Application of MS-Based Metabolomic Approaches in Analysis of Starfish and Sea Cucumber Bioactive Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
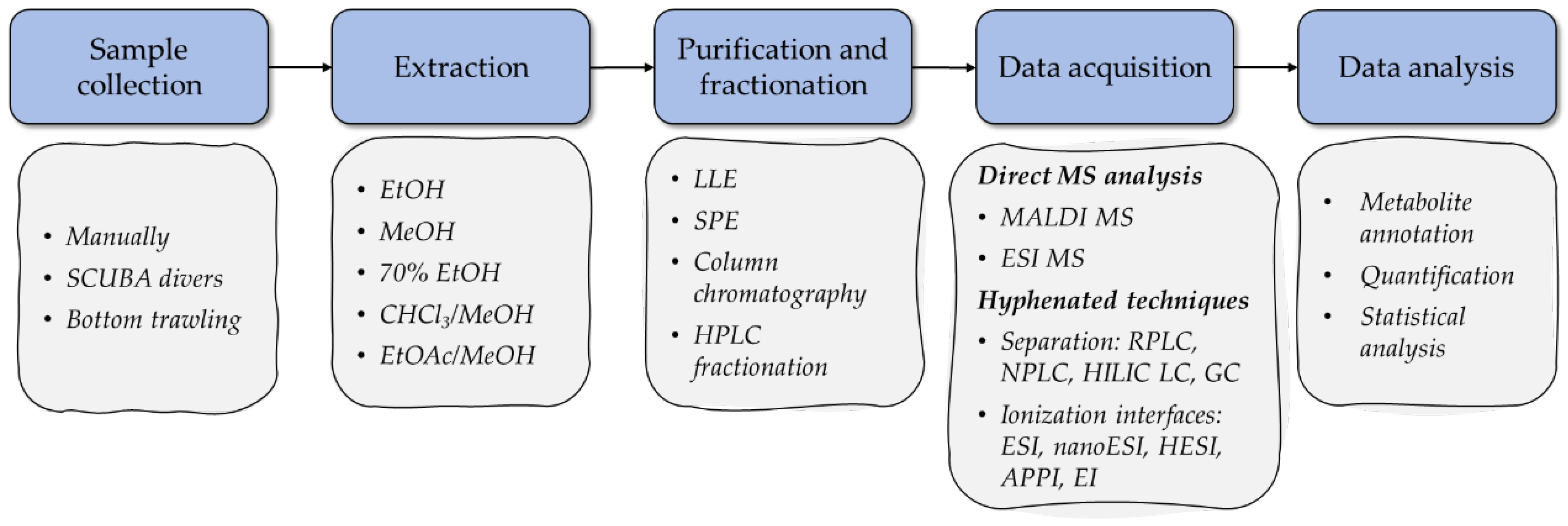
2. Overview of MS-Based Metabolomic Workflows in the Analysis of Starfish and Sea Cucumber Bioactive Compounds
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Analysis
3. MS-Based Metabolomic Profiling Approaches to the Study of Starfish and Sea Cucumber Bioactive Compounds
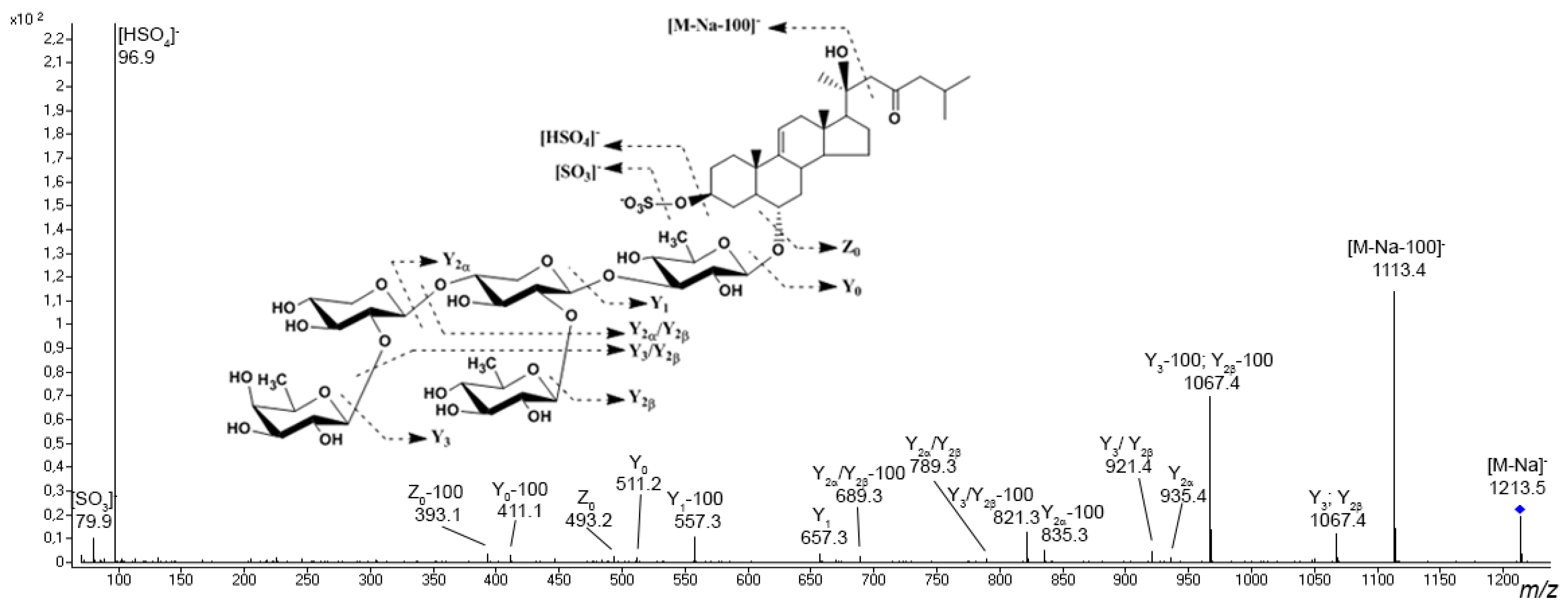
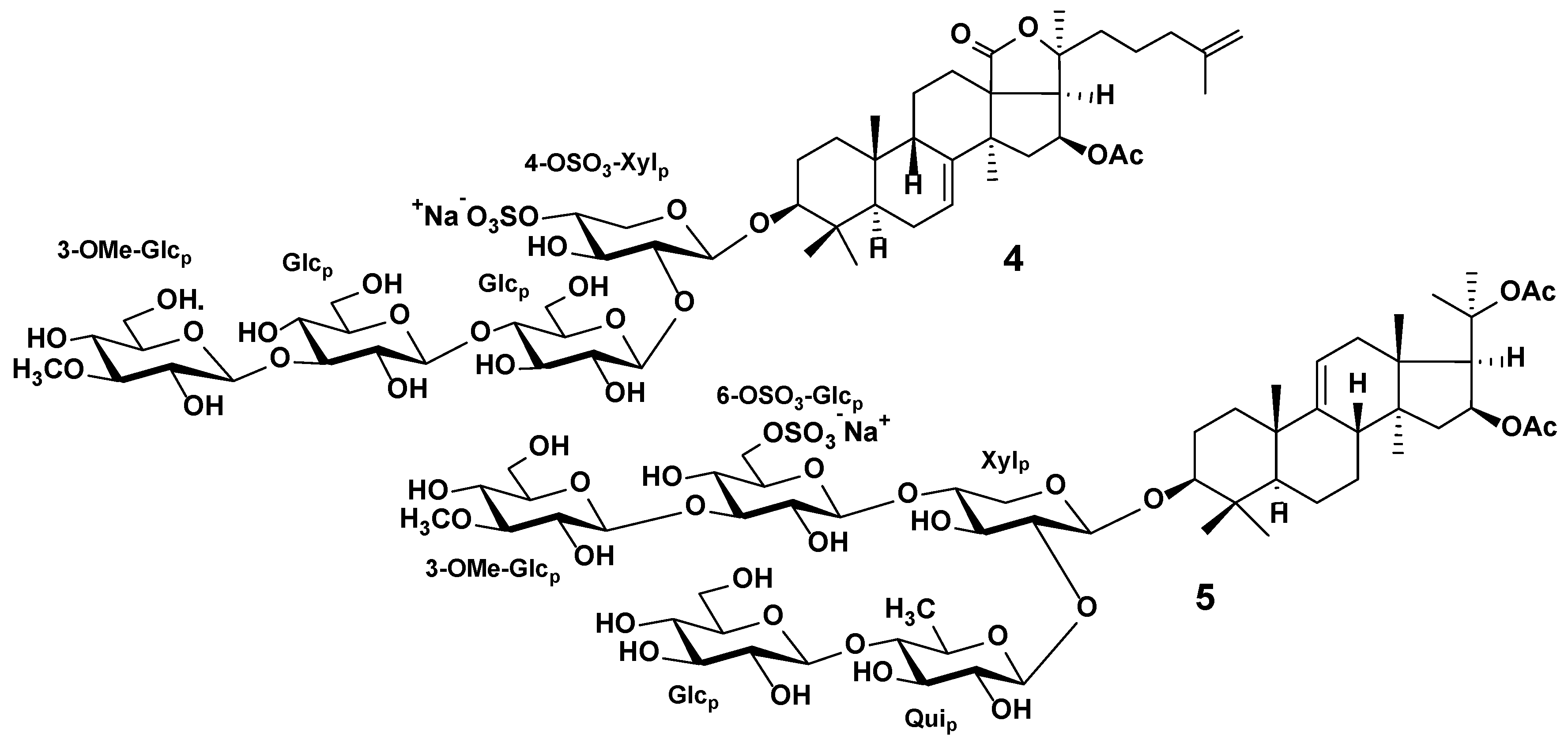
3.1. Starfish Polar Steroid Compounds
| Species Name | Extraction | Purification Methods | MS Approach | Research Results | Number of Detected Analytes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asteroidea | ||||||
| Asterias rubens | MSPD extraction | RPLC-NMR-ESI-IT MS | A combination of MSPD extraction with on-flow LC–NMR–MS for rapid chemical screening and structural elucidation was applied; a series of new asterosaponins were found and their structures were established | 17 asterosaponins | [84] | |
| A. rubens | 90% MeOH | LLE, CC | MALDI-QTOF MS; MALDI-TOF/TOF MSI; RPLC-ESI-QQQ MS | A series of known and new asterosaponins were detected and characterized; localization, inter- and intra-organ variability of asterosaponin were described | 26 asterosaponins | [85,86] |
| Aphelasterias japonica | EtOH | SPE | RPLC-ESI-QTOF MS | A series of new polar steroid compounds were detected and characterized; a theoretical scheme of biogenesis of several polar steroids was proposed | 33 asterosaponins, 28 polyhydroxylated glycosides, 7 polyhydroxysteroids | [77] |
| Patiria pectinifera | EtOH | SPE | RPLC-ESI-QTOF MS | A series of new polar steroid compounds were detected and characterized; peculiarities of the biosynthesis of the starfish polar steroids were discussed. Changes in steroid metabolome induced by environmental factors were studied | 35 asterosaponins, 22 polyhydroxysteroids, and 15 polyhydroxylated glycosides | [78,87] |
| Luidia senegalensis | 70% EtOH | SPE | RPLC-ESI-IT MS | New asterosaponins were detected and annotated | 5 asterosaponins, 2 polyhydroxysteroids | [88] |
| Lethasterias fusca | EtOH | LLE, SPE | nanoRPLC-CSI-QTOF MS | A series of new polar steroids compounds were detected and their fragmentation behaviors were extensively investigated; variations in the distribution of individual representatives in different organs were found | 106 asterosaponins, 81 polyhydroxylated glycosides, 14 polyhydroxysteroids | [79,89] |
| Echinaster sepositus | 60% MeOH | LLE | ESI-QOrbitrap MS | New asterosaponins were detected and annotated; significant inter-organ variability in asterosaponins was demonstrated | 11 asterosaponins | [90] |
| Heliaster helianthus | EtOH | LLE, CC | ESI-QTOF MS | The presence of sulfated steroidal glycosides in the fractions studied was confirmed and their structures were established | 1 asterosaponin, 2 polyhydroxylated glycosides | [91] |
| Holothuroidea | ||||||
| Holothuria forskali | 70% EtOH | LLE, CC | MALDI-QTOF MS; RPLC-ESI-QTOF MS | A series of triterpene glycosides were detected and characterized; variations in triterpene glycoside composition in Cuvierian tubules and body walls were demonstrated | 26 triterpene glycosides | [92] |
| H. forskali | 70% EtOH | LLE, CC | MALDI-TOF/TOF MS; MALDI-TOF/TOF MSI | Statistical differences in triterpene glycoside distribution between control and stressed groups were described | 8 triterpene glycosides | [93] |
| H. atra, H. leucospilota, Pearsonothuria graeffei, Actinopyga echinites, Bohadschia subrubra | 70% EtOH | LLE, CC | MALDI-QTOF MS; RPLC-ESI-QTOF MS | A series of new and known glycosides were detected and characterized; variations between species and between body compartments were established | H. atra—4, H. leucospilota—6, P. graeffei—8, A. echinites—10, B. subrubra—19 triterpene glycosides | [94] |
| H. forskali | 70% EtOH | LLE, CC | MALDI-QTOF MS; RPLC-ESI-QTOF MS | Localization of triterpene glycosides in the body wall tissues was described; variations of secreted glycosides were found in the seawater surroundings of non-stressed and stressed animals | 8 triterpene glycosides | [95] |
| H. scabra, H. impatiens, H. fuscocinerea | 70% EtOH | LLE, HPLC | nanoRPLC-ESI-QTOF MS; MALDI-FTICR MS | Triterpene glycoside compositions of three sea cucumber species were described; variations and sample-specific compounds were found | H. scabra—32, H. impatiens—32, H. fuscocinerea—33 triterpene glycosides | [96] |
| H. scabra | MeOH | LLE, CC | MALDI-QTOF MS | The triterpene glycoside composition of the H. scabra body wall was characterized, as was processed holothurian, | 6 triterpene glycosides | [97] |
| H. sanctori | MeOH | LLE, CC | MALDI-QTOF MS | Qualitative and quantitative differences in the body wall and Cuvierian tubules of composition were described | 18 triterpene glycosides | [98] |
| Eupentacta fraudatrix | EtOH | SPE | RPLC-ESI-QTOF MS | A series of triterpene glycosides were discovered and characterized; qualitative and quantitative variations in the body wall and viscera were found | 54 triterpene glycosides | [99] |
| H. scabra | SPE | RPLC-multimode source-QTOF MS | Several known and new triterpene glycosides were identified in conditioned water of H. scabra | 16 triterpene glycosides | [100] | |
| H. forskali | MeOH | LLE | MALDI-QTOF MS; RPLC-ESI-QQQ MS; RPLC-ESI-IM-QTOF MS | The triterpene glycoside compositions of the body wall, gonads, and Cuvierian tubules of H. forskali were described | 26 triterpene glycosides | [101] |
| H. leucospilota | 70% EtOH; H2O or n-BuOH | LLE | MALDI-TOF/TOF MS; MALDI-TOF/TOF MSI | The presence of triterpene glycosides was confirmed in the body wall and epidermis extracts; epidermal pigmented cells were reported to involve in the accumulation and release of the triterpene glycosides to the surrounding seawater | 12 triterpene glycosides | [102] |
| H. atra | EtOAc/MeOH | LLE | RPLC-ESI-QOrbitrap MS | A combination of LC-MS profiling and molecular networking followed by target compound isolation was applied; variations in triterpene glycoside composition between H. atra from the Persian Gulf and previously reported results were described | 15 triterpene glycosides (4—isolated as pure compounds) | [103] |
| Apostichopus japonicus | 70% EtOH | LLE | RPLC-ESI-QOrbitrap MS | Variability in triterpene glycoside composition among different types of A. japonicus was described | 5 triterpene glycosides | [104] |
| H. polii, H. leucospilota, H. atra, H. edulis, Bohadschia marmorata, Actinopyga mauritiana | 96% EtOH | LLE | RPLC-ESI-QOrbitrap MS | MS-based profiling results were applied for chemotaxonomy of sea cucumber species | 4 triterpene glycosides; 15 fatty acids, 45 triacylglycerols | [105] |
| H. whitmaei, H. hilla, H. atra, H. edulis, Bohadschia argus, B. vittiensis, Bohadschia sp., Actinopyga echinites, A. mauritiana | MeOH:EtOAc, MeOH | LLE, SPE, HPLC | RPLC-ESI-QTOF MS | A series of triterpene glycosides were detected in crude extracts; anti-fouling activity of sea cucumber extracts was found to be species-specific and related to total concentration of triterpene glycosides. | 102 triterpene glycosides in crude extracts (including 23 triterpene glycosides in B. argus fractions) | [106] |
| H. scabra | MeOH | flash chromatography, LLE | MALDI-QTOF MS; RPLC-ESI-IM-QTOF MS | The qualitative and quantitative composition of triterpene glycosides in dried viscera and its desulfation by microwave activation products were described | 26 triterpene glycosides | [107] |
3.2. Sea Cucumber Triterpene Glycosides
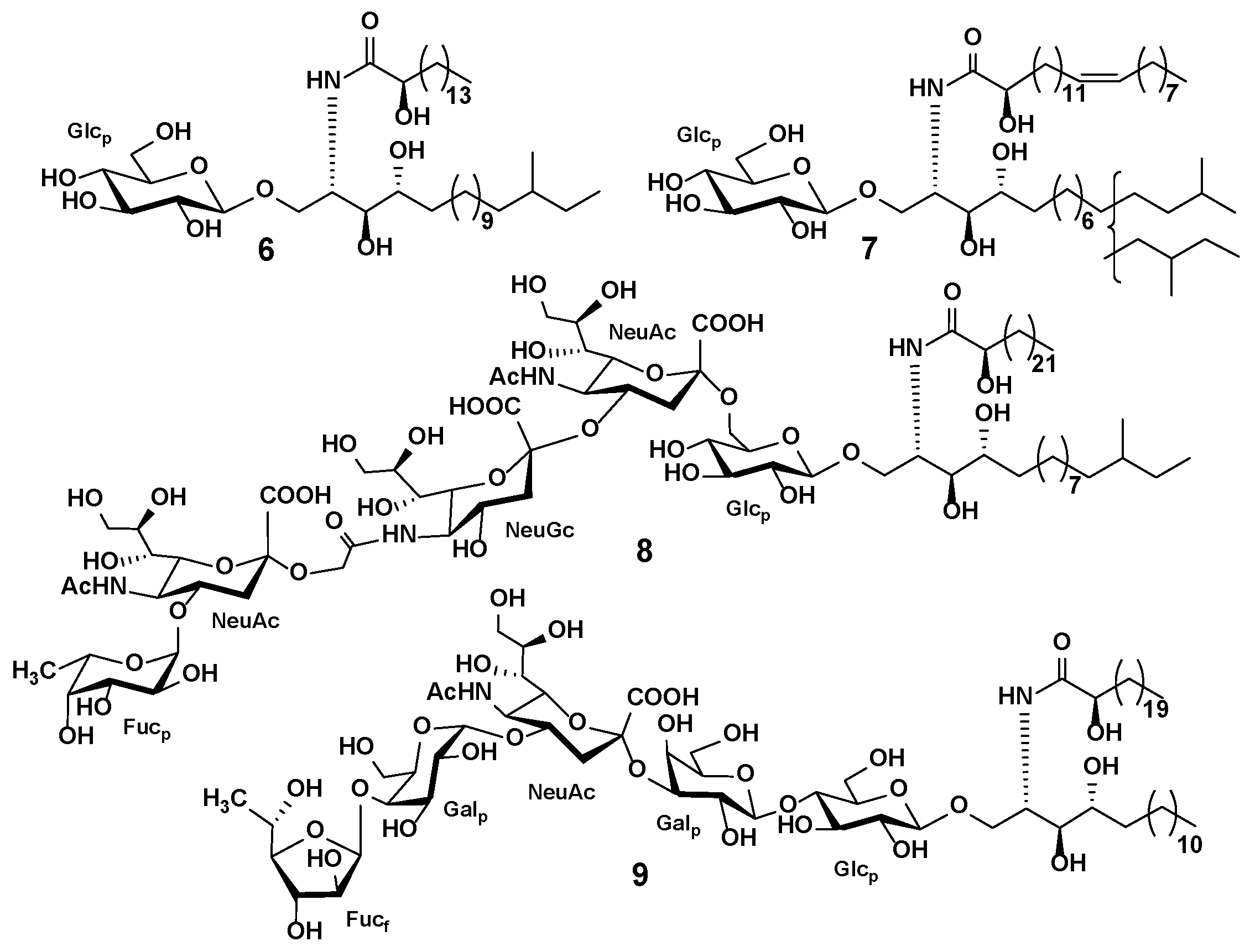
3.3. Starfish and Sea Cucumber Lipids
| Species Name | Extraction | Purification Method | MS Approach | Research Findings | Number of Analytes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acaudina molpadioides, Cucumaria frondosa, Apostichopus japonicus | CHCl3/MeOH | LLE, CC | RPLC-ESI-ITTOF MS | Cerebroside compositions of three sea cucumber species were characterized; many novel glucocerebroside structures were described | Cerebroside molecular species: A. japonicus—26, C. frondosa—40, A. molpadioides—12 | [143] |
| A. japonicus, Thelenota ananas, A. molpadioides, Bohadschia marmorata | CHCl3/MeOH | LLE, SPE | RPLC-ESI-QTOF MS | A series of cerebrosides from four sea cucumber species were detected and annotated; the relation of long-chain base structures and fatty acids to sea cucumber genera were described | Cerebroside molecular species: A. japonicus—55, T. ananas— 107, A. molpadioides—87, B. marmorata— 75 | [59] |
| Pearsonothria graeffei | CHCl3/MeOH | LLE, SPE | RPLC-ESI-QTOF MS | A series of cerebrosides of the sea cucumber P. graeffei were detected and annotated; characteristic structural features of sea cucumber cerebrosides were described | 89 cerebroside molecular species | [144] |
| C. frondosa | CHCl3/MeOH/H2O | LLE, CC | RPLC-HESI-QOrbitrap MS | The sphingolipid composition of the sea cucumber C. frondosa was investigated; the relationship between sea cucumber sphingolipid structures and pro-apoptotic activities was discussed | 35 cerebroside molecular species, 8 ceramide molecular species, 2 sphingosines | [145] |
| Asterias amurensis | Bligh and Dyer protocol | CC | RPLC-ESI-ITTOF MS | Cerebroside composition and distribution in viscera of the starfish A. amurensis were investigated; the potential usefulness of starfish as a source of raw material for cerebrosides was discussed | 23 cerebrosides molecular species | [146] |
| Parastichopus califormicus, C. frondosa, Isostichopus fuscus, Holothuria mexicana, H. polli, Bohadschia marmorata | Bligh and Dyer protocol | NPLC-ESI-TripleTOF MS | A series of phospholipids, including rare representatives, were detected and annotated; qualitative and quantitative variations between sea cucumber species were established; the possibility of using phospholipid data for classification was shown | From 295 to 445 molecular species from 7 phospholipid classes (PG, PE, PI, PS, LPE, PC, LPC) | [142] | |
| B. marmorata, I. fuscus, H. polli, H. mexicana, C. frondosa P. califormicus | H2O | LLE, SPE | HILIC LC-HESI-QOrbitrap MS | Seventeen ganglioside subclasses, including rare and new ganglioside structures, were discovered in six sea cucumber species; variations and characteristic features of the ganglioside composition of sea cucumbers were described | 17 ganglioside subclasses | [147] |
3.4. Multi-Class Profiling Studies
4. Applications of Metabolome-Oriented Approaches in Studies of Starfish and Sea Cucumbers
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 175–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 23, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, C. Marine natural products in medicinal chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-X.; Fan, X.; Shi, J.-G. A novel pyrrole oligoglycoside from the starfish Asterina pectinifera. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.W.; Chen, X.Q.; Dong, G.; Zhou, X.F.; Chai, X.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W.D.; Liu, Y. Isolation and structural characterisation of five new and 14 known metabolites from the commercial starfish Archaster typicus. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.W. Managing sea cucumber fisheries with an ecosystem approach. In FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper; No. 520; Lovatelli, A., Vasconcellos, M., Yimin, Y., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2010; 157p, ISBN 978-92-5-106489-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bordbar, S.; Anwar, F.; Saari, N. High-value components and bioactives from sea cucumbers for functional foods—A review. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1761–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Himaya, S.W.A.; Kim, S.K. Triterpenoids of marine origin as anti-cancer agents. Molecules 2013, 18, 7886–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.R.; Freitas, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P.; Duarte, A.C. Bioactive compounds derived from echinoderms. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 29365–29382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khotimchenko, Y. Pharmacological potential of sea cucumbers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzara, V.; Arizza, V.; Luparello, C.; Mauro, M.; Vazzana, M. Bright spots in the darkness of cancer: A review of starfishes-derived compounds and their anti-tumor action. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Farooqi, A.A.; Xu, B. Comprehensive review on signaling pathways of dietary saponins in cancer cells suppression. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, M.; Cui, J.; Xu, J.; Xue, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y. Effects of dietary sea cucumber saponin on the gene expression rhythm involved in circadian clock and lipid metabolism in mice during nighttime-feeding. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumphoochai, K.; Chalorak, P.; Suphamungmee, W.; Sobhon, P.; Meemon, K. Saponin-enriched extracts from body wall and Cuvierian tubule of Holothuria leucospilota reduce fat accumulation and suppress lipogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4158–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Xue, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, Z.; Leng, K.; Wang, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y. Sea cucumber cerebrosides and long-chain bases from Acaudina molpadioides protect against high fat diet-induced metabolic disorders in mice. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3428–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luparello, C.; Mauro, M.; Lazzara, V.; Vazzana, M. Collective locomotion of human cells, wound healing and their control by extracts and isolated compounds from marine invertebrates. Molecules 2020, 25, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minale, L.; Riccio, R.; Zollo, F. Steroidal Oligoglycosides and polyhydroxysteroids from echinoderms. Prog. Chem. Org. Nat. Prod. 1993, 62, 75–308. [Google Scholar]
- Chludil, H.D.; Murray, A.P.; Seldes, A.M.; Maier, M.S. Biologically active triterpene glycosides from sea cucumbers (Holothuroidea, Echinodermata). In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Atta-ur-Rahman, Ed.; Elsevier Science Publisher: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 28, pp. 587–615. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Himaya, S.W.A. Triterpene glycosides from sea cucumbers and their biological activities. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 65, 297–319. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Stonik, V.A. Progress in the studies of triterpene glycosides from sea cucumbers (Holothuroidea, Echinodermata) Between 2017 and 2021. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2021, 16, 1934578X211053934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Stonik, V.A.; Elyakov, G.B. Triterpene glycosides of sea cucumbers (Holothuroidea, Echinodermata) as taxonomic markers. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Stonik, V.A. Non-holostane aglycones of sea cucumber triterpene glycosides. Structure, biosynthesis, evolution. Steroids 2019, 147, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stonik, V.A.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A. New polar steroids from starfish. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 1587–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Stonik, V.A. Steroid glycosides from marine organisms. Steroids 2011, 76, 425–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Xu, T.; Yang, B.; Lin, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Chemical constituents and bioactivities of starfish. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 740–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchina, N.; Kicha, A.; Malyarenko, T.; Stonik, V. Recent studies of polar steroids from starfish: Structures, biological activities and biosynthesis. In Advances in Natural Products Discovery; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 191–224. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.M.; Miao, Z.; Xie, C.L.; Zhang, J.W.; Yang, X.W. Chemical constituents and bioactivities of starfishes: An update. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e1900638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonik, V.A.; Kicha, A.A.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Ivanchina, N.V. Asterosaponins: Structures, taxonomic distribution, biogenesis and biological activities. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Aminin, D.L.; Avilov, S.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Stonik, V.A. Triterpene glycosides from sea cucucmbers (Holothurioidea, Echinodermata). Biological activities and functions. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry (Bioactive Natural Products); Atta-ur-Rahman, Ed.; Elsevier Science Publisher: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 35, pp. 135–196. ISBN 1572-5995. [Google Scholar]
- Careaga, V.P.; Maier, M.S. Cytotoxic triterpene glycosides from sea cucumbers. In Handbook of Anticancer Drugs from Marine Origin; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 515–528. ISBN 978-3-319-07145-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfender, J.L.; Litaudon, M.; Touboul, D.; Queiroz, E.F. Innovative omics-based approaches for prioritisation and targeted isolation of natural products-new strategies for drug discovery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Rivera, G.; Ballesteros-Vivas, D.; Parada-Alfonso, F.; Ibañez, E.; Cifuentes, A. Recent applications of high resolution mass spectrometry for the characterization of plant natural products. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydoğan, C. Recent advances and applications in LC-HRMS for food and plant natural products: A critical review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 1973–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boughton, B.A.; Thinagaran, D.; Sarabia, D.; Bacic, A.; Roessner, U. Mass spectrometry imaging for plant biology: A review. Phytochem. Rev. 2016, 15, 445–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Quinn, K.; Cruickshank-Quinn, C.; Reisdorph, R.; Reisdorph, N. The application of ion mobility mass spectrometry to metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2018, 42, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandramouli, K. Marine proteomics: Challenges and opportunities. J. Data Min. Genom. Proteom. 2016, 7, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, K.A.; Welsh, K.; Walker, M.C.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A. Metabolomic tools used in marine natural product drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 499–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayona, L.M.; de Voogd, N.J.; Choi, Y.H. Metabolomics on the study of marine organisms. Metabolomics 2022, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, J.D.; Parrish, C.C. Mass spectrometry-based lipidomics in the characterization of individual triacylglycerol (TAG) and phospholipid (PL) species from marine sources and their beneficial health effects. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2022, 30, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, B.; Luckas, B. Determination of marine biotoxins relevant for regulations: From the mouse bioassay to coupled LC-MS methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulitquer, S.; Potin, P.; Tonon, T. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics to elucidate functions in marine organisms and ecosystems. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics—The link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonn, N.; Novais, S.C.; Silva, C.S.E.; Morais, H.A.; Correia, J.P.S.; Lemos, M.F.L. Stress responses of the sea cucumber Holothuria forskali during aquaculture handling and transportation. Mar. Biol. Res. 2016, 12, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Zhang, L.; Huo, D.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S. Metabolomic analysis of coelomic fluids reveals the physiological mechanisms underlying evisceration behavior in the sea cucumber Apostichopus Jpn. Aquac. 2021, 543, 736960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuckovic, D. Current trends and challenges in sample preparation for global metabolomics using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1523–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.H.S. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matyash, V.; Liebisch, G.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Shevchenko, A.; Schwudke, D. Lipid extraction by methyl-tert-butyl ether for high-throughput lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashkes, Y.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Levina, E.V.; Stonik, V.A. Mass spectra of polyhydrosysteroids of the starfish Patiria pectinifera. Chem. Nat. Compd. 1985, 21, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, T.; Nanri, H.; Itakura, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Taguchi, S.; Higuchi, R.; Kawasaki, T.; Higuchi, T. Biologically active glycosides from Asteroidea, III. Steroid oligoglycosides from the starfish Acanthaster planci L., 2. Structures of two newly characterized genuine sapogenins and an oligoglycoside sulfate. Liebigs Ann. Der Chem. 1983, 1983, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Marsal, S.; JuliÃ, A. Analytical methods in untargeted metabolomics: State of the art in 2015. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Orešič, M. MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röst, H.L.; Sachsenberg, T.; Aiche, S.; Bielow, C.; Weisser, H.; Aicheler, F.; Andreotti, S.; Ehrlich, H.C.; Gutenbrunner, P.; Kenar, E.; et al. OpenMS: A flexible open-source software platform for mass spectrometry data analysis. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsugawa, H.; Ikeda, K.; Takahashi, M.; Satoh, A.; Mori, Y.; Uchino, H.; Okahashi, N.; Yamada, Y.; Tada, I.; Bonini, P.; et al. A lipidome atlas in MS-DIAL 4. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Cong, P.; Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. Reversed-phase liquid chromatography–quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry for high-throughput molecular profiling of sea cucumber cerebrosides. Lipids 2015, 50, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksenov, A.A.; Da Silva, R.; Knight, R.; Lopes, N.P.; Dorrestein, P.C. Global chemical analysis of biology by mass spectrometry. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis: Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfender, J.L.; Nuzillard, J.M.; Van Der Hooft, J.J.J.; Renault, J.H.; Bertrand, S. Accelerating metabolite identification in natural product research: Toward an ideal combination of liquid chromatography-high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry and nmr profiling, in silico databases, and chemometrics. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 704–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horai, H.; Arita, M.; Kanaya, S.; Nihei, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Suwa, K.; Ojima, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, S.; Aoshima, K.; et al. MassBank: A public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Maille, G.O.; Want, E.J.; Qin, C.; Trauger, S.A.; Brandon, T.R.; Custodio, D.E.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. METLIN a metabolite mass spectral database. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krettler, C.A.; Thallinger, G.G. A map of mass spectrometry-based in silico fragmentation prediction and compound identification in metabolomics. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böcker, S. Searching molecular structure databases using tandem MS data: Are we there yet? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanstrup, J.; Neumann, S.; Vrhovšek, U. PredRet: Prediction of retention time by direct mapping between multiple chromatographic systems. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9421–9428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Hinzman, A.A.; Kang, E.L.; Szczesniak, R.D.; Lu, L.J. Computational and statistical analysis of metabolomics data. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1492–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, R.; Minale, L.; Pagonis, S.; Pizza, C.; Zollo, F.; Pusset, J. A novel group of highly hydroxylated steroids from the starfish Protoreaster nodosus. Tetrahedron 1982, 38, 3615–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Ojika, M.; Sakagami, Y. Linckosides A and B, two new neuritogenic steroid glycosides from the Okinawan starfish Linckia laevigata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, I.; Kobayashi, M. Saponin and sapogenol. XXVI. Steroidal saponins from the starfish Acanthaster planci L. (crown of thorns). 2. Structure of the major saponin thornasteroside A. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1978, 26, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Malyarenko, O.S.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Ermakova, S.P. Effects of polar steroids from the starfish Patiria (=asterina) pectinifera in combination with x-ray radiation on colony formation and apoptosis induction of human colorectal carcinoma cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyarenko, O.S.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Usoltseva, R.V.; Silchenko, A.S.; Kicha, A.A.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Ermakova, S.P. Fucoidan from brown algae Fucus evanescens potentiates the anti-proliferative efficacy of asterosaponins from starfish Asteropsis carinifera in 2D and 3D models of melanoma cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyarenko, O.S.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Usoltseva, R.V.; Surits, V.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Ermakova, S.P. Combined anticancer effect of sulfated laminaran from the brown alga Alaria angusta and polyhydroxysteroid glycosides from the starfish Protoreaster lincki on 3D colorectal carcinoma HCT 116 cell line. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, R.S.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A. Metabolite profiling of polar steroid constituents in the far eastern starfish Aphelasterias japonica using LC-ESI MS/MS. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 1152–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, R.S.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A. LC-ESI MS/MS profiling of polar steroid metabolites of the Far Eastern starfish Patiria (=Asterina) Pectinifera. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, R.S.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S. Structural characterization of polar steroid compounds of the Far Eastern starfish Lethasterias fusca by nanoflow liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 30, 743–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domon, B.; Costello, C.E. A systematic nomenclature for carbohydrate fragmentations in FAB-MS/MS spectra of glycoconjugates. Glycoconj. J. 1988, 5, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamisawa, T.; Hirabayashi, J. Fragmentations of isomeric sulfated monosaccharides using electrospray ion trap mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.G.; Ducatti, D.R.B.; Grindley, T.B.; Duarte, M.E.R.; Noseda, M.D. ESI-MS differential fragmentation of positional isomers of sulfated oligosaccharides derived from carrageenans and agarans. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 21, 1404–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, R.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S. Stereospecific fragmentation of starfish polyhydroxysteroids in electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 71, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandvoss, M.; Weltring, A.; Preiss, A.; Levsen, K.; Wuensch, G. Combination of matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and direct on-line liquid chromatography-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy-tandem mass spectrometry as a new efficient approach for the rapid screening of natural products: Application to the t. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 917, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeyer, M.; De Winter, J.; Caulier, G.; Eeckhaut, I.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P. Molecular diversity and body distribution of saponins in the sea star Asterias rubens by mass spectrometry. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 168, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeyer, M.; Wisztorski, M.; Decroo, C.; De Winter, J.; Caulier, G.; Hennebert, E.; Eeckhaut, I.; Fournier, I.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P. Inter- and intra-organ spatial distributions of sea star saponins by MALDI imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8813–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, R.S.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Grebnev, B.B.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A. LC–MS-based metabolome analysis on steroid metabolites from the starfish Patiria (=Asterina) pectinifera in conditions of active feeding and stresses. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangerina, M.M.P.; Cesário, J.P.; Pereira, G.R.R.; Costa, T.M.; Valenti, W.C.; Vilegas, W. Chemical profile of the sulphated saponins from the starfish Luidia senegalensis collected as by-catch fauna in Brazilian coast. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2018, 8, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, R.S.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Grebnev, B.B.; Stonik, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S. The distribution of asterosaponins, polyhydroxysteroids and related glycosides in different body components of the Far Eastern starfish Lethasterias fusca. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmoune, B.; Bachari-Houma, F.; Chibane, M.; Jéhan, P.; Guegan, J.P.; Dahmoune, F.; Aissou-Akrour, C.; Mouni, L.; Ferrières, V.; Hauchard, D. Saponin contents in the starfish Echinaster sepositus: Chemical characterization, qualitative and quantitative distribution. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2021, 96, 104262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.S.; Centurión, R.; Muniain, C.; Haddad, R.; Eberlin, M.N. Identification of sulfated steroidal glycosides from the starfish Heliaster helianthus by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Arkivoc 2006, 2007, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyck, S.; Gerbaux, P.; Flammang, P. Elucidation of molecular diversity and body distribution of saponins in the sea cucumber Holothuria forskali (Echinodermata) by mass spectrometry. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 152, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dyck, S.; Flammang, P.; Meriaux, C.; Bonnel, D.; Salzet, M.; Fournier, I.; Wisztorski, M. Localization of secondary metabolites in marine invertebrates: Contribution of MALDI MSI for the study of saponins in Cuvierian tubules of H. forskali. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyck, S.; Gerbaux, P.; Flammang, P. Qualitative and quantitative saponin contents in five sea cucumbers from the Indian ocean. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyck, S.; Caulier, G.; Todesco, M.; Gerbaux, P.; Fournier, I.; Wisztorski, M.; Flammang, P. The triterpene glycosides of Holothuria forskali: Usefulness and efficiency as a chemical defense mechanism against predatory fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondoc, K.G.V.; Lee, H.; Cruz, L.J.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Juinio-Meñez, M.A. Chemical fingerprinting and phylogenetic mapping of saponin congeners from three tropical holothurian sea cucumbers. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 166, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caulier, G.; Flammang, P.; Rakotorisoa, P.; Gerbaux, P.; Demeyer, M.; Eeckhaut, I. Preservation of the bioactive saponins of Holothuria scabra through the processing of trepang. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2013, 54, 685–690. [Google Scholar]
- Caulier, G.; Mezali, K.; Soualili, D.L.; Decroo, C.; Demeyer, M.; Eeckhaut, I.; Gerbaux, P.; Flammang, P. Chemical characterization of saponins contained in the body wall and the Cuvierian tubules of the sea cucumber Holothuria (Platyperona) sanctori (Delle Chiaje, 1823). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2016, 68, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, R.S.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Dolmatov, I.Y.; Stonik, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S. Metabolite profiling of triterpene glycosides of the far eastern sea cucumber Eupentacta fraudatrix and their distribution in various body components using LC-ESI QTOF-MS. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitu, S.A.; Bose, U.; Suwansa-ard, S.; Turner, L.H.; Zhao, M.; Elizur, A.; Ogbourne, S.M.; Shaw, P.N.; Cummins, S.F. Evidence for a saponin biosynthesis pathway in the body wall of the commercially significant sea cucumber Holothuria scabra. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decroo, C.; Colson, E.; Demeyer, M.; Lemaur, V.; Caulier, G.; Eeckhaut, I.; Cornil, J.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P. Tackling saponin diversity in marine animals by mass spectrometry: Data acquisition and integration. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 3115–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroyraya, M.; Kaewphalug, W.; Anantachoke, N.; Poomtong, T.; Sobhon, P.; Srimongkol, A.; Suphamungmee, W. Saponins enriched in the epidermal layer of Holothuria leucospilota body wall. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2018, 81, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grauso, L.; Yegdaneh, A.; Sharifi, M.; Mangoni, A.; Zolfaghari, B.; Lanzotti, V. Molecular networking-based analysis of cytotoxic saponins from sea cucumber Holothuria atra. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.L.; Kim, E.A.; Luo, H.M.; Jiang, Y.F.; Oh, J.Y.; Heo, S.J.; Jeon, Y.J. Characterization and anti-tumor activity of saponin-rich fractions of South Korean sea cucumbers (Apostichopus japonicus). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, N.E.; Salem, H.K.; Eissa, S.H.; Kabbash, A.M.; Kandeil, M.A.; Salem, M.A. Chemotaxonomic study of the most abundant Egyptian sea-cucumbers using ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS). Chemoecology 2020, 30, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, E.; Goebeler, N.; Kellermann, M.Y.; Rohde, S.; Reverter, M.; Striebel, M.; Schupp, P.J. Anti-fouling effects of saponin-containing crude extracts from tropical Indo-Pacific sea cucumbers. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarino, P.; Colson, E.; Caulier, G.; Eeckhaut, I.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P. Microwave-assisted desulfation of the hemolytic saponins extracted from Holothuria scabra viscera. Molecules 2022, 27, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagnuolo, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Feroxosides A-B, two norlanostane tetraglycosides from the Caribbean sponge Ectyoplasia ferox. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 4049–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandvoss, M.; Pham, L.H.; Levsen, K.; Preiss, A.; Mügge, C.; Wünsch, G. Isolation and structural elucidation of steroid oligoglycosides from the starfish Asterias rubens by means of direct online LC-NMR-MS hyphenation and one- and two-dimensional NMR investigations. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 2000, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicha, A.A.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Gorshkova, I.A.; Ponomarenko, L.P.; Likhatskaya, G.N.; Stonik, V.A. The distribution of free sterols, polyhydroxysteroids and steroid glycosides in various body components of the starfish Patiria (=Asterina) pectinifera. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 128, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicha, A.A.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Stonik, V.A. Seasonal variations in the levels of polyhydroxysteroids and related glycosides in the digestive tissues of the starfish Patiria (Asterina) pectinifera. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 136, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Fedorov, S.N.; Stepanov, V.G.; Dong, Z.; Stonik, V.A. Constituents of the sea cucumber Cucumaria okhotensis. Structures of okhotosides B1-B3 and cytotoxic activities of some glycosides from this species. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andrijaschenko, P.V.; Popov, R.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Chingizova, E.A.; Kalinin, V.I. Kurilosides A1, A2, C1, D, E and F—triterpene glycosides from the far eastern sea cucumber Thyonidium (=Duasmodactyla) kurilensis (Levin): Structures with unusual non-holostane aglycones and cytotoxicities. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminin, D.; Menchinskaya, E.; Pisliagin, E.; Silchenko, A.; Avilov, S.; Kalinin, V. Anticancer activity of sea cucumber triterpene glycosides. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1202–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminin, D.L.; Pislyagin, E.A.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I. Immunomodulatory and anticancer activity of sea cucumber triterpene glycosides. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Atta-ur-Rahman, Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 75–94. ISBN 9780444632944. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Q.; Keesing, J.K.; Liu, D. A Review of sea cucumber aquaculture, ranching, and stock enhancement in China. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2016, 24, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Q.; Xu, J.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, J.H.; Xue, C.H.; Wangy, Y.M. Effects of bioactive components of sea cucumber on the serum, liver lipid profile and lipid absorption. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 2214–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, R.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Grebnev, B.B.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kalinin, V.I. Cucumariosides F1 and F2, two new triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Eupentacta fraudatrix and their LC-ESI MS/MS identification in the starfish Patiria pectinifera, a predator of the sea cucumber. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 57, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decroo, C.; Colson, E.; Lemaur, V.; Caulier, G.; De Winter, J.; Cabrera-Barjas, G.; Cornil, J.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P. Ion mobility mass spectrometry of saponin ions. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 33, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, Y.; Zhang, W.; Franco, C. Discovery of novel saponins from the viscera of the sea cucumber Holothuria lessoni. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2633–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chataway, T.; Franco, C. Structural elucidation of novel saponins in the sea cucumber Holothuria lessoni. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4439–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, Y.; Franco, C.M.M. Structure elucidation of new acetylated saponins, Lessoniosides A, B, C, D, and E, and non-acetylated saponins, Lessoniosides F and G, from the viscera of the sea cucumber Holothuria lessoni. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 597–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, Y.; Zhang, W.; Franco, C.M.M.; Franco, C.M.M. Distribution of saponins in the sea cucumber Holothuria lessoni; the body wall versus the viscera, and their biological activities. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajahan, A.; Heiss, C.; Ishihara, M.; Azadi, P. Glycomic and glycoproteomic analysis of glycoproteins—a tutorial. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4483–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert Ozupek, N.; Cavas, L. Triterpene glycosides associated antifouling activity from Holothuria tubulosa and H. polii. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2017, 13, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyarenko, T.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Stonik, V.A.; Ivanchina, N.V. Sphingolipids of asteroidea and holothuroidea: Structures and biological activities. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Wangüemert, M.; Roggatz, C.C.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Barreira, L.; da Silva, M.M.; Custódio, L. A new insight into the influence of habitat on the biochemical properties of three commercial sea cucumber species. Int. Aquat. Res. 2018, 10, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtel, P.J.; Oliveira, A.C.M.; Demir, N.; Smiley, S. Chemical composition of the giant red sea cucumber, Parastichopus californicus, commercially harvested in Alaska. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 1, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svetashev, V.I.; Levin, V.S.; Lam, C.N.; Nga, D.T. Lipid and fatty acid composition of holothurians from tropical and temperate waters. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1991, 98, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, K.L.; Pond, D.W.; Billett, D.S.M.; Tyler, P.A. Feeding ecology of deep-sea seastars (Echinodermata: Asteroidea): A fatty-acid biomarker approach. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 255, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergé, J.P.; Barnathan, G. Fatty acids from lipids of marine organisms: Molecular biodiversity, roles as biomarkers, biologically active compounds, and economical aspects. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2005, 96, 49–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.H.; Kuo, C.H. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-based analytical strategies for fatty acid analysis in biological samples. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 28, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Row, K.H. Development of gas chromatography analysis of fatty acids in marine organisms. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2013, 51, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginger, M.L.; Santos, V.L.C.S.; Wolff, G.A. A preliminary investigation of the lipids of abyssal holothurians from the north-east Atlantic Ocean. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2000, 80, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetashev, V.I.; Kharlamenko, V.I. Fatty acids of abyssal echinodermata, the sea star Eremicaster vicinus and the sea urchin Kamptosoma abyssale: A New Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Detected, 22:6(n-2). Lipids 2020, 55, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, N.; Sawaguchi, S.; Tokuda, M.; Unuma, T. Fatty acid composition in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus fed with microbially degraded dietary sources. Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X. Identification of the geographical origins of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) in northern China by using stable isotope ratios and fatty acid profiles. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Han, D.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y. Regional differences in fatty acid composition of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) and scallop (Patinopecten yesoensis) in the coastal areas of China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 31, 100782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbs, A.B.; Svetashev, V.I.; Rodkina, S.A. Differences in lipid class and fatty acid composition between wild and cultured sea cucumbers, Apostichopus japonicus, explain modification and deposition of lipids. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostetsky, E.Y.; Velansky, P.V.; Sanina, N.M. Phospholipids of the organs and tissues of echinoderms and tunicates from Peter the great bay (Sea of Japan). Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2012, 38, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostetsky, E.Y.; Sanina, N.M.; Velansky, P.V. The thermotropic behavior and major molecular species composition of the phospholipids of echinoderms. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2014, 40, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cong, P.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. Characterizing the phospholipid composition of six edible sea cucumbers by NPLC-Triple TOF-MS/MS. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 94, 103626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Duan, J.; Xue, C.; Feng, T.; Dong, P.; Sugawara, T.; Hirata, T. Analysis and comparison of glucocerebroside species from three edible sea cucumbers using liquid chromatography ion trap time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12246–12253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Cong, P.; Wang, Y.; Sugawara, T.; Xue, C.; Xu, J. High throughput analysis of cerebrosides from the sea cucumber Pearsonothria graeffei by liquid chromatography—Quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Oleo Sci. 2015, 64, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Song, Y.; Tao, S.; Cong, P.; Wang, X.; Xue, C.; Xu, J. Structure of sphingolipids from sea cucumber Cucumaria frondosa and structure-specific cytotoxicity against human HepG2 cells. Lipids 2016, 51, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Kanie, Y.; Kanie, O.; Shimizu, Y. A unique structural distribution pattern discovered for the cerebrosides from starfish Asterias amurensis. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 473, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Cong, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xue, C.; Xu, J. Characterizing gangliosides in six sea cucumber species by HILIC–ESI-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbs, A.B.; Ermolenko, E.V.; Grigorchuk, V.P.; Sikorskaya, T.V.; Velansky, P.V. Current progress in lipidomics of marine invertebrates. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degroote, S.; Wolthoorn, J.; Vanmeer, G. The cell biology of glycosphingolipids. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 15, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennekes, T.; Van Den Berg, R.J.B.H.N.; Boot, R.G.; Van Der Marel, G.A.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Aerts, J.M.F.G. Glycosphingolipids-Nature, function, and pharmacological modulation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 8848–8869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidhar, P.; Radhika, P.; Krishna, N.; Rao, D.V.; Rao, C.B. Sphingolipids from marine organisms: A review. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2003, 9, 117–142. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Feng, T.Y.; Zhang, B.; Sugawara, T.; Xue, C.H. Isolation and anti-fatty liver activity of a novel cerebroside from the sea cucumber Acaudina molpadioides. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Li, Z.J.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.F.; Xue, Y.; Xue, C.H.; Takahashi, K.; Wang, Y.M. The anti-tumor activities of cerebrosides derived from sea cucumber Acaudina molpadioides and starfish Asterias amurensis in vitro and in vivo. J. Oleo Sci. 2012, 61, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, T.; Zaima, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Sakai, S.; Noguchi, R.; Hirata, T. Isolation of sphingoid bases of sea cucumber cerebrosides and their cytotoxicity against human colon cancer cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2906–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawatake, S.; Nakamura, K.; Inagaki, M.; Higuchi, R. Isolation and structure determination of six glucocerebrosides from the starfish Luidia maculata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Sasaki, K.; Harada, Y.; Isobe, R.; Higuchi, R. Constituents of Holothuroidea, 12. Isolation and structure of glucocerebrosides from the sea cucumber Holothuria pervicax. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamada, K.; Hara, E.; Miyamoto, T.; Higuchi, R.; Isobe, R.; Honda, S. Isolation and structure of biologically active glycosphingolipids from the sea cucumber Cucumaria echinata. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 1998, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Wakabayashi, M.; Nagaregawa, Y.; Inagaki, M.; Higuchi, R.; Iha, M.; Teruya, K. Biologically active glycosides from Asteroidea, 40 two new gangliosides, acanthagangliosides I and J from the starfish Acanthaster planci. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 2000, 2295–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisu, E.; Flangea, C.; Serb, A.; Rizzi, A.; Zamfir, A.D. High-performance separation techniques hyphenated to mass spectrometry for ganglioside analysis. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 1591–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, T.; Aida, K.; Duan, J.; Hirata, T. Analysis of glucosylceramides from various sources by liquid chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry. J. Oleo Sci. 2010, 59, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhameed, R.F.A.; Eltamany, E.E.; Hal, D.M.; Ibrahim, A.K.; AboulMagd, A.M.; Al-Warhi, T.; Youssif, K.A.; Abd El-Kader, A.M.; Hassanean, H.A.; Fayez, S.; et al. New cytotoxic cerebrosides from the red sea cucumber Holothuria spinifera supported by in-silico studies. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darya, M.; Sajjadi, M.M.; Yousefzadi, M.; Sourinejad, I.; Zarei, M. Antifouling and antibacterial activities of bioactive extracts from different organs of the sea cucumber Holothuria leucospilota. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2020, 74, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drazen, J.C.; Phleger, C.F.; Guest, M.A.; Nichols, P.D. Lipid, sterols and fatty acid composition of abyssal holothurians and ophiuroids from the North-East Pacific Ocean: Food web implications. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 151, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, J.; Wright, A.D.; Burns, K.; De Nys, R. Chemical antifouling defences of sea stars: Effects of the natural products hexadecanoic acid, cholesterol, lathosterol and sitosterol. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 385, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.M.; Vinholes, J.; De Pinho, P.G.; Valentão, P.; Mouga, T.; Teixeira, N.; Andrade, P.B. A gas chromatography-mass spectrometry multi-target method for the simultaneous analysis of three classes of metabolites in marine organisms. Talanta 2012, 100, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Torres, V.; Rodríguez-Pérez, C.; Herranz-López, M.; Martín-García, B.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Arráez-Román, D.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Micol, V. Marine invertebrate extracts induce colon cancer cell death via ros-mediated dna oxidative damage and mitochondrial impairment. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telahigue, K.; Ghali, R.; Nouiri, E.; Labidi, A.; Hajji, T. Antibacterial activities and bioactive compounds of the ethyl acetate extract of the sea cucumber Holothuria forskali from Tunisian coasts. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2020, 100, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharenko, A.; Romanchenko, D.; Thinh, P.D.; Pikula, K.; Thuy Hang, C.T.; Yuan, W.; Xia, X.; Chaika, V.; Chernyshev, V.; Zakharenko, S.; et al. Features and advantages of supercritical CO2 extraction of sea cucumber Cucumaria frondosa japonica Semper, 1868. Molecules 2020, 25, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.M.; Han, L.W.; Zhang, S.S.; Li, X.B.; He, Q.X.; Han, J.; Wang, X.M.; Liu, K.C. Targeted discovery and identification of novel nucleoside biomarkers in Apostichopus japonicus viscera using metabonomics. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2019, 38, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Geng, Y.F.; Qin, L.; Dong, X.P.; Xu, X.B.; Du, M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Thornton, M.; Yang, J.F.; Dong, L. Characterization of volatile compounds in different dried sea cucumber cultivars. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Sun, L.; Zhang, L.; Ru, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, H. Metabolome responses of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus to multiple environmental stresses: Heat and hypoxia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, M.; Storey, K.B. Metabolic response of longitudinal muscles to acute hypoxia in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka): A metabolome integrated analysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2019, 29, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, J.; Ru, X.; Cao, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H. Differences in feeding, intestinal mass and metabolites between a thermotolerant strain and common Apostichopus japonicus under high summer temperature. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Z.; Huang, R.; Tran, N.T.; Wu, J.; Yang, F.; Ge, H.; Zhong, C.; Sun, Q.; et al. Transcriptome and metabolome analyses of sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus in Southern China during the summer aestivation period. J. Ocean Univ. China 2021, 20, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, B.; Sun, Y.; Chang, Y.; Ding, J. Metabolomics analysis for skin ulceration syndrome of Apostichopus japonicus based on UPLC/Q-TOF MS. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Han, L.; Gao, C.; Chang, Y.; Ding, J. UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-based metabonomics study on Apostichopus japonicus in various aquaculture models. Aquac. Res. 2021, 53, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, S.; Chen, Z.; Dong, Y.; He, P.; Wang, B.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; Guan, X.; et al. Divergent metabolic responses to sex and reproduction in the sea cucumber Apostichopus Japonicus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 39, 100845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, H. Reproduction affects locomotor behaviour and muscle physiology in the sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus. Anim. Behav. 2017, 133, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. Comparative metabolomic analysis of the body wall from four varieties of the sea cucumber Apostichopus Japonicus. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Sun, J.; Yang, H. Metabolomic analysis of white, green and purple morphs of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus during body color pigmentation process. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 39, 100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Zhao, W.; Han, L.; Ding, J.; Chang, Y. Metabolomics analysis of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) in different geographical origins using UPLC–Q-TOF/MS. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Yang, H.; Brinkman, R. The effect of melatonin on locomotor behavior and muscle physiology in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Zhang, L.; Fan, X.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, H. The effect of pedal peptide-type neuropeptide on locomotor behavior and muscle physiology in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 559348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popov, R.S.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S. Application of MS-Based Metabolomic Approaches in Analysis of Starfish and Sea Cucumber Bioactive Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050320
Popov RS, Ivanchina NV, Dmitrenok PS. Application of MS-Based Metabolomic Approaches in Analysis of Starfish and Sea Cucumber Bioactive Compounds. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(5):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050320
Chicago/Turabian StylePopov, Roman S., Natalia V. Ivanchina, and Pavel S. Dmitrenok. 2022. "Application of MS-Based Metabolomic Approaches in Analysis of Starfish and Sea Cucumber Bioactive Compounds" Marine Drugs 20, no. 5: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050320
APA StylePopov, R. S., Ivanchina, N. V., & Dmitrenok, P. S. (2022). Application of MS-Based Metabolomic Approaches in Analysis of Starfish and Sea Cucumber Bioactive Compounds. Marine Drugs, 20(5), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050320








