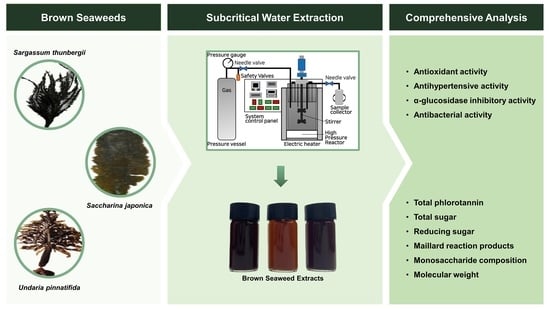
Exploring Bioactive Compounds in Brown Seaweeds Using Subcritical Water: A Comprehensive Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Proximate Composition
2.2. Extraction Efficiency
2.3. Color and Maillard Reaction Products (MRPs)
2.4. Total Phlorotannin Content (TPC), Total Sugar Content (TSC), and Reducing Sugar Content (RSC)
2.5. Monosaccharide Composition and Molecular Weight Analysis
2.6. Antioxidant Activity
2.7. Antihypertensive Activity
2.8. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity
| Trait | TPC | TSC | RSC | ABTS+ | DPPH | FRAP | α-Glucosidase Inhibitory |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC | 1 | 0.659 ns | 0.888 ** | 0.841 ** | 0.980 ** | 0.994 ** | 0.473 ns |
| TSC | - | 1 | 0.897 ** | 0.238 ns | 0.524 ns | 0.623 ns | 0.974 ** |
| RSC | - | 1 | 0.560 ns | 0.810 ** | 0.878 ** | 0.788 * | |
| ABTS+ | 1 | 0.912 ** | 0.854 ** | 0.017 ns | |||
| DPPH | 1 | 0.983 ** | 0.321 ns | ||||
| FRAP | 1 | 0.436 ns | |||||
| α-glucosidase inhibitory | 1 |
2.9. Antibacterial Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Proximate Composition Analysis
3.3. Subcritical Water Extraction
3.4. Color
3.5. MRP
3.6. TPC
3.7. Total Sugar and RSC
3.8. Monosaccharide Analysis
3.9. Molecular Weight Analysis
3.10. Biological Activity
3.10.1. Antioxidant Activity (DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP Assay)
3.10.2. Antihypertensive Activity
3.10.3. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carina, D.; Sharma, S.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaiswal, S. Seaweeds polysaccharides in active food packaging: A review of recent progress. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, M.; Allahgholi, L.; Sardari, R.R.; Hreggviðsson, G.O.; Nordberg Karlsson, E. Extraction and modification of macroalgal polysaccharides for current and next-generation applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, M.M.; Patel, I.C. A review on phytoconstituents of marine brown algae. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, N.C.; Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.; Cardoso, S.M. Brown macroalgae as valuable food ingredients. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pádua, D.; Rocha, E.; Gargiulo, D.; Ramos, A.A. Bioactive compounds from brown seaweeds: Phloroglucinol, fucoxanthin and fucoidan as promising therapeutic agents against breast cancer. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 14, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, S.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Marine bioactives as functional food ingredients: Potential to reduce the incidence of chronic diseases. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1056–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Han, J.M.; Surendhiran, D.; Chun, B.S. Physicochemical and biofunctional properties of Sargassum thunbergii extracts obtained from subcritical water extraction and conventional solvent extraction. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2022, 182, 105535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Hyun, J.; Wang, K.; Fu, X.; Xu, J.; Gao, X.; Park, Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Antioxidant and anti-photoaging effects of a fucoidan isolated from Turbinaria ornata. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Selvaraj, B.; Lee, J.W. Anticancer effects of seaweed-derived bioactive compounds. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworowska, A.; Murtaza, A. Seaweed Derived Lipids Are a Potential Anti-Inflammatory Agent: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Nassef, M.; Bases, E.; Shafay, S.E.; El-Shenody, R. Antitumor immunity and therapeutic properties of marine seaweeds-derived extracts in the treatment of cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Singh, V.; Chauhan, K. Antidiabetic potential of seaweed and their bioactive compounds: A review of developments in last decade. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomartire, S.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. An Overview to the Health Benefits of Seaweeds Consumption. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermund, D.B.; Liu, W.; Holdt, S.L.; Jacobsen, C.; Getachew, A.T. Extraction of bioactives from brown seaweed using sub and supercritical fluids: Influence of the extract on the storage stability of fish oil enrich mayonnaise. Front. Food. Sci. Technol. 2023, 2, 1082490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez-Fernández, N.; Domínguez, H.; Torres, M.D. Functional Features of Alginates Recovered from Himanthalia elongata Using Subcritical Water Extraction. Molecules 2021, 26, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Puyana, M.; Herrero, M.; Mendiola, J.A.; Ibáñez, E. Subcritical water extraction of bioactive components from algae. In Functional Ingredients from Algae for Foods and Nutraceuticals; Domínguez, H., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 534–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoloi, A.; Goosen, N.J. A greener alternative using subcritical water extraction to valorize the brown macroalgae Ecklonia maxima for bioactive compounds. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 2307–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, N.M.; Putra, N.R.; Jamaludin, R.; Norodin, N.S.M.; Sarkawi, N.S.; Hamzah, M.H.S.; Nasir, H.M.; Zaidel, D.N.A.; Yunus, M.A.C.; Salleh, L.M. Valorisation of plant seed as natural bioactive compounds by various extraction methods: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Viñas, M.; Rodríguez-Seoane, P.; Flórez-Fernández, N.; Torres, M.D.; Díaz-Reinoso, B.; Moure, A.; Domínguez, H. Subcritical water for the extraction and hydrolysis of protein and other fractions in biorefineries from agro-food wastes and algae: A review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wen, C.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y.; Ma, H. Recent advances in the extraction of bioactive compounds with subcritical water: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Jeong, Y.R.; Chun, B.S. Physiological activities and bioactive compound from laver (Pyropia yezoensis) hydrolysates by using subcritical water hydrolysis. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 148, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentati, F.; Tounsi, L.; Djomdi, D.; Pierre, G.; Delattre, C.; Ursu, A.V.; Fendri, I.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P. Bioactive polysaccharides from seaweeds. Molecules 2020, 25, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus Raposo, M.F.; De Morais, R.M.S.C.; de Morais, A.M.M.B. Bioactivity and applications of sulphated polysaccharides from marine microalgae. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winarni, S.; Zainuri, M.; Endrawati, H.; Arifan, F.; Setyawan, A.; Wangi, A.P. Analysis proximate of sargassum seaweed sp. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1943, 012173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.S.N.; Zabot, G.L.; Mazutti, M.A.; Ugalde, G.A.; Rezzadori, K.; Tres, M.V. Optimization of subcritical water hydrolysis of pecan wastes biomasses in a semi-continuous mode. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryee, A.N.; Agyei, D.; Akanbi, T.O. Recovery and utilization of seaweed pigments in food processing. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 19, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, A.T.; Chun, B.S. Influence of pretreatment and modifiers on subcritical water liquefaction of spent coffee grounds: A green waste valorization approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3719–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravana, P.S.; Choi, J.H.; Park, Y.B.; Woo, H.C.; Chun, B.S. Evaluation of the chemical composition of brown seaweed (Saccharina japonica) hydrolysate by pressurized hot water extraction. Algal Res. 2016, 13, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajandouz, E.H.; Tchiakpe, L.S.; Ore, F.D.; Benajiba, A.; Puigserver, A. Effects of pH on caramelization and Maillard reaction kinetics in fructose-lysine model systems. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, A.; Baroutian, S. Subcritical water extraction for recovery of phenolics and fucoidan from New Zealand Wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) seaweed. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2022, 190, 105732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.V.; Saravana, P.S.; Woo, H.C.; Chun, B.S. Ionic liquid-assisted subcritical water enhances the extraction of phenolics from brown seaweed and its antioxidant activity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 196, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangestuti, R.; Haq, M.; Rahmadi, P.; Chun, B.S. Nutritional value and biofunctionalities of two edible green seaweeds (Ulva lactuca and Caulerpa racemosa) from Indonesia by subcritical water hydrolysis. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Algieri, F.; Gálvez, J. Potential role of seaweed polyphenols in cardiovascular-associated disorders. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravana, P.S.; Yin, S.; Choi, J.H.; Park, Y.B.; Woo, H.C.; Chun, B.S. Biological properties of fucoxanthin in oil re-covered from two brown seaweeds using supercritical CO2 extraction. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3422–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, G.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J.; Ewart, H.S. Chemical structures and bioactivities of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 196–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez-Fernández, N.; Torres, M.D.; González-Muñoz, M.J.; Domínguez, H. Recovery of bioactive and gelling extracts from edible brown seaweed Laminaria ochroleuca by non-isothermal autohydrolysis. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Cheng, J.; Ding, L.; Song, W.; Qi, F.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Subcritical water hydrolysis of rice straw for reducing sugar production with focus on degradation by-products and kinetic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 186, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.N.; Ray, C.A. Control of Maillard reactions in foods: Strategies and chemical mechanisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4537–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Vinosha, M.; Marudhupandi, T.; Rajasekar, P.; Prabhu, N.M. Isolation of fucoidan from Sargassum polycystum brown algae: Structural characterization, in vitro antioxidant and anticancer activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alboofetileh, M.; Rezaei, M.; Tabarsa, M.; You, S.; Mariatti, F.; Cravotto, G. Subcritical water extraction as an efficient technique to isolate biologically-active fucoidans from Nizamuddinia zanardinii. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Zakharov, D.V.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Terninko, I.I.; Generalova, Y.E.; Smekhova, I.E.; Shikov, A.N. The Biochemical composition and antioxidant properties of Fucus vesiculosus from the Arctic region. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumashi, A.; Ushakova, N.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E.; D’Incecco, A.; Piccoli, A.; Totani, L.; Tirani, N.; Morozevich, G.E.; Berman, A.E.; Bilan, M.I.; et al. A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borazjani, N.J.; Tabarsa, M.; You, S.; Rezaei, M. Purification, molecular properties, structural characterization, and immunomodulatory activities of water soluble polysaccharides from Sargassum angustifolium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.C.; Park, J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, M.H.; Nam, S.Y.; Chun, B.S. Influences of Molecular Weights on Physicochemical and Biological Properties of Collagen-Alginate Scaffolds. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, W.; Ban, C.; Park, G.; Yu, T.K.; Suh, J.Y.; Woo, H.; Kim, D.H. Catalytic hydrothermal conversion of macroalgae-derived alginate: Effect of pH on production of furfural and valuable organic acids under subcritical water conditions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 399, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Ho, T.C.; Razack, S.A.; Haq, M.; Roy, V.C.; Park, J.S.; Kang, H.W.; Chun, B.S. Oligochitosan recovered from shrimp shells through subcritical water hydrolysis: Molecular size reduction and biological activities. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2023, 196, 105868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, I.J.; Won, M.H.; You, S. Antioxidant properties of extract and fractions from Enteromorpha prolifera, a type of green seaweed. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindleysides, S.; Quek, S.Y.; Miller, M.R. Inhibition of fish oil oxidation and the radical scavenging activity of New Zealand seaweed extracts. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abirami, R.G.; Kowsalya, S. Quantification and correlation study on derived phenols and antioxidant activity of seaweeds from Gulf of Mannar. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants 2017, 23, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhane, M.B.; Haddar, A.; Ghazala, I.; Jeddou, K.B.; Helbert, C.B.; Ellouz-Chaabouni, S. Optimization of polysaccharides extraction from watermelon rinds: Structure, functional and biological activities. Food Chem. 2017, 216, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.L.; Liu, D.; Ma, C.B. Review on the angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor peptides from marine proteins. Appl. Biochem. 2013, 169, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, K.; Bid, H.K.; Konwar, R. Reinventing the ACE inhibitors: Some old and new implications of ACE inhibition. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Hou, X.; Li, X.; Qu, M.; Tong, C.; Li, W. Metabolomics analysis of alloxan-induced diabetes in mice using UPLC–Q-TOF-MS after Crassostrea gigas polysaccharide treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, Y.X.; Lim, P.E.; Maggs, C.A.; Phang, S.M.; Sharifuddin, Y.; Green, B.D. Anti-diabetic potential of selected Malaysian seaweeds. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 2137–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.F.; Lai, S.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, D.; Liu, B.; Ai, C.; Wan, X.Z.; Gao, L.Y.; Chen, X.H.; Zhao, C. Anti-diabetic effect of oligosaccharides from seaweed Sargassum confusum via JNK-IRS1/PI3K signalling pathways and regulation of gut microbiota. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndayishimiye, J.; Lim, D.J.; Chun, B.S. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of oils obtained from a mixture of citrus by-products using a modified supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Ind. Eng. 2018, 57, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouarab-Chibane, L.; Forquet, V.; Lantéri, P.; Clément, Y.; Léonard-Akkari, L.; Oulahal, N.; Degraeve, P.; Bordes, C. Antibacterial properties of polyphenols: Characterization and QSAR (Quantitative structure–activity relationship) models. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbensgaard, A.; Mordhorst, H.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Hansen, E.B. The role of outer membrane proteins and lipopolysaccharides for the sensitivity of Escherichia coli to antimicrobial peptides. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Jubeh, B.; Karaman, R. Resistance of gram-negative bacteria to current antibacterial agents and approaches to resolve it. Molecules 2020, 25, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, E.M.; Oliveira, M.; Mondala, J.R.; Curtin, J.; Tiwari, B.K.; Garcia-Vaquero, M. Antimicrobials from seaweeds for food applications. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, R.; Yu, S.; Zhao, W. A novel α-glucosidase inhibitor polysaccharide from Sargassum fusiforme. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022, 57, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Extraction Efficiency (%) | Color | MRPs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | 294 nm | 420 nm | 294/420 | ||
| S. thunbergii | 68.40 ± 0.44 b | 32.23 ± 0.26 ab | 1.63 ± 0.10 b | 0.60 ± 0.18 b | 2.851 ± 0.017 b | 0.306 ± 0.001 ab | 9.328 ± 0.029 b |
| U. pinnatifida | 81.88 ± 1.35 a | 34.42 ± 0.89 a | 4.53 ± 0.38 a | 2.92 ± 0.33 a | 2.163 ± 0.028 c | 0.188 ± 0.003 c | 11.506 ± 0.155 a |
| S. japonica | 69.02 ± 0.92 b | 30.33 ± 2.34 b | 1.63 ± 0.23 b | 0.48 ± 0.22 b | 2.980 ± 0.029 a | 0.305 ± 0.008 ab | 9.772 ± 0.156 b |
| Species | Chemical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Phlorotannin (mg PGE/g of Dry Sample) | Total Sugar (mg glucose/g of Dry Sample) | Reducing Sugar (mg glucose/g of Dry Sample) | |
| S. thunbergii | 38.82 ± 0.17 a | 116.66 ± 0.19 a | 53.27 ± 1.57 a |
| U. pinnatifida | 31.32 ± 0.50 b | 23.88 ± 0.42 c | 39.03 ± 0.52 c |
| S. japonica | 37.94 ± 0.30 a | 33.27 ± 0.51 b | 46.00 ± 1.82 b |
| Species | Monosaccharides Composition (%) | Molecular Weight (Da) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fucose | Galactose | Glucose | Xylose | Mannose | Mn | Mw | PI | |
| S. thunbergii | 36.71 | 21.49 | 22.96 | 11.37 | 7.47 | 498 | 1514 | 3.04 |
| U. pinnatifida | 19.55 | 48.84 | 17.99 | 4.02 | 9.61 | 444 | 1145 | 2.58 |
| S. japonica | 29.24 | 46.64 | 14.39 | 4.99 | 4.73 | 331 | 982 | 2.97 |
| Species | Antioxidant Activities | Antihypertensive Activity (%) | α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABTS+ Radical Scavenging (mg TE/g of Dry Sample) | DPPH Radical Scavenging (mg TE/g of Dry Sample) | FRAP Assays (mg TE/g of Dry Sample) | |||
| S. thunbergii | 88.62 ± 2.35 b | 45.56 ± 0.23 a | 34.47 ± 0.49 a | 56.55 ± 0.26 c | 68.05 ± 1.15 b |
| U. pinnatifida | 79.13 ± 1.78 c | 35.29 ± 0.24 b | 27.02 ± 0.56 b | 58.71 ± 0.10 b | 38.52 ± 0.80 c |
| S. japonica | 124.77 ± 2.47 a | 46.35 ± 0.01 a | 33.95 ± 0.51 a | 59.77 ± 0.14 b | 34.74 ± 1.49 d |
| Reference material | - | 99.60 ± 0.28 a | 99.28 ± 0.26 a | ||
| Conditions (mg/mL) | Gram-Positive | Gram-Negative | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. cereus | S. aureus | E. coli | S. enterica | ||
| Inhibition Zone (mm) | |||||
| S. thunbergii | 10 | - | 13 | - | - |
| 20 | 14 | 17 | 11 | - | |
| 30 | 15 | 18 | 13 | - | |
| 40 | 17 | 19 | 14 | 12 | |
| 50 | 18 | 22 | 14 | 14 | |
| U. pinnatifida | 10 | - | - | - | - |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | |
| 30 | - | 11 | - | - | |
| 40 | 11 | 14 | - | - | |
| 50 | 13 | 15 | 11 | - | |
| S. japonica | 10 | - | 12 | - | - |
| 20 | - | 15 | - | - | |
| 30 | - | 16 | - | - | |
| 40 | 12 | 17 | - | 13 | |
| 50 | 14 | 18 | - | 14 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.-S.; Han, J.-M.; Shin, Y.-N.; Park, Y.-S.; Shin, Y.-R.; Park, S.-W.; Roy, V.C.; Lee, H.-J.; Kumagai, Y.; Kishimura, H.; et al. Exploring Bioactive Compounds in Brown Seaweeds Using Subcritical Water: A Comprehensive Analysis. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060328
Park J-S, Han J-M, Shin Y-N, Park Y-S, Shin Y-R, Park S-W, Roy VC, Lee H-J, Kumagai Y, Kishimura H, et al. Exploring Bioactive Compounds in Brown Seaweeds Using Subcritical Water: A Comprehensive Analysis. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(6):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060328
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jin-Seok, Ji-Min Han, Yu-Na Shin, Ye-Seul Park, Ye-Ryeon Shin, Sin-Won Park, Vikash Chandra Roy, Hee-Jeong Lee, Yuya Kumagai, Hideki Kishimura, and et al. 2023. "Exploring Bioactive Compounds in Brown Seaweeds Using Subcritical Water: A Comprehensive Analysis" Marine Drugs 21, no. 6: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060328
APA StylePark, J.-S., Han, J.-M., Shin, Y.-N., Park, Y.-S., Shin, Y.-R., Park, S.-W., Roy, V. C., Lee, H.-J., Kumagai, Y., Kishimura, H., & Chun, B.-S. (2023). Exploring Bioactive Compounds in Brown Seaweeds Using Subcritical Water: A Comprehensive Analysis. Marine Drugs, 21(6), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060328