Heavy Metal Accumulation in Water, Soil, and Plants of Municipal Solid Waste Landfill in Vientiane, Laos
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Research Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Chemical Analysis for Heavy Metals
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Concentration of Heavy Metals in Surface and Groundwater
3.2. Concentration of Heavy Metals in Soil
3.3. Concentrations of Heavy Metals in Plants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Waste Management in ASEAN Countries. 2017. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/21134/waste_mgt_asean_summary.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 30 June 2018).
- Bakis, R.; Tuncan, A. An investigation of heavy metal and migration through groundwater from the landfill area of Eskisehir in Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 176, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusti, L. A review of waste management practices and their impact on human health. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2227–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esakku, S.; Palanivelu, K.; Joseph, K. Assessment of heavy metals in a municipal solid waste dumpsite. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Sustainable Landfill Management, Chennai, India, 3–5 December 2003; Volume 35, pp. 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kanmani, S.; Gandhimathi, R. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil due to leachate migration from an open dumping site. Appl. Water Sci. 2012, 13, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, R.J.; Gronow, J.R.; Voulvoulis, N. Household hazardous waste in municipal landfills: Contaminants in leachate. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 337, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chary, N.S.; Kamala, C.; Raj, D.S. Assessing risk of heavy metals from consuming food grown on sewage irrigated soils and food chain transfer. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 2008, 69, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nica, D.V.; Bura, M.; Gergen, I.; Harmanescu, M.; Bordean, D. Bioaccumulative and conchological assessment of heavy metal transfer in a soil-plant-snail food chain. Chem. Cent. J. 2012, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdisciplinary Toxicol. 2014, 13, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muddarisna, N.; Krisnayanti, B.D.; Utami, S.R.; Utami, E.; Handayanto, E. Phytoremediation of mecury-contaminated soil using three wild plant species and its effect on maize growth. Applied Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2013, 1, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, M.; Kiran, B.; Rani, S.; Rani, A.; Kaur, B.; Mittal, N. Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables irrigated with water from different sources. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, S. Heavy metals in food crops, soil, and water in the Lihe River Watershed of the Taihu Region and their potential health risks when ingested. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, W. The essential trace elements. Science 1981, 213, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchuweti, M.; Birkett, J.; Chinyanga, E.; Zvauya, R.; Scrimshaw, M.; Lester, J. Heavy metal content of vegetables irrigated with mixtures of wastewater and sewage sludge in Zimbabwe: Implications for human health. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 112, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metals toxicity and the environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 101, pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Öman, C.B.; Junestedt, C. Chemical characterization of landfill leachates-400 parameters and compounds. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1876–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, B.O.; Anumol, T.; Barlaz, M.; Snyder, S.A. Investigating landfill leachate as a source of trace organic pollutants. Chemosphere 2015, 127, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; Volume 548, pp. 93–118, INBN-13: 978-1-4200-9370. [Google Scholar]
- Hinchman, R.R.; Negri, M.C.; Gatliff, E.G. Phytoremediation: Using green plants to clean up contaminated soil, groundwater and wastewater. In Proceedings of the International Topical Meeting on Nuclear and Hazardous Waste Management, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–23 August 1996; Volume 96, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, M.; Ghaly, A.E.; Mahmoud, N.; Cote, R. Phytoaccumulation of heavy metals by aquatic plants. Environ. Int. 2004, 29, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivaisi, A.K. The potential for constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment and reuse in developing countries: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2001, 16, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madera-Parra, C.A.; Peña-Salamanca, E.J.; Peña, M.R.; Rousseau, D.P.; Lens, P.N. Phytoremediation of landfill leachate with Colocasia esculenta, Gynerum sagittatumand, and Heliconia psittacorumin constructed wetlands. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2014, 17, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate and Clean Air Coalition Municipal Solid Waste Initiative (CCAC). Solid Waste Management City Profile, Vientiane Capital, LAO People’s Democratic Republic. 2015. Available online: http://www.waste.ccacoalition.org/sites/default/files/files/vientiane_city_profile_vientiane_capital_lao.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2018).
- Vodyanitskii, Y.N. Biochemical processes in soil and groundwater contaminated by leachates from municipal landfills (mini review). Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2016, 14, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy metals in contaminated soils: A review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. Isrn Ecol. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontario Ministry of the Environment and Climate Change (MOECC). Protocol for the Sampling and Analysis of Industrial/Municipal Wastewater. 2016. Available online: http://www.downloads.ene.gov.on.ca/envision/env_reg/er/documents/2016/011–7834_Protocol.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2018).
- Government of Western Australia. Field Sampling Guideline: A Guideline for Field Sampling for Surface Water Quality Monitoring Programs. 2009. Available online: https://www.water.wa.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0020/2936/87154.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2018).
- Gworek, B.; Dmuchowski, W.; Koda, E.; Marecka, M.; Baczewska, A.H.; Brągoszewska, P.; Osiński, P. Impact of the municipal solid waste Łubna landfill on environmental pollution by heavy metals. Water 2016, 8, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SHIMADZU. Environmental Analyses-Shimadzu Analysis Guidebook. 2005. Available online: https://applicationstation.ssi.shimadzu.com/sites/default/files/environmental-analyses-guidebook.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2018).
- Andersen, K.J.; Kisser, M.I. Digestion of Solid Matrices–Desk Study Horizontal; Eurofins A/A: Kwai Chung, Denmark, 2004; Volume 59, pp. 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment, Laos, MONEL. Agreement on National Environmental Standards of Laos (ANESs); MONREL: Vientiane, Laos, 2009.
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 554, pp. 327–433. ISBN 978-92-4-1548151. [Google Scholar]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Permissible Limits of Heavy Metals in Soil and Plants; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, G.; Brewer, P.A.; Macklin, M.G.; Balteanu, D.; Driga, B.; Serban, M.; Zaharia, S. The solid-state partitioning of contaminant metals and as in river channel sediments of the mining affected Tisa drainage basin, northwestern Romania and eastern Hungary. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ryan Kristopher, R.G.; Parilla, R. Analysis of heavy metals in Cebu city sanitary landfill, Philippines. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2014, 17, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kar, D.; Sur, P.; Mandai, S.K.; Saha, T.; Kole, R.K. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2008, 5, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, M.S.; Uyanik, A.; Kutbay, H.G. Accumulation of heavy metals in water, sediments and wetland plants of Kizilirmak Delta (Samsun, Turkey). Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2015, 17, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsi, A.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. A field investigation of the quantity and quality of leachate from a municipal solid waste landfill in a Mediterranean climate (Thessaloniki, Greece). Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 6, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, P.; Barlaz, M.A.; Rooker, A.P.; Baun, A.; Ledin, A.; Christensen, T.H. Present and long-term composition of MSW landfill leachate: A review. Crit. Rev. Eniron. Sci. Tech. 2002, 41, 297–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arao, T.; Ishikawa, S.; Murakami, M.; Abe, K.; Maejima, Y.; Makino, T. Heavy metal contamination of agricultural soil and countermeasures in Japan. Paddy Water Environ. 2010, 8, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calace, N.; Liberatori, A.; Petronio, B.M.; Pietroletti, M. Characteristics of different molecular weight fractions of organic matter in landfill leachate and their role in soil sorption of heavy metals. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 113, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.K.; Zeng, X.; Li, J. Environmental pollution of electronic waste recycling in India: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.Y.; Shen, D.S.; Wang, H.T.; Lu, W.J.; Zhao, Y. Heavy metal source analysis in municipal solid waste (MSW): Case study on Cu and Zn. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafisoye, O.B.; Adefioye, T.; Osibote, O.A. Heavy metals contamination of water, soil, and plants around an electronic waste dumpsite. Environ. Study 2013, 22, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Samadder, S.R.; Prabhakar, R.; Khan, D.; Kishan, D.; Chauhan, M.S. Analysis of the contaminants released from municipal solid waste landfill site: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakmak, I.; Marschner, H. Effect of zinc nutritional status on activities of superoxide radical and hydrogen peroxide scavenging enzymes in bean leaves. In Plant Nutrition-from Genetic Engineering to Field Practice; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Athar, M.; Vohora, S.B. Heavy Metals and Environment, 1st ed.; K.K. Gupta for New Age International: New Delhi, India, 1995; Volume 224, pp. 58–63. ISBN 81-224-0769-2. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, U.N.; Sinha, S. Distribution of metals in aquatic edible plants: Trapa natans (Roxb.) Makino and Ipomoea aquatica Forsk. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2001, 70, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durowoju, O.S.; Odiyo, J.O.; Ekosse, G.I.E. Variations of heavy metals from geothermal spring to surrounding soil and Mangifera indica–Siloam village, Limpopo province. Sustainability 2016, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.; Irshad, M.; Fawad, M.; Ali, Z.; Eneji, A.E.; Aurangzeb, N.; Ali, B. Effect of cyclic phytoremediation with different wetland plants on municipal wastewater. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2014, 16, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Ueno, Y.; Sikder, M.T.; Kurasaki, M. Phytofiltration of arsenic and cadmium from the water environmnt using Micranthemum umbrosum (JF Gmel) SF Blake as a hyperaccumulator. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2013, 15, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanu, L.B.; Gupta, A. Phytoremediation of lead using Ipomoea aquatica Forsk. in hydroponic solution. Chemosphere 2016, 156, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbaruko, B.C.; Friday, O.V. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in some fauna and flora. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2007, 6, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cao, L.; Dou, S. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and health risk assessment in three benthic bivalves along the coast of Laizhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, R.; Khan, M.; Masab, M.; Rehman, H.U.; Rauf, N.U.; Shahab, S.; Shaheen, Z. Accumulation of heavy metals (Ni, Cu, Cd, Cr, Pb, Zn, Fe) in the soil, water and plants and analysis of physico-chemical parameters of soil and water collected from Tanda Dam Kohat. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2015, 7, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, P.; Anh, L.H.; Wagner, J.; Reichenbach, J.; Hebner, A. Solid waste management in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam: Moving towards a circular economy? Sustainability 2017, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukalang, N.; Clarke, B.; Ross, K. Barriers to effective municipal solid waste management in a rapidly urbanizing area in Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Site | Latitude | Longitude | Description of Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface water sampling sites | |||
| W1 | 18°4′50.45″ | 102°51′13.20″ | Leachate and wastewater were runoff from the landfill to the wetland (upstream) |
| W2 | 18°4′53.85″ | 102°51′13.35″ | Leachate and wastewater were runoff from the landfill to wetland (middle stream) |
| W3 | 18°5′0.20″ | 102°51′12.26″ | Leachate and wastewater were runoff from the landfill to wetland (downstream) |
| Groundwater sampling sites | |||
| G1 | 18°4′28.40″ | 102°51′12.31″ | Available groundwater (well) inside landfill used for the landfill management’s office and waste pickers |
| G2 | 18°5′3.26″ | 102°51′11.70″ | Available well used for domestic purposes of farmers was outside the landfill about 70 m away |
| Soil sampling sites | |||
| S1 | 18°4′48.32″ | 102°50′50.46″ | Random samples of soils in the landfill were near recharge canals |
| S2 | 18°4′45.62″ | 102°50′57.60″ | Random samples of soils in the landfill were near recharge canals |
| S3 | 18°4′33.17″ | 102°51′0.81″ | Random samples of soils in the landfill were near recharge canals |
| S4 | 18°5′2.90″ | 102°51′12.59″ | Random samples of soils were outside the landfill site about 60 m away |
| Plant sampling sites | |||
| IA1 | 18°4′46.82″ | 102°50′55.98″ | Random samples of Ipomoea aquatica in the wastewater or leachate area (inside landfill) |
| IA2 | 18°4′26.91″ | 102°51′11.23″ | Random samples of I. aquatica in the fish pond was near the landfill’s office. |
| P1 | 18°4′33.17″ | 102°51′0.81″ | Random samples of grass in the landfill |
| P2 | 18°5′2.90″ | 102°51′12.59″ | Random samples of grass were outside the landfill site about 70 m away |
| Site | Heavy Metal | Wet Season | Dry Season | Standards (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ANESs | WHO | ||
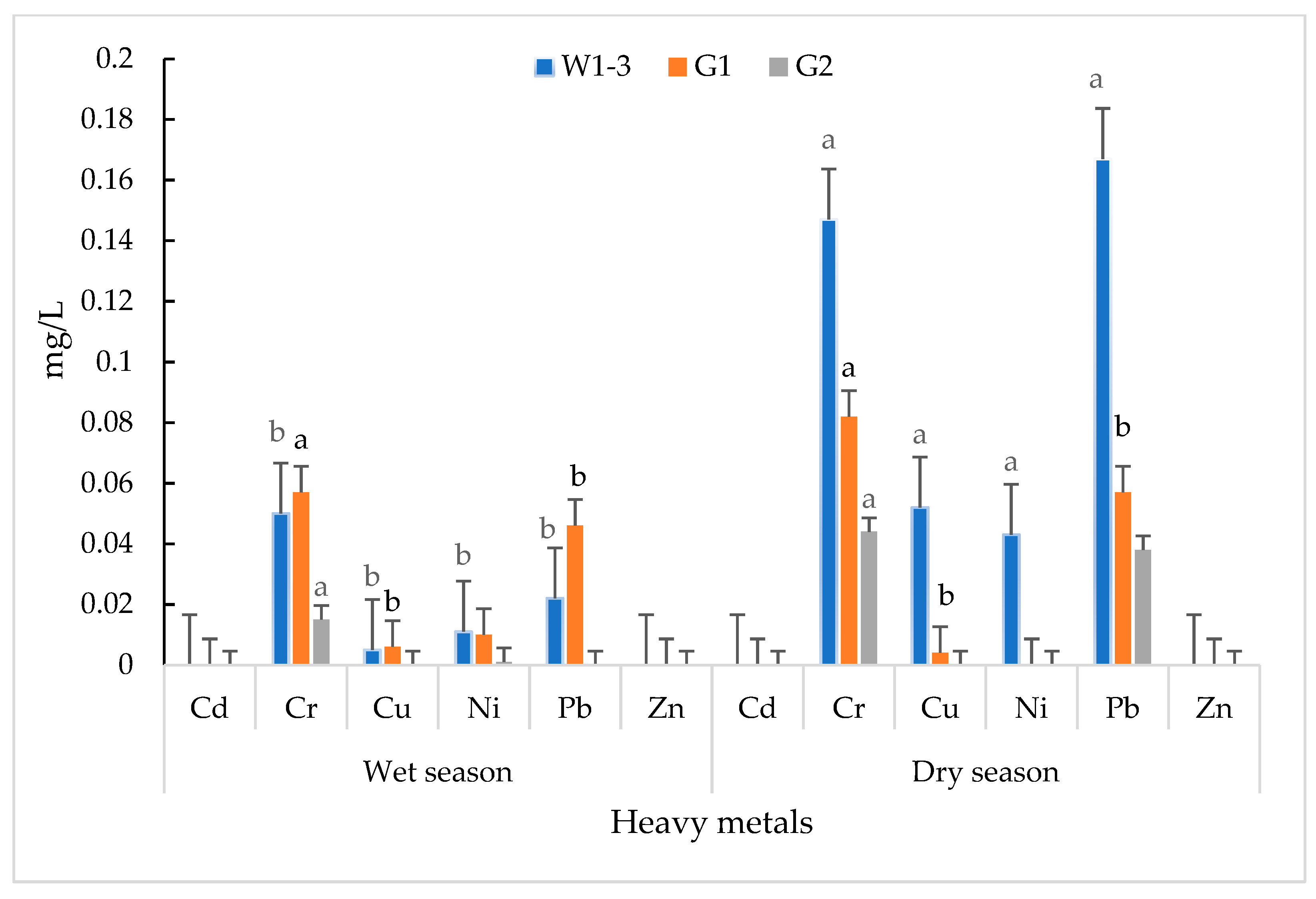
| W1-3 | Cd | ND | ND | 0.03 | - |
| Cr | 0.05 ± 0.015 b | 0.19 ± 0.057 a | 0.5 | - | |
| Cu | 0.01 ± 0.005 b | 0.05 ± 0.018 a | 0.5 | - | |
| Ni | 0.01 ± 0.001 b | 0.04 ± 0.005 a | 0.2 | - | |
| Pb | 0.02 ± 0.008 b | 0.17 ± 0.042 a | 0.2 | - | |
| Zn | ND | ND | 1.0 | - | |
| G1 | Cd | ND | ND | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| Cr | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.020 a | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| Cu | 0.01 ± 0.011 a | 0.004 ± 0.01 a | 1.50 | 2.00 | |
| Ni | 0.01 ± 0.010 | ND | 0.02 | 0.07 | |
| Pb | 0.05 ± 0.020 a | 0.06 ± 0.013 a | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Zn | ND | ND | 5.00 | 3.00 | |
| G2 | Cd | ND | ND | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| Cr | 0.02 ± 0.019 a | 0.04 ± 0.022 a | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| Cu | ND | ND | 1.50 | 2.00 | |
| Ni | 0.001 ± 0.001 b | ND | 0.02 | 0.07 | |
| Pb | ND | 0.04 ± 0.014 a | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Zn | ND | ND | 5.00 | 3.00 | |
| Sites | Heavy Metal | Wet Season | Dry Season | Dutch Standards | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Tv | Iv | ||
| S1–3 | Cd | 3.76 ± 0.33 a | 3.73 ± 1.12 a | 0.8 | 12.0 |
| Cr | 39.67 ± 3.78 a | 48.08 ± 13.67 a | 100.0 | 380.0 | |
| Cu | 66.82 ± 27.52 a | 54.06 ± 20.99 a | 36.0 | 190.0 | |
| Ni | 19.43 ± 0.84 a | 19.94 ± 4.91 a | 35.0 | 210.0 | |
| Pb | 80.17 ± 19.33 a | 67.99 ± 19.07 a | 85.0 | 530.0 | |
| Zn | 77.46 ± 57.88 a | 52.48 ± 34.59 a | 140.0 | 720.0 | |
| S4 | Cd | 1.02 ± 0.64 b | 1.06 ± 0.05 b | 0.8 | 12.0 |
| Cr | 10.02 ± 4.24 b | 19.33 ± 1.95 b | 100.0 | 380.0 | |
| Cu | 7.96 ± 2.79 b | 11.70 ± 0.50 b | 36.0 | 190.0 | |
| Ni | 5.65 ± 1.72 b | 9.61 ± 0.06 b | 35.0 | 210.0 | |
| Pb | 16.03 ± 5.40 b | 21.47 ± 0.42 b | 85.0 | 530.0 | |
| Zn | 4.39 ± 2.68 b | 4.79 ± 0.56 b | 140.0 | 720.0 | |
| Plant Name/Site | Samples | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet Season | |||||||
| I. aquatica | Leaves | ND | 17.00 ± 4.27 a | 8.30 ± 5.12 a | 0.24 ± 0.34 a | 13.26 ± 7.06 a | 1.54 ± 0.64 a |
| Stem | ND | 18.63 ± 6.10 a | 9.63 ± 9.75 a | ND | 7.48 ± 7.11 a | 8.54 ± 11.97 a | |
| Roots | 0.16 ± 0.21 a | 26.62 ± 1.54 a | 36.79 ± 13.32 a | 11.01 ± 9.74 a | 38.94 ± 15.85 a | 26.27 ± 6.46 a | |
| Grass/P1 | Leaves | ND | 11.32 ± 2.05 b | 21.10 ± 2.36 b | 0.25 ± 0.24 b | 2.85 ± 2.69 b | 4.27 ± 7.39 c |
| Stems | 3.07 ± 1.57 b | 40.47 ± 25.75 b | 55.50 ± 37.50 b | 15.93 ± 13.81 b | 47.30 ± 36.84 b | 38.47 ± 6.12 ab | |
| Roots | 8.24 ± 3.13 a | 164.33 ± 50 a | 193.7 ± 30.02 a | 71.33 ± 22.08 a | 181 ± 49 a | 55.03 ± 8.09 a | |
| Grass/P2 WHO standards | Leaves | ND | 11.14 ± 2.75 b | 21 ± 14.53 b | 0.55 ± 0.08 b | 3.31 ± 2.97 b | 0.33 ± 0.57 c |
| Stems | ND | 12.03 ± 2.29 b | 63.2 ± 17.34 b | 0.08 ± 0.14 b | 2.83 ± 2.72 b | 15.86 ± 11.12 bc | |
| Roots | 1.32 ± 1.72 b | 20.22 ± 24.25 b | 29.97 ± 34.42 b | 5.13 ± 8.89 b | 21.07 ± 26.92 b | 35.27 ± 16.64 ab | |
| 0.02 | 1.30 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 2.00 | 0.60 | ||
| Dry Season | |||||||
| I. aquatica | Leaves | ND | 15.37 ± 1.27 a | 21.60 ± 7.68 a | 0.39 ± 0.29 a | 9.66 ± 1.64 a | 27.60 ± 24.00 a |
| Stems | 0.11 ± 0.15 a | 16.68 ± 5.44 a | 35.98 ± 17.04 a | 0.65 ± 0.30 a | 9.12 ± 2.55 a | 8.25 ± 3.02 a | |
| Roots | 1.12 ± 1.16 a | 26.10 ± 5.94 a | 49.23 ± 0.47 a | 5.79 ± 3.13 a | 34.66 ± 4.05 a | 29.18 ± 24.45 a | |
| Grass/P1 | Leaves | 0.96 ± 0.93 a | 35.37 ± 4.65 a | 218.7 ± 9.07 a | 2.45 ± 0.85 a | 16.27 ± 3.04 a | 37.8 ± 23.19 a |
| Stems | 0.07 ± 0.13 a | 7.52 ± 2.56 c | 8.42 ± 0.5 d | 0.40 ± 0.70 a | 0.38 ± 0.66 b | 8.52 ± 9.59 a | |
| Roots | 2.07 ± 1.83 a | 18.7 ± 4.06 b | 48 ± 13.42 c | 4.57 ± 1.91 a | 8.91 ± 3.85 ab | 33.1 ± 23.31 a | |
| Grass/P2 WHO standards | Leaves | 0.63 ± 0.60 a | 42.47 ± 4.61 a | 159 ± 6.24 b | 1.9 ± 2.11 a | 13.36 ± 7.58 a | 22.9 ± 31.02 a |
| Stems | 0.09 ± 0.15 a | 7.07 ± 2.74 e | 7.55 ± 2.44 d | 0.72 ± 1.25 a | 0.25 ± 0.27 b | 7.07 ± 12.24 a | |
| Roots | 1.05 ± 1.82 a | 13.5 ± 2.98 be | 39.4 ± 18.71 c | 2.37 ± 2.64 a | 5.37 ± 6.21 ab | 17.7 ± 24.37 a | |
| 0.02 | 1.30 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 2.00 | 0.60 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vongdala, N.; Tran, H.-D.; Xuan, T.D.; Teschke, R.; Khanh, T.D. Heavy Metal Accumulation in Water, Soil, and Plants of Municipal Solid Waste Landfill in Vientiane, Laos. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16010022
Vongdala N, Tran H-D, Xuan TD, Teschke R, Khanh TD. Heavy Metal Accumulation in Water, Soil, and Plants of Municipal Solid Waste Landfill in Vientiane, Laos. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleVongdala, Noudeng, Hoang-Dung Tran, Tran Dang Xuan, Rolf Teschke, and Tran Dang Khanh. 2019. "Heavy Metal Accumulation in Water, Soil, and Plants of Municipal Solid Waste Landfill in Vientiane, Laos" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16010022
APA StyleVongdala, N., Tran, H.-D., Xuan, T. D., Teschke, R., & Khanh, T. D. (2019). Heavy Metal Accumulation in Water, Soil, and Plants of Municipal Solid Waste Landfill in Vientiane, Laos. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16010022









