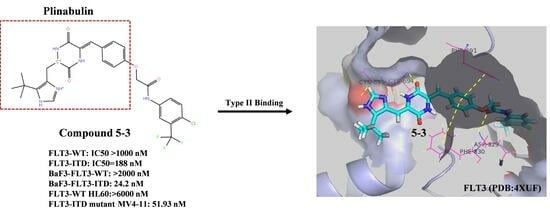
The Novel Diketopiperazine Derivative, Compound 5-3, Selectively Inhibited the Proliferation of FLT3-ITD Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
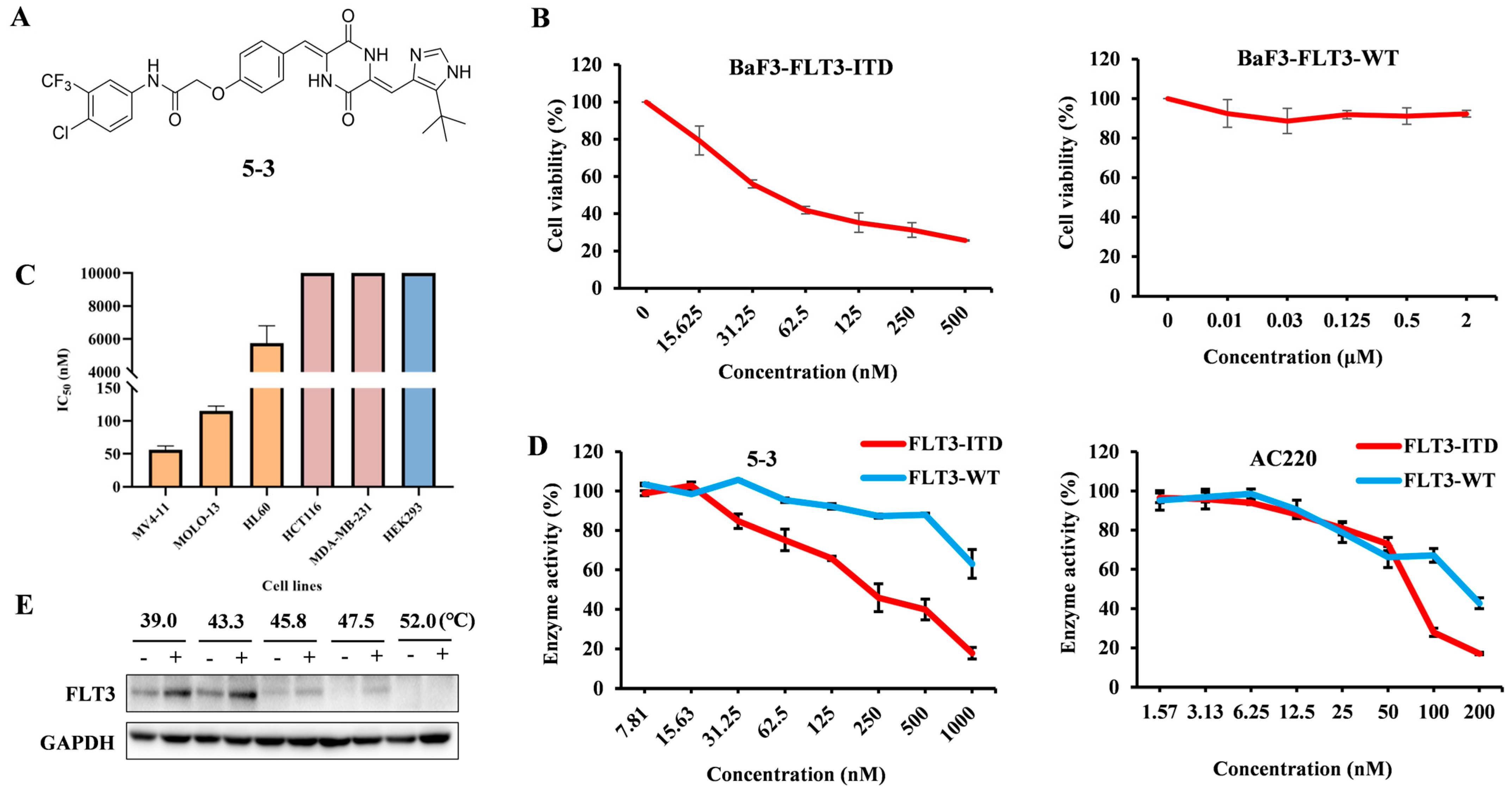
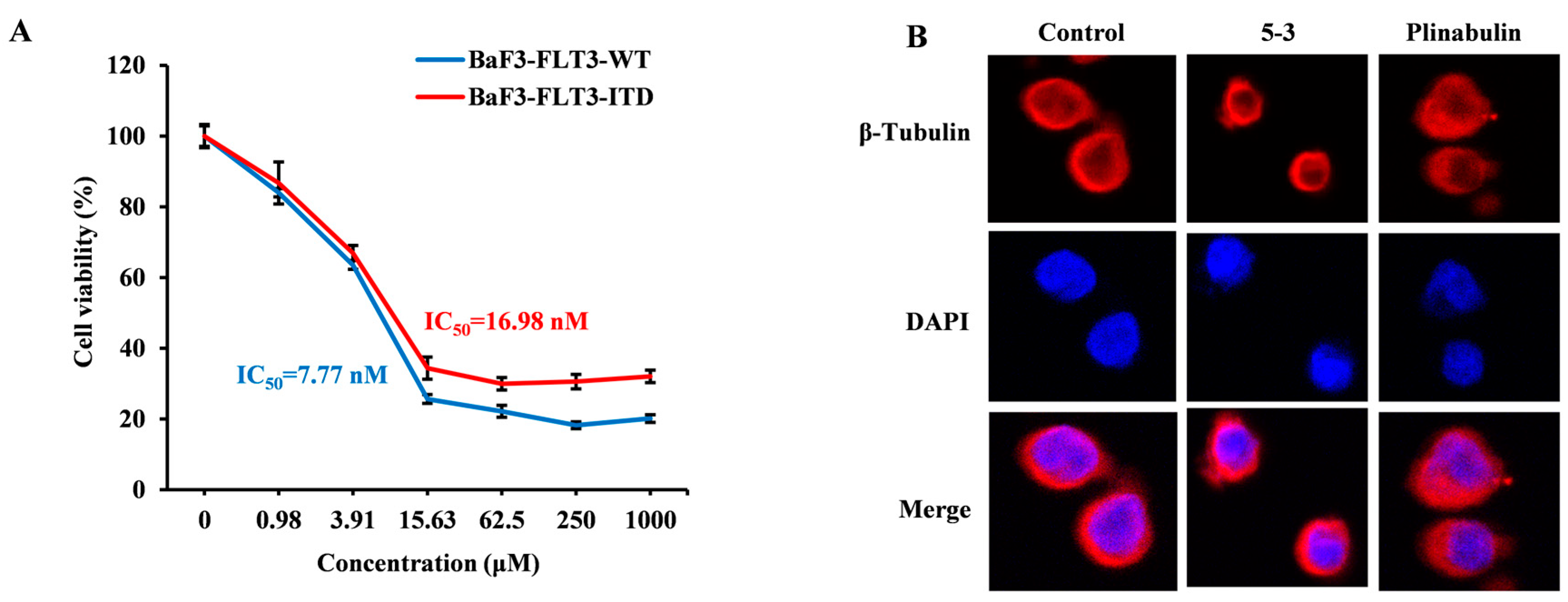
2.1. 5-3 Potently and Selectively Inhibits Thegrowth of Mutant FLT3-Expressingleukemia Cells in Vitro
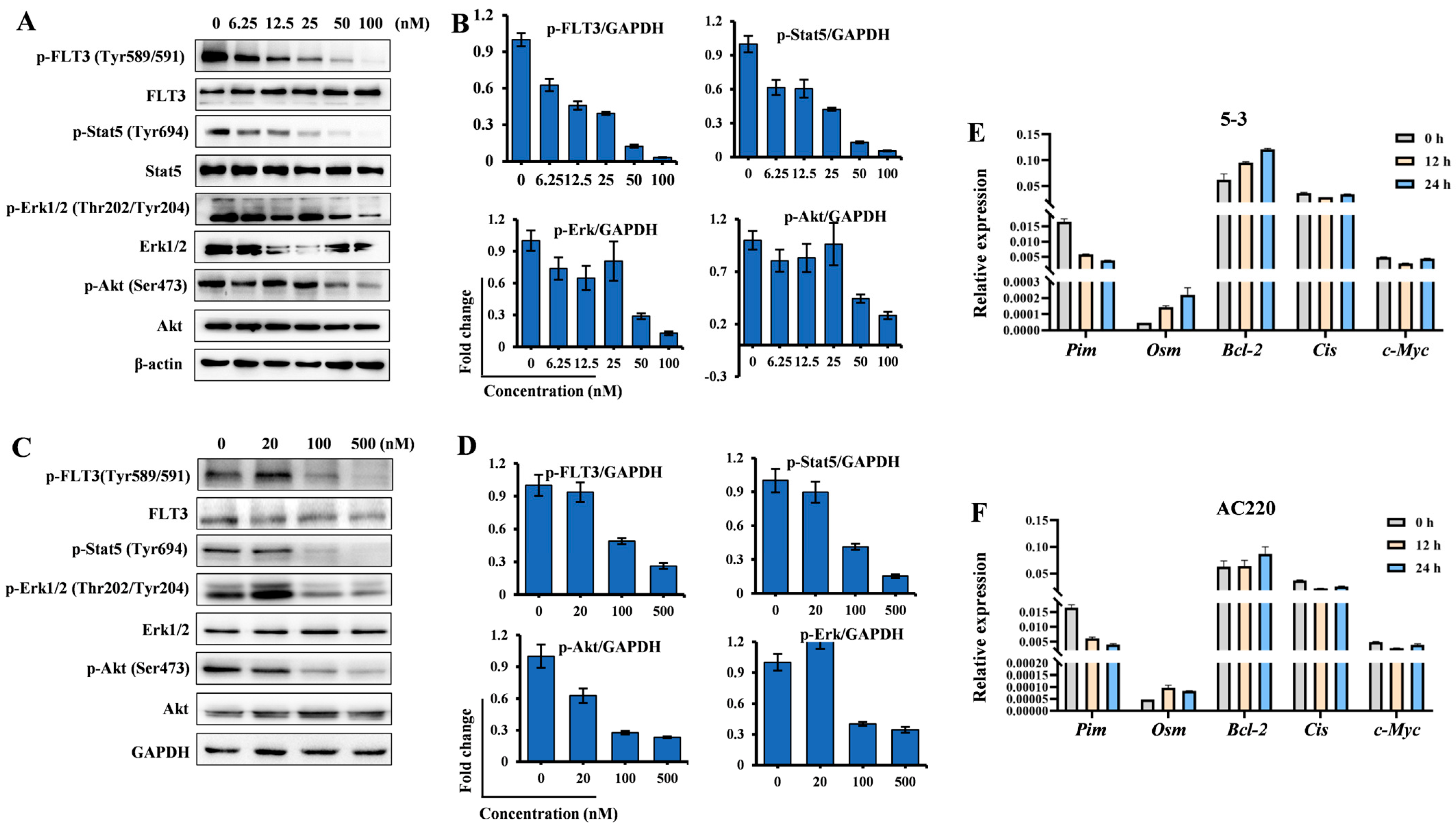
2.2. 5-3 Significantly Suppressed FLT3 Signaling Pathway
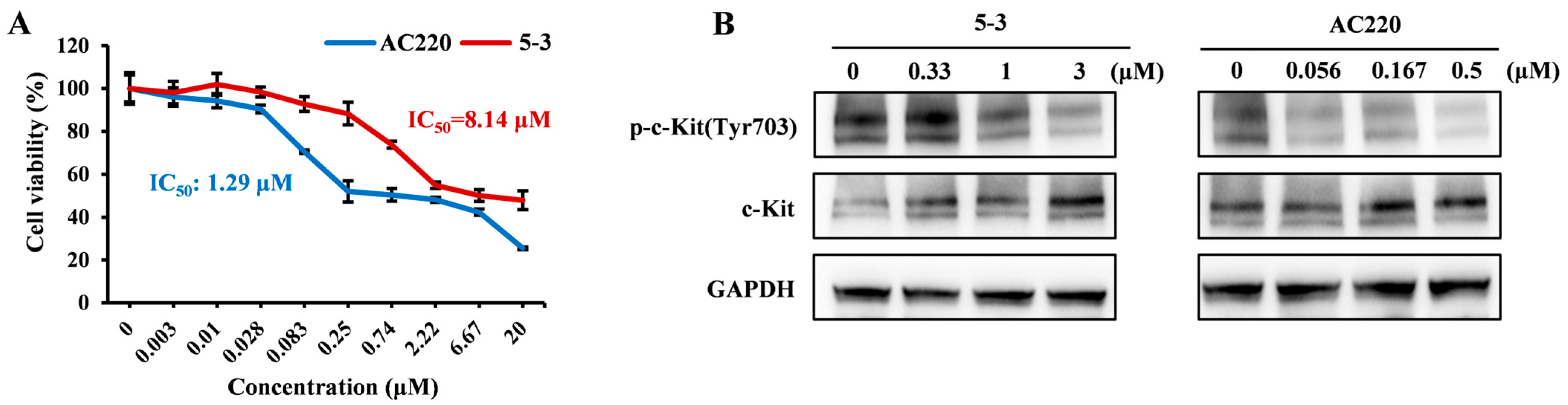
2.3. Exerted Weaker Effect than AC220 on the Phosphorylation of c-KIT
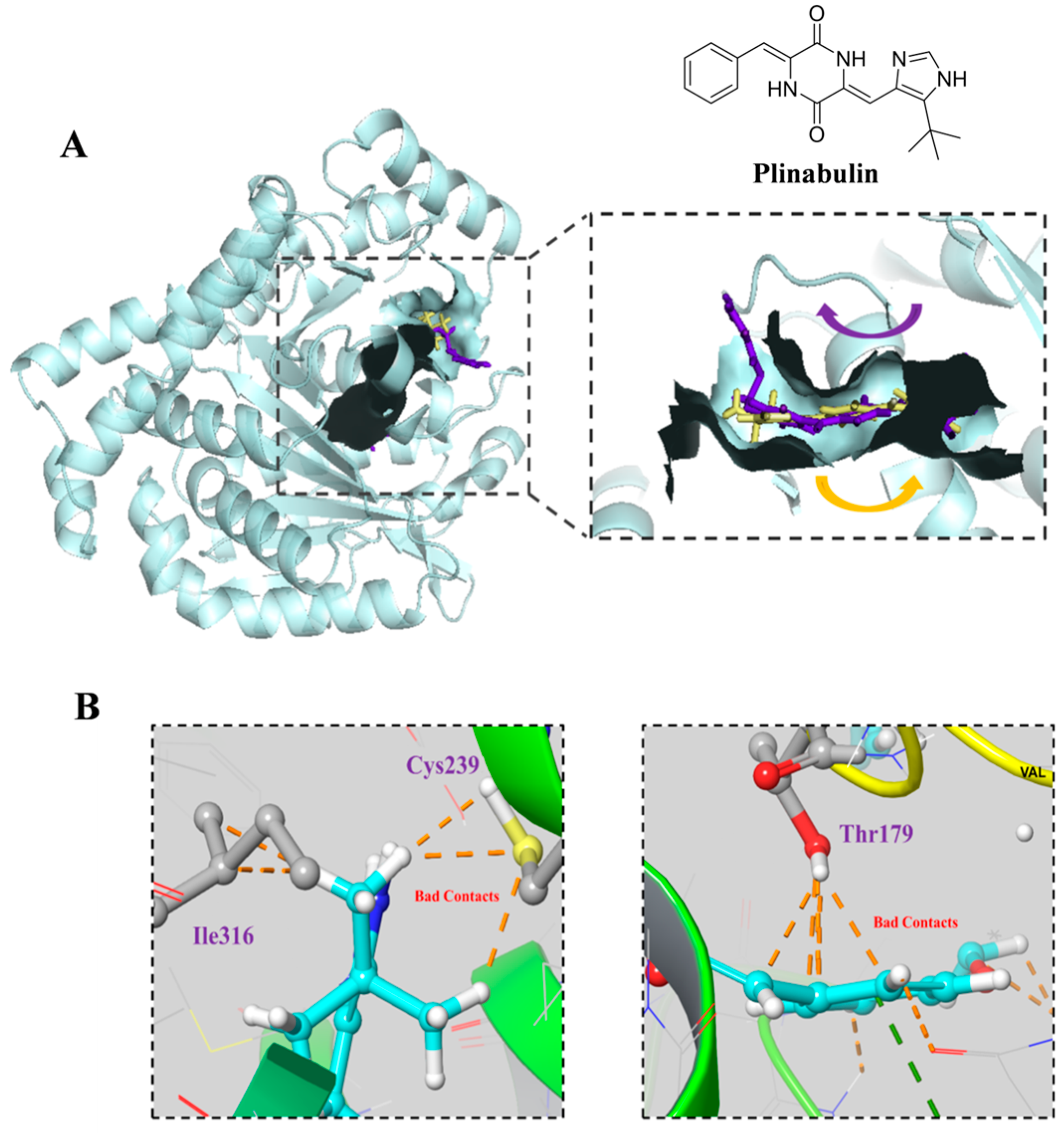
2.4. 5-3 Specifically Targeting FLT3 Rather than β-Tubulin
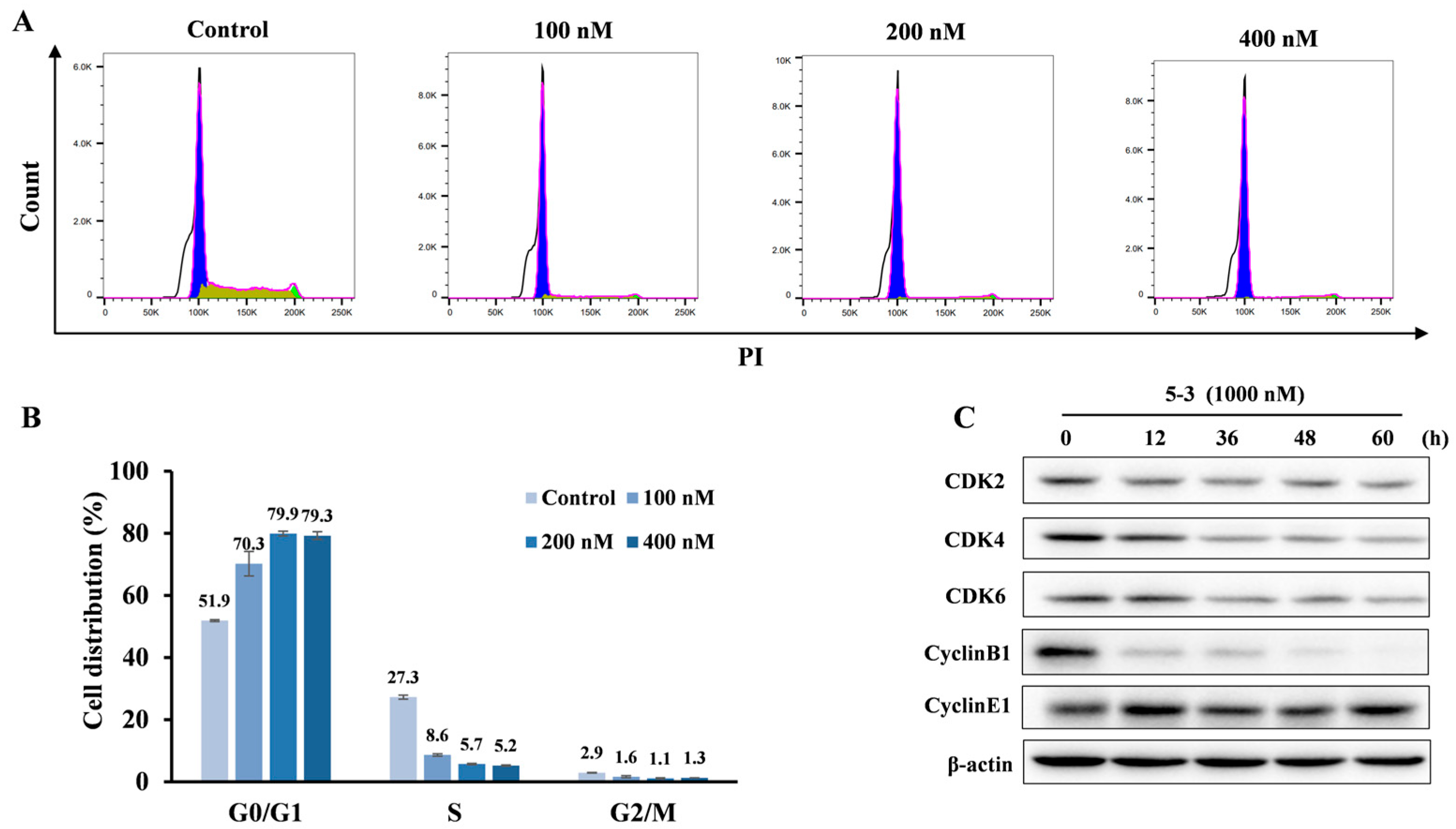
2.5. 5-3 Induced FLT3-ITD Mutant AML Cells G1 Arrest a Dose-Dependent Manner
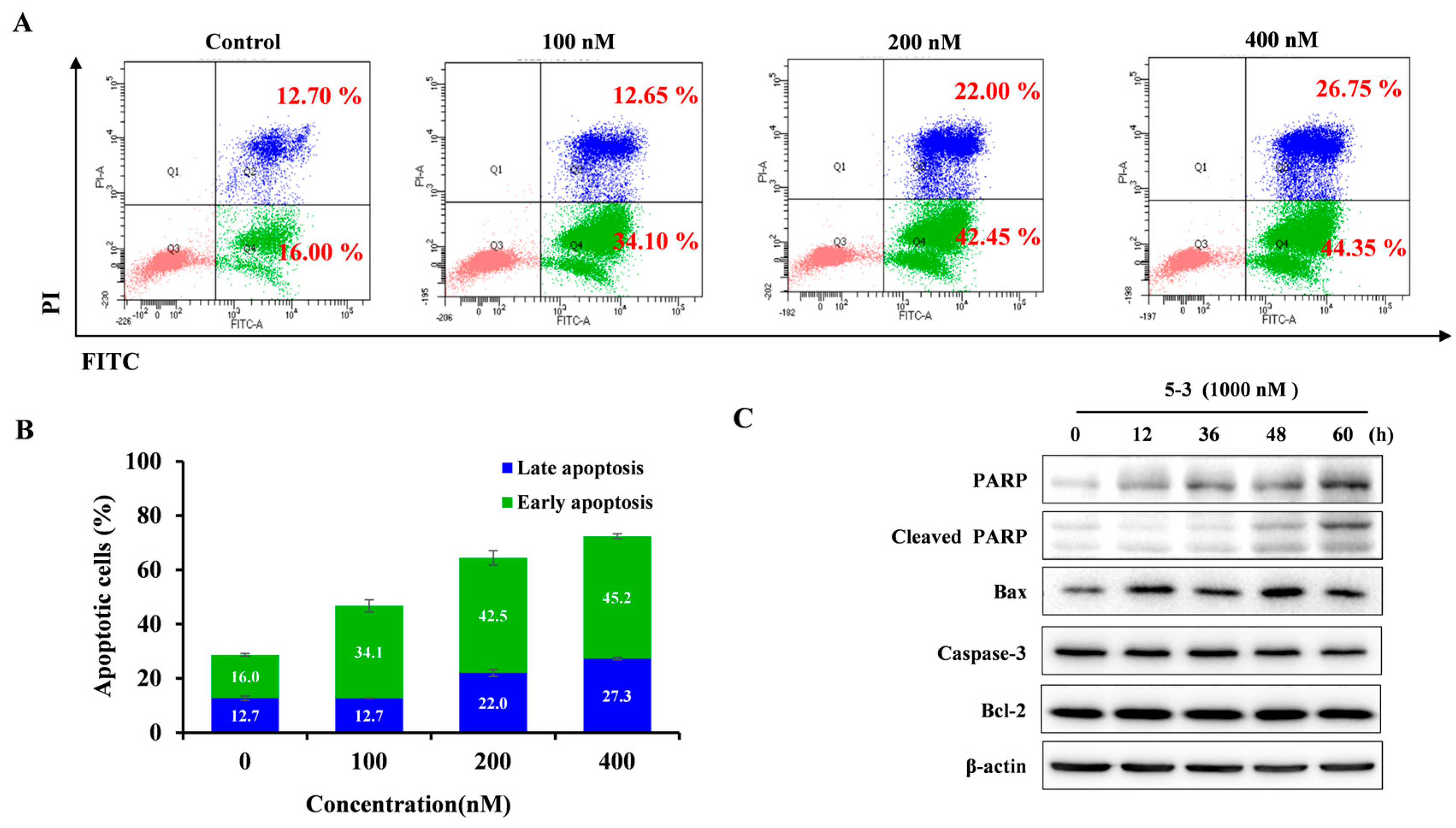
2.6. 5-3 Resulted Obvious Apoptosis in FLT3-ITD Mutant AML
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Compounds, Cell Lines and Plasmids
4.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.3. Immunofluorescence
4.4. Western Blotting Analysis
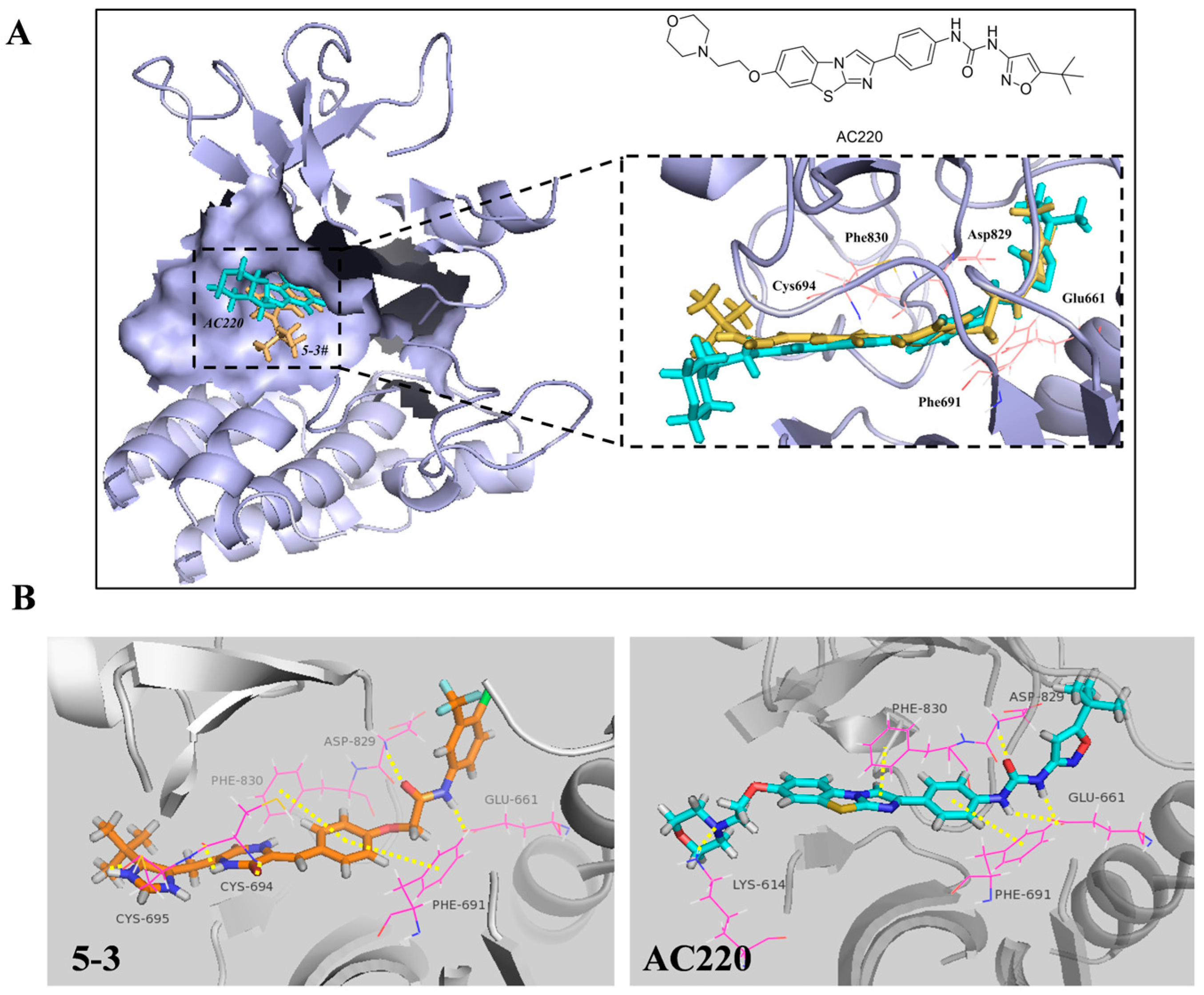
4.5. Molecular Docking
4.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
4.7. ADP-Glo Assay
4.8. Cell Thermodynamic Stability Analysis (CETSA)
4.9. Cell Apoptosis Detection
4.10. Cell Cycle Detection
4.11. Real Time PCR
| Cis | Forward primer 5′-GCATAGCCAAGACCTTCTCCTAC-3′ |
| Reverse primer 5′-ACGTGCCTTCTGGCATCTTCTG-3′ | |
| Bcl-2 | Forward primer 5′-CTTTGAGTTCGGTGGGGTCA-3′ |
| Reverse primer 5′-GGGCCGTACAGTTCCACAAA-3′ | |
| Pim | Forward primer 5′-TCTACTCAGGCATCCGCGTCTC-3′ |
| Reverse primer 5′-CTTCAGCAGGACCACTTCCATG-3′ | |
| Osm | Forward primer 5′-CACACAGAAACCCCAGTCCCA-3′ |
| Reverse primer 5′-GACACCATCGTTCCCGTCCTA-3′ | |
| c-Myc | Forward primer 5′-CACTAACATCCCACGCTCTGA-3′ |
| Reverse primer 5′-AAATCATCGCAGGCGGAACA-3′ | |
| GAPDH | Forward primer 5′-ACAACTTTGGTATCGTGGAAGG-3′ |
| Reverse primer 5′-GCCATCACGCCACAGTTTC-3′ |
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| FLT3 | Fms-liketyrosine receptor kinase 3 |
| ITD | internal tandemduplication |
| TKD | Tyrosine kinase domain |
| CETSA | Cellular thermal shift assay |
| DKPs | Diketopiperazines |
| AC220 | Quizartinib |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| IOD | Immunofluorescence optical density |
| GAFF | General amber force field |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| DEPC | Diethyl pyrocarbonate |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
References
- Kantarjian, H.M.; DiNardo, C.D.; Kadia, T.M.; Daver, N.G.; Altman, J.K.; Stein, E.M.; Jabbour, E.; Schiffer, C.A.; Lang, A.; Ravandi, F. Acute myeloid leukemia management and research in 2025. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 46–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daver, N.; Schlenk, R.F.; Russell, N.H.; Levis, M.J. Targeting FLT3 mutations in AML: Review of current knowledge and evidence. Leukemia 2019, 33, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Q.Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Rao, G.W.; Zheng, Q. Targeting FLT3 for treating diseases: FLT3 inhibitors. Drug Discov. Today 2025, 30, 104367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.S.; Kim, H.J. FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: A review focusing on clinically applicable drugs. Blood Res. 2022, 57, 6–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellen, W.; Cheng, M.; Abigail, E.C.; Martin, S.; Hong, L.T.; Prafulla, C.G.; Sara, J.B.; Xiao, L.; Jing, Y.; Jin, W.; et al. Comparison of effects of midostaurin, crenolanib, quizartinib, gilteritinib, sorafenib and BLU-285 on oncogenic mutants of KIT, CBL and FLT3 in haematological malignancies. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 187, 488–501. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Y.Y.; Singh, V.K.; Coumar, M.S.; Hsu, Y.C.; Wang, W.C.; Song, J.S.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, W.H.; Wu, S.H.; Hsu, J.T.; et al. Homology modeling of DFG-in FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) and structure-based virtual screening for inhibitor identification. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11702–11713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarver, T.C.; Hill, J.E.; Rahmat, L.; Perl, A.E.; Bahceci, E.; Mori, K.; Smith, C.C. Gilteritinib is a clinically active FLT3 inhibitor with broad activity against FLT3 kinase domain mutations. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, L.; Joshi, S.K.; Traer, E. Profile of quizartinib for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed/refractory FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukemia: Evidence to date. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidel, F.; Solem, F.K.; Breitenbuecher, F.; Lipka, D.B.; Kasper, S.; Thiede, M.H.H.; Brandts, C.; Serve, H.; Roesel, J.; Giles, F.; et al. Clinical resistance to the kinase inhibitor PKC412 in acute myeloid leukemia by mutation of Asn 676 in the FLT3 tyrosine kinase domain. Blood 2006, 107, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, M.P.; Abraham, W.R. Antimicrobial and biofilm inhibiting diketopiperazines. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 3564–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohn, H.; Widger, W. The molecular basis for the mode of action of bicyclomucin. Curr. Drug Targets Infect. Disord. 2005, 5, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musetti, R.; Polizzotto, R.; Vecchione, A.; Borselli, S.; Zulini, L.; D’Ambrosio, M.; di Toppi, L.S.; Pertot, I. Antifungal activity of diketopiperazines extracted from Alternaria alternate against Plasmopara viticola an ultrastructural study. Micron 2007, 38, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ström, K.; Sjögren, J.; Broberg, A.; Schnürer, J. Lactobacillus plantarum MiLAB 393 produces the antifungal cyclic dipeptides cyclo(LPhe-L-Pro) and cyclo(L-Phe-trans-4-OH-L-Pro) and 3-phenyllacticacid. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4322–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, P.L.; Carrasco, L. Gliotoxin: Inhibitor of poliovirus RNA synthesisthat blocks the viral RNA polymerase 3Dpol. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 1971–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanoh, K.; Kohno, S.; Katada, J.; Hayashi, Y.; Muramatsu, M.; Uno, I. Antitumor activity of phenylahistin in vitro and in vivo. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 1130–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzaki, H.; Yanagisawa, S.; Nitoda, T. Enzymatic synthesis of dehydro cyclo(His-Phe)s, analogs of the potent cell cycle inhibitor, dehydrophenylahistin, and their inhibitory activities toward cell division. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 2341–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waring, P.; Beaver, J. Gliotoxin and related epipolythiodioxopiperazines. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1996, 27, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.K.; Hwang, I.K.; Rosenthal, M.J.; Harris, D.M.; Yamaguchi, D.T.; Yip, I.; Go, V.L. Anti-hyperglycemic activity of zinc plus cyclo(His-Pro) in genetically diabetic Goto-Kakizaki and aged rats. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2003, 228, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Bi, S.; Li, Y.; Tian, S.; Xu, H.; Fu, L.; Wang, S.; Tang, Y.; Qiu, P. Design, synthesis and anti-tumor evaluation of plinabulin derivatives as potential agents targeting β-tubulin. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 91, 129370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkentin, A.A.; Lopez, M.S.; Lasater, E.A.; Lin, K.; He, B.L.; Leung, A.Y. Overcoming myelosuppression due to synthetic lethal toxicity for FLT3-targeted acute myeloid leukemia therapy. eLife 2014, 3, 03445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.C.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, H.; Amin, K.; Bewersdorf, J.P.; Zeidan, A.M. A review of FLT3 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev. 2021, 52, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, R.; Cheng, H.E.; Sun, Y. Efficacy and safety of FLT3 inhibitors in monotherapy of hematological and solid malignancies: A systemic analysis of clinical trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1294668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorn, J.A.; Wang, Q.; Fujimura, E.; Barros, T.; Kuriyan, J. Crystal structure of the FLT3 kinase domain bound to the inhibitor quizartinib (AC220). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Kang, N.; Yang, F.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X.; Wang, H.; Bai, S.; Cheng, C.C.; Xu, J.; Hu, W.; et al. Discovery of FLT3-ITD inhibitor clifutinib: A novel biphenylacetylene urea derivative in clinical trials for the treatment of relapsed/refractory FLT3-ITD+ acute myeloid leukemia. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 7955–7972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Li, X.; Chen, C.; Wu, H.; Qi, Z.; Hu, C.; Yu, K.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Discovery of 1-(4-(4-Amino-3-(4-(2-morpholinoethoxy)-phenyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-dpyrimidin-1-yl)phenyl)-3-(5-(tertbutyl)isoxazol-3-yl)urea (CHMFL-FLT3-213) as a highly potent type II FLT3 kinase inhibitor capable of overcoming a variety of FLT3 kinase mutants in FLT3-ITD positive AML. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 8407–8424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, P.; Ge, W. MZH29 is a novel potent inhibitor that overcomes drug resistance FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, D.; Liu, M.; Xie, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, P.; Ren, R. A dual inhibitor overcomes drug-resistant FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, J.; Ren, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Jia, K.; Huang, F.; Cheng, Z.; Sheng, T.; et al. Discovery of a potent FLT3 inhibitor (LT-850-166) with the capacity of overcoming a variety of FLT3 mutations. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 14664−14701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Du, J.; Hui, H.; Kan, S.; Huo, T.; Zhao, K.; Wu, T.; Guo, Q.; Lu, N. LT-171-861, a novel FLT3 inhibitor, shows excellent preclinical efficacy for the treatment of FLT3 mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Theranostics 2021, 11, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Sala, G.; Olieric, N.; Sharma, A.; Viti, F.; de Asis Balaguer Perez, F.; Huang, L.; Tonra, J.R.; Lloyd, G.K.; Decherchi, S.; Diaz, J.F.; et al. Structure, thermodynamics, and kinetics of plinabulin binding to two tubulin isotypes. Chem 2019, 5, 2969–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, P.J.; Huang, L.; Du, L.; Wu, Y.; Bishop, J.; Dalsing-Hernandez, J.; Kotlarczyk, K.; Gonzales, P.; Carew, J.; Nawrocki, S.; et al. Plinabulin, an inhibitor of tubulin polymerization, targets KRAS signaling through disruption of endosomal recycling. Biomed. Rep. 2019, 10, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonra, J.R.; Lloyd, G.K.; Mohanlal, R.; Huang, L. Plinabulin ameliorates neutropenia induced by multiple chemotherapies through a mechanism distinct from G-CSF therapies. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2020, 85, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, S.; Li, W. Antitumor activity of the microtubule inhibitor MBRI-001 against human hepatocellular carcinoma as monotherapy or in combination with sorafenib. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 81, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bi, S.; Cao, Y.; Fang, S.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Yu, R.; Yang, J.; Tang, Y.; Qiu, P. The Novel Diketopiperazine Derivative, Compound 5-3, Selectively Inhibited the Proliferation of FLT3-ITD Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070289
Bi S, Cao Y, Fang S, Chu Y, Zhang Z, Li M, Yu R, Yang J, Tang Y, Qiu P. The Novel Diketopiperazine Derivative, Compound 5-3, Selectively Inhibited the Proliferation of FLT3-ITD Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(7):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070289
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Shijie, Yating Cao, Shiyuan Fang, Yanyan Chu, Zixuan Zhang, Meng Li, Rilei Yu, Jinbo Yang, Yu Tang, and Peiju Qiu. 2025. "The Novel Diketopiperazine Derivative, Compound 5-3, Selectively Inhibited the Proliferation of FLT3-ITD Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells" Marine Drugs 23, no. 7: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070289
APA StyleBi, S., Cao, Y., Fang, S., Chu, Y., Zhang, Z., Li, M., Yu, R., Yang, J., Tang, Y., & Qiu, P. (2025). The Novel Diketopiperazine Derivative, Compound 5-3, Selectively Inhibited the Proliferation of FLT3-ITD Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells. Marine Drugs, 23(7), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070289