Aerophobin-1 from the Marine Sponge Aplysina aerophoba Modulates Osteogenesis in Zebrafish Larvae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Toxicity and Osteogenic Activity of the Sponge Extract
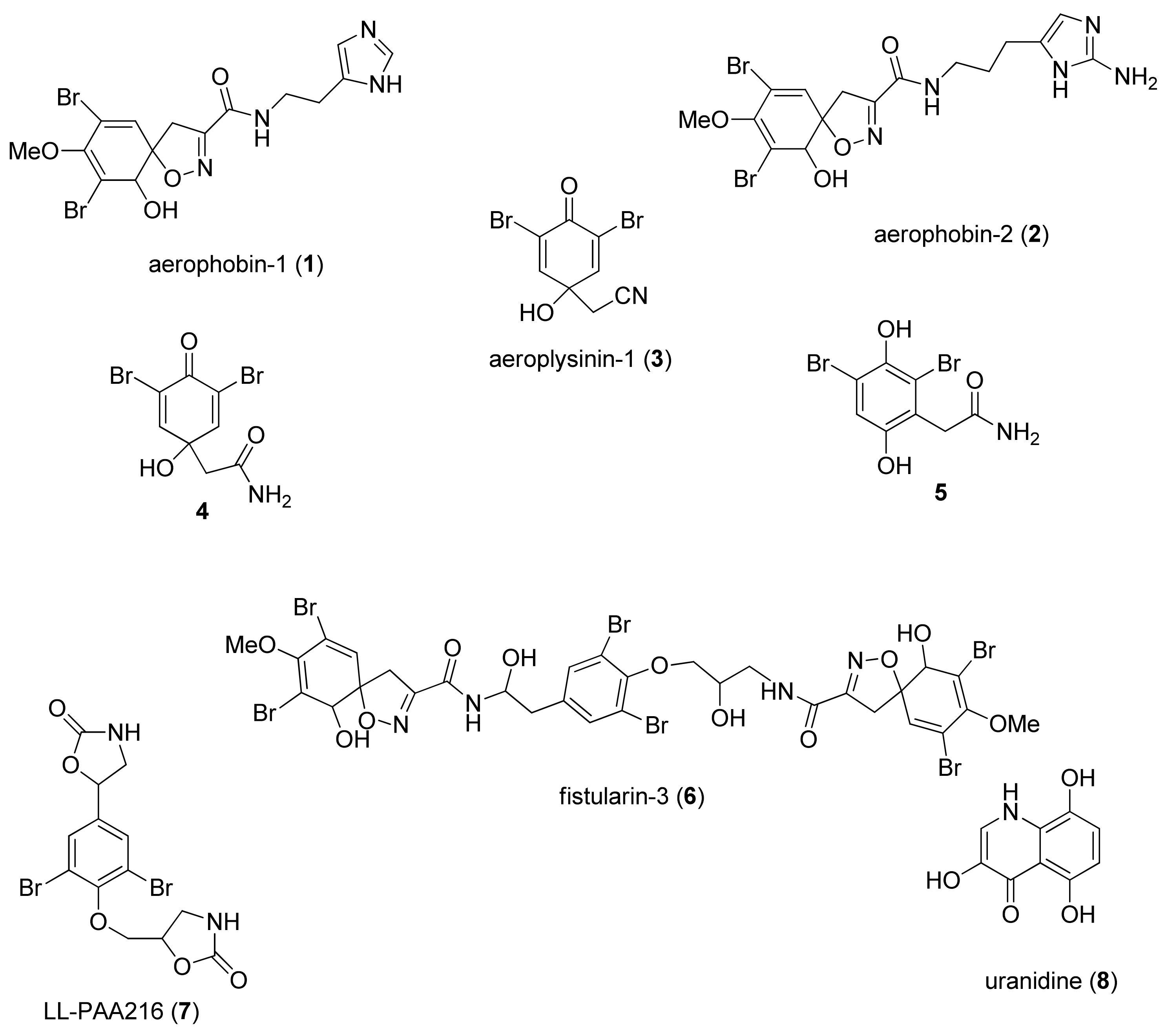
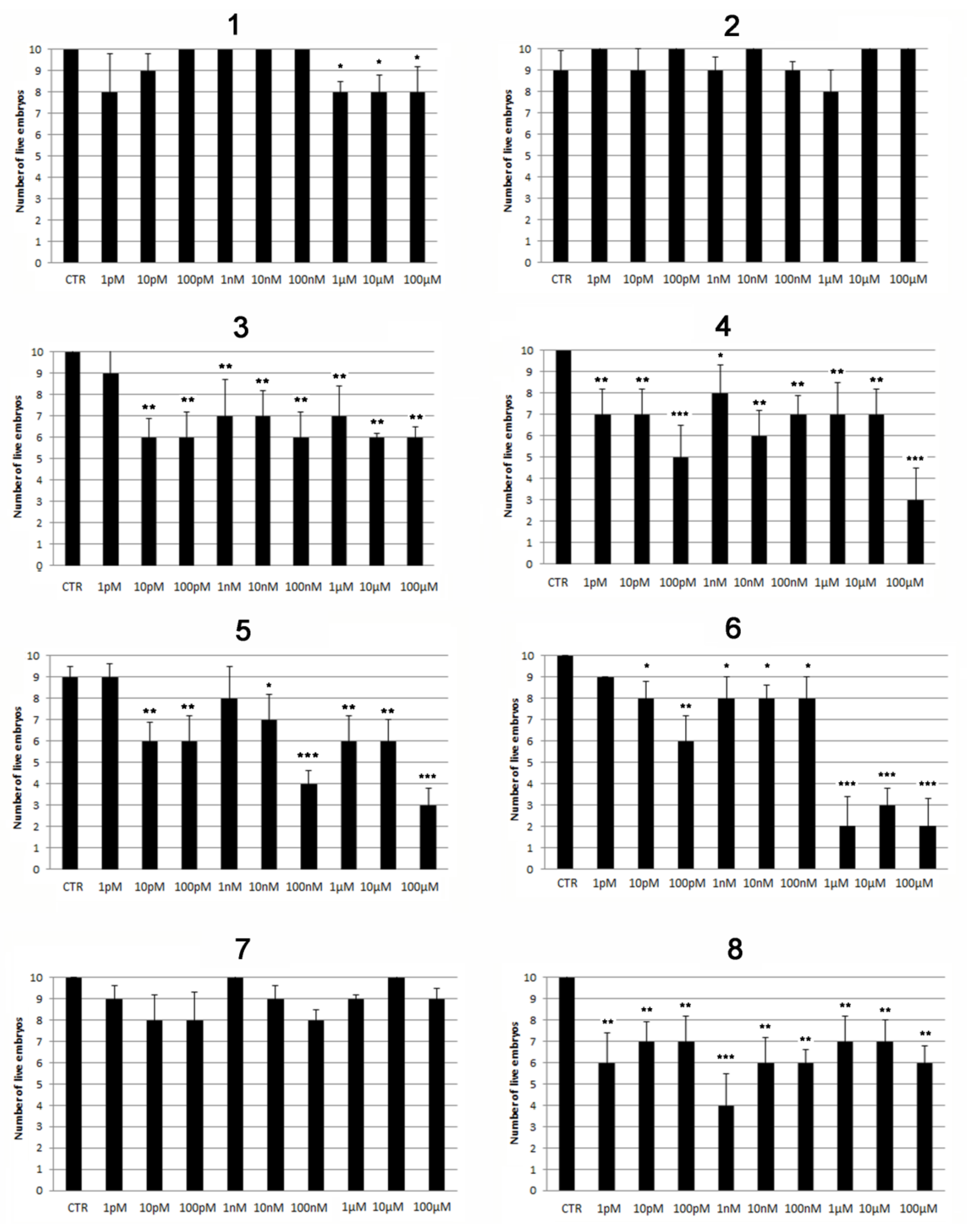
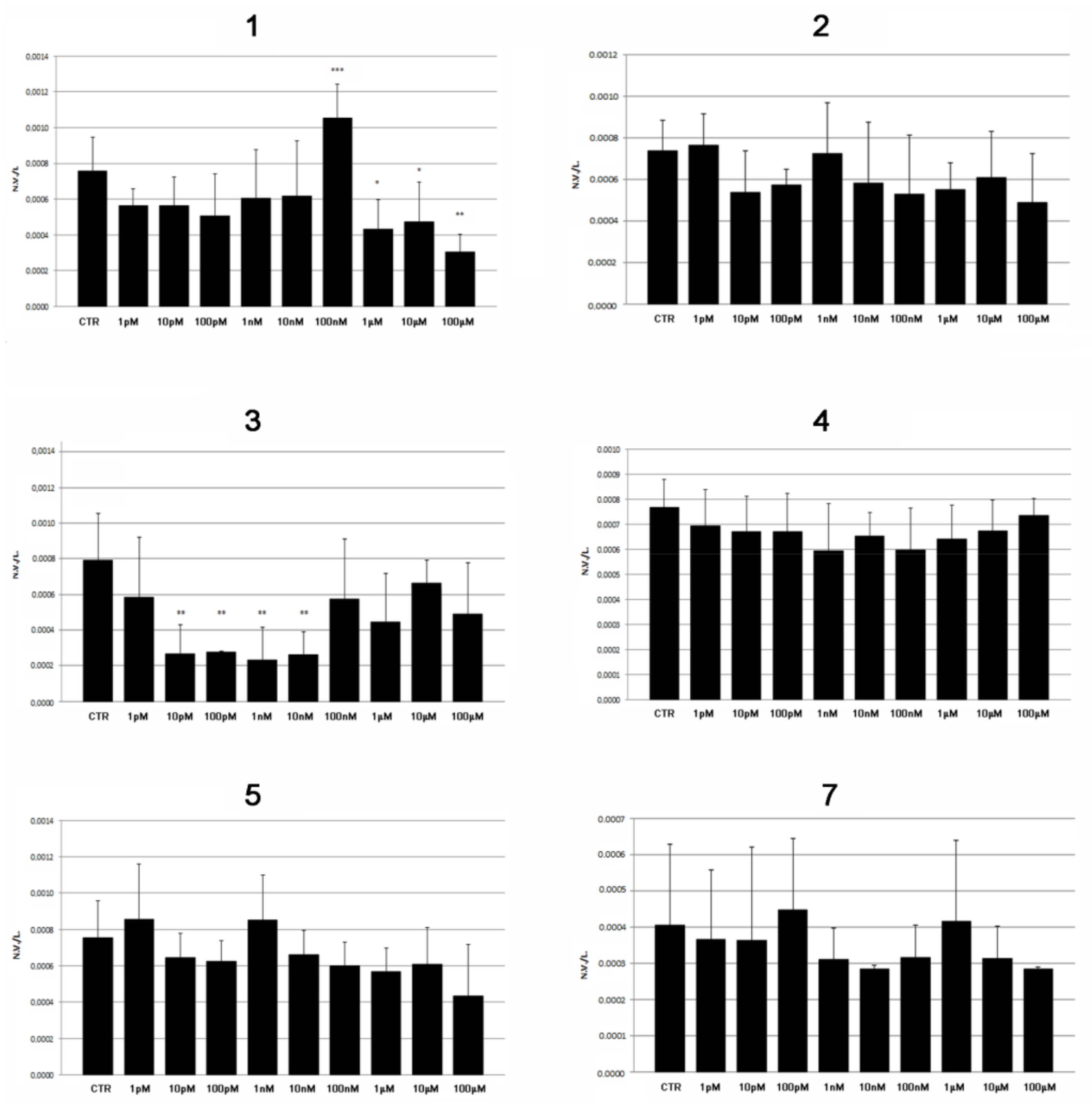
2.2. Modulatory Effects of Pure Compounds 1–8 on Zebrafish Embryo Osteogenesis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Biological Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation Procedures
4.4. Ethics Statement
4.5. Animals
4.6. Zebrafish Treatment
4.7. Histochemical Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiménez, C. Marine Natural Products in Medicinal Chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghareeb, M.A.; Tammam, M.A.; El-Demerdash, A.; Atanasov, A.G. Insights about clinically approved and Preclinically investigated marine natural products. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2020, 2, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigwart, J.D.; Blasiak, R.; Jaspars, M.; Jouffray, J.-B.; Tasdemir, D. Unlocking the potential of marine biodiscovery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaugule, S.R.; Indap, M.M.; Chiplunkar, S.V. Marine natural products: New avenue in treatment of osteoporosis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Angkouw, E.D.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; De Voogd, N.J.; Tsukamoto, S. Ceylonamides A-F, Nitrogenous Spongian Diterpenes That Inhibit RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis, from the Marine Sponge Spongiaceylonensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, M.; Shrestha, S.K.; Kim, H.; Gerwick, W.H.; Soh, Y. Kalkitoxin reduces osteoclast formation and resorption and protects against inflammatory bone loss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, D.; Jin, H.; Ye, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, K.; Kuek, V.; Xu, K.; Qiu, H.; Chen, P.; et al. Hymenialdisine: A Marine Natural Product That Acts on Both Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts and Prevents Estrogen-Dependent Bone Loss in Mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2020, 35, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Bao, J.; Zhang, H. Arthpyrone L, a New Pyridone Alkaloid from a Deep-Sea Arthrinium sp., Inhibits Proliferation of MG63 Osteosarcoma Cells by Inducing G0/G1 Arrest and Apoptosis. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2000639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Rixiati, Y.; Huang, H.; Shi, Y.J.; Huang, C.; Jiao, B. Asperolide A prevents bone metastatic breast cancer via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/c-Fos/NFATc1 signaling pathway. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 8173–8185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Li, S.-M.; Gao, L.; Zheng, J.-J.; Wu, Y.-W.; Shao, C.-L.; Ren, W.-H.; Zhi, K. CHNQD-00603 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells by the miR-452-3p-Mediated Autophagy Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Luo, D.; Luesch, H. Advances in exploring the therapeutic potential of marine natural products. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 147, 104373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-Y.; Choi, T.-I.; Lee, Y.-R.; Choe, S.-K.; Kim, C.-H. Zebrafish as an animal model for biomedical research. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnovali, M.; Banfi, G.; Mariotti, M. Zebrafish Models of Human Skeletal Disorders: Embryo and Adult Swimming Together. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1253710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmel, C.B.; DeLaurier, A.; Ullmann, B.; Dowd, J.; McFadden, M. Modes of developmental outgrowth and shaping of a craniofacial bone in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, B.; Santos Lopes, S. The importance of Zebrafish in biomedical research. Acta Med. Port. 2013, 26, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, N.C.; Mabee, P.M. Developmental Morphology of the Axial Skeleton of the Zebrafish, Danio rerio (Ostariophysi: Cyprinidae). Dev. Dyn. 2003, 228, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.; Schröder, H.; Wang, X. The Understanding of the Metazoan Skeletal System, Based on the Initial Discoveries with Siliceous and Calcareous Sponges. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, N.S.; Montes, R.C.; Tavares, J.F.; da Silva, M.S.; da Cunha, E.V.L.; de Athayde-Filho, P.F.; Rodrigues, L.C.; da Silva Dias, C.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M. Brominated Compounds from Marine Sponges of the Genus Aplysina and a Compilation of Their 13C NMR Spectral Data. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2316–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Sakuma, Y.; Kobayashi, J. Suberedamines A and B, New Bromotyrosine Alkaloids from a Sponge Suberea Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 980–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, B.; Ebel, R.; Elbrächter, M.; Kirchner, M.; Proksch, P. Defense metabolites from the marine sponge Verongia aerophoba. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1996, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puyana, M.; Pawlik, J.; Blum, J.; Fenical, W. Metabolite variability in Caribbean sponges of the genus Aplysina. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2015, 25, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peng, J.; Li, J.; Hamann, M.T. The Marine Bromotyrosine Derivatives. In Alkaloids: Chemistry and Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 59–262. ISBN 0124695612. [Google Scholar]
- Sirimangkalakitti, N.; Olatunji, O.J.; Changwichit, K.; Saesong, T.; Chamni, S.; Chanvorachote, P.; Ingkaninan, K.; Plubrukarn, A.; Suwanborirux, K. Bromotyrosine Alkaloids with Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity from the Thai Sponge Acanthodendrilla sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1934578X1501001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göthel, Q.; Sirirak, T.; Köck, M. Bromotyrosine-derived alkaloids from the Caribbean sponge Aplysina lacunosa. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 2334–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, G.; De Rosa, S.; De Stefano, S.; Spinella, A.; Sodano, G. The zoochrome of the sponge Verongia aerophoba (“Uranidine”). Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 2925–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De FCesário, H.P.S.; Silva, F.C.O.; Ferreira, M.K.A.; de Menezes, J.E.S.A.; dos Santos, H.S.; Nogueira, C.E.S.; de LSilva, K.S.B.; Hajdu, E.; Silveira, E.R.; Pessoa, O.D.L. Anxiolytic-like effect of brominated compounds from the marine sponge Aplysina fulva on adult zebrafish (Danio rerio): Involvement of the GABAergic system. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 146, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Föger-Samwald, U.; Dovjak, P.; Azizi-Semrad, U.; Kerschan-Schindl, K.; Pietschmann, P. Osteoporosis: Pathophysiology and therapeutic options. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 1017–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yamauchi, K.; Mitsunaga, T. A review on osteoclast diseases and osteoclastogenesis inhibitors recently developed from natural resources. Fitoterapia 2020, 142, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio), 5th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dynam. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M.; Varga, Z.M. Anesthesia and euthanasia in zebrafish. ILAR J. 2012, 53, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.B.; Kimmel, C.B. A two-color acid-free cartilage and bone stain for zebrafish larvae. Biotech. Histochem. 2007, 82, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | Significant Toxic Effects | Pro-Osteogenic Activity Minimum Dose Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | Timing | ||
| Acetone extract | ≥3 mg/L | 5 dpf | 3 µM |
| 1 | ≥1 μM | 5 dpf | 100 nM |
| 2 | none (until 100 µM) | 5 dpf | none |
| 3 | ≥10 pM | 5 dpf | none |
| 4 | ≥1 pM | 5 dpf | none |
| 5 | ≥10 pM | 5 dpf | none |
| 6 | ≥10 pM | 48 hpf (PE) | NE |
| 7 | none (until 100 µM) | 5 dpf | none |
| 8 | ≥1 pM | 1 hpf | NE |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carnovali, M.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Mollo, E.; Roussis, V.; Banfi, G.; Carbone, M.; Mariotti, M. Aerophobin-1 from the Marine Sponge Aplysina aerophoba Modulates Osteogenesis in Zebrafish Larvae. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020135
Carnovali M, Ciavatta ML, Mollo E, Roussis V, Banfi G, Carbone M, Mariotti M. Aerophobin-1 from the Marine Sponge Aplysina aerophoba Modulates Osteogenesis in Zebrafish Larvae. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(2):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020135
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarnovali, Marta, Maria Letizia Ciavatta, Ernesto Mollo, Vassilios Roussis, Giuseppe Banfi, Marianna Carbone, and Massimo Mariotti. 2022. "Aerophobin-1 from the Marine Sponge Aplysina aerophoba Modulates Osteogenesis in Zebrafish Larvae" Marine Drugs 20, no. 2: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020135
APA StyleCarnovali, M., Ciavatta, M. L., Mollo, E., Roussis, V., Banfi, G., Carbone, M., & Mariotti, M. (2022). Aerophobin-1 from the Marine Sponge Aplysina aerophoba Modulates Osteogenesis in Zebrafish Larvae. Marine Drugs, 20(2), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020135