Red Seaweed (Rhodophyta) Phycocolloids: A Road from the Species to the Industry Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Red Seaweed Polysaccharides: Agar and Carrageenan
2.1. Chemical Composition
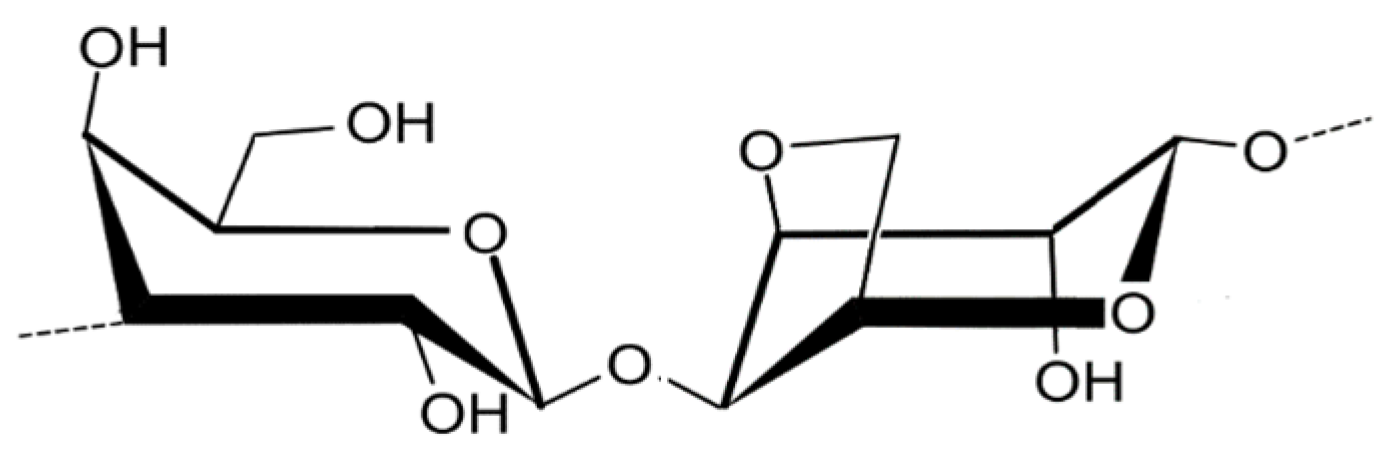
2.1.1. Agar
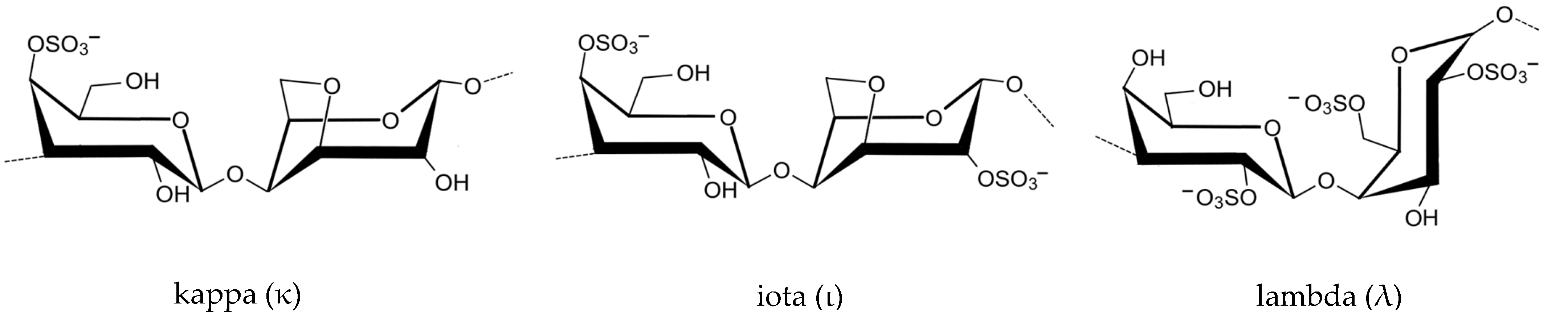
2.1.2. Carrageenan
2.2. Historical Background
3. Seaweed Polysaccharides’ Current Industrial Applications
3.1. Food Industry
3.2. Pharmaceutical and Medicine Industry
3.3. Cosmetic Industry
3.4. Agriculture Industry
4. Drivers of Polysaccharide Production
4.1. Abiotic Factors
4.2. Biotic Factors
4.3. Red Seaweed Polysaccharide Studies in Polysaccharide Production
4.3.1. Carrageenan
Effect of Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR)
Effect of Light
Effect of Other Abiotic Factors
4.3.2. Agar
Effect of Seasonal Changes of Environmental Conditions
Effect of Salinity
Effect of Light Deprivation
Effect of Temperature
Effect of Nitrogen Availability
Effect of Sulphate and pH Concentration
Effect of Wave Exposure/Water Movement
Effect of Life Stage and Epiphytes/Epibionts
4.4. Additional Considerations
5. Extraction Technologies and Safety Measures for Phycocolloid Production
5.1. Industrial Extraction Methods
5.1.1. Agar
5.1.2. Carrageenan
5.2. Industrial Safety Measures
5.3. Technical Characteristics of Agar and Carrageenan
5.3.1. Agar
5.3.2. Carrageenan
5.4. RD of Polysacharide Extraction Methods
6. Industrial Innovation: Emerging Applications of Seaweed Polysaccharides
6.1. Pharmaceutical Applications
6.2. Food Packaging
7. Future Road for Red Seaweed Polysaccharide Exploitation
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, L.D.; Bahcevandziev, K.; Pereira, L. Production of bio-fertilizer from Ascophyllum nodosum and Sargassum muticum (Phaeophyceae). J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L. Macroalgae. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirtawijaya, G.; Negara, B.F.S.P.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, M.G.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, J.S. The Influence of Abiotic Factors on the Induction of Seaweed Callus. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, E. The polysaccharides of green, red and brown seaweeds: Their basic structure, biosynthesis and function. Br. Phycol. J. 1979, 14, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Lim, Y.Y.; Leow, A.T.C.; Namasivayam, P.; Abdullah, J.O.; Ho, C.L. Factors affecting yield and gelling properties of agar. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 1527–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Véliz, K.; Chandía, N.; Rivadeneira, M.; Thiel, M. Seasonal variation of carrageenans from Chondracanthus chamissoi with a review of variation in the carrageenan contents produced by Gigartinales. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 3139–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Khalid, S.; Usman, A.; Hussain, Z.; Wang, Y. Algal Polysaccharides, Novel Application, and Outlook. In Algae Based Polymers, Blends, and Composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 115–153. ISBN 9780128123607. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.K.; Lim, Y.Y.; Leow, A.T.C.; Namasivayam, P.; Ong Abdullah, J.; Ho, C.L. Biosynthesis of agar in red seaweeds: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, V.; Torres, M.D.; Domínguez, H.; Pinto, I.S.; Costa, I.; Guedes, A.C. Seasonal and spatial compositional variation of the red algae Mastocarpus stellatus from the Northern coast of Portugal. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 35, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuai, S.A.H. Characterization of agar extracted from Gracilaria species collected along Tanzanian coast. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Lai, T.K.; Tye, Y.Y.; Rizal, S.; Chong, E.W.N.; Yap, S.W.; Hamzah, A.A.; Fazita, M.R.N.; Paridah, M.T. A review of extractions of seaweed hydrocolloids: Properties and applications. Express Polym. Lett. 2018, 12, 296–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafting, J.T.; Craigie, J.S.; Stengel, D.B.; Loureiro, R.R.; Buschmann, A.H.; Yarish, C.; Edwards, M.D.; Critchley, A.T. Prospects and challenges for industrial production of seaweed bioactives. J. Phycol. 2015, 51, 821–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Poza, S.; Leandro, A.; Cotas, C.; Cotas, J.; Marques, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. The Evolution Road of Seaweed Aquaculture: Cultivation Technologies and the Industry 4.0. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlander, M. Advances in cultivation of Gelidiales. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Buia, M.C.; Palumbo, A.; Mohany, M.; Wadaan, M.A.M.; Hozzein, W.N.; Beemster, G.T.S.; AbdElgawad, H. Ocean acidification affects biological activities of seaweeds: A case study of Sargassum vulgare from Ischia volcanic CO2 vents. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roleda, M.Y.; Hurd, C.L. Seaweed nutrient physiology: Application of concepts to aquaculture and bioremediation. Phycologia 2019, 58, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, A.; Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; Marques, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Seaweed’s Bioactive Candidate Compounds to Food Industry and Global Food Security. Life 2020, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Freitas, A.C.; Pereira, L.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P.; Vasconcelos, M.W.; Roriz, M.; Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M.; Gomes, A.M.P.; Duarte, A.C. Chemical composition of red, brown and green macroalgae from Buarcos bay in Central West Coast of Portugal. Food Chem. 2015, 183, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Critchley, A.T.; Amado, A.M.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.A. A comparative analysis of phycocolloids produced by underutilized versus industrially utilized carrageenophytes (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, P.; Subhash, G.V.; Khade, M.; Savant, S.; Musale, A.; Kumar, G.R.K.; Chelliah, M.S.; Dasgupta, S. Empowering blue economy: From underrated ecosystem to sustainable industry. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 291, 112697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Gheda, S.F.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.A. Analysis by Vibrational Spectroscopy of Seaweed Polysaccharides with Potential Use in Food, Pharmaceutical, and Cosmetic Industries. Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2013, 2013, 537202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvizu-Higuera, D.L.; Rodríguez-Montesinos, Y.E.; Murillo-Álvarez, J.I.; Muñoz-Ochoa, M.; Hernández-Carmona, G. Effect of alkali treatment time and extraction time on agar from Gracilaria vermiculophylla. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, P.; Etxabide, A.; Leceta, I.; Peñalba, M.; De La Caba, K. Extraction of agar from Gelidium sesquipedale (Rodhopyta) and surface characterization of agar based films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertasa, M.; Dodero, A.; Alloisio, M.; Vicini, S.; Riedo, C.; Sansonetti, A.; Scalarone, D.; Castellano, M. Agar gel strength: A correlation study between chemical composition and rheological properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 123, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupérez, P.; Saura-Calixto, F. Dietary fibre and physicochemical properties of edible Spanish seaweeds. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2001, 212, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, G.; Torres, M.D.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; Hilliou, L. Effect of pre-extraction alkali treatment on the chemical structure and gelling properties of extracted hybrid carrageenan from Chondrus crispus and Ahnfeltiopsis devoniensis. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 50, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.D.; Chenlo, F.; Moreira, R. Rheology of κ/ι-hybrid carrageenan from Mastocarpus stellatus: Critical parameters for the gel formation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Amado, A.M.; Critchley, A.T.; van de Velde, F.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.A. Identification of selected seaweed polysaccharides (phycocolloids) by vibrational spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR and FT-Raman). Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, L.; Grenha, A. Sulfated Seaweed Polysaccharides as Multifunctional Materials in Drug Delivery Applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, A.O.; Byankina Barabanova, A.O.; Glazunov, V.P.; Yakovleva, I.M.; Yermak, I.M. Seasonal variations in a polysaccharide composition of Far Eastern red seaweed Ahnfeltiopsis flabelliformis (Phyllophoraceae). J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L. Seaweeds as source of bioactive substances and skin care therapy-Cosmeceuticals, algotheraphy, and thalassotherapy. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, K.; Kontogiorgos, V. Seaweed Polysaccharides (Agar, Alginate Carrageenan). In Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 240–250. ISBN 9780128140451. [Google Scholar]
- Bixler, H.J.; Porse, H. A decade of change in the seaweed hydrocolloids industry. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ścieszka, S.; Klewicka, E. Algae in food: A general review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3538–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.; van de Velde, F. Portuguese carrageenophytes: Carrageenan composition and geographic distribution of eight species (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta). Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L. Carrageenan: A review. Vet. Med. 2013, 58, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, R.R.; Cornish, M.L.; Neish, I.C. Applications of Carrageenan: With Special Reference to Iota and Kappa Forms as Derived from the Eucheumatoid Seaweeds. Trop. Seaweed Farming Trends Probl. Oppor. 2017, 9, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, O.; Sukhikh, S.; Larina, V.; Kalashnikova, O.; Kashirskikh, E.; Prosekov, A.; Noskova, S.; Ivanova, S.; Fendri, I.; Smaoui, S.; et al. Algae: Study of Edible and Biologically Active Fractions, Their Properties and Applications. Plants 2022, 11, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L. (Ed.) Therapeutic and Nutritional Uses of Algae; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; ISBN 9781315152844. [Google Scholar]
- McHugh, D.J. A Guide to the Seaweed Industry; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2003; ISBN 9251049580. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Carmona, G.; Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; Hernández-Garibay, E. Conventional and alternative technologies for the extraction of algal polysaccharides. In Functional Ingredients from Algae for Foods and Nutraceuticals; Dominguez, H., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 475–516. ISBN 9780857095121. [Google Scholar]
- Cotas, J.; Leandro, A.; Monteiro, P.; Pacheco, D.; Figueirinha, A.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; da Silva, G.J.; Pereira, L. Seaweed Phenolics: From Extraction to Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanna, B.; Mishra, A. Nutraceutical Potential of Seaweed Polysaccharides: Structure, Bioactivity, Safety, and Toxicity. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Gul, I.; Basharat, A.; Qamar, S.A. Polysaccharides-based bio-nanostructures and their potential food applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 176, 540–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.W.; Li, R.Q.; An, J.X.; Xie, T.Q.; Han, Z.Y.; Xu, R.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, X.Z. Prebiotics-Encapsulated Probiotic Spores Regulate Gut Microbiota and Suppress Colon Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, E.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Antibacterial derivatives of marine algae: An overview of pharmacological mechanisms and applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivasagan, P.; Oh, J. Marine polysaccharide-based nanomaterials as a novel source of nanobiotechnological applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, N.; Malik, A.; Naik, S. Antiviral activity of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae and its application in combating COVID-19: Mini review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 13, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jesus Raposo, M.F.; De Morais, A.M.B.; De Morais, R.M.S.C. Marine polysaccharides from algae with potential biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2967–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajadimajd, S.; Bahramsoltani, R.; Iranpanah, A.; Kumar Patra, J.; Das, G.; Gouda, S.; Rahimi, R.; Rezaeiamiri, E.; Cao, H.; Giampieri, F.; et al. Advances on Natural Polyphenols as Anticancer Agents for Skin Cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 151, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L. A review of the nutrient composition of selected edible seaweeds. In Seaweed: Ecology, Nutrient Composition and Medicinal Uses; Pomin, V.H., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhan, X.; Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Review for carrageenan-based pharmaceutical biomaterials: Favourable physical features versus adverse biological effects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, T.; Cotas, J.; Pacheco, D.; Pereira, L. Seaweeds Compounds: An Ecosustainable Source of Cosmetic Ingredients? Cosmetics 2021, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. Reduction of heavy metal (Pb2+) biosorption in zebrafish model using alginic acid purified from Ecklonia cava and two of its synthetic derivatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Seca, A.M.L.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Michalak, I.; Trincone, A.; Mishra, A.P.; Nigam, M.; Zam, W.; Martins, N. Current Trends on Seaweeds: Looking at Chemical Composition, Phytopharmacology, and Cosmetic Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, R.H.; Chaineux, M.-C.P. The Healing Sea: A Sustainable Coastal Ocean Resource: Thalassotherapy. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 2009, 838–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboa, E.M.; Conde, E.; Soto, M.L.; Pérez-Armada, L.; Domínguez, H. Cosmetics from Marine Sources BT. In Springer Handbook of Marine Biotechnology; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1015–1042. ISBN 978-3-642-53971-8. [Google Scholar]
- Mamede, M.; Cotas, J.; Bahcevandziev, K.; Pereira, L. Seaweed Polysaccharides in Agriculture: A Next Step towards Sustainability. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Carpena, M.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Echave, J.; Soria-Lopez, A.; Garcia-Perez, P.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Cao, H.; Nie, S.; Xiao, J.; et al. Seaweed polysaccharides: Emerging extraction technologies, chemical modifications and bioactive properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1901–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomartire, S.; Cotas, J.; Pacheco, D.; Marques, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Environmental Impact on Seaweed Phenolic Production and Activity: An Important Step for Compound Exploitation. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomartire, S.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Novel Technologies for Seaweed Polysaccharides Extraction and Their Use in Food with Therapeutically Applications-A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Lee, Z.J.; Ye, S.; Barrow, C.J.; Dunshea, F.R.; Suleria, H.A.R. A Review on Seaweeds and Seaweed-Derived Polysaccharides: Nutrition, Chemistry, Bioactivities, and Applications. Food Rev. Int. 2024, 40, 1312–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azanza, R.V.; Ask, E. Reproductive Biology and Eco-physiology of Farmed Kappaphycus and Eucheuma. In Tropical Seaweed Farming Trends, Problems and Opportunities; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi, D.Y.; Segal, Y.; Ben-Valid, S.; Paz, G.; Tsubery, M.N.; Salomon, E.; Abelson, A.; Israel, Á. Enrichment of nutritional compounds in seaweeds via abiotic stressors in integrated aquaculture. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 80, 103067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Duan, D. The Cell Wall Polysaccharides Biosynthesis in Seaweeds: A Molecular Perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 902823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentati, F.; Tounsi, L.; Djomdi, D.; Pierre, G.; Delattre, C.; Ursu, A.V.; Fendri, I.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P. Bioactive Polysaccharides from Seaweeds. Molecules 2020, 25, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pong-Masak, P.R.; Sarira, N.H. Effect of Depth on the Growth and Carrageenan Content of Seaweed Kappaphycus alvarezii Cultivated Using Verticulture Method. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 147, 01011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyani, S.; Tuwo, A.; Syamsuddin, R.; Jompa, J.; Cahyono, I. Relationship of the viscosity of carrageenan extracted from Kappaphycus alvarezii with seawater physical and chemical properties at different planting distances and depth. AACL Bioflux 2021, 14, 328–336. [Google Scholar]
- Estevez, J.M.; Ciancia, M.; Cerezo, A.S.; Phyllophora, G.; Hooker, G. Carrageenans Biosynthesized by Carposporophytes of Red Seaweeds Gigartina skottsbergii (Gigartinaceae) and Gymnogongrus torulosus (Phyllophoraceae) 1 Carrageenans biosynthesized by gametophytic and tetrasporic plants of seaweeds belonging to the Gigar. J. Phycol. 2002, 350, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tasende, M.G.; Cid, M.; Fraga, M.I. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of carrageenan content in gametophytes of Mastocarpus stellatus (Stackhouse) Guiry along Galician coast (NW Spain). J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakibia, J.G.; Bolton, J.J.; Keats, D.W.; Raitt, L.M. Seasonal changes in carrageenan yield and gel properties in three commercial eucheumoids grown in southern Kenya. Bot. Mar. 2006, 49, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; Robledo, D. Carrageenan of Eucheuma isiforme (Solieriaceae, Rhodophyta) from Nicaragua. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qari, R.; Abbas, Q.; Khan, A.R. Carrageenan Content in Three Species of Hypnea (H. musciformis Wulfen J. V. Lamouroux, H. pannosa J. Agardh and H. valentiae Turner Montagne) of Karachi Coast. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 8, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournet, I.; Zinoun, M.; Deslandes, E.; Diouris, M.; Floc’h, J.Y. Floridean starch and carrageenan contents as responses of the red alga Solieria chordalis to culture conditions. Eur. J. Phycol. 1999, 34, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.; Gabaldón, J.A.; Gómez-López, V.M. Degradation of an azo dye by a fast and innovative pulsed light/H2O2 advanced oxidation process. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 136, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, T.; Hanisak, M.D.; Koehn, F.E.; Mollion, J.; Moreau, S. Studies on carrageenans and effects of seawater phosphorus concentration on carrageenan content and growth of Agardhiella subulata (C. Agardh) Kraft and Wynne (Rhodophyceae, Solieriaceae). J. Appl. Phycol. 1990, 2, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breden, P.C.; Bird, K.T. Effects of environmental factors on carrageenan from Gymnogongrus griffithsiae (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 1994, 6, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiesow, A.C. (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales). III. Seasonal Variation of Carrageenan, Total Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1973, 24, 286–299. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigueza, M.R.C.; Montaño, M.N.E. Bioremediation potential of three carrageenophytes cultivated in tanks with seawater from fish farms. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 19, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, T.; Gallant, T.; Davison, I. Phosphorus and Nitrogen Nutrition in Chondrus crispus (Rhodophyta): Effects on Total Phosphorus and Nitrogen Content, Carrageenan Production, and Photosynthetic Pigments and Metabolism1. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, C.; Subba Rao, P.V. Growth rate and carrageenan yield of cultivated Kappaphycus alvarezii (Doty) Doty in the coastal waters of Bay of Bengal at Chepala Timmapuram, Andhra Pradesh, east coast of India. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; Robledo, D. Carrageenan of Eucheuma isiforme (Solieriaceae, Rhodophyta) from Yucatán, Mexico. II. Seasonal variations in carrageenan and biochemical characteristics. Bot. Mar. 2006, 49, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei Jeliani, Z.; Sohrabipour, J.; Soltani, M.; Rabiei, R.; Yousefzadi, M. Seasonal variations in growth and phytochemical compounds of cultivated red alga, Hypnea flagelliformis, in southern coastlines of Iran. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 2459–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, R.P.; Yoneshigue-Valentin, Y.; Pereira Dos Santos, C. Spatial and temporal variation of Hypnea musciformis carrageenan (Rhodophyta-Gigartinales) from natural beds in Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Góes, H.G.; Reis, R.P. Temporal variation of the growth, carrageenan yield and quality of Kappaphycus alvarezii (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales) cultivated at Sepetiba bay, southeastern Brazilian coast. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, L.; Oliveira, E.C.; Bleicher-Lhonneur, G.; Boulenguer, P.; Pereira, R.T.L.; Von Seckendorff, R.; Shimoda, V.T.; Leflamand, A.; Vallée, P.; Critchley, A.T. The effects of selected cultivation conditions on the carrageenan characteristics of Kappaphycus alvarezii (Rhodophyta, Solieriaceae) in Ubatuba Bay, São Paulo, Brazil. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 19, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, A.Q.; Yunque, D.A.; Tibubos, K.; Critchley, A.T. Use of Acadian marine plant extract powder from Ascophyllum nodosum in tissue culture of Kappaphycus varieties. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durako, M.J.; Dawes, C.J. A comparative seasonal study of two populations of Hypnea musciformis from the East and West Coasts of Florida, USA I. Growth and chemistry. Mar. Biol. 1980, 59, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öğretmen, Ö.Y.; Kaya, Y. Seasonal changes in the yield and gel properties of agar extracted from Gelidium latifolium (Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 3091–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeliani, Z.Z.; Yousefzadi, M.; Pour, J.S.; Toiserkani, H. Growth, phytochemicals, and optimal timing of planting Gracilariopsis persica: An economic red seaweed. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollando, J.A.; Mwakumanya, M.A.; Nyonje, B.M. The viability of red alga (Gracilaria salicornia) seaweed farming for commercial extraction of agar at kibuyuni in kwale county South Coast Kenya. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2019, 7, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Afonso, C.; Correia, A.P.; Freitas, M.V.; Baptista, T.; Neves, M.; Mouga, T. Seasonal Changes in the Nutritional Composition of Agarophyton vermiculophyllum (Rhodophyta, Gracilariales) from the Center of Portugal. Foods 2021, 10, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qari, R.; Haider, S. Biochemical Analysis, Yield of Agar and its Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Marine Red Seaweeds of Hypnea musciformis (Wulfen) J. V. Lamouroux, Hypnea pannosa J. Agardh, Hypnea valentiae (Turner) Montagne from Karachi Coast. Acta Sci. Microbiol. 2020, 3, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, B.; Aouini, R.; Akrout, H. Gracilaria bursa-pastoris of Bizerte lagoon (north of Tunisia): A spatio-temporal study of some hydro biological parameters, agar yield and quality. Item Type J. Contrib. 2017, 44, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Chirapart, A.; Praiboon, J. Comparison of the photosynthetic efficiency, agar yield, and properties of Gracilaria salicornia (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta) with and without adelphoparasite. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fethi, M.; Ghedifa, A. Ben Optimum ranges of combined abiotic factor for Gracilaria gracilis aquaculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 3025–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeragurunathan, V.; Prasad, K.; Malar Vizhi, J.; Singh, N.; Meena, R.; Mantri, V.A. Gracilaria debilis cultivation, agar characterization and economics: Bringing new species in the ambit of commercial farming in India. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 2609–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, Z.; Mu, H.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X. Impact of alkali pretreatment on yield, physico-chemical and gelling properties of high quality agar from Gracilaria tenuistipitata. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, M.; Filizadeh, Y.; Rafiee, F.; Daghooghi, B.; Arganji, G.-R.; Rameshi, H.; Rajabi, I. The Effect of Some Environmental Factors on Biomass and Agar Content of Gracilaria corticata (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta). J. Phycol. Res. 2017, 1, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Véliz, K.; Chandía, N.; Karsten, U.; Lara, C.; Thiel, M. Geographic variation in biochemical and physiological traits of the red seaweeds Chondracanthus chamissoi and Gelidium lingulatum from the south east Pacific coast. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gao, K. Growth, pigments, UV-absorbing compounds and agar yield of the economic red seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis (Rhodophyta) grown at different depths in the coastal waters of the South China Sea. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ben Said, R.; Mensi, F.; Majdoub, H.; Ben Said, A.; Ben Said, B.; Bouraoui, A. Effects of depth and initial fragment weights of Gracilaria gracilis on the growth, agar yield, quality, and biochemical composition. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2499–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunsom, C.; Prathep, A. Effects of salinity, light intensity and sediment on growth, pigments, agar production and reproduction in Gracilaria tenuistipitata from Songkhla Lagoon in Thailand. Phycol. Res. 2012, 60, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirapart, A.; Munkit, J.; Lewmanomont, K. Changes in yield and quality of agar from the agarophytes, Gracilaria fisheri and G. tenuistipitata var. liui cultivated in earthen ponds. Kasetsart J.-Nat. Sci. 2006, 40, 529–540. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, Y.; Yadav, A.; Kumar, M.A.; Kavale, M.G.; Prasad, K.; Mantri, V.A. ‘Proof of concept’ of how tube-net diameter affects growth and agar content in industrially important farmed red seaweed Gracilaria dura. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wen, J.; Chen, W.; Du, H. Physiological effects of nitrogen deficiency and recovery on the macroalga Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis (Rhodophyta). J. Phycol. 2019, 55, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirapart, A.; Praiboon, J.; Boonprab, K.; Puangsombat, P. Epiphytism differences in the commercial species of Gracilaria, G. fisheri, G. tenuistipitata, and G. salicornia, from Thailand. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 3413–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Namasivayam, P.; Abdullah, J.O.; Ho, C.L. Transcriptome profiling of sulfate deprivation responses in two agarophytes Gracilaria changii and Gracilaria salicornia (Rhodophyta). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.K.; Lim, Y.Y.; Ho, C.L. pH affects growth, physiology and agar properties of agarophyte Gracilaria changii (Rhodophyta) under low light intensity from Morib, Malaysia. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 30, 100738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.C.; Saito, R.M.; Santos Neto, J.F.; Garófalo, G.M.C. Temporal and spatial variation in agar from a population of Pterocladia capillacea (Gelidiales, Rhodophyta) from Brazil. Hydrobiologia 1996, 326, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; Robledo, D.; Armisén, R.; García-Reina, G. Seasonal changes in agar characteristics of two populations of Pterocladia capillacea in Gran Canaria, Spain. J. Appl. Phycol. 1996, 8, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inácio, A.C.; Morais, T.; Cotas, J.; Pereira, L.; Bahcevandziev, K. Cultivation of Gracilaria gracilis in an Aquaculture System at Mondego River (Portugal) Estuary Adjacent Terrain. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Water Energy Food and Sustainability (ICoWEFS 2021), Leiria, Portugal, 10–12 May 2021; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, M.; Fortunato, D.; Cotas, J.; Pacheco, D.; Morais, T.; Pereira, L. Agar content of estuarine seaweed Gracilaria using different cultivation methods. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, R.D.; Sousa, A.M.M.; Gonçalves, M.P.; Nilsson, M.; Hilliou, L. Production and properties of agar from the invasive marine alga, Gracilaria vermiculophylla (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2010, 22, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, K.H.M.M.; Guaratini, T.; Barros, M.P.; Falcão, V.R.; Tonon, A.P.; Lopes, N.P.; Campos, S.; Torres, M.A.; Souza, A.O.; Colepicolo, P.; et al. Metabolites from algae with economical impact. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 146, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupert, R.; Rodrigues, K.F.; Thien, V.Y.; Yong, W.T.L. Carrageenan From Kappaphycus alvarezii (Rhodophyta, Solieriaceae): Metabolism, Structure, Production, and Application. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 859635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, J.; Anandhakumar, R.; Shanmugam, M. Effect of alkaline treatment on the sulfate content and quality of semi-refined carrageenan prepared from seaweed Kappaphycus alvarezii Doty (Doty) farmed in Indian waters. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, P.R. The Encyclopedia of Separation Science. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2004, 23, III–IV. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Rai, D.K.; Hossain, M. Analytical techniques for bioactives from seaweed. In Seaweed Sustainability; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 271–287. [Google Scholar]
- Nishino, T.; Yokoyama, G.; Dobashi, K.; Fujihara, M.; Nagumo, T. Isolation, purification, and characterization of fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from the brown seaweed Ecklonia kurome and their blood-anticoagulant activities. Carbohydr. Res. 1989, 186, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotas, J.; Leandro, A.; Pacheco, D.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.M.; Pereira, L. A comprehensive review of the nutraceutical and therapeutic applications of red seaweeds (Rhodophyta). Life 2020, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.J.; Wan Aida, W.M.; Maskat, M.Y.; Mamot, S.; Ropien, J.; Mazita Mohd, D. Isolation and antioxidant capacity of fucoidan from selected Malaysian seaweeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 42, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchman, D.; Sinha, S. Determination of Products of Lipid Oxidation by Infrared Spectroscopy. In Oxidative Stress Biomarkers and Antioxidant Protocols; Armstrong, D., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Cotas, J.; Figueirinha, A.; Pereira, L.; Batista, T. The effect of salinity on Fucus ceranoides (Ochrophyta, Phaeophyceae) in the Mondego River (Portugal). J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogolitsyn, K.; Parshina, A.; Druzhinina, A.; Ovchinnikov, D.; Krasikov, V.; Khviyuzov, S. Physicochemical characteristics of the active fractions of polyphenols from Arctic macrophytes. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 4277–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, P.; Cotas, J.; Pacheco, D.; Figueirinha, A.; da Silva, G.J.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Seaweed as Food: How to Guarantee Their Quality? In Sustainable Global Resources of Seaweeds Volume 2; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 309–321. [Google Scholar]
- Vandanjon, L.; Burlot, A.-S.; Zamanileha, E.F.; Douzenel, P.; Ravelonandro, P.H.; Bourgougnon, N.; Bedoux, G. The Use of FTIR Spectroscopy as a Tool for the Seasonal Variation Analysis and for the Quality Control of Polysaccharides from Seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ordóñez, E.; Rupérez, P. FTIR-ATR spectroscopy as a tool for polysaccharide identification in edible brown and red seaweeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Yin, J.-Y.; Nie, S.-P.; Xie, M.-Y. Applications of infrared spectroscopy in polysaccharide structural analysis: Progress, challenge and perspective. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, A.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Di Domenico, A.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Lambrée, C.; Leblanc, J.C.; et al. Re-evaluation of agar (E 406) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashedy, S.H.; Abd El Hafez, M.S.M.; Dar, M.A.; Cotas, J.; Pereira, L. Evaluation and Characterization of Alginate Extracted from Brown Seaweed Collected in the Red Sea. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, M.; Aggett, P.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Filipič, M.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Kuhnle, G.G.; et al. Re-evaluation of carrageenan (E 407) and processed Eucheuma seaweed (E 407a) as food additives. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gericke, M.; Amaral, A.J.R.; Budtova, T.; De Wever, P.; Groth, T.; Heinze, T.; Höfte, H.; Huber, A.; Ikkala, O.; Kapuśniak, J.; et al. The European Polysaccharide Network of Excellence (EPNOE) research roadmap 2040: Advanced strategies for exploiting the vast potential of polysaccharides as renewable bioresources. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 326, 121633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, M. Novel Extraction Methods, Yield, Structural and Rheological Properties of Carrageenan from Novel Kappaphycus alvarezii Strains from the Philippines. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cotas, J.; Tavares, J.O.; Silva, R.; Pereira, L. Seaweed as a Safe Nutraceutical Food: How to Increase Human Welfare? Nutraceuticals 2024, 4, 323–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K. Algal extracts: Technology and advances. Eng. Life Sci. 2014, 14, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K. Algae as production systems of bioactive compounds. Eng. Life Sci. 2015, 15, 160–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Duan, G.; Yang, H. Recent advances in exploiting carrageenans as a versatile functional material for promising biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuge, K.; Okabe, M.; Yoshimura, T.; Sumi, T.; Tachibana, H.; Yamada, K. Dietary Effects of Porphyran from Porphyra yezoensis on Growth and Lipid Metabolism of Sprague-Dawley Rats. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2004, 10, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Gao, X.; Cheng, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. The Structural Characteristics of Seaweed Polysaccharides and Their Application in Gel Drug Delivery Systems. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangha, J.S.; Kandasamy, S.; Khan, W.; Bahia, N.S.; Singh, R.P.; Critchley, A.T.; Prithiviraj, B. λ-carrageenan suppresses tomato chlorotic dwarf viroid (TCDVd) replication and symptom expression in tomatoes. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2875–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomartire, S.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Algal Phycocolloids: Bioactivities and Pharmaceutical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Li, L.; Mao, S. Applications of Carrageenan in Advanced Drug Delivery. In Seaweed Polysaccharides; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 283–303. [Google Scholar]
- Zia, K.M.; Tabasum, S.; Nasif, M.; Sultan, N.; Aslam, N.; Noreen, A.; Zuber, M. A review on synthesis, properties and applications of natural polymer based carrageenan blends and composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 282–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandya, Y.; Bakshi, M.; Sharma, A.; Pandya, Y.H.; Pandya, H. Agar-agar extraction, structural properties and applications: A review. Pharma Innov. J. 2022, 6, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.R.V.; Alves, V.D.; Coelhoso, I.M. Polysaccharide-Based Membranes in Food Packaging Applications. Membranes 2016, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Shen, M.; Luo, Y.; Wu, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J. Advanced applications of chitosan-based hydrogels: From biosensors to intelligent food packaging system. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, L.; Mu, R.J.; Gong, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Pang, J.; Wu, C. Effects of konjac glucomannan on the structure, properties, and drug release characteristics of agarose hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzibra, A.; Aasfar, A.; El Arroussi, H.; Khouloud, M.; Dhiba, D.; Kadmiri, I.M.; Bamouh, A. Polysaccharides extracted from Moroccan seaweed: A promising source of tomato plant growth promoters. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2953–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; Rocha, C.P.; Araújo, G.S.; Figueirinha, A.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Bahcevandziev, K.; Pereira, L. Seaweeds’ carbohydrate polymers as plant growth promoters. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balina, K.; Romagnoli, F.; Blumberga, D. Seaweed biorefinery concept for sustainable use of marine resources. Energy Procedia 2017, 128, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardilhó, S.; Cotas, J.; Pereira, L.; Oliveira, M.B.; Dias, J.M. Marine macroalgae in a circular economy context: A comprehensive analysis focused on residual biomass. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 60, 107987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardilhó, S.; Cotas, J.; Pacheco, D.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Bahcevandziev, K.; Pereira, L.; Figueirinha, A.; Dias, J.M. Valorisation of marine macroalgae waste using a cascade biorefinery approach: Exploratory study. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 385, 135672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Industry | Polysaccharide | Main Applications | Specific Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Industry | Agar | - Food additive (E406, GRAS approved) | - Low-quality agar in food products |
| - Popular in jellies | - High-quality agar in limited food items | ||
| Carrageenan | - Food additive (E407, GRAS approved) | - Common use as a jellifying agent | |
| - Processed meat products stabilization | - Binds milk molecules, retains water | ||
| - Protective coating on fresh-cut packaged food | - Gas barrier, reduces respiration, slows discoloration, and maintains texture in packaged foods | ||
| Pharmaceutical | Agar | - Pharmaceutical-grade growth media | - Decreases blood glucose, prevents red blood cell aggregation- Acts as bulking agents in laxatives, suppositories, capsules, tablets, and anticoagulants |
| - Drug delivery systems | - Production and encapsulation of monoclonal antibodies, interferons, steroids, and alkaloids | ||
| - Functional foods with health benefits | - Decreases blood glucose, prevents red blood cell aggregation | ||
| - Medical analysis | - Highly purified agar (agarose) used in molecular biology (electrophoresis, immune diffusion, gel chromatography) | ||
| Carrageenan | - Pharmaceutical drugs and agents | - Tetracycline production (immobilizes bacteria for antibiotic production)- Produces D-aspartic acid for semi-synthetic antibiotics- Inhibits viruses like human papillomavirus, dengue, influenza A, and herpes virus | |
| - Functional foods with health benefits | - Cholesterol-lowering effects, immunomodulatory activity, and antioxidant activities | ||
| Cosmetic | Agar | - Structural ingredient | - Used in creams, hand lotions, liquid soap, deodorants, foundation, exfoliant, cleanser, shaving cream, face moisturizer/lotion, acne and anti-aging treatments |
| Carrageenan | - Structural ingredient | - Applications include toothpastes, hair wash products, lotions, medications, sun blocks, shaving creams, deodorant sticks, sprays, and foams | |
| Agriculture | Agar | - Structural ingredient | - Acts as moisture-holding hydrogel, reducing irrigation frequency, improving soil aeration, and limiting erosion- Soil conditioner, improves water retention, soil permeability, and plant performance |
| Carrageenan | - Functional ingredient | - Regulates plant metabolic processes, including purine and pyrimidine synthesis, nitrogen and sulphur absorption- Activates plant defense systems, provides resistance to abiotic and biotic stressors | |
| - Regulates physiological and biochemical processes in plants (e.g., cell division, photosynthesis) |
| Factor | Effect on Carrageenan | Effect on Agar |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (high concentrations) | Inverse relationship with carrageenan content (Neish effect) | Inverse relationship with agar content; higher nitrogen availability may increase gel strength |
| Phosphorus | Probably inverse relationship with carrageenan content | Phosphate may increase gel strength and possibly yield |
| Temperature | Detrimental effects above thermal tolerance on quantity and quality | Generally positive relation with agar content up |
| Salinity | No clear pattern | Positive effect of both high and low salinities, although not unanimous |
| Depth | No significant effect on content | Effect on agar remains unresolved |
| Water Motion (Wave Action) | Possible influence on carrageenan content | Inconclusive effects on agar content |
| Carbon Sources | may enhance carrageenan content under nitrogen enrichment | Not specifically mentioned |
| pH | Not specifically mentioned | Not specifically mentioned |
| Sulphate Deprivation | Not specifically mentioned | May reduce agar content |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendes, M.; Cotas, J.; Pacheco, D.; Ihle, K.; Hillinger, A.; Cascais, M.; Marques, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Red Seaweed (Rhodophyta) Phycocolloids: A Road from the Species to the Industry Application. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22100432
Mendes M, Cotas J, Pacheco D, Ihle K, Hillinger A, Cascais M, Marques JC, Pereira L, Gonçalves AMM. Red Seaweed (Rhodophyta) Phycocolloids: A Road from the Species to the Industry Application. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(10):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22100432
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendes, Madalena, João Cotas, Diana Pacheco, Kay Ihle, Alina Hillinger, Miguel Cascais, João Carlos Marques, Leonel Pereira, and Ana M. M. Gonçalves. 2024. "Red Seaweed (Rhodophyta) Phycocolloids: A Road from the Species to the Industry Application" Marine Drugs 22, no. 10: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22100432
APA StyleMendes, M., Cotas, J., Pacheco, D., Ihle, K., Hillinger, A., Cascais, M., Marques, J. C., Pereira, L., & Gonçalves, A. M. M. (2024). Red Seaweed (Rhodophyta) Phycocolloids: A Road from the Species to the Industry Application. Marine Drugs, 22(10), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22100432










