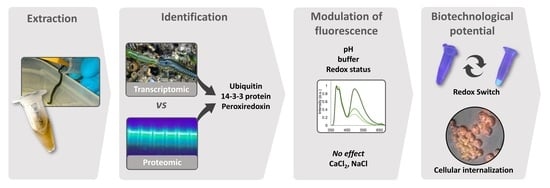
Endogenous Fluorescent Proteins in the Mucus of an Intertidal Polychaeta: Clues for Biotechnology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
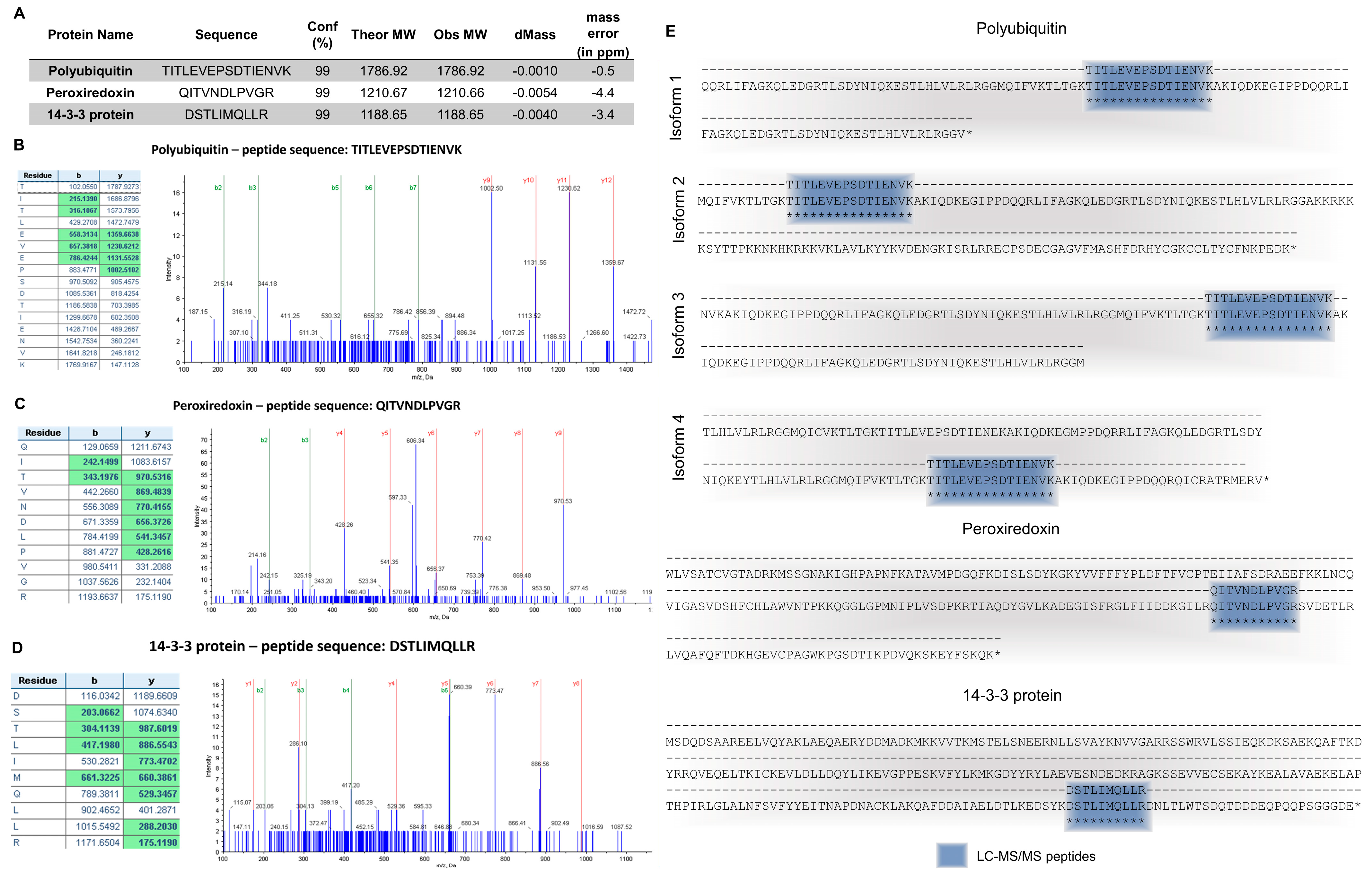
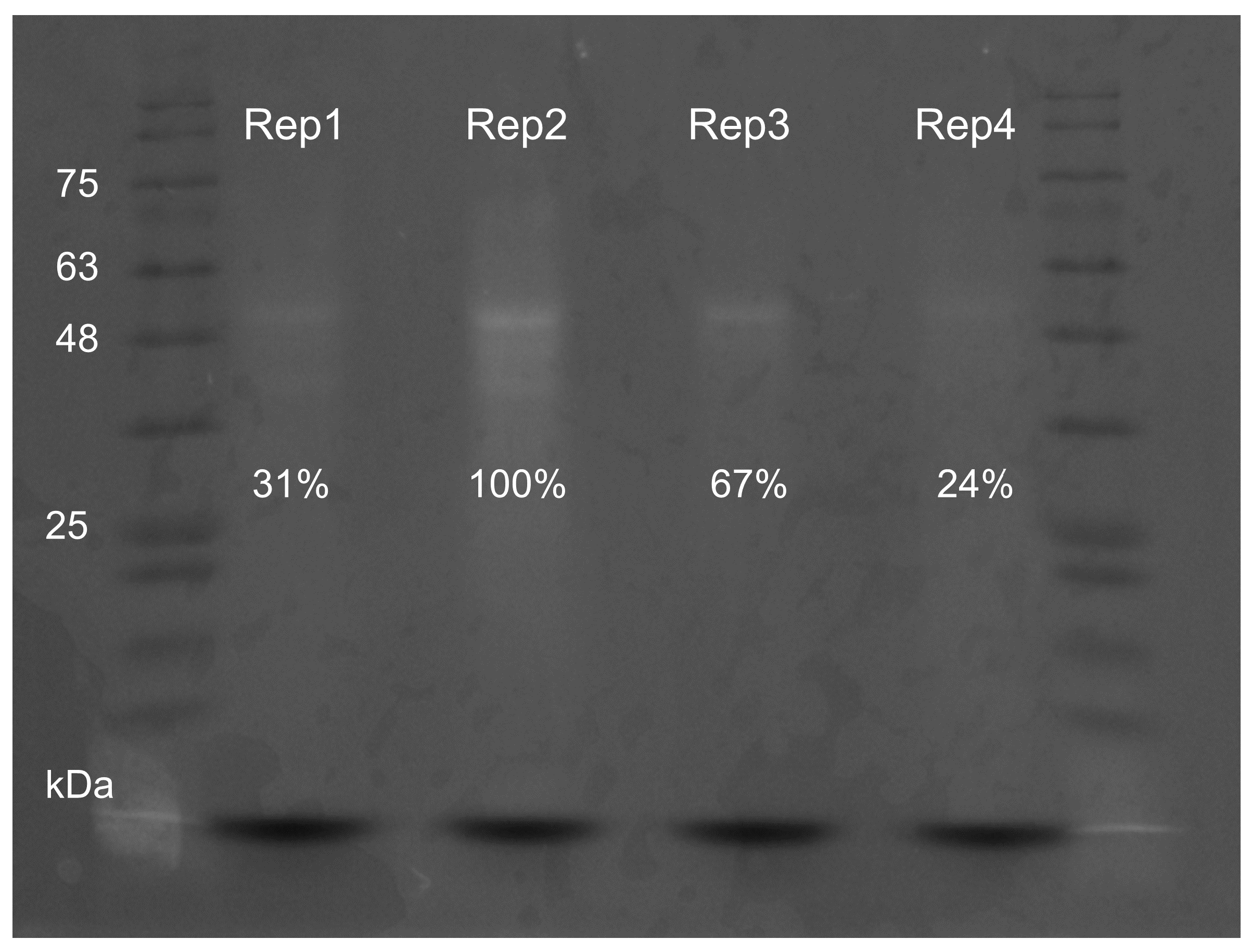
2.1. Molecular Characterization
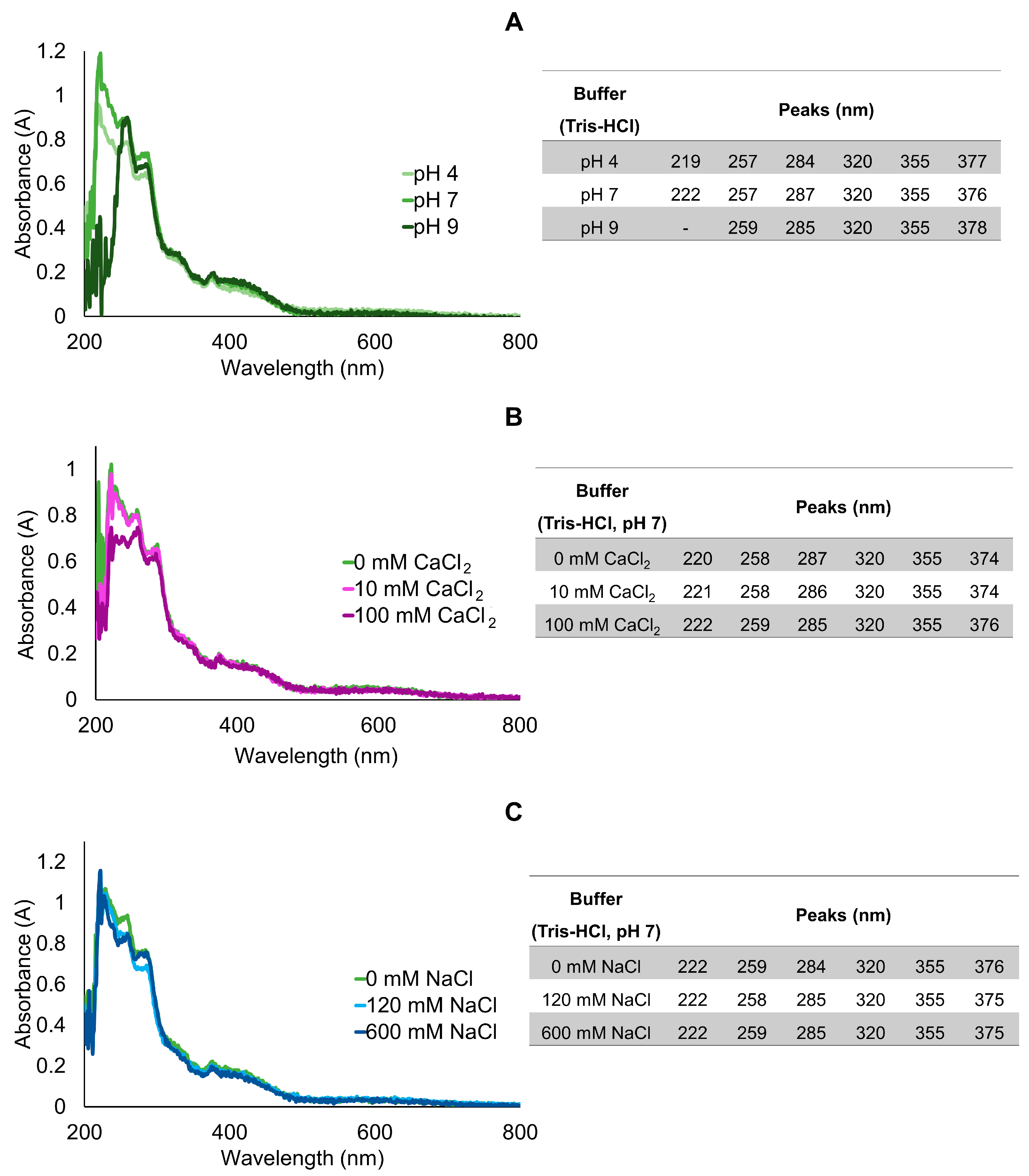
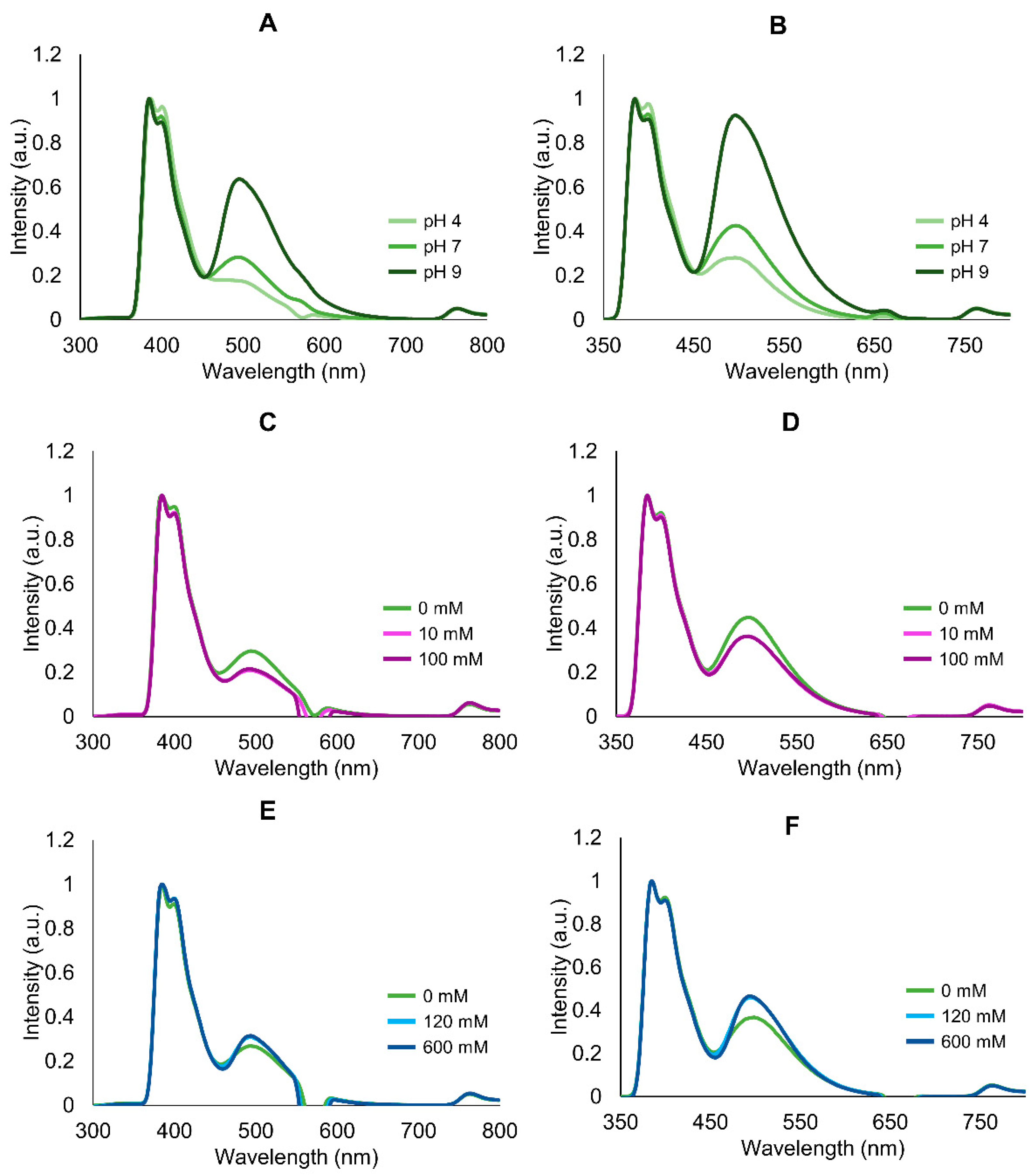
2.2. Modulation of Absorption and Fluorescence
2.3. Histological Localization of the Fluorescent Secretions
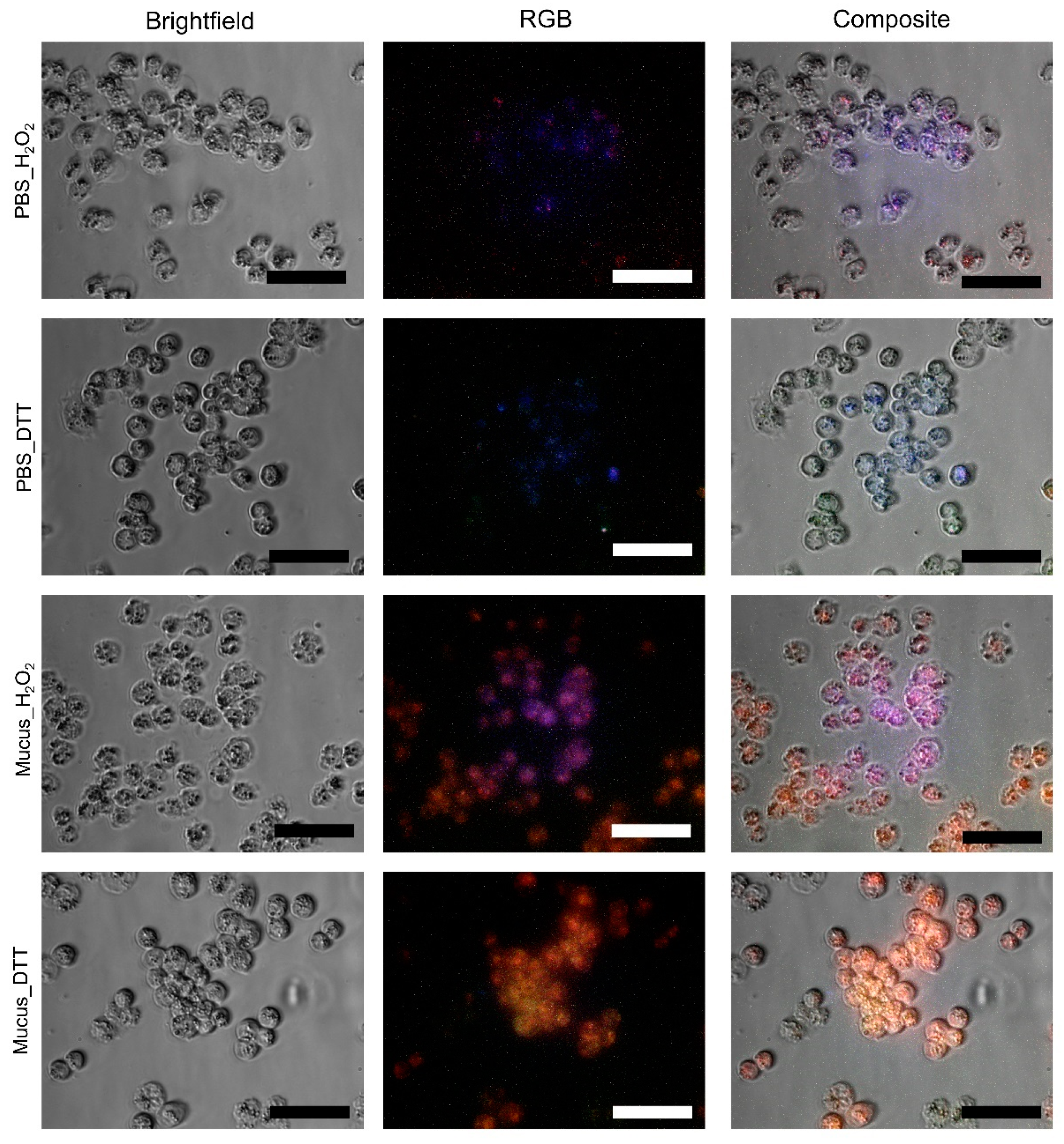
2.4. Internalization by A2780 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Protein Extraction
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Molecular Characterization
4.3.1. Protein Separation
4.3.2. Protein Identification (LC-MS/MS)
4.3.3. Protein Identification (Multiomics Matching)
4.4. Histology
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Fluorochrome Internalization Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lagorio, M.G.; Cordon, G.B.; Iriel, A. Reviewing the relevance of fluorescence in biological systems. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 1538–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimomura, O. Bioluminescence: Chemical Principles and Methods; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2006; ISBN 9812568018. [Google Scholar]
- Tsien, R.Y. The green fluorescent protein. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 509–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widder, E.A. Bioluminescence in the ocean: Origins of biological, chemical, and ecological diversity. Science. 2010, 328, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, J.S.; Schelly, R.C.; Smith, W.L.; Davis, M.P.; Tchernov, D.; Pieribone, V.A.; Gruber, D.F. The covert world of fish biofluorescence: A phylogenetically widespread and phenotypically variable phenomenon. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, A.; Larkum, A.; Cox, G.; Kühl, M.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Fluorescent pigments in corals are photoprotective. Nature 2000, 408, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnett, R.; Head, E.J.; Herring, P.J. Porphyrin pigments of some deep-sea medusae. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1979, 59, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddock, S.H.D.; Dunn, C.W.; Pugh, P.R.; Schnitzler, C.E. Ecology: Bioluminescent and red-fluorescent lures in a deep-sea siphonophore. Science 2005, 309, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanam, R. Biology and Ecology of Venomous Marine Cnidarians; Springer: Singapore, 2016; ISBN 9781771883313. [Google Scholar]
- Shagin, D.A.; Barsova, E.V.; Yanushevich, Y.G.; Fradkov, A.F.; Lukyanov, K.A.; Labas, Y.A.; Semenova, T.N.; Ugalde, J.A.; Meyers, A.; Nunez, J.M.; et al. GFP-like Proteins as Ubiquitous Metazoan Superfamily: Evolution of Functional Features and Structural Complexity. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deheyn, D.D.; Kubokawa, K.; Mccarthy, J.K.; Murakami, A.; Porrachia, M.; Rouse, G.W.; Holland, N.D. Endogenous green fluorescent protein (GFP) in amphioxus. Biol. Bull. 2007, 213, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, T.D.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Leggat, W. Imaging the fluorescence of marine invertebrates and their associated flora. J. Microsc. 2008, 232, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, A.P.; Costa, P.M. The hidden biotechnological potential of marine invertebrates: The Polychaeta case study. Environ. Res. 2019, 173, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomaeus, T.; Purschke, G.; Hausen, H. Polychaete phylogeny based on morphological data—A comparison of current attempts. In Morphology, Molecules, Evolution and Phylogeny in Polychaeta and Related Taxa; Bartolomaeus, T., Purschke, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 341–356. [Google Scholar]
- Nicol, J.A.C. Studies on Chaetopterus variopedatus (Renier). I. The light-producing glands. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1952, 30, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, G.; Nicol, J. Pigments of Chaetopterus variopedatus (Polychaeta). Proc. R. Soc. B 1959, 150, 509–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresneau, C.; Arrio, B.; Lecuyear, B.; Dupaixn, A.; Lescure, N.; Vvolfin, P. The fluorescent product of scaleworm bioluminescent reaction: An in vitro study. Photochem. Photobiol. 1984, 39, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Rodrigo, A.P.; Cabrita, L.; Henriques, P.; Parola, A.J.; Costa, P.M. The complexity of porphyrin-like pigments in a marine annelid sheds new light on haem metabolism in aquatic invertebrates. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, A.P.; Grosso, A.R.; Baptista, P.V.; Fernandes, A.R.; Costa, P.M. A transcriptomic approach to the recruitment of venom proteins in a marine Polychaeta. Toxins 2021, 13, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, A.P.; Lopes, A.; Baptista, P.V.; Costa, M.H.; Fernandes, A.R.; Costa, P.M. The great biotechnological potential of a marine polychaete: An alliance between toxin and natural fluorescence. In Proceedings of the IMMR’18—International Meeting on Marine Research 2018, Peniche, Portugal, 5–6 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, A.P.; Mendes, V.M.; Manadas, B.; Grosso, A.R.; Baptista, P.V.; Costa, P.M.; Fernandes, A.R.; Biology, C.; Caparica, M. De Specific antiproliferative properties of proteinaceous toxin secretions from the marine annelid Eulalia sp. onto ovarian cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, A.P.; Martins, C.; Costa, M.H.; Alves de Matos, A.P.; Costa, P.M. A morphoanatomical approach to the adaptive features of the epidermis and proboscis of a marine Polychaeta: Eulalia viridis (Phyllodocida: Phyllodocidae). J. Anat. 2018, 233, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshchina, V.V.; Yashina, A.V.; Yashin, V.A.; Gol’tyaev, M. Fluorescence of Biologically Active compounds in Plant Secretory Cells. In Research Methods in Plant Science; Studium Press: Houston, TX, USA, 2011; pp. 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Catic, A.; Ploegh, H.L. Ubiquitin—Conserved protein or selfish gene? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicke, L.; Schubert, H.L.; Hill, C.P. Ubiquitin-binding domains. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Maldonado, M.A. The ubiquitin-proteasome system and its role in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 3, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Melani, R.D.; Skinner, O.S.; Fornelli, L.; Domont, G.B.; Compton, P.D.; Kelleher, N.L. Mapping proteoforms and protein complexes from king cobra venom using both denaturing and native top-down proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 2423–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebner, P.; Versteeg, G.A.; Ikeda, F. Ubiquitin enzymes in the regulation of immune responses. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 52, 425–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.N.; Kausar, S.; Cui, H. The biological role of peroxiredoxins in innate immune responses of aquatic invertebrates. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 89, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.R.G.; Nisbet, A.J.; Frew, D.; Bartley, Y.; Oliver, E.M.; McLean, K.; Inglis, N.F.; Watson, E.; Corripio-Miyar, Y.; McNeilly, T.N. Characterisation of a niche-specific excretory-secretory peroxiredoxin from the parasitic nematode Teladorsagia circumcincta. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hemert, M.J.; Yde Steensma, H.; Van Paul, G. 14-3-3 Proteins: Key regulators of cell division, signalling and apoptosis. BioEssays 2001, 23, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulvila, J.; Vanha-aho, L.-M.; Kleino, A.; Vaha-Makila, M.; Vuoksio, M.; Eskelinen, S.; Hultmark, D.; Kocks, C.; Hallman, M.; Parikka, M.; et al. Cofilin regulator 14-3-3 is an evolutionarily conserved protein required for phagocytosis and microbial resistance. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.M.; Brinchmann, M.F. Skin mucus proteins of lumpsucker (Cyclopterus lumpus). Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 9, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, B.H.; Peatman, E. Mucosal Health in Aquaculture; Elsevier Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2015; ISBN 9780124171930. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, B.; Fernandes, J.M.O.; Caipang, C.M.A.; Kiron, V.; Rombout, J.H.W.M.; Brinchmann, M.F. Proteome reference map of the skin mucus of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) revealing immune competent molecules. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruana, N.J.; Cooke, I.R.; Faou, P.; Finn, J.; Hall, N.E.; Norman, M.; Pineda, S.S.; Strugnell, J.M. A combined proteomic and transcriptomic analysis of slime secreted by the southern bottletail squid, Sepiadarium austrinum (Cephalopoda). J. Proteom. 2016, 148, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchinfuso, D.G.; Taylor, P.; Ross, E.; Ignatchenko, A.; Ignatchenko, V.; Kislinger, T.; Pearson, B.J.; Moran, M.F. Proteomic profiling of the planarian Schmidtea mediterranea and its mucous reveals similarities with human secretions and those predicted for parasitic flatworms. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Giri, B.R.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, G. 14-3-3 protein and ubiquitin C acting as SjIAP interaction partners facilitate tegumental integrity in Schistosoma japonicum. Int. J. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Yasuda, S.; Li, X.; Fukao, Y.; Tohge, T.; Fernie, A.R.; Matsukura, C.; Ezura, H.; Sato, T.; Yamaguchi, J.; et al. Characterization of ubiquitin ligase SlATL31 and proteomic analysis of 14-3-3 targets in tomato fruit tissue (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Proteom. 2016, 143, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.P.; Park, C.M.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, E.; Jeong, M.; Shin, J.Y.; Yun, C.H.; Kim, K.; Chock, P.B.; Chae, H.Z. Structural and biochemical analyses reveal ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-L1 as a specific client of the peroxiredoxin II chaperone. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 640, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loumaye, E.; Andersen, A.C.; Clippe, A.; Degand, H.; Dubuisson, M.; Zal, F.; Morsomme, P.; Rees, J.F.; Knoops, B. Cloning and characterization of Arenicola marina peroxiredoxin 6, an annelid two-cysteine peroxiredoxin highly homologous to mammalian one-cysteine peroxiredoxins. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, Y.; Martínez-Morcillo, F.J.; Esteban, M.Á.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Cuesta, A. Fish peroxiredoxins and their role in immunity. Biology 2015, 4, 860–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, M.; Lima, J.C.; Bastos, M.; Santos, H.; Maçanita, A.L. Unfolding of ubiquitin studied by picosecond time-resolved fluorescence of the tyrosine residue. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 2609–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhuo, Y.; Solntsev, K.M.; Reddish, F.; Tang, S.; Yang, J.J. Effect of Ca2+ on the steady-state and time-resolved emission properties of the genetically encoded fluorescent sensor catcher. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.J.; Taylor, L.; Ananthanarayanan, V.S. Role of calcium in stabilizing the structure of hyalin, a major protein component of the sea urchin extraembryonic hyaline layer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 152, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romoser, V.A.; Hinkle, P.M.; Persechini, A. Detection in living cells of Ca2+-dependent changes in the fluorescence emission of an indicator composed of two green fluorescent protein variants linked by a calmodulin-binding sequence. A new class of fluorescent indicators. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 13270–13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, N.; Martins, M.; Rodrigo, A.P.; Martins, C.; Costa, P.M. Explorations on the ecological role of toxin secretion and delivery in jawless predatory Polychaeta. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subach, F.V.; Subach, O.M.; Gundorov, I.S.; Morozova, K.S.; Kiryl, D.; Cuervo, A.M.; Verkhusha, V.V. Monomeric fluorescent timers that change color from blue to red report on cellular trafficking. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hames, B.D. Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins: A Practical Approach, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ornstein, L.; Davis, J. Disc electroforesis. I Background and Theory. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1964, 121, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabilloud, T. A comparison between low background silver diammine and silver nitrate protein stains. Electrophoresis 1992, 13, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.M. The Handbook of Histopathological Practices in Aquatic Environments; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; ISBN 9780128120323. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigo, A.P.; Lopes, A.; Pereira, R.; Anjo, S.I.; Manadas, B.; Grosso, A.R.; Baptista, P.V.; Fernandes, A.R.; Costa, P.M. Endogenous Fluorescent Proteins in the Mucus of an Intertidal Polychaeta: Clues for Biotechnology. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040224
Rodrigo AP, Lopes A, Pereira R, Anjo SI, Manadas B, Grosso AR, Baptista PV, Fernandes AR, Costa PM. Endogenous Fluorescent Proteins in the Mucus of an Intertidal Polychaeta: Clues for Biotechnology. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(4):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040224
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigo, Ana P., Ana Lopes, Ricardo Pereira, Sandra I. Anjo, Bruno Manadas, Ana R. Grosso, Pedro V. Baptista, Alexandra R. Fernandes, and Pedro M. Costa. 2022. "Endogenous Fluorescent Proteins in the Mucus of an Intertidal Polychaeta: Clues for Biotechnology" Marine Drugs 20, no. 4: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040224
APA StyleRodrigo, A. P., Lopes, A., Pereira, R., Anjo, S. I., Manadas, B., Grosso, A. R., Baptista, P. V., Fernandes, A. R., & Costa, P. M. (2022). Endogenous Fluorescent Proteins in the Mucus of an Intertidal Polychaeta: Clues for Biotechnology. Marine Drugs, 20(4), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040224