Mutagenesis of the Peptide Inhibitor of ASIC3 Channel Introduces Binding to Thumb Domain of ASIC1a but Reduces Analgesic Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
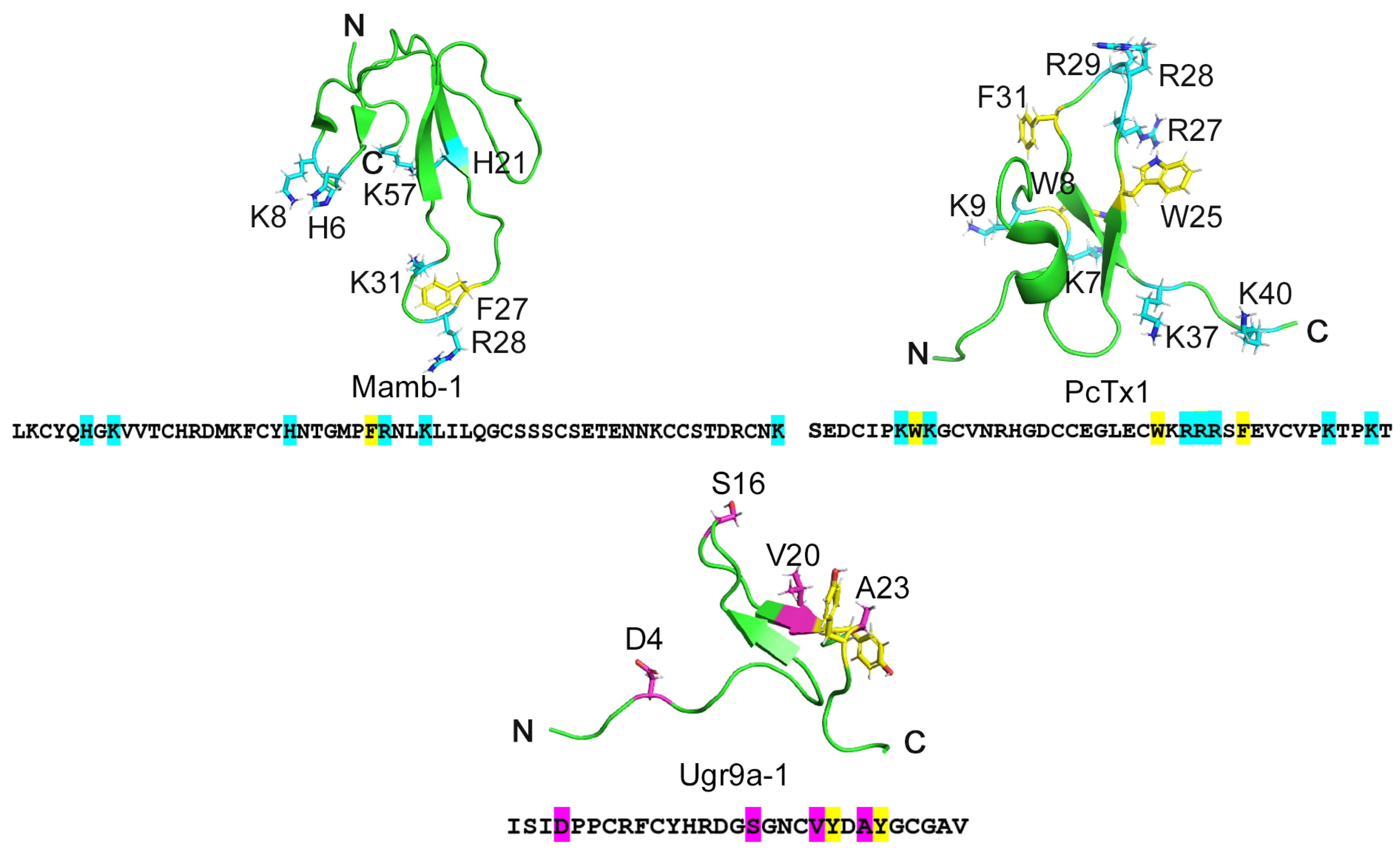
2.1. Changing the Selectivity of the Ugr9a-1 Peptide Based on Comparison with ASIC1a Channel Inhibitors
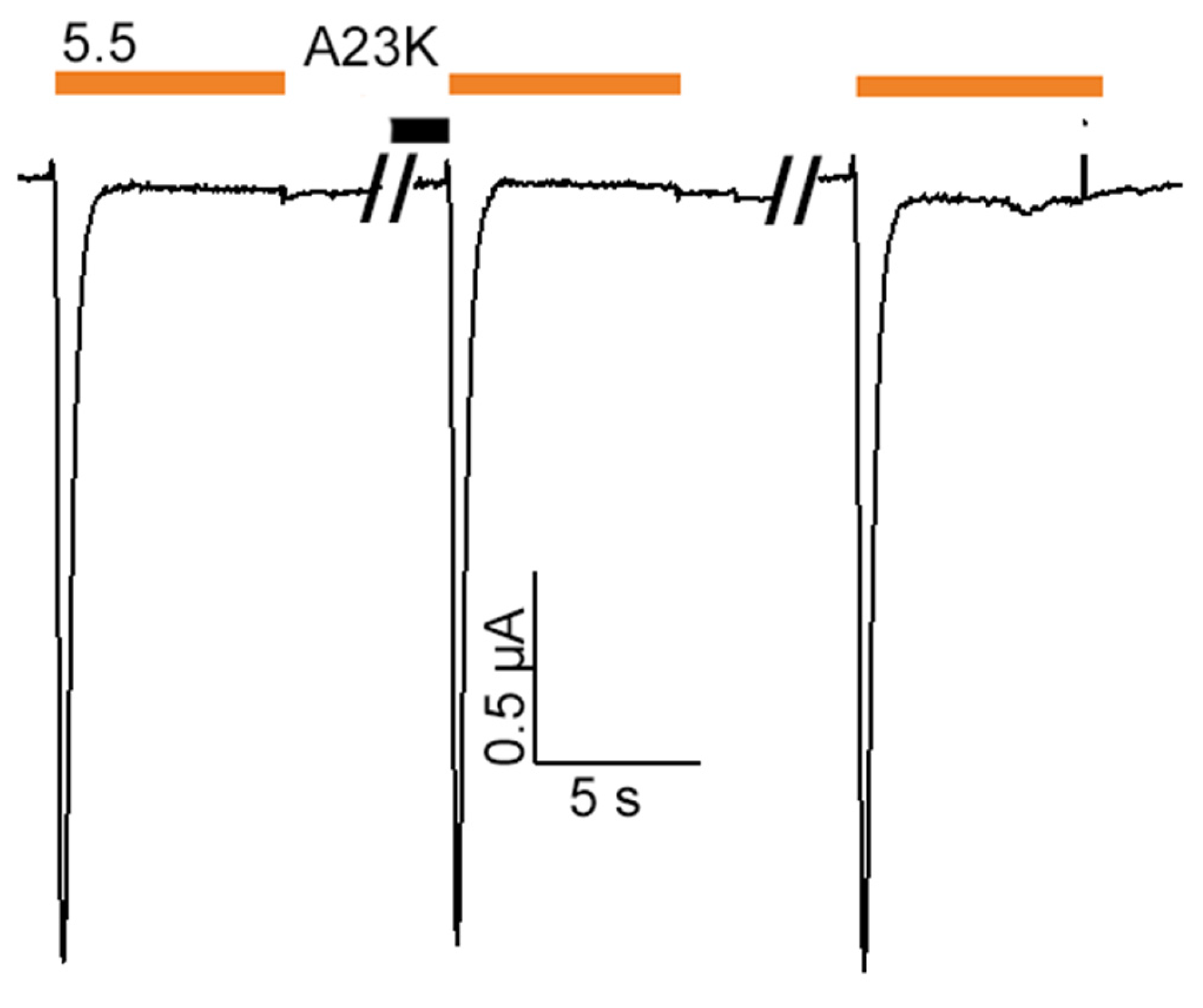
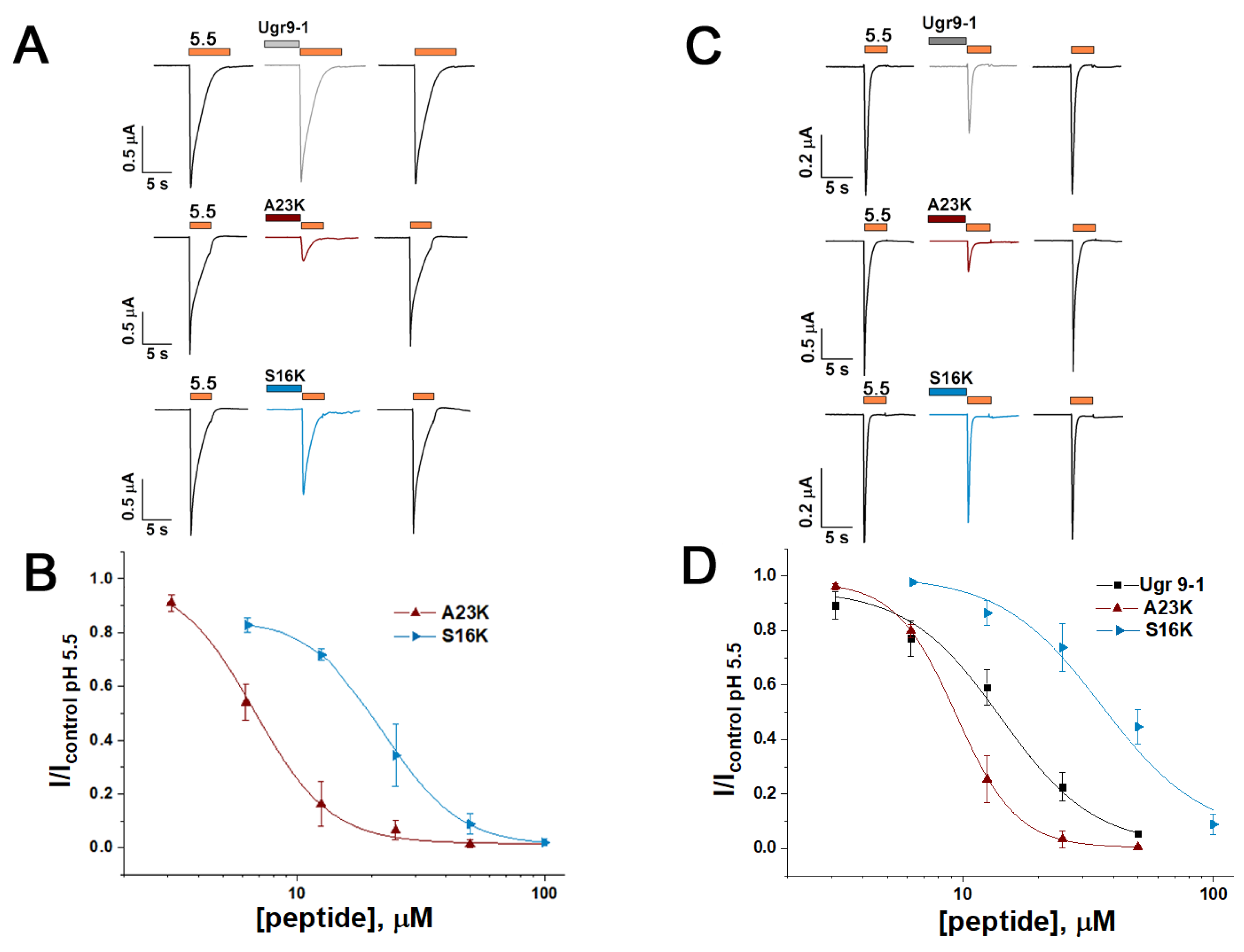
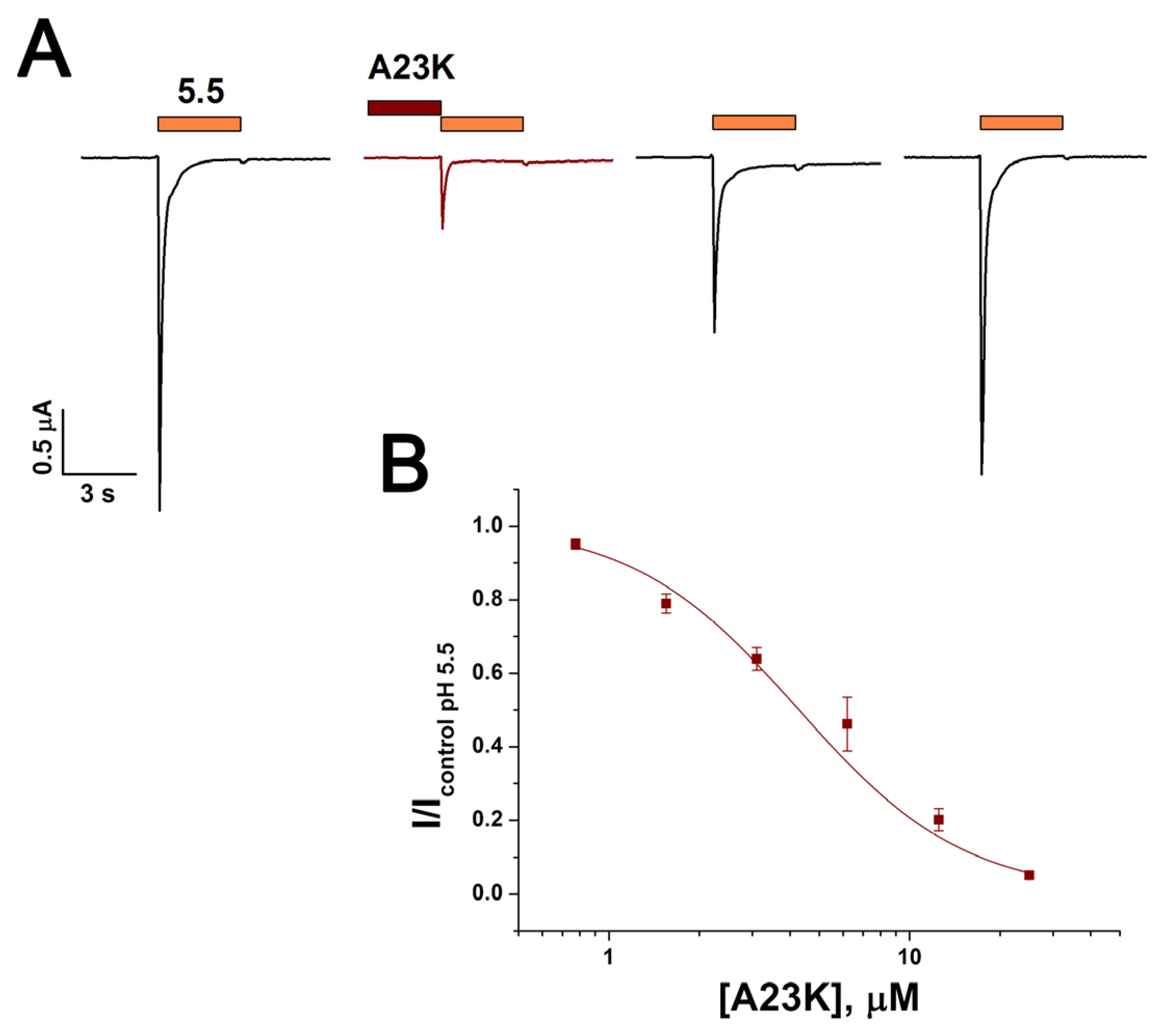
2.2. Mutations Alter the Activity and Selectivity of the Ugr9-1 Peptide
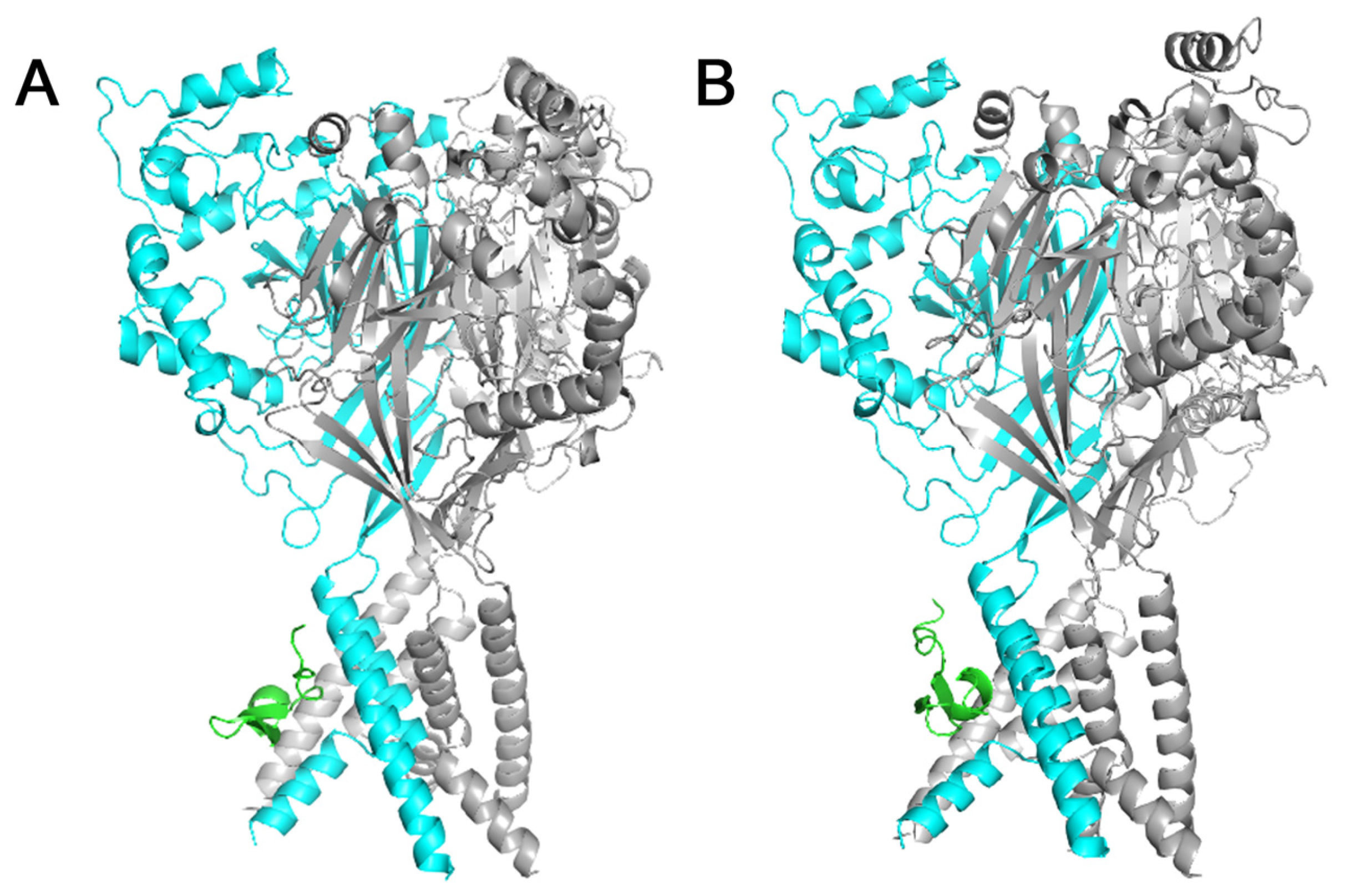
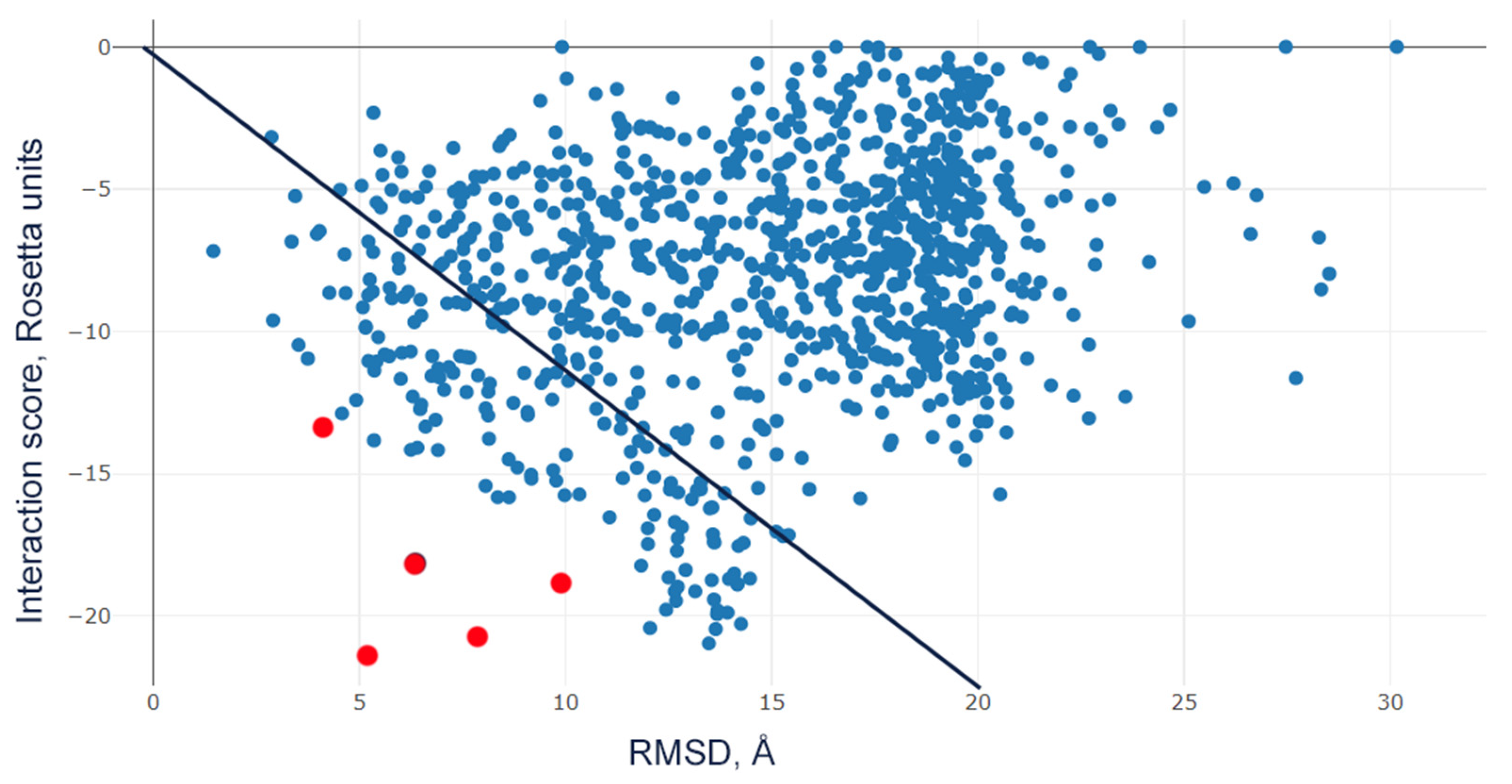
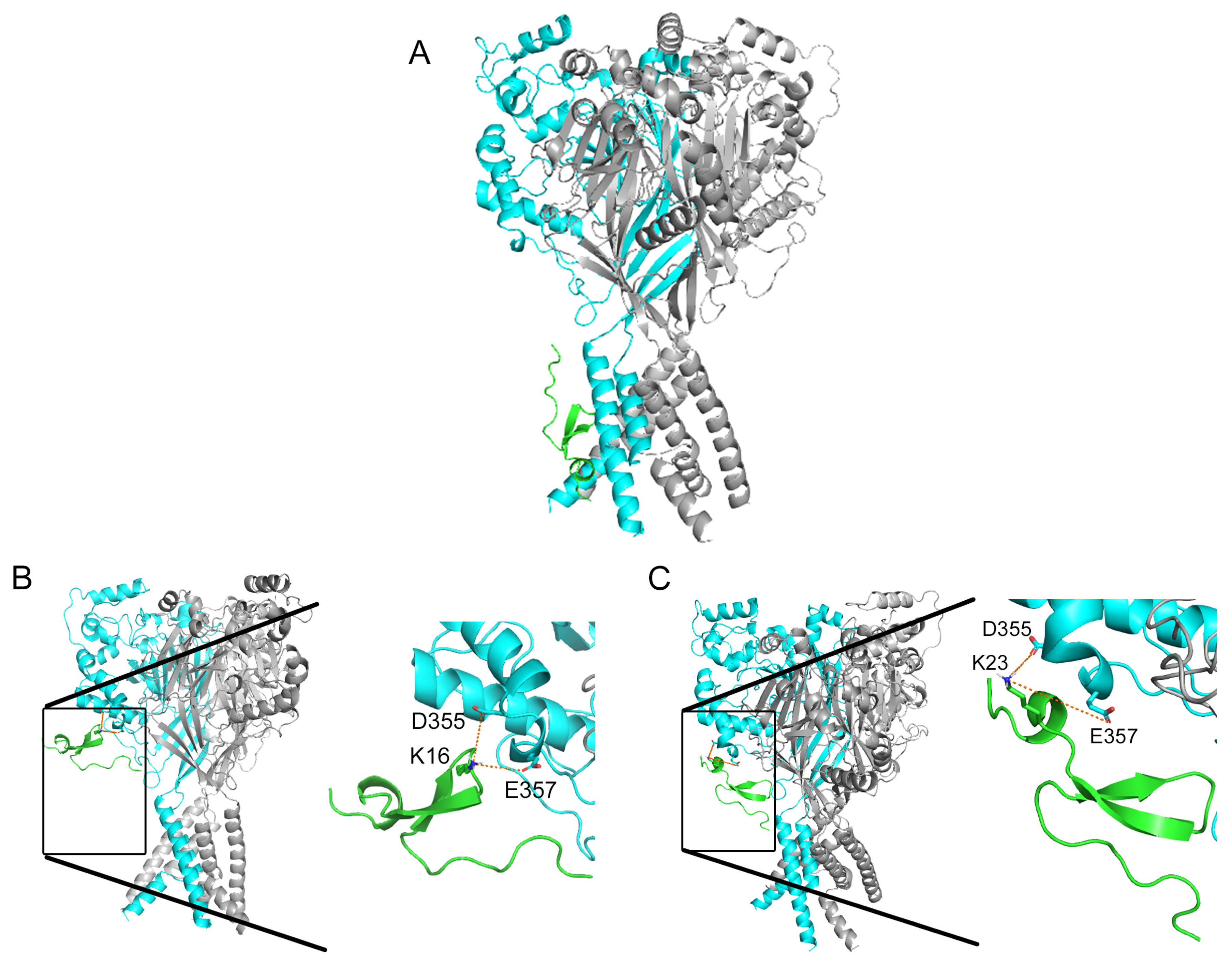
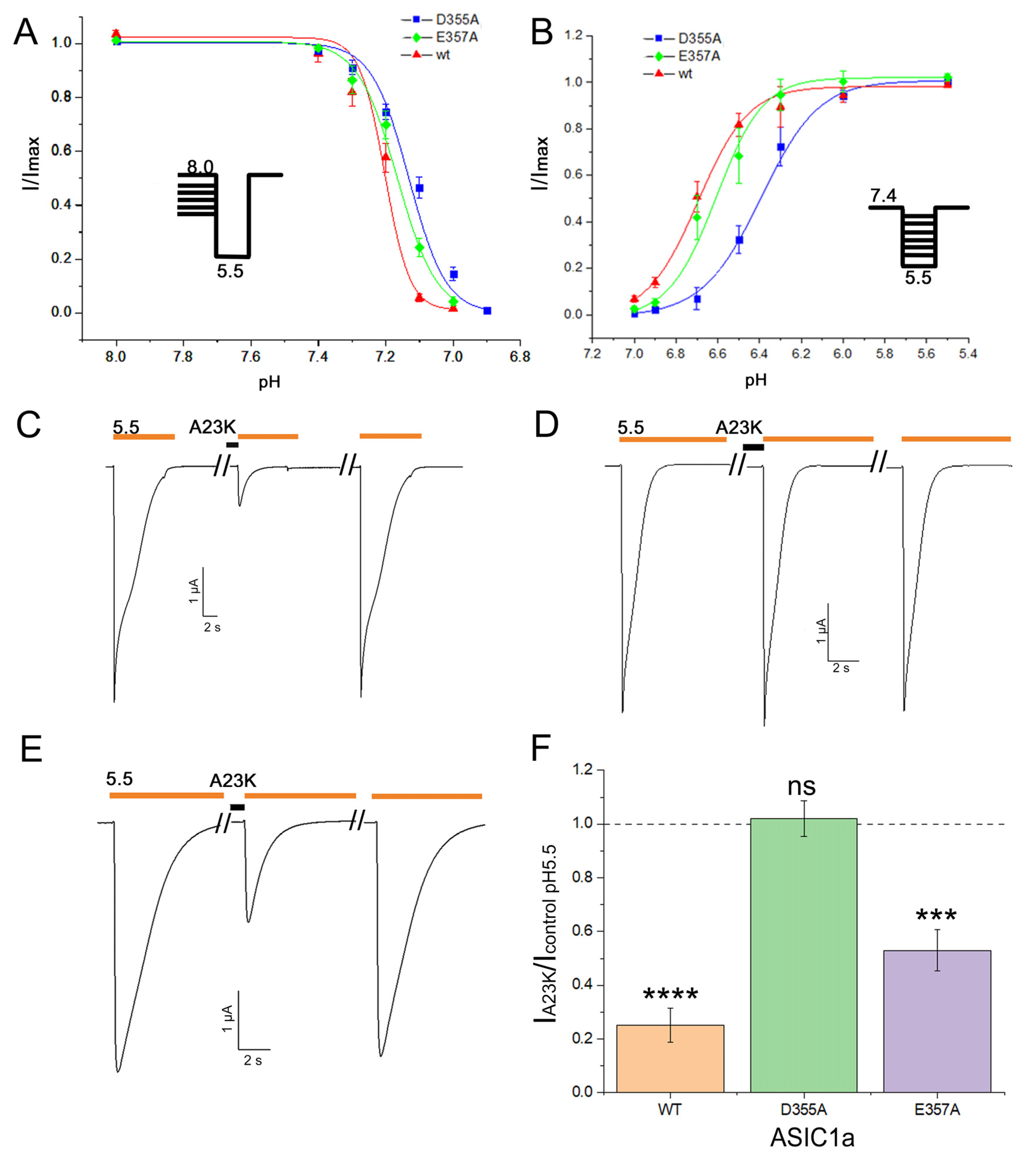
2.3. Residue D355 of the Thumb Domain Is Critical for Ligand Binding to the ASIC1a Channel
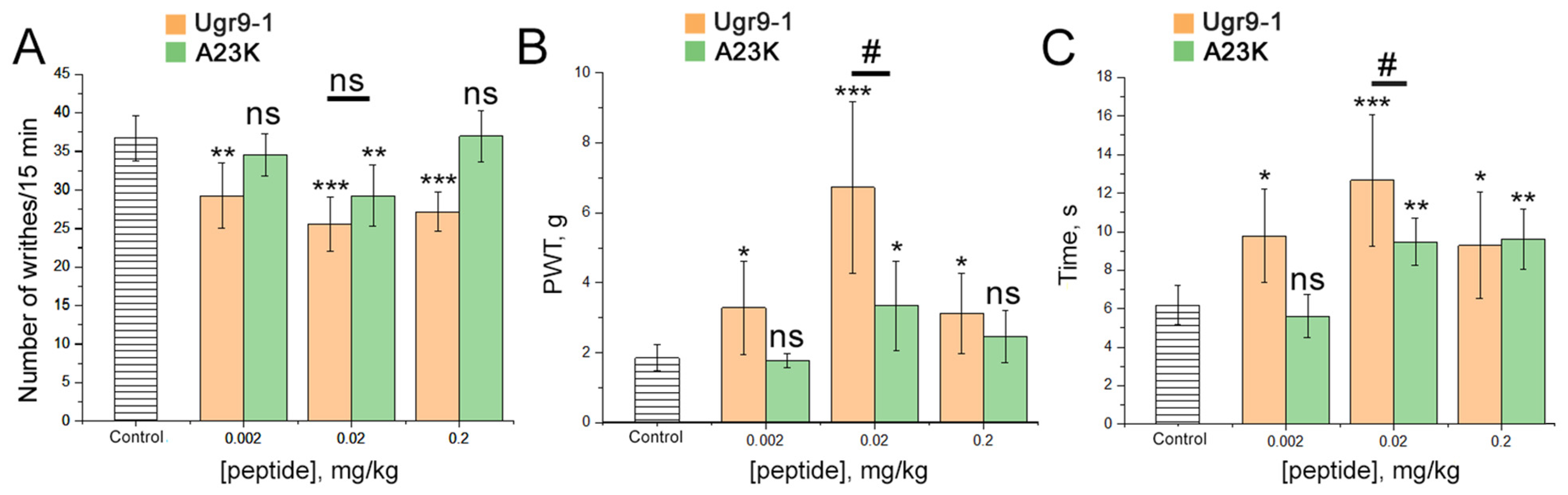
2.4. Loss of Selectivity to ASIC3 Channel Leads to the Impaired Analgesic Effect
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Peptides
4.2. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Rat ASIC1a
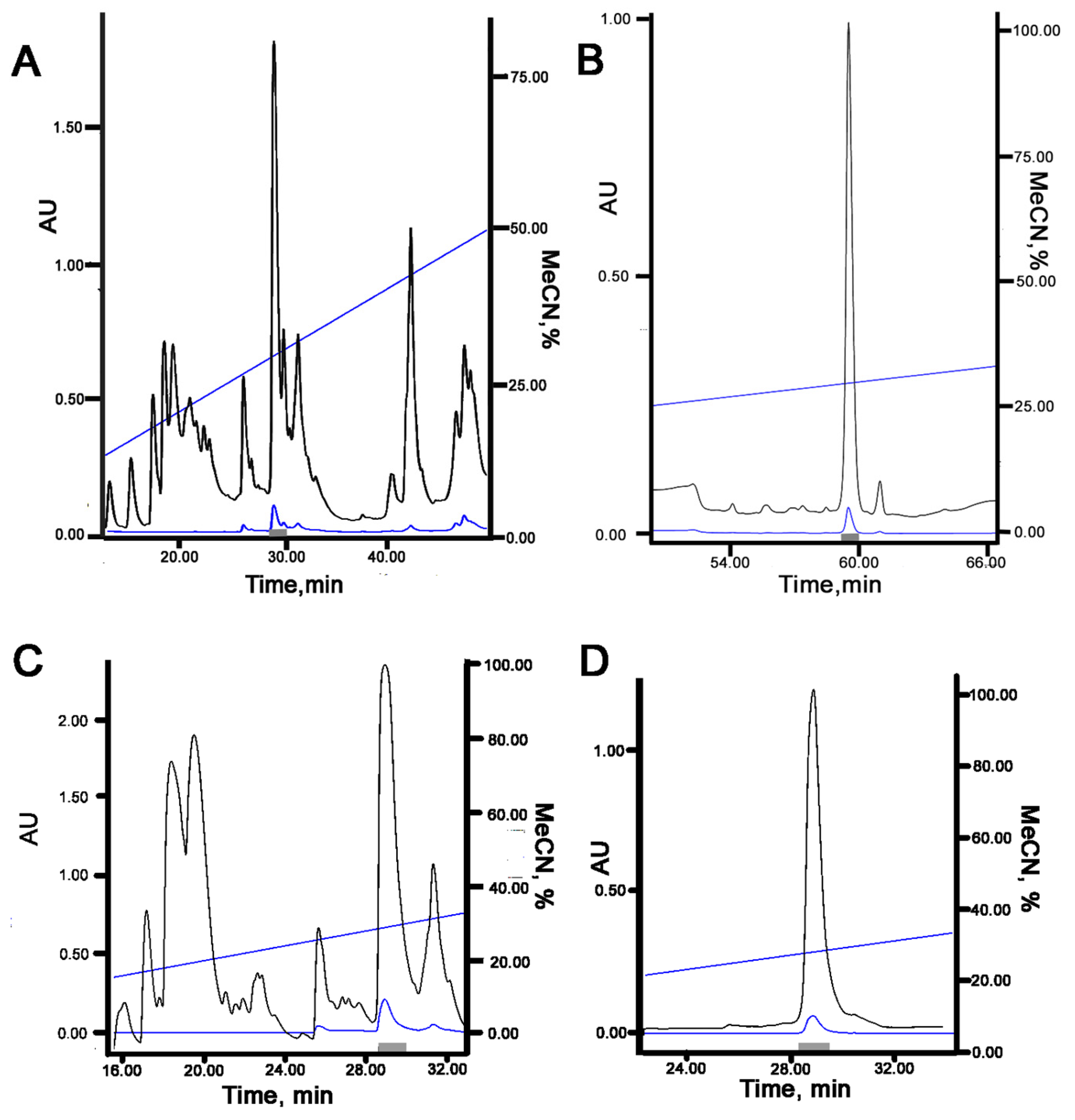
4.3. Recombinant Peptide Production
4.4. Isolation of Xenopus laevisoocytes and mRNA Injection
4.5. Electrophysiological Recordings
4.6. Animal Tests
4.7. Molecular Docking of Peptide Ligands with the Rat ASIC1a Channel
4.8. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Mean ± S.E.M | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D4K | −16.543 | −12.403 | −11.957 | −11.343 | −10.045 | −12.458 ± 1.634 |
| V20K | −17.407 | −13.596 | −12.592 | −12.343 | −12.938 | −13.775 ± 1.453 |
References
- Kellenberger, S.; Schild, L. Epithelial Sodium Channel/Degenerin Family of Ion Channels: A Variety of Functions for a Shared Structure. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 735–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, S.; Schild, L. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCI. Structure, Function, and Pharmacology of Acid-Sensing Ion Channels and the Epithelial Na+ Channel. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.-H.; Chin, Y.; Fong, Y.-O.; Lee, C.-H.; Han, D.-S.; Lin, J.-H.; Sun, W.-H.; Chen, C.-C. Acidosis-related pain and its receptors as targets for chronic pain. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 247, 108444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.-S.; Kung, C.-C.; Huang, S.-L.; Lin, S.-C.; Sun, W.-H. TDAG8, TRPV1, and ASIC3 involved in establishing hyperalgesic priming in experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wemmie, J.A.; Chen, J.; Askwith, C.C.; Hruska-Hageman, A.M.; Price, M.P.; Nolan, B.C.; Yoder, P.G.; Lamani, E.; Hoshi, T.; Freeman, J.H.; et al. The Acid-Activated Ion Channel ASIC Contributes to Synaptic Plasticity, Learning, and Memory. Neuron 2002, 34, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinovskii, A.P.; Pushkarev, A.P.; Mikhailenko, A.D.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Belozerova, O.A.; Shmygarev, V.I.; Yatskin, O.N.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Kozlov, S.A.; Osmakov, D.I.; et al. Dual Modulator of ASIC Channels and GABAA Receptors from Thyme Alters Fear-Related Hippocampal Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Jiang, T.; Mamat, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Meng, H. The Role of ASIC1a in Epilepsy: A Potential Therapeutic Target. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooj, A.K.; McNicholas, C.M.; Bartoszewski, R.; Bebok, Z.; Benos, D.J.; Fuller, C.M. Glioma-specific Cation Conductance Regulates Migration and Cell Cycle Progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4053–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mango, D.; Nisticò, R. Neurodegenerative Disease: What Potential Therapeutic Role of Acid-Sensing Ion Channels? Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, N.; Yoshioka, C.; Gouaux, E. Gating mechanisms of acid-sensing ion channels. Nature 2018, 555, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasti, J.; Furukawa, H.; Gonzales, E.B.; Gouaux, E. Structure of acid-sensing ion channel 1 at 1.9 Å resolution and low pH. Nature 2007, 449, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baconguis, I.; Gouaux, E. Structural plasticity and dynamic selectivity of acid-sensing ion channel–spider toxin complexes. Nature 2012, 489, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, R.J.P.; Benz, J.; Stohler, P.; Tetaz, T.; Joseph, C.; Huber, S.; Schmid, G.; Hügin, D.; Pflimlin, P.; Trube, G.; et al. Structure of the Acid-sensing ion channel 1 in complex with the gating modifier Psalmotoxin 1. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diochot, S.; Baron, A.; Salinas, M.; Douguet, D.; Scarzello, S.; Dabert-Gay, A.S.; Debayle, D.; Friend, V.; Alloui, A.; Lazdunski, M.; et al. Black mamba venom peptides target acid-sensing ion channels to abolish pain. Nature 2012, 490, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, T.; Lingueglia, E.; Salinas, M. Pharmacological modulation of Acid-Sensing Ion Channels 1a and 3 by amiloride and 2-guanidine-4-methylquinazoline (GMQ). Neuropharmacology 2017, 125, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzuca, M.; Heurteaux, C.; Alloui, A.; Diochot, S.; Baron, A.; Voilley, N.; Blondeau, N.; Escoubas, P.; Gélot, A.; Cupo, A.; et al. A tarantula peptide against pain via ASIC1a channels and opioid mechanisms. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 943–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diochot, S.; Alloui, A.; Rodrigues, P.; Dauvois, M.; Friend, V.; Aissouni, Y.; Eschalier, A.; Lingueglia, E.; Baron, A. Analgesic effects of mambalgin peptide inhibitors of acid-sensing ion channels in inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 2016, 157, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmakov, D.I.; Kozlov, S.A.; Andreev, Y.A.; Koshelev, S.G.; Sanamyan, N.P.; Sanamyan, K.E.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Bondarenko, D.A.; Murashev, A.N.; Mineev, K.S.; et al. Sea Anemone Peptide with Uncommon β-Hairpin Structure Inhibits Acid-sensing Ion Channel 3 (ASIC3) and Reveals Analgesic Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23116–23127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmakov, D.I.; Koshelev, S.G.; Andreev, Y.A.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Bondarenko, D.A.; Murashev, A.N.; Grishin, E.V.; Kozlov, S.A. Conversed mutagenesis of an inactive peptide to ASIC3 inhibitor for active sites determination. Toxicon 2016, 116, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, Y.; Osmakov, D.; Koshelev, S.; Maleeva, E.; Logashina, Y.; Palikov, V.; Palikova, Y.; Dyachenko, I.; Kozlov, S. Analgesic Activity of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 3 (ASIC3) Inhibitors: Sea Anemones Peptides Ugr9-1 and APETx2 versus Low Molecular Weight Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, N.J.; Deplazes, E.; Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Chassagnon, I.R.; Lin, X.; Mobli, M.; Mark, A.E.; Rash, L.D.; King, G.F. Molecular dynamics and functional studies define a hot spot of crystal contacts essential for PcTx1 inhibition of acid-sensing ion channel 1a. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4985–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourier, G.; Salinas, M.; Kessler, P.; Stura, E.A.; Leblanc, M.; Tepshi, L.; Besson, T.; Diochot, S.; Baron, A.; Douguet, D.; et al. Mambalgin-1 Pain-relieving Peptide, Stepwise Solid-phase Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Functional Domain for Acid-sensing Ion Channel 1a Inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 2616–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, M.; Kessler, P.; Douguet, D.; Sarraf, D.; Tonali, N.; Thai, R.; Servent, D.; Lingueglia, E. Mambalgin-1 pain-relieving peptide locks the hinge between α4 and α5 helices to inhibit rat acid-sensing ion channel 1a. Neuropharmacology 2021, 185, 108453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauson, A.J.; Carattino, M.D. The thumb domain mediates acid-sensing ion channel desensitization. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 11407–11419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusser, S.A.; Borg, C.B.; Colding, J.M.; Pless, S.A. Conformational decoupling in acid-sensing ion channels uncovers mechanism and stoichiometry of PcTx1-mediated inhibition. Elife 2022, 11, e73384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, M.; Rash, L.D.; Baron, A.; Lambeau, G.; Escoubas, P.; Lazdunski, M. The receptor site of the spider toxin PcTx1 on the proton-gated cation channel ASIC1a. J. Physiol. 2006, 570, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gründer, S.; Augustinowski, K. Toxin binding reveals two open state structures for one acid-sensing ion channel. Channels 2012, 6, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Salinas, M.; Besson, T.; Delettre, Q.; Diochot, S.; Boulakirba, S.; Douguet, D.; Lingueglia, E. Binding Site and Inhibitory Mechanism of the Mambalgin-2 Pain-relieving Peptide on Acid-sensing Ion Channel 1a. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 13363–13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusser, S.A.; Pless, S.A. Acid-sensing ion channels as potential therapeutic targets. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 1035–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlen, C.J.; Chesler, A.T.; Sharif-Naeini, R.; Medzihradszky, K.F.; Zhou, S.; King, D.; Sánchez, E.E.; Burlingame, A.L.; Basbaum, A.I.; Julius, D. A heteromeric Texas coral snake toxin targets acid-sensing ion channels to produce pain. Nature 2011, 479, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmakov, D.I.; Koshelev, S.G.; Palikov, V.A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Shaykhutdinova, E.R.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Andreev, Y.A.; Kozlov, S.A. Alkaloid Lindoldhamine Inhibits Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a and Reveals Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Toxins 2019, 11, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belozerova, O.A.; Osmakov, D.I.; Vladimirov, A.; Koshelev, S.G.; Chugunov, A.O.; Andreev, Y.A.; Palikov, V.A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Shaykhutdinova, E.R.; Gvozd, A.N.; et al. Sevanol and Its Analogues: Chemical Synthesis, Biological Effects and Molecular Docking. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimers, C.; Lee, C.-H.; Kalbacher, H.; Tian, Y.; Hung, C.-H.; Schmidt, A.; Prokop, L.; Kauferstein, S.; Mebs, D.; Chen, C.-C.; et al. Identification of a cono-RFamide from the venom of Conus textile that targets ASIC3 and enhances muscle pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3507–E3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadi, M.; Anyango, S.; Deshpande, M.; Nair, S.; Natassia, C.; Yordanova, G.; Yuan, D.; Stroe, O.; Wood, G.; Laydon, A.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: Massively expanding the structural coverage of protein-sequence space with high-accuracy models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D439–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyskov, S.; Gray, J.J. The RosettaDock server for local protein-protein docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W233–W238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Mean ± S.E.M. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wtUgr9a-1 | −20.092 | −14.285 | −11.330 | −13.981 | −6.628 | −13.263 ± 3.427 |
| S16K | −24.197 | −17.937 | −17.211 | −14.510 | −13.917 | −17.554 ± 2.810 |
| A23K | −21.513 | −20.793 | −18.842 | −18.171 | −13.359 | −18.536 ± 2.216 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khasanov, T.A.; Maleeva, E.E.; Koshelev, S.G.; Palikov, V.A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Kozlov, S.A.; Andreev, Y.A.; Osmakov, D.I. Mutagenesis of the Peptide Inhibitor of ASIC3 Channel Introduces Binding to Thumb Domain of ASIC1a but Reduces Analgesic Activity. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090382
Khasanov TA, Maleeva EE, Koshelev SG, Palikov VA, Palikova YA, Dyachenko IA, Kozlov SA, Andreev YA, Osmakov DI. Mutagenesis of the Peptide Inhibitor of ASIC3 Channel Introduces Binding to Thumb Domain of ASIC1a but Reduces Analgesic Activity. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(9):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090382
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhasanov, Timur A., Ekaterina E. Maleeva, Sergey G. Koshelev, Victor A. Palikov, Yulia A. Palikova, Igor A. Dyachenko, Sergey A. Kozlov, Yaroslav A. Andreev, and Dmitry I. Osmakov. 2024. "Mutagenesis of the Peptide Inhibitor of ASIC3 Channel Introduces Binding to Thumb Domain of ASIC1a but Reduces Analgesic Activity" Marine Drugs 22, no. 9: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090382
APA StyleKhasanov, T. A., Maleeva, E. E., Koshelev, S. G., Palikov, V. A., Palikova, Y. A., Dyachenko, I. A., Kozlov, S. A., Andreev, Y. A., & Osmakov, D. I. (2024). Mutagenesis of the Peptide Inhibitor of ASIC3 Channel Introduces Binding to Thumb Domain of ASIC1a but Reduces Analgesic Activity. Marine Drugs, 22(9), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090382






