Improvement Effect and Regulation Mechanism of Oyster Peptide on Dexamethasone-Induced Osteoporotic Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
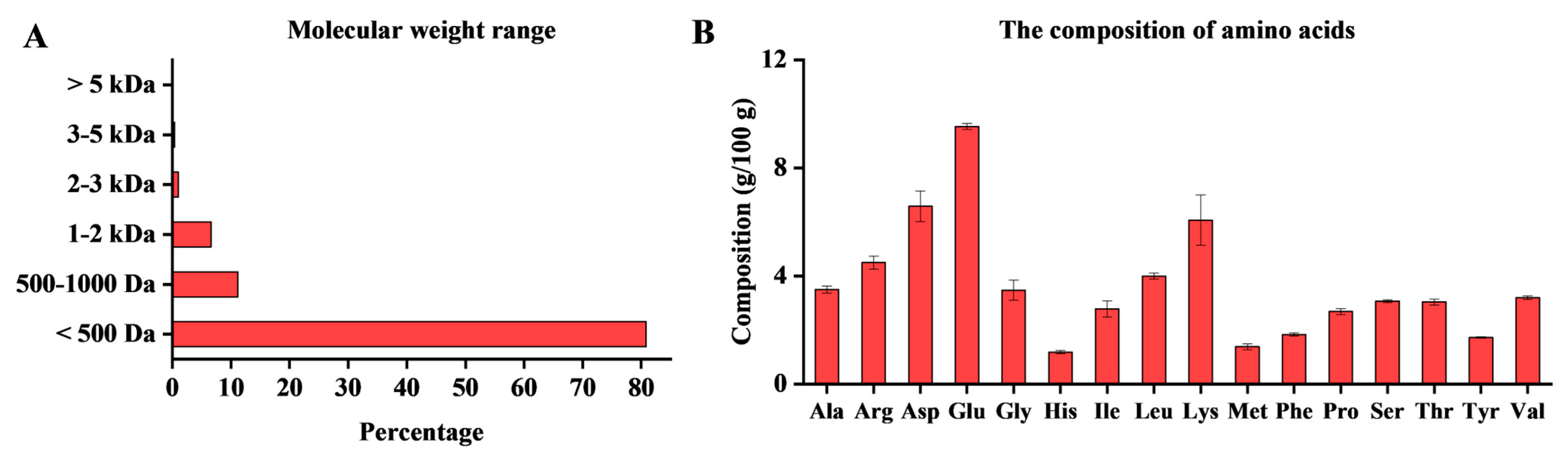
2.1. Composition Analysis of OP
2.2. Effects of OP on Body Weight and Organs
2.3. Protective Effect of OP Against Bone Loss
2.4. OP Ameliorates Bone Loss by Promoting Bone Formation
2.5. OP Ameliorates Bone Loss by Inhibiting Bone Resorption
2.6. Screening of Potential Anti-Osteoporotic Active Peptides
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. OP Preparation
4.3. Protein Content, Amino Acid Composition, and Molecular Weight Distribution of OP
4.4. Animal Experiment Design
4.5. Histopathological Analysis
4.6. Micro-Computed Tomography Analysis
4.7. Determination of Bone Formation and Bone Absorption Indicators
4.8. Peptidomics
4.9. Proteomics
4.10. Molecular Docking Simulation
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AS | Alendronate Sodium |
| BALP | Bone Alkaline Phosphatase |
| BV | Bone Volume |
| Cath-K | Cathepsin K |
| CTX-1 | C-Terminal Telopeptide of Type I Collagen |
| DEX | Dexamethasone, Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate |
| DIA | Data-Independent Acquisition |
| DPD | Deoxypyridine |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| MMP-9 | Matrix Metallopeptidase 9 |
| OCN | Osteocalcin |
| OG | Gushukang Granules, Osteoporosis Granules |
| OP | Oyster Peptide |
| OPG | Osteoprotegerin |
| OPH | High-Dose Oyster Peptide |
| OPL | Low-Dose Oyster Peptide |
| OPM | Medium-Dose Oyster Peptide |
| PINP | N-Terminal Propeptides of Procollagen Type Ⅰ |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| Runx2 | Runt-Related Transcription Factor 2 |
| Tb.N | Trabecular Number |
| Tb.Sp | Trabecular Separation |
| Tb.Th | Trabecular Thickness |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| TRACP-5b | Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase 5b |
| TV | Tissue Volume |
| OVX | Ovariectomy |
References
- Salari, N.; Ghasemi, H.; Mohammadi, L.; Behzadi, M.H.; Rabieenia, E.; Shohaimi, S.; Mohammadi, M. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Fu, D. Advances in pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies for osteoporosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 237, 108168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhukhan, S.; Sethi, S.; Rajender, S.; Mithal, A.; Chattopadhyay, N. Understanding the characteristics of idiopathic osteoporosis by a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine 2023, 82, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, F.; Meng, K.; Gu, Z.; Yun, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, Q.; Pan, F.; Shen, X.; Xia, G.; et al. Arecanut (Areca catechu L.) seed polyphenol-ameliorated osteoporosis by altering gut microbiome via LYZ and the immune system in estrogen-deficient rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Lu, L.; Yu, X. The relationship between bone marrow adipose tissue and bone metabolism in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 52, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregson, C.L.; Armstrong, D.J.; Bowden, J.; Cooper, C.; Edwards, J.; Gittoes, N.J.L.; Harvey, N.; Kanis, J.; Leyland, S.; Low, R.; et al. UK clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Arch. Osteoporos. 2022, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, Y. Anti-osteoporosis effects and underpinning mechanisms of food-derived bioactive peptides: A review. Trends. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; Yang, K.; Tao, L. Oxidative stress: A common pathological state in a high-risk population for osteoporosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F.; Saeid, A. Bioactivity of marine-derived peptides and proteins: A review. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Ruan, C.; Sang, H.; Zhu, B. Oyster mantle-derived exosomes alleviate osteoporosis by regulating bone homeostasis. Biomaterials 2024, 311, 122648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, J. Recent advances in seafood bioactive peptides and their potential for managing osteoporosis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1187–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Hou, Z.; Liu, B.; Guo, X.; Zhu, B.; Hu, Y. Study on the antioxidant and antiosteoporotic activities of the oyster peptides prepared by ultrasound-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 112, 107211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhang, M.; Shao, C.; Li, G.; Bai, H.; Dai, G.; Chen, Q.; Kong, W.; Fu, X.; Wang, C. Chinese marine materia medica resources: Status and potential. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Weini, C.; Miao, J.; Guang, Z.; Hongtao, G.; Aiping, L. Exploring the rules of chinese and western medicine used in the treatment of osteoporosis by text mining. World Sci. Technol. 2012, 14, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Ji, X.; Wong, S.K.; Ekeuku, S.O.; Chin, K.-Y. Ejiao as a preventive agent for osteoporosis-a scoping review of current evidence. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2025, 20, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, P.D.; Kim, M.H.; Lim, H.S.; Oh, H.A.; Nam, S.Y.; Han, N.R.; Kim, M.J.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, H.M. Taurine, a major amino acid of oyster, enhances linear bone growth in a mouse model of protein malnutrition. Biofactors 2015, 41, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, D.F.; Coleone, A.P.; Lima, F.C.D.A.; Batagin-Neto, A. Reactivity of amino acids and short peptide sequences: Identifying bioactive compounds via DFT calculations. Mol. Divers. 2024, 29, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzetti, M.; Rucci, N. Osteoblast differentiation and signaling: Established concepts and emerging topics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udagawa, N.; Koide, M.; Nakamura, M.; Nakamichi, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Uehara, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Furuya, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Fukuda, C.; et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2021, 39, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y.; Wulamu, W.; Jia, L.; Liu, B.; Zheng, H.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, R. Inhibition of EGFR Pathway suppresses M1 macrophage polarization and osteoclastogenesis, mitigating titanium particle-induced bone resorption. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 9725–9742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Yang, C.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Meng, S.; Liu, R.; Huang, L.; Yang, K. Research progress on the regulatory mechanism of integrin-mediated mechanical stress in cells involved in bone metabolism. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shi, P.; Xu, Z.; Fan, F.; Wang, Z.; Du, M. Oral administration of oyster peptide prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice. eFood 2020, 1, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molagoda, I.M.N.; Jayasingha, J.; Choi, Y.H.; Park, E.K.; Jeon, Y.J.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, G.Y. Fermented oyster extract promotes insulin-like growth factor-1-mediated osteogenesis and growth rate. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, M. Extraction and characterization of matrix protein from pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigs) shell and its anti-osteoporosis properties in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 9066–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Wang, G.; Wu, G. Protein hydrolysates in animal nutrition: Industrial production, bioactive peptides, and functional significance. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.; Tian, Y.; Feng, X.; Bo, Y.; Leng, Z.; Dong, P.; Xue, C.; Wang, J. Novel peptides from sea cucumber intestinal hydrolysates promote longitudinal bone growth in adolescent mice through accelerating cell cycle progress by regulating glutamine metabolism. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 7730–7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, S.; Abou-Elsoud, M.; Liu, W.; Cui, R.; Li, Z.; Shu, D.; Cai, Z.; Huang, X. Phosvitin phosphopeptides and peptides-calcium chelate promote calcium deposition in a three-cell co-culture system by modulating the OPG/RANKL/RANK signaling pathway. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Ren, H.; Shang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; Tang, K.; Tang, J.; Yang, Z.; Liang, D.; et al. Foxf1 knockdown promotes BMSC osteogenesis in part by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss. eBioMedicine 2020, 52, 102626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, W.; Masson, A.; Li, Y.P. Cell signaling and transcriptional regulation of osteoblast lineage commitment, differentiation, bone formation, and homeostasis. Cell Discov. 2024, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, P.N.; Saranya, I.; Selvamurugan, N. RUNX2 regulation in osteoblast differentiation: A possible therapeutic function of the lncRNA and miRNA-mediated network. Differentiation 2024, 140, 100803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwi Susetyo, H.; Dwiningsih, S.R.; Widjiati, W.W.; Arsana, I.W. The Effects of Increasing Doses of Nigella Sativa and Conjugated Estrogen on Bone-Specific Alkaline Phosphatase (B-ALP), Procollagen Type 1 N-Terminal Propeptide (P1NP), Carboxy Terminal Crosslinked Telopeptide of Type 1 Collagen (CTX-1), and Osteoprotege. Pharmacogn. J. 2024, 16, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, M. Shell water-soluble matrix protein from oyster shells promoted proliferation, differentiation and mineralization of osteoblasts in vitro and vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 201, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, M.A.; Mohamed, A.S.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Fahmy, S.R. Allolobophora caliginosa coelomic fluid and extract alleviate glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in mice by suppressing oxidative stress and regulating osteoblastic/osteoclastic-related markers. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xu, Z.; Wu, D.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Du, M. Characterizations and the Mechanism Underlying Osteogenic Activity of Peptides from Enzymatic Hydrolysates of Stichopus japonicus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15611–15623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daponte, V.; Henke, K.; Drissi, H. Current perspectives on the multiple roles of osteoclasts: Mechanisms of osteoclast-osteoblast communication and potential clinical implications. eLife 2024, 13, e95083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Wang, F.; Ai, C.; Li, L.; Wu, F. Tangeretin suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and alleviates postmenopausal osteoporosis by inhibiting Notch signaling. Regen. Ther. 2025, 30, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Wu, B.; Li, S.; Zhu, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Cui, H.; Bai, Q.; Wang, J. Equol exerts a protective effect on postmenopausal osteoporosis by upregulating OPG/RANKL pathway. Phytomedicine 2023, 108, 154509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquiaga, M.; Saag, K.G. Risk for osteoporosis and fracture with glucocorticoids. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 36, 101793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Xie, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Huang, Y.; Huang, W.; Ma, T.; Luo, Y.; et al. Schisandrin A induces osteoblast differentiation to treat glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis through activating Wnt pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2025, 776, 152230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikebuchi, Y.; Aoki, S.; Honma, M.; Hayashi, M.; Sugamori, Y.; Khan, M.; Kariya, Y.; Kato, G.; Tabata, Y.; Penninger, J.M.; et al. Coupling of bone resorption and formation by RANKL reverse signalling. Nature 2018, 561, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Shen, J.; Yang, K.; Lv, G.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J. The role of the PI3K/Akt pathway in adenosine’s mechanism of action in osteoporosis with oxidative stress: A wet-dry experimental approach strategy. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 120, 106366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.; Yang, Y.; Wei, L.; Cao, Y.; Ma, J.; Zheng, X.; Teng, J.; Qin, N. Luteolin rescues postmenopausal osteoporosis elicited by OVX through alleviating osteoblast pyroptosis via activating PI3K-AKT signaling. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Zou, J. The role of integrin family in bone metabolism and tumor bone metastasis. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, R.; Gu, J.; Yang, F.; Wen, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, C.; Geng, B.; Xia, Y. Integrin αVβ3 mediates estrogen to enhance osteoblast proliferation, differentiation, and alleviate OVX-induced postmenopausal osteoporosis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2025, 252, 106800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, C.C.-W.; Au-Yeung, C.; Wong, K.-Y.; Chan, Z.; Zhou, L.-P.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wong, M.-S. Icariin promotes cell adhesion for osteogenesis in bone marrow stromal cells via binding to integrin α5β1. Phytomedicine 2024, 133, 155887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.-J.; Li, Y.-S.; Zhang, F.-J. Osteopontin, a bridge links osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1012508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, P.B.; de Almeida, G.S.; Orsi, R.d.O.; Zambuzzi, W.F.; Fernandes, C.J.D.C. Aqueous extracts of propolis modulate ECM remodeling and calcium levels during pre-osteoblast differentiation. Tissue Cell 2025, 97, 103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, G.; Guo, J.; Chang, B.; Yi, X.; Yao, T. Role and mechanism of Integrin α5β1 in bone formation and disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2025, 13, 1632710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valat, A.; Fourel, L.; Sales, A.; Machillot, P.; Bouin, A.P.; Fournier, C.; Bosc, L.; Arboleas, M.; Bourrin-Reynard, I.; Wagoner Johnson, A.J.; et al. Interplay between integrins and cadherins to control bone differentiation upon BMP-2 stimulation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1027334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Azim, M.; Di Martino, J.S. ECM, integrins, and DDRs: A nexus of cancer progression, therapy, and future directions. Matrix Biol. 2025, 138, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Deng, G.; Song, Z.; He, T.; Nergiz-Unal, R.; Li, C.; Yu, T.; Huang, Y. Collagen peptides promote osteogenesis and angiogenesis by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in mice. Chin. Med. J. 2025, 138, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tollabi, M.; Poursalehi, Z.; Mehrafshar, P.; Bakhtiari, R.; Hosseinpour Sarmadi, V.; Tayebi, L.; Haramshahi, S.M.A. Insight into the role of integrins and integrins-targeting biomaterials in bone regeneration. Connect. Tissue Res. 2024, 65, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Huang, L.; Chen, Y.; Jin, J.; Xu, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, K.; Sun, Y. Hydrolyzed egg yolk peptide prevented osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in ovariectomized rats. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




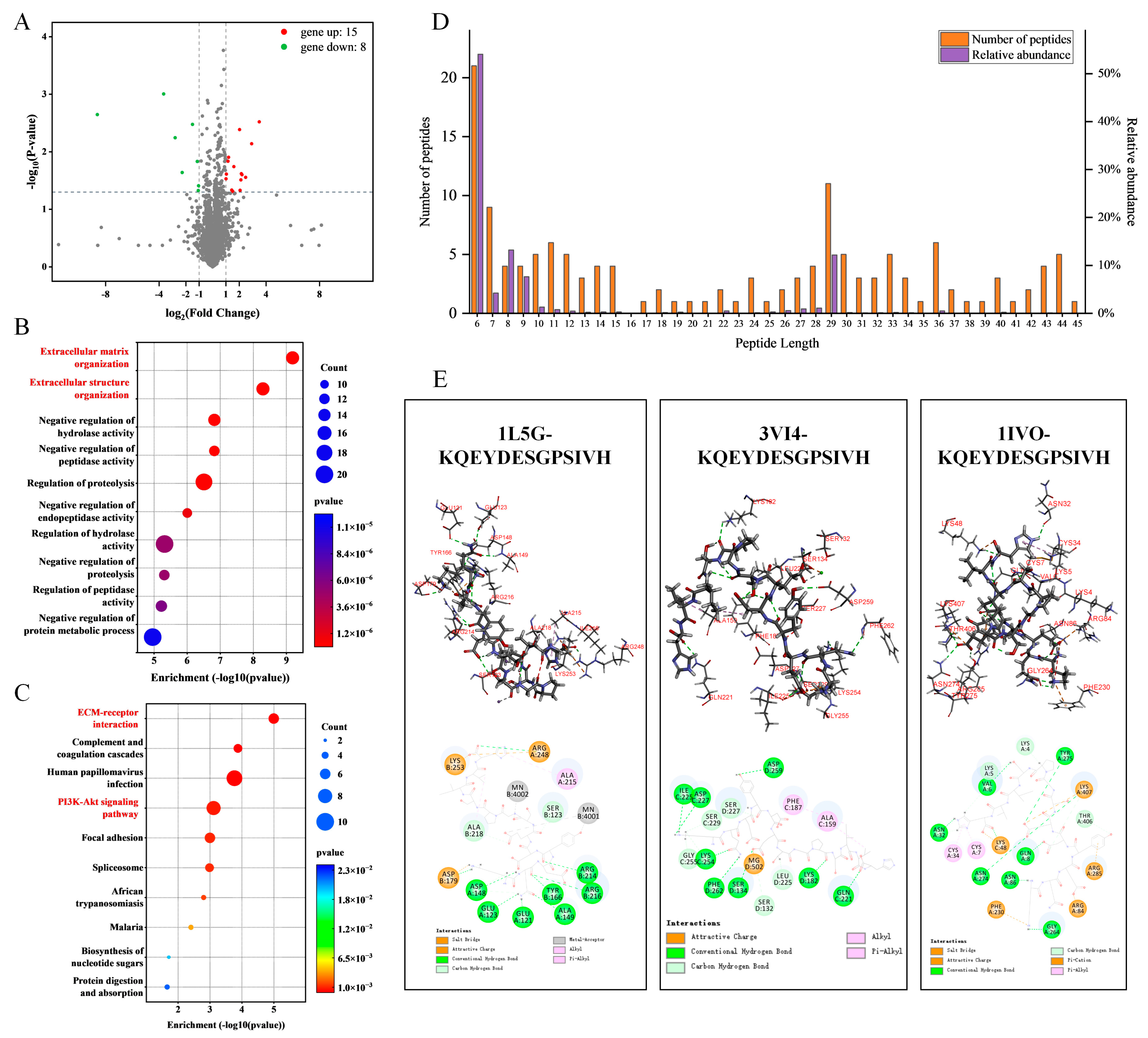

| Peptide Sequence | Length | Molecular Mass (Da) | Bioactive Score | Toxicity | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integrins α5β1 | Integrins αvβ3 | EGFR | |||||
| GQKDSYVGDEAQSKRGILT | 19 | 2052.03 | 0.2472 | Nontoxic | 295.89 | 240.23 | 272.95 |
| GQKDSYVGDEAQSKRGILTL | 20 | 2165.12 | 0.2789 | Nontoxic | 290.02 | 138.42 | 281.91 |
| KDAENRATEAERTVSKL | 17 | 1918.00 | 0.0956 | Nontoxic | 274.91 | 246.31 | 252.32 |
| TTTAEREIVRDIKEK | 15 | 1788.98 | 0.0291 | Nontoxic | 270.52 | 246.22 | 253.89 |
| TTAEREIVRDIKEK | 14 | 1687.93 | 0.0333 | Nontoxic | 242.33 | 225.85 | 236.60 |
| SYVGDEAQSKRGIL | 14 | 1522.79 | 0.3127 | Nontoxic | 226.72 | 208.52 | 203.97 |
| DLAGRDLTDYLMKIL | 15 | 1736.93 | 0.3487 | Nontoxic | 225.92 | 233.64 | 225.00 |
| TAEREIVRDIKEK | 13 | 1586.89 | 0.0446 | Nontoxic | 225.29 | 225.06 | 226.24 |
| AEREIVRDIKE | 11 | 1357.74 | 0.0588 | Nontoxic | 223.52 | 190.44 | 206.26 |
| DVDIRKDLYAN | 11 | 1321.67 | 0.1576 | Nontoxic | 219.93 | 179.26 | 207.68 |
| AEREIVRDIKEK | 12 | 1485.84 | 0.0673 | Nontoxic | 212.54 | 225.03 | 215.12 |
| DLAGRDLTDYLMK | 13 | 1510.76 | 0.3423 | Nontoxic | 209.64 | 208.75 | 198.61 |
| KQEYDESGPSIVH | 13 | 1488.70 | 0.1903 | Nontoxic | 209.09 | 197.81 | 190.45 |
| DLAGRDLTDYL | 11 | 1251.62 | 0.2583 | Nontoxic | 204.29 | 191.17 | 189.01 |
| DLAGRDLTDYLM | 12 | 1398.66 | 0.3555 | Nontoxic | 203.28 | 212.97 | 180.42 |
| KSYELPDGQVITIG | 14 | 1519.80 | 0.2720 | Nontoxic | 199.99 | 140.55 | 194.27 |
| KQEYDESGPSIV | 12 | 1351.64 | 0.1908 | Nontoxic | 196.70 | 186.03 | 171.52 |
| EYDESGPSIVHR | 12 | 1388.64 | 0.1670 | Nontoxic | 188.00 | 152.92 | 166.65 |
| LESSTAGGVAS | 11 | 978.47 | 0.0860 | Nontoxic | 169.15 | 154.10 | 142.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, W.; Ma, W.; Qin, X.; Cao, W.; Lin, H. Improvement Effect and Regulation Mechanism of Oyster Peptide on Dexamethasone-Induced Osteoporotic Rats. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23090356
Yang W, Ma W, Qin X, Cao W, Lin H. Improvement Effect and Regulation Mechanism of Oyster Peptide on Dexamethasone-Induced Osteoporotic Rats. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(9):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23090356
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Wei, Wenyu Ma, Xiaoming Qin, Wenhong Cao, and Haisheng Lin. 2025. "Improvement Effect and Regulation Mechanism of Oyster Peptide on Dexamethasone-Induced Osteoporotic Rats" Marine Drugs 23, no. 9: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23090356
APA StyleYang, W., Ma, W., Qin, X., Cao, W., & Lin, H. (2025). Improvement Effect and Regulation Mechanism of Oyster Peptide on Dexamethasone-Induced Osteoporotic Rats. Marine Drugs, 23(9), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23090356






