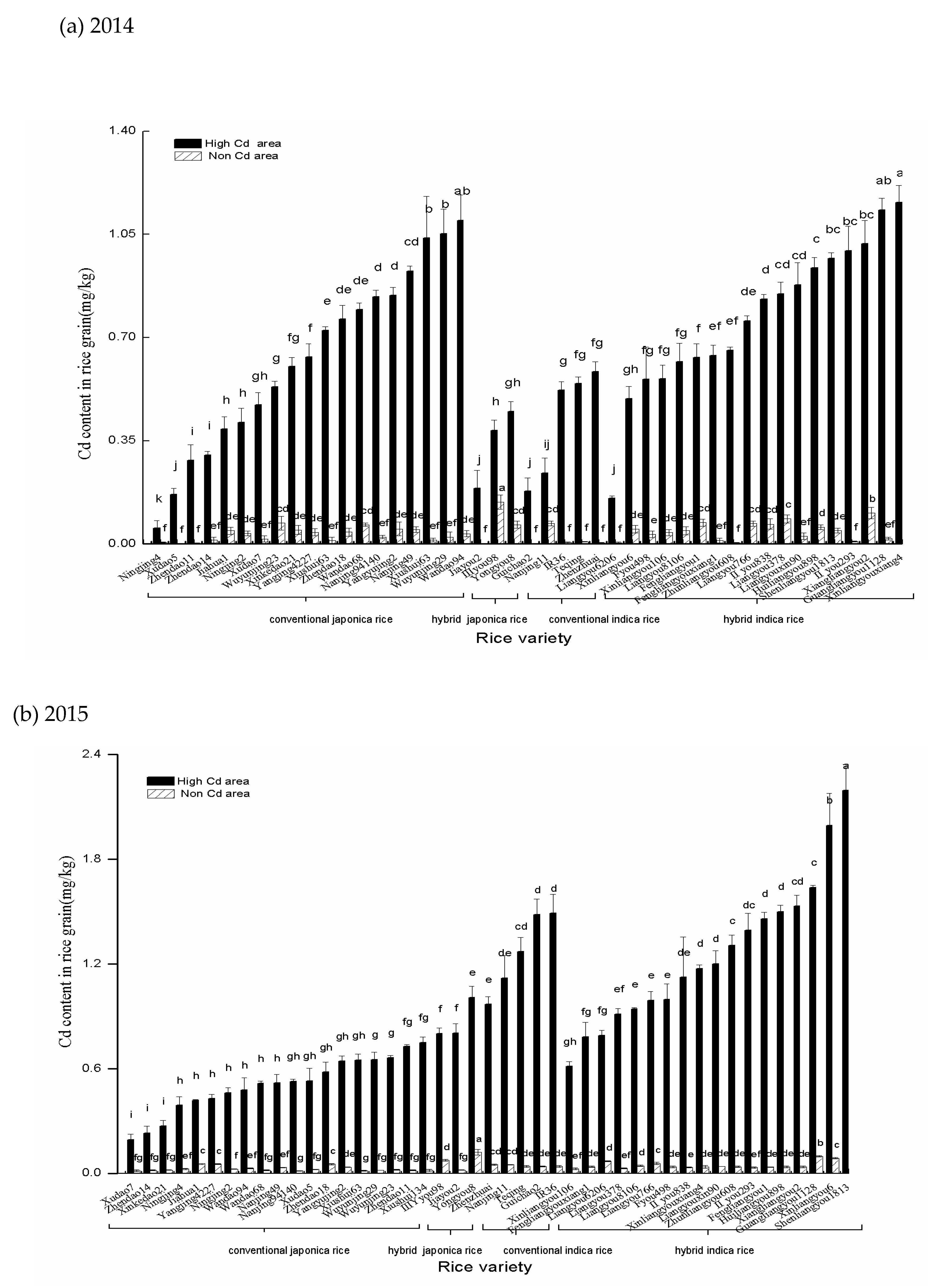
3.1. Cd Accumulation in Rice Varieties
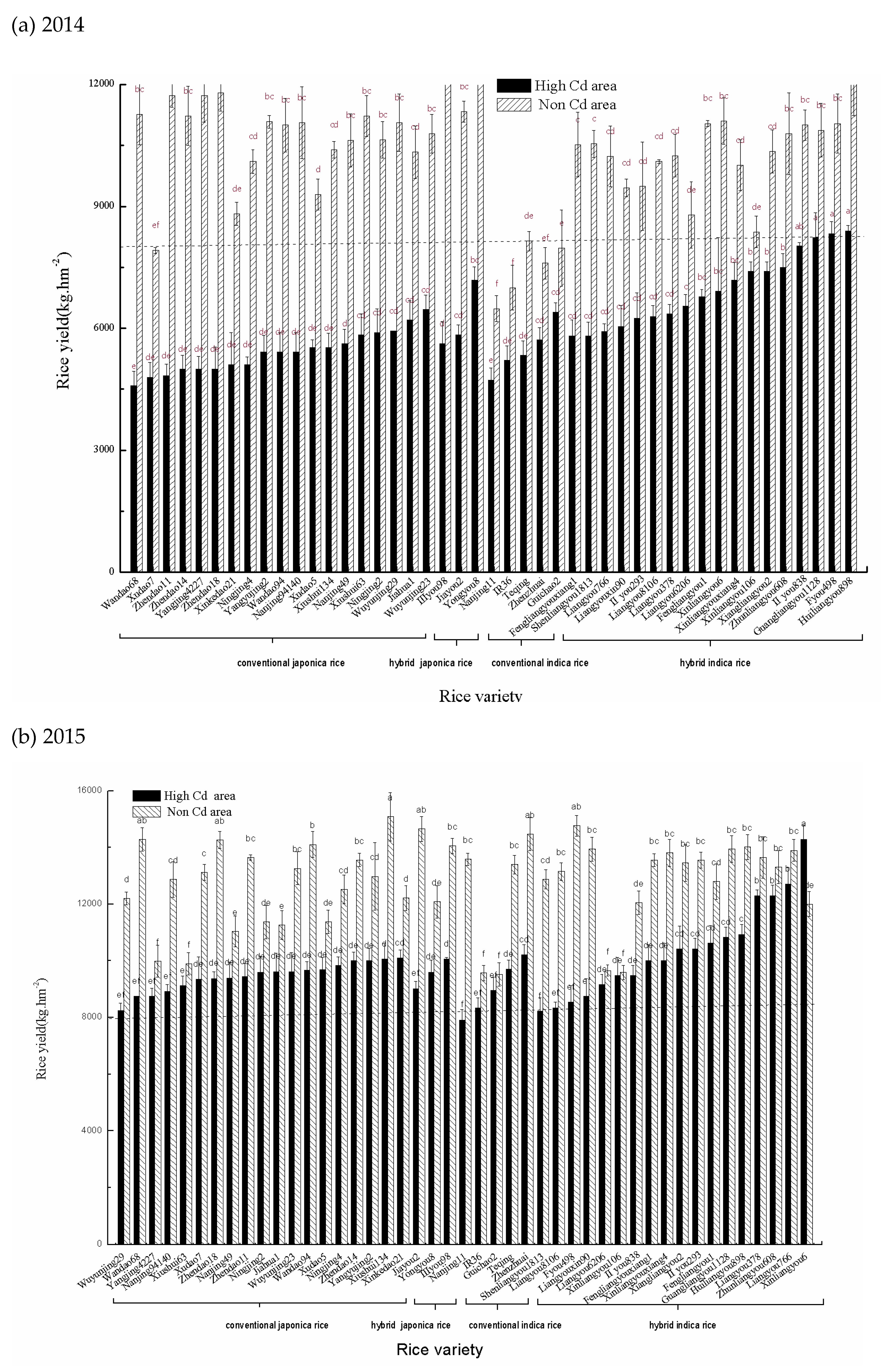
3.2. Yields of Rice Varieties and Their Sensitivity to Cd
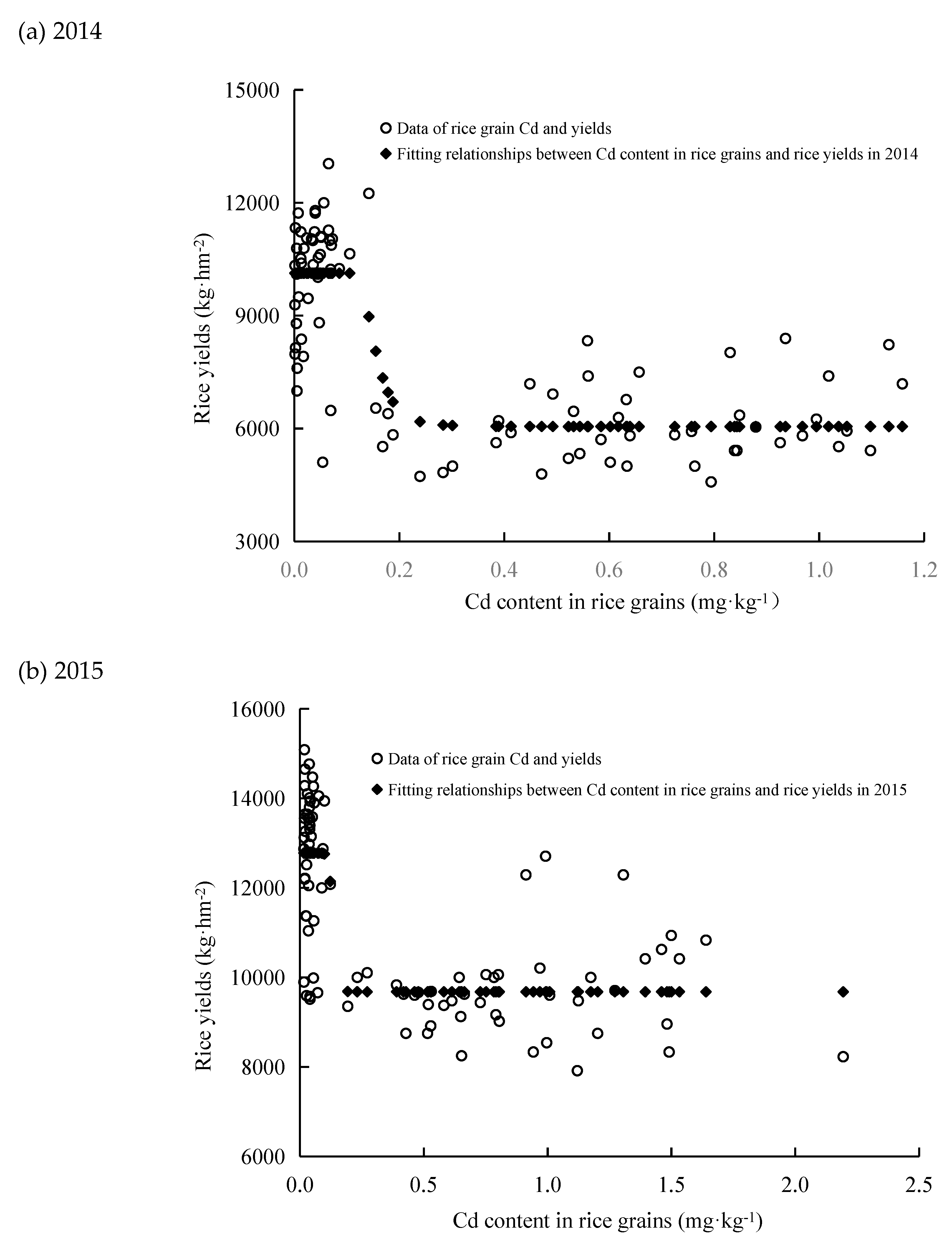
3.3. Relationship between Rice Grain Cd Accumulation and Rice Yields
3.4. Effects of Soil Amendments with a Mixture of Lime, Organic Fertilizers, and Porous Ceramics on Rice Cd Contents
3.5. Effects of a Mixture of Lime, Organic Fertilizer, and Porous Ceramics Nanomaterials on Soil Available Cd Content
3.6. Effects of Lime, Organic Fertilizers, and Porous Ceramics on Rice Yields
4. Discussion
4.1. Criteria for Low Accumulation Rice Varieties
4.2. Mechanisms of Low Accumulation of Cd in Crops
4.3. Cd Grain Accumulation among Different Rice Varieties
4.4. Effects of Cd on Crop Growth and Development
4.5. Effect of Soil Amendment on the Accumulation of Cd in Crops
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.C.; Yan, W.D.; An, Z.; Liu, Q.; Shi, W.M.; Cao, Z.H.; Wong, M.H. Status of trace elements in paddy soil and sediment in Taihu Lake region. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaney, R.L.; Reeves, P.G.; Ryan, J.A.; Simmons, R.W.; Welch, R.M.; Scott Angle, J. An improved understanding of soil Cd risk to humans and low cost methods to phytoextract Cd from contaminated soils to prevent soil Cd risks. Biometals 2004, 17, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penner, G.A.; Bezte, L.J.; Leisle, D.; Clarke, J. Identification of PAPD markers linked to a gene governing cadmium uptake in durum wheat. Genome 1995, 38, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.M.; Channey, L.R.; Schneiter, A.A. Genotypic variation in kernel cadmium concentration in sunflower germplasm under varying soil conditions. Crop Sci. 1995, 35, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Li, K.Q.; Xu, J.K.; Liang, J.S.; Lu, X.L.; Yang, J.C.; Zhu, Q.S. Interaction of Cd and five mineral nutrients for uptake and accumulation in different rice cultivars and genotypes. Field Crops Res. 2003, 83, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, L.; Pan, G. Variation of grain Cd and Zn concentrations of 110 hybrid rice cultivars grown in a low-Cd paddy soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, J.W.; Fang, W.; Yuan, J.G.; Yang, Z.Y. Cadmium accumulation in different rice cultivars and screening for pollution-safe cultivars of rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, S.; Ae, N.; Sugiyama, M.; Murakami, M.; Arao, T. Genotypic variation in shoot cadmium concentration in rice and soybean in soils with different levels of cadmium contamination. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2005, 51, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.M.; Liang, K.J.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, M.X.; Lin, W.X. Interactive effect of genotype and environment on the genetic covariance of characterization of heavymetal accumulation in ediblerice grain (Oryza sativa L.). Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2006, 14, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.Z.; Ma, Y.H.; Xu, L.L.; Fu, H.H.; Nie, J.R. Agro-ecological Remediation Technologies on Heavy Metal Contamination in Cropland Soils. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2013, 30, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, S.J.; Yu, H.; Feng, W.Q.; Qin, Y.S.; Liao, M.L.; Wang, C.Q.; Tu, S.H. Effects of different organic material and lime on wheat grow and cadmium uptake. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 25, 214–217. [Google Scholar]
- Lahori, A.H.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Guo, Z.Y.; Mahar, M.; Li, R.H.; Awasthi, M.K.; Sial, T.A.; Kumbhar, F.; Wang, P.; Shen, F.; et al. Potential use of lime combined with additives on (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of heavy metals from Pb/Zn smelter contaminated soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.M.; Ma, Y.H.; Wang, C.S.S.; Li, J.X.; Ye, W.L.; Wu, L.C.; Cui, J.Y. Remediation Technology Against Heavy Metal Pollution in Farmland Soil with Different Pollution Levels. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2016, 32, 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, M.; Ae, N.; Ishikawa, S. Phytoextraction of cadmium by rice (Oryza Sativa, L.), soybean (Glycine max(L.) Merr.), and maize (ZeaMays, L.). Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.L.; Chen, N.C.; Xu, S.G.; Zhou, J.M.; Xie, Z.Y.; Li, Z.A. Breeding Rice Cultivars with Low Accumulation of Cadmium: Cultivars Versus Types. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2009, 28, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.Y.; Yuan, F.; Li, X.L.; Zhou, T.F.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.R.; Chen, Y.N.; Chen, F.R.; Jia, S.J. Spatial variance and pollution analysis of soil heavy metals in Tongling mining area, South China. Earth Sci. Front. 2008, 15, 256–263. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.T.; Zhou, Q.X.; Sun, Y.B.; Yu, Z.G. Genotypic Variation of Cadmium Accumulation in Chinese cabbage (BrassicapekinensisL). J. Basicsci. Eng. 2010, 18, 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Jiang, X.X.; Gao, H.J. Pollutiion assesssment and source analysis of soil heavy mental in Taihulake Basin. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2017, 11, 247–253. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Dong, J.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, G. Subcellular distribution and chemical form of Cd and Cd-Zn interaction in different barley genotypes. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.M.; Li, J.X.; Hu, Z.Y.; Ye, W.L.; Wu, W.G.; Ma, Y.H. Review on Application of Low Accumulation Crops on Remediation of Farmland Contaminated by Heavy Metals. Crops 2018, 1, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, L.E.; Mills, R.F. P(1B)-ATPases-an ancient family of transition metal pumps with diverse functions in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.P.; Dou, C.M.; Chen, Y.X.; Chen, X.C.; Shi, J.Y.; Yu, M.G.; Xu, J. Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in Phytolacca americana L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittman, J.K. Managing the manganese: Molecular mechanisms of manganese transport and homeostasis. New Phytol. 2005, 167, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, H.J.; Jäger, H.J. Subcellular distribution and chemical form of cadmium in bean plants. Plant Physiol. 1980, 65, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, S.; Suzui, N.; Ito-Tanabata, S.; Ishii, S.; Igura, M.; Abe, T.; Kuramata, M.; Kawachi, N.; Fujimaki, S. Real-time imaging and analysis of differences in cadmium dynamics in rice cultivars(Oryza sativa) using position-emitting 107 Cd tracer. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y. Differences in Genotypes of Cadmium Tolerance in Rice and Mechanisms of Exogenous GSH to Alleviate Cadmium Toxicity; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.L.; Zhang, C.H.; Ju, T.; Ge, Y. Differential responses of GSH and GST in two rice cultivars under Cd stress. J. Ago-Environ. Sci. 2009, 28, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, Z.; Hajika, M.; Komatsu, S. Comparative proteome analysis of high and low cadmium accumulating soybeans under cadmium stress. Amino Acids 2012, 6, 2393–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Xu, B.B.; Song, Q.J.; Liu, X.M.; Xu, J.M.; Brookes, P.C. The identification of ‘hotspots’ of heavy metal pollution in soil–rice systems at a regional scale in eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Z.-Y.; Su, S.-W.; Lai, H.-Y.; Guo, H.-Y.; Chen, T.-C.; Chen, Z.-S. Remediation techniques and heavy metal uptake by different rice varieties in metal-contaminated soils of Taiwan: New aspects for food safety regulation and sustainable agriculture. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 56, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, K.R.; Zhou, L.J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Xie, J.H.; Tu, N.M. Genotype difference of brown rices in Cd content. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2006, 22, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, M. Concentrations of cadmium, lead, mercury and arsenic in Chinese market milled rice and associated population health risk. Food Control 2010, 21, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.H.; Tang, S.Q.; Wei, X.J.; Shao, J.N.; Jiao, G.A.; Sheng, Z.H.; Luo, J.; Hu, P.S. The cadmium and lead content of the grain produced by leading Chinese rice cultivars. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.B.; Huang, D.Y.; Zhu, Q.H.; Wang, S.L.; Shou, L.; He, H.B.; Zhu, H.H.; Xu, C. A three-season field study on the in-situ remediation of Cd-contaminated paddy soil using lime, two industrial by-products, and a low-Cd-accumulation rice cultivar. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 136, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.F.; Xin, J.L.; Dai, H.W.; Zhou, W.J. Effects of interaction between cadmium (Cd) and selenium (Se) on grain yield and Cd and Se accumulation in a hybrid rice (Oryza sativa) system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 25, 9537–9546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.G.; Cai, G.L.; Qian, M.; Wang, D.K.; Xu, J.K.; Yang, J.C.; Zhu, Q.S. Effect of Cd on the growth, dry matter accumulation and grain yield of different rice cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.L. Molecular Mechanism of Heavy Metal Toxicity and Tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) and Wheat (Triticum Aestivum, L.); Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.H.; Wen, Y.M.; Shu, Q. Fraction transformation of cadmium and zinc in soils. Urban Environ. Urban Ecol. 2001, 14, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Ren, S.R. Long-term effects of combined application of chemical nitrogen with organic materials on crop yields, soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in fluvo-aquic soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 151, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.H.; Gu, D.J.; Liu, L.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.C. Changes in grain yield of rice and emission of greenhouse gases from paddy fields after application of organic fertilizers made from maize straw. Rice Sci. 2014, 21, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Fang, Z.Y.; Huang, Q.W.; Zhang, R.F.; Li, R.; Shen, B. Effects of organic-inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice -wheat cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Rong, X.M.; Xie, G.X.; Zhang, Y.P.; Peng, J.W.; Song, H.X. Effects of organic fertilizers on yield and quality of rice grains and nitrogen use efficiency. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. 2010, 36, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.L. Remediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils by Lime: A Review. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 25, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Bolan, N.S.; Adriano, D.C.; Mani, P.A.; Duraisamy, A. Immobilization and phytoavailability of cadmium in variable charge soils II. Effect of lime addition. Plant Soil 2003, 251, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, R.S.; Chen, P.; Song, X.F. Characteristics of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with cement solidification treatment. J. Energy Inst. 2016, 89, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.N.; Jin, H.L.; Zhou, L. Experimental Research on Passivator Used in Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Repair. Energy Energy Conserv. 2015, 11, 105–106. [Google Scholar]
- Mallampati, S.R.; Mitoma, Y.; Okuda, T.; Sakita, S.; Kakeda, M. Enhanced heavy metal immobilization in soil by grinding with addition of nanometallic Ca/CaO dispersion mixture. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallampati, S.R.; Mitoma, Y.; Okuda, T.; Sakita, S.; Simion, C. Simultaneous decontamin- ation of cross-polluted soils with heavy metals and PCBs using a nano-metallic Ca/Cao dispersion mixture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9270–9277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Degree of Pollution | Soil Available Cd | Soil Total Cd | pH | CEC | Alkaline Hydrolytic Nitrogen | Soil Available Phosphorus | Rapidly Available Potassium | Organic Matters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | cmol·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | g·kg−1 | ||
| Non-Cd area | 0.172 | 0.261 | 6.51 | 14.79 | 123.57 | 19.78 | 81.25 | 25.71 |
| Low-Cd area | 0.361 | 0.389 | 5.93 | 13.56 | 133.35 | 19.25 | 136.67 | 22.47 |
| High-Cd area | 1.36 | 1.83 | 5.03 | 12.95 | 120.27 | 19.15 | 74.32 | 23.66 |
| Rice Varieties | High-Cd area | High-Cd Area + Soil Amendments | Low-Cd Area | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice Grain Cd Content (mg·kg−1) | bioavailable Cd Content in Soils (mg·kg−1) | Rice Grain Cd Content (mg·kg−1) | Bioavailable Cd Content in Soils (mg·kg−1) | Rice Grain Cd Content (mg·kg−1) | Bioavailable Cd Content in Soils (mg·kg−1) | ||
| Indica rice variety | Liangyou 8106 | 0.81 ± 0.03a | 0.96 ± 0.06a | 0.42 ± 0.03b | 0.47 ± 0.05b | 0.039 ± 0.003c | 0.38 ± 0.03c |
| Zhenzhuai | 0.56 ± 0.03a | 1.12 ± 0.09a | 0.14 ± 0.02b | 0.64 ± 0.05b | |||
| Liangyou 766 | 0.56 ± 0.06a | 0.67 ± 0.12a | 0.26 ± 0.03b | 0.59 ± 0.09a | 0.081 ± 0.002c | 0.41 ± 0.02b | |
| Teqing | 0.53 ± 0.08a | 1.32 ± 0.08a | 0.18 ± 0.01b | 0.86 ± 0.05b | 0.039 ± 0.003c | 0.41 ± 0.01c | |
| Xinliangyou 106 | 0.48 ± 0.02a | 1.07 ± 0.10a | 0.17 ± 0.02b | 0.99 ± 0.14a | 0.023 ± 0.004c | 0.41 ± 0.08b | |
| Liangyou 6206 | 0.38 ± 0.05a | 0.92 ± 0.05a | 0.22 ± 0.02b | 0.81 ± 0.07a | |||
| Fengliangyouxiang1 | 0.35 ± 0.01a | 1.21 ± 0.05a | 0.27 ± 0.07a | 1.07 ± 0.07b | 0.042 ± 0.003b | 0.34 ± 0.03c | |
| Nanjing 11 | 0.29 ± 0.04a | 0.60 ± 0.04a | 0.23 ± 0.02a | 0.57 ± 0.04a | |||
| Japonica rice variety | Xinkedao 21 | 0.52 ± 0.05a | 1.11 ± 0.09a | 0.13 ± 0.01b | 0.73 ± 0.07b | ||
| Zhendao 18 | 0.26 ± 0.02a | 1.24 ± 0.07a | 0.09 ± 0.02b | 1.22 ± 0.09a | 0.029 ± 0.004c | 0.36 ± 0.06b | |
| Yangjing 4227 | 0.25 ± 0.02a | 1.48 ± 0.06a | 0.15 ± 0.02b | 0.85 ± 0.09b | 0.023 ± 0.003c | 0.41 ± 0.01c | |
| Wandao 68 | 0.24 ± 0.04a | 1.25 ± 0.05a | 0.23 ± 0.02a | 1.03 ± 0.09b | |||
| Zhendao 14 | 0.22 ± 0.03a | 1.01 ± 0.13a | 0.14 ± 0.04a | 0.24 ± 0.03b | |||
| Jiayou 2 | 0.17 ± 0.03a | 1.11 ± 0.09a | 0.11 ± 0.01b | 0.38 ± 0.03b | |||
| Xudao 7 | 0.14 ± 0.02a | 1.08 ± 0.06a | 0.03 ± 0.01b | 0.62 ± 0.03b | 0.038 ± 0.003b | 0.35 ± 0.05c | |
| Xudao 5 | 0.14 ± 0.03a | 0.96 ± 0.08a | 0.02 ± 0.005b | 0.66 ± 0.06b | 0.045 ± 0.002b | 0.26 ± 0.04c | |
| Xiushui 63 | 0.14 ± 0.01a | 1.08 ± 0.18a | 0.02 ± 0.005b | 0.75 ± 0.09b | 0.034 ± 0.002c | 0.41 ± 0.04c | |
| Zhendao 11 | 0.12 ± 0.02a | 0.60 ± 0.08a | 0.05 ± 0.004b | 0.59 ± 0.04a | |||
| Ningjing 4 | 0.11 ± 0.02a | 0.86 ± 0.10a | 0.11 ± 0.02a | 0.65 ± 0.07b | 0.060 ± 0.003b | 0.40 ± 0.04c | |
| Rice Variety | Rice Yields (kg·hm−2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Cd Area | High-Cd Area + Soil Amendment | Low-Cd Area | ||
| Indica rice variety | Liangyou 8106 | 9520 ± 24a | 8967 ± 17a | 11339 ± 32b |
| Zhenzhuai | 8453 ± 24a | 8259 ± 27a | ||
| Liangyou 766 | 8225 ± 13a | 7661 ± 11b | 11379 ± 18c | |
| Teqing | 8685 ± 23a | 8759 ± 23a | 11772 ± 35b | |
| Xinliangyou 106 | 9331 ± 20a | 9370 ± 22a | 12384 ± 20b | |
| Liangyou 6206 | 8817 ± 24a | 8535 ± 24a | ||
| Fengliangyouxiang 1 | 8841 ± 5a | 8850 ± 12a | 12169 ± 10b | |
| Nanjing 11 | 8789 ± 34a | 8880 ± 27a | ||
| Japonic rice variety | Xinkedao 21 | 8975 ± 38a | 8520 ± 12a | |
| Zhendao 18 | 8441 ± 34a | 8483 ± 11a | 12088 ± 12b | |
| Yangjing 4227 | 8834 ± 18a | 8891 ± 6a | 11474 ± 23b | |
| Wandao 68 | 8730 ± 35a | 8667 ± 13a | ||
| Zhendao 14 | 7694 ± 14a | 7661 ± 21a | ||
| Jiayou 2 | 9778 ± 28a | 9004 ± 11b | ||
| Xudao 7 | 9330 ± 28a | 9231 ± 11a | 12003 ± 16b | |
| Xudao 5 | 7490 ± 14a | 7271 ± 12a | 10934 ± 10b | |
| Xiushui 63 | 8442 ± 19a | 8036 ± 41a | 11276 ± 20b | |
| Zhendao 11 | 9165 ± 31a | 8849 ± 13a | ||
| Ningjing 4 | 7471 ± 28a | 7436 ± 21a | 11441 ± 23b | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Wu, W.; Han, F.; Li, J.; Ye, W.; Fu, H.; Yan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q. Agronomic Management and Rice Varieties Controlling Cd Bioaccumulation in Rice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16132376
Chen L, Wu W, Han F, Li J, Ye W, Fu H, Yan Y, Ma Y, Wang Q. Agronomic Management and Rice Varieties Controlling Cd Bioaccumulation in Rice. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(13):2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16132376
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Liangmei, Wenge Wu, Fengxiang Han, Jiangxia Li, Wenling Ye, Huanhuan Fu, Yonghua Yan, Youhua Ma, and Qiang Wang. 2019. "Agronomic Management and Rice Varieties Controlling Cd Bioaccumulation in Rice" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 13: 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16132376
APA StyleChen, L., Wu, W., Han, F., Li, J., Ye, W., Fu, H., Yan, Y., Ma, Y., & Wang, Q. (2019). Agronomic Management and Rice Varieties Controlling Cd Bioaccumulation in Rice. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(13), 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16132376







