Obesity Inequalities According to Place of Birth: The Role of Education
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Study Population
2.2. Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
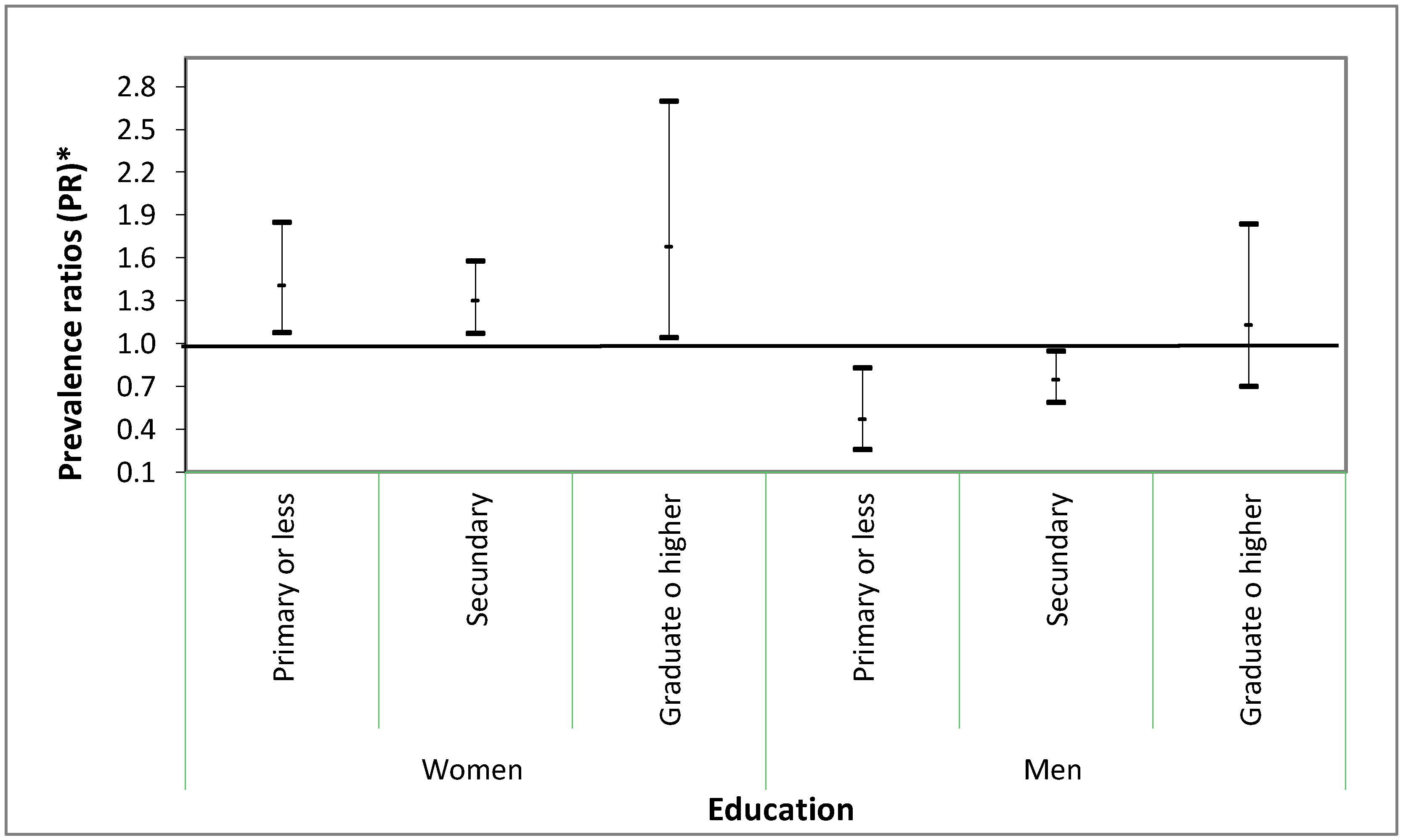
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Naghavi, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegal, K.M.; Kit, B.K.; Orpana, H.; Graubard, B.I. Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2013, 309, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, W.P.T.; McPherson, K. The costs of overweight. Lancet Public Health 2017, 2, e203–e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesare, M.D.; Bentham, J.; Stevens, G.A.; Zhou, B.; Danaei, G.; Lu, Y.; Cowan, M.J.; Riley, L.M.; Hajifathalian, K.; Fortunato, L.; et al. Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: A pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19.2 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Peralta, M.; Naia, A.; Loureiro, N.; de Matos, M.G. Prevalence of adult overweight and obesity in 20 European countries, 2014. Eur. J. Public Health 2018, 28, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, L.; Divajeva, D.; Marsh, T.; McPherson, K.; Brown, M.; Galea, G.; Breda, J. The future burden of obesity-related diseases in the 53 WHO European-Region countries and the impact of effective interventions: A modelling study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenbach, J.P.; Stirbu, I.; Roskam, A.J.; Schaap, M.M.; Menvielle, G.; Leinsalu, M.; Kunst, A.E. Socioeconomic inequalities in health in 22 European countries. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2468–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevenot, C. Inequality in OECD countries. Scand. J. Public Health 2017, 45, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmot, M.; Wilkinson, R.G. Social Determinants of Health: The Solid Facts, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-92-890-1401-4. [Google Scholar]
- Malmusi, D.; Borrell, C.; Benach, J. Migration-related health inequalities: Showing the complex interactions between gender, social class and place of origin. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 71, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Alvarez, E.; Gonzalez-Rabago, Y.; Bacigalupe, A.; Martin, U.; Lanborena Elordui, N. Immigration and health: Social inequalities between native and immigrant populations in the Basque Country (Spain). Gac. Sanit. 2014, 28, 274–280. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrell, C.; Muntaner, C.; Sole, J.; Artazcoz, L.; Puigpinos, R.; Benach, J.; Noh, S. Immigration and self-reported health status by social class and gender: The importance of material deprivation, work organisation and household labour. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2008, 62, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Perez, I.; Bermudez-Tamayo, C.; Rodriguez-Barranco, M. Socio-economic factors linked with mental health during the recession: A multilevel analysis. Int. J. Equity Health 2017, 16, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, A.C.; Wandell, P.; Riserus, U.; Arnlov, J.; Borne, Y.; Engstrom, G.; Leander, K.; Gigante, B.; Hellenius, M.L.; de Faire, U. Differences in anthropometric measures in immigrants and Swedish-born individuals: Results from two community-based cohort studies. Prev. Med. 2014, 69, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkshoorn, H.; Nicolaou, M.; Ujcic-Voortman, J.K.; Schouten, G.M.; Bouwman Notenboom, A.J.; Berns, M.P.; Verhoeff, A.P. Overweight and obesity in young Turkish, Moroccan and Surinamese migrants of the second generation in the Netherlands. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujcic-Voortman, J.K.; Bos, G.; Baan, C.A.; Verhoeff, A.P.; Seidell, J.C. Obesity and body fat distribution: Ethnic differences and the role of socio-economic status. Obes. Facts 2011, 4, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toselli, S.; Gualdi-Russo, E.; Boulos, D.N.; Anwar, W.A.; Lakhoua, C.; Jaouadi, I.; Khyatti, M.; Hemminki, K. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in adults from North Africa. Eur. J. Public Health 2014, 24, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaux, M.; Sassi, F. Social inequalities in obesity and overweight in 11 OECD countries. Eur. J. Public Health 2013, 23, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskam, A.J.; Kunst, A.E.; Van Oyen, H.; Demarest, S.; Klumbiene, J.; Regidor, E.; Helmert, U.; Jusot, F.; Dzurova, D.; Mackenbach, J.P. Comparative appraisal of educational inequalities in overweight and obesity among adults in 19 European countries. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallus, S.; Lugo, A.; Murisic, B.; Bosetti, C.; Boffetta, P.; La Vecchia, C. Overweight and obesity in 16 European countries. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrington, D.S.; Baquero, M.C.; Borrell, L.N.; Crawford, N.D. Racial/ethnic disparities in obesity among US-born and foreign-born adults by sex and education. Obesity 2010, 18, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Vaznaugh, E.V.; Kawachi, I.; Subramanian, S.V.; Sanchez, B.N.; Acevedo-Garcia, D. Differential effect of birthplace and length of residence on body mass index (BMI) by education, gender and race/ethnicity. Soc. Sci. Med. 2008, 67, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Caro, A.; Vallejo-Torres, L.; Lopez-Valcarcel, B. Unconditional quantile regressions to determine the social gradient of obesity in Spain 1993–2014. Int. J. Equity Health 2016, 15, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Statistics of Spain NIE. Population Figures at 1 January 2018. Available online: http://www.ine.es/prensa/pad_2018_p.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2018). (In Spanish).
- Gutierrez-Fisac, J.L.; Marin-Guerrero, A.; Regidor, E.; Guallar-Castillón, P.; Banegas, J.R.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F. Length of residence and obesity among immigrants in Spain. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 13, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín-Guerrero, A.C.; Gutiérrez-Fisac, J.L.; Guallar-Castillón, P.; Banegas, J.R.; Regidor, E.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F. Prevalence of obesity in immigrants in Madrid. Med. Clin. 2010, 134, 483–485. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat. Migrant Integration Statistics-Education Statistics Explained [Internet]. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Migrant_integration_statistics_-_education (accessed on 8 February 2018).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Database on Body Mass Index. 2013. Available online: http://www.who.int/bmi (accessed on 15 September 2017).
- Domingo-Salvany, A.; Bacigalupe, A.; Carrasco, J.M.; Espelt, A.; Ferrando, J.; Borrell, C. Proposals for social class classification based on the Spanish National Classification of Occupations 2011 using neo-Weberian and neo-Marxist approaches. Gac. Sanit. 2013, 27, 263–272. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Alvarez, E.; Gonzalez-Rábago, Y.; Borrell, L.N.; Lanborena, N. Perceived discrimination and self-rated health in the immigrant population of the Basque Country, Spain. Gac. Sanit. 2017, 31, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, L.P.; Dias, S.F.; Martins, M.D. Association between length of residence and overweight among adult immigrants in Portugal: A nationwide cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.N.; Meyer, H.E.; Wandel, M.; Dalen, I.; Holmboe-Ottesen, G. Ethnic differences in obesity among immigrants from developing countries, in Oslo, Norway. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosper, K.; Nicolaou, M.; van Valkengoed, I.; Nierkens, V.; Stronks, K. Social and cultural factors underlying generational differences in overweight: A cross-sectional study among ethnic minorities in the Netherlands. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Fernandez, J.; Grillo, F.; Tichit, C.; Parizot, I.; Chauvin, P. Overweight according to geographical origin and time spent in France: A cross sectional study in the Paris metropolitan area. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, S.; Kidd, M.P.; McDonald, J.T.; Biddle, N. The Healthy Immigrant Effect: Patterns and Evidence from Four Countries. J. Int. Migr. Integr. 2014, 16, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, A.; Gil-Alonso, F. Immigration and changing labour force structure in the southern European Union. Population 2007, 62, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averett, S. Obesity and labor market outcomes. IZA World Labor 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.A.; Fitzhugh, E.C.; Bassett, D.R., Jr.; McLaughlin, J.E.; Strath, S.J.; Swartz, A.M.; Thompson, D.L. Relationship of leisure-time physical activity and occupational activity to the prevalence of obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2001, 25, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlavy, A.C.; Garcy, A.M.; Rostila, M. Educational mismatch and health status among foreign-born workers in Sweden. Soc. Sci. Med. 2016, 154, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Coso, E.; Miret-Gamundi, P. The labour trajectories of immigrant women in Spain: Are there signs of upward social mobility? Demogr. Res. 2014, 31, 337–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahonen, E.Q.; Lopez-Jacob, M.J.; Vazquez, M.L.; Porthe, V.; Gil-González, D.; García, A.M.; Ruiz-Frutos, C.; Benach, J.; Benavides, F.G. Invisible work, unseen hazards: The health of women immigrant household service workers in Spain. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2010, 53, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwa, S.A.; Must, A.; Perea, F.C.; Boulos, R.J.; Economos, C.D. Occupational Physical Activity and Weight-Related Outcomes in Immigrant Mothers. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 51, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyholm, M.; Gullberg, B.; Merlo, J.; Lundqvist-Persson, C.; Rastam, L.; Lindblad, U. The validity of obesity based on self-reported weight and height: Implications for population studies. Obesity 2007, 15, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | Women | Men | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immigrants n = 1338 | Natives n = 12,624 | Total n = 13,962 | p-Value * | Immigrants n = 1093 | Natives n = 12,665 | Total n = 13,758 | p-Value * | |
| % (SE) ** | % (SE) | % (SE) | % (SE) | % (SE) | % (SE) | |||
| Survey year | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 2011 | 50.6 (1.7) | 49.4 (0.5) | 49.6 (0.5) | 52.7 (1.9) | 49.6 (0.5) | 49.9 (0.5) | ||
| 2014 | 49.4 (1.7) | 50.6 (0.5) | 50.6 (0.5) | 47.3 (1.9) | 50.4 (0.5) | 50.1 (0.5) | ||
| Region of origin | ||||||||
| Europe | 24.3 (1.5) | 22.7 (1.6) | ||||||
| Africa | 16.2 (1.4) | 27.0 (1.7) | ||||||
| Latin America | 54.2 (1.7) | 44.8 (1.9) | ||||||
| Asia | 5.3 (0.8) | 5.5 (0.9) | ||||||
| Age (years) | 36.8 (0.35) | 41.9 (0.14) | 41.2 (0.13) | <0.001 | 36.8 (0.42) | 41.7 (0.14) | 41.1 (0.13) | <0.001 |
| 18–24 | 11.3 (1.2) | 10.6 (0.4) | 10.7 (0.4) | <0.001 | 13.8 (1.4) | 10.3 (0.4) | 10.7 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| 25–44 | 65.2 (1.6) | 45.4 (0.5) | 48.3 (0.5) | 62.4 (1.9) | 46.8 (0.5) | 48.7 (0.5) | ||
| 45–64 | 23.4 (1.4) | 44.0 (0.5) | 41.0 (0.5) | 23.8 (1.6) | 42.9 (0.5) | 40.6 (0.5) | ||
| Educational attainment | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Primary or less | 18.3 (1.4) | 13.7 (0.4) | 14.4 (0.4) | 18.6 (1.5) | 14.5 (0.4) | 15.0 (0.4) | ||
| Secondary | 67.8 (1.6) | 61.1 (0.5) | 62.0 (0.5) | 69.0 (1.7) | 66.5 (0.5) | 66.8 (0.5) | ||
| Graduate or higher | 13.9 (1.1) | 25.3 (0.5) | 23.6 (0.4) | 12.3 (1.1) | 19.1 (0.4) | 18.2 (0.4) | ||
| Social Class | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Manual | 83.1 (1.2) | 55.9 (0.5) | 59.8 (0.5) | 84.0 (1.4) | 58.4 (0.5) | 61.4 (0.5) | ||
| Non-manual | 16.9 (1.2) | 44.1 (0.5) | 40.2 (0.5) | 16.0 (1.4) | 41.6 (0.5) | 38.6 (0.5) | ||
| Employment status | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Employed | 52.4 (1.7) | 54.4 (0.5) | 54.1 (0.5) | 56.6 (1.9) | 66.4 (0.5) | 65.3 (0.5) | ||
| Unemployed | 22.8 (1.4) | 17.2 (0.4) | 18.0 (0.4) | 33.5 (1.8) | 18.2 (0.4) | 20.0 (0.4) | ||
| Others | 24.7 (1.5) | 28.5 (0.5) | 27.9 (0.5) | 9.9 (1.2) | 15.4 (0.4) | 14.7 (0.4) | ||
| Living arrangement | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Married/Couple | 43.7 (1.7) | 41.0 (0.5) | 41.4 (0.5) | 61.7 (1.8) | 58.0 (0.5) | 58.4 (0.5) | ||
| Other | 56.3 (1.7) | 59.0 (0.5) | 58.6 (0.5) | 38.3 (1.8) | 42.0 (0.5) | 41.6 (0.5) | ||
| Self-rated health | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Good | 71.1 (1.6) | 76.0 (0.4) | 75.3 (0.4) | 81.1 (1.5) | 81.2 (0.4) | 81.2 (0.4) | ||
| Poor | 28.9 (1.6) | 24.0 (0.4) | 24.7 (0.4) | 18.9 (1.5) | 18.8 (0.4) | 18.8 (0.4) | ||
| Smoking status | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Current Smoker | 17.0 (1.2) | 29.4 (0.5) | 27.6 (0.5) | 32.4 (1.5) | 35.9 (0.5) | 35.5 (0.5) | ||
| Former Smoker | 10.8 (1.0) | 21.2 (0.4) | 19.7 (0.4) | 18.7 (1.5) | 26.1 (0.5) | 25.2 (0.4) | ||
| Never smoked | 72.2 (1.5) | 49.5 (0.5) | 52.7 (0.5) | 48.9 (1.9) | 38.0 (0.5) | 39.3 (0.5) | ||
| Alcohol consumption | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Frequent | 16.9 (1.2) | 28.6 (0.5) | 26.9 (0.4) | 36.5 (1.8) | 55.4 (0.5) | 53.2 (0.5) | ||
| Occasional | 36.8 (1.6) | 36.2 (0.5) | 36.3 (0.5) | 28.8 (1.7) | 28.3 (0.5) | 28.3 (0.5) | ||
| Not last year/never | 46.3 (1.7) | 35.2 (0.5) | 36.8 (0.5) | 34.7 (1.8) | 16.3 (0.4) | 18.5 (0.4) | ||
| Workplace physical activity | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Sedentary | 77.6 (1.4) | 85.8 (0.4) | 84.6 (0.4) | 68.0 (1.7) | 76.6 (0.4) | 75.6 (0.4) | ||
| Active | 22.4 (14) | 14.2 (0.4) | 15.4 (0.4) | 32.0 (1.7) | 23.4 (0.4) | 24.4 (0.4) | ||
| Leisure-time physical activity | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Sedentary | 54.4 (1.7) | 41.1 (0.5) | 43.0 (0.5) | 40.5 (1.9) | 33.2 (0.5) | 34.0 (0.5) | ||
| Active | 45.6 (1.7) | 58.9 (0.5) | 570 (0.5) | 59.5 (1.9) | 66.8 (0.5) | 66.0 (0.5) | ||
| Daily Consumption of fruit and vegetable | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Yes | 37.5 (1.7) | 39.6 (0.5) | 39.3 (0.5) | 29.2 (1.7) | 28.8 (0.5) | 28.8 (0.5) | ||
| No | 62.5 (1.7) | 60.4 (0.5) | 60.7 (0.5) | 70.8 (1.7) | 71.2 (0.5) | 71.2 (0.5) | ||
| BMI, Kg/M2 | 25.7 (0.18) | 24.5 (0.05) | 24.7 (0.05) | <0.001 | 25.9 (0.13) | 26.4 (0.04) | 26.3 (0.04) | <0.001 |
| Characteristic | Women | Men | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immigrants n = 1338 | Natives n = 12,624 | Total n = 13,962 | p-Value * | Immigrants n = 1093 | Natives n = 12,665 | Total n = 13,758 | p-Value * | |
| % (SE) | % (SE) | % (SE) | % (SE) | % (SE) | % (SE) | |||
| Overall | 20.0 (1.4) | 12.5 (0.3) | 13.6 (0.4) | <0.001 | 12.5 (1.2) | 16.9 (0.4) | 16.4 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| Survey year | 0.257 | 0.192 | ||||||
| 2011 | 16.3 (1.9) | 12.7 (0.5) | 13.2 (0.5) | 12.9 (1.7) | 17.4 (0.6) | 16.9 (0.5) | ||
| 2014 | 23.8 (2.1) | 12.3 (0.5) | 14.0 (0.5) | 12.0 (2.1) | 16.5 (0.5) | 16.0 (0.5) | ||
| Region of origin | ||||||||
| Europe | 15.4 (2.8) | 13.4 (2.6) | ||||||
| Africa | 30.9 (4.3) | 10.7 (2.3) | ||||||
| Latin America | 20.5 (1.9) | 13.8 (1.9) | ||||||
| Asia | 2.7 (1.7) | 6.1 (3.4) | ||||||
| Age (years) | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 18–24 | 6.4 (2.5) | 4.4 (0.8) | 4.7 (0.8) | 2.8 (1.5) | 5.4 (0.9) | 5.0 (0.8) | ||
| 25–44 | 18.4 (1.7) | 9.7 (0.5) | 11.4 (0.5) | 12.4 (1.5) | 13.7 (0.5) | 13.5 (0.5) | ||
| 45–64 | 30.9 (3.4) | 17.3 (0.6) | 18.4 (0.6) | 18.4 (3.0) | 23.2 (0.6) | 22.9 (0.6) | ||
| Educational attainment | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Primary or less | 35.2 (4.4) | 25.6 (1.2) | 27.4 (1.3) | 10.3 (2.8) | 24.8 (1.2) | 22.7 (1.1) | ||
| Secondary | 17.5 (1.6) | 12.3 (0.4) | 13.2 (0.5) | 12.5 (1.5) | 17.1 (0.5) | 16.5 (0.5) | ||
| Graduate or higher | 12.1(2.7) | 5.8 (0.5) | 6.3 (0.5) | 15.5 (3.4) | 10.5 (0.7) | 10.9 (0.7) | ||
| Social class | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Manual | 21.7 (1.6) | 15.7 (0.5) | 16.9 (0.5) | 11.8 (1.3) | 19.5 (0.5) | 18.3 (0.5) | ||
| Non-manual | 11.4 (2.5) | 8.4 (0.4) | 8.6 (0.4) | 16.0 (3.2) | 13.3 (0.5) | 13.5 (0.5) | ||
| Employment status | <0.001 | 0.016 | ||||||
| Employed | 16.1 (1.8) | 9.4 (0.4) | 10.3 (0.4) | 12.1 (1.5) | 16.2 (0.5) | 15.7 (0.4) | ||
| Unemployed | 22.1 (2.9) | 16.0 (1.0) | 17.1 (0.9) | 15.2 (2.5) | 18.9 (1.0) | 18.2 (0.9) | ||
| Others | 26.2 (3.4) | 16.3(0.7) | 17.6 (0.8) | 5.3 (2.5) | 18.0 (1.0) | 17.0 (1.0) | ||
| Living arrangement | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Married/Couple | 23.4 (2.1) | 14.2 (0.5) | 15.5 (0.5) | 16.7 (1.8) | 20.0 (0.5) | 19.5 (0.5) | ||
| Other | 15.6 (1.9) | 10.0 (0.5) | 10.9 (0.5) | 5.6 (1.1) | 12.8 (0.5) | 12.0 (0.5) | ||
| Self-rated health | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Good | 14.8 (1.5) | 9.6 (0.4) | 10.3 (0.4) | 11.9 (1.3) | 14.9 (0.4) | 14.5 (0.4) | ||
| Poor | 32.7 (3.2) | 21.6 (0.9) | 23.5 (0.9) | 14.9 (1.3) | 26.0 (1.0) | 24.6 (1.0) | ||
| Smoking status | 0.032 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Current smoker | 21.0 (3.5) | 10.9 (0.6) | 11.8 (0.6) | 9.2 (1.9) | 15.5 (0.6) | 14.8 (0.6) | ||
| Former smoker | 22.0 (3.9) | 12.4 (0.8) | 13.1 (0.8) | 17.3 (3.2) | 23.2 (0.8) | 22.7 (0.8) | ||
| Never smoked | 19.4 (1.7) | 13.5 (0.5) | 14.7 (0.5) | 12.8 (1.8) | 14.0 (0.6) | 13.8 (0.6) | ||
| Alcohol consumption | <0.001 | 0.110 | ||||||
| Frequent | 14.0 (2.7) | 8.8 (0.5) | 9.2 (0.6) | 13.8 (2.1) | 16.4 (0.5) | 16.2 (0.5) | ||
| Occasional | 17.5 (2.2) | 11.2 (0.5) | 12.2 (0.6) | 14.2 (2.5) | 16.3 (0.7) | 16.1 (0.7) | ||
| Not last year/never | 24.1 (2.3) | 16.8 (0.7) | 18.1 (0.7) | 9.7 (1.8) | 20.0 (1.1) | 17.7 (0.9) | ||
| Workplace physical activity | 0.718 | 0.273 | ||||||
| Sedentary | 19.7 (1.6) | 12.5 (0.4) | 13.4 (0.4) | 12.8 (1.5) | 17.2 (0.4) | 16.7 (0.4) | ||
| Active | 20.9 (3.1) | 12.7 (0.9) | 14.4 (1.0) | 11.7 (2.2) | 16.2 (0.8) | 15.5 (0.7) | ||
| Leisure-time physical activity | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Sedentary | 22.8 (2.1) | 16.0 (0.6) | 17.2 (0.6) | 12.2 (1.8) | 24.0 (0.8) | 22.4 (0.7) | ||
| Active | 16.7 (1.9) | 10.1 (0.4) | 10.8 (0.4) | 12.7 (1.6) | 13.4 (0.4) | 13.3 (0.4) | ||
| Daily Consumption of fruit and vegetables | 0.409 | 0.471 | ||||||
| Yes | 19.8 (2.4) | 13.0 (0.5) | 13.4 (0.5) | 12.5 (1.2) | 17.4 (0.7) | 16.8 (0.7) | ||
| No | 20.1 (1.8) | 12.2 (0.4) | 13.9 (0.6) | 12.4 (1.5) | 16.8 (0.5) | 16.2 (0.4) | ||
| Place of Birth | Unadjusted | Model 1 * | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women | ||||||
| Natives | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Immigrants | 1.60 (1.3–1.86) | 1.60 (1.3–1.86) | 1.73 (1.5–2.00) | 1.73 (1.5–2.01) | 1.56 (1.3–1.81) | 1.42 (1.2–1.64) |
| Men | ||||||
| Natives | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Immigrants | 0.74 (0.60–0.89) | 0.73 (0.6–0.89) | 0.83 (0.6–1.01) | 0.79 (0.6–0.95) | 0.75 (0.6–0.92) | 0.73 (0.5–0.89) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez-Alvarez, E.; Lanborena, N.; Borrell, L.N. Obesity Inequalities According to Place of Birth: The Role of Education. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081620
Rodriguez-Alvarez E, Lanborena N, Borrell LN. Obesity Inequalities According to Place of Birth: The Role of Education. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(8):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081620
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez-Alvarez, Elena, Nerea Lanborena, and Luisa N. Borrell. 2018. "Obesity Inequalities According to Place of Birth: The Role of Education" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 8: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081620
APA StyleRodriguez-Alvarez, E., Lanborena, N., & Borrell, L. N. (2018). Obesity Inequalities According to Place of Birth: The Role of Education. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(8), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081620





