Novel PPAR-γ Agonist from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton crassocaule: Modulating Glucose Uptake and Lipid Droplet Formation
Abstract
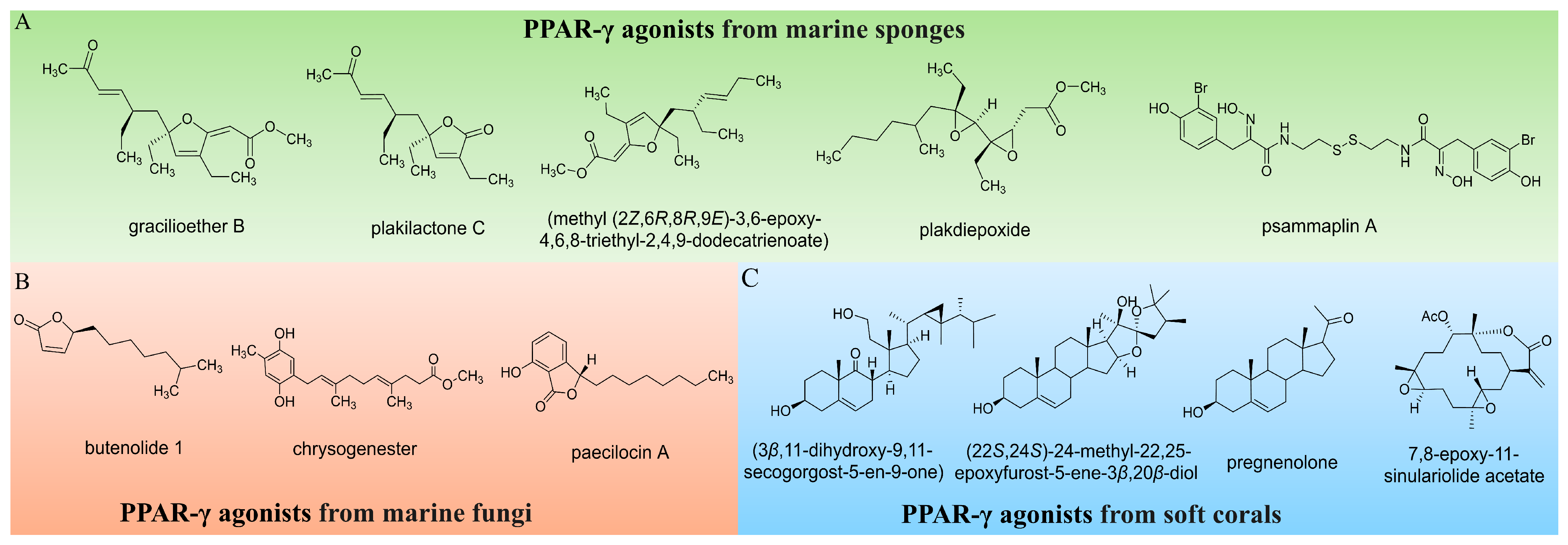
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
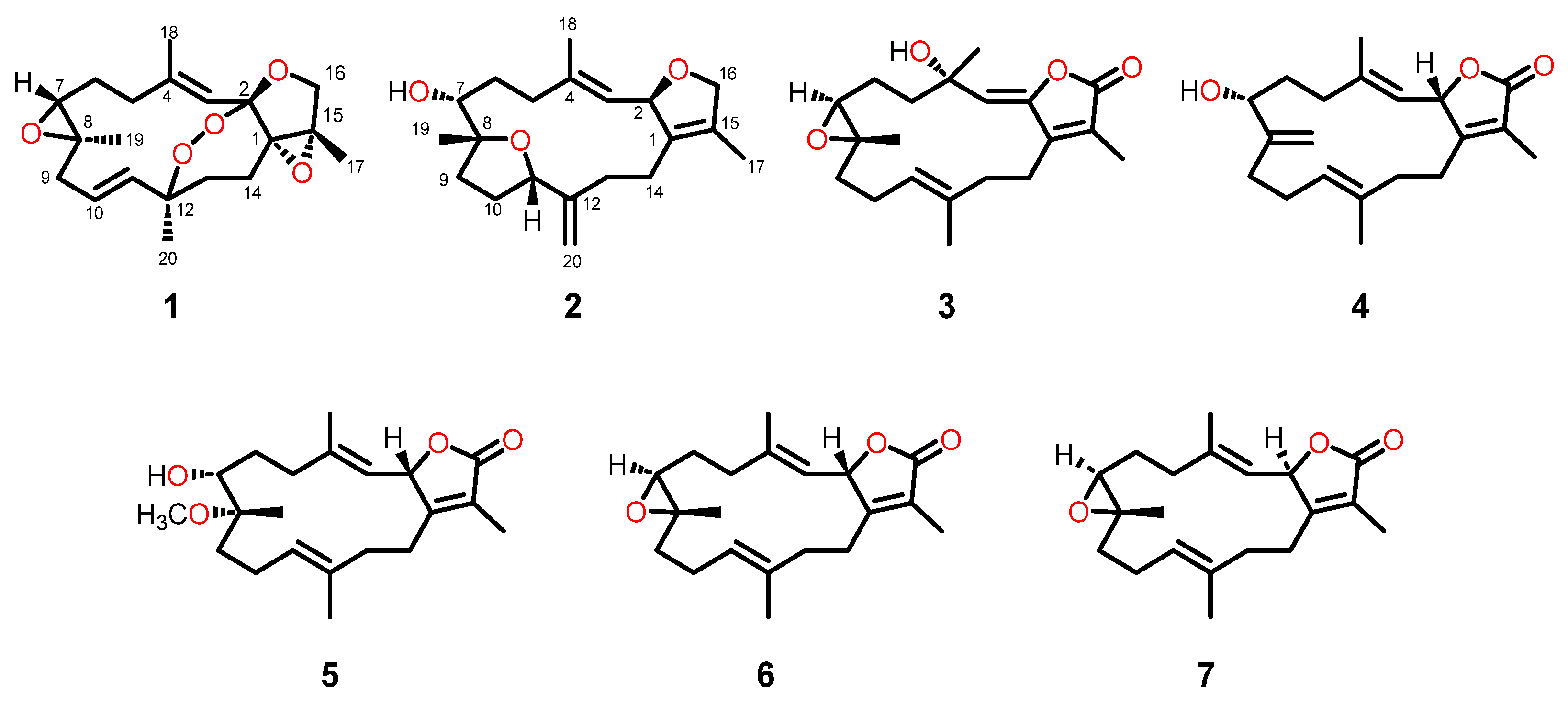
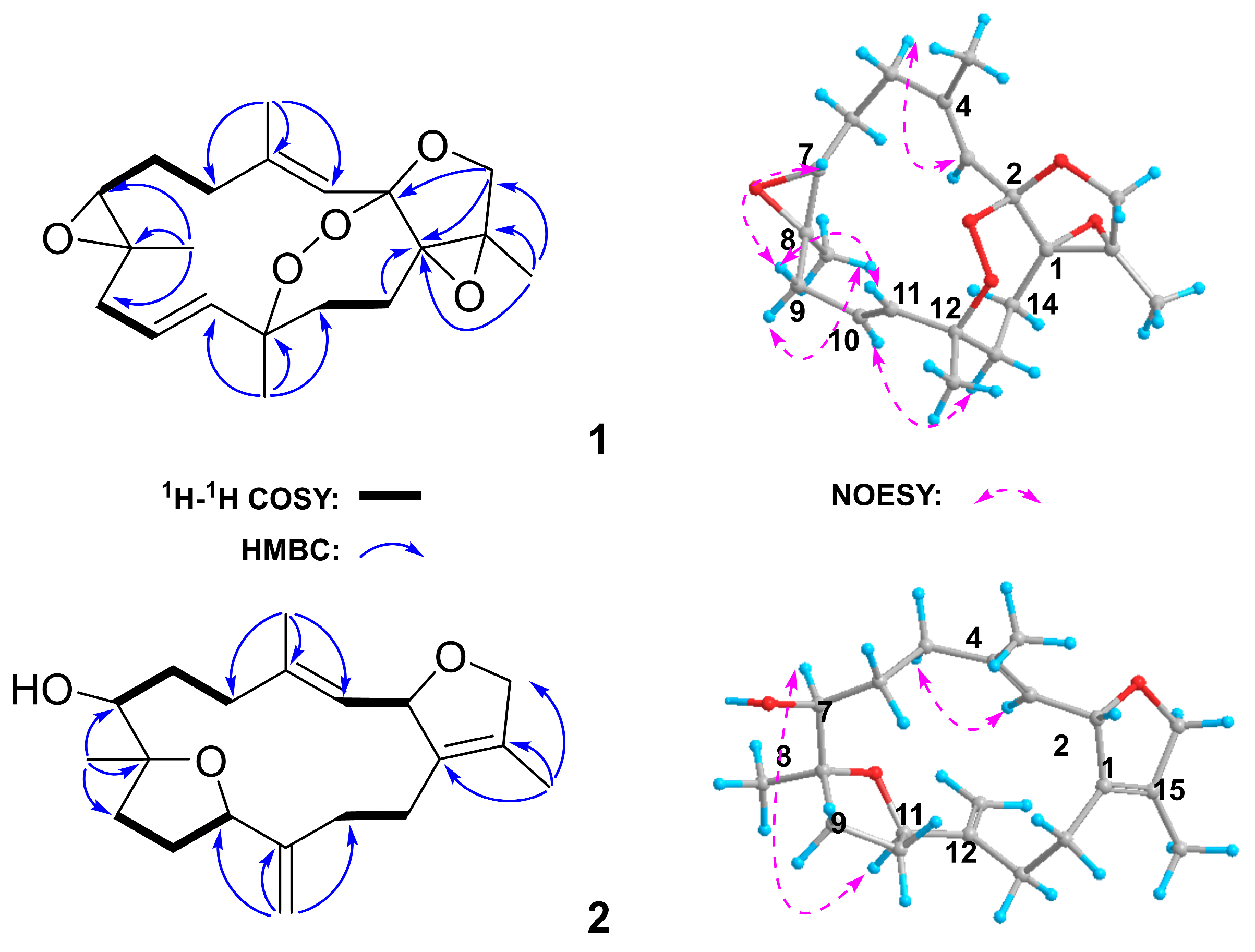
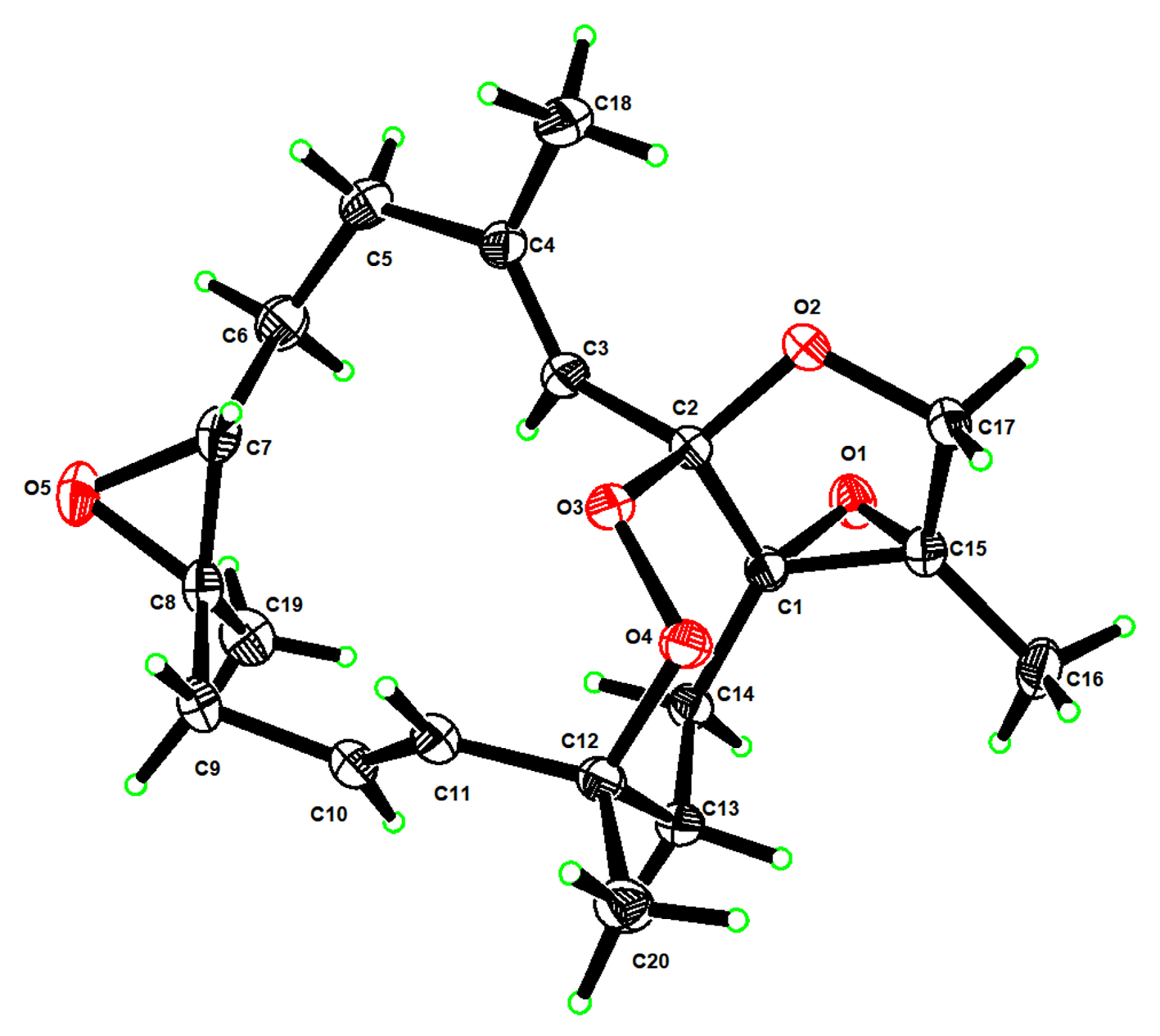
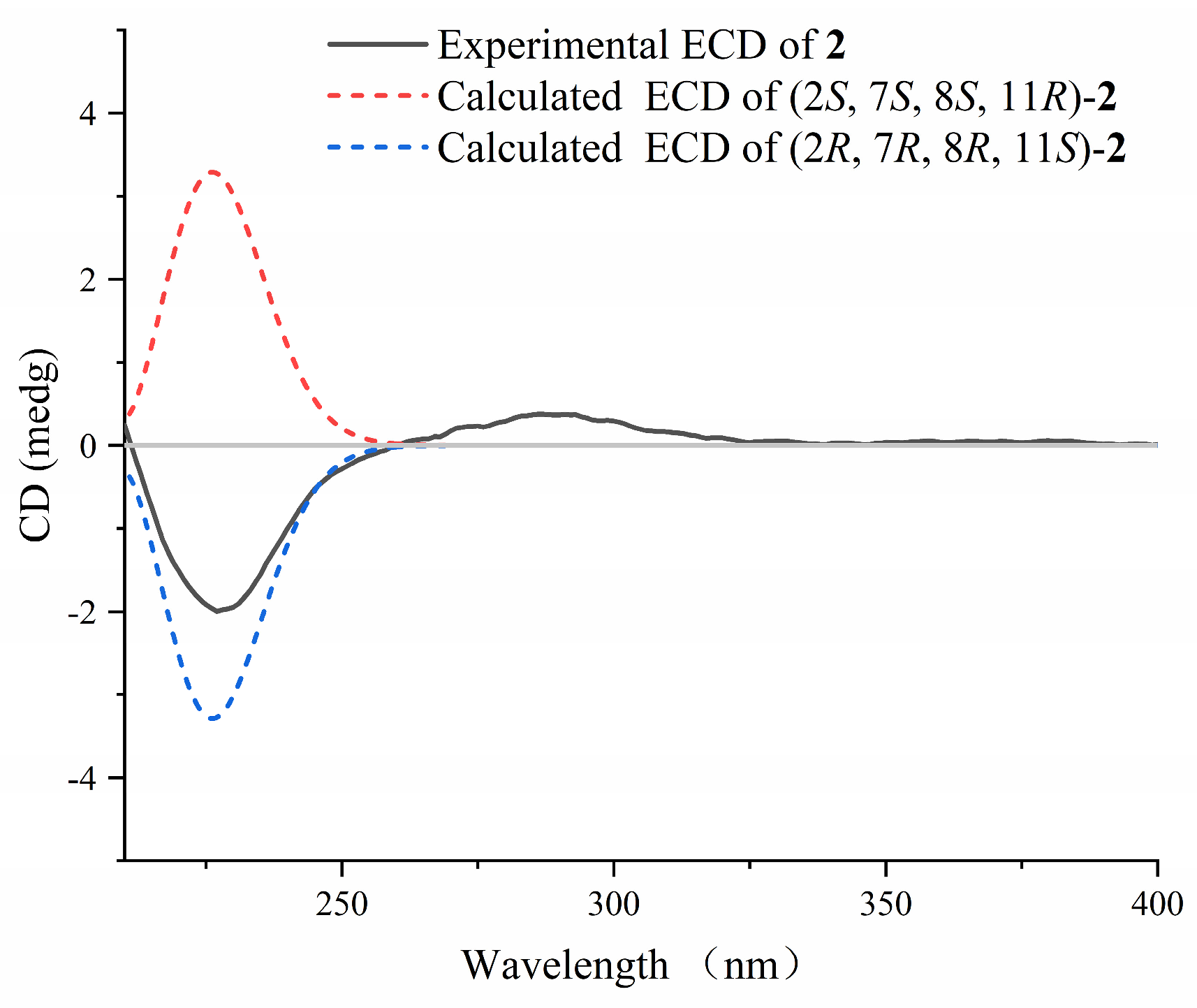
2.1. Isolation and Structural Elucidation
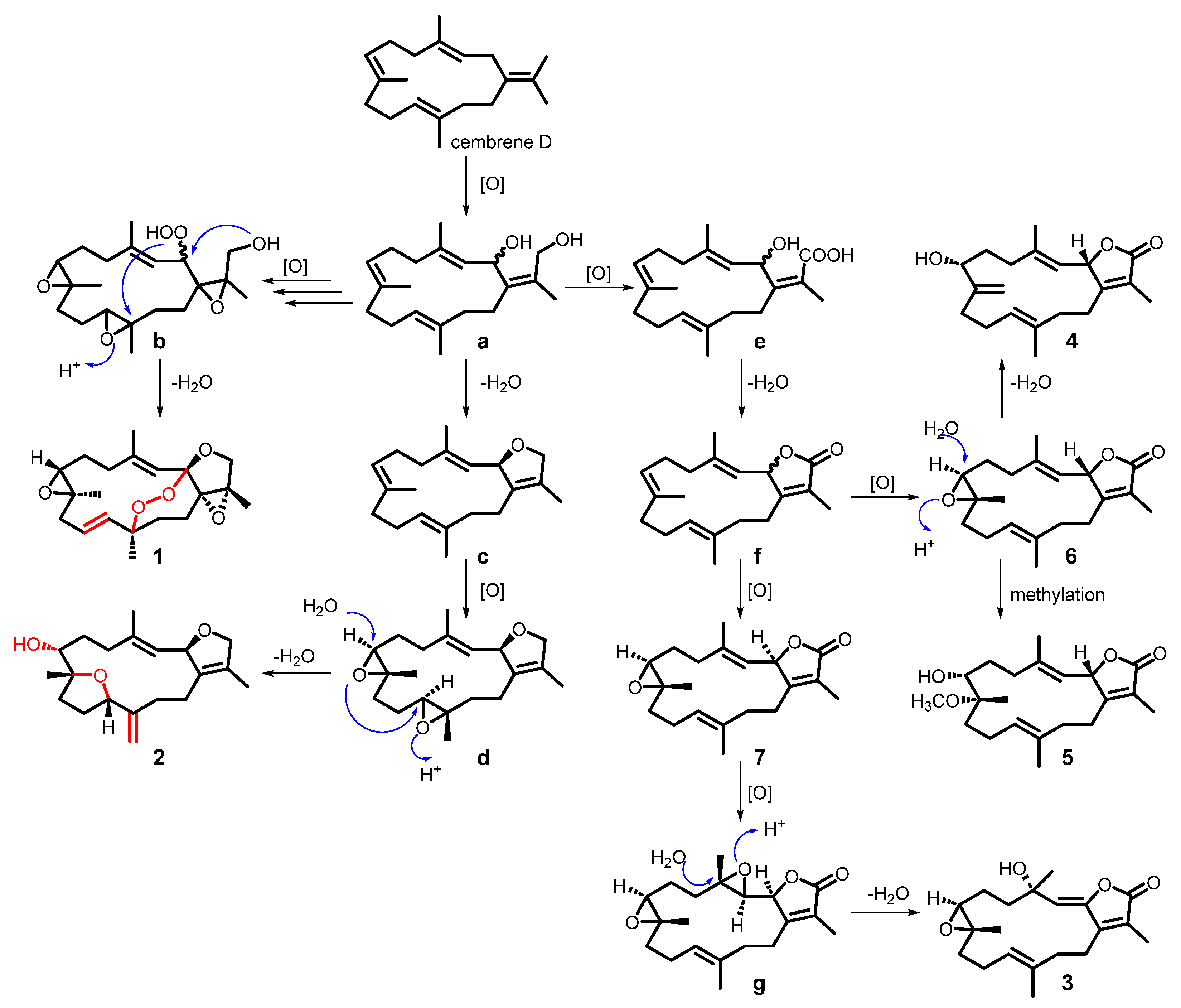
2.2. Plausible Biosynthetic Pathway of the Isolated Compounds
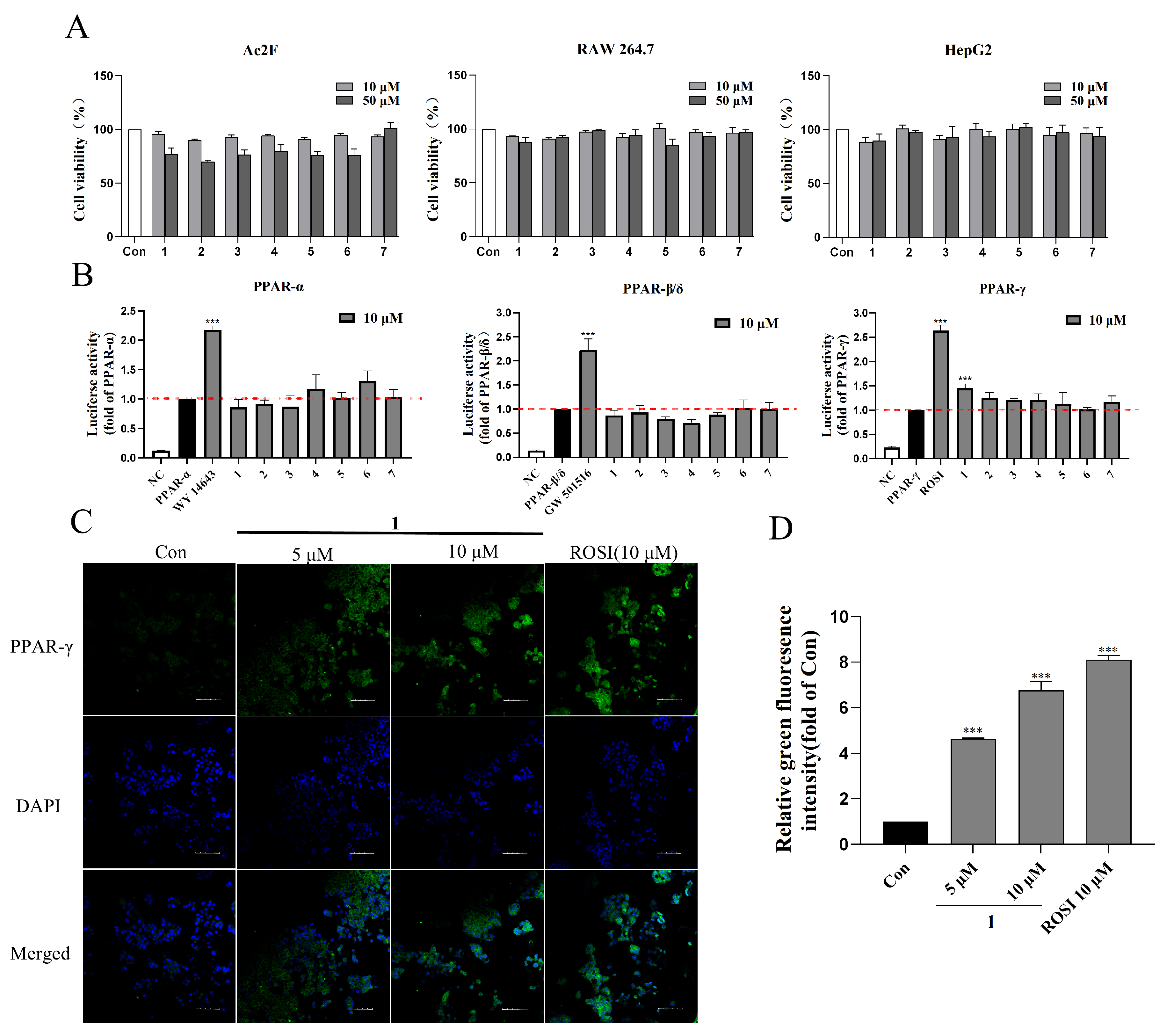
2.3. PPARs Agonistic Activity of Compounds 1–7
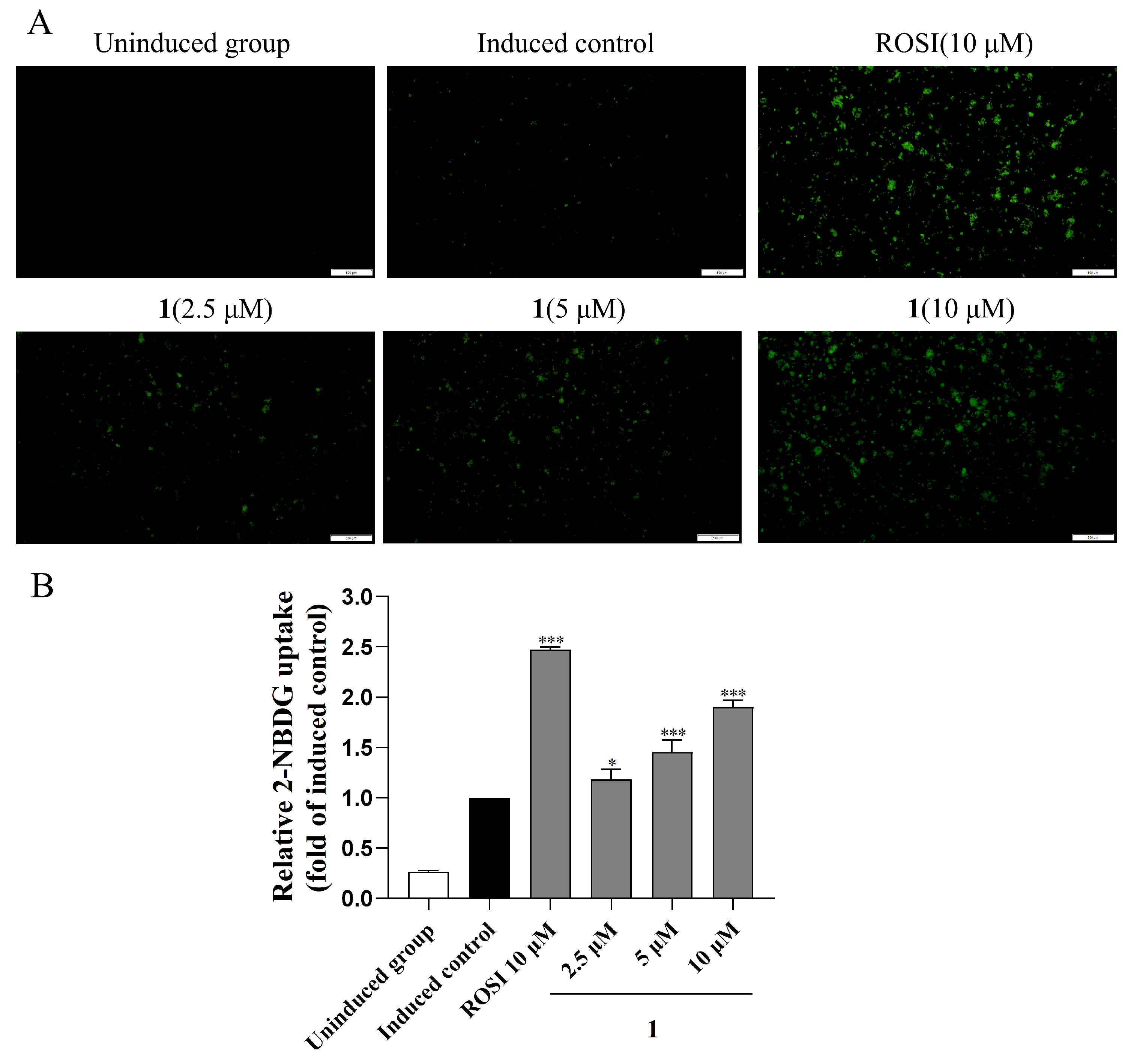
2.4. Glucose Uptake Ability of Compound 1
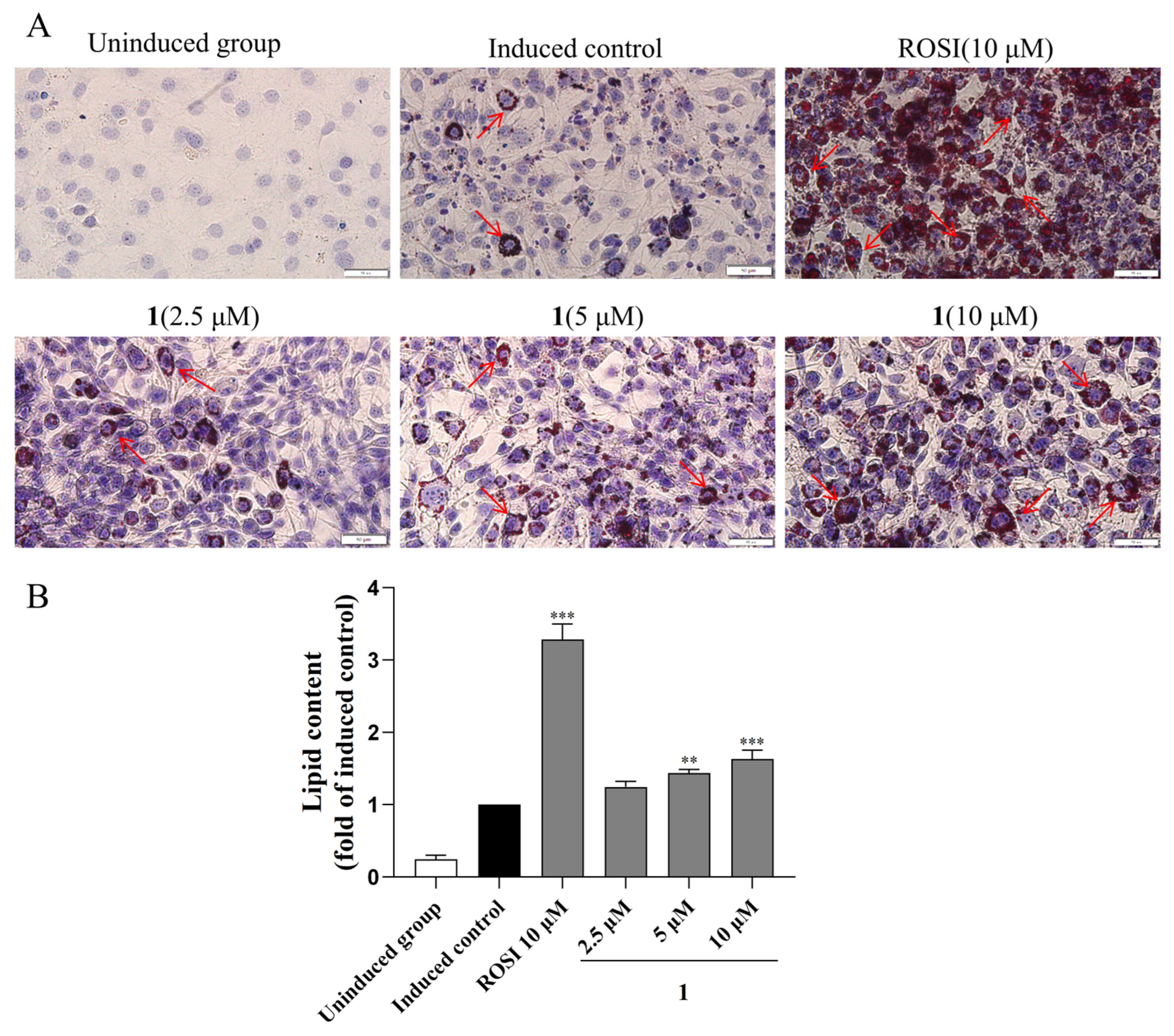
2.5. Adipogenesis and Lipid Accumulation Effects of Compounds 1
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Materials
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Spectroscopic Data of Compounds
3.5. Calculation Section
3.6. X-Ray Crystallographic Analysis for Compound 1
3.7. Cell Culture and Cell Viability
3.8. Luciferase Assay
3.9. Immunofluorescence
3.10. Molecular Docking
3.11. Glucose Uptake Assay
3.12. Adipocyte Differentiation Assay
3.13. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berger, J.; Moller, D.E. The Mechanisms of Action of PPARs. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 409–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grygiel-Górniak, B. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and their ligands: Nutritional and clinical implications—A review. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaigne, D.; Butruille, L.; Staels, B. PPAR control of metabolism and cardiovascular functions. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francque, S.; Szabo, G.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Byrne, C.D.; Cusi, K.; Dufour, J.-F.; Roden, M.; Sacks, F.; Tacke, F. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Chaudhary, R. Potentials of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) α, β/δ, and γ: An in-depth and comprehensive review of their molecular mechanisms, cellular Signalling, immune responses and therapeutic implications in multiple diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 155, 114616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.V.; Greyson, C.R.; Schwartz, G.G. PPAR-γ as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease: Evidence and uncertainty. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1738–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Cable, E.E.; Schnabl, B. Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor delta and liver diseases. Hepatol. Commun. 2025, 9, e0646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, M.J.; Alam, O.; Alam, M.J.; Shaquiquzzaman, M.; Alam, M.M.; Naidu, V.G.M. Synthesis, Docking, In Vitro and In Vivo Antidiabetic Activity of Pyrazole Based 2,4-Thiazolidinedione Derivatives as PPAR-γ Modulators. Arch. Pharm. 2018, 351, 1700223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, H.; Ye, J.; Tong, H.; Wang, M.; Sun, G. Ginsenoside Rg3 Protects against Diabetic Cardiomyopathy and Promotes Adiponectin Signaling via Activation of PPAR-γ. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Zhou, X.E.; Shi, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Suino-Powell, K.; Ma, L.; Gao, H.; et al. Identification and structural insight of an effective PPARγ modulator with improved therapeutic index for anti-diabetic drug discovery. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 2260–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aniello, E.; Amodeo, P.; Vitale, R. Marine Natural and Nature-Inspired Compounds Targeting Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptors (PPARs). Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, T.H.; Ha, T.T.; Minh, C.V.; Kiem, P.V.; Huong, H.T.; Ngan, N.T.T.; Nhiem, N.X.; Tung, N.H.; Thao, N.P.; Thuy, D.T.T.; et al. Cytotoxic and PPARs transcriptional activities of sterols from the Vietnamese soft coral Lobophytum laevigatum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 2845–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.-R.; Chiu, C.-F.; Hu, J.-L.; Feng, C.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Bai, L.-Y.; Sheu, J.-H. A Sterol from Soft Coral Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, L.-M.; Yu, D.-D.; Su, M.-Z.; Cui, L.; Guo, Y.-W. In Vitro Insights into the Role of 7,8-Epoxy-11-Sinulariolide Acetate Isolated from Soft Coral Sinularia siaesensis in the Potential Attenuation of Inflammation and Osteoclastogenesis. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-M.; Lin, J.-J.; Su, J.-H.; Liu, C.-I. 13-Acetoxysarcocrassolide induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through mitochondrial dysfunction and suppression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K signalling pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 2276–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, H.A.; Raafat, K.M.; Temraz, T.A.; Noureldin, N.; Breitinger, H.-G.; Breitinger, U. Sarcophine and (7S, 8R)-dihydroxydeepoxysarcophine from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum as In Vitro and In Vivo Modulators of Glycine Receptors. Neurotoxicology 2020, 80, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, S.; Zeng, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, C.; Su, M. Two New Diterpenoids Formed by Transannular Diels–Alder Cycloaddition from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton tortuosum, and Their Antibacterial and PPAR-β Agonist Activities. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, K.A.; Hamann, M.T.; Waddling, C.A.; Jensen, C.; Lee, S.K.; Dunstan, C.A.; Pezzuto, J.M. Structurally Novel Bioconversion Products of the Marine Natural Product Sarcophine Effectively Inhibit JB6 Cell Transformation. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 7449–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; Abdel-Latif, F.F.; Alsaid, M.S.; Shahat, A.A.; Paré, P.W. Trochelioid A and B, new cembranoid diterpenes from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum. Phytochem. Lett. 2013, 6, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.E.; El-Beih, A.A.; Moustafa, A.Y.; Hamdy, A.A.; Alhammady, M.A.; Selim, R.M.; Abdel-Rehim, M.; Paré, P.W. Cytotoxic cembranoids from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1809–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolinski, K.; Hinton, J.F.; Pulay, P. Efficient implementation of the gauge-independent atomic orbital method for NMR chemical shift calculations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 8251–8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-W.; Cuadrado, C.; Yao, L.-G.; Daranas, A.H.; Guo, Y.-W. Quantum Mechanical–NMR-Aided Configuration and Conformation of Two Unreported Macrocycles Isolated from the Soft Coral Lobophytum sp.: Energy Calculations versus Coupling Constants. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 4093–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditchfield, R. Molecular Orbital Theory of Magnetic Shielding and Magnetic Susceptibility. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 56, 5688–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mándi, A.; Kurtán, T. Applications of OR/ECD/VCD to the structure elucidation of natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 889–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.-M.; Li, S.-W.; Su, M.-Z.; Yao, L.-G.; Appendino, G.; Guo, Y.-W. Structurally Diverse Diterpenoids from the Sanya Bay Nudibranch Hexabranchus sanguineus and Its Sponge-Prey Chelonaplysilla sp. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202203858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Revision A.1.; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]

| No. | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH Mult. (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH Mult. (J in Hz) | δC, Type | |
| 1 | 65.72, qC | 133.24, qC | ||
| 2 | 112.39, qC | 5.45 brs | 85.35, CH | |
| 3 | 5.37 brs | 117.80, CH | 5.20 d (9.62) | 126.80, CH |
| 4 | 143.57, qC | 139.56, qC | ||
| 5 | 2.23 m | 36.38, CH2 | 2.28 m | 37.19, CH2 |
| 2.34 m | 2.28 m | |||
| 6 | 2.05 m | 26.08, CH2 | 1.33 m | 28.08, CH2 |
| 1.73 m | 2.15 m | |||
| 7 | 2.64 dd (7.31, 3.32) | 61.58, CH | 4.34 d (9.15) | 67.85, CH |
| 8 | 61.83, qC | 80.74, qC | ||
| 9 | 2.77 dd (12.23, 3.46) | 44.27, CH2 | 1.59 m | 30.03, CH2 |
| 1.76 m | 2.23 m | |||
| 10 | 5.50 m | 123.43, CH | 1.50 m | 25.90, CH2 |
| 2.10 m | ||||
| 11 | 5.64 d (16.08) | 135.97, CH | 4.63 dd (12.17, 3.13) | 84.52, CH |
| 12 | 86.53, qC | 147.7, qC | ||
| 13 | 1.76 m | 32.67, CH2 | 1.95 m | 30.76, CH2 |
| 2.16 m | 2.23 m | |||
| 14 | 1.74 m | 23.52, CH2 | 2.20 m | 27.49, CH2 |
| 2.60 m | 2.06 m | |||
| 15 | 68.75, qC | 128.50, qC | ||
| 16 | 3.97 d (9.81) | 71.05, CH2 | 4.48 d (11.91) | 78.51, CH2 |
| 4.07 d (9.81) | 4.56 dd (11.82 5.20) | |||
| 17 | 1.68 s | 12.39, CH3 | 1.68 s | 10.39, CH3 |
| 18 | 1.93 s | 19.44, CH3 | 1.83 s | 15.91, CH3 |
| 19 | 1.41 s | 17.74, CH3 | 1.03 s | 18.78, CH3 |
| 20 | 1.22 s | 26.99, CH3 | 4.96 s | 115.00, CH2 |
| 5.00 s | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, J.-A.; Sun, M.; Qi, Y.; Li, S.-W.; Zhang, L.-T.; Pan, S.-M.; Guo, Y.-W.; Su, M.-Z.; Luo, H. Novel PPAR-γ Agonist from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton crassocaule: Modulating Glucose Uptake and Lipid Droplet Formation. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23120450
Zeng J-A, Sun M, Qi Y, Li S-W, Zhang L-T, Pan S-M, Guo Y-W, Su M-Z, Luo H. Novel PPAR-γ Agonist from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton crassocaule: Modulating Glucose Uptake and Lipid Droplet Formation. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(12):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23120450
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Jian-Ang, Min Sun, Yi Qi, Song-Wei Li, Li-Ting Zhang, Si-Min Pan, Yue-Wei Guo, Ming-Zhi Su, and Hui Luo. 2025. "Novel PPAR-γ Agonist from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton crassocaule: Modulating Glucose Uptake and Lipid Droplet Formation" Marine Drugs 23, no. 12: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23120450
APA StyleZeng, J.-A., Sun, M., Qi, Y., Li, S.-W., Zhang, L.-T., Pan, S.-M., Guo, Y.-W., Su, M.-Z., & Luo, H. (2025). Novel PPAR-γ Agonist from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton crassocaule: Modulating Glucose Uptake and Lipid Droplet Formation. Marine Drugs, 23(12), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23120450







