A Novel α4/7-Conotoxin QuIA Selectively Inhibits α3β2 and α6/α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subtypes with High Efficacy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
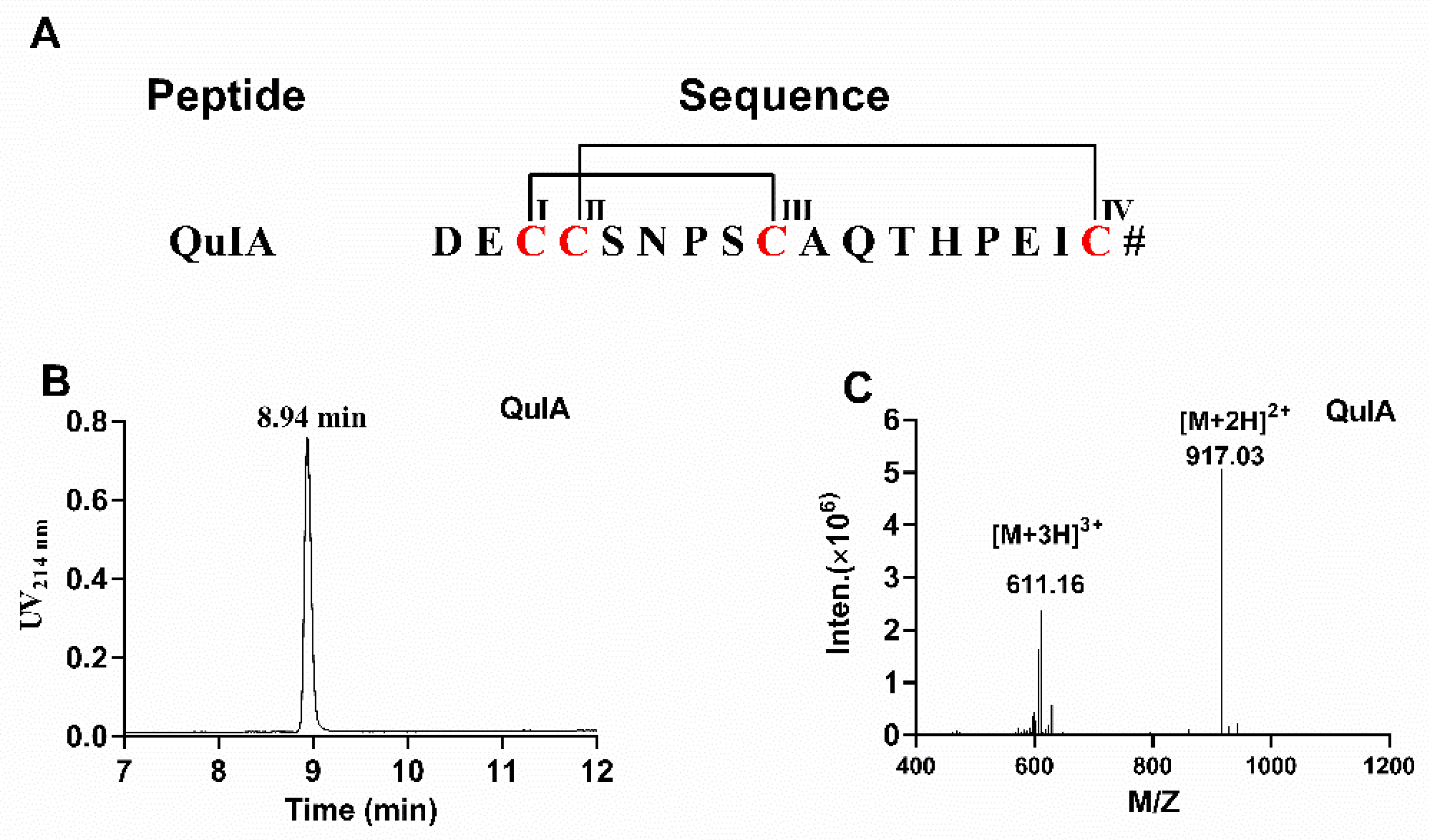
2.1. Chemical Synthesis of α-4/7 QuIA
2.2. Effect of α-Conotoxin QuIA on Different nAChR Subtypes
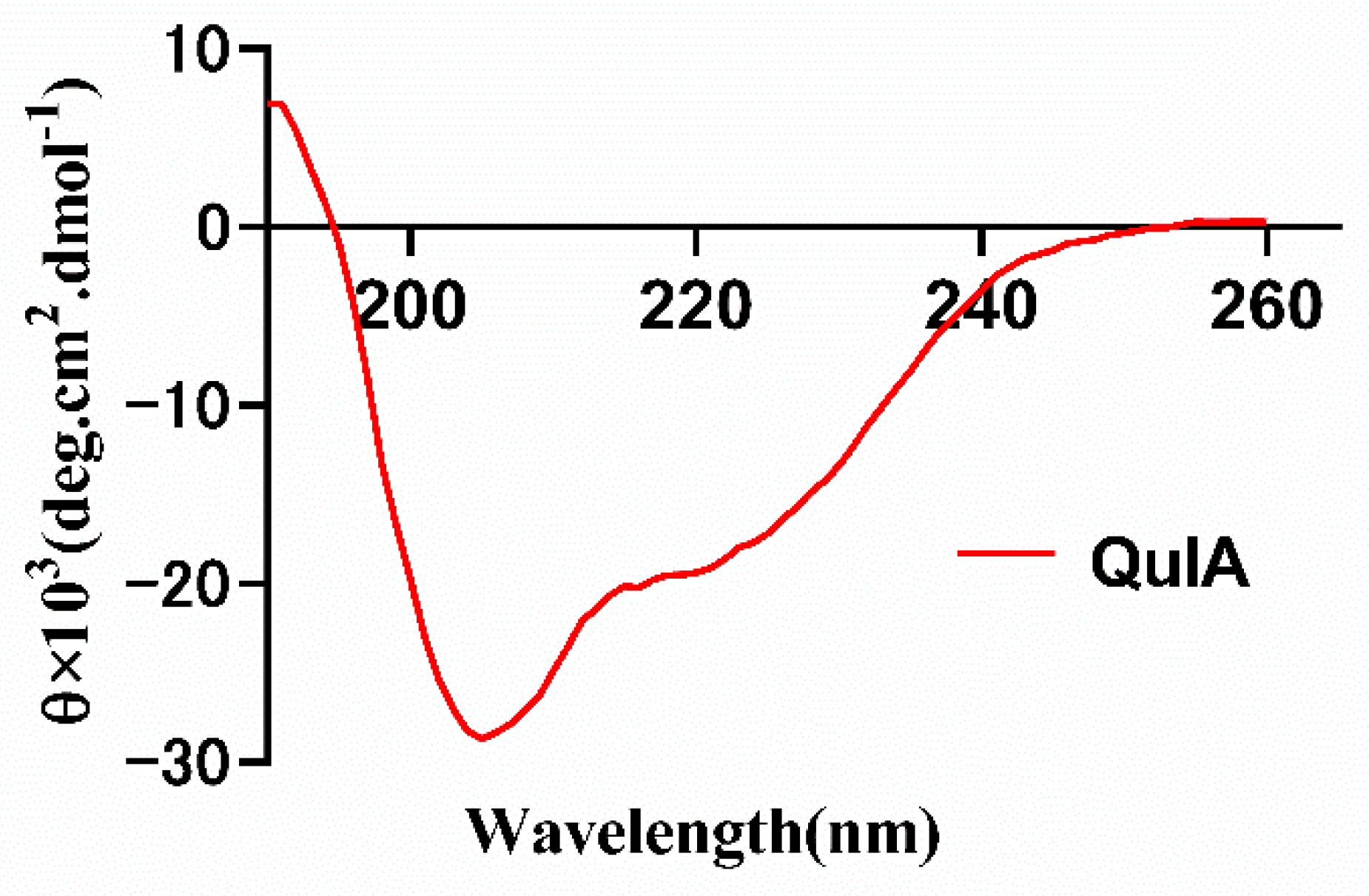
2.3. CD Spectrum of QuIA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Peptide Synthesis
4.3. Establishment of nAChRs Model and cRNA Preparation and Injection
4.4. Electrophysiology
4.5. Data Analysis
4.6. Determination of the Secondary Structure Using Circular Dichroism
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terlau, H.; Olivera, B.M. Conus venoms: A rich source of novel ion channel-targeted peptides. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akondi, K.B.; Muttenthaler, M.; Dutertre, S.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Discovery, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships of conotoxins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5815–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, A.H.; Muttenthaler, M.; Dutertre, S.; Himaya, S.W.A.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Conotoxins: Chemistry and Biology. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 11510–11549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Dutertre, S.; Vetter, I.; Christie, M.J. Conus venom Peptide pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 259–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halai, R.; Craik, D.J. Conotoxins: Natural product drug leads. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, L.; McIntosh, J.M. α-conotoxins as pharmacological probes of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albuquerque, E.X.; Pereira, E.F.; Alkondon, M.; Rogers, S.W. Mammalian nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: From structure to function. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 73–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gotti, C.; Clementi, F.; Fornari, A.; Gaimarri, A.; Guiducci, S.; Manfredi, I.; Moretti, M.; Pedrazzi, P.; Pucci, L.; Zoli, M. Structural and functional diversity of native brain neuronal nicotinic receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurst, R.; Rollema, H.; Bertrand, D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: From basic science to therapeutics. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2013, 137, 22–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, J.A.; Gu, S.; Davini, W.B.; Bredt, D.S. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor redux: Discovery of accessories opens therapeutic vistas. Science 2021, 373, 6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Vivanco, A.; Hone, A.J.; Scadden, M.L.; Carmona-Hidalgo, B.; McIntosh, J.M.; Albillos, A. Monkey adrenal chromaffin cells express α6β4* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perez-Alvarez, A.; Hernandez-Vivanco, A.; McIntosh, J.M.; Albillos, A. Native α6β4* nicotinic receptors control exocytosis in human chromaffin cells of the adrenal gland. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wieskopf, J.S.; Mathur, J.; Limapichat, W.; Post, M.R.; Al-Qazzaz, M.; Sorge, R.E.; Martin, L.J.; Zaykin, D.V.; Smith, S.B.; Freitas, K.; et al. The nicotinic α6 subunit gene determines variability in chronic pain sensitivity via cross-inhibition of P2X2/3 receptors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 287ra72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hone, A.J.; Meyer, E.L.; McIntyre, M.; McIntosh, J.M. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in dorsal root ganglion neurons include the α6β4* subtype. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hone, A.J.; McIntosh, J.M. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in neuropathic and inflammatory pain. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 1045–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuryatov, A.; Olale, F.; Cooper, J.; Choi, C.; Lindstrom, J. Human α6 AChR subtypes: Subunit composition, assembly, and pharmacological responses. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 2570–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowell, C.; Olivera, B.M.; Garrett, J.E.; Staheli, S.T.; Watkins, M.; Kuryatov, A.; Yoshikami, D.; Lindstrom, J.M.; McIntosh, J.M. α-conotoxin PIA is selective for α6 subunit-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 8445–8452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hout, M.; Valdes, A.; Christensen, S.B.; Tran, P.T.; Watkins, M.; Gajewiak, J.; Jensen, A.A.; Olivera, B.M.; McIntosh, J.M. α-Conotoxin VnIB from Conus ventricosus is a potent and selective antagonist of α6β4* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuropharmacology 2019, 157, 107691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, L.; Dowell, C.; Watkins, M.; Stitzel, J.A.; Olivera, B.M.; McIntosh, J.M. α-conotoxin BuIA, a novel peptide from Conus bullatus, distinguishes among neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azam, L.; Maskos, U.; Changeux, J.P.; Dowell, C.D.; Christensen, S.; De Biasi, M.; McIntosh, J.M. α-Conotoxin BuIA[T5A;P6O]: A novel ligand that discriminates between α6β4 and α6β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and blocks nicotine-stimulated norepinephrine release. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 5113–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Peng, C.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, T.; Huang, Y.; Shi, Q. High Throughput Identification of Novel Conotoxins from the Vermivorous Oak Cone Snail (Conus quercinus) by Transcriptome Sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, B.; Peng, C.; Yang, J.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Q. Cone Snails: A Big Store of Conotoxins for Novel Drug Discovery. Toxins 2017, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Li, C.; Dong, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhangsun, D.; Luo, S. Discovery Methodology of Novel Conotoxins from Conus Species. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spies, M.; Lips, K.S.; Kurzen, H.; Kummer, W.; Haberberger, R.V. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors containing subunits α3 and α5 in rat nociceptive dorsal root ganglion neurons. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2006, 30, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limapichat, W.; Dougherty, D.A.; Lester, H.A. Subtype-specific mechanisms for functional interaction between α6β4* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and P2X receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 86, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertrand, D.; Terry, A.V., Jr. The wonderland of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 151, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, T.T.; Olivera, B.M.; Han, K.H.; Christensen, S.B.; Dowell, C.; Tsigelny, I.; Ho, K.Y.; Taylor, P.; McIntosh, J.M. α-conotoxin OmIA is a potent ligand for the acetylcholine-binding protein as well as α3β2 and α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 24678–24686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, S.; Akondi, K.B.; Zhangsun, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Y.; Christensen, S.; Dowell, C.; Daly, N.L.; Craik, D.J.; et al. Atypical α-conotoxin LtIA from Conus litteratus targets a novel microsite of the α3β2 nicotinic receptor. T J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 12355–12366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, S.; Zhangsun, D.; Schroeder, C.I.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Weltzin, M.M.; Eberhard, S.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; et al. A novel α4/7-conotoxin LvIA from Conus lividus that selectively blocks α3β2 vs. α6/α3β2β3 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 1842–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIntosh, J.M.; Dowell, C.; Watkins, M.; Garrett, J.E.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M. α-conotoxin GIC from Conus geographus, a novel peptide antagonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33610–33615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hone, A.J.; Kaas, Q.; Kearns, I.; Hararah, F.; Gajewiak, J.; Christensen, S.; Craik, D.J.; McIntosh, J.M. Computational and Functional Mapping of Human and Rat α6β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Reveals Species-Specific Ligand-Binding Motifs. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1685–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucci, L.; Grazioso, G.; Dallanoce, C.; Rizzi, L.; De Micheli, C.; Clementi, F.; Bertrand, S.; Bertrand, D.; Longhi, R.; De Amici, M.; et al. Engineering of α-conotoxin MII-derived peptides with increased selectivity for native α6β2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3775–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartier, G.E.; Yoshikami, D.; Gray, W.R.; Luo, S.; Olivera, B.M.; McIntosh, J.M. A new α-conotoxin which targets α3β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7522–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, S.; Zhangsun, D.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Christensen, S.; Harvey, P.J.; Akcan, M.; Craik, D.J.; McIntosh, J.M. Characterization of a novel α-conotoxin TxID from Conus textile that potently blocks rat α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9655–9663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franco, A.; Kompella, S.N.; Akondi, K.B.; Melaun, C.; Daly, N.L.; Luetje, C.W.; Alewood, P.F.; Craik, D.J.; Adams, D.J.; Mari, F. RegIIA: An α4/7-conotoxin from the venom of Conus regius that potently blocks α3β4 nAChRs. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kompella, S.N.; Hung, A.; Clark, R.J.; Mari, F.; Adams, D.J. Alanine scan of α-conotoxin RegIIA reveals a selective α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIntosh, J.M.; Plazas, P.V.; Watkins, M.; Gomez-Casati, M.E.; Olivera, B.M.; Elgoyhen, A.B. A novel α-conotoxin, PeIA, cloned from Conus pergrandis, discriminates between rat α9α10 and α7 nicotinic cholinergic receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30107–30112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hone, A.J.; Ruiz, M.; Scadden, M.; Christensen, S.; Gajewiak, J.; Azam, L.; McIntosh, J.M. Positional scanning mutagenesis of α-conotoxin PeIA identifies critical residues that confer potency and selectivity for α6/α3β2β3 and α3β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 25428–25439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hone, A.J.; Scadden, M.; Gajewiak, J.; Christensen, S.; Lindstrom, J.; McIntosh, J.M. α-Conotoxin PeIA[S9H,V10A,E14N] potently and selectively blocks α6β2β3 versus α6β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Pan, S.; Xu, M.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Kasheverov, I.E.; et al. High Selectivity of an α-Conotoxin LvIA Analogue for α3β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Is Mediated by β2 Functionally Important Residues. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13656–13668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Subtype | IC50(nM) a | Hill Slope a |
|---|---|---|
| rα3β2 | 55.7 (39.71–79.78) | 0.8 (0.7–1.2) |
| rα6/α3β4 | 90.68 (67.72–122.0) | 0.8 (0.6–1.1) |
| rα3β4 | >10,000 b | ND |
| rα7 | >20,000 b | ND |
| mα1β1δɛ | >10,000 b | ND |
| rα4β2 | >10,000 b | ND |
| rα9α10 | >10,000 b | ND |
| hα9α10 | >10,000 b | ND |
| rα6/α3β2β3 | >10,000 b | ND |
| α-CTx | Organism | Sequence | Target a | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QuIA | C.quercinus/ C. ebraeus | DECCSNPSCAQTHPEIC# | rα3β2 ≈ rα6β4 | This work |
| MII | C.magus | GCCSNPVCHLEHSNLC# | rα6β2β3 > rα3β2 > rα6β4 | [32,33] |
| TxID | C.textile | GCCSHPVCSAMSPIC# | rα3β4 > rα6β4 ≫ rα2β4 | [34] |
| VnIB | C. ventricosus | GGCCSHPVCYTKNPNCG# | rα6β4 > rα3β4 ≫ rα6β2β3 | [18] |
| PIA | C. purpurascens | RDPCCSNPVCTVHNPQIC# | rα6β2β3 > rα6β4 ≈ rα3β2 > rα3β4 | [17] |
| BuIA | C. bullatus | GCCSTPPCAVLYC# | rα6β2β3 > rα6β4 > rα3β2 > rα3β4 | [19,20] |
| RegIIA | C. regius | GCCSHPACNVNNPHIC# | rα3β2 > rα3β4 ≈ rα6β2 | [35,36] |
| PeIA | C. pergrandis | GCCSHPACSVNHPELC# | rα3β2 ≈ rα6/α3β4 ≈rα6/α3β2β3 > rα6β4 | [37,38,39] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhangsun, D.; Wu, Y.; Luo, S. A Novel α4/7-Conotoxin QuIA Selectively Inhibits α3β2 and α6/α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subtypes with High Efficacy. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020146
Wang L, Wu X, Zhu X, Zhangsun D, Wu Y, Luo S. A Novel α4/7-Conotoxin QuIA Selectively Inhibits α3β2 and α6/α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subtypes with High Efficacy. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(2):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020146
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liujun, Xixi Wu, Xiaopeng Zhu, Dongting Zhangsun, Yong Wu, and Sulan Luo. 2022. "A Novel α4/7-Conotoxin QuIA Selectively Inhibits α3β2 and α6/α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subtypes with High Efficacy" Marine Drugs 20, no. 2: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020146
APA StyleWang, L., Wu, X., Zhu, X., Zhangsun, D., Wu, Y., & Luo, S. (2022). A Novel α4/7-Conotoxin QuIA Selectively Inhibits α3β2 and α6/α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subtypes with High Efficacy. Marine Drugs, 20(2), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020146







