Fucoxanthin Attenuates Free Fatty Acid-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Lipid Metabolism/Oxidative Stress/Inflammation via the AMPK/Nrf2/TLR4 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
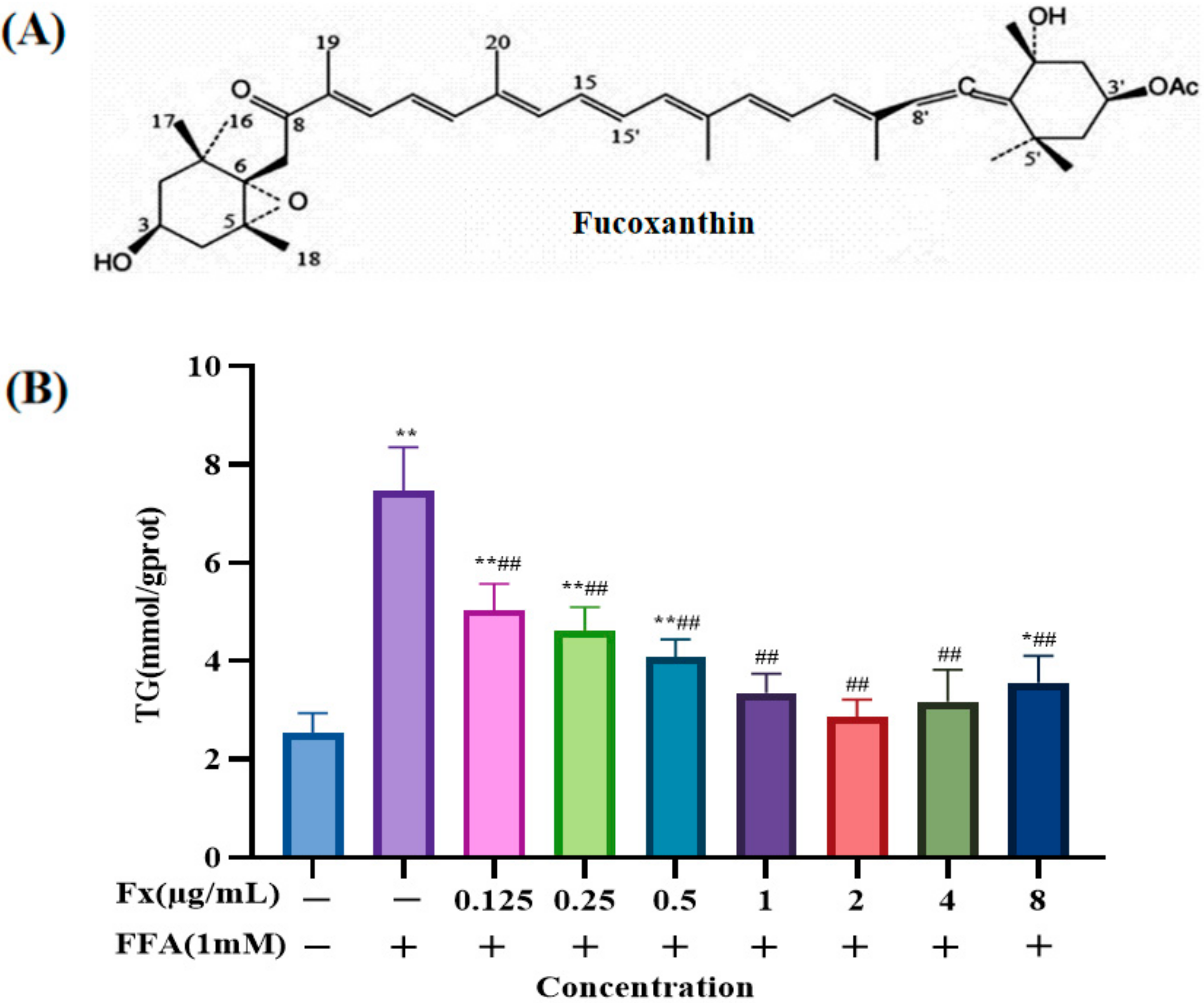
2.1. Determination of the Dosing Concentration
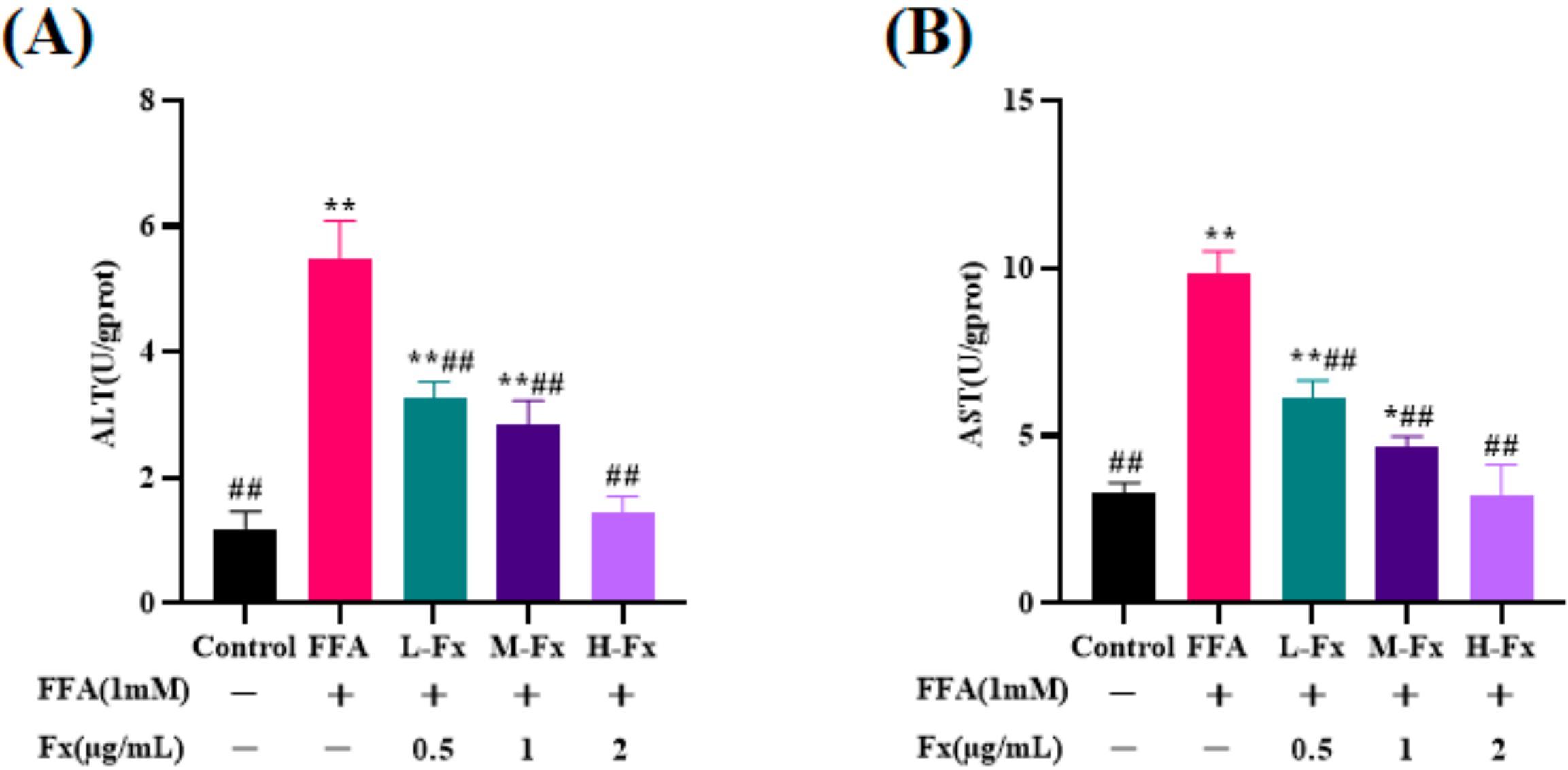
2.2. Effect of Fucoxanthin on Intracellular Alanine Transaminase (ALT) and Aspartate Transaminase (AST) Viability
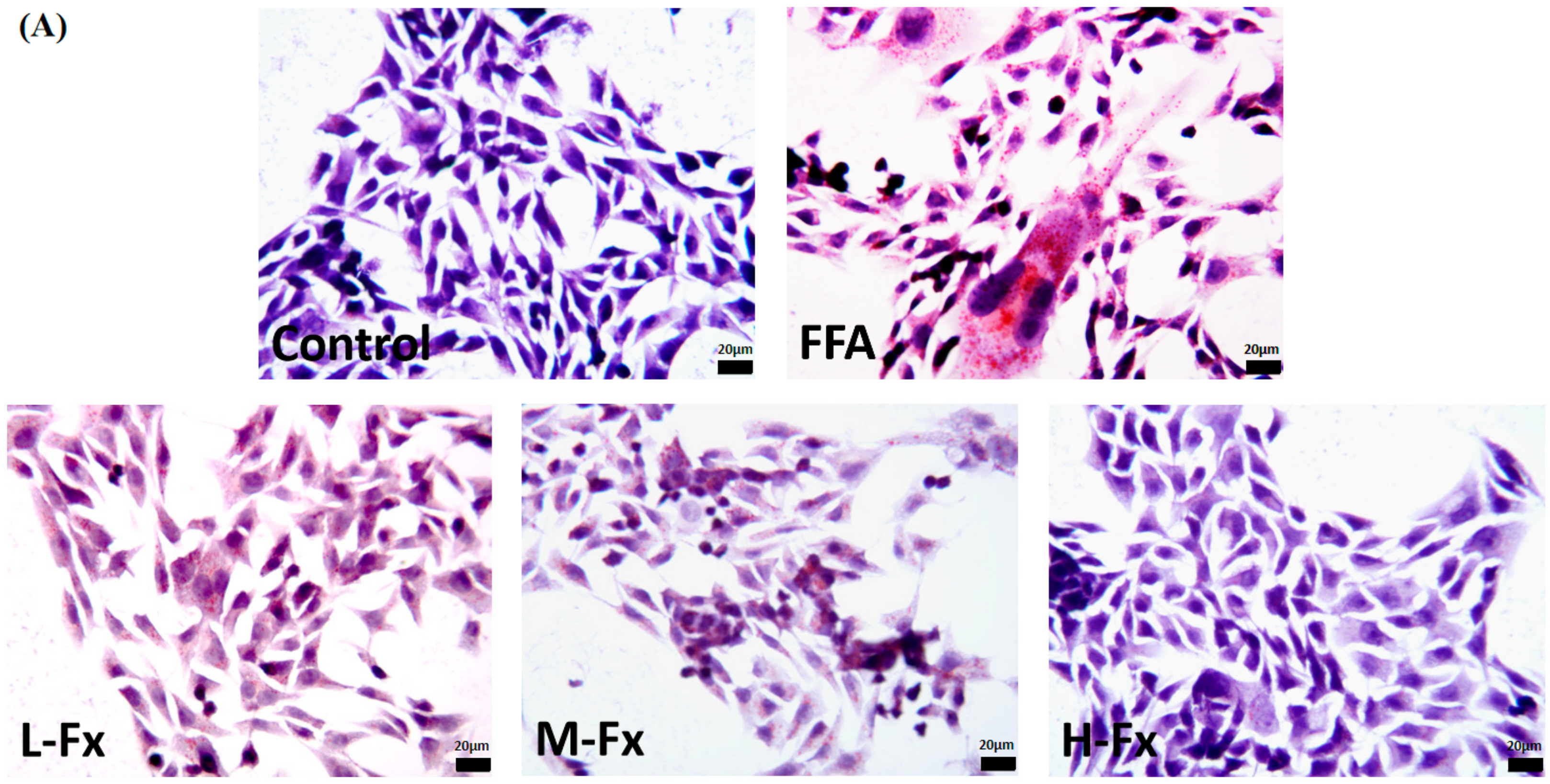
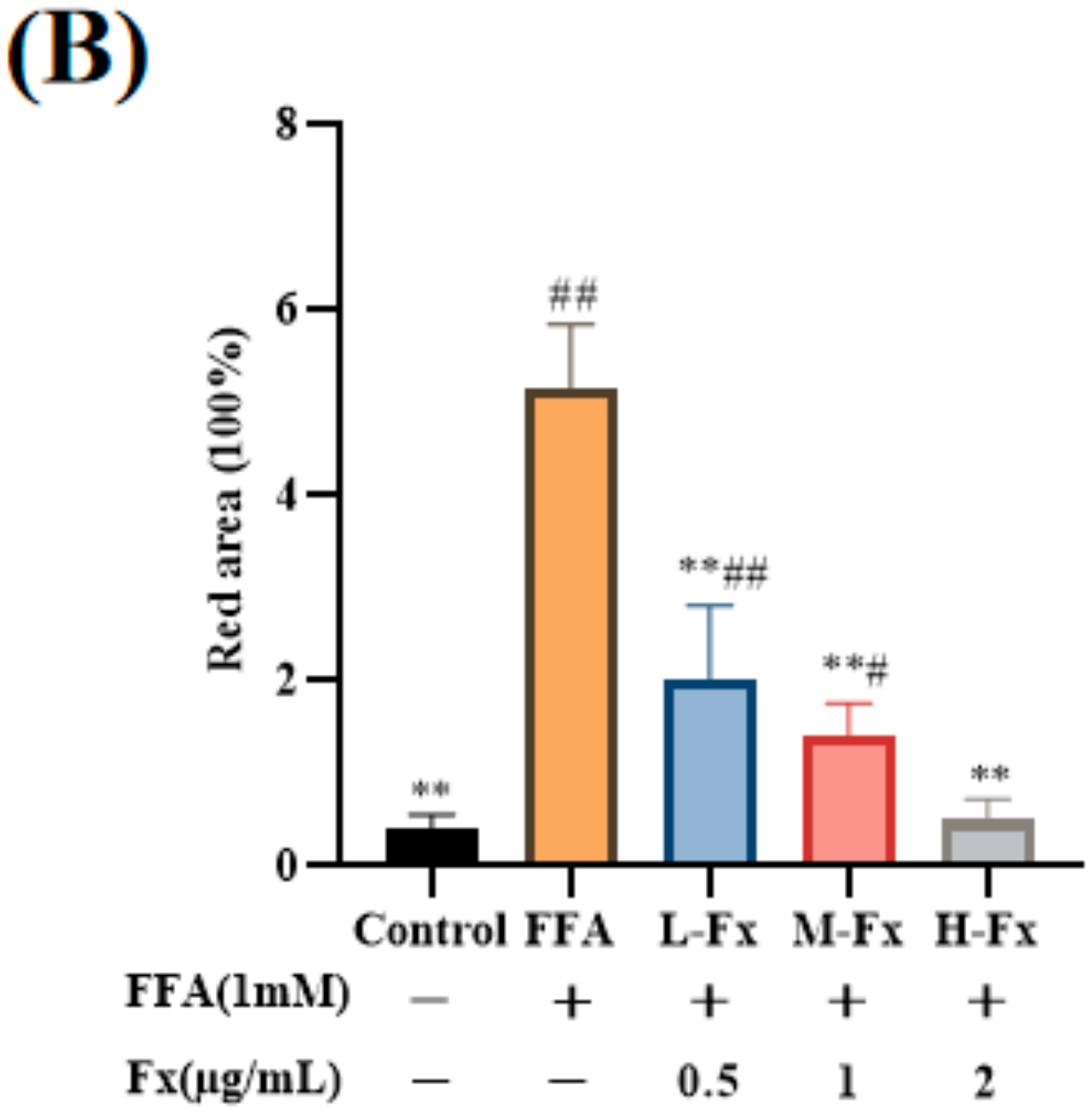
2.3. Effect of Fucoxanthin on Intracellular Lipid Accumulation
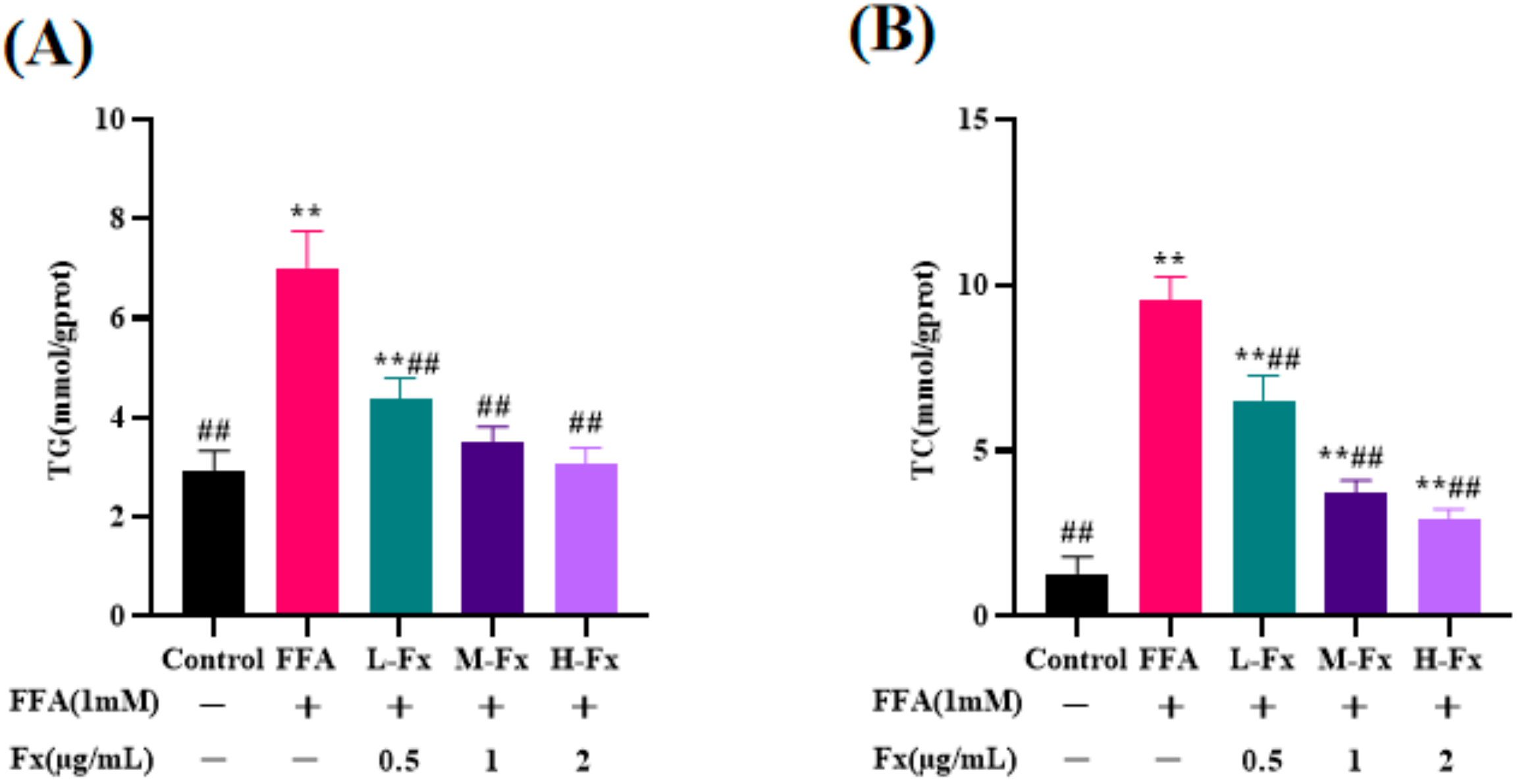
2.4. Effect of Fucoxanthin on Intracellular TG and Total Cholesterol (TC) Content
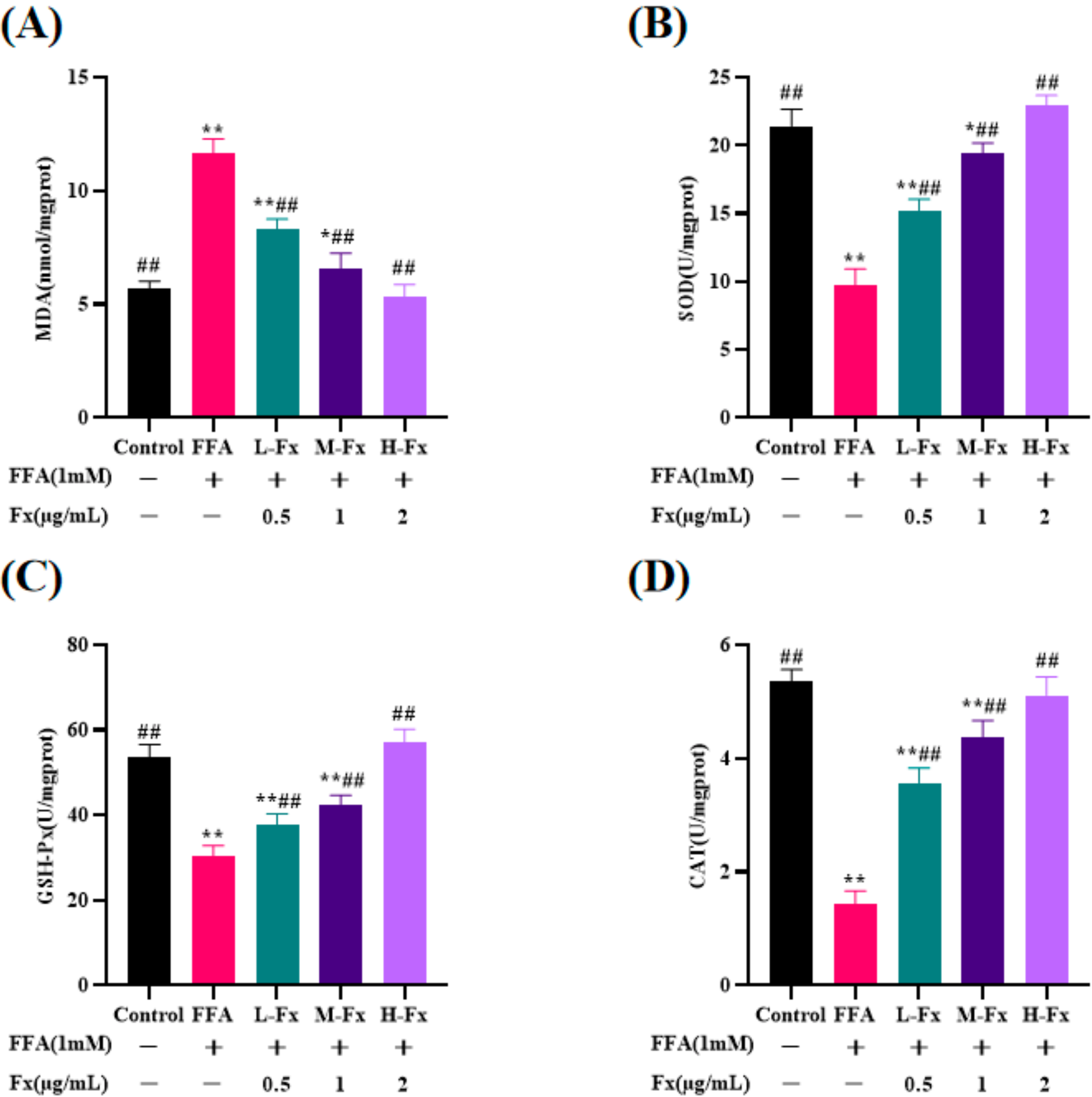
2.5. Effect of Fucoxanthin on Intracellular Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
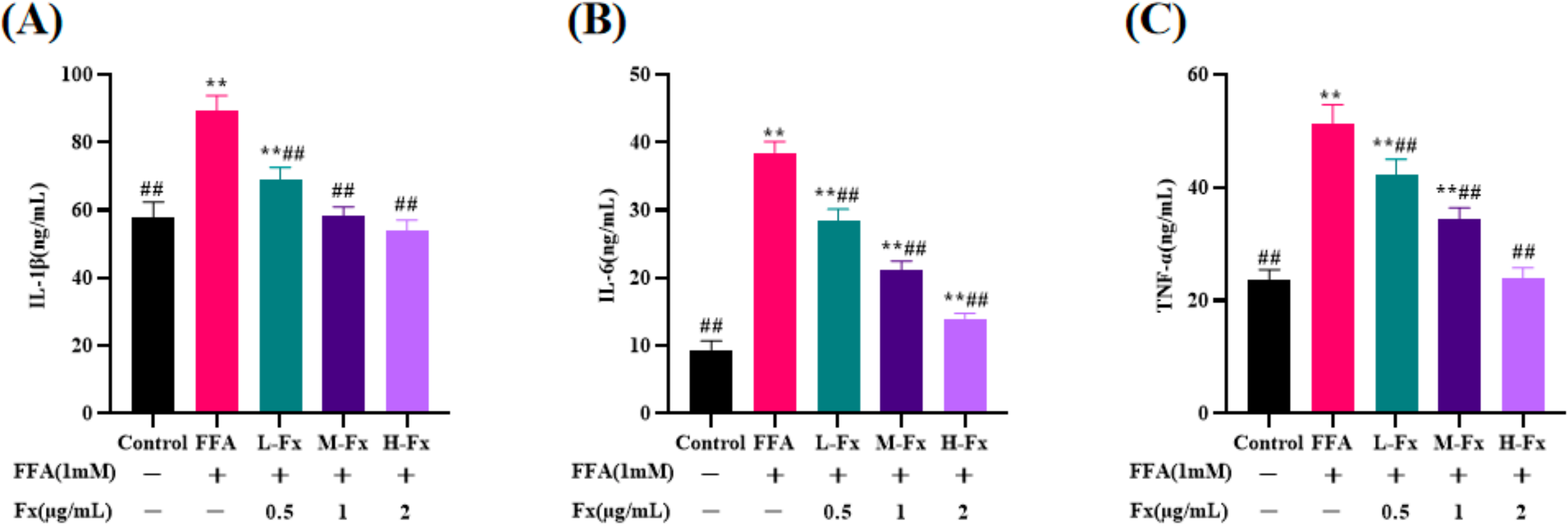
2.6. Effect of Fucoxanthin on Intracellular Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Content
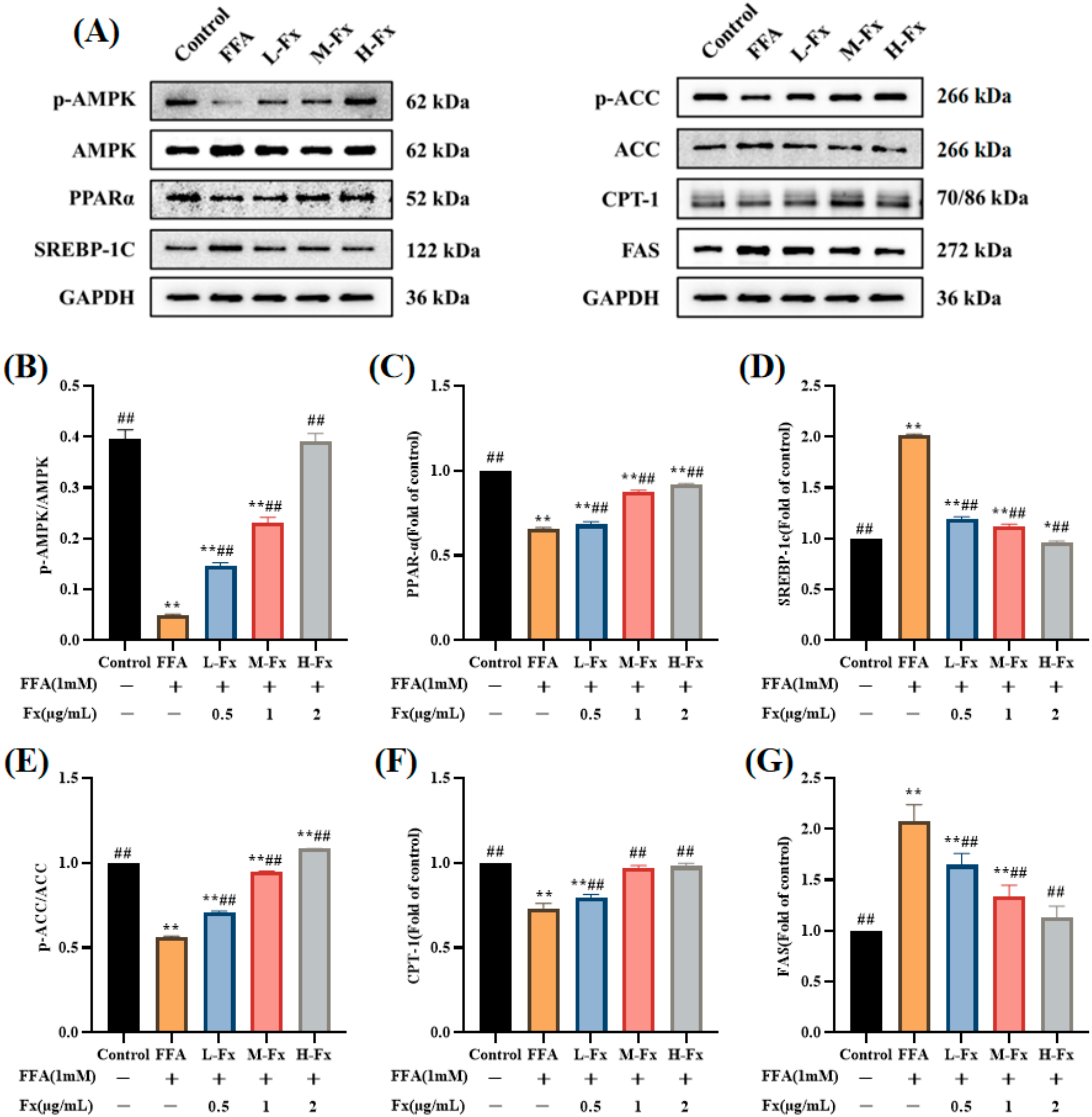
2.7. Effects of AMPK Activation and Expression of Genes Related to Lipid Metabolism
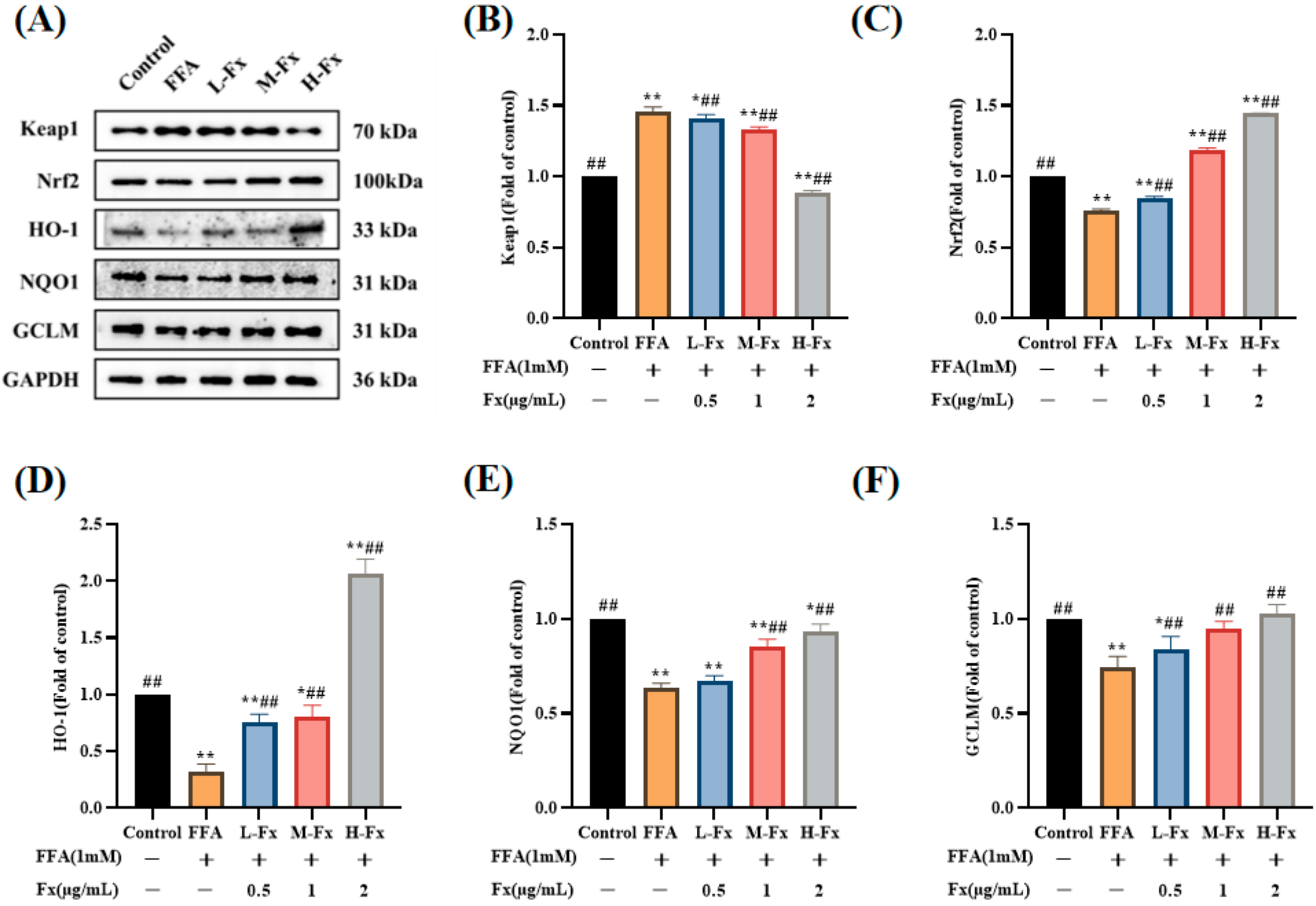
2.8. Effects of Fucoxanthin on the Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Response
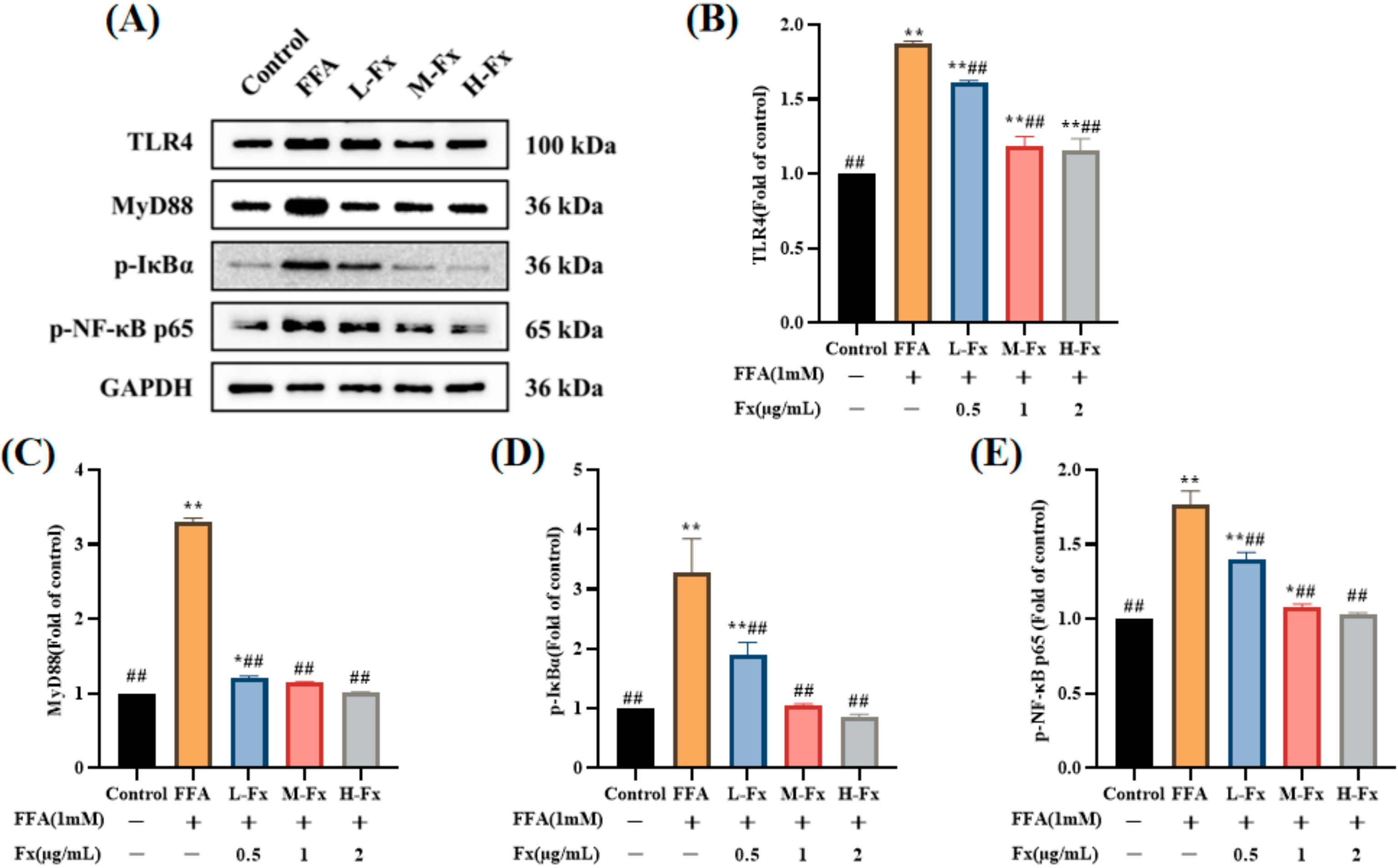
2.9. Effect of Fucoxanthin on the TLR4-Induced Inflammatory Response
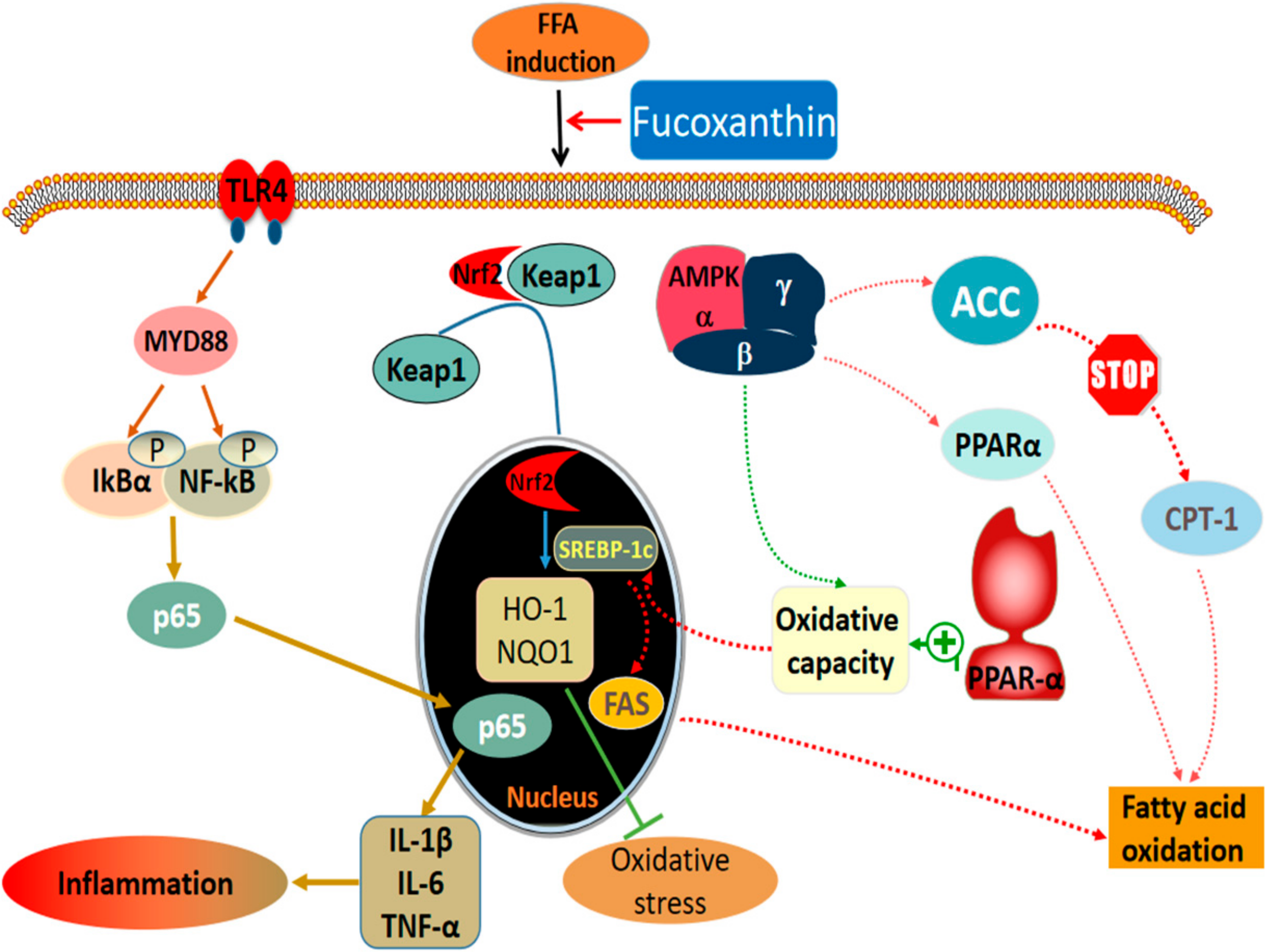
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Establishment of NAFLD Cell Model
4.4. Measurement of Lipid and Peroxidation Levels
4.5. ALT and AST Activity in Cells
4.6. Measurement of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Cells
4.7. Oil Red O Staining
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Varghese, Z.; Ruan, X.Z. The molecular pathogenic role of inflammatory stress in dysregulation of lipid homeostasis and hepatic steatosis. Genes Dis. 2014, 1, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lauschke, V.M.; Mkrtchian, S.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. The role of microRNAs in liver injury at the crossroad between hepatic cell death and regeneration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawano, Y.; Cohen, D.E. Mechanisms of hepatic triglyceride accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertuccio, P.; Turati, F.; Carioli, G.; Rodriguez, T.; La Vecchia, C.; Malvezzi, M.; Negri, E. Global trends and predictions in hepatocellular carcinoma mortality. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 302–309. [Google Scholar]
- Reimer, K.C.; Wree, A.; Roderburg, C.; Tacke, F. New drugs for NAFLD: Lessons from basic models to the clinic. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 8–23. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, C.; Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Kroemer, G. Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 583–594. [Google Scholar]
- Peverill, W.; Powell, L.W.; Skoien, R. Evolving concepts in the pathogenesis of NASH: Beyond steatosis and inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8591–8638. [Google Scholar]
- Marra, F.; Lotersztajn, S. Pathophysiology of NASH: Perspectives for a targeted treatment. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 5250–5269. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Ma, W.; Ding, L.; Li, S.; Dou, X.; Song, Z. The TLR4-IRE1alpha pathway activation contributes to palmitate-elicited lipotoxicity in hepatocytes. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 3572–3581. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.; Wang, K.; Zhi, Y.; Shen, W.; Huang, L. Gypenosides improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high-fat diet induced through regulating LPS/TLR4 signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 3042–3053. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, X.; Cheng, G.; Pu, S.; Cai, S. The preventive effect of phenolic-rich extracts from Chinese sumac fruits against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats induced by a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Ke, H.; Li, Y.; Xie, L.; Su, H.; Xie, J.; Mo, J.; Chen, W. Malvidin-3-O-Glucoside from Blueberry Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Transcription Factor EB-Mediated Lysosomal Function and Activating the Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 4663–4673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.V.; Tsou, Y.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Lu, W.J.; Hwang, P.A. Effects of Low-Molecular-Weight Fucoidan and High Stability Fucoxanthin on Glucose Homeostasis, Lipid Metabolism, and Liver Function in a Mouse Model of Type II Diabetes. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 113–127. [Google Scholar]
- Vasantharaja Raguraman, S.A.L.; MubarakAli, D.; Narendrakumar, G.; Thirugnanasambandam, R.; Kirubagaran, R.; Thajuddin, N. Unraveling rapid extraction of fucoxanthin from Padina tetrastromatica: Purification, characterization and biomedical application. Process Biochem. 2018, 73, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Nasab, S.B.; Homaei, A.; Pletschke, B.I.; Salinas-Salazar, C.; Castillo-Zacarias, C.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Marine resources effective in controlling and treating diabetes and its associated complications. Process Biochem. 2020, 92, 313–342. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Yuan, J.P.; Wu, C.F.; Wang, J.H. Fucoxanthin, a marine carotenoid present in brown seaweeds and diatoms: Metabolism and bioactivities relevant to human health. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1806–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Gammone, M.A.; Riccioni, G.; D’Orazio, N. Marine Carotenoids against Oxidative Stress: Effects on Human Health. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6226–6246. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Ren, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Wu, H.; Song, S.; Yan, C. Fucoxanthin alleviates palmitate-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 cells through improving lipid metabolism and attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3361–3370. [Google Scholar]
- Takatani, N.; Kono, Y.; Beppu, F.; Okamatsu-Ogura, Y.; Yamano, Y.; Miyashita, K.; Hosokawa, M. Fucoxanthin inhibits hepatic oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis model mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 528, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Ferramosca, A.; Di Giacomo, M.; Zara, V. Antioxidant dietary approach in treatment of fatty liver: New insights and updates. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4146–4157. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Hu, S.; Park, Y.K.; Lee, J.Y. Health Benefits of Carotenoids: A Role of Carotenoids in the Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 24, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shih, P.H.; Shiue, S.J.; Chen, C.N.; Cheng, S.W.; Lin, H.Y.; Wu, L.W.; Wu, M.S. Fucoidan and Fucoxanthin Attenuate Hepatic Steatosis and Inflammation of NAFLD through Modulation of Leptin/Adiponectin Axis. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-L.; Huang, W.-C.; Liou, C.-J. Fucoxanthin attenuates fatty acid-induced lipid accumulation in FL83B hepatocytes through regulated Sirt1/AMPK signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, B.; He, Y.; Chen, F.; Cheng, K.W. Lipid-Lowering Bioactivity of Microalga Nitzschia laevis Extract Containing Fucoxanthin in Murine Model and Carcinomic Hepatocytes. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1004. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muradian, K.; Vaiserman, A.; Min, K.J.; Fraifeld, V.E. Fucoxanthin and lipid metabolism: A minireview. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Tian, X.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, P.; Huang, F.; Ding, G.; Yang, Z. Protective Effects of Fucoxanthin against Alcoholic Liver Injury by Activation of Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Defense and Inhibition of TLR4-Mediated Inflammation. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 552–567. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.; Hwang, J.T.; Park, J.H.; Choi, H.K. Free fatty acid-induced histone acetyltransferase activity accelerates lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2019, 13, 196–204. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhai, T.; You, J.; Chen, Y. Silibinin ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in mice with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating CFLAR-JNK pathway. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 745–757. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liao, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, F. Effects of daphnetin on lipid metabolism, insulin resistance and oxidative stress in OA-treated HepG2 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 4673–4684. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Li, M.; Kalavagunta, P.K.; Li, J.; He, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ahmad, O.; Yin, H.; Wang, T.; Shang, J. Protective effects of cichoric acid on H(2)O(2)-induced oxidative injury in hepatocytes and larval zebrafish models. Biomed. Pharm. 2018, 104, 679–685. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.G.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J.Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.X.; Qu, H.Q.; Wang, B.L.; Zhu, M. Liraglutide Ameliorates Lipotoxicity-Induced Oxidative Stress by Activating the NRF2 Pathway in HepG2 Cells. Horm. Metab. Res. 2020, 52, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Meng, L.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y. Feprazone Prevents Free Fatty Acid (FFA)-Induced Endothelial Inflammation by Mitigating the Activation of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 4850–4856. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, C.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Huo, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Sun, P.; Ma, X.; Meng, Q.; et al. Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 against lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury in mice through inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 61, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ning, C.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Huo, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Sun, P.; Ma, X.; Meng, Q.; et al. Hepatoprotective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 from Panax ginseng on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury by activating Nrf2 signaling pathway in mice. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Cai, S.Y.; Boyer, J.L. Mechanisms of bile acid mediated inflammation in the liver. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 56, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Masarone, M.; Rosato, V.; Dallio, M.; Gravina, A.G.; Aglitti, A.; Loguercio, C.; Federico, A.; Persico, M. Role of Oxidative Stress in Pathophysiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 9547613. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Huang, W. Ginsenosides Rg1 from Panax ginseng: A Potential Therapy for Acute Liver Failure Patients? Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 538059. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.C.; Liao, P.C.; Huang, C.H.; Hu, S.; Huang, S.C.; Wu, S.J. Osthole attenuates lipid accumulation, regulates the expression of inflammatory mediators, and increases antioxidants in FL83B cells. Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 91, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Geisler, S.; Holmström, K.M.; Skujat, D.; Fiesel, F.C.; Rothfuss, O.C.; Kahle, P.J.; Springer, W. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy is dependent on VDAC1 and p62/SQSTM1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 119–131. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, F.; Wong, N.K.; He, J.; Zhang, R.; Sun, R.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Koike, K.; et al. Global liver disease burdens and research trends: Analysis from a Chinese perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 212–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Tang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, D.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, J.; Tian, X.; et al. Carnosol-mediated Sirtuin 1 activation inhibits Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 to attenuate liver fibrosis. Pharm. Res. 2018, 128, 327–337. [Google Scholar]
- Giudetti, A.M.; Guerra, F.; Longo, S.; Beli, R.; Romano, R.; Manganelli, F.; Nolano, M.; Mangini, V.; Santoro, L.; Bucci, C. An altered lipid metabolism characterizes Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2B peripheral neuropathy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158805. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y. CD36 tango in cancer: Signaling pathways and functions. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4893–4908. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quintana-Castro, R.; Aguirre-Maldonado, I.; Soto-Rodríguez, I.; Deschamps-Lago, R.A.; Gruber-Pagola, P.; Urbina de Larrea, Y.K.; Juárez-Rivera, V.E.; Ramos-Manuel, L.E.; Alexander-Aguilera, A. Cd36 gene expression in adipose and hepatic tissue mediates the lipids accumulation in liver of obese rats with sucrose-induced hepatic steatosis. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2020, 147, 106404. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Shan, T.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y. AMPK facilitates intestinal long-chain fatty acid uptake by manipulating CD36 expression and translocation. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 4852–4869. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Ge, Z.; Wang, H.; Feng, W.; Sun, X.; Chu, X.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Bi, Y. Prolactin improves hepatic steatosis via CD36 pathway. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg, H.N. Selective Trafficking of Fatty Acids in the Liver: Add Them2 to the List of Influencers. Hepatology 2019, 70, 462–464. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Yang, C.; Du, R.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Gao, Y.; Huang, W. Ginsenoside Rg1 Ameliorates Palmitic Acid-Induced Hepatic Steatosis and Inflammation in HepG2 Cells via the AMPK/NF-κB Pathway. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 2019, 7514802. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, J.; Zheng, J.; Tian, X.; Xu, B.; Yuan, F.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z.; Huang, F. Fucoxanthin Attenuates Free Fatty Acid-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Lipid Metabolism/Oxidative Stress/Inflammation via the AMPK/Nrf2/TLR4 Signaling Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040225
Ye J, Zheng J, Tian X, Xu B, Yuan F, Wang B, Yang Z, Huang F. Fucoxanthin Attenuates Free Fatty Acid-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Lipid Metabolism/Oxidative Stress/Inflammation via the AMPK/Nrf2/TLR4 Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(4):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040225
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Jiena, Jiawen Zheng, Xiaoxiao Tian, Baogui Xu, Falei Yuan, Bin Wang, Zuisu Yang, and Fangfang Huang. 2022. "Fucoxanthin Attenuates Free Fatty Acid-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Lipid Metabolism/Oxidative Stress/Inflammation via the AMPK/Nrf2/TLR4 Signaling Pathway" Marine Drugs 20, no. 4: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040225
APA StyleYe, J., Zheng, J., Tian, X., Xu, B., Yuan, F., Wang, B., Yang, Z., & Huang, F. (2022). Fucoxanthin Attenuates Free Fatty Acid-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Lipid Metabolism/Oxidative Stress/Inflammation via the AMPK/Nrf2/TLR4 Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs, 20(4), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040225






