Abstract
α-Amylase inhibitors (aAIs) have been applied for the efficient management of type 2 diabetes. The aim of this study was to search for potential aAIs produced by microbial fermentation. Among various bacterial strains, Pseudomonas aeruginosa TUN03 was found to be a potential aAI-producing strain, and shrimp heads powder (SHP) was screened as the most suitable C/N source for fermentation. P. aeruginosa TUN03 exhibited the highest aAIs productivity (3100 U/mL) in the medium containing 1.5% SHP with an initial pH of 7–7.5, and fermentation was performed at 27.5 °C for two days. Further, aAI compounds were investigated for scaled-up production in a 14 L-bioreactor system. The results revealed a high yield (4200 U/mL) in a much shorter fermentation time (12 h) compared to fermentation in flasks. Bioactivity-guided purification resulted in the isolation of one major target compound, identified as hemi-pyocyanin (HPC) via gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance. Its purity was analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography. HPC demonstrated potent α-amylase inhibitory activity comparable to that of acarbose, a commercial antidiabetic drug. Notably, HPC was determined as a new aAI. The docking study indicated that HPC inhibits α-amylase by binding to amino acid Arg421 at the biding site on enzyme α-amylase with good binding energy (−9.3 kcal/mol) and creating two linkages of H-acceptors.
1. Introduction
The fishery processing industry has been producing increasingly large amounts of byproducts, with the globally reported accessible waste of 27.85 million tons per year [1]. Among various fishery wastes, marine chitinous wastes (MCWs) including crab shells, squid pens, shrimp shells, and shrimp heads are abundantly available as fishery byproducts. Recently, these materials have been extensively used for the extraction and bioproduction of many active compounds [2]. MCWs have been utilized as carbon/nitrogen (C/N) sources for fermentation to produce various added valuable compounds such as enzymes, exopolysaccharide, chitosan oligomer, and N-acetyl-d-glucosamine [3,4], antioxidant, anti-NO, and anti-cancer compounds [5,6,7], biofertilizers [8], insecticidal materials [9], dye, and biosorbents [10]. MCWs have also been used for the extraction of astaxanthin, β-carotene esters, and essential amino acids [11,12]. Recently, MCWs were extensively used for the bioproduction of α-glucosidase inhibitors. In this work, MCWs were investigated for the production of α-amylase inhibitors (aAIs; anti-diabetic compounds) via microbial fermentation.
Diabetes mellitus is a global health issue that significantly reduces the quality of life and health of people [13]. Among the two major types of diabetes mellitus, type 2 (T2D) accounts for 90% of diabetic cases [14]. In recent years, natural carbohydrate digestive enzyme inhibitors (CDEIs), including α-glucosidase inhibitors and aAIs, have been proved as a potentially effective therapy for the management of T2D [15,16,17,18]. Though some commercial inhibitors such as acarbose, voglibose, and miglitol are available, the use of these commercial drugs may cause some side effects; thus, the investigation of natural sources of inhibitors with improved safety is required [18].
CDEIs may be obtained from various natural sources including medicinal plants [16,18,19,20,21]. However, herbal CDEIs are difficult to obtain in large amounts [22,23,24]. Microbial fermentation is another approach to produce natural compounds including CDEIs [2,3,5,17,22]. In our previous works, we reported the production and purification of α-glucosidase inhibitors from microbes [17,24] and extensively used MCWs as C/N sources for the production of α-glucosidase inhibitors via fermentation [7,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. Given our past research on recycling organic wastes into value-added anti-diabetic compounds, in this study, we investigated the use of CDEIs for the cost-effective production of aAIs via microbial fermentation. The production of aAIs was further scaled up in a 14 L-bioreactor system, and the major active compounds were isolated and identified. Then, a docking study was performed to elucidate the interaction of the inhibitor with the target enzyme.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Screening Active α-Amylase Inhibitors Producing Strain
More than 100 bacterial strains obtained from our previous studies were assessed by fermentation to produce aAIs. Of these, the supernatants of seven strains showed positive anti-α-amylase activity (Table 1), with inhibition values ranging from 47–89%. Three bacterial strains, i.e., Bacillus cereus RB.DS.05, Pseudomonas aeruginosa TUN03, and B. atrophaeus H10, demonstrated the highest inhibition values (approximately 90%). For further confirmation of the results, the activities of the supernatants were tested at various dilutions and expressed as productivity (U/mL). P. aeruginosa TUN03 indicated the highest activity in the supernatant, with a productivity of 2430 U/mL. Thus, this strain was chosen for further investigation.

Table 1.
The α-amylase inhibitory activity of tested bacterial strains.
The use of Pseudomonas aeruginosa has been reported in agriculture [32,33,34,35], environment management [36,37], and for the production of secondary metabolites such as rhamnolipid, vanillin, enzymes, pigments, and plant promoting compounds with a wide range of applications [38,39,40,41,42,43]. Based on our recent review of published studies, there is no report on the use of this genus for the production of aAIs via fermentation. Thus, the finding of α-amylase inhibitory activity in this strain enriches the bioactivity catalog of P. aeruginosa.
2.2. Production of α-Amylase Inhibitors via P. aeruginosa TUN03 Fermentation
To establish the fermentation process to produce aAIs with optimal productivity, some factors, including the effect of C/N sources and culture conditions, were examined. Then, aAIs were scaled-up for production in a 14 L-bioreactor system.
2.2.1. The Effect of C/N Sources on aAI Production by P. aeruginosa TUN03
Various marine chitinous materials such as squid pen powder (SPP), shrimp head powder (SHP), demineralized shrimp shell powder (de-SSP), demineralized crab shell powder (de-CSP), and a commercial medium nutrient broth (NB) were used as the sole C/N source of P. aeruginosa TUN03 for fermentation and comparison of aAI production. As shown in Figure 1a, the medium containing SHP, SPP, and NB showed the highest activity on day 2 of fermentation, with respective inhibition values of 88, 85, and 72%. For better clarity of the results, the activity was also calculated and expressed as productivity (U/mL). The result presented in Figure 1b indicates that SHP was the most suitable C/N source and provided the highest productivity (2448 U/mL). Therefore, this substrate was chosen for the cost-effective production of aAIs in further experiments. Bacterial growth was also assessed but showed no correlation with aAI production (data not shown); thus, this factor was also not taken into account in the subsequent experiments. Shrimp industrial waste has been used for the production of chitin, protein, carotenoids, dye adsorbents, enzymes, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitor compounds [2,44,45,46]. Shrimp head is also used as fish meal [47,48]. Recently, shrimp head was extensively investigated as a C/N source for the production of α-glucosidase inhibitors [29,30,31]. In contrast to previous studies, in this work, we highlight the novel and potential use of this low-cost material as the sole C/N source for the production of aAIs via microbial fermentation.
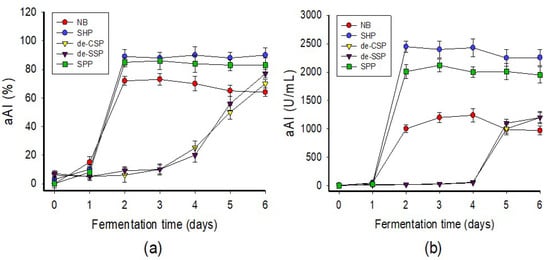
Figure 1.
Screening of suitable C/N sources for fermentation. The C/N sources were used at 1% in fermentation at 30 °C, 150 rpm (shaking speed) for six days. The α-amylase inhibitory activity of the fermented culture broth was tested daily and expressed as % (a) or U/mL (b).
2.2.2. The Effect of Culture Conditions on aAI Production by P. aeruginosa TUN03
To enhance aAI productivity, some culture conditions such as concentration of SHP, culture temperature, initial pH of the culture medium, and cultivation medium volume were investigated for their effect on aAI production by P. aeruginosa TUN03 fermentation (Figure 2). As presented in Figure 2a, suitable concentrations of SHP were determined to be 1.5–2%. In the interest of saving input material, 1.5% SHP was chosen for the next experiments. The data in Figure 2b indicate that P. aeruginosa TUN03 provided the highest aAI yield (2785–2850 U/mL) with a cultivation temperature in the range of 27.5–32.5 °C. As such, 27.5 °C was set as the optimum cultivation temperature in order to minimize energy consumption. P. aeruginosa TUN03 was found to produce considerable amounts of aAIs with the initial pH of the culture medium of 7–7.5 (Figure 2c). The initial pH of the culture medium was applied for further investigations of cultivation medium volume. The result in Figure 2d shows the aAI production by P. aeruginosa TUN03 on a small scale (20–30 mL of medium in a 100 mL flask). Overall, P. aeruginosa TUN03 achieved the highest productivity of aAIs when a 30 mL medium containing 1.5% SHP was used with an initial pH of 7–7.75 in a 100 mL–flask and fermented at 27.5 °C for two days.
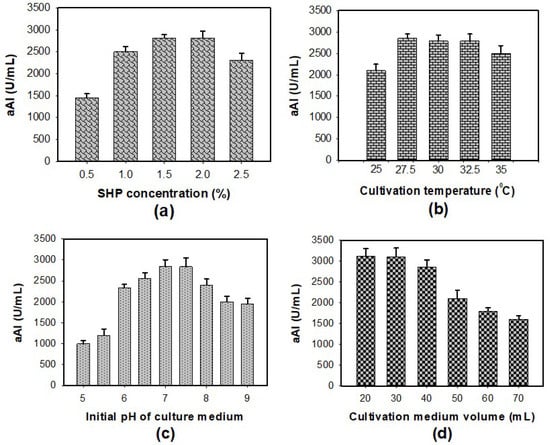
Figure 2.
The effect of SHP concentration (a), cultivation temperature (b), initial pH of the culture medium (c), and cultivation medium volume (d) on aAI productivity in P. aeruginosa TUN03 fermentation.
2.2.3. Scaled-Up of Production of α-Amylase Inhibitors Using a 14 L-Bioreactor System
In microbial technology, reactor systems are considered strong tools for scaling-up the bioproduction of active secondary metabolites and significantly reducing cultivation time [2,49,50]. In this work, we utilized a 14 L-bioreactor system for fermentation to scale up the production of aAIs. As shown in Figure 3, aAIs were produced after 4 h of fermentation and reached the highest productivity, i.e., 4200 U/mL, at 12 h. These experimental data indicated that the scale-up in a bioreactor system yields significantly higher aAI productivity in a much shorter fermentation time than that in a flask. Previously, several studies reported the production of antidiabetic compounds via microbial fermentation [26,27,28,29,30,31]. However, in most of these works, compounds were produced on small scales in flasks. In this work, we attempted the large-scale production of antidiabetic compounds in a 14 L-bioreactor system and achieved positive outcomes.
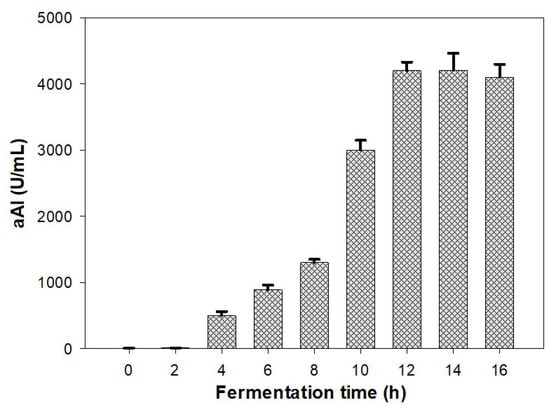
Figure 3.
Scaled-up production of aAIs in a 14 L-bioreactor system. Standard errors (SE) are shown as error bars.
2.3. Determination and Isolation of Major Active Compound from the Culture Broth
Phenazine compounds are produced in significant quantities by P. aeruginosa. Thus, these compounds may play an important role in the bioactivities of P. aeruginosa. We found that the density of these pigments seemed to increase along with aAI production during P. aeruginosa TUN03 fermentation. On the other hand, earlier studies reported microbial aAIs as proteins [51,52]. Thus, to quickly predict the most active component, the supernatant was used to prepare some samples, including the crude pigment phenazines (the chloroform layer, named CPP), the residue water layer (named RWL), the crude protein (the supernatant was precipitated by ethanol, named CP) and the crude sample (the supernatant was vaporized to dried powder, named CS) to evaluate the inhibitory activity of α-amylase. The processes of preparation, purification, and identification of the target compounds are summarized in Figure 4.
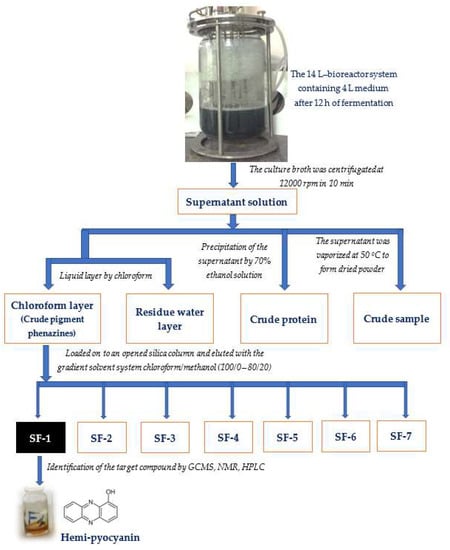
Figure 4.
The process of preparation, purification, and identification of target compounds (α-amylase inhibitors).
As shown in Figure 5a, the protein potion and the residue water layer showed no activity, while the pigment phenazines displayed high levels of activity, with a maximum inhibition of 89% (at a concentration of 1 mg/mL), which is much higher than that of a crude sample with maximum inhibition of 88% (at a concentration of 4 mg/mL). The results indicated that pigment phenazines were the major α-amylase inhibitor compounds in the sample. Thus, this portion with pigments was further separated using an opened silica column, and seven sub-fractions (SF-1, SF-2, SF-3, SF-4, SF-5, SF-6, and SF-7) were obtained. Then, the activity of these substrates was tested, and is presented in Figure 5b. The component SF-1 was found to exhibit the strongest activity (91%), while components SF-2, SF-3, and SF-4 displayed inhibition values under 26%, and SF-6 and SF-7 demonstrated very weak activity. The active phenazine compound SF-1 obtained in the yellow form was identified based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GCMS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR, including 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, DEPT 135, DEPT 90, and DEPT 45) analyses; the spectra are presented in the Supplementary Materials, Figures S1–S6. This compound was further confirmed to possess the high level of purity achieved using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) profiles (Figure 6).
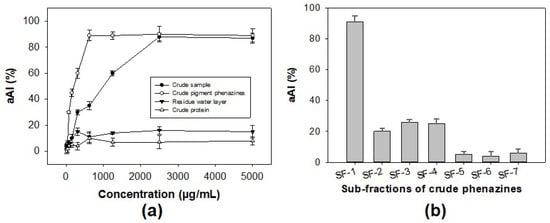
Figure 5.
The bioactivity-guided purification process of α-amylase inhibitor compound. The α-amylase inhibitory activity of some major portions extracted from a crude sample tested at various concentrations (a) and sub-fractions of the crude pigment phenazine portion tested at a concentration of 150 µg/mL (b).
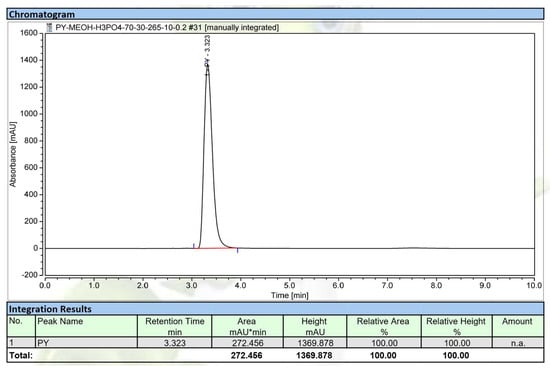
Figure 6.
The HPLC profile of the purified compound, hemi-pyocyanin. The UV detection wavelength was 292 nm.
As shown in Figure S1A, a major peak appeared with a retention time of 13.09 in the GC profile of the purified component SF-1. For further analysis, the mass of this peak was compared to those of known compounds in the chemical bank of the GCMS system (Figure S1B). On this basis, it was assumed that this compound was hydroxyphenazine, with the chemical formula C12H8N2O. The chemical structure of this compound was further identified based on an analysis of its NMR spectrum. Compound SF-1 was obtained as a yellow amorphous powder. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 8.25 (1H, m) δH: 8.21–8.25 (2H, m), δH: 7.76–7.89 (4H, m), δH: 7.24–7.26 (1H, m) (Figure S2). 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 151.7, 144.3, 144.5, 141.2, 134.7, 131.9, 130.8, 130.5, 129.7, 129.2, 119.9 and 108.9 (see Figure S3).
The 1H-NMR chemical shift of SF-1 indicated that 8 H atoms with δH from 7.0 to 8.5 ppm should be in the aromatic rings. Of these, the H with δH: 8.25 should be assigned to be the H atom of the hydroxyl group, while the other seven H atoms should be located in aromatic rings at 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9 with δH: 8.21–8.25 (2H, m), δH: 7.76–7.89 (4H, m), δH: 7.24–7.26 (1H, m), respectively.
The 13C-NMR of SF-1 provided the signals of 12 C. Of these, the C atom (δC: 151.7) was assigned to the C of hydroxyl group (C-OH) in the aromatic rings, while other C atoms were assigned to aromatic rings at 2, 3, 4, 4a, 5a, 6, 7, 8, 9, 9a, 10a with δC: 144.3, 144.5, 141.2, 134.7, 131.9, 130.8, 130.5, 129.7, 129.2, 119.9 and 108.9, respectively. In addition, the 13C-NMR chemical shift coupling with spectra of DEPT 135, DEPT 90, and DEPT 45 (Figures S4–S6) also indicated that this compound contained seven groups of CH and 5 C. These observations allowed us to identify this compound as hemi-pyocyanin (also known as 1-hydroxyphenazine); the NMR spectra of this compound corresponded to that of 1-hydrophenazine, identified in an earlier report [53].
To check the purity grade of the isolated compound, HPLC was performed, and the purified HPC (SF-1) also appeared as a clear single peak (Figure 6). The purity of the obtained peak (HPC) was found to be 100% and 97.8% by HPLC using a UV detector and GCMS using an MS detector (ITQ 900), respectively. These results confirmed the high purity of the HPC. This compound was then further tested in detail for aAI activity (Figure 7). For comparison, this active compound and acarbose were tested at various concentrations. HPC showed potential α-amylase inhibition with maximum inhibition and IC50 values of 92.2% and 3.1 µg/mL, respectively (Figure 7). The activity of this compound was comparable to that of acarbose, a commercial antidiabetic drug with maximum inhibition and IC50 values of 91% and 4.2 µg/mL, respectively. It has been reported that HPC has potential medicinal effects, such as anti-cancer activity against cell lines 1321N1 and A549 [54,55], antibacterial activity against human pathogenic bacterial strains Candida albicans, Aspergillus fumigatus, Escherichia coli, Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria [55,56,57], and anti-inflammatory activities [58]. HPC has also reportedly been used in agriculture against various fungal and bacterial strains [53,59]. However, to the best of our knowledge and as per our review of the literature, no report has been published to date on the α-amylase inhibitory activity of HPC. Thus, the new finding in this work may facilitate the novel use of HPC in medicines.
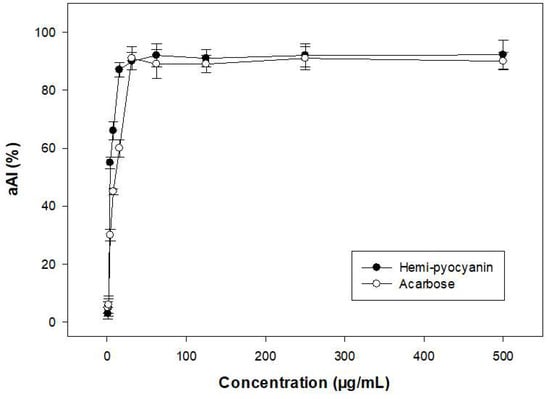
Figure 7.
α-amylase inhibitory activity of purified hemi-pyocyanin and acarbose.
Post-prandial hyperglycemia has been recognized as playing important role in the development of T2D, i.e., by controlling the levels of plasma glucose required to delay or prevent T2D [60]. The compound has been suggested as a safe and complementary treatment for T2D. The inhibition of glycosidase with, for example, a-amylase and a-glucosidase, which convert dietary starch into glucose, has been considered a method for controlling plasma glucose [61,62]. It is reported that the a-(1,4)-glycosidic linkages of starch are degraded by α-amylase to produce maltose and glucose; then, maltose molecules are further hydrolyzed to glucose by α-glucosidase before entering the blood via intestinal epithelial absorption. Therapy using glycosidase inhibitors was considered a more effective method than controlling insulin secretion for convenience and economic reasons, as well as the reduced side-effects [63]. In addition, aAIs are known to prevent dietary starches from being absorbed by the human body by acting as starch blockers. As such, they have also been used as slimming pills [64]. In this study, HPC demonstrated novel potential inhibition against a mammalian α-amylase with a comparable effect to that of acarbose, a commercial antidiabetic drug. Thus, HPC could be a good candidate for the management of T2D and obesity.
2.4. Docking Study Showing the Interaction of Hemi-Pyocyanin at the Binding Site of α-Amylase
A docking study was performed to explore the interactions of ligands (HPC and acarbose) and the target enzyme α-amylase. Before examining docking, the structures of ligands and a protein enzyme were prepared using ChemBioOffice 2018 and MOE-2015.10 software. The molecular structures are shown in Figure 8.
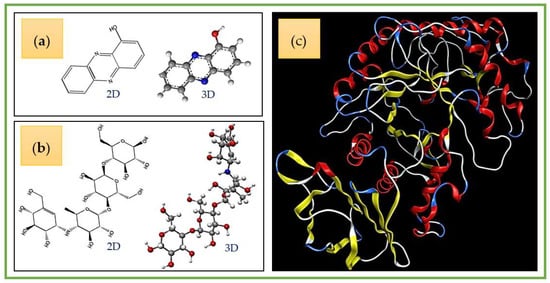
Figure 8.
The 2-D and 3-D structures of hemi-pyocyanin (a) and acarbose (b), and the crystal structure of α-amylase (c).
The active zones of the ligands on the target protein were determined using the site finder function in MOE. The output data of MOE indicated that there are active zones (AZ-1, AZ-2, AZ-3, and AZ-4) of the ligands on the enzyme α-amylase (Figure 9). Of these, the HPC inhibitor was found to be the most active in zone AZ-2, while acarbose demonstrated potential inhibition against α-amylase in active zone AZ-1. AZ-1 contains up to 36 amino acids (Val49, Val50, Val51, Thr52, Asn53, Trp58, Trp59, Tyr62, Gln63, His101, Gly104, Ser105, Gly106, Ala107, Ala108, Tyr151, Leu162, Val163, Gly164, Leu165, Arg195, Asp197, Ala198, Lys200, His201, Glu233, Val234, Ile235, Glu240, His299, Asp300, Arg303, Gly304, His305, Gly306 and Asp356), while AZ-2 contains up to 28 (Ala3, Pro4, Gln5, Thr6, Gln7, Ser8, Gly9, Arg10, Thr11, Arg92, Trp221, Phe222, Pro223, Arg252, Ser289, Asp290, Pro332, Tyr333, Gly334, Phe335, Thr336, Arg398, Val401, Asp402, Gly403, Gln404, Pro405 and Arg421). Thus, these active zones were chosen to assess the docking performance of acarbose and hemi-pyocyanin, respectively.
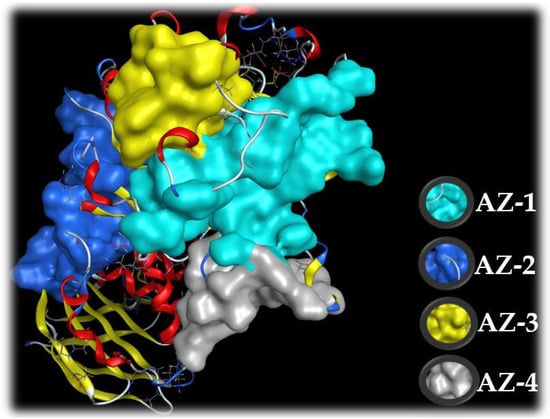
Figure 9.
The four active zones (AZ) on the target enzyme, α-amylase, based on MOE output data using the site finder function.
In the docking simulation, the Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD) value was used to define whether the interactions between the ligand and the target protein enzyme were accepted or not. When RMSD reached a value higher than 3.0 Å, the interaction was considered as non-significant. Interaction is widely accepted when this value is under 2.0 Å [65]. As shown in Table 2, both HPC and acarbose are bound with α-amylase with RMSD values of 1.68 and 1.59, respectively, indicating that these two ligands successfully bound to the target enzyme. To evaluate the potential inhibition of the ligands toward the target enzyme, a docking score (DS) was used. A ligand is defined as a potent inhibitor when it has a binding energy value of under −3.20 kcal/mol [66]. In this work, HPC and acarbose were found to bind with α-amylase to generate DS values of −9.3 and −12.1 kcal/mol, respectively, which are much lower than −3.20 kcal/mol. Thus, this result confirmed that both these compounds are potential α-amylase inhibitors.

Table 2.
Docking simulation results of ligands binding with target enzyme α-amylase (aA).
Simultaneous interactions of ligands with the target enzyme were examined; the details are presented in Figure 10. HPC interacts with α-amylase at active zone AZ-2 via the creation of two linked H-acceptors with amino acid Arg421. These two linkages are formed by the connection of the receptor group –NH2 of Arg421 to O1 and N2 of HPC with a distance and energy binding of 3.20 Å, −0.7 kcal/mol, and 3.1 Å, −1.7 kcal/mol, respectively. Acarbose was found to bind at active zone AZ-1 on α-amylase via the formation of four linkages, including one H-donor and three H-acceptor linkages. Asp300 and Gln63 in the active zone were found to connect with O6 and O10 of acarbose to form one linkage H-donor and one linkage H-acceptor with distances and energy binding of 2.65 Å, −2.8 kcal/mol, and 3.05 Å, −1.1 kcal/mol, respectively, while the amino acid Lys200 connected with O8 and O16 of acarbose to generate two H-acceptor linkages with a distance and energy binding of 3.37 Å, −1.9 kcal/mol, and 3.04 Å, −2.1 kcal/mol, respectively.
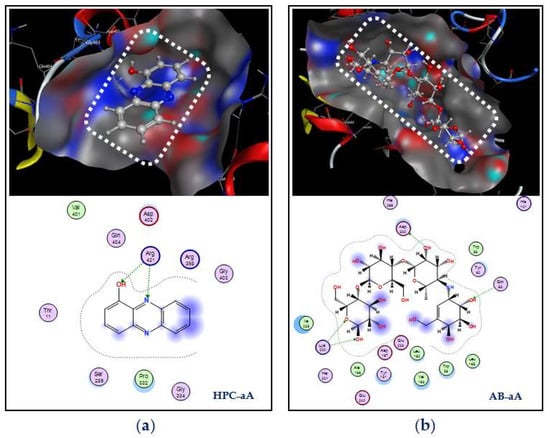
Figure 10.
Docking study of hemi-pyocyanin (HPC) and acarbose with the α-amylase enzyme. The interactions and binding of the ligands HPC and acarbose with the α-amylase enzyme are labeled as HPC–aA (a) and AB–aA (b), respectively.
Based on the in vitro activity and a docking study on the inhibition against α-amylase, the biosynthesized and purified HPC was shown to be a potential α-amylase inhibitor with activity comparable to that of acarbose. As such it may be recommended as a potent candidate antidiabetic drug. However, further studies using various animal models and clinical studies are required for the development of this potential compound into an antidiabetic drug.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Bacterial strains were obtained from our previous works [43,67]. Discarded marine chitinous materials such as shrimp shells, shrimp heads, crab shells, and squid pens were obtained from Shin-Ma Frozen Food Co. (I-Lan, Taiwan). Porcine pancreatic α-amylase (type VI-B) and acarbose were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis City, MO, USA). Shrimp shells and crab shells were demineralized as per the method presented in our previous study [68]. Silica gel (Geduran® Si 60, size: 0.040–0.063 mm) was purchased from Merck Sigma Chemical Co (St. Louis City, MO, USA). The nutrient broth was purchased from Creative Life Science Co., Taipei, Taiwan, and some solvents used in this work were obtained from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis City, MO, USA).
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. α-Amylase Inhibitor Production via Microbial Fermentation Experiments
Screening of Active α-Amylase Inhibitors Produced from Discarded Marine Chitinous Material Which Was Suitable for Fermentation
The bacterial strains were obtained as in our previous works, and were examined for use in the fermentation of SHP. A liquid medium of 30 mL (initial pH 6.8) containing 1% SHP, 0.1% K2HPO4, and 0.05% MgSO4·7H2O in a 100 mL-Erlenmeyer flask was fermented using different strains at 30 °C with a shaking speed of 150 rpm for four days. Then, the supernatant was harvested by centrifugation at 12000 rpm for 10 min and used to detect the inhibitory activity of α-amylase. The most active strain, P. aeruginosa TUN03, was used for further experiments to screen the most suitable C/N sources. A total of four marine chitinous discards, i.e., SPP, SHP, de-SSP, and de-CSP, and a commercial medium nutrient broth (NB) were used as the sole C/N sources. These C/N sources were used at 1% concentrations in a basal salt medium of 0.1% K2HPO4 and 0.05% MgSO4·7H2O. Fermentation was performed at 30 °C with a shaking speed of 150 rpm for six days. The supernatant was harvested on a daily basis and used for the detection of activity. SHP was found to be the most suitable material for fermentation and was used for our subsequent investigation.
The Effect of Culture Conditions on aAI Production by P. aeruginosa TUN03
To achieve higher aAI productivity, some culture conditions were tested. A 30 mL liquid medium in a 100 mL-Erlenmeyer flask containing different concentrations of SHP (0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, and 2.5%), 0.1% K2HPO4, and 0.05% MgSO4·7H2O was fermented by P.s aeruginosa TUN03 at 30 °C with a shaking speed of 150 rpm. The activity of the supernatant was tested after two days of fermentation. SHP (1.5%) was chosen for further experimentation to investigate the effect of culture temperature (25, 27.5, 30, 32.5, and 35 °C), the initial pH of the culture medium (5, 5.5, 6, 6.5, 7, 7.5, 8, 8.5, and 9), and cultivation medium volume (20, 30, 40, 50, 60, and 70 mL). The following experiments were designed based on the optimal conditions achieved in previous experiments.
Scale-Up of Production of α-Amylase Inhibitors Using a 14 L-bioreactor System
The optimal culture conditions investigated in the aforementioned experiments were applied to scale up the production of aAIs in a 14 L-bioreactor system (the 14 L BioFlo/CelliGen 115 bioreactor system—Eppendorf North America, Enfield, Connecticut, CT, USA). First, 500 mL bacterial seeds were pre-incubated in 250 mL flasks at 30 °C for two days and then transferred to the fermenter with 4.5 L of medium containing 1.5% SHP, 0.1% K2HPO4 and 0.05% MgSO4·7H2O, with an initial pH of 7. Fermentation was performed at 2.75 °C at a shaking speed of 150 rpm, with a dissolved oxygen content of 1.0 vvm for 16 h. Sampling was done every 2 h. The supernatant was harvested by centrifugation of the sample at 12,000 rpm for 10 min, and was used to detect aAI activity.
3.2.2. α-Amylase Inhibitory Activity Assay
The inhibitory activity of α-amylase was assessed using the method of Bernfeld [69] with modifications. One hundred and fifty microliters of the α-amylase solution (0.25 U/mL) was mixed with 50 µL sample (supernatants or compounds at different concentrations) and kept at 37 °C for 10 min. Then, 200 µL soluble starch (0.25%) was added to start the reaction, which was kept at 37 °C for a further 20 min. The amount of reducing sugar produced by the action of the enzyme was measured at OD540nm. The enzymatic inhibitory activity was estimated using the following equation:
where E is the optical density of the reaction containing the sample (inhibitor) and enzyme, and C is the optical density of the reaction containing enzyme and the same volume of distilled water instead of the sample [70]. The IC50 (µg/mL) and productivity (U/mL) were defined and calculated using the method presented by Nguyen et al. (2016) [71]. In this assay, the enzyme (0.25 U/mL) and substrate (0.25 % w/v) were both prepared in 10 mM CaCl2 solution in 20 mM Tris–HCl buffer at pH 7 before use.
α-amylase inhibitory activity (%) = (C − E)/C × 100
3.2.3. Extraction, Identification and Purity Confirmation of α-Amylase Inhibitors
Extraction of α-amylase inhibitors: The culture broth obtained from the fermentation in the 14 L-bioreactor system was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 10 min to harvest the supernatant, which was further used to prepare some of the samples. The supernatant was separated from the chloroform layer to obtain the crude pigment phenazines (in the chloroform layer) and the residue water layer. The crude protein contained in the supernatant was obtained by precipitation with 70% ethanol solution. The supernatant was also vaporized at 50 °C to dried powder (crude sample). The crude pigment phenazines exhibited the most activity and were therefore further used to isolate the target components using an opened silica column (Geduran® Si 60, size: 0.040–0.063 mm, 30 × 2 cm) with a gradient solvent system, i.e., chloroform/methanol (100/0—80/20), to obtain seven sub-fractions: SF-1, SF-2, and SF-3, (eluted in chloroform/methanol of 100/0), SF-4 (eluted in chloroform/methanol of 100/5), SF-5 and SF-6 (eluted in chloroform/methanol of 100/10), and SF-7 (eluted in chloroform/methanol of 100/20). Component SF-1 was found to be active, and was identified using GCMS and NMR. Its purity was further confirmed by HPLC analysis.
Identification of α-amylase inhibitors: GCMS was conducted to test the presence of active phenazine compounds. Helium gas (99.999%) was used as a carrier gas at a constant flow rate of 1 mL/min, and 1 μL of an injection volume was employed (a split ratio of 10:1). The injector temperature was maintained at 250 °C, the ion-source temperature was 250 °C and the oven temperature was programmed to 70 °C (isothermal for 1 min), with an increase of 15 °C/min to 200 °C, ending with a 2 min isothermal at 200 °C. MS data were acquired at 70 eV, a scanning interval of 0.5 s, and fragments from 50 to 650 Da.
Purity confirmation of α-amylase inhibitors using HPLC: The compound was dissolved in methanol, and then filtered through a 0.22 µm membrane. The sample solution (2 µL) was injected into the HPLC system (Thermo-Ultimate 3000 UPLC system–ThermoScientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and separated by a column (Hypersil GOLD aQ C18 column, 150 mm × 2.1 mm, particle size: 3 µm) using the solvent systems of methanol/acidified 0.1% H3PO4 (70/30 v/v) with the flow rate of 0.2 mL/min. The UV detection wavelength was 265 nm.
3.2.4. Docking Study
A docking study was performed following the steps described in our earlier reports [2,25].
Preparation of the target protein: The structural data of the protein enzyme (α-amylase) were obtained from the Worldwide Protein Data Bank. The 3-D structure was produced using MOE QuickPrep based on the positions of the ligand within 4.5 Å and the presence of important amino acids. The active zones were found using the site finder in MOE, and all of the water molecules were removed before the creation of the enzymic action zones.
Preparation of ligands: The structures (2D and 3D) of HPC and acarbose were prepared using the ChemBioOffice 2018 software, and optimized using the MOE-2015.10 software with parameters of Force field MMFF94x, R-Field 1:80, cutoff, Rigid water molecules, space group p1, cell size 10, 10, 10, cell shape 90, 90, 90, and gradient 0.01 RMS kcal.mol−1A−2.
Docking performance: Docking was performed on the HPC and acarbose ligands toward the target enzyme α-amylase using the MOE-2015.10 software. The output data, including energy biding (docking score, DS), RMSD, linkages types, amino acid compositions, distances, and the energy biding of each linkage, were recorded.
4. Conclusions
α-Amylase inhibitors (aAIs) have been used as an effective therapy for type-2 diabetes, which remains a global health issue. Though some commercial inhibitors are available, these drugs may cause side effects. Thus, the investigation of natural sources of inhibitors which are safe to use is required. The aim of this study was to evaluate the potential aAIs produced by microbial fermentation. P. aeruginosa TUN03 was selected as a potential aAI-producing strain, and SHP was found to be the most suitable C/N source for the production of aAIs via fermentation. In this way, high yields of aAIs were achieved. Further scaled up production of aAIs with higher yields and much shorter fermentation times via the utilization of a 14 L-bioreactor system was also attempted. The bioactivity-guided purification resulted in the isolation of one major active compound. This purified compound was identified as hemi-pyocyanin (HPC). Subsequently, a docking study was conducted to elucidate the interaction of this inhibitor with the target enzyme, α-amylase. This study provides some new findings, as summarized below:
- -
- This study was the first to report on the use of discarded marine chitinous material for the cost-effective production of α-amylase inhibitor compounds via microbial fermentation.
- -
- P. aeruginosa TUN03 was found to be a novel α-amylase inhibitor-producing strain.
- -
- The production of α-amylase inhibitor compounds was successfully scaled up, i.e., in a 14 L-bioreactor system, achieving high productivity (4200 U/mL) in a short fermentation time (12 h).
- -
- Hemi-pyocyanin, a major active compound purified from the culture broth, was identified as a new and potent α-amylase inhibitor.
- -
- In a docking study, hemi-pyocyanin was found to bind to the target enzyme with a good docking score (−9.3 kcal/mol) via linking with amino acid Arg421 and the creation of two H-acceptor linkages.
The results of this work indicate that discarded shrimp heads are a valuable source material for the cost-effective bioproduction of a novel α-amylase inhibitor HPC which may be a good candidate for the development of new antidiabetic drugs. However, further studies using various animal models and clinical studies are required for the development of this compound into an antidiabetic drug.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/md20050283/s1, Figure S1. The gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GCMS) profile of purified compound SF-1. The GC profile (A) and MS profile (B); Figure S2. 1H NMR spectrum of compound SF-1, measured in CDCl3 at 600 MHz; Figure S3. 13C NMR spectrum of compound SF-1, measured in CDCl3 at 151 MHz; Figure S4. DEPT 135 spectrum of compound SF-1, measured in CDCl3 at 151 MHz; Figure S5. DEPT 90 spectrum of compound SF-1, measured in CDCl3 at 151 MHz; Figure S6. DEPT 45 spectrum of compound SF-1, measured in CDCl3 at 151 MHz.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.B.N., T.H.N. and S.-L.W.; methodology V.B.N., S.-L.W., T.H.N. and A.D.N.; software and validation, T.H.N., M.D.D. and V.B.N.; formal analysis, V.B.N., C.T.D., T.N.T., A.D.N. and S.-L.W.; investigation, T.H.N., M.D.D. and V.B.N.; resources, V.B.N.; data curation, A.D.N., S.-L.W. and V.B.N.; writing—original draft preparation, V.B.N.; writing—review and editing, S.-L.W., A.D.N., T.H.N. and V.B.N.; supervision, V.B.N.; visualization and project administration, V.B.N. and S.-L.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a grant from Tay Nguyen University (T2021-52CBTĐ) and supported in part by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (MOST 110-2320-B-032-001; MOST-110-2923-B-032-001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Caruso, G.; Floris, R.; Serangeli, C.; Di Paola, L. Fishery Wastes as a Yet Undiscovered Treasure from the Sea: Biomolecules Sources, Extraction Methods and Valorization. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.-L.; Nguyen, A.D.; Phan, T.Q.; Techato, K.; Pradit, S. Bioproduction of Prodigiosin from Fishery Processing Waste Shrimp Heads and Evaluation of Its Potential Bioactivities. Fishes 2021, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-L.; Liang, T.-W.; Yen, Y.-H. Bioconversion of chitin-containing wastes for the production of enzymes and bioactive materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.; Doan, C.T.; Nguyen, M.T.; Nguyen, V.B.; Vo, T.P.K.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.-L. An Exochitinase with N-Acetyl-β-Glucosaminidase-Like Activity from Shrimp Head Conversion by Streptomyces speibonae and Its Application in Hydrolyzing β-Chitin Powder to Produce N-Acetyl-d-Glucosamine. Polymers 2019, 11, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, D.N.; Wang, S.-L. Microbial Reclamation of Chitin and Protein-Containing Marine By-Products for the Production of Prodigiosin and the Evaluation of Its Bioactivities. Polymers 2020, 12, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.H.; Liang, T.W.; Liu, K.C.; Hsu, Y.W.; Hsu, H.; Wang, S.L. Isolation and identification of a novel antioxidant with antitumor activity from Serratia ureilytica using squid pen as fermentation substrate. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, T.H.; Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Nguyen, A.D.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Wang, S.-L. Production and Bioactivity-Guided Isolation of Antioxidants with α-Glucosidase Inhibitory and Anti-NO Properties from Marine Chitinous Materials. Molecules 2018, 23, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-L.; Huang, T.-Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liang, T.-W.; Yen, Y.-H.; Sakata, Y. Bioconversion of squid pen by Lactobacillus paracasei subsp paracasei TKU010 for the production of proteases and lettuce growth enhancing biofertilizers. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5436–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.-W.; Chen, C.-H.; Wang, S.-L. Production of insecticidal materials from Pseudomonas tamsuii. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2014, 41, 7965–7971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.-W.; Lo, B.-C.; Wang, S.-L. Chitinolytic Bacteria-Assisted Conversion of Squid Pen and Its Effect on Dyes and Pigments Adsorption. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4576–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Brown, J.A. Carotenoid Pigments in Seafoods and Aquaculture. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1998, 38, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildberg, A.; Stenberg, E. A new process for advanced utilization of shrimp waste. Process. Biochem. 2001, 36, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group; Gerstein, H.C.; Miller, M.E.; Byington, R.P.; Goff, D.C., Jr.; Bigger, J.T.; Buse, J.B.; Cushman, W.C.; Genuth, S.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; et al. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 8, 2545–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, S.H.; Hamdy, O.; Mohan, V.; Hu, F.B. Prevention and management of type 2 diabetes: Dietary components and nutritional strategies. Lancet 2014, 383, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, B.; Sharma, N.; Satija, S.; Mehta, M.; Vyas, M.; Khatik, G.L.; Khurana, N.; Hansbro, P.M.; Williams, K.; Dua, K. Recent Developments in Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors for Management of Type-2 Diabetes: An Update. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2510–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Kumar, V.; Nayak, S.K.; Wadhwa, P.; Kaur, P.; Sahu, S.K. Alpha-amylase as molecular target for treatment of diabetes mellitus: A comprehensive review. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2021, 98, 539–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.L. New novel α-glucosidase inhibitors produced by microbial conversion. Process Biochem. 2018, 65, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.L.; Nguyen, A.D.; Vo, T.P.K.; Zhang, L.J.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Kuo, Y.H. Isolation and identification of novel α-amylase inhibitors from Euonymus laxiflorus Champ. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 1411–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirir, A.M.; Daou, M.; Yousef, A.F.; Yousef, L.F. A review of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors from plants as potential candidates for the treatment of type-2 diabetes. Phytochem. Rev. 2021, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.S.; Ruqaiya, K.; Zaheer, U.H.; Pharkphoom, P. α-Glucosidase inhibitory effect of rhinacanthins-rich extract from Rhinacanthus nasutus leaf and synergistic effect in combination with acarbose. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 36, 325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, A.S.; Wantana, R.; Nisaudah, R.; Ruqaiya, K.; Zaheer, U.H.; Pharkphoom, P. Anti-hyperglycemic and anti-hyperlipidemic effects of rhinacanthins-rich extract from Rhinacanthus nasutus leaves in nicotinamide-streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 113, 108702. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Cheng, Y.-Q.; Yamaki, K.; Li, L.-T. Anti-α-glucosidase activity of Chinese traditionally fermented soybean (douchi). Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H.; Yamagami, T.; Ohshima, K. Long-term ingestion of Touchi-extract, an α-glucosidase inhibitor, by borderline and mild type-2 diabetic subjects is safe and significantly reduces blood glucose levels. Nutr. Res. 2003, 23, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wang, S.L. Biosynthesis of α-glucosidase inhibitors by a newly isolated bacterium, Paenibacillus sp. TKU042 and its effect on reducing plasma glucose in a mouse model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.T.; Techato, K.; Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.-L.; Nguyen, A.D.; Phan, T.Q.; Doan, M.D.; Phoungthong, K. Utilization of Cassava Wastewater for Low-Cost Production of Prodigiosin via Serratia marcescens TNU01 Fermentation and Its Novel Potent α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Effect. Molecules 2021, 26, 6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, A.D.; Le, T.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Wang, S.-L. Bioprocessing shrimp shells for rat intestinal α-glucosidase inhibitor and its effect on reducing blood glucose in a mouse model. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 4829–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.-L. Utilization of Fishery Processing By-Product Squid Pens for α-Glucosidase Inhibitors Production by Paenibacillus sp. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.-L. Reclamation of Marine Chitinous Materials for the Production of α-Glucosidase Inhibitors via Microbial Conversion. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-L.; Su, Y.-C.; Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D. Reclamation of shrimp heads for the production of α-glucosidase inhibitors by Staphylococcus sp. TKU043. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 4929–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-H.; Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.-L. Conversion of shrimp heads to α-glucosidase inhibitors via co-culture of Bacillus mycoides TKU040 and Rhizobium sp. TKU041. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 4597–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.-L. Production of potent antidiabetic compounds from shrimp head powder via Paenibacillus conversion. Process Biochem. 2018, 76, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalimi, K.; Suprapta, D.N. Induction of plant resistance against soyabean stunt virus using some formulations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. ISSAAS 2011, 17, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Uzair, B.; Kausar, R.; Bano, S.A.; Fatima, S.; Badshah, M.; Habiba, U.; Fasim, F. Isolation and Molecular Characterization of a Model Antagonistic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Divulging In Vitro Plant Growth Promoting Characteristics. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6147380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.I.; Salama, A.S.A.; El-Ashry, R.M.; Othman, A.E.I. Serratia marcescens and Pseudomonas aeruginosa are promising candidates as biocontrol agents against root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.). Middle East J. Agric. Res. 2019, 8, 828–838. [Google Scholar]
- Afzal, S.; Tariq, S.; Sultana, V.; Ara, J.; Syed, E.H. Managing the root diseases of okra with endo-root plant growth promoting Pseudomonas and Trichoderma viride associated with healthy okra roots. Pak. J. Bot. 2013, 45, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Purwanti, I.F.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Imron, M.F. Potential of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from aluminium-contaminated site in aluminium removal and recovery from wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 15, 100422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Zhu, C.; Lundaa, T.; Scherr, K.E. Isolation and identification of biosurfactant producing and crude oil degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yuan, M.; Lei, L.; Li, C.; Xu, X. Enhanced production of mono-rhamnolipid in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and application potential in agriculture and petroleum industry. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 323, 124605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashengroph, M.; Nahvi, I.; Zarkesh-Esfahani, H.; Momenbeik, F. Use of Growing Cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for Synthesis of the Natural Vanillin via Conversion of Isoeugenol. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2011, 10, 749–757. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, A.; Pal, P.; Mandal, A.; Sinha, C.; Lalee, A.; Das, M.; Kaity, S.; Mitra, D. Estimation of biosurfactant activity of an alkaline protease producing bacteria isolated from municipal solid waste. Cent. Eur. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 1, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-H.; Boyapati, G.; Song, K.-B.; Rhee, S.-K.; Kim, C.-H. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of the estA gene encoding enzyme for producing (R)-β-acetylmercaptoisobutyric acid from Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1001. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2000, 90, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.-M. Pyoverdines: Pigments, siderophores and potential taxonomic markers of fluorescent Pseudomonas species. Arch. Microbiol. 2000, 174, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.N.; Wang, S.-L.; Nguyen, A.D.; Doan, M.D.; Tran, D.M.; Nguyen, T.H.; Ngo, V.A.; Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Do, V.C.; et al. Potential Application of Rhizobacteria Isolated from the Central Highland of Vietnam as an Effective Biocontrol Agent of Robusta Coffee Nematodes and as a Bio-Fertilizer. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Guo, N.; Sun, J.; Xue, C. Comprehensive utilization of shrimp waste based on biotechnological methods: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, C.-L.; Wang, S.-L. Proteases Production and Chitin Preparation from the Liquid Fermentation of Chitinous Fishery By-Products by Paenibacillus elgii. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Wang, C.-L.; Wang, S.-L. Microbial Conversion of Shrimp Heads to Proteases and Chitin as an Effective Dye Adsorbent. Polymers 2020, 12, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nargis, A.; Ahmed, K.; Ahmed, G.; Hossain, M.; Rahman, M. Nutritional Value and Use of Shrimp Head Waste as Fish Meal. Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2007, 41, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J. Application of dried shrimp head in the diets of sea cucumber Holothuria scabra. J. Surv. Fish. Sci. 2021, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-H.; Wang, S.-L.; Nguyen, D.-N.; Nguyen, A.-D.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Doan, M.-D.; Ngo, V.-A.; Doan, C.-T.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Nguyen, V.-B. Bioprocessing of Marine Chitinous Wastes for the Production of Bioactive Prodigiosin. Molecules 2021, 26, 3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, K.V.; Zainul, A.Z.; Wan, A.A. Optimization of culture conditions for flexirubin production by Chryseobacterium artocarpi CECT 8497 using response surface methodology. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2014, 62, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Svensson, B.; Fukuda, K.; Nielsen, P.K.; Bønsager, B.C. Proteinaceous α-amylase inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom 2004, 1696, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladotun, A.F.; Anthony, A.O. Characterisation of alpha-amylase inhibitor from Streptomyces xinghaiensis AAI2 in solid substrate. Sci. Afr. 2022, 15, e01086. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.T.; Ye, F.C.; Pang, C.P.; Yong, T.Q.; Tang, W.D.; Xiao, J.; Shang, C.H.; Lu, Z.J. Isolation and identification of bioactive substance 1-hydroxyphenazine from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its antimicrobial activity. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 71, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, A.J.; Anoopkumar-Dukie, S.; Perkins, A.V.; Davey, A.K.; Grant, G.D. Inhibition of autophagy by 3-methyladenine protects 1321N1 astrocytoma cells against pyocyanin- and 1-hydroxyphenazine-induced toxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, M.S.; Walawalkar, Y.D.; Furtado, I. Purification and molecular and biological characterisation of the 1-hydroxyphenazine, produced by an environmental strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 3091–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.R.; Taylor, G.W.; Rutman, A.; Hoiby, N.; Cole, P.J.; Wilson, R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyocyanin and 1-hydroxyphenazine inhibit fungal growth. J. Clin. Pathol. 1999, 52, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, S.; Wirach, W.; Chanokporn, P.; Chalerm, R. Isolation and analysis of antibacterial substance produced from P. aeruginosa TISTR 781. KKU Sci. J. 2009, 37, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Thwe, A.A.; Liu, T.T.; Dafei, G.; Wanhua, L.; Changhua, S.; Lu, S.J. Anti-inflammatory effects of an extract from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its purified product 1-hydroxyphenazine on RAW264.7 cells. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 2762–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharni, S.; Alam, M.; Kalani, K.; Abdul, K.; Samad, A.; Srivastava, S.K.; Patra, D.D. Production, purification, and characterization of antifungal metabolite from Pseudomonas aeruginosa SD12, a new strain obtained from tannery waste polluted soil. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, A.D. Postprandial hyperglycaemia and α-glucosidase inhibitors. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1998, 40, S51–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, P.; Bai, G. Two novel aminooligosaccharides isolated from the culture of Streptomyces coelicoflavus ZG0656 as potent inhibitors of α-amylase. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMelo, E.B.; Gomes, A.; Carvalha, I. α- and β-Glucosidase inhibitors: Chemical structure and biological activity. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 10277–10302. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-T.; Rioux, L.-E.; Turgeon, S.L. Alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase inhibition is differentially modulated by fucoidan obtained from Fucus vesiculosus and Ascophyllum nodosum. Phytochemistry 2014, 98, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, M. Seed storage proteins: The enzyme inhibitors. Methods Plant Biochem. 1991, 5, 259–305. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Fang, Y.; Moreno, J.; Ramanujam, J.; Jarrell, M.; Brylinski, M. Assessing the similarity of ligand binding conformations with the Contact Mode Score. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2016, 64, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, T.M.C.; Rajesh, S.S.; Bhaskar, B.V.; Devi, S.; Rammohan, A.; Sivaraman, T.; Rajendra, W. Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation, biological evaluation and 2D QSAR analysis of flavonoids from Syzygium alternifolium as potent anti-Helicobacter pylori agents. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 18277–18292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.L.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.H.; Trinh, T.H.T.; Nong, T.T.; Nguyen, T.U.; Nguyen, V.N.; Nguyen, A.D. Reclamation of rhizobacteria newly isolated from black pepper plant roots as potential biocontrol agents of root-knot nematodes. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 5293–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-L.; Yeh, P.-Y. Production of a surfactant- and solvent-stable alkaliphilic protease by bioconversion of shrimp shell wastes fermented by Bacillus subtilis TKU007. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernfeld, P. Amylase α and β. Methods Enzymol. 1955, 1, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yu, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Chen, F. Novel peptides derived from egg white protein inhibiting alpha-glucosidase. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Wang, S.-L. Porcine pancreatic α-amylase inhibitors from Euonymus laxiflorus Champ. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 43, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).