Comparative Venomics of the Cryptic Cone Snail Species Virroconus ebraeus and Virroconus judaeus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
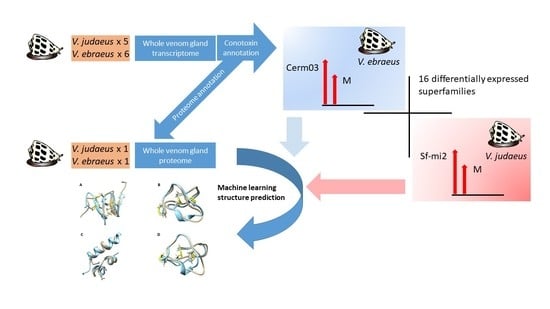
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Sequence Data and Assembly Quality
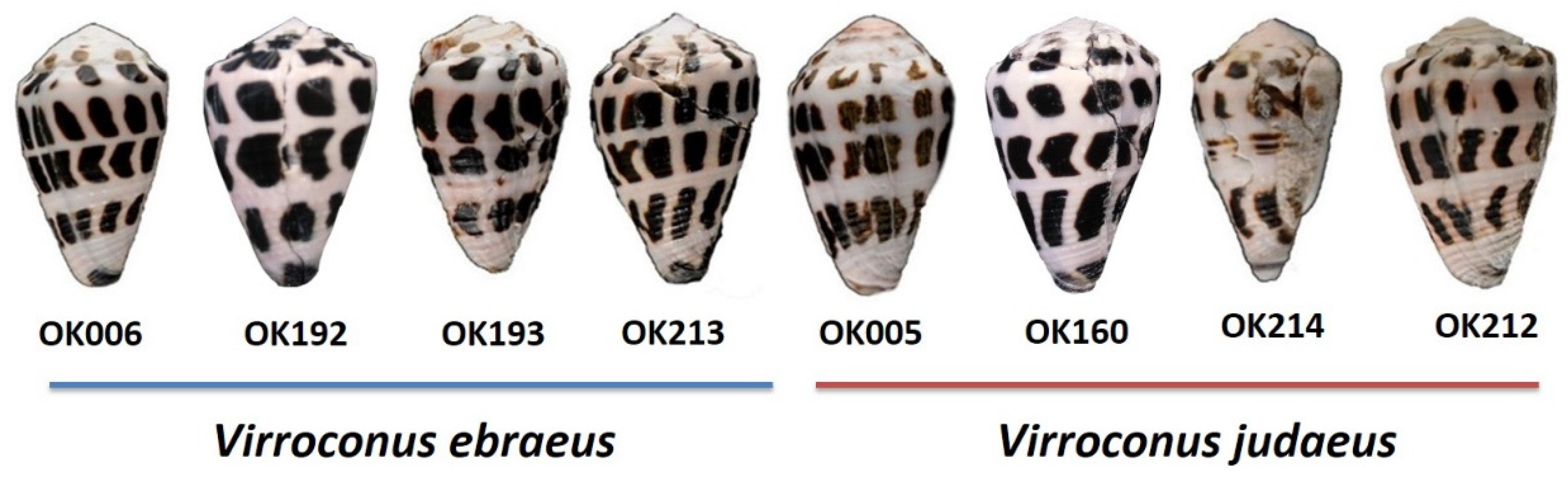
2.2. Identification of Virroconus Samples
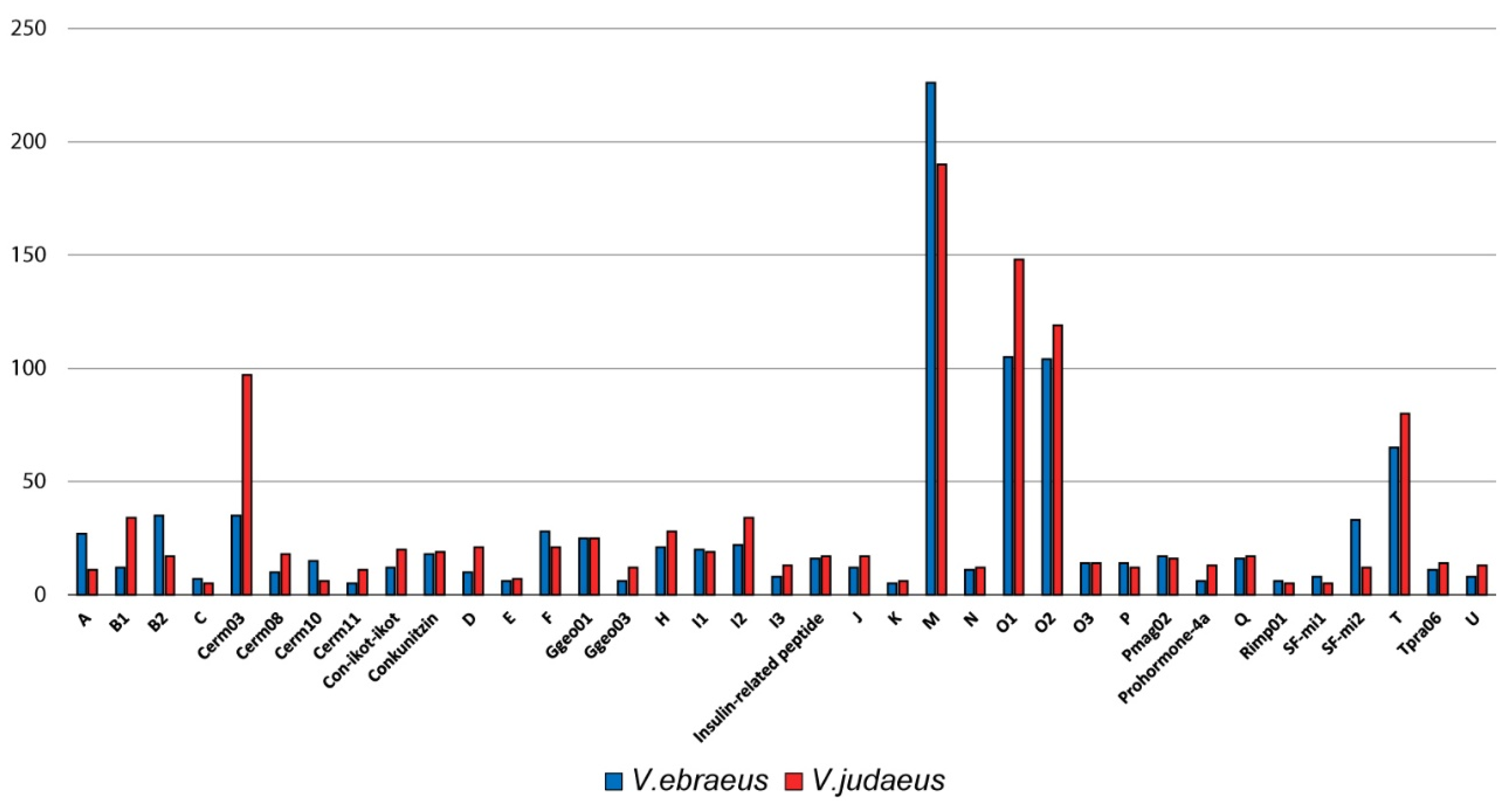
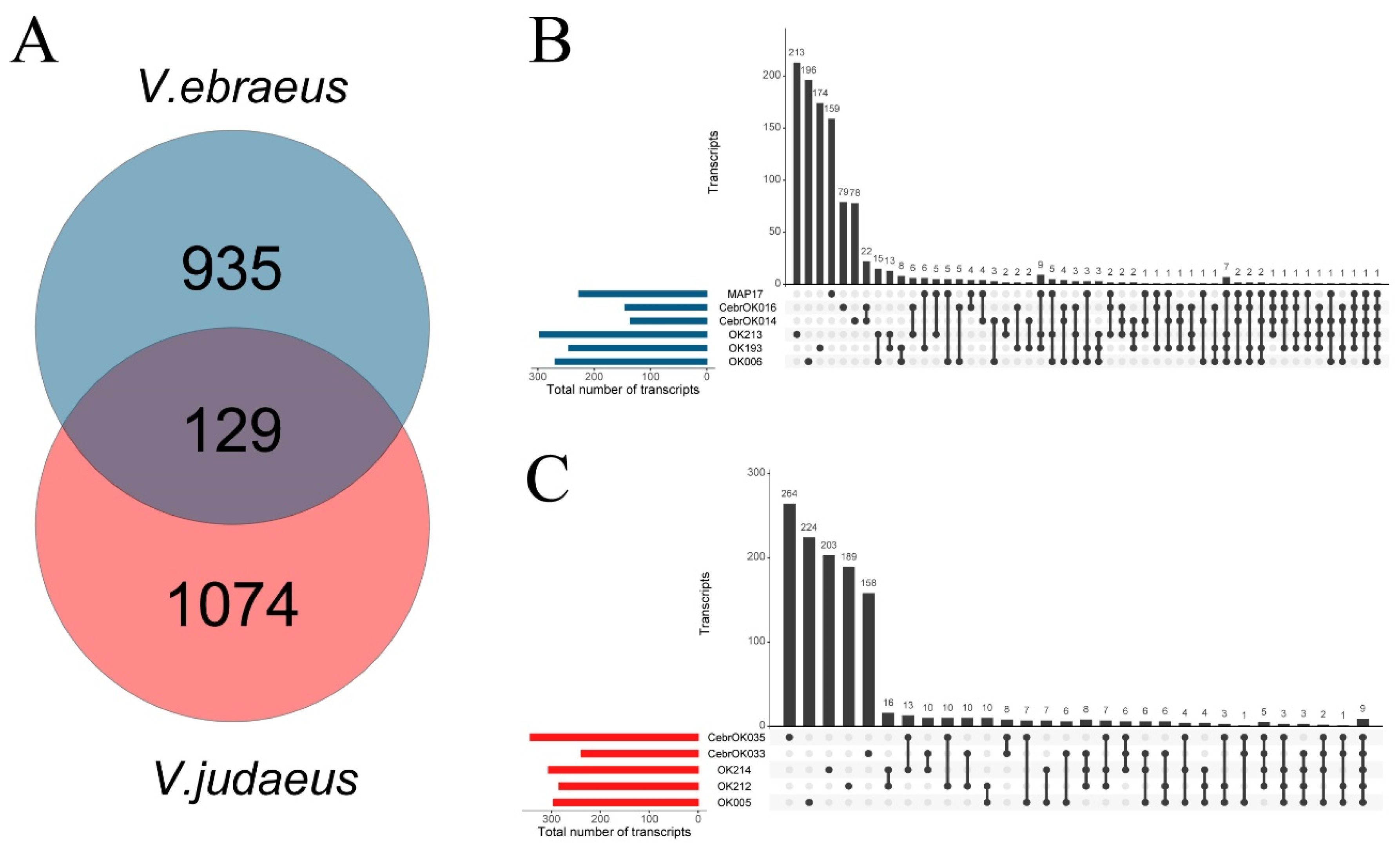
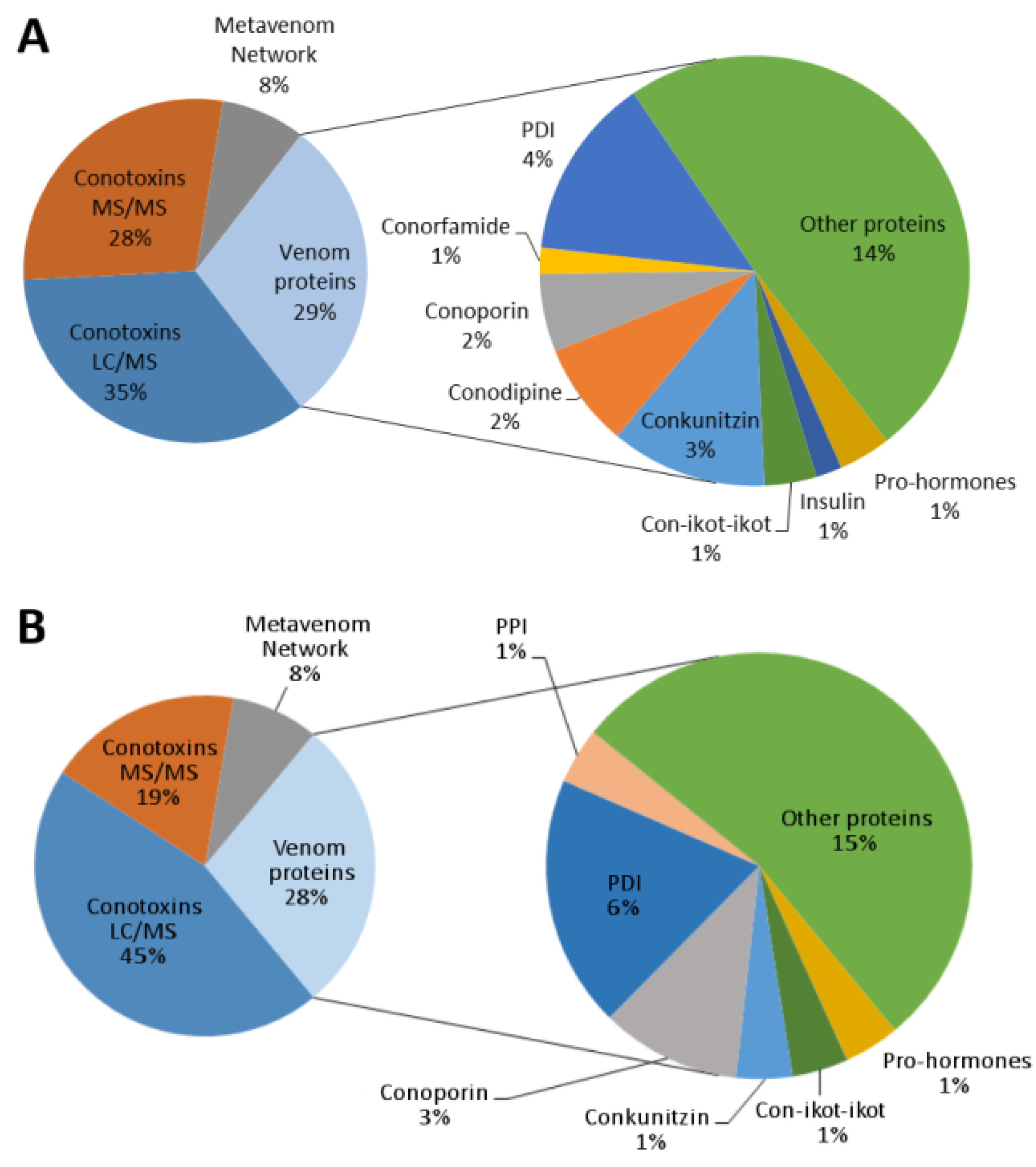
2.3. Conotoxin Precursor Diversity and Relative Abundance in V. ebraeus and V. judaeus
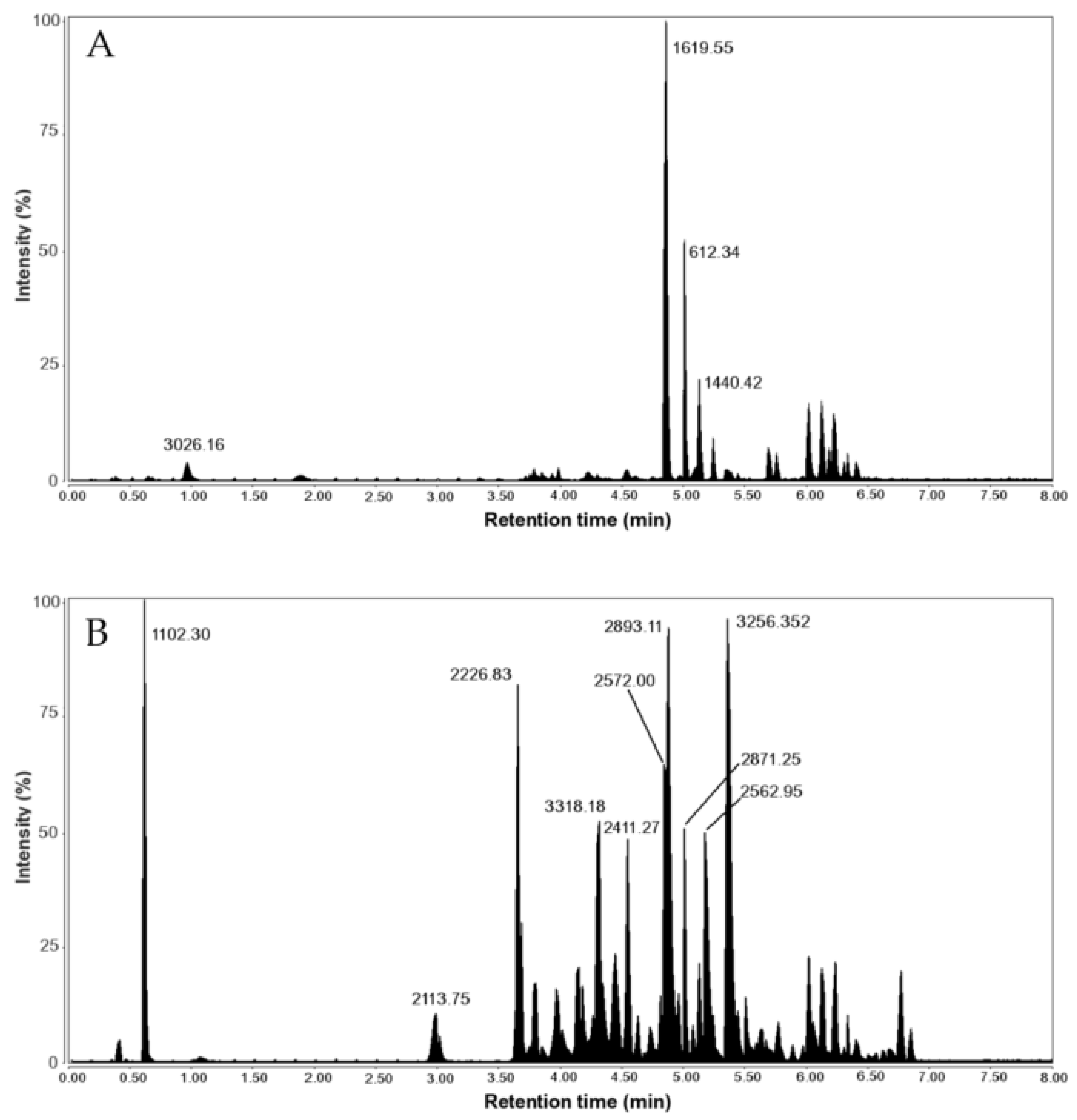
2.4. Venom Duct Proteome
2.5. New Putative Conotoxin Precursor Superfamilies Identified in Virroconus
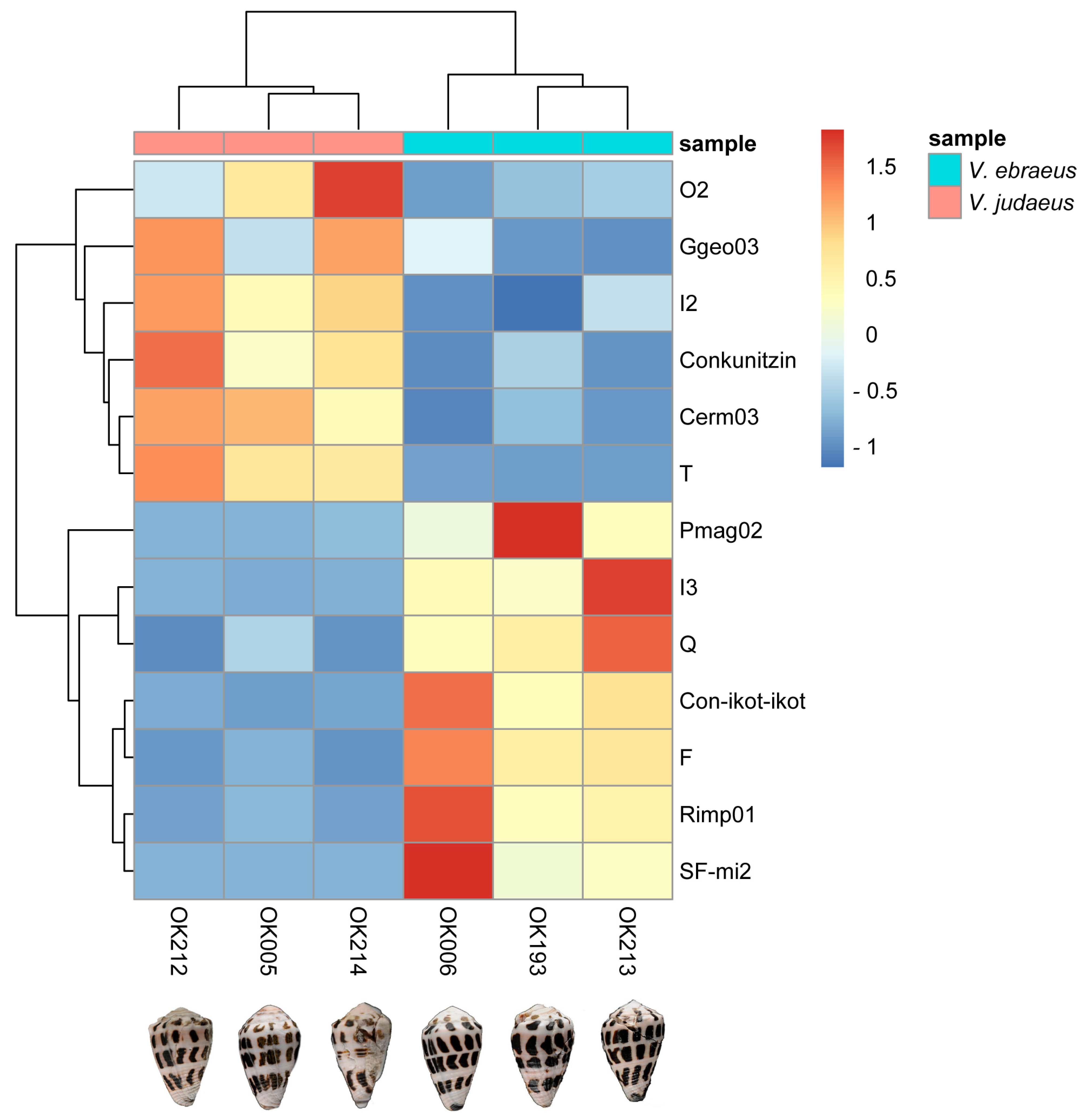
2.6. Differences in Conotoxin Precursor Expression between V. ebraeus and V. judaeus
2.7. Molecular Modeling
2.7.1. OK005_J_237
2.7.2. OK006_E_244
2.7.3. OK193_E_124
2.7.4. OK213_E_290
2.7.5. Eb6.9
2.7.6. CebrOK033_J_232
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Sampling and Venom Duct Processing
3.2. Transcriptomic Analysis of the V. ebraeus and V. judaeus Venom Duct
3.2.1. Transcriptome Assembly
3.2.2. Conotoxin Precursor Prediction and Classification
3.2.3. Shared Conotoxins between V. ebraeus and V. judaeus
3.3. Virroconus Species Identification
3.4. Differential Expression Analyses
3.5. Proteomic Analysis of the V. ebraeus and V. judaeus Venom Ducts
3.5.1. Venom Extraction
3.5.2. RP-UHPLC/MS Analysis
3.5.3. Shotgun Proteomics (LC-MS/MS)
3.5.4. Bioinformatic Integration of Proteomic and Transcriptomic Data
3.6. Molecular Modeling
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tucker, J.K.; Tenorio, M.J. Systematic Classification of Recent and Fossil Conoidean Gastropods, with Keys to the Genera of Cone Shells; Conchbooks: Hackenheim, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-39-3976-726-8. [Google Scholar]
- Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.; Vetter, I.; Hamilton, B.; Sunagar, K.; Lavergne, V.; Dutertre, V.; Fry, B.G.; Antunes, A.; Veter, D.J.; et al. Evolution of separate predation- and defence-evoked venoms in carnivorous cone snails. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buczek, O.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G. Propeptide does not act as an intramolecular chaperone but facilitates protein disulfide isomerase-assisted folding of a conotoxin precursor. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, J.L.; Lin, Z.; Imperial, J.S.; Antunes, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Olivera, B.M.; Schmidt, E.W. Small Molecules in the Cone Snail Arsenal. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 4933–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, S.D.; Li, Q.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Gajewiak, J.; Yandell, M.; Papenfuss, A.T.; Purcell, A.W.; Norton, R.S.; Safavi-Hermami, H. Hormone-like peptides in the venoms of marine cone snails. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2017, 244, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abalde, S.; Dutertre, S.; Zardoya, R. A Combined Transcriptomics and Proteomics Approach Reveals the Differences in the Predatory and Defensive Venoms of the Molluscivorous Cone Snail Cylinder ammiralis (Caenogastropoda: Conidae). Toxins 2021, 13, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalde, S.; Tenorio, M.J.; Afonso, C.M.; Zardoya, R. Conotoxin Diversity in Chelyconus ermineus (Born, 1778) and the Convergent Origin of Piscivory in the Atlantic and Indo-Pacific Cones. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 2643–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardos-Blas, J.R.; Irisarri, I.; Abalde, S.; Tenorio, M.J.; Zardoya, R. Conotoxin Diversity in the Venom Gland Transcriptome of the Magician’s Cone, Pionoconus magus. Mar. Drugs. 2019, 17, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abalde, S.; Tenorio, M.J.; Afonso, C.M.; Zardoya, R. Comparative transcriptomics of the venoms of continental and insular radiations of West African cones. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20200794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drukewitz, S.H.; von Reumont, B.M. The Significance of Comparative Genomics in Modern Evolutionary Venomics. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rockel, D.; Korn, W.; Kohn, A.J. Manual of the Living Conidae. Indo-Pacific Region; Christa, H., Ed.; Wiesbaden: Hemmen, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bergh, R. Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Coniden. Nova Acta Kaiser. Leopold.-Carol. Deut. Akad. Naturf. 1895, 65, 67–214. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, T.F.; Kohn, A.J.; Matheny, A.M. Cryptic species differentiated in Conus ebraeus, a widespread tropical marine gastropod. Biol. Bull. 2009, 217, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wood, A.W.; Duda, T.F., Jr. Reticulate evolution in Conidae: Evidence of nuclear and mitochondrial introgression. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 161, 107182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuong, M.A.; Mahardika, G.N.; Alfaro, M.E. Dietary breadth is positively correlated with venom complexity in cone snails. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grandal, M.; Hoggard, M.; Neely, B.; Davis, W.C.; Marí, F. Proteogenomic Assessment of Intraspecific Venom Variability: Molecular Adaptations in the Venom Arsenal of Conus purpurascens. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2021, 20, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abalde, A.; Tenorio, M.J.; Uribe, J.E.; Zardoya, R. Conidae phylogenomics and evolution. Zool. Script 2019, 48, 194–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardos-Blas, J.R.; Irisarri, I.; Abalde, S.; Afonso, C.M.; Tenorio, M.J.; Zardoya, R. The genome of the venomous snail Lautoconus ventricosus sheds light on the origin of conotoxin diversity. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassio, G.; Modica, M.V.; Mary, L.; Zaharias, P.; Fedosov, A.E.; Gorson, J.; Kantor, Y.I.; Holford, M.; Puillandre, N. Venom Diversity and Evolution in the Most Divergent Cone Snail Genus Profundiconus. Toxins 2018, 11, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barua, A.; Mikheyev, A.S. An ancient, conserved gene regulatory network led to the rise of oral venom systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2021311118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holford, M.; Daly, M.; King, G.F.; Norton, R.S. Venoms to the rescue. Science 2018, 361, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, L.R. Developmental modularity and phenotypic novelty within a biphasic life cycle: Morphogenesis of a cone snail venom gland. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.H.; Dutertre, S.; Kaas, Q.; Lavergne, V.; Kubala, P.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Transcriptomic messiness in the venom duct of Conus miles contributes to conotoxin diversity. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2013, 12, 3824–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, A.H.; Dekan, Z.; Smout, M.J.; Wilson, D.; Dutertre, S.; Vetter, I.; Lewis, R.J.; Loukas, A.; Daly, N.L.; Alewood, P.F. Conotoxin Phi-MiXXVIIA from the Superfamily G2 Employs a Novel Cysteine Framework that Mimics Granulin and Displays Anti-Apoptotic Activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 14973–14976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Barghi, N.; Lu, A.; Fedosov, A.E.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Lluisma, A.O.; Concepcion, G.P.; Yandell, M.; Olivera, B.M.; Safavi-Hemami, H. Divergence of the Venom Exogene Repertoire in Two Sister Species of Turriconus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 2211–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krug, P.J. Patterns of Speciation in Marine Gastropods: A Review of the Phylogenetic Evidence for Localized Radiations in the Sea. Am. Malacol. Bull. 2011, 29, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, T.F., Jr.; Remigio, E.A. Variation and evolution of toxin gene expression patterns of six closely related venomous marine snails. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 3018–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nybakken, J.; Perron, F. Ontogenetic change in the radula of Conus magus (Gastropoda). Mar. Biol. 1988, 98, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nybakken, J. Ontogenetic change in the Conus radula, its form, distribution among the radula types, and significance in systematics and ecology. Malacologia 1990, 32, 35–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.J.; Smith, A.B.; Schroeder, C.I.; Yasuda, T.; Lewis, R.J. ω-Conotoxin CVID inhibits a pharmacologically distinct voltage-sensitive calcium channel associated with transmitter release from preganglionic nerve terminals. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 4057–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safavi-Hemami, H.; Gajewiak, J.; Karanth, S.; Robinson, S.D.; Ueberheide, B.; Douglass, A.D.; Schlegel, A.; Imperial, J.S.; Watkins, M.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; et al. Specialized insulin is used for chemical warfare by fish-hunting cone snails. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menting, J.G.; Gajewiak, J.; MacRaild, C.A.; Chou, D.H.; Disotuar, M.M.; Smith, N.A.; Miller, C.; Erchegyi, J.; Rivier, J.E.; Olivera, B.M.; et al. A minimized human insulin-receptor-binding motif revealed in a Conus geographus venom insulin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.H.; Bradley, E.K.; Miljanich, G.P.; Nadasdi, L.; Ramachandran, J.; Basus, V.J. Solution structure of omega-conotoxin GVIA using 2-D NMR spectroscopy and relaxation matrix analysis. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 7396–7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuis, J.R.; Dekan, Z.; Wingerd, J.S.; Smith, J.J.; Munasinghe, N.R.; Bhola, R.F.; Imlach, W.L.; Herzig, V.; Armstrong, D.A.; Rosengren, K.J.; et al. Pharmacological characterisation of the highly NaV1.7 selective spider venom peptide Pn3a. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flinn, J.P.; Pallaghy, P.K.; Lew, M.J.; Murphy, R.; Angus, J.A.; Norton, R.S. Role of disulfide bridges in the folding, structure and biological activity of omega-conotoxin GVIA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1434, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, A.; Dekan, Z.; Kaas, Q.; Agwa, A.J.; Starobova, H.; Alewood, P.F.; Schroeder, C.I.; Mobli, M.; Deuis, J.R.; Vetter, I. Mapping the Molecular Surface of the Analgesic NaV1.7-Selective Peptide Pn3a Reveals Residues Essential for Membrane and Channel Interactions. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrews, S. FastQC. 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaas, Q.; Yu, R.; Jin, A.H.; Dutertre, S.; Craik, D.J. ConoServer: Updated content, knowledge, and discovery tools in the conopeptide database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D325–D330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apweiler, R.; Bairoch, A.; Wu, C.H.; Barker, W.C.; Boeckmann, B.; Ferro, S.; Gasteiger, E.; Huang, H.; Lopez, R.; Magrane, M.; et al. UniProt: The Universal Protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D115–D119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.D.; Li, Q.; Lu, A.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Yandell, M.; Olivera, B.M.; Safavi-Hemami, H. The Venom Repertoire of Conus gloriamaris (Chemnitz, 1777), the Glory of the Sea. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform. 2013, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conway, J.R.; Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N. UpSetR: An R package for the visualization of intersecting sets and their properties. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2938–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. Conserved primers for PCR amplification of mitochondrial DNA from different invertebrate phyla. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotech. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Abascal, F.; Zardoya, R.; Telford, M.J. TranslatorX: Multiple alignment of nucleotide sequences guided by amino acid translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W7–W13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, N.; Dawson, J.A.; Thomson, J.A.; Ruotti, V.; Rissman, A.I.; Smits, B.M.; Haag, J.D.; Gould, M.N.; Stewart, R.M.; Kendziorski, C. EBSeq: An empirical Bayes hierarchical model for inference in RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirdita, M.; Schütze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold—Making protein folding accessible to all. BioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera-A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Sample Name | Species | Sampling Location | SRA Number | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Illumina HiSeq | Transcripts | BUSCO (metazoa_odb10; n = 954) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OK006 | V. ebraeus | Okinawa (Japan) | SRR17653519 | 58,508,016 | 57,760,881 | 2500 | 68,809 | C:32.4%[S:25.2%,D:7.2%],F:11.3%,M:56.3% | This work |
| OK193 | V. ebraeus | Ishigaki (Japan) | SRR17653518 | 56,956,142 | 56,523,495 | 2500 | 68,514 | C:33.1%[S:25.7%,D:7.4%],F:11.4%,M:55.5% | This work |
| OK213 | V. ebraeus | Ishigaki (Japan) | SRR17653517 | 67,857,352 | 67,318,628 | 2500 | 66,731 | C:31.8%[S:24.4%,D:7.4%],F:12.9%,M:55.3% | This work |
| MAP17 | V. ebraeus | Bali (Indonesia) | SRR2609538 | 20,828,802 | 20,560,135 | 2000 | 57,781 | C:30.0%[S:25.4%,D:4.6%],F:22.5%,M:47.5% | [15] |
| CebrOK014 | V. ebraeus | Okinawa (Japan) | SRR14407590 | 25,173,828 | 22,036,629 | 4000 | 38,810 | C:6.9%[S:5.7%,D:1.2%],F:8.9%,M:84.2% | [14] |
| CebrOK016 | V. ebraeus | Okinawa (Japan) | SRR14407576 | 29,931,016 | 26,127,506 | 4000 | 62,828 | C:11.3%[S:9.4%,D:1.9%],F:11.5%,M:77.2% | [14] |
| OK005 | V. judaeus | Okinawa (Japan) | SRR17653516 | 58,301,376 | 57,429,299 | 2500 | 63,846 | C:31.6%[S:26.1%,D:5.5%],F:13.5%,M:54.9% | This work |
| OK212 | V. judaeus | Ishigaki (Japan) | SRR17653515 | 79,281,440 | 78,688,495 | 2500 | 95,899 | C:45.6%[S:36.1%,D:9.5%],F:14.2%,M:40.2% | This work |
| OK214 | V. judaeus | Ishigaki (Japan) | SRR17653514 | 89,729,936 | 89,161,848 | 2500 | 111,328 | C:48.6%[S:37.2%,D:11.4%],F:13.9%,M:37.5% | This work |
| CebrOK033 | V. judaeus | Okinawa (Japan) | SRR14407588 | 33,908,028 | 30,229,897 | 4000 | 82,404 | C:25.2%[S:19.3%,D:5.9%],F:20.9%,M:53.9% | [14] |
| CebrOK035 | V. judaeus | Okinawa (Japan) | SRR14407589 | 30,737,140 | 26,518,858 | 4000 | 77,472 | C:16.0%[S:13.1%,D:2.9%],F:20.0%,M:64.0% | [14] |
| RT (min) | Peak Mass (Da) | Peptide Sequence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| V. ebraeus | 0.97 | 3026.162 | TCTGNCRLCGAICCCEPKVCRNNQCIDD |
| 4.98 | 1619.544 | CCKYPLCAAGCSCCTT | |
| 5.03 | 1440.425 | CCC(Btr)RCTRSLH | |
| 5.71 | 2340.781 | CCTFO(hVa)CTACYCCRMHOQHP | |
| 5.76 | 1620.554 | RCCQIVPQCC(Gla)WN | |
| V. judaeus | 3.66 | 2226.812 | ICPGMCLGGYGK(Gla)PFCHCT(Gla)(Nh2) |
| 4.32 | 3318.187 | YTONDA(Gla)SS(hVa)CYFLCLMGIDLD(Gla)CNCO(Gla)(Nh2) | |
| 4.85 | 2571.977 | MTLLLEDGCCTRPRCTGACSCCQD | |
| 4.88 | 2893.113 | ECTRSGGACNSHTQCCDDFCSTATSTCI(Nh2) | |
| 5.23 | 2562.951 | LOCCYI(Gla)(Btr)CSRRCICDOLEO(Nh2) | |
| 5.23 | 2562.951 | LOCCYI(Gla)(Btr)CSRRCLCNOLEO | |
| 5.23 | 2562.951 | LOCCYI(Gla)(Btr)CSRRCICNOLEO | |
| 5.38 | 3256.334 | FCONOCQSCOSOG(Gla)C(hVa)RPYTGHTFFLHL | |
| 5.38 | 3026.162 | TCTGNCRLCGAICCCEPKVCRNNQCIDD |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pardos-Blas, J.R.; Tenorio, M.J.; Galindo, J.C.G.; Zardoya, R. Comparative Venomics of the Cryptic Cone Snail Species Virroconus ebraeus and Virroconus judaeus. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020149
Pardos-Blas JR, Tenorio MJ, Galindo JCG, Zardoya R. Comparative Venomics of the Cryptic Cone Snail Species Virroconus ebraeus and Virroconus judaeus. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(2):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020149
Chicago/Turabian StylePardos-Blas, José Ramón, Manuel J. Tenorio, Juan Carlos G. Galindo, and Rafael Zardoya. 2022. "Comparative Venomics of the Cryptic Cone Snail Species Virroconus ebraeus and Virroconus judaeus" Marine Drugs 20, no. 2: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020149
APA StylePardos-Blas, J. R., Tenorio, M. J., Galindo, J. C. G., & Zardoya, R. (2022). Comparative Venomics of the Cryptic Cone Snail Species Virroconus ebraeus and Virroconus judaeus. Marine Drugs, 20(2), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020149