Evaluation of an Early-Warning System for Heat Wave-Related Mortality in Europe: Implications for Sub-seasonal to Seasonal Forecasting and Climate Services
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Temperature-Mortality Model
2.2. Climate Forecasts
3. Results
3.1. Excess Mortality Probability Maps Using Climate Forecasts at Increasing Lead Times

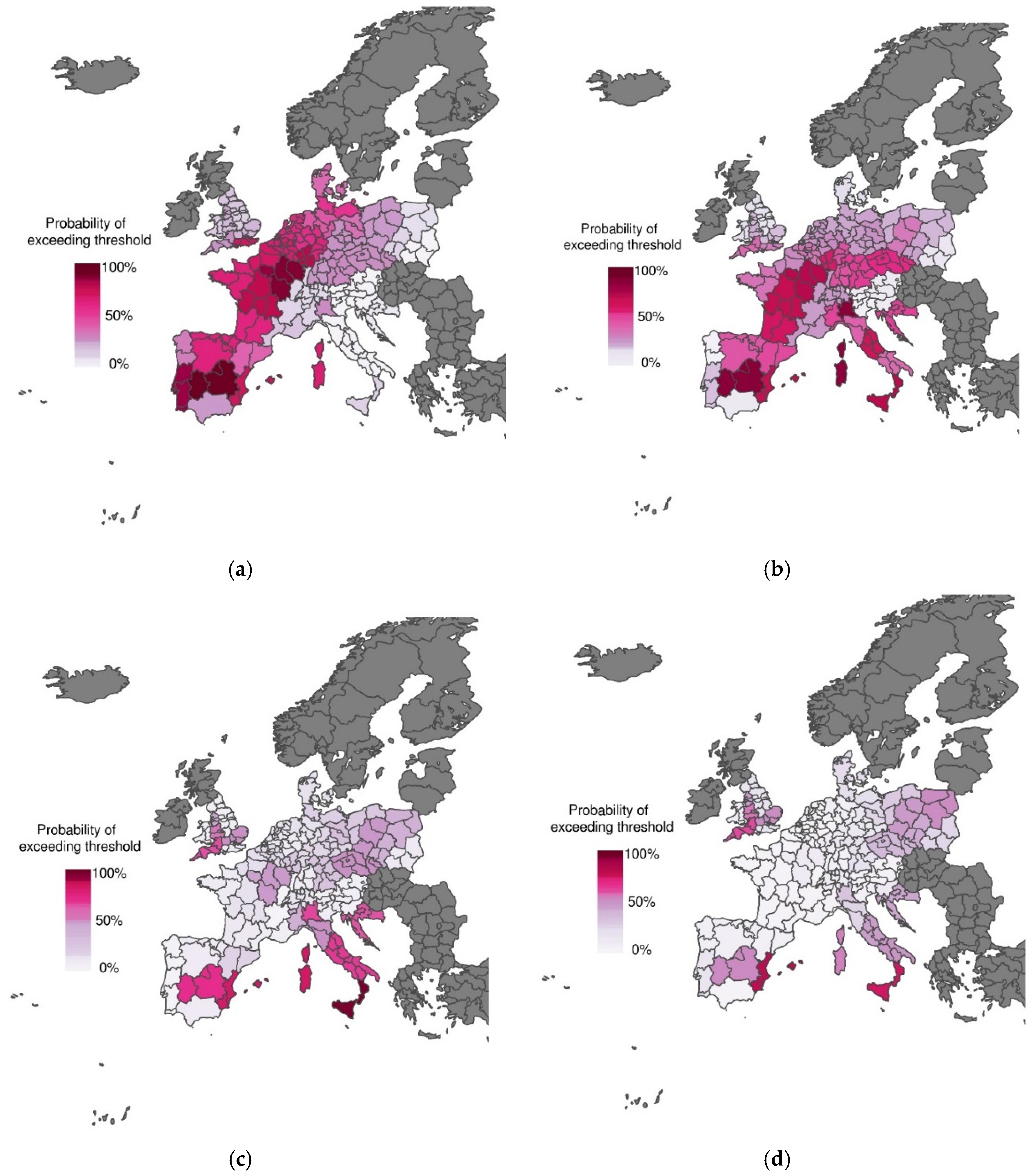
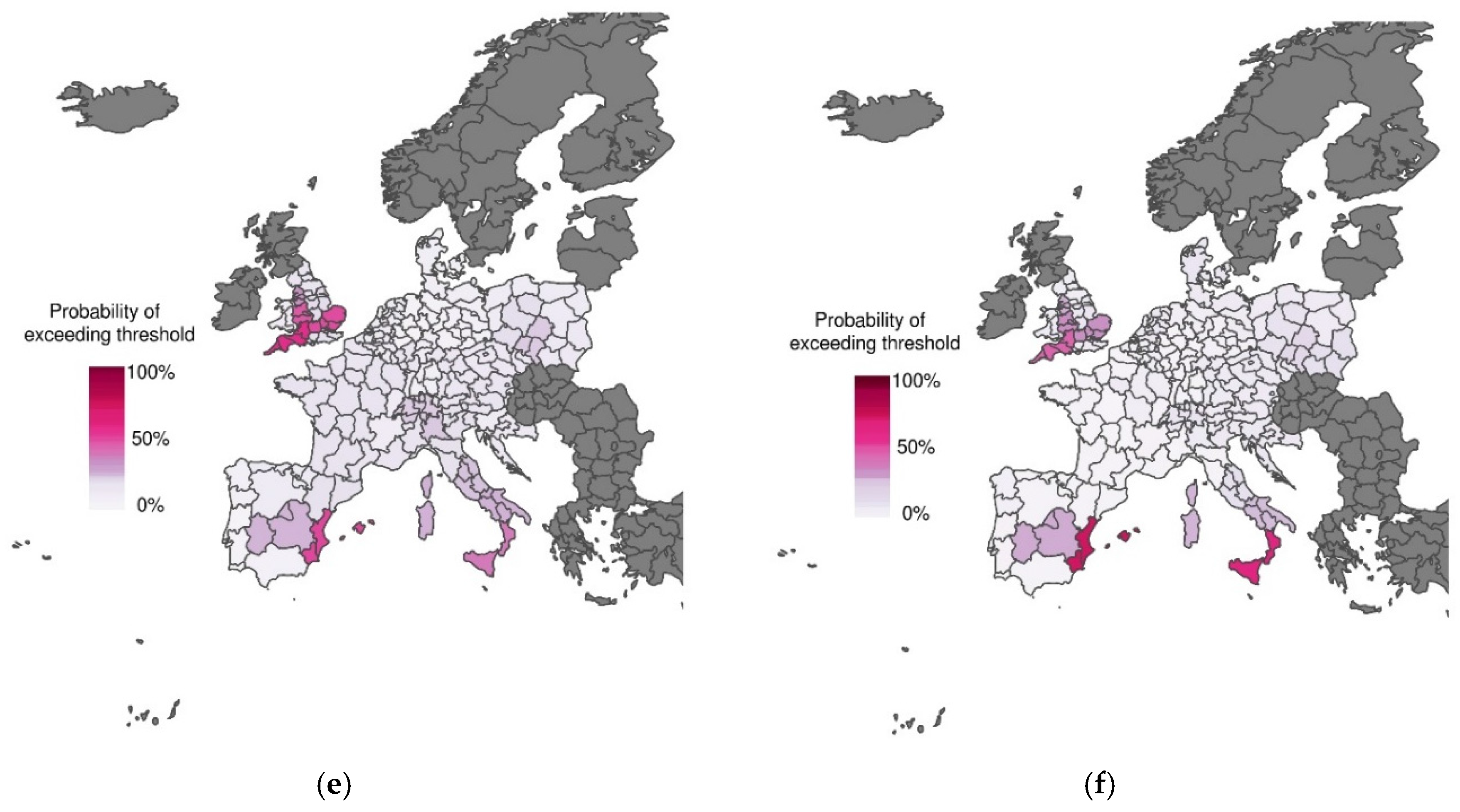
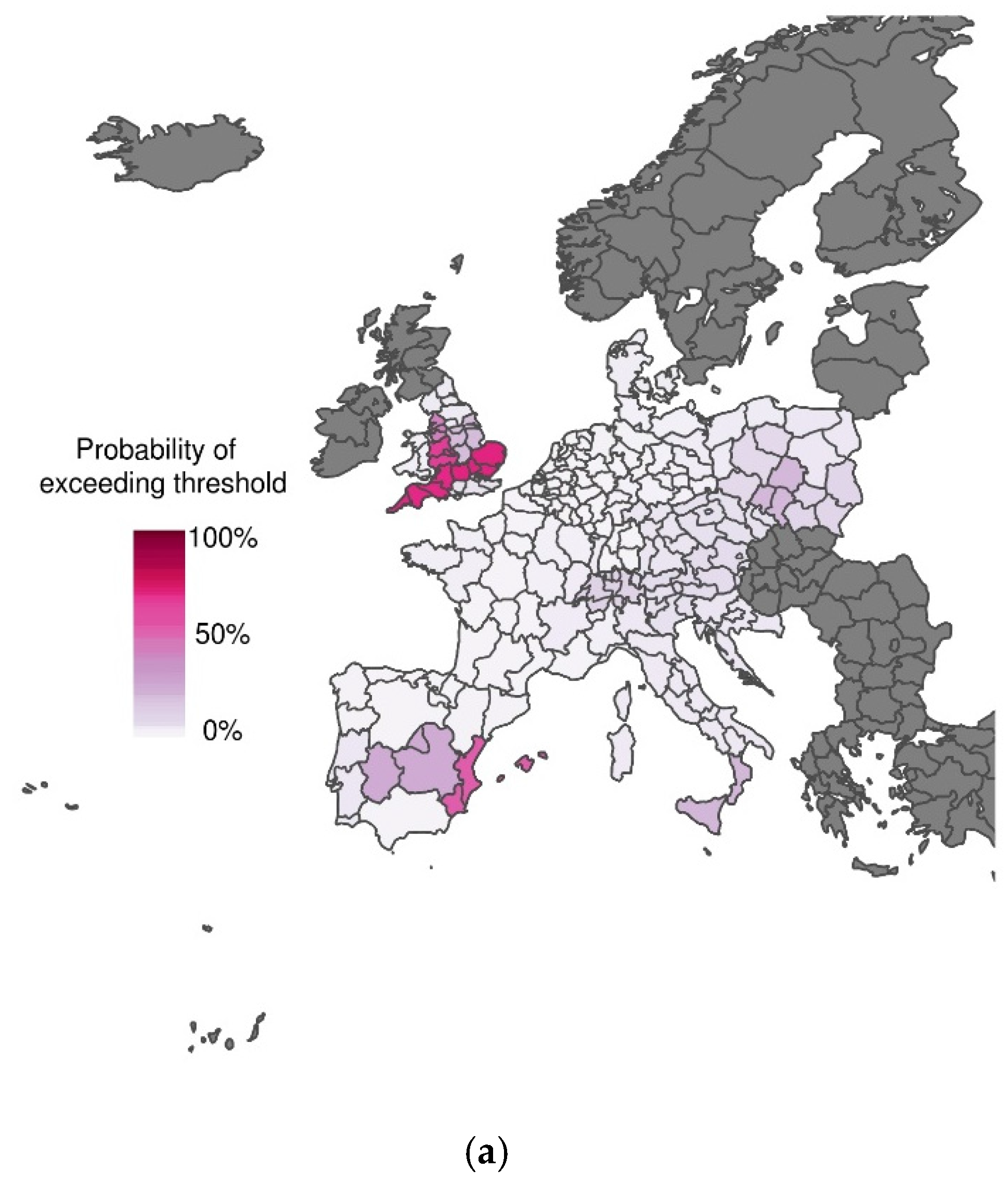
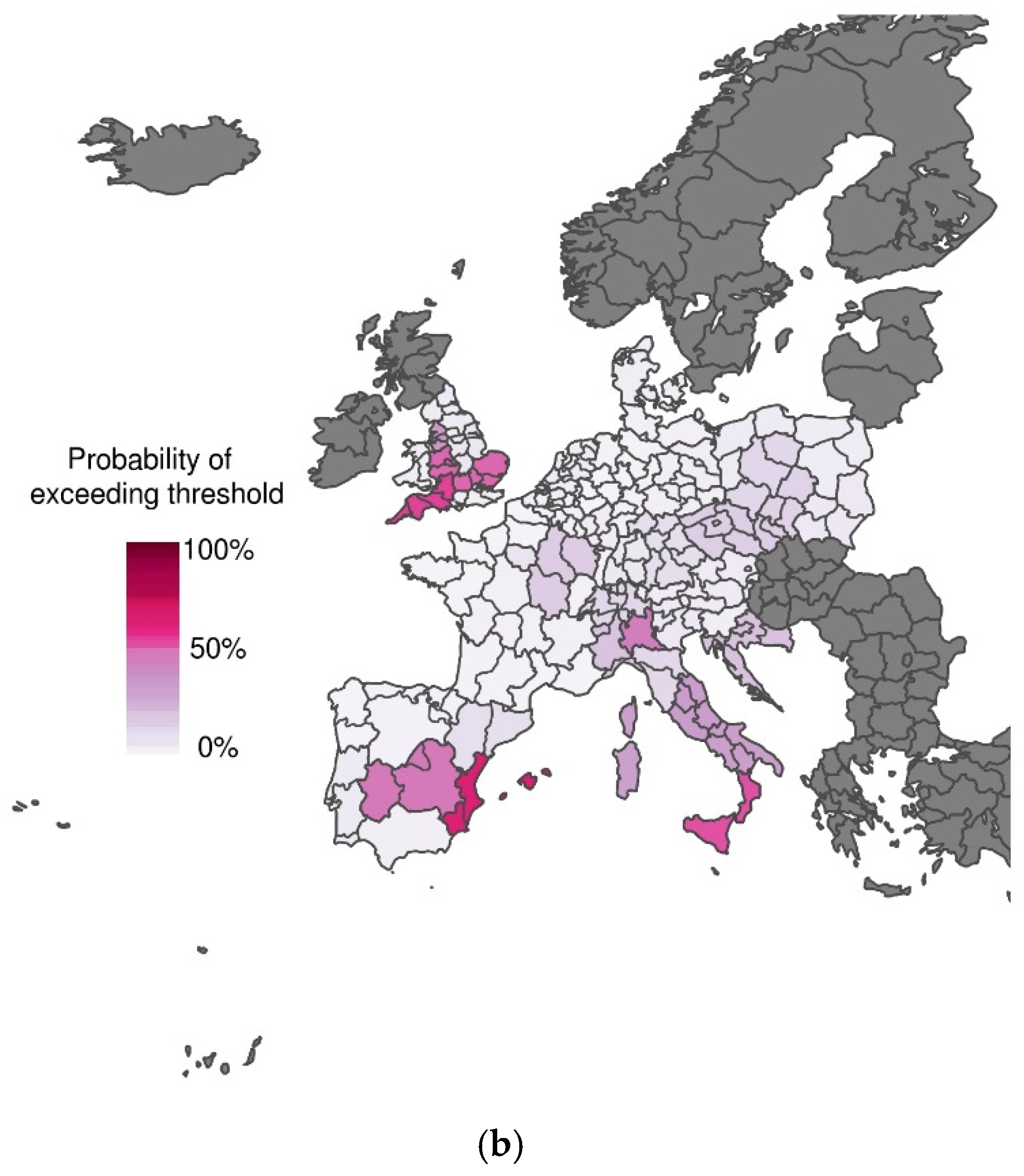
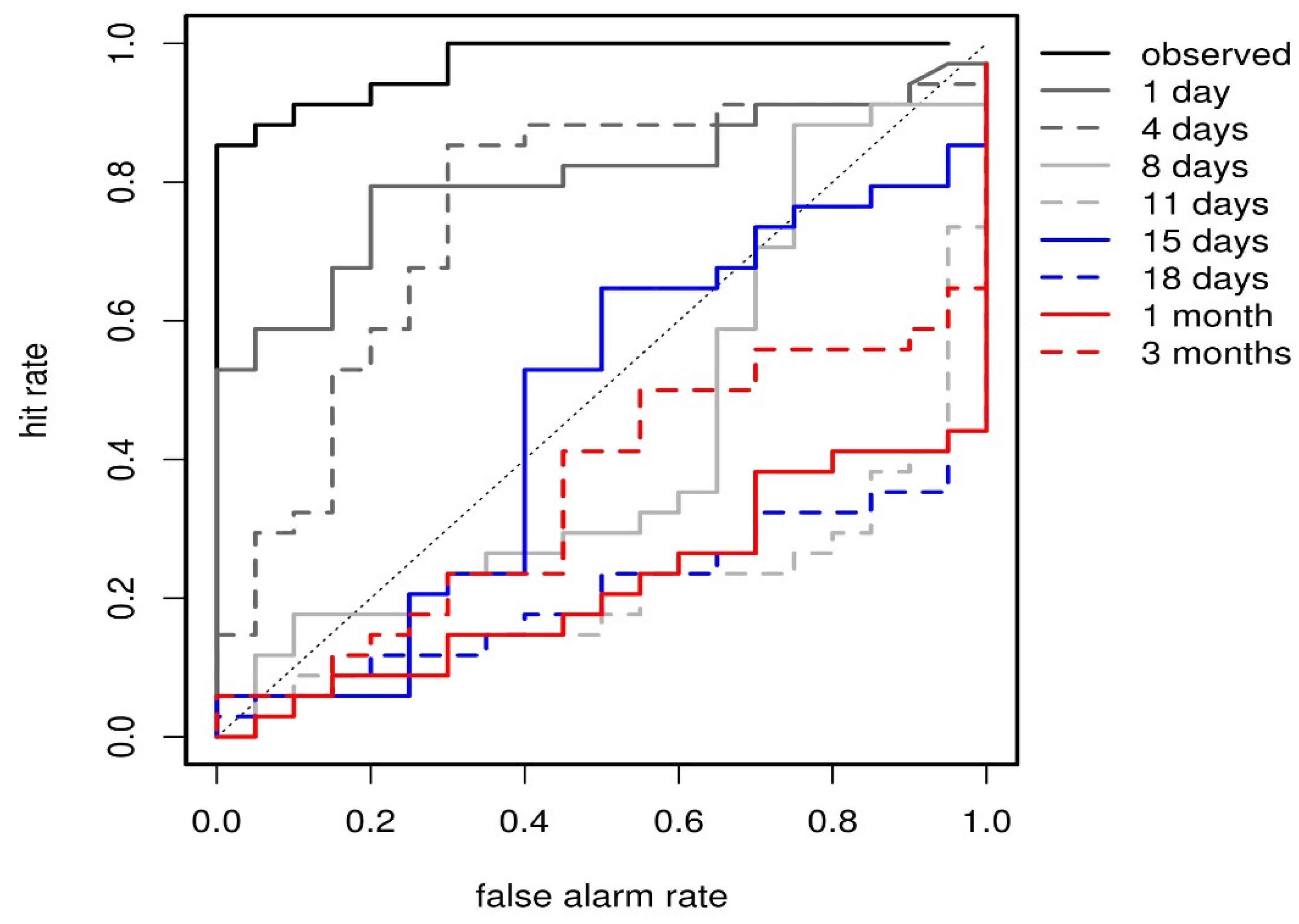
3.2. Skill Assessment for Increasing Forecast Lead Time
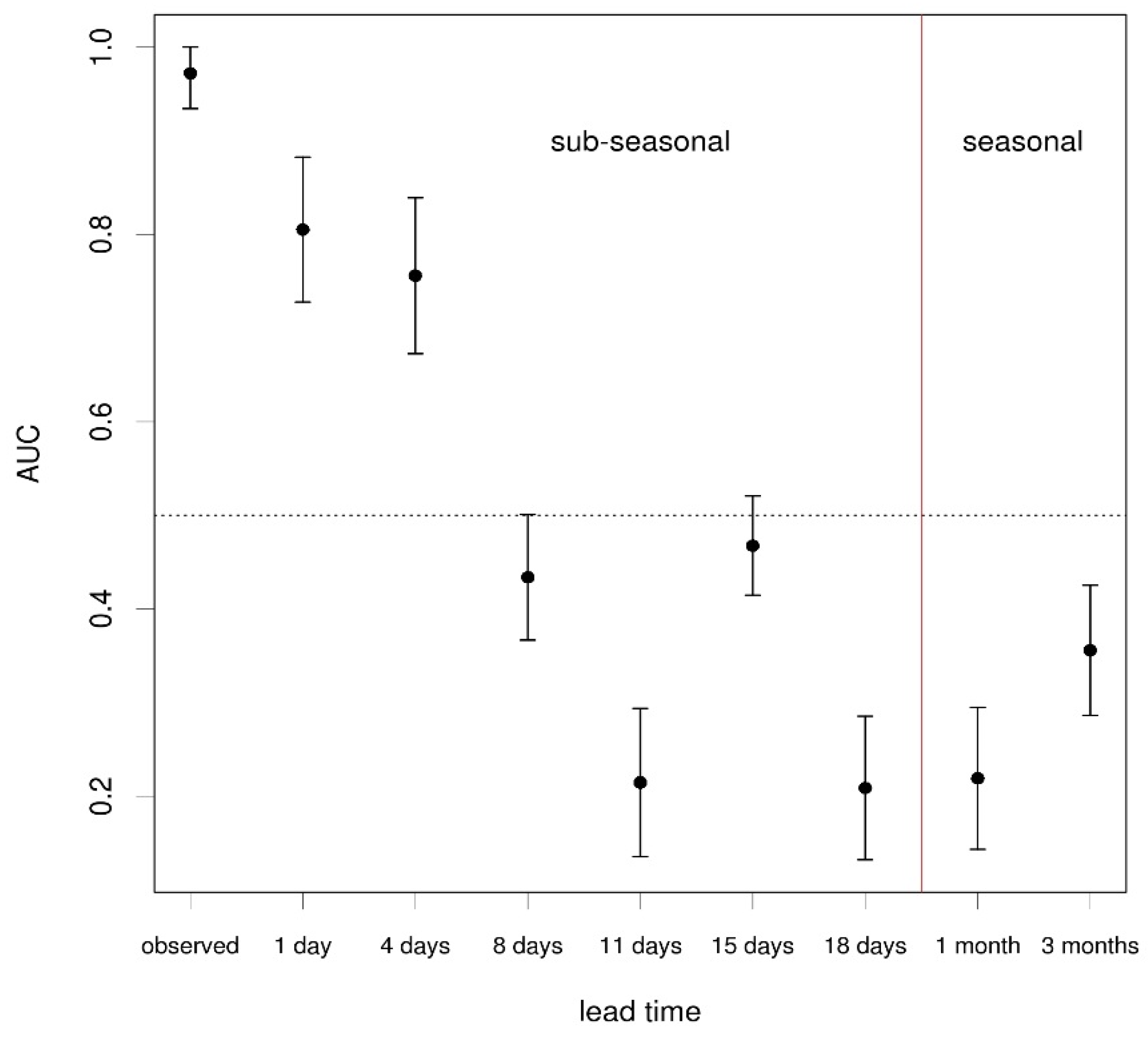
| Climate Forecast Lead Time | Mean AUC (95% Confidence Intervals) |
| Observed | 0.97 (0.93, 1.00) |
| 1 day | 0.81 (0.73, 0.88) |
| 4 days | 0.76 (0.67, 0.84) |
| 8 days | 0.43 (0.37, 0.5) |
| 11 days | 0.21 (0.14, 0.29) |
| 15 days | 0.47 (0.41, 0.52) |
| 18 days | 0.21 (0.13, 0.29) |
| 1 month | 0.22 (0.14, 0.29) |
| 3 months | 0.36 (0.29, 0.43) |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patz, J.A.; Campbell-Lendrum, D.; Holloway, T.; Foley, J.A. Impact of regional climate change on human health. Nature 2005, 438, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostro, B.; Barrera-Gómez, J.; Ballester, J.; Basagaña, X.; Sunyer, J. The impact of future summer temperature on public health in Barcelona and Catalonia, Spain. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Meyer, L. IPCC Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Climate Change, Impacts and Vulnerability in Europe 2012; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi, F. Climate change hot-spots. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robine, J.-M.; Cheung, S.L.K.; Roy, S.L.; Oyen, H.V.; Griffiths, C.; Michel, J.-P.; Herrmann, F.R. Death toll exceeded 70,000 in Europe during the summer of 2003. C. R. Biol. 2008, 331, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouillet, A.; Rey, G.; Wagner, V.; Laaidi, K.; Empereur-Bissonnet, P.; Le Tertre, A.; Frayssinet, P.; Bessemoulin, P.; Laurent, F.; De Crouy-Chanel, P.; et al. Has the impact of heat waves on mortality changed in France since the European heat wave of summer 2003? A study of the 2006 heat wave. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 37, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aström, C.; Orru, H.; Rocklöv, J.; Strandberg, G.; Ebi, K.L.; Forsberg, B. Heat-related respiratory hospital admissions in Europe in a changing climate: A health impact assessment. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e001842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajat, S.; Barnard, L.T.; Butler, C. Heat-related and cold-related mortality and morbidity. In Climate Change and Global Health; CABI International: Wallingford, UK, 2014; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Quantitative Risk Assessment of the Effects of Climate Change on Selected Causes of Death, 2030s and 2050s; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ballester, J.; Robine, J.-M.; Herrmann, F.R.; Rodó, X. Long-term projections and acclimatization scenarios of temperature-related mortality in Europe. Nat. Commun. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.R.; Woodward, A.; Campbell-Lendrum, D.; Chadee, D.; Honda, Y.; Liu, Q.; Olwoch, J.M.; Revich, B.; Sauerborn, R. Human health: Impacts, adaptation, and co-benefits. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel of Climate Change; Field, C.B., Barros, V.R., Dokken, D.J., Mach, K.J., Mastrandrea, M.D., Bilir, T.E., Chatterjee, M., Ebi, K.L., Estrada, Y.O., Genova, R.C., Girma, B., Kissel, E.S., Levy, A.N., MacCracken, S., Mastrandrea, P.R., White, L.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 709–754. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparrini, A.; Guo, Y.; Hashizume, M.; Lavigne, E.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J.; Tobias, A.; Tong, S.; Rocklöv, J.; Forsberg, B.; et al. Mortality risk attributable to high and low ambient temperature: A multicountry observational study. Lancet 2015, 386, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, G.; Ermakov, S.; Komarov, Y.; McDonald, C.; Keatinge, W. Cold related mortalities and protection against cold in Yakutsk, eastern Siberia: Observation and interview study. BMJ 1998, 317, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobb, J.F.; Peng, R.D.; Bell, M.L.; Dominici, F. Heat-related mortality and adaptation to heat in the United States. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner, M.I.; Matthies, E.F.; Dalbokova, D.; Menne, B. Are European countries prepared for the next big heat-wave? Eur. J. Public Health 2014, 24, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, G.R.; Bessemoulin, P.; Ebi, K.L.; Menne, B. Heatwaves and Health: Guidance on Warning-System Development; World Meteorological Organization and World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Matthies, F.; Bickler, G.; Marin, N.; Hales, S. WHO Europe, Heat–Health Action Plans; Matthies, F., Bickler, G., Marin, N., Hales, S., Eds.; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, R.; Ballester, J.; Creswick, J.; Robine, J.-M.; Herrmann, F.R.; Rodó, X. Evaluating the performance of a climate-driven mortality model during heat waves and cold spells in Europe. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 1279–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dee, D.; Uppala, S.; Simmons, A.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, F.; Stockdale, T.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Buizza, R.; Ferranti, L.; Magnusson, L.; Mogensen, K.; Palmer, T.; Vitart, F. The New ECMWF Seasonal Forecast System (System 4); European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts: Reading, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vitart, F. Monthly forecasting at ECMWF. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 2761–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlstein, I.; Spirig, C.; Liniger, M.A.; Appenzeller, C. Estimating daily climatologies for climate indices derived from climate model data and observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2808–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzanas, R.; Fernández, J.; Magariño, M.E.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; José Doblas-Reyes, F.; Nikulin, G.; Buontempo, C. Assessing the Drift of Seasonal Forecasts. In EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts; Copernicus Publications: Göttingen, Germany, 2014; Volume 16, p. 15360. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, S.J.; Graham, N.E. Areas beneath the relative operating characteristics (ROC) and relative operating levels (ROL) curves: Statistical significance and interpretation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 128, 2145–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, J.; Bithell, J. Bootstrap confidence intervals: When, which, what? A practical guide for medical statisticians. Stat. Med. 2000, 19, 1141–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaife, A.; Arribas, A.; Blockley, E.; Brookshaw, A.; Clark, R.; Dunstone, N.; Eade, R.; Fereday, D.; Folland, C.; Gordon, M.; et al. Skillful long-range prediction of European and North American winters. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 2514–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodhomme, C.; Doblas-Reyes, F.; Bellprat, O.; Dutra, E. Impact of land-surface initialization on sub-seasonal to seasonal forecasts over Europe. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitart, F. Evolution of ECMWF sub-seasonal forecast skill scores. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 140, 1889–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lowe, R.; García-Díez, M.; Ballester, J.; Creswick, J.; Robine, J.-M.; Herrmann, F.R.; Rodó, X. Evaluation of an Early-Warning System for Heat Wave-Related Mortality in Europe: Implications for Sub-seasonal to Seasonal Forecasting and Climate Services. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13020206
Lowe R, García-Díez M, Ballester J, Creswick J, Robine J-M, Herrmann FR, Rodó X. Evaluation of an Early-Warning System for Heat Wave-Related Mortality in Europe: Implications for Sub-seasonal to Seasonal Forecasting and Climate Services. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2016; 13(2):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13020206
Chicago/Turabian StyleLowe, Rachel, Markel García-Díez, Joan Ballester, James Creswick, Jean-Marie Robine, François R. Herrmann, and Xavier Rodó. 2016. "Evaluation of an Early-Warning System for Heat Wave-Related Mortality in Europe: Implications for Sub-seasonal to Seasonal Forecasting and Climate Services" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 13, no. 2: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13020206
APA StyleLowe, R., García-Díez, M., Ballester, J., Creswick, J., Robine, J.-M., Herrmann, F. R., & Rodó, X. (2016). Evaluation of an Early-Warning System for Heat Wave-Related Mortality in Europe: Implications for Sub-seasonal to Seasonal Forecasting and Climate Services. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(2), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13020206




