Harnessing Thalassochemicals: Marine Saponins as Bioactive Agents in Nutraceuticals and Food Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Saponin Extraction, Stability, and Bioavailability
2.1. Extraction Methods and Challenges
2.2. Critical Challenges in the Structural Identification of Marine Saponins
2.3. Limitations in Structural Identification and Experimental Proposal
2.4. Stability and Bioavailability
2.4.1. Enhancing Stability
2.4.2. Improving Bioavailability: Conflicting Evidence and Future Direction
2.4.3. Recent Technological Advancements
3. Physico-Chemical, Molecular, and Biochemical Properties of Saponins
3.1. Structure and Classification
3.2. Biosynthesis and Bioactivities
3.3. Structural Trends and Their Implications for Computational Modeling
4. Structure–Activity Relationships (SARs) of Terrestrial and Marine Saponins
4.1. SAR of Terrestrial Saponins
4.2. SAR of Marine Saponins
4.3. QSAR Analysis of Saponins
4.4. SAR of Marine Saponins: Expanded Evidence and Bioassay Correlation
5. Saponins in Pharma/Nutraceuticals and Food Technology
5.1. Role of Saponins as Nutraceuticals
5.1.1. Bioactivities of Saponins
5.1.2. Saponins as Nutraceuticals
6. Practical Applications and Case Studies
6.1. Therapeutic and Biotechnological Uses
6.2. Cosmetic Innovations
6.3. Industrial Applications
6.4. Research and Development
6.5. The Potential of Thalassochemicals: Marine Saponins
6.6. Conclusion on Practical Applications
7. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Timilsena, Y.P.; Phosanam, A.; Stockmann, R. Perspectives on Saponins: Food Functionality and Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tang, X.; Liu, F.; Mao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W.; Cui, S. Sources, metabolism, health benefits and future development of saponins from plants. Food Res. Int. 2024, 197, 115226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, A.; Hour, Y.; Lee, Y.C. An outlook on the versatility of plant saponins: A review. Fitoterapia 2024, 174, 105858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kholif, A.E. A Review of Effect of Saponins on Ruminal Fermentation, Health and Performance of Ruminants. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, A.; Kim, H.; Moon, J.Y.; Mohan, A.; Lee, Y.C. Exploring the imminent trends of saponins in personal care product development: A review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 205, 117489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanlayavattanakul, M.; Mersni, D.; Lourith, N. Plant-derived saponins and their prospective for cosmetic and personal care products. Bot. Stud. 2024, 65, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hao, R.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Huang, K.; Cao, H.; Farag, M.A.A.; Battino, M.; Daglia, M.; Capanoglu, E.; et al. Health benefits of saponins and its mechanisms: Perspectives from absorption, metabolism, and interaction with gut. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 9311–9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, J. Research progress on chemical diversity of saponins in Panax ginseng. Chin. Herb. Med. 2024, 16, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Morikawa, T.; Nakamura, S.; Muraoka, O.; Yoshikawa, M. New biofunctional effects of oleanane-type triterpene saponins. J. Nat. Med. 2023, 77, 644–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Thakur, K.; Battino, M.; Cao, H.; Farag, M.A.; Xiao, J.; Wei, Z. Asparagus saponins: Effective natural beneficial ingredient in functional foods, from preparation to applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 12284–12302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.Y.; Li, S.; Pei, W.J.; Gu, Y.L.; Piao, X.L. Natural Saponins on Cholesterol-Related Diseases: Treatment and Mechanism. Phytother. Res. 2025, 39, 1292–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, N.; Wang, L.; Zeng, M.; Wang, Y.; Yu, B.; Zeng, W.; Jiang, X.; Suo, Y. Saponins as therapeutic candidates for atherosclerosis. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 1651–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majnooni, M.B.; Fakhri, S.; Ghanadian, S.M.; Bahrami, G.; Mansouri, K.; Iranpanah, A.; Farzaei, M.H.; Mojarrab, M. Inhibiting Angiogenesis by Anti-Cancer Saponins: From Phytochemistry to Cellular Signaling Pathways. Metabolites 2023, 13, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Lv, N.; Wang, L.; Gan, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, L. Therapeutic Candidates for Alzheimer’s Disease: Saponins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.J.; Wang, T.; Cummins, S.F. Asteroid Saponins: A Review of Their Bioactivity and Selective Cytotoxicity. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Balhara, V.; Castillo, A.M.J.; Balsevich, J.; Johnston, L.J. Interaction of saponin 1688 with phase separated lipid bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Monje-Galvan, V. Effect of Glycone Diversity on the Interaction of Triterpenoid Saponins and Lipid Bilayers. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 7, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondevilla, J.C.; Hanashima, S.; Mukogawa, A.; Miyazato, D.G.; Umegawa, Y.; Murata, M. Effect of the number of sugar units on the interaction between diosgenyl saponin and membrane lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2023, 1865, 184145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreij, R.; Prevost, S.; Dargel, C.; Dattani, R.; Hertle, Y.; Wrede, O.; Hellweg, T. Interaction of the Saponin Aescin with Ibuprofen in DMPC Model Membranes. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4446–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Hong, C.; Zou, W.; Ye, Z.; Lu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ding, Y. Recent advances in the anti-tumor activities of saponins through cholesterol regulation. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 15, 1469392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Luo, H.; Fan, L.; Tian, X.; Tang, A.; Wu, X.; Dong, K.; Su, Z. Potential Immunoregulatory Mechanism of Plant Saponins: A Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Sun, Y.; Bai, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, Q.; Kuang, H. Effects of saponins from Chinese herbal medicines on signal transduction pathways in cancer: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1159985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagbohun, O.F.; Joseph, J.S.; Oriyomi, O.V.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Saponins of North Atlantic Sea Cucumber: Chemistry, Health Benefits, and Future Prospectives. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Monje-Galvan, V. In Vitro and In Silico Studies of Antimicrobial Saponins: A Review. Processes 2023, 11, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stitou, M.; Toufik, H.; Bouachrine, M.; Lamchouri, F. Quantitative structure-activity relationships analysis, homology modeling, docking and molecular dynamics studies of triterpenoid saponins as Kirsten rat sarcoma inhibitors. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoa, N.M.; Phong, N.V.; Yang, S.Y.; Min, B.S.; Kim, J.A. Spectroscopic analysis, kinetic mechanism, computational docking, and molecular dynamics of active metabolites from the aerial parts of Astragalus membranaceus Bunge as tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 134, 106464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, B.J.; Olubiyi, O.O.; Wang, X.; Fisusi, F.A.; Akinniyi, G.A.; Van Heerden, F.R.; Strodel, B. Schistosomiasis: Snail-vector control, molecular modelling and dynamic studies of bioactive N-acetylglycoside saponins from Tetrapleura tetraptera. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2018, 77, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iksen, I.; Witayateeraporn, W.; Wirojwongchai, T.; Suraphan, C.; Pornputtapong, N.; Singharajkomron, N.; Nguyen, H.M.; Pongrakhananon, V. Identifying molecular targets of Aspiletrein-derived steroidal saponins in lung cancer using network pharmacology and molecular docking-based assessments. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewe, J.; Schoning, V.; Danton, O.; Schenk, A.; Boonen, G. Machine Learning-Based Analysis Reveals Triterpene Saponins and Their Aglycones in Cimicifuga racemosa as Critical Mediators of AMPK Activation. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Chang, W.; Xu, Y.; Lin, F. Prediction of Hemolytic Toxicity for Saponins by Machine-Learning Methods. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Sun, M.; Jiang, M.; Shi, X.; Xu, X.; Ding, M.; Chen, B.; Yu, H.; et al. Machine learning prediction for constructing a universal multidimensional information library of Panax saponins (ginsenosides). Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Xian, B.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, T.; Chen, S.; Wen, F.; Pei, J. Machine learning and bioinformatics-based insights into the potential targets of saponins in Paris polyphylla smith against non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1005896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Huo, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Z. Ultrasonic extraction and antioxidant evaluation of oat saponins. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 109, 106989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, T.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Y.; Jia, F.; He, K.; Yang, Y. Quantitative Changes and Transformation Mechanisms of Saponin Components in Chinese Herbal Medicines during Storage and Processing: A Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H. Naturally Occurring Polyhydroxylated Spirostanol Saponins, A Review of the Classification, Sources, Biosynthesis, Biological Activities, and Toxicity. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 22, e202401720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, M.; Huang, J.; Qiu, Q.; Liang, Y.; Meng, J.; Park, R.Y.; Li, P.C.H.; Sun, Y. Development of organic three-phase laminar flow microfluidic chip for extraction of ginsenosides from Panax ginseng. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 236, 115724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa-Cansigno, C.; Serviere-Zaragoza, E.; Morales-Martinez, T.K.; Ascacio-Valdes, J.A.; Morreeuw, Z.P.; Gauyat, C.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Reyes, A.G. The antioxidant and anti-elastase activity of the brown seaweed Sargassum horridum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) and their early phenolics and saponins profiling for green cosmetic applications. Algal Res.—Biomass Biofuels Bioprod. 2023, 75, 103271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, K. Effects of Different Culture Times Genes Expression on Ginsenoside Biosynthesis of the Ginseng Adventitious Roots in Panax ginseng. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharenko, A.; Romanchenko, D.; Thinh, P.D.; Pikula, K.; Hang, C.T.T.; Yuan, W.; Xia, X.; Chaika, V.; Chernyshev, V.; Zakharenko, S.; et al. Features and Advantages of Supercritical CO2 Extraction of Sea Cucumber Cucumaria frondosa japonica Semper, 1868. Molecules 2020, 25, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tao, L.; Zhang, X.; Hao, F.; Zhao, S.; Han, L.; Bai, C. Recent Advances in Separation and Analysis of Saponins in Natural Products. Separations 2022, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.J.; Wang, P.w.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.Y.; Cao, X.; Luo, Y.Q.; Li, Q.; Njolibimi, M.; Li, W.j.; Hong, B.; et al. A high-permeability method for extracting purple yam saponins based on ultrasonic-assisted natural deep eutectic solvent. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Xie, P.; Huang, L. Enhanced and Green Extraction of Saponins from Gleditsia sinensis Lam. Pods by Ultrasound-Assisted Deep Eutectic Solvents: Optimization and Comprehensive Characterization. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2025, 18, 1919–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; You, L.; Pedisic, S.; Shao, P. Saponins Based on Medicinal and Edible Homologous Plants: Biological Activity, Delivery Systems and Its Application in Healthy Foods. Food Bioeng. 2024, 3, 464–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Jia, M.; Yang, X.; Chai, Y.; Bao, Y. Interaction between lactic acid bacteria and Polygonatum sibiricum saponins and its application to microencapsulated co-delivery. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 138959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Liao, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, H.; Kuang, J.; Li, J.; Guo, J.; Huang, T.; Li, J. Tea saponin-Zein binary complex as a quercetin delivery vehicle: Preparation, characterization, and functional evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; El-Demerdash, A.; Owen, C.; Srivastava, V.; Wu, D.; Kikuchi, S.; Reed, J.; Hodgson, H.; Harkess, A.; Shu, S.; et al. Unlocking saponin biosynthesis in soapwort. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2024, 21, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, J.; Bujak, P.; Dlugosz, M. Permeabilization of Calendula officinalis L. hairy root cultures for the release of accumulated triterpenoid saponins. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2024, 159, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Pack, S.P. Marine-Derived Bioactive Ingredients in Functional Foods for Aging: Nutritional and Therapeutic Perspectives. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosri, N.; Khalifa, S.A.M.; Attia, N.F.; Du, M.; Yin, L.; Abolibda, T.Z.; Zhai, K.; Guo, Z.; El-Seedi, H.R. Advancing sustainability in the green engineering of nanocomposites based on marine-derived polymers and their applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegal, J.; Jeong, E.J.; Yang, M.H. A Review of the Different Methods Applied in Ginsenoside Extraction From Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius Roots. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19868393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razgonova, M.P.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Kalenik, T.K.; Nosyrev, A.E.; Stratidakis, A.K.; Mezhuev, Y.O.; Burykina, I.T.; Nicolae, A.C.; Arsene, A.L.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; et al. Supercritical fluid technology and supercritical fluid chromatography for application in ginseng extracts. Farmacia 2019, 67, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.N.T.; Vuong, Q.V.; Bowyer, M.C.; Scarlett, C.J. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don (Patricia White cultivar) stem for maximizing saponin yield and antioxidant capacity. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Le, M.D.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Khong, T.T.; Nguyen, V.H.; Nguyen, H.N.; Huynh, B.N.D.; Tran, H.T.M.; Trang, T.S. Microwave-assisted extraction for optimizing saponin yield and antioxidant capacity from cacao pod husk (Theobroma cacao L.). J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decroo, C.; Colson, E.; Lemaur, V.; Caulier, G.; De Winter, J.; Cabrera-Barjas, G.; Cornil, J.M.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P. Ion mobility mass spectrometry of saponin ions. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 33, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, P.; Savoca, A.; Gabriele, M.; Pasini, D.; Bombardelli, E.; Monti, D. Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Saponins: Challenges and Perspectives. Molecules 2023, 28, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.R.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Saponin Mass Spectrometry Databases: Trends and Gaps in Structural Coverage. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Shim, S.L.; Jang, E.S.; Choi, S.G. Ginsenoside stability and antioxidant activity of Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng CA meyer) extract as affected by temperature and time. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 200, 116205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, F.; Weiss, J.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Lutein-enriched emulsion-based delivery systems: Influence of emulsifiers and antioxidants on physical and chemical stability. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulier, G.; Flammang, P.; Rakotorisoa, P.; Gerbaux, P.; Demeyer, M.; Eeckhaut, I. Preservation of the bioactive saponins of Holothuria scabra through the processing of trepang. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2013, 54, 685–690. [Google Scholar]
- Phrompittayarat, W.; Wittaya-Areekul, S.; Jetiyanon, K.; Putalun, W.; Tanaka, H.; Ingkaninan, K. Stability Studies of Saponins in Bacopla monnieri Dried Ethanolic Extracts. Planta Medica 2008, 74, 1756–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Song, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, K.; Su, D.; Feng, Y.; Yang, S. Comparative pharmacokinetic profiles of five poorly soluble pulchinenosides in different formulations from Pulsatilla chinensis saponins extracts for enhanced bioavailability. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.H.; Yang, X.L.; Xiao, W.; Wang, Z.Z.; Ding, G.; Huang, W.Z.; Yang, Z.L.; Zhang, C.F. Microcrystalline Preparation of Akebia Saponin D for its Bioavailability Enhancement in Rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Pan, L.; Qi, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Guo, L.; Zhou, J. Systematic review of recent advances in pharmacokinetics of four classical Chinese medicines used for the treatment of cerebrovascular disease. Fitoterapia 2013, 88, 50–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Chemical Characterization and Bioaccessibility of Bioactive Compounds from Saponin-Rich Extracts and Their Acid-Hydrolysates Obtained from Fenugreek and Quinoa. Foods 2020, 9, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmappa, R.; Wang, S.; Zheng, M.; Misra, R.C.; Huang, A.C.; Saalbach, G.; Chang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Hinman, V.; Bao, Z.; et al. Biosynthesis of saponin defensive compounds in sea cucumbers. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, Y.S.; Ryu, C.H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.M.; Jeon, H.; Won, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. Micro-/nano-sized delivery systems of ginsenosides for improved systemic bioavailability. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskov, I.A.; Savic, I.M.; Stanisavljevic, N.D.G.; Kundakovic-Vasovic, T.D.; Selgrad, J.S.R.; Gajic, I.M.S. Stabilization of Black Locust Flower Extract via Encapsulation Using Alginate and Alginate-Chitosan Microparticles. Polymers 2024, 16, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Xue, B.; Yang, C.; Miao, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Q.; Cai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; He, H.; et al. Biopharmaceutical characters and bioavailability improving strategies of ginsenosides. Fitoterapia 2018, 129, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J.; Deng, M.; Yang, L. Influence of ginsenoside Rh1 and F1 on human cytochrome P450 enzymes. Planta Medica 2006, 72, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yue, P.; Yang, M. Novel breviscapine nanocrystals modified by panax notoginseng saponins for enhancing bioavailability and synergistic anti-platelet aggregation effect. Colloids Surf. B—Biointerfaces 2019, 175, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, D.; Ron, O.; Baardsen, G.; Smedsgaard, J.; Koppe, W.; Froklaer, H. Soyasaponins resist extrusion cooking and are not degraded during gut passage in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6428–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.R.; Yau, L.F.; Zhang, R.; Xia, Y.; Ma, J.; Ho, H.M.; Hu, P.; Hu, M.; Liu, L.; Jiang, Z.H. Transformation of Ginsenosides from Notoginseng by Artificial Gastric Juice Can Increase Cytotoxicity toward Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2558–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, D.; Lee, Y.Y.; Chen, N.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, C. Physicochemical and In Vitro Digestion Properties of Curcumin-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles with Different Solid Lipids and Emulsifiers. Foods 2023, 12, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Liang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, H. Preparation and evaluation of lecithin/zein hybrid nanoparticles for the oral delivery of Panax notoginseng saponins. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 164, 105882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, P.J.; Sorensen, P.M. Characterization of saponin foam from Saponaria officinalis for food applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, T.B.; Santamaria-Echart, A.; Colucci, G.; Plasencia, P.; Costa, P.S.; Dias, M.M.; Pinho, S.P.; Barreiro, M.F. Saponin-based natural nanoemulsions as alpha-tocopherol delivery systems for dermal applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 391, 123371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Zhang, L.; Liao, W.; Liu, J.; Mao, L.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) stabilized by natural or synthetic emulsifiers for lutein delivery: Improved physicochemical stability, antioxidant activity, and bioaccessibility. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Y.; Su, W.W.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Zeng, X. Gut microbiota-mediated metabolism of Panaxnotoginseng saponins and its role in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Tradit. Med. Res. 2024, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Gong, L.; Lv, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, T.; Yang, S.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, Bioavailability, Excretion and Metabolism Studies of Akebia Saponin D in Rats: Causes of the Ultra-Low Oral Bioavailability and Metabolic Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 621003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Koo, H.B.; Jeon, S.W.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Jun, K.M.; Choi, Y.E. Modification of ginsenoside saponin composition via the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of protopanaxadiol 6-hydroxylase gene in Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confalonieri, M.; Carelli, M.; Gianoglio, S.; Moglia, A.; Biazzi, E.; Tava, A. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Targeted Mutagenesis of CYP93E2 Modulates the Triterpene Saponin Biosynthesis in Medicago truncatula. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 690231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, K.; Yano, R.; Tochigi, S.; Fujisawa, Y.; Tsuchinaga, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Takada, Y.; Kaga, A.; Anai, T.; Tsukamoto, C.; et al. Genetic and functional characterization of Sg-4 glycosyltransferase involved in the formation of sugar chain structure at the C-3 position of soybean saponins. Phytochemistry 2018, 156, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Zhang, P.; Ge, F.; Liu, D.Q.; Chen, C.Y. Enhancement of triterpenoid saponins biosynthesis in Panax notoginseng cells by co-overexpressions of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase and squalene synthase genes. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 122, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naha, S.; Kaur, S.; Bhattacharya, R.; Cheemanapalli, S.; Iyyappan, Y. ANPS: Machine learning based server for identification of anti-nutritional proteins in plants. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2024, 24, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Li, F.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Bao, J.; Lin, J.; Jiang, W. Optimizing the extraction process of total saponins from Panax vietnamensis based on response surface analysis and backpropagation neural network-genetic algorithm. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 220, 119252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, S.S.S.S.; Rajamanickam, C.; Saraswathy, S.; Venkatesan, K.; Balakumbahan, R.; Vijayasamundeeswari, A.; Sankar, C. Sapindaceae fruits: A comprehensive overview on phytochemicals, nutraceuticals and health benefits application. Plant Sci. Today 2024, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen-Sanchez, J.S.; Rojas-Villacorta, W.; de Albuquerque, R.D.D.G. Andean Fabaceae Species with Pharmacological Potential: Exploration of Antioxidant, Anticarcinogenic, and Antimicrobial Properties. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaoita, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Machida, K. Terpenoids and Related Compounds from Plants of the Family Compositae (Asteraceae). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolnik, A.; Olas, B. The Plants of the Asteraceae Family as Agents in the Protection of Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.S.; Akhtar, N.; Alsayegh, A.A.; Abusudah, W.F.; Almohmadi, N.H.; Shaheen, H.M.; Singh, T.G.; De Waard, M. Bioactive Compounds, Pharmacological Actions, and Pharmacokinetics of Genus Acacia. Molecules 2022, 27, 7340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xia, B.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Li, C.; Lin, L. Research progress in steroidal saponins from the genus Polygonatum: Chemical components, biosynthetic pathways and pharmacological effects. Phytochemistry 2023, 213, 113731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porte, S.; Joshi, V.; Shah, K.; Chauhan, N.S. Plants’ steroidal saponins—A review on its pharmacology properties and analytical techniques. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 8, 350–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kaul, S.; Dhar, M.K. A systematic review on ethnobotany, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Dioscorea bulbifera L. (Dioscoreaceae). S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 170, 367–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Rodriguez, B.; Gutierrez-Uribe, J.A.; Guajardo-Flores, D.; Santos-Zea, L. Microencapsulation of steroidal saponins from agave sap concentrate using different carriers in spray drying. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2022, 28, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Chaudhuri, P.K. Structural characteristics, bioavailability and cardioprotective potential of saponins. Integr. Med. Res. 2018, 7, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Zhi, Z.; Hu, Y.; Ge, J.; Ye, X.; Tian, D.; Linhardt, R.J.; Chen, S. 4-O-Sulfation in sea cucumber fucodians contribute to reversing dyslipidiaemia caused by HFD. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Dave, D.; Shahidi, F. Sulfated polysaccharides in sea cucumbers and their biological properties: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawas, U.W.; Abou El-Kassem, L.T.; Shaher, F.M.; Ghandourah, M.; Al-Farawati, R. Sulfated Triterpene Glycosides from the Saudi Red Sea Cucumber Holothuria atra with Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activities. Thalassas 2021, 37, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grauso, L.; Yegdaneh, A.; Sharifi, M.; Mangoni, A.; Zolfaghari, B.; Lanzotti, V. Molecular Networking-Based Analysis of Cytotoxic Saponins from Sea Cucumber Holothuria atra. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, H.; Kushwaha, A.; Behera, P.C.; Shahi, N.C.; Kushwaha, K.P.S.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, K.K. The Pink Oyster Mushroom, Pleurotus djamor (Agaricomycetes): A Potent Antioxidant and Hypoglycemic Agent. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2021, 23, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, B.; Li, J.; Dong, N.; Chang, X.; Wang, J.; Peng, H.; Zha, L.; Gui, S. Identification and functional characterization of two trans-isopentenyl diphosphate synthases and one squalene synthase involved in triterpenoid biosynthesis in Platycodon grandiflorus. Planta 2023, 258, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, Z.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, H. Cloning and functional characterization of the oxidative squalene cyclase gene in the deep-sea holothurian Chiridota sp. Gene 2024, 894, 147971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Liang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J. Both the mevalonate and the non-mevalonate pathways are involved in ginsenoside biosynthesis. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanan, P.; Yang, T.J.; Song, Y.H. Genes and Regulatory Mechanisms for Ginsenoside Biosynthesis. J. Plant Biol. 2023, 66, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, L. Triterpenoid saponin biosynthesis genes and their expression patterns during the development of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 2295–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, R.; Pedersen, M.C.; Hannappel, Y.; Schweins, R.; Prevost, S.; Dattani, R.; Arleth, L.; Hellweg, T. Aescin-Induced Conversion of Gel-Phase Lipid Membranes into Bicelle-like Lipid Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16244–16255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, N.N.Q.; Fukushima, E.O.; Muranaka, T. Structure and hemolytic activity relationships of triterpenoid saponins and sapogenins. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, F.; Yang, S.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L. Research Progress on the Anti-Cancer Effects of Astragalus membranaceus Saponins and Their Mechanisms of Action. Molecules 2024, 29, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Qi, Z.; Shan, S.; Xie, D.; Tan, X. Advances in Separation, Biological Properties, and Structure–Activity Relationship of Triterpenoids Derived from Camellia oleifera Abel. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 4574–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, P.; Colson, E.; André, J.; Gerbaux, P. Horse Chestnut Saponins—Escins, Isoescins, Transescins, and Desacylescins. Molecules 2023, 28, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Kim, H.; Wang, P. Development of semisynthetic saponin immunostimulants. Med. Chem. Res. 2024, 33, 1292–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Wei, J.; Niu, Y.; Yang, M.; Jin, Y.; Du, Y.; Sun, Q. Investigation of Pharmacodynamic Material Basis of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma and Its Processed Products Based on Plant Metabolomics and Molecular Docking Technology. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 37, e9473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y. Syntheses of Natural Products OSW-1, Superstolide A and Their Derivatives. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, K.; Dang, Y.; Yu, B. Synthesis of Sea Cucumber Saponins with Antitumor Activities. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 12080–12096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baviskar, B.A.; Deore, S.L.; Jadhav, A.I. QSAR Studies of Triterpenoid Saponin Analogues for Nematicidal Activity. Pharm. Methods 2019, 10, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baviskar, B.A.; Deore, S.L.; Jadhav, A.I. 2D and 3D QSAR Studies of Saponin Analogues as Antifungal Agents against Candida albicans. J. Young Pharm. 2020, 12, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepnik, K.; Kukula-Koch, W. In Silico Studies on Triterpenoid Saponins Permeation through the Blood–Brain Barrier Combined with Postmortem Research on the Brain Tissues of Mice Affected by Astragaloside IV Administration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepnik, K.; Nowak-Terpiłowska, A. In Vitro and In Silico Studies on the Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability of Triterpenoid Saponins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3573. [Google Scholar]
- Horobin, R.W.; Stockert, J.C. How to Target Small-Molecule Fluorescent Imaging Probes to the Plasma Membrane—The Influence and QSAR Modelling of Amphiphilicity, Lipophilicity, and Flip-Flop. Molecules 2023, 28, 7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vien, L.T.M.; Kicha, A.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A. Triterpene Tetraglycosides from Stichopus herrmanni Semper, 1868. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.I.; Sharma, R.K.; Kumar, Y.; Saqulain, S. Pharmacological aspects & medicinal uses of Trigonella foenum-graecum: A Current Review. Int. J. Ayurvedic Med. 2021, 12, 776–786. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Murakami, T.; Matsuda, H. Medicinal foodstuffs.: X.: Structures of new triterpene glycosides, gymnemosides-c, -d, -e, and -f, from the leaves of Gymnema sylvestre R. BR.:: Influence of gymnema glycosides on glucose uptake in rat small intestinal fragments. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 2034–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.J.; Kim, H.D.; Lee, E.S.; Jang, G.Y.; Seong, H.A. Heat Treatment Enhances the Neuroprotective Effects of Crude Ginseng Saponin by Increasing Minor Ginsenosides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, G.; Oakenfull, D. A mechanism for the hypocholesterolemic activity of saponins. Br. J. Nutr. 1986, 55, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Hsieh, H.J.; Hsieh, C.H.; Hwang, D.F. Antioxidative and anticancer activities of various ethanolic extract fractions from crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster planci). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 38, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baecker, C.; Jenett-Siems, K.; Siems, K.; Wurster, M.; Bodtke, A.; Lindequist, U. Cytotoxic Saponins from the Seeds of Pittosporum angustifolium. Z. Naturforsch. Sect. C—J. Biosci. 2014, 69, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibulski, S.P.; Mourglia-Ettlin, G.; Teixeira, T.F.; Quirici, L.; Roehe, P.M.; Ferreira, F.; Silveira, F. Novel ISCOMs from Quillaja brasiliensis saponins induce mucosal and systemic antibody production, T-cell responses and improved antigen uptake. Vaccine 2016, 34, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleck, J.D.; Betti, A.H.; da Silva, F.P.; Troian, E.A.; Olivaro, C.; Ferreira, F.; Verza, S.G. Saponins from Quillaja saponaria and Quillaja brasiliensis: Particular Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activities. Molecules 2019, 24, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, C.; Mueller-Goymann, C.C. Saponin Interactions with Model Membrane Systems Langmuir Monolayer Studies, Hemolysis and Formation of ISCOMs. Planta Medica 2016, 82, 1496–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Lin, J.; Huang, Q.; Liang, P.; Huang, J.; Jian, C.; Lin, C.; Li, X. Panax notoginseng Saponins Attenuate Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation-Induced Injury in Human SH-SY5Y Cells by Regulating the Expression of Inflammatory Factors through miR-155. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.M.I.; Latha, P.B.; Vijaya, T.; Rao, D.S. The Saponin-Rich Fraction of a Gymnema sylvestre R. Br. Aqueous Leaf Extract Reduces Cafeteria and High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity. Z. Naturforsch. Sect. C—J. Biosci. 2012, 67, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Ma, J.; Jin, S.; Wang, T.; Sui, Y.; Chen, L. Effects of saponins Rb1 and Re in American ginseng combined intervention on immune system of aging model. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1392868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Sour Jujube (Ziziphus jujuba var. spinosa): A Bibliometric Review of Its Bioactive Profile, Health Benefits and Trends in Food and Medicine Applications. Foods 2024, 13, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, R.; Liu, R.; Liu, R.; Sui, W.; Geng, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, T.; Zhang, M. Sodium alginate-sodium hyaluronate-hydrolyzed silk for microencapsulation and sustained release of kidney tea saponin: The regulation of human intestinal flora in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 249, 126117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Meng, Y.; Du, Z.; Guo, M.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, P.; Hua, K.; Lu, Y.; Guo, X. The Synergistic Mechanism of Total Saponins and Flavonoids in Notoginseng-Safflower against Myocardial Infarction Using a Comprehensive Metabolomics Strategy. Molecules 2022, 27, 8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Song, W.; Chang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Fang, D.; Qiao, W. The Synergistic Antidepressant Effect: Compatibility of Alkaloids with Saponins from Ziziphi Spinosae Semen. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 5755980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, T. Preclinical Development of Semisynthetic Saponin Immunological Adjuvant Titerquil-1055 in the Context of an Influenza Vaccine; Adjuvance Technologies, Inc.: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Passos, F.R.S.; Araújo, H.G.; Monteiro, B.S.; Shanmugam, S.; Araújo, A.A.D.; Almeida, J.R.G.D.; Thangaraj, P.; Quintans, L.J.; Quintans, J.D.S. Anti-inflammatory and modulatory effects of steroidal saponins and sapogenins on cytokines: A review of pre-clinical research. Phytomedicine 2021, 96, 153842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huis In ’t Veld, L.G.; Cornelissen, L.A.; van den Bogaard, L.; Ansems, M.; Ho, I.N.; Adema, G.J. Saponin-based adjuvant uptake and induction of antigen cross-presentation by CD11b+dendritic cells and macrophages. NPJ Vaccines 2025, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Farris, E.; Swanson, R.V.; Das, S.; Yang, Y.; Martin, T.; Khader, S.A. Saponin TQL1055 adjuvant-containing vaccine confers protection upon Mycobacterium tuberculosis challenge in mice. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2024, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefpour, P.; Zhang, Y.J.; Maiorino, L.; Melo, M.B.; Arainga Ramirez, M.A.; Kumarapperuma, S.C.; Xiao, P.; Silva, M.; Li, N.; Michaels, K.K.; et al. Modulation of antigen delivery and lymph node activation in nonhuman primates by saponin adjuvant saponin/monophosphoryl lipid A nanoparticle. PNAS Nexus 2024, 3, pgae529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swart, M.; Allen, J.; Reed, B.; Gil, A.I.; Verspuij, J.; Schmit-Tillemans, S.; Chakkumkal, A.; Findeis, M.; Hafner, A.V.; Harjivan, C.; et al. Plant Cell Culture-Derived Saponin Adjuvant Enhances Immune Response Against a Stabilized Human Metapneumovirus Pre-Fusion Vaccine Candidate. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Algaissi, A.; Lai, C.C.; Chang, C.K.; Lin, J.S.; Wang, Y.S.; Chang, B.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, W.T.; Fan, Y.Q.; et al. Subunit vaccines with a saponin-based adjuvant boost humoral and cellular immunity to MERS coronavirus. Vaccine 2023, 41, 3337–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, A.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, B.; Wang, B.; Yang, J. Steroidal saponins: Natural compounds with the potential to reverse tumor drug resistance (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2024, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prithviraj, T. Plant-derived glycosides in cancer treatment: Diverse strategies for tumor suppression. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymouri, F.; Karimi, E. Development of chitosan-folate modified PLGA nanoparticles for targeted delivery of diosgenin as an anticancer agent. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.L.d.O.; Marinho, P.A.F.; de Oliveira, A.M.; de Souza, T.A.; Cibulski, S.P.; Alves, H.d.S. Apodanthera glaziovii (Cucurbitaceae) Shows Strong Anti-Inflammatory Activity in Murine Models of Acute Inflammation. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, F.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, H.; Lin, M.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. Saponins from Dolichos lablab seeds with anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 151, 107692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieu, N.V.; Vinh, L.B.; Phong, N.V.; Cong, P.V.; Dat, N.T.; Dan, N.V.; Duc, N.V.; Tao, H.M.; Tam, L.T.; Anh, L.T.; et al. Two New Steroidal Saponins with Potential Anti-Inflammatory Effects from the Aerial Parts of Gnetum formosum Markgr. Plants 2024, 13, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.W.; Guan, Y.H.; Lv, Z.; Yang, S.C.; Zhang, G.H.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zhao, M.; Chen, J.W. Optimization of saponin extraction from the leaves of Panax notoginseng and Panax quinquefolium and evaluation of their antioxidant, antihypertensive, hypoglycemic and anti-inflammatory activities. Food Chem.—X 2024, 23, 101642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.H.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Wei, X.; Yin, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, Y. Anti-inflammatory activity of a new lactone isolated from the leaves of Ardisia crenata Sims. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 21, e202300983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Cao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J. Extraction and biological activities of polysaccharides and saponins from Aralia elata: A review. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Diao, M.; Li, J.; Xie, N. Production and pharmaceutical research of minor saponins in Panax notoginseng (Sanqi): Current status and future prospects. Phytochemistry 2024, 223, 114099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, F.; Garcia, F.; Garcia, G.; Chabalgoity, J.A.; Rossi, S.; Baz, M. Intranasal Delivery of Quillaja brasiliensis Saponin-Based Nanoadjuvants Improve Humoral Immune Response of Influenza Vaccine in Aged Mice. Vaccines 2024, 12, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagchandani, S.H.; Yang, L.; Lam, J.H.; Maiorino, L.; Ben-Akiva, E.; Rodrigues, K.A.; Romanov, A.; Suh, H.; Aung, A.; Wu, S.; et al. Two-dose priming immunization amplifies humoral immunity by synchronizing vaccine delivery with the germinal center response. Sci. Immunol. 2024, 9, eadl3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plieskatt, J.; Bang, P.; Wood, G.K.; Naghizadeh, M.; Singh, S.K.; Jore, M.M.; Theisen, M. Clinical formulation development of Plasmodium falciparum malaria vaccine candidates based on Pfs48/45, Pfs230, and PfCSP. Vaccine 2024, 42, 1980–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Min, H.; Yao, S.; Yao, G.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, B.; Chen, M.; Liu, F.; Cui, L.; Zheng, L.; et al. Evaluation of different types of adjuvants in a malaria transmission-blocking vaccine. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 131, 111817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, E.; Ruiz, S.; Garinot, M.; Chavagnac, C.; Agrawal, P.; Escobar, J.; Revet, L.; Asensio, M.J.; Piras, F.; Fang, F.G.; et al. SPA14 liposomes combining saponin with fully synthetic TLR4 agonist provide adjuvanticity to hCMV vaccine candidate. NPJ Vaccines 2024, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wu, M.; Fang, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Shao, Z. Saponins enhance the stability and cost-efficiency of human embryonic stem cell culture. Cell Regen. 2025, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Ren, J.; Ma, X.; Liu, L.; Yu, S.; Li, X.; Li, H. Polyphylla saponin I has antiviral activity against influenza A virus. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 18963–18971. [Google Scholar]
- Karpova, E.A.; Kostikova, V.A.; Khramova, E.P.; Shaldaeva, T.M.; Vasil’eva, O.Y.; Mazurkova, N.A.; Filippova, E.I.; Mazurkov, O.Y.; Makarevich, E.V. Roots of Rosa majalis Herrm. as a source of antioxidants and anti-influenza agents. Rend. Lincei-Sci. Fis. Nat. 2024, 35, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Wu, S.T.; Zheng, X.; You, P.T.; Liu, Y.W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.Q. Chikusetsusaponin IVa Targets Nrf2 to Inhibit H9N2 Avian Influenza Virus Infection. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2024, 21, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranweerapaiboon, K.; Garon, A.; Seidel, T.; Janta, S.; Plubrukarn, A.; Chaithirayanon, K.; Langer, T. in vitro and in silico studies of holothurin A on androgen receptor in prostate cancer. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 12674–12682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothiaraj, G.; Manoranjani, M.; Pitchaikani, S.; Seker, G.K.; Saravanan, K.M.; Rajan, M.; Shakila, H. Investigation of therapeutic and immunomodulatory activity of Bacopa saponin from Bacopa monnieri. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 151, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, J.; Shao, P.; Kai, D.; Yang, L.; Sun, P.; Feng, S. Novel Nanoliposomes Synergistically Modulated by Sitogluside and Dioscin: Stability, Bioavailability, and Capacity To Alleviate Hyperuricaemia. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 73, 2596–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Lv, D.; Ma, S.; Gao, M.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C. Panax notoginseng saponins and acetylsalicylic acid co-delivered liposomes for targeted treatment of ischemic stroke. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 667, 124782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.; Zhang, J.; Hou, J.; Feng, R.; Yin, J. Pharmacokinetics study of ginsenoside Rg1 liposome by pulmonary administration. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, N. Advanced Development of LQ. A Liposome-Based Saponin-Containing Adjuvant for Use in Pansarbecovirus Vaccines. Awarded Grant. 2023. Available online: https://www.pandemicpact.org/grants/P35404 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Guo, L.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Guo, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, C. Saponin-enriched sea cucumber extracts exhibit an antiobesity effect through inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity and upregulation of LXR-β signaling. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1312–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yanagita, R.C.; Liu, C.; Hu, X.; Dong, P.; Xue, C.; Xue, Y. Effects of two sulfated triterpene saponins echinoside A and holothurin A on the inhibition of dietary fat absorption and obesity reduction. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhakumari, G.; Stephen, J. Antimitotic effects of holothurin. Cytologia 1988, 53, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wargasetia, T.L.; Ratnawati, H.; Widodo, N. Anticancer Potential of Holothurin A, Holothurin B, and Holothurin B3 from the Sea Cucumber Holothuria scabra. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2231, 040084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

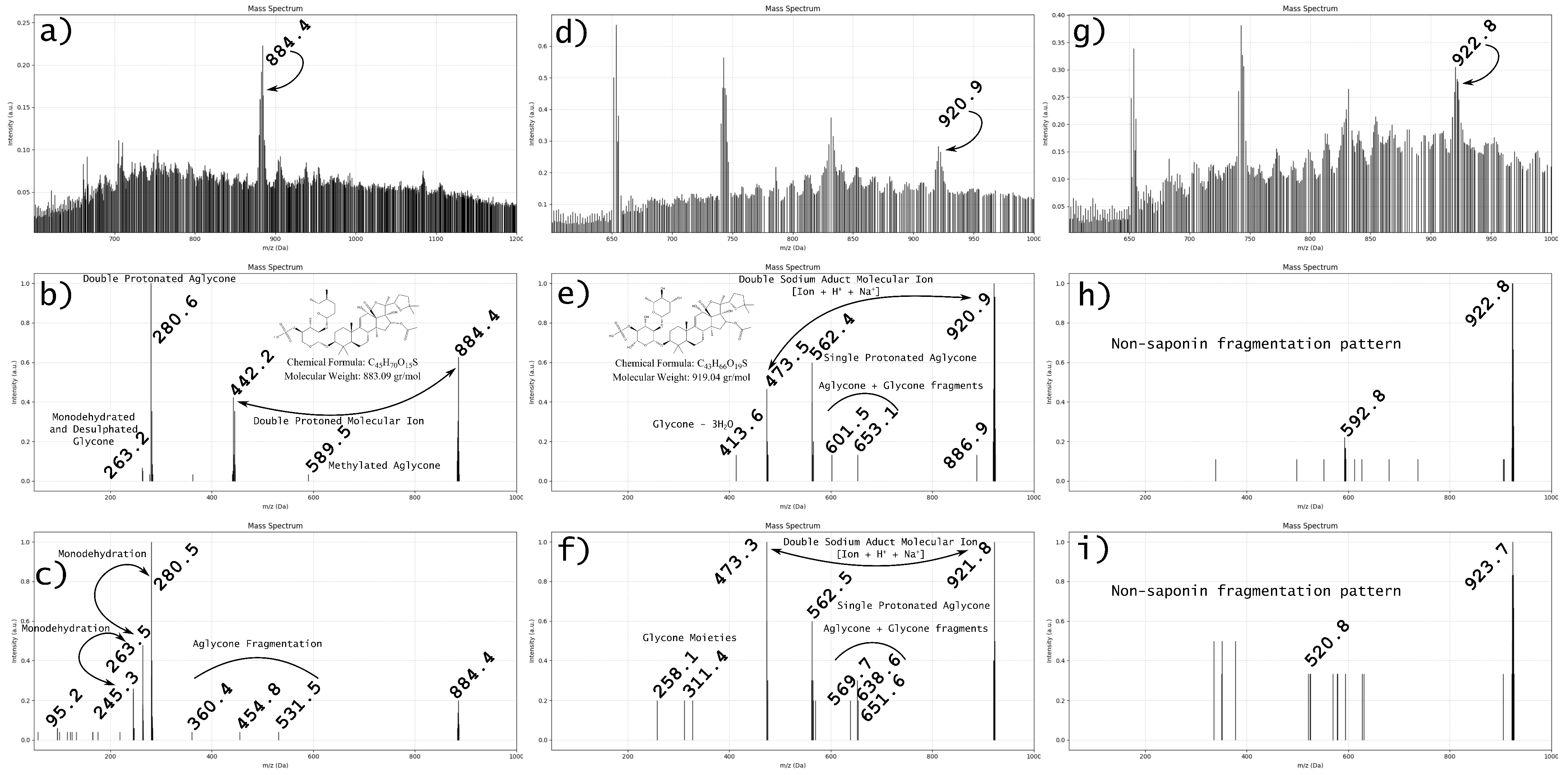



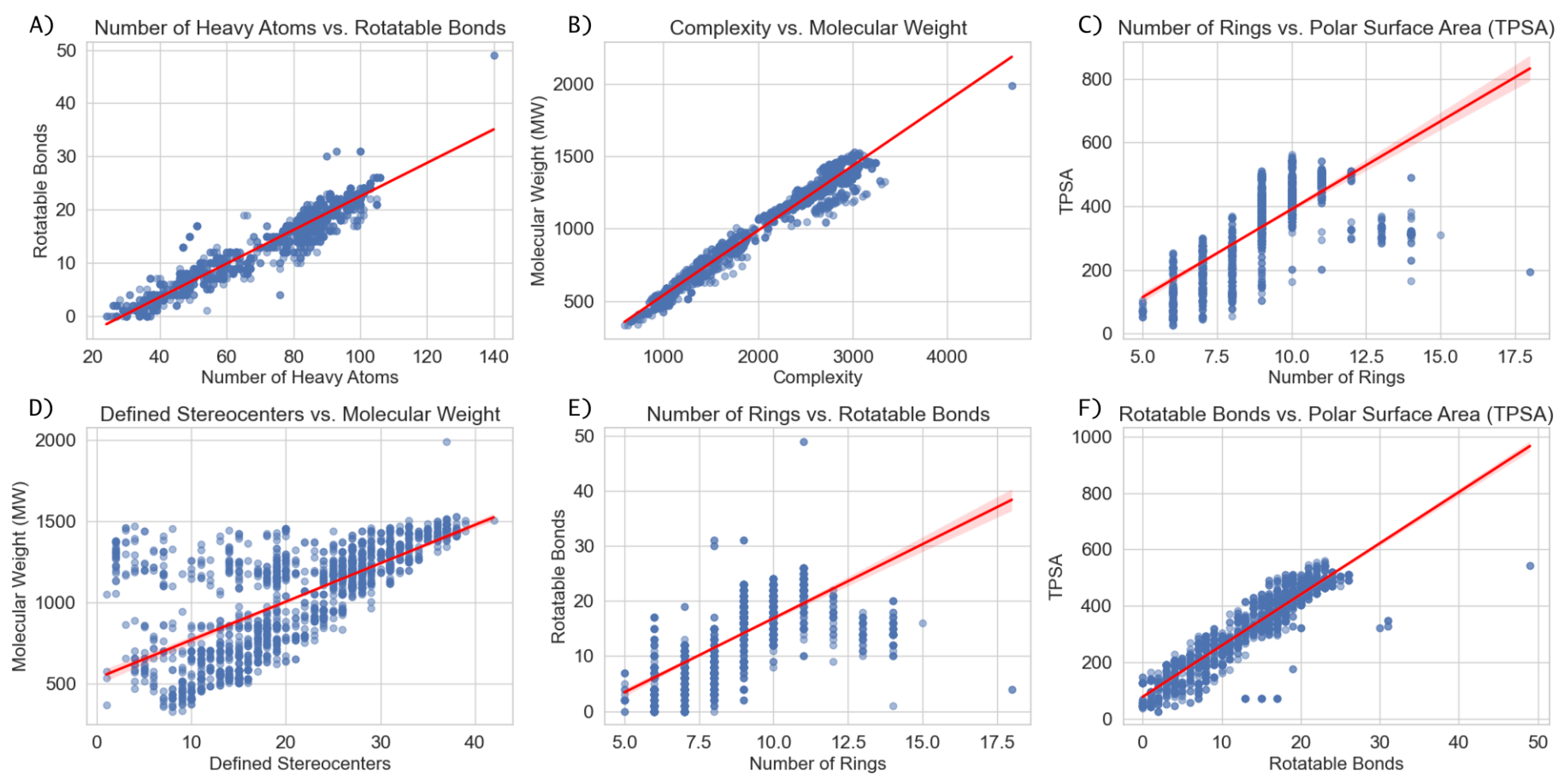
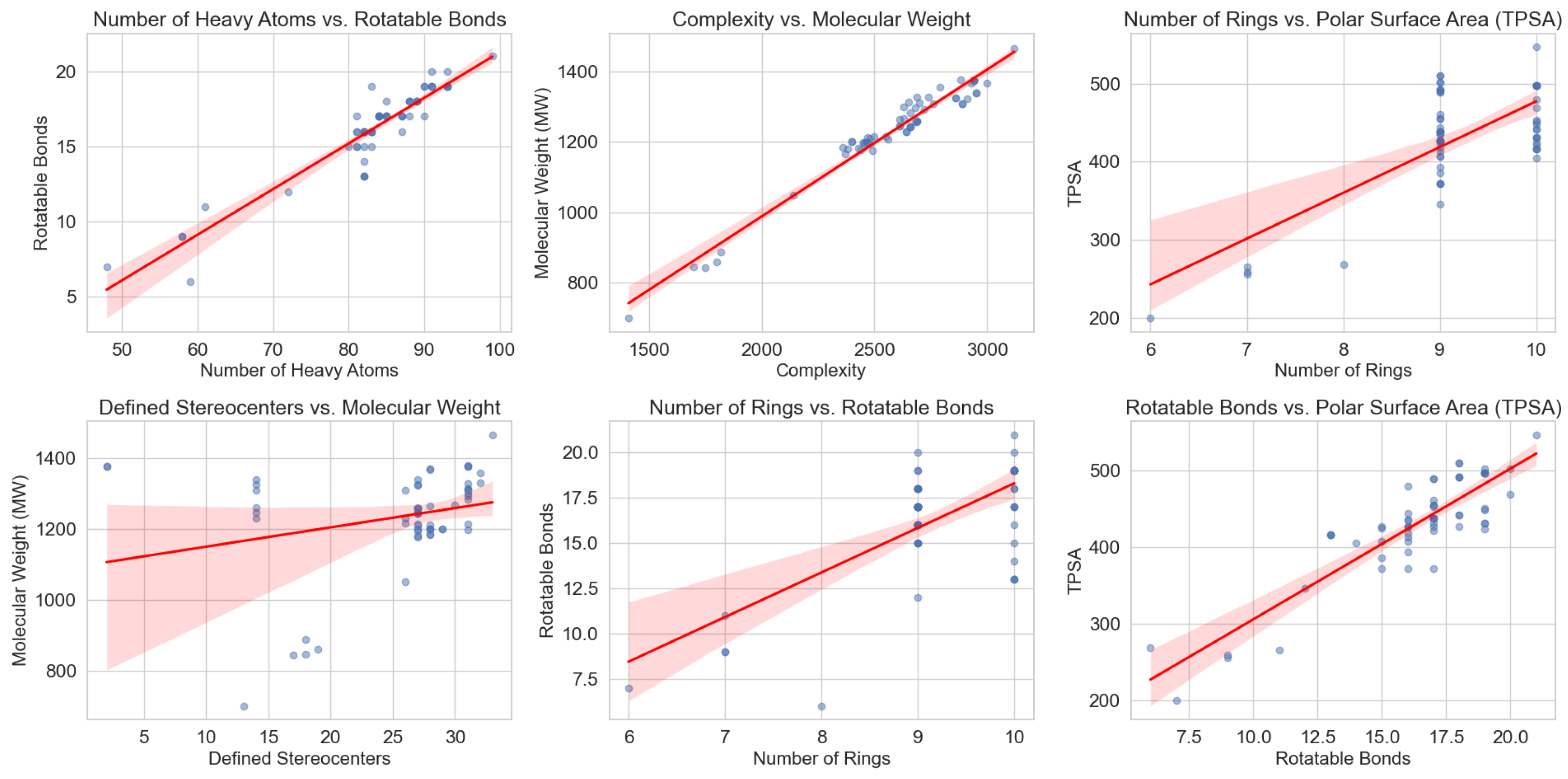



| Analytical Limitation | Consequence | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Incomplete Q1 scan before MS/MS | Coeluting ions may be misassigned | Full-range MS1 scan before fragmentation |
| Overreliance on [M+Na]+ or [M+H]+ adducts | Incorrect MW assignment | Include adduct pattern mapping and isotopic distribution |
| Lack of collision energy ramping | Missed fragmentation thresholds | Perform stepped CID (e.g., 10, 20, 30, 40 eV) |
| Absence of NMR confirmation | Misassigned aglycone or glycosidic linkage | Use NMR or at least FTIR if quantity allows |
| No ion mobility used | Isomeric saponins not separated | Apply IM-MS or alternative orthogonal LC methods |
| Compound/Saponin | Marine Source | Structural Features | Biological Activity | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Holothurin A3 | Holothuria scabra | Tetrasaccharide chain, holostane-type, sulfate group | Cytotoxic against KB (0.87 µg/mL) and HepG2 (0.32 µg/mL) | Induces apoptosis, membrane disruption |
| Holothurin A4 | Holothuria scabra | Tetrasaccharide chain, holostane-type, sulfate group | Cytotoxic against KB (1.12 µg/mL) and HepG2 (0.57 µg/mL) | Induces apoptosis, membrane disruption |
| Scabraside A | Holothuria scabra | Sulfated glycoside, acylated | 0.05–0.25 µM (HL-60); moderate on A549 | Cell membrane interaction, induces apoptosis |
| Scabraside B | Holothuria scabra | Sulfated glycoside, acylated | 0.05–0.25 µM (HL-60); moderate on A549 | Cell membrane interaction, induces apoptosis |
| Fuscocineroside C | Holothuria fuscocinerea | 22,25-epoxy group, monosulfated tetrasaccharide | 0.58 µM (BEL-7402) | Apoptosis via calcium-mediated signaling |
| Holothurin A | Holothuria fuscocinerea | 17-hydroxy, similar to Fuscocineroside C | Less active than Fuscocineroside C (HL-60) | Apoptosis (less potent) |
| Echinoside A | Holothuria scabra | Tetrasaccharide, sulfate, holostane nucleus | Strong cytotoxicity across cancer lines | Apoptosis, possibly via caspase activation |
| Holothurin B | Holothuria scabra | Sulfated glycoside, holostane | Cytotoxic against multiple lines | Likely apoptosis, membrane lysis |
| 24-dehydroechinoside A | Stichopus herrmanni | Tetrasaccharide chain, 24-dehydro, holostane core | 0.19–1.17 µM across five cancer cell lines | Apoptosis, cell cycle arrest |
| Holothurin A6 | Stichopus herrmanni | New glycoside, similar to Holothurin A5 | Similar profile to 24-dehydroechinoside A | Similar to 24-dehydroechinoside A (apoptosis) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Domínguez-Arca, V.; Hellweg, T.; Antelo, L.T. Harnessing Thalassochemicals: Marine Saponins as Bioactive Agents in Nutraceuticals and Food Technologies. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060227
Domínguez-Arca V, Hellweg T, Antelo LT. Harnessing Thalassochemicals: Marine Saponins as Bioactive Agents in Nutraceuticals and Food Technologies. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(6):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060227
Chicago/Turabian StyleDomínguez-Arca, Vicente, Thomas Hellweg, and Luis T. Antelo. 2025. "Harnessing Thalassochemicals: Marine Saponins as Bioactive Agents in Nutraceuticals and Food Technologies" Marine Drugs 23, no. 6: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060227
APA StyleDomínguez-Arca, V., Hellweg, T., & Antelo, L. T. (2025). Harnessing Thalassochemicals: Marine Saponins as Bioactive Agents in Nutraceuticals and Food Technologies. Marine Drugs, 23(6), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060227







