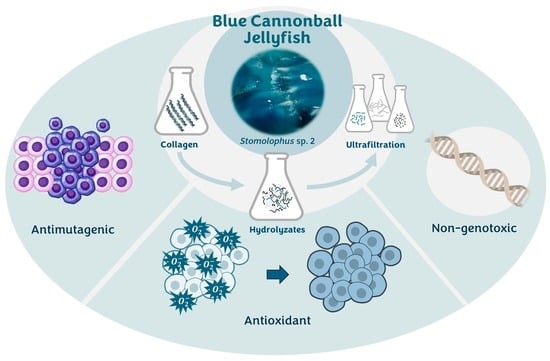
Bioactivity and in Silico Insights of Collagen-Derived Peptides from Jellyfish (Stomolophus sp. 2) Mesoglea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Collagen and Hydrolysates: Yield and Properties
2.2. Fractions Characterization
2.2.1. Antioxidant Capacity
2.2.2. Antimutagenic Capacity
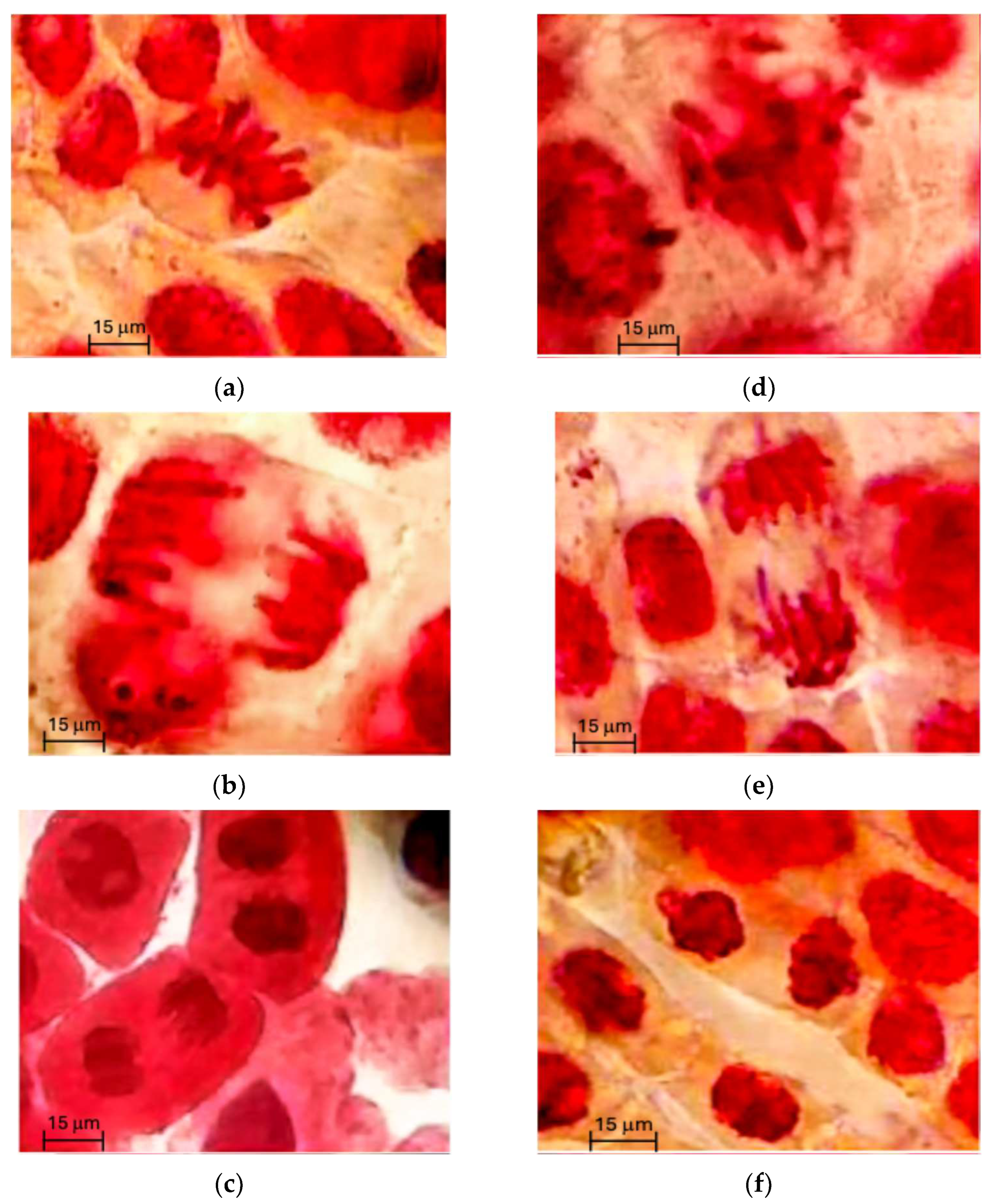
2.2.3. Genotoxicity of Hydrolysates and Fraction < 3 kDa
2.2.4. Amino Acid Content of Jellyfish Hydrolysates
2.2.5. Bioactive Peptides Identified by Informatics Analysis
| Peptide Identified | Average Mass 2 | Ppm 3 | Length 4 | Bioactive Probability 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KGNEGPPGEKGL | 1181 | 6.9 | 12 | 0.56 |
| KGQPGPGGSADF | 1116 | 6.9 | 12 | 0.62 |
| PGQNGLRGADGIKGEPGL | 1734 | 9.6 | 18 | 0.63 |
| KGAVGEPGPKGDL | 1412 | 7.4 | 14 | 0.62 |
| KGEPGESGGL | 929 | 0.4 | 10 | 0.56 |
| GDTGLDGEKGNKGEPGARGEI | 2199 | 9.5 | 22 | 0.47 |
| KGDAGTNGL | 831 | 6.3 | 9 | 0.42 |
| AGVEGPPGPPGF | 1080 | 6.1 | 12 | 0.80 |
| GPPGDQGPQGL | 1219 | 0.7 | 12 | 0.84 |
| GSQGPTGEKGANGLPGL | 1708 | 1.1 | 18 | 0.78 |
| PPGDQGPQGL | 964 | 6.6 | 10 | 0.77 |
| GNAGPKGEPGESGGL | 1495 | 2.3 | 16 | 0.63 |
| PRGDPGQKGEPGQ | 1420 | 5.2 | 14 | 0.25 |
| KGARGLNGTGGEKGSRGPRGF | 2215 | 6.4 | 22 | 0.50 |
| GRDGAGVKGNAGPKGEPGESGGL | 2179 | 3.9 | 24 | 0.36 |
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemicals
4.2. Collagen Extraction
4.3. Preparation of Enzymatic Hydrolysates
4.4. Membrane Ultrafiltration
4.5. Analysis
4.5.1. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH)
4.5.2. Amino Acid Profile of Hydrolysates
4.5.3. Antioxidant Activity of Hydrolysates and Fractions
4.5.4. Antimutagenic Activity of Hydrolysates and Fractions
4.5.5. Genotoxicity Test of Hydrolysate and Fraction 3
4.5.6. Nano LC-MS/MS Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| JCH | Jellyfish collagen hydrolysates |
| F1 | Fraction molecular weight > 10 kDa |
| F2 | Fraction 10 kDa > molecular weight > 3 kDA |
| F3 | Fraction molecular weight > 3 kDa |
| ABTS | 2,2′-azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic-acid) |
| FRAP | Ferric reducing antioxidant power |
| AAPH | 2,2′-azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride |
| SET | Single-electron transfer |
| HAT | Hydrogen atom transfer |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| UHPLC | Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| ORAC | Oxygen radical absorbance capacity |
References
- Cisneros-Mata, M.A.; Mangin, T.; Bone, J.; Rodriguez, L.; Smith, S.L.; Gaines, S.D. Fisheries Governance in the Face of Climate Change: Assessment of Policy Reform Implications for Mexican Fisheries. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotz, L.; Cisneros-Montemayor, A.M.; Cisneros-Mata, M.Á. The Race for Jellyfish: Winners and Losers in Mexico’s Gulf of California. Mar. Policy 2021, 134, 104775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Salinas, L.C.; López-Martínez, J.; Morandini, A.C. The Young Stages of the Cannonball Jellyfish (Stomolophus sp. 2) from the Central Gulf of California (Mexico). Diversity 2021, 13, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, G.; Martinez, K.A.; Martín, J.; Reyes, F.; D’Ambra, I.; Lauritano, C. Jellyfish as an Alternative Source of Bioactive Antiproliferative Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarms, G.; Morandini, A. World Atlas of Jellyfish; Dölling und Galitz Verlag: Aamburg, Germany, 2019; p. 816. [Google Scholar]
- Banha, T.N.S.; Morandini, A.C.; Rosário, R.P.; Martinelli Filho, J.E. Scyphozoan jellyfish (Cnidaria, Medusozoa) from Amazon Coast: Distribution, Temporal Variation and Length–Weight Relationship. J. Plankton Res. 2020, 42, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastré-Velásquez, C.D.; Rodríguez-Armenta, C.M.; Minjarez-Osorio, C.; Re-Vega, E.D.L. Estado actual del conocimiento de la medusa bola de cañón (Stomolophus meleagris). Epistemus 2022, 16, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagarhpa. Favorece Gobierno de Sonora a Pescadores Con Asistencia Técnica y de Organización En El Golfo de Santa Clara. Available online: https://sagarhpa.sonora.gob.mx/acerca-de/acciones/favorece-gobierno-de-sonora-a-pescadores-con-asistencia-tecnica-y-de-organizacion-en-el-golfo-de-santa-clara (accessed on 19 September 2025).
- Villalba-Urquidy, B.d.S.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Toro-Sánchez, C.L.D.; Medina, I.; Burgos-Hernández, A.; Brauer, J.M.E.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.d.C. Collagen Extracts from Blue Cannonball Jellyfish (Stomolophus meleagris): Antioxidant Properties, Chemical Structure, and Proteomic Identification. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2025, 37, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza-Espinoza, D.M.; Del Carmen Santacruz-Ortega, H.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Aubourg, S.P.; Salazar-Leyva, J.A.; Rodríguez-Felix, F.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Chemical-Structural Identification of Crude Gelatin from Jellyfish (Stomolophus meleagris) and Evaluation of Its Potential Biological Activity. Fishes 2023, 8, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, P.G.; Suh, J.H.; Pegg, R.B.; Chen, J.; Mis Solval, K. The Emergence of Jellyfish Collagen: A Comprehensive Review on Research Progress, Industrial Applications, and Future Opportunities. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 141, 104206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Shi, P.; Cao, Y.; Shi, B.; Shen, H.; Zhao, S.; Gao, Y.; Chi, H.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y. Isolation and Purification of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Prepared by Marine Bacillus Velezensis Z-1 Protease. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, L.; Chi, C.-F.; Ma, J.-H.; Luo, H.-Y.; Xu, Y. Purification and Characterisation of a Novel Antioxidant Peptide Derived from Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Protein Hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.-M.; Yang, X.-R.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Gelatin and Antioxidant Peptides from Gelatin Hydrolysate of Skipjack Tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) Scales: Preparation, Identification and Activity Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Qiu, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.-M.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Novel Antioxidant Collagen Peptides of Siberian Sturgeon (Acipenserbaerii) Cartilages: The Preparation, Characterization, and Cytoprotection of H2O2-Damaged Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs). Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, T.-B.; He, T.-P.; Li, H.-B.; Tang, H.-W.; Xia, E.-Q. The Structure-Activity Relationship of the Antioxidant Peptides from Natural Proteins. Molecules 2016, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Geng, H.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, P. Jellyfish Peptide as an Alternative Source of Antioxidant. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B. Effects of Collagen and Collagen Hydrolysate from Jellyfish (Rhopilema esculentum) on Mice Skin Photoaging Induced by UV Irradiation. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, H183–H188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upata, M.; Siriwoharn, T.; Makkhun, S.; Yarnpakdee, S.; Regenstein, J.M.; Wangtueai, S. Tyrosinase Inhibitory and Antioxidant Activity of Enzymatic Protein Hydrolysate from Jellyfish (Lobonema smithii). Foods 2022, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soufi-Kechaou, E.; Derouiniot-Chaplin, M.; Ben Amar, R.; Jaouen, P.; Berge, J.-P. Recovery of Valuable Marine Compounds from Cuttlefish By-Product Hydrolysates: Combination of Enzyme Bioreactor and Membrane Technologies: Fractionation of Cuttlefish Protein Hydrolysates by Ultrafiltration: Impact on Peptidic Populations. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2017, 20, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sila, A.; Bougatef, A. Antioxidant Peptides from Marine By-Products: Isolation, Identification and Application in Food Systems. A Review. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raksha, N.; Halenova, T.; Vovk, T.; Kostyuk, O.; Synelnyk, T.; Andriichuk, T.; Maievska, T.; Savchuk, O.; Ostapchenko, L. Anti-Obesity Effect of Collagen Peptides Obtained from Diplulmaris antarctica, a Jellyfish of the Antarctic Region. Croat. Med. J. 2023, 64, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Jia, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Z.; Liu, C. Purification and Characterization of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from Jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, B. Production of the Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptide from Hydrolysates of Jellyfish (Rhopilema esculentum) Collagen. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2012, 5, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.W.; Haubner, R.; Würtele, G.; Hull, E.; Spiegelhalder, B.; Bartsch, H. Olives and Olive Oil in Cancer Prevention. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. Off. J. Eur. Cancer Prev. Organ. ECP 2004, 13, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-C.; Pan, B.S.; Chang, C.-L.; Shiau, C.-Y. Low-Molecular-Weight Peptides as Related to Antioxidant Properties of Chicken Essence. J. Food Drug Anal. 2005, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, J.; Alejandre-Durán, E.; Pueyo, C. Genetic Differences between the Standard Ames Tester Strains TA100 and TA98. Mutagenesis 1993, 8, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, H.; Kumar, V.; Roy, B.K. Assessment of Genotoxicity of Some Common Food Preservatives Using Allium cepa L. as a Test Plant. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttuso, P.; Nogueira, N.; Gueroun, S.K.M.; Javidpour, J.; Canning-Clode, J.; Andrade, C.A.P. Is Jellyfish a Suitable Ingredient for Aquafeed? A Comprehensive Review of Nutritional Potential and Limitation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1539725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, C.; Haslam, N.J.; Pollastri, G.; Shields, D.C. Towards the Improved Discovery and Design of Functional Peptides: Common Features of Diverse Classes Permit Generalized Prediction of Bioactivity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Miao, J.; Chen, B.; Guo, J.; Ou, Y.; Liang, X.; Yin, Y.; Tong, X.; Cao, Y. Purification, Identification, and Antioxidative Mechanism of Three Novel Selenium-Enriched Oyster Antioxidant Peptides. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauser, K.R.; Baker, P.; Burlingame, A.L. Role of Accurate Mass Measurement (±10 Ppm) in Protein Identification Strategies Employing MS or MS/MS and Database Searching. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2871–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felician, F.F.; Yu, R.-H.; Li, M.-Z.; Li, C.-J.; Chen, H.-Q.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, T.; Qi, W.-Y.; Xu, H.-M. The Wound Healing Potential of Collagen Peptides Derived from the Jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2019, 22, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkus, B.; Arslan, Y.E.; Bayrac, A.T.; Kantarcioglu, I.; Emregul, K.C.; Emregul, E. Development of a Novel Aptasensor Using Jellyfish Collagen as Matrix and Thrombin Detection in Blood Samples Obtained from Patients with Various Neurodisease. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słoczyńska, K.; Powroźnik, B.; Pękala, E.; Waszkielewicz, A.M. Antimutagenic Compounds and Their Possible Mechanisms of Action. J. Appl. Genet. 2014, 55, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, M.-K.; Seong, N.-W.; Kang, G.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, J.-C.; Moon, C. Genotoxicity Evaluation of Collagen Peptide Derived from Skate (Raja kenojei) Skin: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2024, 20, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.-F.; He, C.-T.; Chen, Y.-T.; Hsieh, P.-S. Lipoic Acid Suppresses Portal Endotoxemia-Induced Steatohepatitis and Pancreatic Inflammation in Rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2761–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcarea, C.; Laslo, V.; Memete, A.R.; Agud, E.; Miere (Groza), F.; Vicas, S.I. Antigenotoxic and Antimutagenic Potentials of Proline in Allium Cepa Exposed to the Toxicity of Cadmium Antigenotoxic and Antimutagenic Potentials of Proline in Allium Cepa Exposed to the Toxicity of Cadmium. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumilaar, S.G.; Hardianto, A.; Dohi, H.; Kurnia, D. A Comprehensive Review of Free Radicals, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Overview, Clinical Applications, Global Perspectives, Future Directions, and Mechanisms of Antioxidant Activity of Flavonoid Compounds. J. Chem. 2024, 2024, 5594386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, İ. Antioxidants: A Comprehensive Review. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 99, 1893–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batinic-Haberle, I.; Tovmasyan, A.; Roberts, E.R.H.; Vujaskovic, Z.; Leong, K.W.; Spasojevic, I. SOD Therapeutics: Latest Insights into Their Structure-Activity Relationships and Impact on the Cellular Redox-Based Signaling Pathways. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 2372–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wan, S.; Liu, J.; Zou, Y.; Liao, S. Antioxidant Activity and Stability Study of Peptides from Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Male Silkmoth. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Lao, F.; Pan, X.; Wu, J. Food Protein-Derived Antioxidant Peptides: Molecular Mechanism, Stability and Bioavailability. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udenigwe, C.C.; Fogliano, V. Food Matrix Interaction and Bioavailability of Bioactive Peptides: Two Faces of the Same Coin? J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Mirdamadi, S.; Safavi, M.; Soleymanzadeh, N. The Stability of Antioxidant and ACE-Inhibitory Peptides as Influenced by Peptide Sequences. LWT 2020, 130, 109710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lin, S.; Ye, H. Water Distribution and Moisture-Absorption in Egg-White Derived Peptides: Effects on Their Physicochemical, Conformational, Thermostable, and Self-Assembled Properties. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faruqui, N.; Williams, D.S.; Briones, A.; Kepiro, I.E.; Ravi, J.; Kwan, T.O.C.; Mearns-Spragg, A.; Ryadnov, M.G. Extracellular Matrix Type 0: From Ancient Collagen Lineage to a Versatile Product Pipeline—JellaGelTM. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 22, 100786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, A.J.; Ekbom, D.C.; Hunter, D.; Voss, S.; Bartemes, K.; Mearns-Spragg, A.; Oldenburg, M.S.; San-Marina, S. Larynx Proteomics after Jellyfish Collagen IL: Increased ECM/Collagen and Suppressed Inflammation. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2022, 7, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Ortíz, F.A.; Morón-Fuenmayor, O.E.; González-Méndez, N.F. Hydroxyproline Measurement by HPLC: Improved Method of Total Collagen Determination in Meat Samples. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2004, 27, 2771–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzideh, Z.; Latiff, A.A.; Gan, C.-Y.; Abedin, M.Z.; Alias, A.K. ACE Inhibitory and Antioxidant Activities of Collagen Hydrolysates from the Ribbon Jellyfish (Chrysaora sp.). Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 52, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.M.; Petersen, D.; Dambmann, C. Improved Method for Determining Food Protein Degree of Hydrolysis. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Ortiz, F.A.; Caire, G.; Higuera-Ciapara, I.; Hernández, G. High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Free Amino Acids in Shrimp. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1995, 18, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. [2] Ferric Reducing/Antioxidant Power Assay: Direct Measure of Total Antioxidant Activity of Biological Fluids and Modified Version for Simultaneous Measurement of Total Antioxidant Power and Ascorbic Acid Concentration. In Methods in Enzymology; Oxidants and Antioxidants Part A; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; Volume 299, pp. 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Prior, R.L.; Hoang, H.; Gu, L.; Wu, X.; Bacchiocca, M.; Howard, L.; Hampsch-Woodill, M.; Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Jacob, R. Assays for Hydrophilic and Lipophilic Antioxidant Capacity (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORACFL)) of Plasma and Other Biological and Food Samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3273–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, D.M.; Ames, B.N. Revised Methods for the Salmonella Mutagenicity Test. Mutat. Res. Mutagen. Relat. Subj. 1983, 113, 173–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Jiménez, G.M.; Burgos-Hernández, A.; Torres-Arreola, W.; López-Saiz, C.M.; Velázquez Contreras, C.A.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Bioactive Peptides from Collagen Hydrolysates from Squid (Dosidicus gigas) by-Products Fractionated by Ultrafiltration. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antioxidant Activity (µmol TE/g *) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | ABTS | FRAP | ORAC |
| Hydrolysates | 7920 ± 0.4 b | 6435 ± 2.1 b | 457 ± 4.3 b |
| F1 (>10 kDa) | 5763 ± 9.0 d | 1244 ± 1.1 d | 223 ± 2.5 d |
| F2 (3–10 kDa) | 6848 ± 3.1 c | 4345 ± 3.8 c | 324 ± 1.1 c |
| F3 (<3 kDa) | 8993 ± 5.2 a | 7622 ± 5.6 a | 599 ± 3.0 a |
| Sample | Dose (mg/Plate) | Revertants/Plate | % Inhibition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Collagen | 2 | 896 ± 3.0 f | 72.6 ± 0.3 |
| 0.2 | 1444 ± 7.0 d | 55.8 ± 0.5 | |
| 0.02 | 2805 ± 3.0 b | 14.1 ± 0.1 | |
| 0.002 | 3245 ± 3.8 a | 0.6 ± 0.1 | |
| Hydrolysate | 2 | 477 ± 6.0 n | 85.4 ± 1.2 |
| 0.2 | 708 ± 7.0 k | 78.3 ± 0.9 | |
| 0.02 | 1323 ± 9.0 e | 59.5 ± 0.7 | |
| 0.002 | 1577 ± 5.2 c | 51.7 ± 0.3 | |
| F1 (>10 kDa) | 2 | 464.9 ± 7.7 n | 85.8 ± 1.7 |
| 0.2 | 598.5 ± 1.0 l | 81.7 ± 0.2 | |
| 0.02 | 725.2 ± 4.4 j | 77.8 ± 0.6 | |
| 0.002 | 822.9 ± 3.0 h | 74.8 ± 0.4 | |
| F2 (3–10 kDa) | 2 | 401.3 ± 1.2 ñ | 87.7 ± 0.3 |
| 0.2 | 590.6 ± 2.2 l | 81.9 ± 0.4 | |
| 0.02 | 706.2 ± 4.1 k | 78.4 ± 0.6 | |
| 0.002 | 814.6 ± 1.7 i | 75.1 ± 0.2 | |
| F3 (<3 kDa) | 2 | 392.5 ± 2.9 ñ | 88.0 ± 0.7 |
| 0.2 | 577.6 ± 3.1 m | 82.3 ± 0.5 | |
| 0.02 | 701.5 ± 1.4 k | 78.6 ± 0.2 | |
| 0.002 | 871.3 ± 3.0 g | 73.3 ± 0.3 | |
| Spontaneous Revertants | 159.3 ± 12.9 | ||
| AFB1 | 3265.4 ± 26.2 |
| Sample | Mitotic Index * (%) | Abnormalities * (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 0.80 c | 0.01 d |
| Sodium azide | 1.32 d | 1.33 a |
| Hydrolysates 1 | 1.01 b | 0.67 c |
| Hydrolysates 2 | 1.05 b | 0.64 b |
| F3 1 | 0.56 a | 0.01 d |
| F3 2 | 1.10 a | 0.05 d |
| Amino Acid | g/100 g Protein * | Antioxidant Relevance (Hydrophobicity) | Nutritional Classification |
| Asp | 0.4 | NH | NEAA |
| Glu | 0.6 | NH | NEAA |
| Lys | 0.2 | NH | EAA |
| Arg | 0.5 | NH | EAA |
| Met | 0.1 | H | EAA |
| Ser | 0.3 | NH | NEAA |
| Thr | 0.1 | NH | EAA |
| Gly | 1.2 | H | NEAA |
| Ala | 0.1 | H | NEAA |
| Val | 0.1 | H | EAA |
| Ile | 0.1 | H | EAA |
| Leu | 0.3 | H | EAA |
| Tyr | 0.1 | H | NEAA |
| Phe | 0.1 | H | EAA |
| Pro | 0.4 | H | NEAA |
| Hyp | 0.2 | H | NEAA |
| Charged (+) | 0.7 | ||
| Charged (−) | 1.0 | ||
| Polar without charge | 0.4 | ||
| No polar | 2.4 | ||
| Aromatics | 0.3 | ||
| Pro + Hyp | 0.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villalba-Urquidy, B.d.S.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Medina, I.; Hernández-Aguirre, L.E.; Chan-Higuera, J.E.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Bioactivity and in Silico Insights of Collagen-Derived Peptides from Jellyfish (Stomolophus sp. 2) Mesoglea. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23110427
Villalba-Urquidy BdS, Torres-Arreola W, Medina I, Hernández-Aguirre LE, Chan-Higuera JE, Ezquerra-Brauer JM. Bioactivity and in Silico Insights of Collagen-Derived Peptides from Jellyfish (Stomolophus sp. 2) Mesoglea. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(11):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23110427
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillalba-Urquidy, Blanca del Sol, Wilfrido Torres-Arreola, Isabel Medina, Laura Estefany Hernández-Aguirre, Jesús Enrique Chan-Higuera, and Josafat Marina Ezquerra-Brauer. 2025. "Bioactivity and in Silico Insights of Collagen-Derived Peptides from Jellyfish (Stomolophus sp. 2) Mesoglea" Marine Drugs 23, no. 11: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23110427
APA StyleVillalba-Urquidy, B. d. S., Torres-Arreola, W., Medina, I., Hernández-Aguirre, L. E., Chan-Higuera, J. E., & Ezquerra-Brauer, J. M. (2025). Bioactivity and in Silico Insights of Collagen-Derived Peptides from Jellyfish (Stomolophus sp. 2) Mesoglea. Marine Drugs, 23(11), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23110427