Heteronemin and Tetrac Induce Anti-Proliferation by Blocking EGFR-Mediated Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
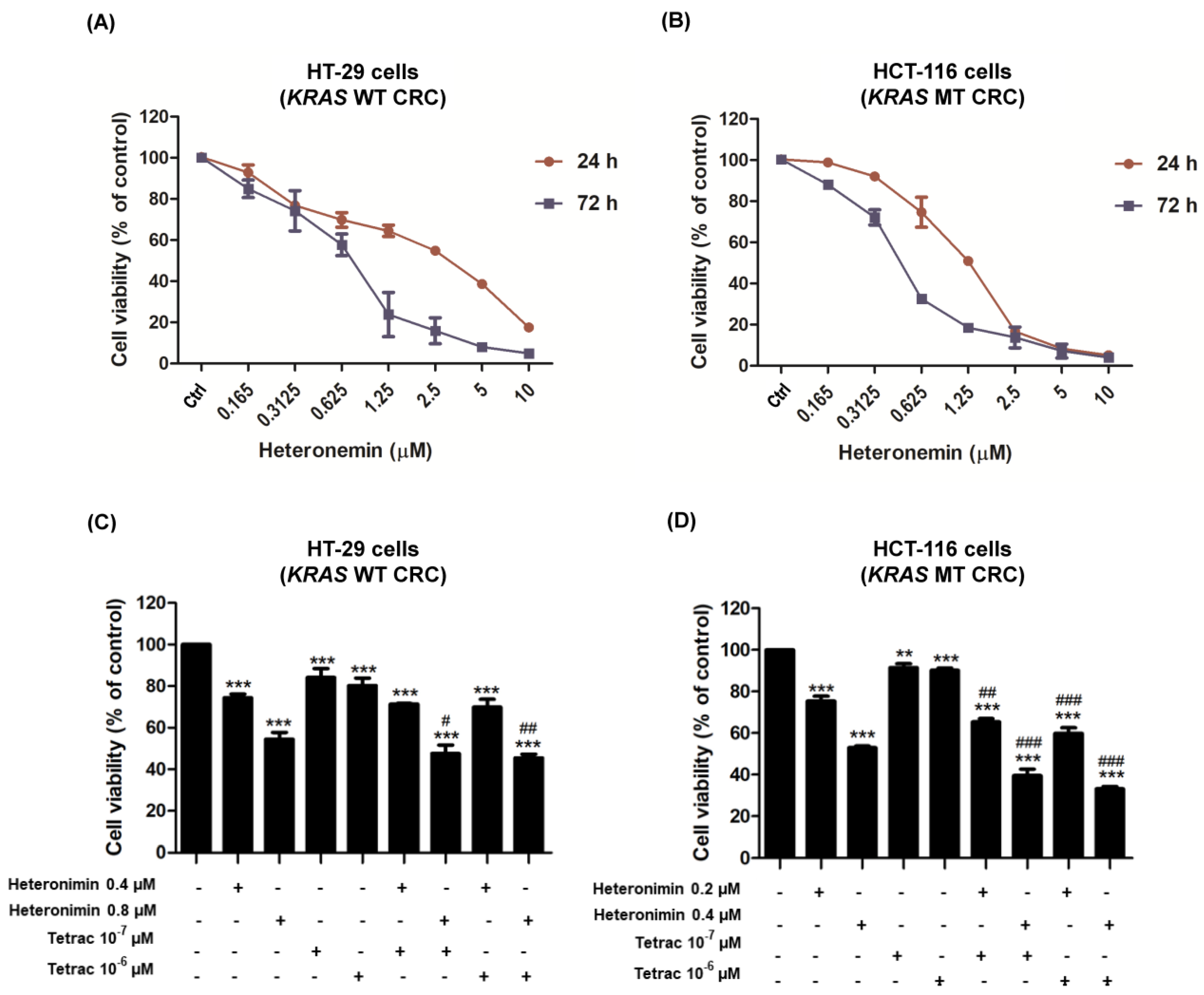
2.1. The Combined Treatment of Heteronemin and Tetrac Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Human CRC Cells with Different KRAS Statuses
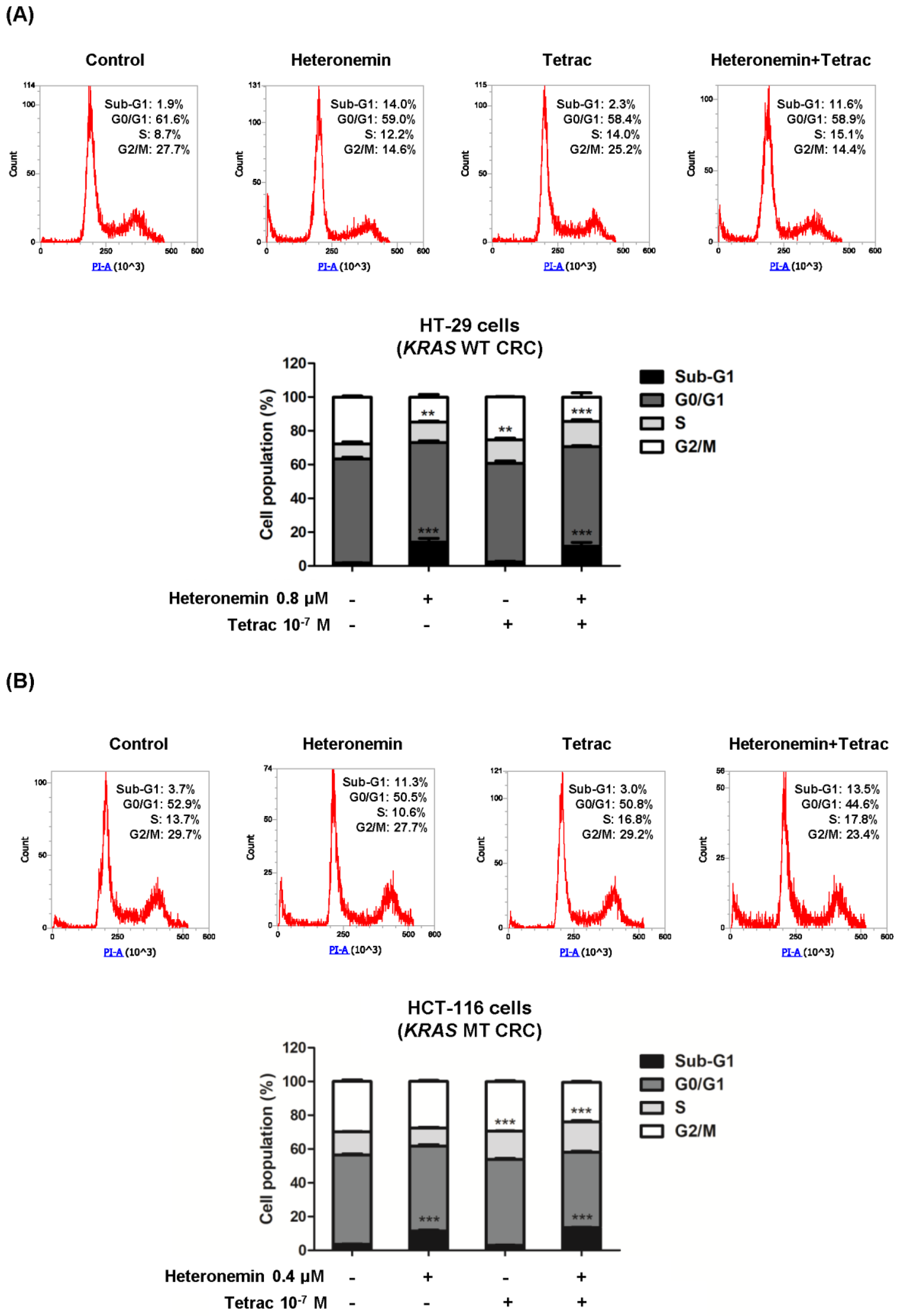
2.2. The Combination of Heteronemin and Tetrac Alters Cell Cycle Arrest at the Sub-G1 and S Phases in Human CRC Cells with Different KRAS Statuses
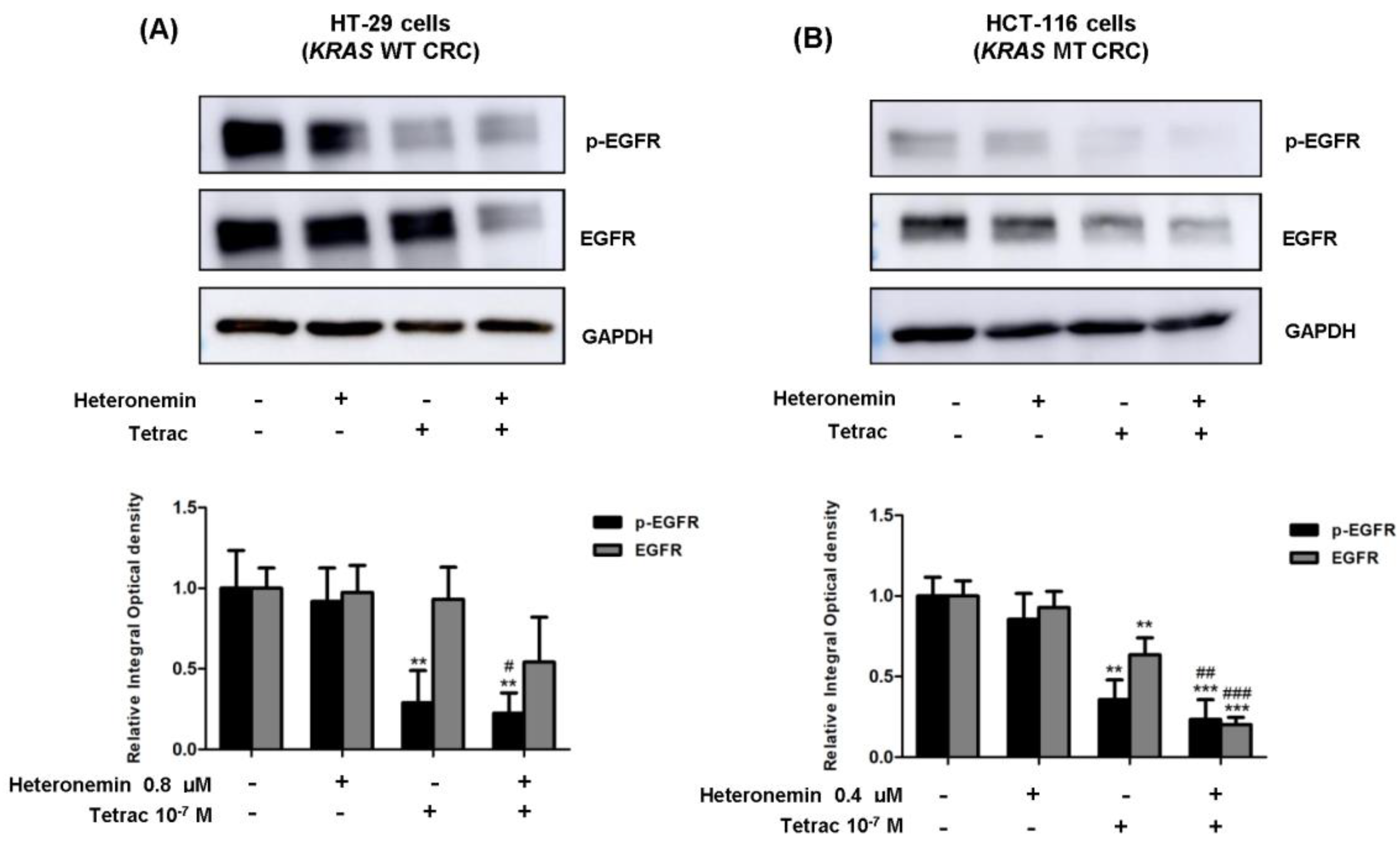
2.3. The Combined Treatment of Heteronemin and Tetrac Suppresses the Phosphorylation of EGFR in Human CRC Cells with Different KRAS Statuses
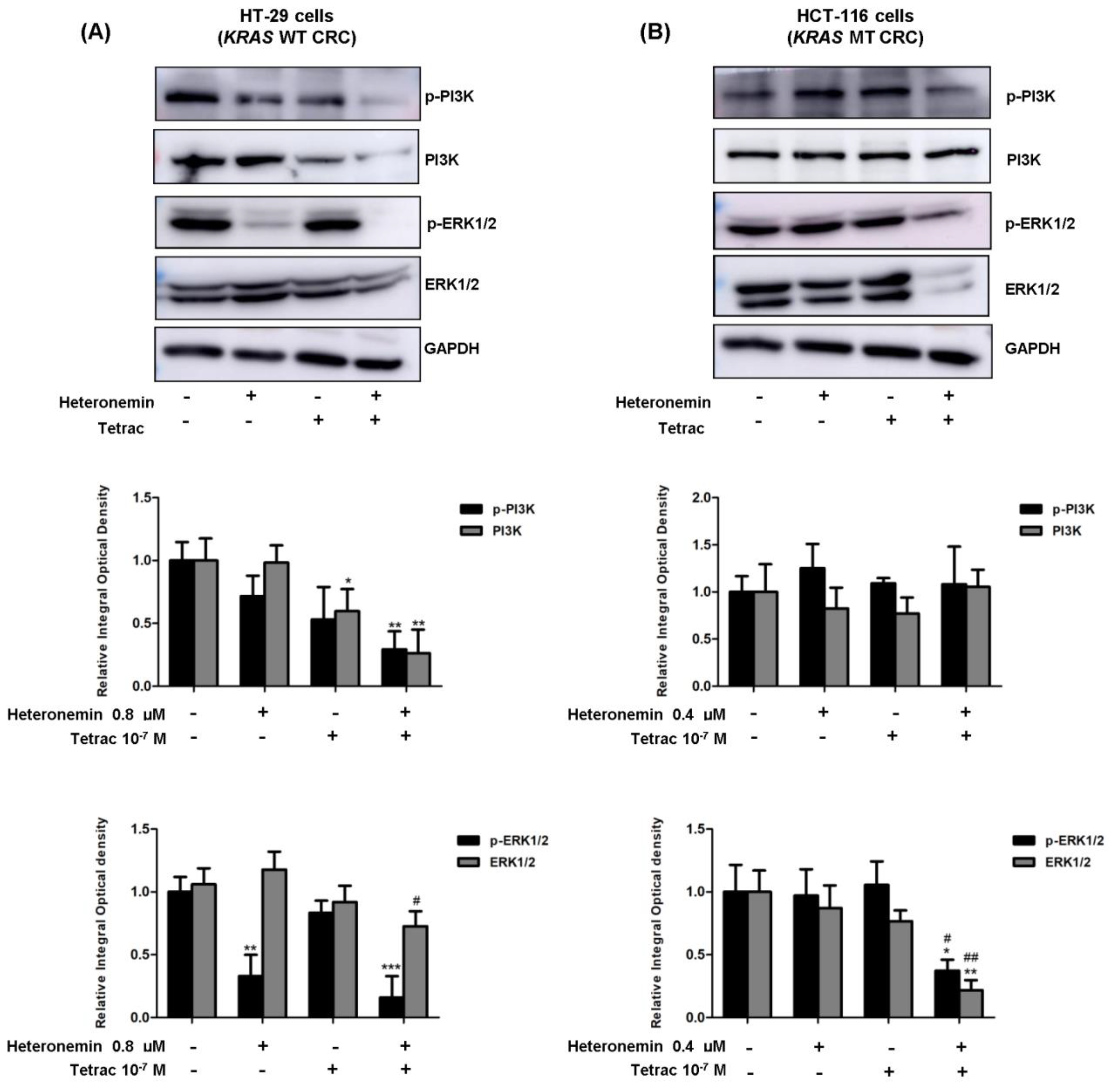
2.4. The Combined Treatment of Heteronemin and Tetrac Downregulates ERK1/2 Phosphorylation and ERK1/2 Protein Levels in Human CRC Cells with Different KRAS Statuses
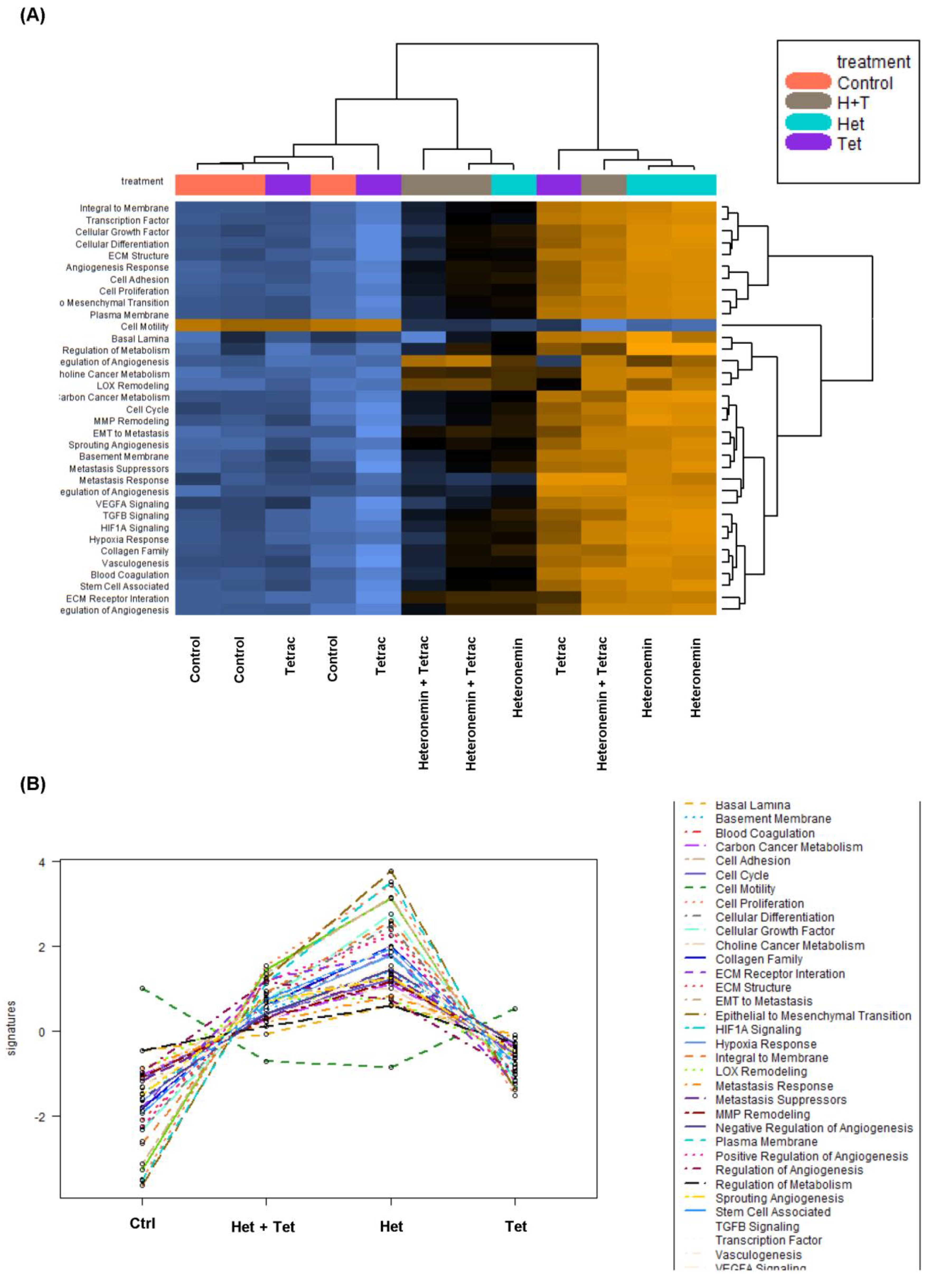
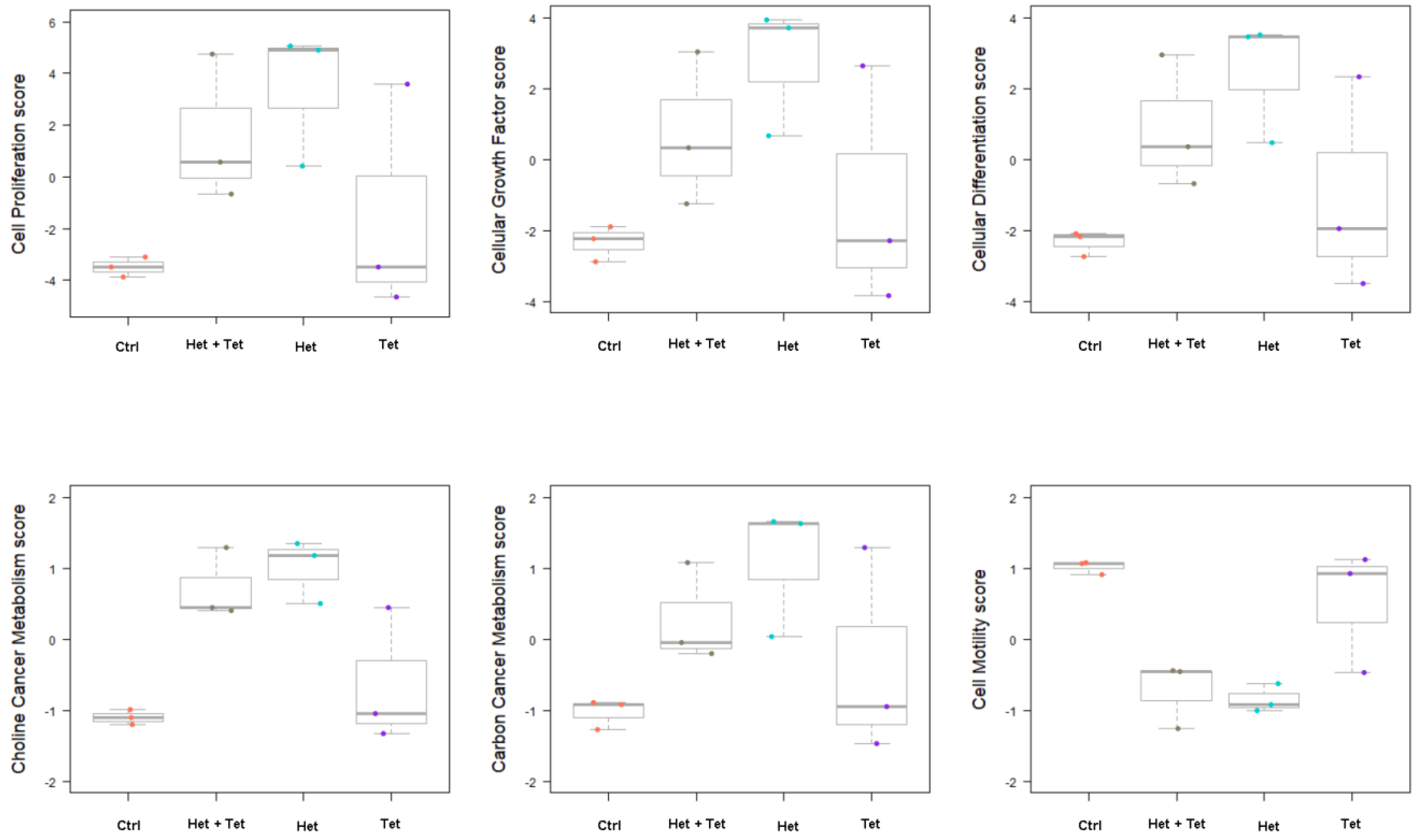
2.5. Heteronemin, Tetrac, and Their Combination Regulate Gene Expression in KRAS Mutant Cells
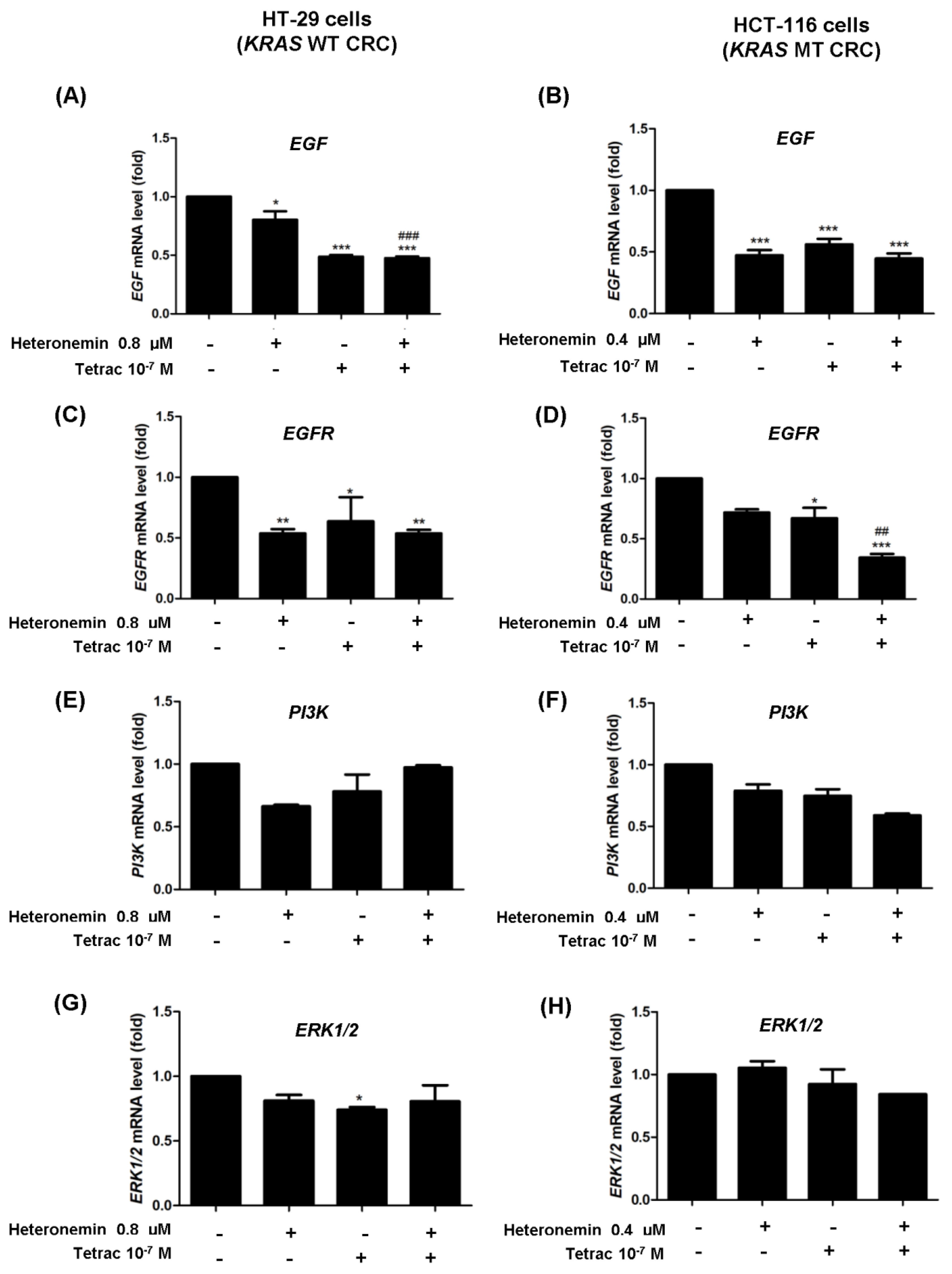
2.6. The Combined Treatment of Heteronemin and Tetrac Downregulated EGF and EGFR mRNA Expressions in Human CRC Cells with Different KRAS Statuses
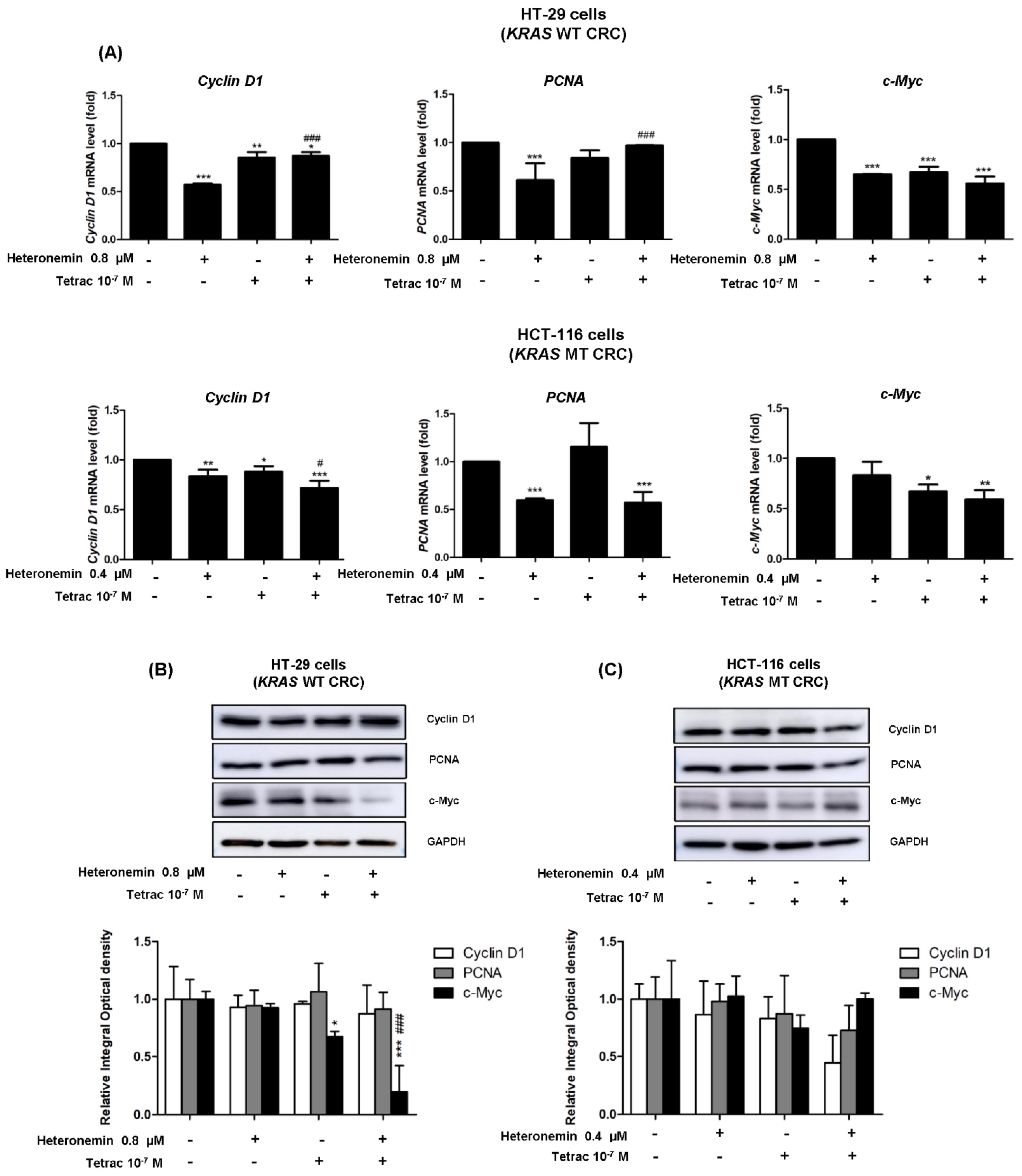
2.7. The Combination of Heteronemin and Tetrac Shows Different Regulations of Cell Cycle Regulators in Human CRC Cells with Different KRAS Statuses
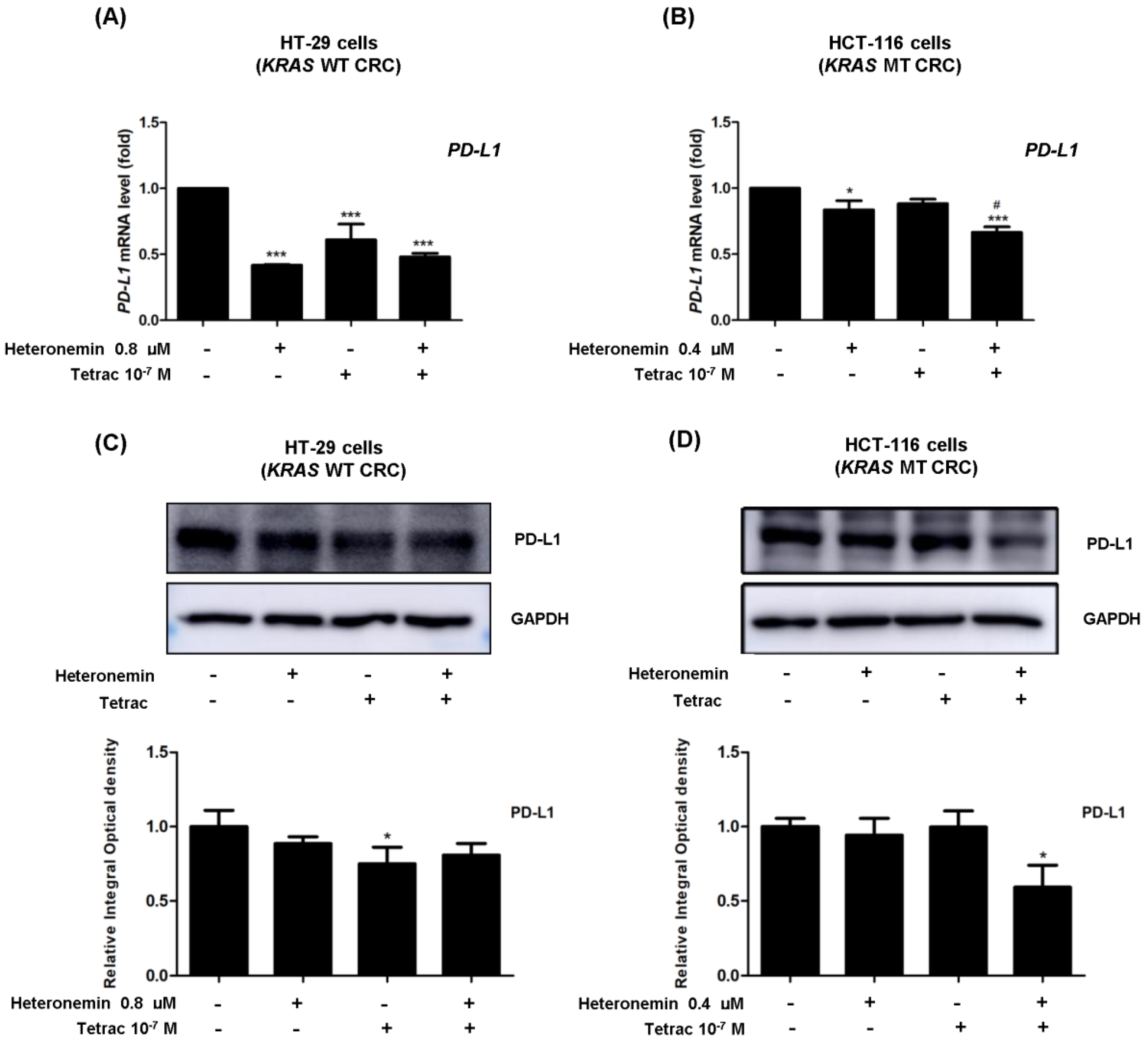
2.8. The Combined Treatment of Heteronemin and Tetrac Suppresses the Expression of PD-L1 in Human CRC Cells with Different KRAS Statuses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. NanoString Gene Expression Analysis
4.7. Reverse-Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattiuzzi, C.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Lippi, G. Concise update on colorectal cancer epidemiology. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.E.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.; Hur, B.Y.; Kim, B.; Kim, D.Y.; Baek, J.Y.; Chang, H.J.; Park, S.C.; Oh, J.H.; et al. Magnetic resonance-based texture analysis differentiating kras mutation status in rectal cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. Off. J. Korean Cancer Assoc. 2020, 52, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jancík, S.; Drábek, J.; Radzioch, D.; Hajdúch, M. Clinical relevance of kras in human cancers. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 150960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabernero, J. The role of vegf and egfr inhibition: Implications for combining anti-vegf and anti-egfr agents. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2007, 5, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, R.B. Epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2003, 2, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, J.M.; Alberts, S.R. Alternate dosing of cetuximab for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Gastrointest. Cancer Res. GCR 2013, 6, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, G. Egfr may participate in immune evasion through regulation of b7-h5 expression in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3769–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapetis, C.S.; Khambata-Ford, S.; Jonker, D.J.; O’Callaghan, C.J.; Tu, D.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Simes, R.J.; Chalchal, H.; Shapiro, J.D.; Robitaille, S.; et al. K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Fang, W.; Zhan, J.; Hong, S.; Tang, Y.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Zhou, T.; Qin, T.; et al. Upregulation of PD-L1 by egfr activation mediates the immune escape in egfr-driven nsclc: Implication for optional immune targeted therapy for nsclc patients with egfr mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2015, 10, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.B.; Yao, H.; Li, C.S.; Liang, L.X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, J.Y.; Xu, J. Rise of PD-L1 expression during metastasis of colorectal cancer: Implications for immunotherapy. J. Dig. Dis. 2017, 18, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Y.; Sung, P.J.; Chang, Y.L.; Pan, S.L.; Teng, C.M. Heteronemin, a spongean sesterterpene, induces cell apoptosis and autophagy in human renal carcinoma cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 738241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, H.N.; Kim, Y.B.; Rimoldi, J.M.; Fronczek, F.R.; Ferreira, D.; Slattery, M. Scalarane sesterterpenoids: Semisynthesis and biological activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1492–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Lu, M.C.; El-Shazly, M.; Lai, K.H.; Wu, T.Y.; Hsu, Y.M.; Lee, Y.L.; Liu, Y.C. Breaking down leukemia walls: Heteronemin, a sesterterpene derivative, induces apoptosis in leukemia molt4 cells through oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and induction of talin expression. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.H.; Huang, T.Y.; Chang, W.J.; Pan, Y.S.; Chu, H.R.; Li, Z.L.; Unson, S.; Chin, Y.T.; Lin, C.Y.; Huang, H.M.; et al. Combined treatment of heteronemin and tetrac induces antiproliferation in oral cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.G.; Liu, Y.C.; Lee, Y.L.; El-Shazly, M.; Lai, K.H.; Shih, S.P.; Ke, S.C.; Hong, M.C.; Du, Y.C.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Heteronemin, a marine sesterterpenoid-type metabolite, induces apoptosis in prostate lncap cells via oxidative and er stress combined with the inhibition of topoisomerase ii and hsp90. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, M.H.; Huang, H.L.; Lin, Y.Y.; Tsui, K.H.; Chen, P.C.; Cheng, S.Y.; Chong, I.W.; Sung, P.J.; Tai, M.H.; Wen, Z.H.; et al. Ba6 induces apoptosis via stimulation of reactive oxygen species and inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation in human lung cancer cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 6342104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, M.; Retnakumari, A.P.; Anwar, S.; Anto, N.P.; Mittal, R.; Shah, S.; Pillai, K.S.; Balachandran, V.S.; Peter, V.; Thomas, R.; et al. Heteronemin, a marine natural product, sensitizes acute myeloid leukemia cells towards cytarabine chemotherapy by regulating farnesylation of ras. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 18115–18127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.Y.; Tey, S.L.; Ho, Y.; Chin, Y.T.; Wang, K.; Whang-Peng, J.; Shih, Y.J.; Chen, Y.R.; Yang, Y.N.; Chen, Y.C.; et al. Heteronemin induces anti-proliferation in cholangiocarcinoma cells via inhibiting tgf-β pathway. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.S.H.; Li, Z.L.; Huang, T.Y.; Su, K.W.; Lin, C.Y.; Huang, C.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Lu, M.C.; Huang, H.M.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Effect of estrogen on heteronemin-induced anti-proliferative effect in breast cancer cells with different estrogen receptor status. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 688607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, Y.F.; Yang, Y.S.H.; Huang, H.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Shih, Y.J.; Li, Z.L.; Whang-Peng, J.; Lin, H.Y.; Davis, P.J. The power of heteronemin in cancers. J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 29, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmohl, K.A.; Nelson, P.J.; Spitzweg, C. Tetrac as an anti-angiogenic agent in cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, R287–R304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, C.C.; Huang, T.Y.; Chu, H.R.; De Luca, R.; Candelotti, E.; Huang, C.H.; Yang, Y.S.H.; Incerpi, S.; Pedersen, J.Z.; Lin, C.Y.; et al. Heteronemin and tetrac derivatives suppress non-small cell lung cancer growth via erk1/2 inhibition. Food Chem. Toxicol. An Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2022, 161, 112850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebbaa, A.; Chu, F.; Davis, F.B.; Davis, P.J.; Mousa, S.A. Novel function of the thyroid hormone analog tetraiodothyroacetic acid: A cancer chemosensitizing and anti-cancer agent. Angiogenesis 2008, 11, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, Y.T.; He, Z.R.; Chen, C.L.; Chu, H.C.; Ho, Y.; Su, P.Y.; Yang, Y.S.H.; Wang, K.; Shih, Y.J.; Chen, Y.R.; et al. Tetrac and ndat induce anti-proliferation via integrin αvβ3 in colorectal cancers with different k-ras status. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, D.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Danielsen, S.A.; Eknæs, M.; Hektoen, M.; Lind, G.E.; Lothe, R.A. Epigenetic and genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nana, A.W.; Chin, Y.T.; Lin, C.Y.; Ho, Y.; Bennett, J.A.; Shih, Y.J.; Chen, Y.R.; Changou, C.A.; Pedersen, J.Z.; Incerpi, S.; et al. Tetrac downregulates β-catenin and hmga2 to promote the effect of resveratrol in colon cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troiani, T.; Napolitano, S.; Della Corte, C.M.; Martini, G.; Martinelli, E.; Morgillo, F.; Ciardiello, F. Therapeutic value of egfr inhibition in crc and nsclc: 15 years of clinical evidence. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, R.; Franklin, R.A.; McCubrey, J.A. Egf induces cell motility and multi-drug resistance gene expression in breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 2820–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choudhary, K.S.; Rohatgi, N.; Halldorsson, S.; Briem, E.; Gudjonsson, T.; Gudmundsson, S.; Rolfsson, O. Egfr signal-network reconstruction demonstrates metabolic crosstalk in emt. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patnaik, S.; George, S.P.; Pham, E.; Roy, S.; Singh, K.; Mariadason, J.M.; Khurana, S. By moonlighting in the nucleus, villin regulates epithelial plasticity. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, F.; Jin, W.; Yan, B.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Yang, W.; Du, W.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Y.; et al. Theabrownin inhibits cell cycle progression and tumor growth of lung carcinoma through c-myc-related mechanism. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. Pd-1/pd-l1 pathway: Current researches in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, E.; Ciardiello, D.; Martini, G.; Troiani, T.; Cardone, C.; Vitiello, P.P.; Normanno, N.; Rachiglio, A.M.; Maiello, E.; Latiano, T.; et al. Implementing anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (egfr) therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: Challenges and future perspectives. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2020, 31, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kittiwisut, S.; Rohena, C.C.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Mooberry, S.L.; Plubrukarn, A. Antiproliferative effects of 12-oxoheteronemin vs heteronemin. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, Z.; Aksoy, O.; Zheng, T.; Fan, Q.W.; Weiss, W.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor and egfrviii in glioblastoma: Signaling pathways and targeted therapies. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1561–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinskii, A.B.; Glinsky, G.V.; Lin, H.Y.; Tang, H.Y.; Sun, M.; Davis, F.B.; Luidens, M.K.; Mousa, S.A.; Hercbergs, A.H.; Davis, P.J. Modification of survival pathway gene expression in human breast cancer cells by tetraiodothyroacetic acid (tetrac). Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3562–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, W.T.; Bow, Y.D.; Fu, P.J.; Li, C.Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Chang, Y.H.; Teng, Y.N.; Li, R.N.; Lu, M.C.; Liu, Y.C.; et al. A marine terpenoid, heteronemin, induces both the apoptosis and ferroptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and involves the ros and mapk pathways. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 7689045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albitar, M.; Sudarsanam, S.; Ma, W.; Jiang, S.; Chen, W.; Funari, V.A.; Agersborg, S. Expression of PD-L1 in colorectal cancer that lack mutations in ras or tp53 genes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, e14500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, S.; Matrone, N.; Muddassir, A.L.; Martini, G.; Sorokin, A.; De Falco, V.; Giunta, E.F.; Ciardiello, D.; Martinelli, E.; Belli, V.; et al. Triple blockade of egfr, mek and PD-L1 has antitumor activity in colorectal cancer models with constitutive activation of mapk signaling and PD-L1 overexpression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2019, 38, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.Y.; Chin, Y.T.; Nana, A.W.; Shih, Y.J.; Lai, H.Y.; Tang, H.Y.; Leinung, M.; Mousa, S.A.; Davis, P.J. Actions of l-thyroxine and nano-diamino-tetrac (nanotetrac) on PD-L1 in cancer cells. Steroids 2016, 114, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.Y.; Chang, T.C.; Chin, Y.T.; Pan, Y.S.; Chang, W.J.; Liu, F.C.; Hastuti, E.D.; Chiu, S.J.; Wang, S.H.; Changou, C.A.; et al. Ndat targets pi3k-mediated PD-L1 upregulation to reduce proliferation in gefitinib-resistant colorectal cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berehu, H.M.; Khan, M.I.; Chakraborty, R.; Lavudi, K.; Penchalaneni, J.; Mohapatra, B.; Mishra, A.; Patnaik, S. Cytotoxic potential of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized from swertia chirayita leaf extract on colorectal cancer cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Het vs. Ctrl | Gene Name | Het vs. Ctrl | Gene Name | Tet vs. Ctrl | Gene Name | Het + Tet vs. Ctrl | Gene Name | Het + Tet vs. Ctrl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACVR1C | 2.48 | ADAM9 | −1.40 | AP1M2 | −1.15 | ADAM17 | 1.55 | AGGF1 | −1.20 |
| ACVRL1 | 1.81 | AKAP2 | −1.10 | DPYSL3 | −1.12 | ADM2 | 2.02 | AKT1 | −1.37 |
| ADAM17 | 1.32 | AKT1 | −1.45 | LAMA5 | −1.10 | ANGPTL2 | 1.56 | AP1M2 | −1.40 |
| ADM2 | 1.97 | AKT2 | −1.32 | MAPK3 | −1.23 | ANGPTL4 | 3.19 | ARAP2 | −1.58 |
| AMH | 1.71 | AP1M2 | −1.50 | OCLN | −1.13 | BTG1 | 1.63 | ATPIF1 | −1.34 |
| ANGPTL4 | 2.16 | ARAP2 | −1.57 | CCDC80 | 2.17 | BMP4 | −2.50 | ||
| ANPEP | 2.54 | ATPIF1 | −1.39 | CHRNA7 | 1.76 | BMP7 | −1.27 | ||
| ARHGDIB | 2.42 | BMP4 | −2.30 | CLDN7 | 1.31 | BMPR2 | −1.77 | ||
| CADM1 | 2.47 | BMP7 | −1.45 | CLU | 2.01 | CALD1 | −1.51 | ||
| CCDC80 | 2.61 | BMPR2 | −1.51 | COL7A1 | 2.10 | CAMK2D | −1.54 | ||
| CCL11 | 2.49 | CALD1 | −1.47 | CTSL | 1.91 | CAV1 | −1.91 | ||
| CD34 | 2.38 | CAMK2D | −1.59 | CXCL8 | 13.62 | CD2AP | −1.24 | ||
| CEACAM6 | 2.45 | CAV1 | −2.04 | CYB561 | 1.13 | CD44 | −1.19 | ||
| CHRNA7 | 1.70 | CD24 | −1.49 | F3 | 1.38 | CD46 | −1.45 | ||
| CKMT1A | 2.70 | CD2AP | −1.25 | FGF2 | 1.64 | CDC42 | −1.27 | ||
| CLDN3 | 1.32 | CD46 | −1.59 | FUT3 | 1.54 | CEP170 | −1.34 | ||
| CLU | 1.59 | CDC42 | −1.34 | GDF15 | 1.98 | CEP295 | −1.17 | ||
| COL1A1 | 2.15 | CDH1 | −1.36 | HAS1 | 1.37 | COL18A1 | −1.52 | ||
| COL5A2 | 1.89 | CDKN1A | −1.37 | HKDC1 | 3.16 | COL6A1 | −1.38 | ||
| COL7A1 | 2.17 | CEP295 | −1.36 | HMOX1 | 2.50 | COL6A2 | −1.08 | ||
| COMP | 2.41 | CREBBP | −1.21 | JUN | 4.77 | CREBBP | −1.25 | ||
| CSPG4 | 1.57 | CRIP2 | −1.39 | KRT7 | 1.78 | CRIP2 | −1.52 | ||
| CTSK | 1.65 | CTNNB1 | −1.46 | LAMA3 | 2.48 | CTNNB1 | −1.43 | ||
| CXCL8 | 8.16 | CTNND1 | −1.49 | LAMA5 | 1.12 | CTSH | −2.07 | ||
| DPT | 2.73 | CTSH | −2.21 | LAMB3 | 3.57 | DAG1 | −1.40 | ||
| ELK3 | 1.23 | DAG1 | −1.35 | LAMC2 | 2.07 | DICER1 | −1.17 | ||
| EPN3 | 1.73 | DICER1 | −1.18 | LLGL2 | 1.14 | DPYSL3 | −1.41 | ||
| FUT3 | 2.03 | DPYSL3 | −1.40 | MCAM | 1.26 | DST | −1.26 | ||
| GJA5 | 2.35 | DSC2 | −1.35 | MISP | 1.65 | EGFR | −1.24 | ||
| HAS1 | 2.14 | DST | −1.34 | MYCL | 2.88 | EIF4E2 | −1.21 | ||
| HKDC1 | 3.34 | EGFR | −1.30 | NDRG1 | 1.93 | ENPEP | −1.32 | ||
| HMOX1 | 2.14 | EIF4E2 | −1.18 | NRP1 | 3.52 | ETV4 | −1.39 | ||
| ICAM1 | 1.54 | ENPEP | −1.35 | PDGFA | 1.34 | EVPL | −1.50 | ||
| IL15 | 1.91 | EP300 | −1.19 | PLAUR | 1.43 | FBLN1 | −1.52 | ||
| IL1A | 1.61 | ETV4 | −1.28 | POPDC3 | 3.04 | FGF9 | −1.57 | ||
| IL1B | 2.57 | F11R | −1.31 | PTPRM | 1.92 | FGFR3 | −1.40 | ||
| JUN | 3.51 | FN1 | −1.41 | RAC2 | 1.17 | FN1 | −1.41 | ||
| KRT7 | 2.46 | GALNT7 | −1.54 | SERPINE1 | 1.81 | FSTL1 | −1.3 | ||
| LAMA3 | 2.51 | GSN | −1.67 | SH2B3 | 1.14 | GALNT7 | −1.52 | ||
| LAMB3 | 2.12 | GTF2I | −1.59 | SH2D3A | 1.45 | GPI | −1.28 | ||
| LAMC2 | 1.79 | HIF1A | −1.28 | SNAI1 | 2.93 | GSN | −1.90 | ||
| LLGL2 | 1.10 | HIPK2 | −1.15 | SPP1 | 3.78 | GTF2I | −1.62 | ||
| LOXL2 | 1.99 | HSD17B12 | −1.32 | THBS1 | 1.53 | ID1 | −1.55 | ||
| MISP | 1.63 | ID1 | −1.60 | VEGFA | 1.67 | ID2 | −2.37 | ||
| MYCL | 3.23 | ID2 | −2.18 | ITGA2 | −1.32 | ||||
| NDRG1 | 1.50 | ITGA1 | −1.40 | ITGB4 | −1.67 | ||||
| NR4A3 | 1.58 | ITGA2 | −1.59 | JAG1 | −2.36 | ||||
| NRP1 | 3.26 | ITGA5 | −1.21 | KDM1A | −1.54 | ||||
| OVOL2 | 1.80 | ITGB4 | −1.60 | KIAA1462 | −1.69 | ||||
| PCOLCE | 2.49 | ITGB8 | −1.50 | LDHA | −1.53 | ||||
| PDGFA | 1.37 | JAG1 | −2.45 | LGALS1 | −1.34 | ||||
| PFKFB1 | 1.52 | KDM1A | −1.63 | LTBP4 | −1.26 | ||||
| POPDC3 | 2.51 | KIAA1462 | −1.54 | MAPK3 | −1.71 | ||||
| PRSS8 | 2.00 | LDHA | −1.52 | MTA1 | −1.18 | ||||
| PTGS2 | 2.55 | LGALS1 | −1.46 | MTBP | −1.22 | ||||
| PTK2B | 1.41 | MAP3K7 | −1.16 | MYO1D | −1.31 | ||||
| PTK6 | 2.12 | MAPK3 | −1.72 | NFAT5 | −1.66 | ||||
| PTPRM | 1.67 | MMP14 | −1.52 | NME1 | −1.39 | ||||
| PTRF | 1.88 | MTA1 | −1.30 | NME4 | −1.48 | ||||
| SDC4 | 1.17 | MTOR | −1.12 | PDGFC | −1.22 | ||||
| SERPINE1 | 1.33 | MYO1D | −1.26 | PIK3R2 | −1.37 | ||||
| SH2D3A | 1.35 | NFAT5 | −1.55 | PLCG1 | −1.33 | ||||
| SHB | 1.79 | NME1 | −1.48 | PLS1 | −1.24 | ||||
| SLC37A1 | 1.83 | NME4 | −1.22 | PNPLA6 | −1.13 | ||||
| SLPI | 2.03 | P3H1 | −1.34 | PTTG1 | −1.56 | ||||
| SNAI1 | 2.31 | PGK1 | −1.49 | RAMP1 | −1.50 | ||||
| SPDEF | 2.11 | PIK3CA | −1.25 | RB1 | −1.30 | ||||
| SPP1 | 3.77 | POPDC3 | 2.51 | RBL1 | −1.46 | ||||
| SRPX2 | 1.62 | PPP2R1A | −1.45 | RBX1 | −1.30 | ||||
| TACSTD2 | 2.45 | PRKCZ | −1.12 | RGCC | −1.93 | ||||
| TBXA2R | 1.95 | PTEN | −1.32 | ROCK2 | −1.52 | ||||
| THBS1 | 1.49 | PTTG1 | −1.68 | SACS | −1.16 | ||||
| THY1 | 2.06 | PXDN | −1.63 | SCNN1A | −1.51 | ||||
| TNFSF13 | 1.67 | RB1 | −1.27 | SET | −1.28 | ||||
| TYMP | 1.46 | RBL1 | −1.76 | SMAD1 | −1.32 | ||||
| WARS | 1.55 | RBL2 | −1.20 | SMAD2 | −1.30 | ||||
| RGCC | −1.55 | SMC3 | −1.27 | ||||||
| ROCK2 | −1.50 | SNRPF | −1.25 | ||||||
| RPS6KB1 | −1.18 | SOD1 | −1.23 | ||||||
| SACS | −1.29 | SOX9 | −1.51 | ||||||
| SCNN1A | −1.74 | ST14 | −1.56 | ||||||
| SERINC5 | −1.37 | STAT1 | −1.18 | ||||||
| SET | −1.23 | SYK | −1.48 | ||||||
| SLC2A1 | −1.19 | TFDP1 | −1.46 | ||||||
| SMAD1 | −1.39 | TGFB1 | −1.31 | ||||||
| SMAD4 | −1.14 | TGFBR2 | −1.21 | ||||||
| SMC3 | −1.37 | TJP3 | −1.43 | ||||||
| SMURF2 | −1.34 | TMC6 | −1.40 | ||||||
| SNAI1 | 2.31 | TSPAN1 | −1.63 | ||||||
| SOD1 | −1.12 | VAMP8 | −1.34 | ||||||
| SOD1 | −1.12 | VCAN | −1.68 | ||||||
| SORD | −1.27 | WWTR1 | −1.20 | ||||||
| SOX9 | −1.48 | ||||||||
| ST14 | −1.55 | ||||||||
| STAT3 | −1.28 | ||||||||
| TCF20 | −1.29 | ||||||||
| TFDP1 | −1.48 | ||||||||
| TGFBR2 | −1.29 | ||||||||
| TIMP1 | −1.45 | ||||||||
| TJP3 | −1.13 | ||||||||
| TMC6 | −1.49 | ||||||||
| TNFSF12 | −1.28 | ||||||||
| TP53 | −1.47 | ||||||||
| TSPAN1 | −1.53 | ||||||||
| VAMP8 | −1.59 | ||||||||
| WARS | 1.55 | ||||||||
| WWTR1 | −1.20 |
| Gene Name | Het vs. Ctrl | p-Value of Het vs. Ctrl | Tet vs. Ctrl | p-Value of Het vs. Ctrl | Het + Tet vs. Ctrl | p-Value of Het vs. Ctrl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APC | 1.03 | 0.80 | 1.05 | 0.68 | −1.05 | 0.58 |
| CTNND1 | −1.49 | 0.06 | −1.23 | 0.37 | −1.36 | 0.13 |
| EGFR | −1.30 | 0.04 | −1.08 | 0.29 | −1.24 | 0.01 |
| IGF1 | 1.79 | 0.19 | 1.16 | 0.42 | 1.21 | 0.42 |
| KRAS | −1.20 | 0.08 | −1.11 | 0.37 | −1.11 | 0.10 |
| PIK3CA (PI3K) | −1.25 | 0.03 | −1.07 | 0.42 | −1.15 | 0.08 |
| PTEN | −1.32 | 0.02 | −1.11 | 0.48 | −1.17 | 0.06 |
| SMAD4 | −1.14 | 0.04 | −1.09 | 0.25 | −1.11 | 0.11 |
| TGFB1 (TGF-β) | −1.11 | 0.06 | −1.04 | 0.30 | −1.31 | 0.02 |
| TGFB2 (TGF-β) | −1.11 | 0.06 | −1.09 | 0.42 | −1.09 | 0.42 |
| TGFBR2 | −1.09 | 0.43 | 1.07 | 0.54 | −1.21 | 0.04 |
| TP53 | −1.47 | 0.04 | −1.10 | 0.46 | −1.39 | 0.01 |
| VEGFA | 1.43 | 0.06 | 1.01 | 0.89 | 1.67 | 0.01 |
| VEGFB | −1.14 | 0.44 | −1.07 | 0.40 | −1.28 | 0.18 |
| Primer Name | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| EGF | TTCTGTGGGAGCAGTGTGA | CCTCACCACCACAGGTTTCT |
| EGFR | AATTTACAGGAAATCCTGCATGGC | GATGCTCTCCACGTTGCACA |
| ERK1/2 | GCAGCTGAGCAATGACCATA | TTGCTTGCAATGTTCTCCTG |
| PI3K | CCTGATCTTCCTCGTGCTGCTC | ATGCCAATGGACAGTGTTCCTCTT |
| PD-L1 | GTTGAAGGACCAGCTCTCCC | ACCCCTGCATCCTGCAATTT |
| CCD1 | CAAGGCCTGAACCTGAGGAG | GATCACTCTGGAGAGGAAGCG |
| PCNA | TCTGAGGGCTTCGACACCTA | TCATTGCCGGCGCATTTTAG |
| c-Myc | TTCGGGTACTGGAAAACCAG | CAGCAGCTCGAATTTCTTCC |
| GAPDH | AGGGCTGCTTTTAACTCTGGT | CCCCACTTGATTTTGGAGGGA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Unson, S.; Chang, T.-C.; Yang, Y.-N.; Wang, S.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Crawford, D.R.; Huang, H.-M.; Li, Z.-L.; Lin, H.-Y.; Whang-Peng, J.; et al. Heteronemin and Tetrac Induce Anti-Proliferation by Blocking EGFR-Mediated Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080482
Unson S, Chang T-C, Yang Y-N, Wang S-H, Huang C-H, Crawford DR, Huang H-M, Li Z-L, Lin H-Y, Whang-Peng J, et al. Heteronemin and Tetrac Induce Anti-Proliferation by Blocking EGFR-Mediated Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(8):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080482
Chicago/Turabian StyleUnson, Sukanya, Tung-Cheng Chang, Yung-Ning Yang, Shwu-Huey Wang, Chi-Hung Huang, Dana R. Crawford, Haw-Ming Huang, Zi-Lin Li, Hung-Yun Lin, Jacqueline Whang-Peng, and et al. 2022. "Heteronemin and Tetrac Induce Anti-Proliferation by Blocking EGFR-Mediated Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cells" Marine Drugs 20, no. 8: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080482
APA StyleUnson, S., Chang, T.-C., Yang, Y.-N., Wang, S.-H., Huang, C.-H., Crawford, D. R., Huang, H.-M., Li, Z.-L., Lin, H.-Y., Whang-Peng, J., Wang, K., Davis, P. J., & Li, W.-S. (2022). Heteronemin and Tetrac Induce Anti-Proliferation by Blocking EGFR-Mediated Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Marine Drugs, 20(8), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080482








