Undaria pinnatifida Fucoidan Enhances Gut Microbiome, Butyrate Production, and Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects in an In Vitro Short-Term SHIME® Coupled to a Caco-2/THP-1 Co-Culture Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
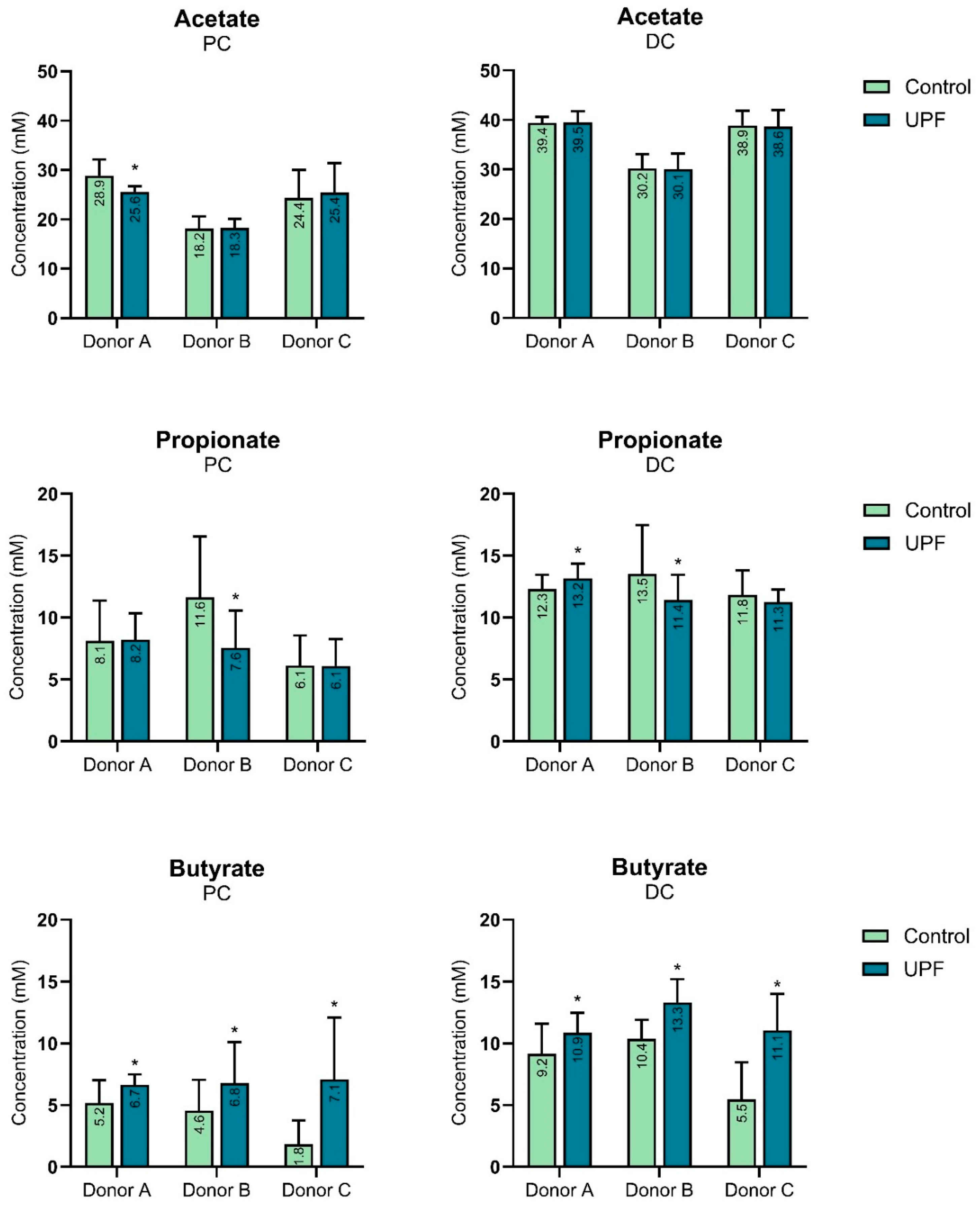
2.1. UPF Effect on SCFAs
2.2. UPF Effect on Microbial Diversity
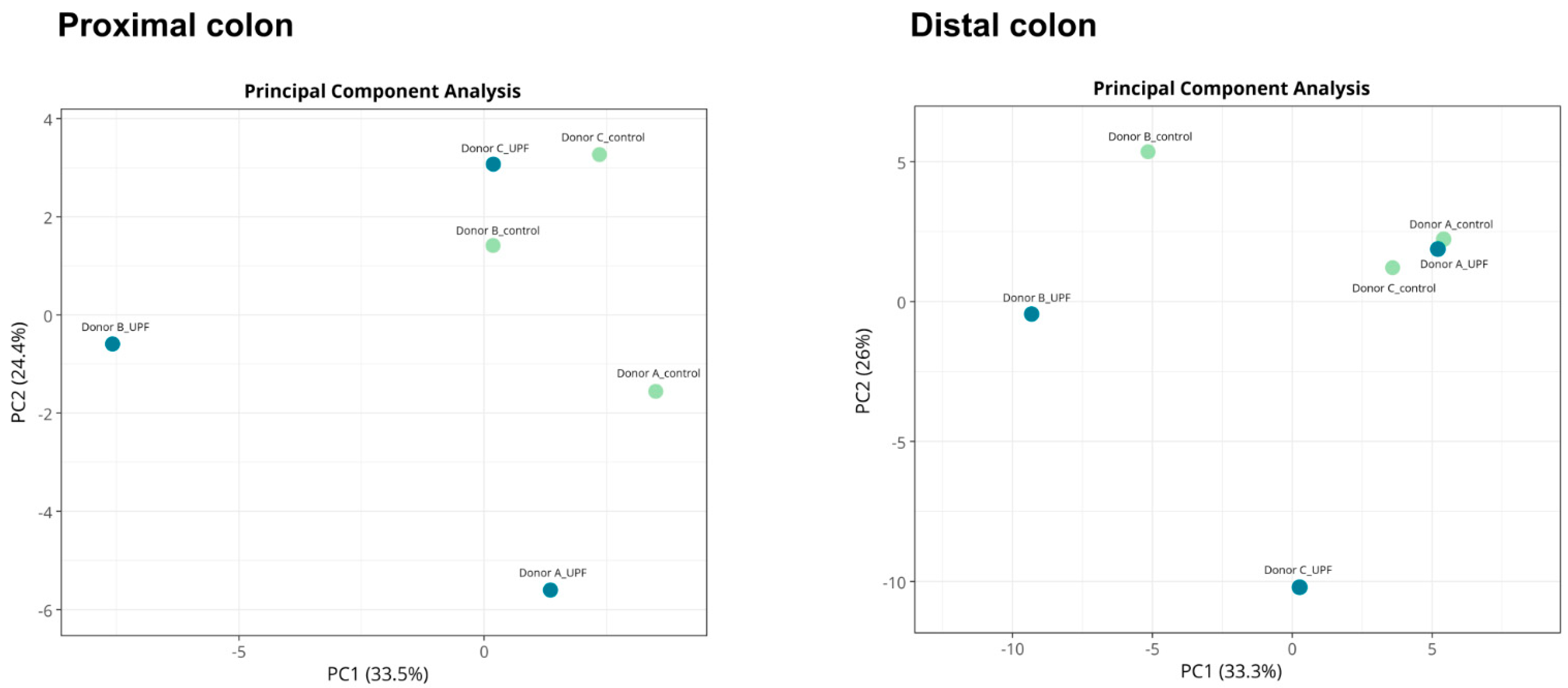
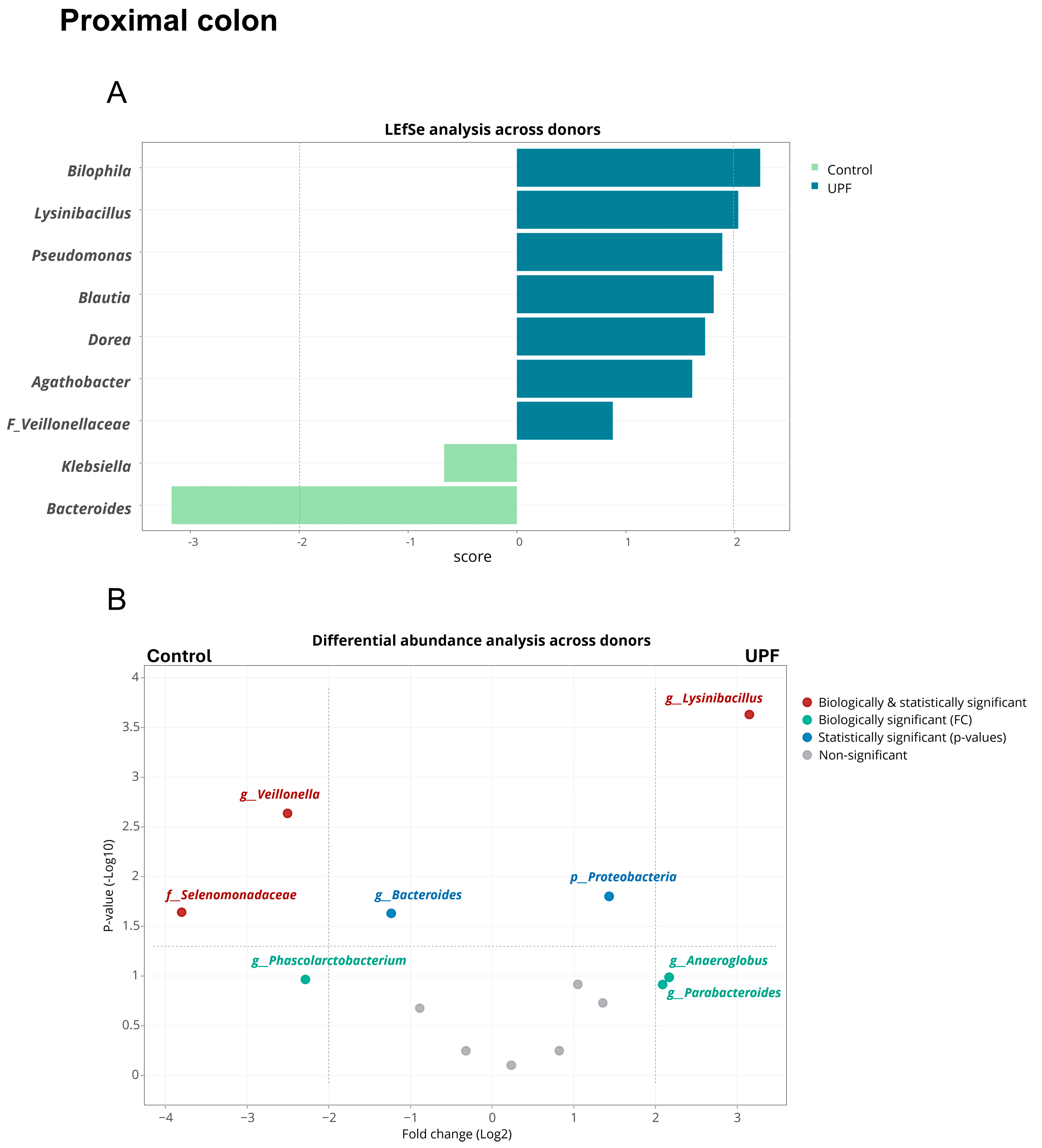
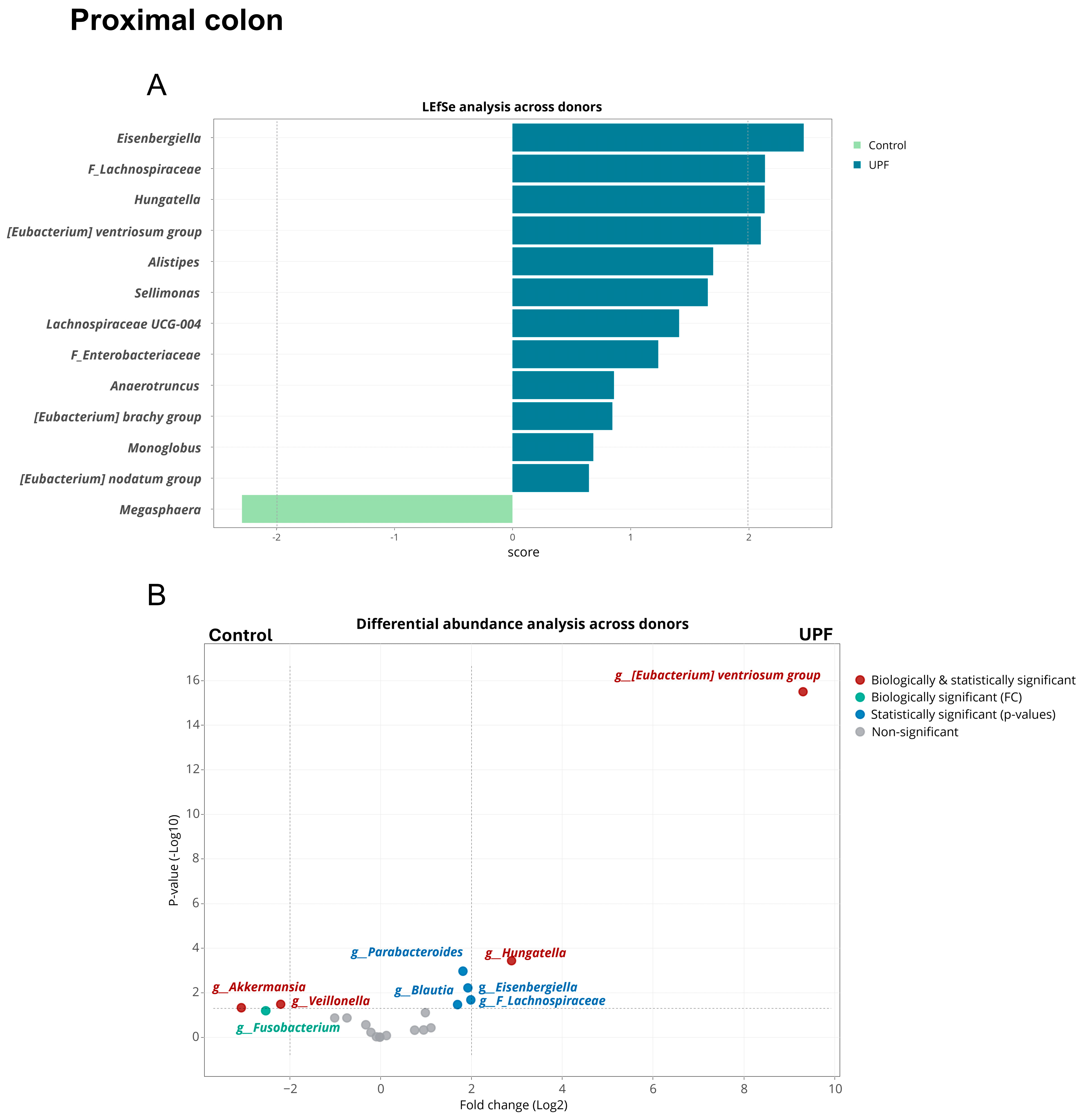
2.3. UPF Effect on Microbial Community Composition
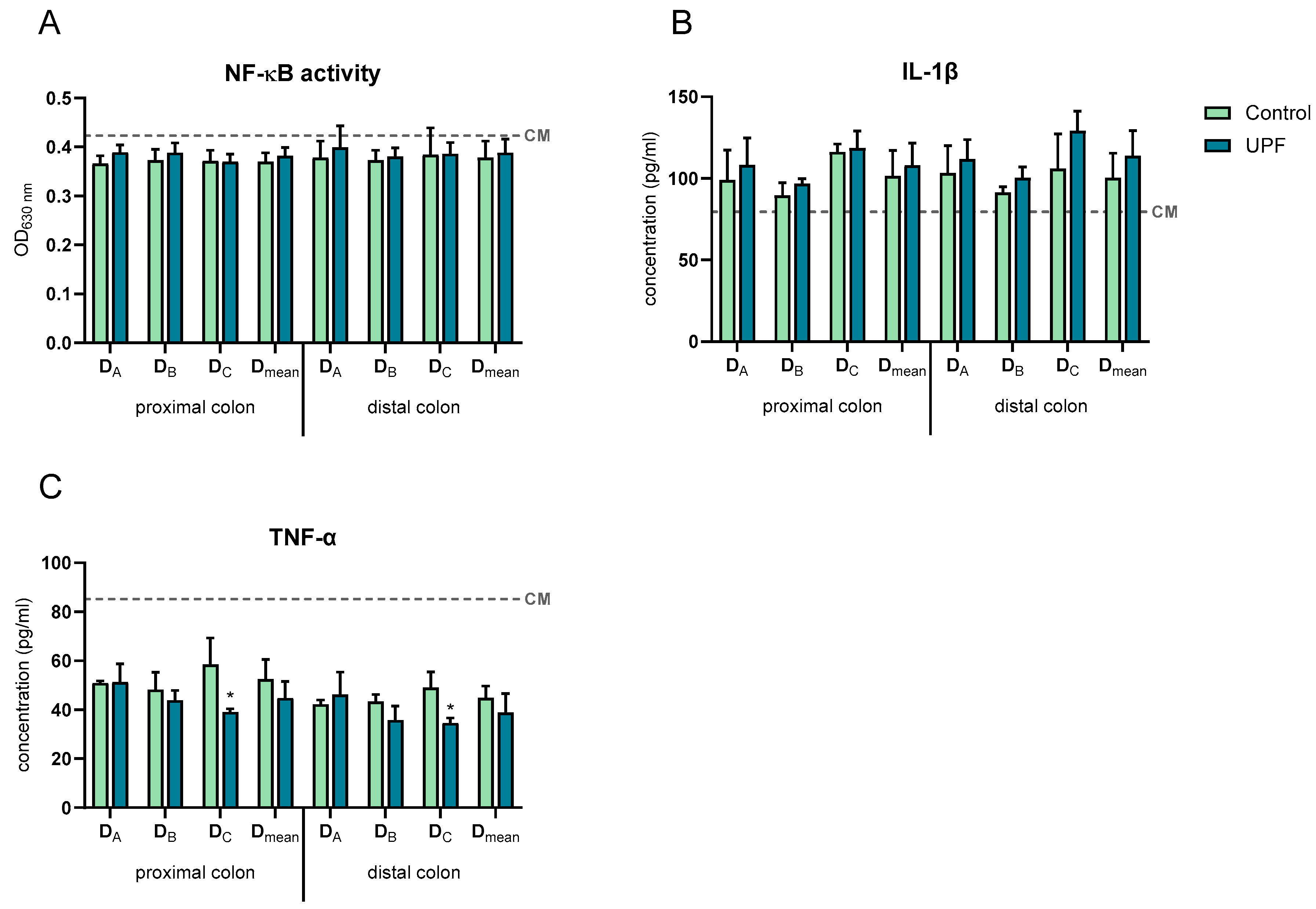
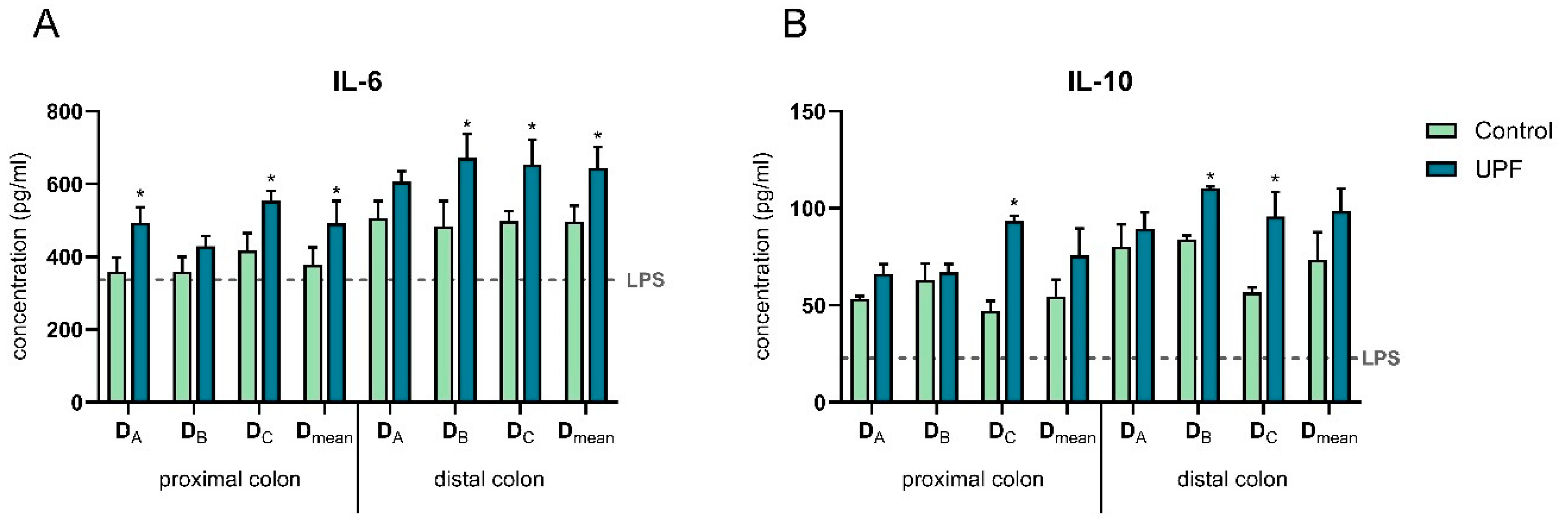
2.4. UPF Effect on Immune Markers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics
4.2. Faecal Sample Donor Description
4.3. Materials Used
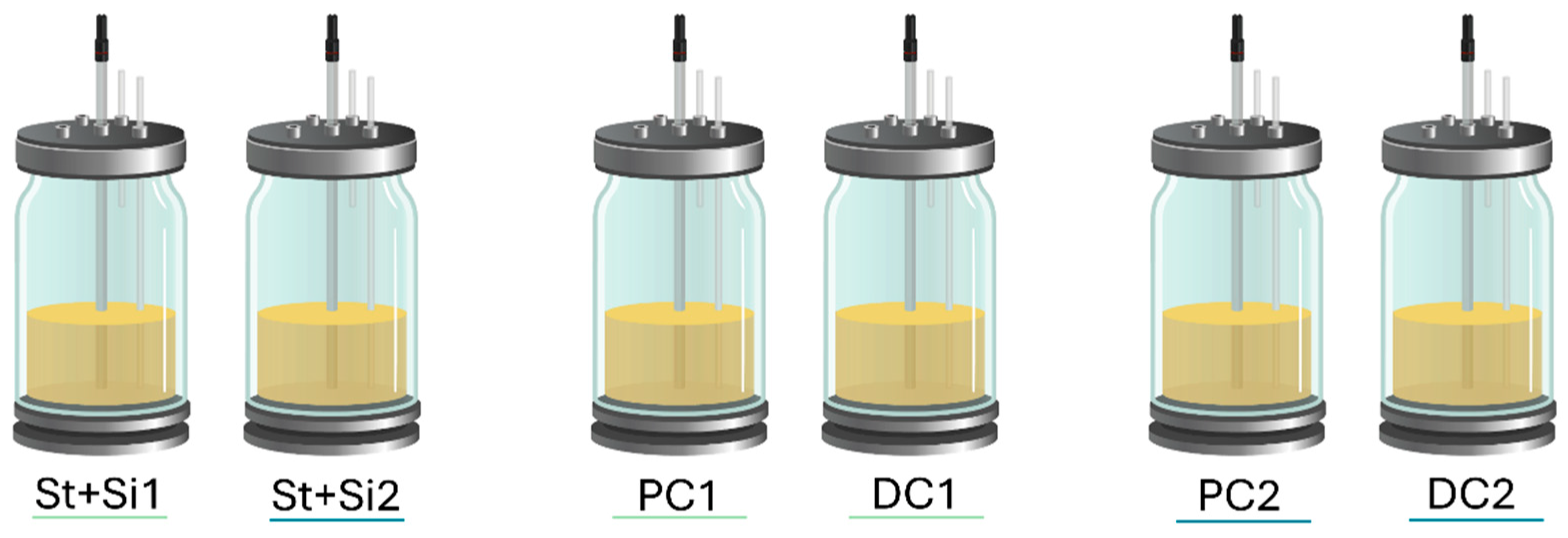
4.4. Experimental Design of the Adapted Short-Term SHIME® Model
4.5. Microbial Community Activity Analysis
4.6. Microbial Community Composition Analysis
4.7. Immune Modulation Analysis
4.8. Data Processing and Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bedu-Ferrari, C.; Biscarrat, P.; Langella, P.; Cherbuy, C. Prebiotics and the Human Gut Microbiota: From Breakdown Mechanisms to the Impact on Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut Microbiome and Health: Mechanistic Insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhogaria, B.; Bhowmik, P.; Kundu, A. Correlation between Human Gut Microbiome and Diseases. Infect. Med. 2022, 1, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; An, L.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Recent Progress in Plant-Derived Polysaccharides with Prebiotic Potential for Intestinal Health by Targeting Gut Microbiota: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 12242–12271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.K.; Singhania, R.R.; Awasthi, M.K.; Varjani, S.; Bhatia, S.K.; Tsai, M.-L.; Hsieh, S.-L.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D. Emerging Prospects of Macro- and Microalgae as Prebiotic. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Chang, S.; Zhang, X.; Luo, F.; Li, W.; Ren, J. The Fate of Dietary Polysaccharides in the Digestive Tract. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 150, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Jung, S.-C.; Kwak, K.; Kim, J.-S. The Role of Prebiotics in Modulating Gut Microbiota: Implications for Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q. Revisit the Effects of Fucoidan on Gut Microbiota in Health and Disease: What Do We Know and What Do We Need to Know? Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2020, 23, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolova, E.; Lukova, P.; Baldzhieva, A.; Katsarov, P.; Nikolova, M.; Iliev, I.; Peychev, L.; Trica, B.; Oancea, F.; Delattre, C.; et al. Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fucoidan: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, M.; Cao, Q.; Ji, A.; Liang, H.; Song, S. Biological Activities of Fucoidan and the Factors Mediating Its Therapeutic Effects: A Review of Recent Studies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Dwan, C.; Wimmer, B.C.; Ronci, M.; Wilson, R.; Johnson, L.; Caruso, V. Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Undaria Pinnatifida Fucoidan in Vivo—A Proteomic Investigation. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Lim, S.Y. Fucoidans and Bowel Health. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lean, Q.Y.; Eri, R.D.; Fitton, J.H.; Patel, R.P.; Gueven, N. Fucoidan Extracts Ameliorate Acute Colitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Xing, M.; Wang, K.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ji, K.; Song, S. Fucoidan Is Not Completely Dependent on Degradation to Fucose to Relieve Ulcerative Colitis. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagamine, T.; Nakazato, K.; Tomioka, S.; Iha, M.; Nakajima, K. Intestinal Absorption of Fucoidan Extracted from the Brown Seaweed, Cladosiphon Okamuranus. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irhimeh, M.R.; Fitton, J.H.; Lowenthal, R.M.; Kongtawelert, P. A Quantitative Method to Detect Fucoidan in Human Plasma Using a Novel Antibody. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 27, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Dwan, C.; Wimmer, B.C.; Wilson, R.; Johnson, L.; Caruso, V. Fucoidan from Undaria Pinnatifida Enhances Exercise Performance and Increases the Abundance of Beneficial Gut Bacteria in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ma, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, P.; Chen, C.; Jia, L.; Li, H. Fucoidan Alleviates Dyslipidemia and Modulates Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet-Induced Mice. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Lv, H.; Yin, T.; Fan, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, H. Fucoidan Protects against High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Modulates Gut Microbiota in Institute of Cancer Research Mice. J. Med. Food 2021, 24, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Jia, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, P.; Song, S.; Ai, C. Undaria Pinnatifida Fucoidan Ameliorates Dietary Fiber Deficiency-Induced Inflammation and Lipid Abnormality by Modulating Mucosal Microbiota and Protecting Intestinal Barrier Integrity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, P.; Fan, S.; Huang, J.; Yu, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, H. Fucoidan and Galactooligosaccharides Ameliorate High-Fat Diet–Induced Dyslipidemia in Rats by Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. Nutrition 2019, 65, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, E.; Cueva, C.; Peláez, C.; Martínez-Cuesta, M.C.; Requena, T. The Computer-Controlled Multicompartmental Dynamic Model of the Gastrointestinal System SIMGI. In The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Duysburgh, C.; Miclotte, L.; Green, J.B.; Watts, K.T.; Sardi, M.I.; Chakrabarti, A.; Khafipour, E.; Marzorati, M. Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Derived Postbiotic Alters Gut Microbiome Metabolism in the Human Distal Colon Resulting in Immunomodulatory Potential in Vitro. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1358456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Abbeele, P.; Duysburgh, C.; Jiang, T.A.; Rebaza, M.; Pinheiro, I.; Marzorati, M. A Combination of Xylooligosaccharides and a Polyphenol Blend Affect Microbial Composition and Activity in the Distal Colon Exerting Immunomodulating Properties on Human Cells. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daguet, D.; Pinheiro, I.; Verhelst, A.; Possemiers, S.; Marzorati, M. Arabinogalactan and Fructooligosaccharides Improve the Gut Barrier Function in Distinct Areas of the Colon in the Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero, J.A.; Killer, J.; Sechovcová, H.; Mrázek, J.; Benada, O.; Fliegerová, K.; Havlík, J.; Kopečný, J. Reclassification of Eubacterium rectale (Hauduroy et al. 1937) Prévot 1938 in a New Genus Agathobacter Gen. Nov. as Agathobacter rectalis Comb. Nov., and Description of Agathobacter ruminis sp. Nov., Isolated from the Rumen Contents of Sheep and Cows. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlier, J.P.; Marchandin, H.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Lorin, V.; Henry, C.; Carriere, C.; Jean-Pierre, H. Anaeroglobus Geminatus Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Novel Member of the Family Veillonellaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, I.; Bouvet, P.; Legeay, C.; Gophna, U.; Weinberger, A. Eisenbergiella tayi Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., Isolated from Human Blood. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, K.; El Abbar, F.; Dobranowski, P.; Manoogian, J.; Butcher, J.; Figeys, D.; Mack, D.; Stintzi, A. Butyrate’s Role in Human Health and the Current Progress towards Its Clinical Application to Treat Gastrointestinal Disease. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recharla, N.; Geesala, R.; Shi, X.-Z. Gut Microbial Metabolite Butyrate and Its Therapeutic Role in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Literature Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiano, A.J.; Gadani, S.P.; Kipnis, J. Interactions of Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Brain Development and Function. Brain Res. 2015, 1617, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canani, R.B. Potential Beneficial Effects of Butyrate in Intestinal and Extraintestinal Diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toribio-Mateas, M. Harnessing the Power of Microbiome Assessment Tools as Part of Neuroprotective Nutrition and Lifestyle Medicine Interventions. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Lee, M.; Chang, E.B. The Gut Microbiome and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piggott, D.A.; Tuddenham, S. The Gut Microbiome and Frailty. Transl. Res. 2020, 221, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Zhu, S.; Wang, B.; Duan, L. Alterations of Gut Microbiota in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on 16S RRNA-Targeted Sequencing: A Systematic Review. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Lee, G.; Son, H.; Koh, H.; Kim, E.S.; Unno, T.; Shin, J.-H. Butyrate Producers, “The Sentinel of Gut”: Their Intestinal Significance with and beyond Butyrate, and Prospective Use as Microbial Therapeutics. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Lordan, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Gut Microbes from the Phylogenetically Diverse Genus Eubacterium and Their Various Contributions to Gut Health. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1802866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radjabzadeh, D.; Bosch, J.A.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Ikram, M.A.; van Meurs, J.B.J.; Luik, A.I.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Lok, A.; van Duijn, C.M.; et al. Gut Microbiome-Wide Association Study of Depressive Symptoms. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Sin, Z.Y.; Yu, J.; Zhao, S.; Xi, Z.; Bruzzone, R.; Tun, H.M. Multi-Cohort Analysis of Depression-Associated Gut Bacteria Sheds Insight on Bacterial Biomarkers across Populations. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, C.F.; Haldor Hansen, T.; Vinberg, M.; Kessing, L.V.; Coello, K. Associations between Short-Chain Fatty Acid Levels and Mood Disorder Symptoms: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha, I.M.G.; Torrinhas, R.; Fonseca, D.; Lyra, C.d.O.; de Sousa Alves Neri, J.L.; Balmant, B.D.; Callado, L.; Charlton, K.; Queiroz, N.; Waitzberg, D.L. Pro-Inflammatory Diet Is Correlated with High Veillonella Rogosae, Gut Inflammation and Clinical Relapse of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; You, H.J.; Bajaj, J.S.; Joo, S.K.; Yu, J.; Park, S.; Kang, H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Distinct Signatures of Gut Microbiome and Metabolites Associated with Significant Fibrosis in Non-Obese NAFLD. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittayanon, R.; Lau, J.T.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Tse, F.; Yuan, Y.; Surette, M.; Moayyedi, P. Differences in Gut Microbiota in Patients with vs without Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 930–946.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, M.I.; Conrads, G.; Abdelbary, M.M.H. Isolation, Identification, and Significance of Salivary Veillonella Spp., Prevotella Spp., and Prevotella Salivae in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1278582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonero, F.; Benefiel, A.C.; Alizadeh-Ghamsari, A.H.; Gaskins, H.R. Microbial Pathways in Colonic Sulfur Metabolism and Links with Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gao, S.; Fu, M.; Sakurai, T.; Terakawa, S. Fucoidan Inhibits Ca2+ Responses Induced by a Wide Spectrum of Agonists for G-protein-coupled Receptors. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 17, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engevik, A.C.; Engevik, M.A. Exploring the Impact of Intestinal Ion Transport on the Gut Microbiota. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, T.C.; Anderson, M.E.; Moots, R.J. The Many Faces of Interleukin-6: The Role of IL-6 in Inflammation, Vasculopathy, and Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 2011, 721608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhendi, A.; Naser, S.A. The Dual Role of Interleukin-6 in Crohn’s Disease Pathophysiology. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1295230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, C.; Bai, J.; Wang, C. In Vitro Fermentation Characteristics of Fucoidan and Its Regulatory Effects on Human Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 141998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.-B.; Yang, G.; Lai, H.; Zheng, Q.; Xia, W.; Zhao, M. Structural Characterization and Human Gut Microbiota Fermentation in Vitro of a Polysaccharide from Fucus Vesiculosus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckburg, P.B.; Bik, E.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Purdom, E.; Dethlefsen, L.; Sargent, M.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Relman, D.A. Diversity of the Human Intestinal Microbial Flora. Science 2005, 308, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filisetti-Cozzi, T.M.C.C.; Carpita, N.C. Measurement of Uronic Acids without Interference from Neutral Sugars. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 197, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodgson, K.S. Determination of Inorganic Sulphate in Studies on the Enzymic and Non-Enzymic Hydrolysis of Carbohydrate and Other Sulphate Esters. Biochem. J. 1961, 78, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irhimeh, M.R.; Fitton, J.H.; Lowenthal, R.M. Fucoidan Ingestion Increases the Expression of CXCR4 on Human CD34+ Cells. Exp. Hematol. 2007, 35, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irhimeh, M.R.; Fitton, J.H.; Lowenthal, R.M. Pilot Clinical Study to Evaluate the Anticoagulant Activity of Fucoidan. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2009, 20, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molly, K.; Vande Woestyne, M.; Verstraete, W. Development of a 5-Step Multi-Chamber Reactor as a Simulation of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1993, 39, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molly, K.; Woestyne, M.V.; De Smet, I.; Verstraete, W. Validation of the Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME) Reactor Using Microorganism-Associated Activities. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 1994, 7, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Abbeele, P.; Belzer, C.; Goossens, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; De Vos, W.M.; Thas, O.; De Weirdt, R.; Kerckhof, F.-M.; Van de Wiele, T. Butyrate-Producing Clostridium Cluster XIVa Species Specifically Colonize Mucins in an in Vitro Gut Model. ISME J. 2013, 7, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possemiers, S.; Bolca, S.; Grootaert, C.; Heyerick, A.; Decroos, K.; Dhooge, W.; De Keukeleire, D.; Rabot, S.; Verstraete, W.; Van de Wiele, T. The Prenylflavonoid Isoxanthohumol from Hops (Humulus lupulus L.) Is Activated into the Potent Phytoestrogen 8-Prenylnaringenin In Vitro and in the Human Intestine. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1862–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Yao, Q.; Ma, G.-L.; Fan, X. Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME®): Current Developments, Applications, and Future Prospects. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boever, P.; Verstraete, W.; Deplancke, B. Fermentation by Gut Microbiota Cultured in a Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem Is Improved by Supplementing a Soygerm Powder. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2599–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, N.; Top, E.M.; Verstraete, W.; Siciliano, S.D. Bioaugmentation as a Tool to Protect the Structure and Function of an Activated-Sludge Microbial Community against a 3-Chloroaniline Shock Load. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duysburgh, C.; Van den Abbeele, P.; Krishnan, K.; Bayne, T.F.; Marzorati, M. A Synbiotic Concept Containing Spore-Forming Bacillus Strains and a Prebiotic Fiber Blend Consistently Enhanced Metabolic Activity by Modulation of the Gut Microbiome in Vitro. Int. J. Pharm. X 2019, 1, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govaert, M.; Rotsaert, C.; Vannieuwenhuyse, C.; Duysburgh, C.; Medlin, S.; Marzorati, M.; Jarrett, H. Survival of Probiotic Bacterial Cells in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract and the Effect of the Surviving Population on the Colonic Microbial Community Activity and Composition. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghyselinck, J.; Verstrepen, L.; Moens, F.; Van Den Abbeele, P.; Bruggeman, A.; Said, J.; Smith, B.; Barker, L.A.; Jordan, C.; Leta, V.; et al. Influence of Probiotic Bacteria on Gut Microbiota Composition and Gut Wall Function in an In-Vitro Model in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Pharm. X 2021, 3, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic Biomarker Discovery and Explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Soneson, C.; Germain, P.-L.; Schmidt, T.S.B.; Mering, C.V.; Robinson, M.D. TreeclimbR Pinpoints the Data-Dependent Resolution of Hierarchical Hypotheses. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
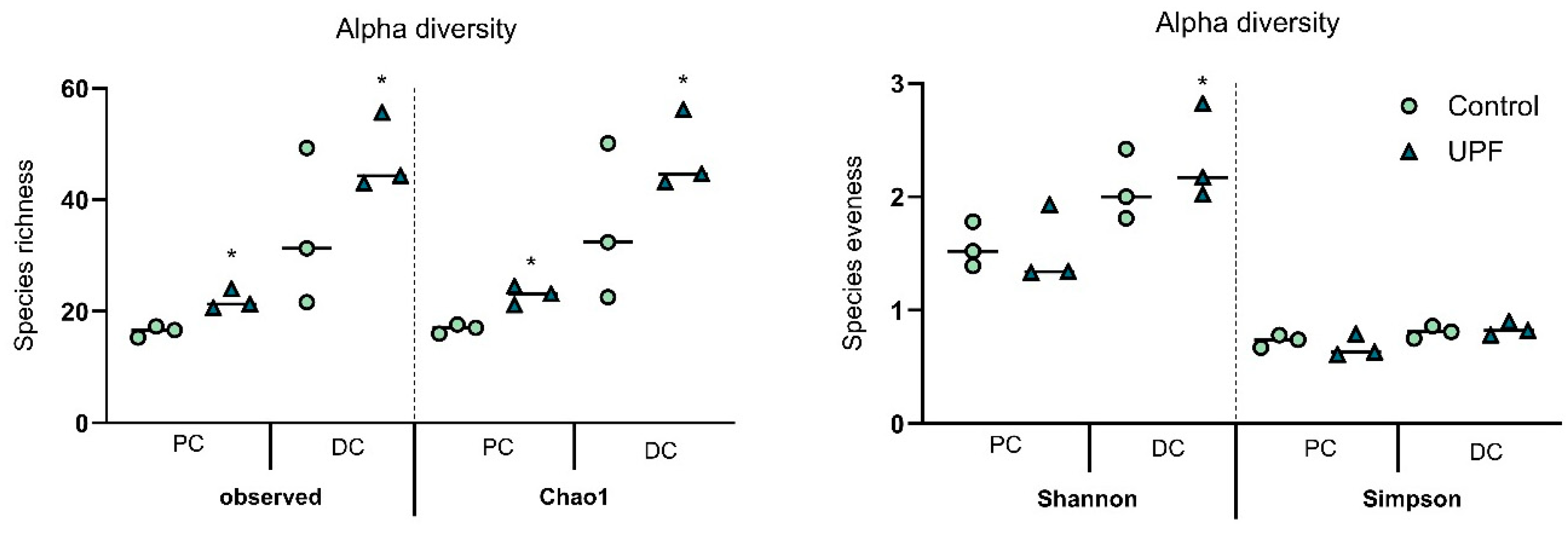

| Alpha-Diversity | Observed | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proximal colon | Control | 16.44 ± 1.81 | 16.92 ± 2.05 | 1.56 ± 0.19 | 0.73 ± 0.06 |
| UPF | 22.00 ± 3.46 | 22.94 ± 3.37 | 1.53 ± 0.37 | 0.68 ± 0.12 | |
| Distal colon | Control | 34.11 ± 13.29 | 35.06 ± 13.08 | 2.08 ± 0.29 | 0.81 ± 0.06 |
| UPF | 47.67 ± 10.69 | 48.02 ± 10.75 | 2.34 ± 0.40 | 0.83 ± 0.06 | |
| Fucoidan Extract | % Total Sugars | % Uronic Acids | % Sulphate | % Fucoidan (Dry Weight) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UPF2022555 | 58.34 | 4.69 | 29.90 | 86.9 | |||||
| Fucoidan Extract | As (ppm) | Cd (ppm) | Fucose | Xylose | Mannose | Galactose | Glucose | Arabinose | Rhamnose |
| UPF2022555 | 7.22 | 1.62 | 44.1 | 0.8 | 4.3 | 45.1 | 2.9 | 1.6 | 1.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wimmer, B.C.; Dwan, C.; De Medts, J.; Duysburgh, C.; Rotsaert, C.; Marzorati, M. Undaria pinnatifida Fucoidan Enhances Gut Microbiome, Butyrate Production, and Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects in an In Vitro Short-Term SHIME® Coupled to a Caco-2/THP-1 Co-Culture Model. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060242
Wimmer BC, Dwan C, De Medts J, Duysburgh C, Rotsaert C, Marzorati M. Undaria pinnatifida Fucoidan Enhances Gut Microbiome, Butyrate Production, and Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects in an In Vitro Short-Term SHIME® Coupled to a Caco-2/THP-1 Co-Culture Model. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(6):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060242
Chicago/Turabian StyleWimmer, Barbara C., Corinna Dwan, Jelle De Medts, Cindy Duysburgh, Chloë Rotsaert, and Massimo Marzorati. 2025. "Undaria pinnatifida Fucoidan Enhances Gut Microbiome, Butyrate Production, and Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects in an In Vitro Short-Term SHIME® Coupled to a Caco-2/THP-1 Co-Culture Model" Marine Drugs 23, no. 6: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060242
APA StyleWimmer, B. C., Dwan, C., De Medts, J., Duysburgh, C., Rotsaert, C., & Marzorati, M. (2025). Undaria pinnatifida Fucoidan Enhances Gut Microbiome, Butyrate Production, and Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects in an In Vitro Short-Term SHIME® Coupled to a Caco-2/THP-1 Co-Culture Model. Marine Drugs, 23(6), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060242






