Abstract
Four new sesquiterpene hydroquinones, xishaeleganins A–D (6–9), along with eleven known related ones (12 and 14–23) were isolated from the Xisha marine sponge Dactylospongia elegans (family Thorectida). Their structures were determined by extensive spectroscopic analysis, ECD calculations, and by comparison with the spectral data reported in the literature. Compounds 7, 15, 20, and 21 showed significant antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, with minimum inhibitory concentration values of 1.5, 2.9, 5.6, and 5.6 µg/mL, which are comparable with those obtained for the positive control vancomycin (MIC: 1.0 µg/mL).
1. Introduction
Metabolites of mixed sesquiterpene and quinone or hydroquinone biosynthesis are common to marine brown algae and sponges. In particular, these intriguing compounds are frequently discovered in the sponges of the genera Fenestraspongia [1], Dysidea [2], Spongia [3], Hyrtios [4], Dactylospongia [5], and Hippospongia [6]. In the last decades, numerous examples of this structure class have been reported, including those where the sesquiterpene unit exists in an acyclic (e.g., 1), bicyclic normal drimane skeleton (e.g., 2), or a rearranged drimane skeleton (4,9-friedodrimane skeleton) as exemplified in 3 (Figure 1). In addition to this, structural variation can focus on the degree of oxygenation and substitution to the aromatic ring. A wide range of remarkable bioactivities have been reported for many of these compounds, such as antiviral [7], antiangiogenic [8], antibacterial [9], antitumor [10], anti-inflammatory [11], and differentiation-inducing activities [12]. Avarone (4) and avarol (5), isolated from the Mediterranean sponge Dysidea avara in 1974, were the first two members of sesquiterpene quinone/hydroquinone [13]. Both 4 and 5 exhibited significant antiviral activity against HIV-I, and their great pharmaceutical potential stimulated the continued interests of chemists and pharmacologists [14,15]. A number of avarol derivatives [16] and related compounds [17] exhibiting interesting activity in enzyme assays measuring inhibition of various functions of HIV-I reverse transcriptase were discovered.
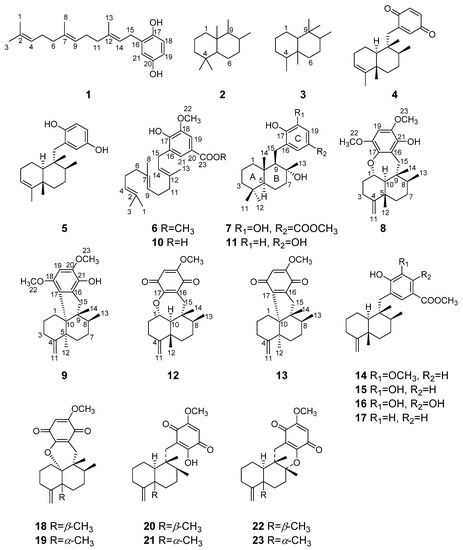
Figure 1.
Structures of compounds 1–23.
As part of our ongoing project towards the isolation of biologically active compounds from Chinese marine benthic invertebrates [18,19,20], a batch of Dactylospongia elegans sponges was collected off the coast of Xisha Island, Hainan Province, China, and chemically investigated. Dactylospongia elegans sponges belonging to the family Thorectida (order Dictyoceratida, class Demospongiae, and phylum Porifera) are prolific sources of biologically active compounds spanning a wide range of structural classes, from meroterpenoids [21,22], steroids [23], to diterpenoids [24], etc. In this report, we describe the isolation of four new sesquiterpene hydroquinones, xishaeleganins A–D (6–9), along with eleven known related ones (12 and 14–23) from the titular animals.
2. Results and Discussion
The frozen animals were cut into pieces and exhaustively extracted with acetone. The Et2O soluble portion of the acetone extract was chromatographed repeatedly over silica gel, Sephadex LH-20, and RP-HPLC to yield pure compounds 6–9, 12, and 14–23 (Figure 1), respectively.
Among them, the known compounds were readily identified as dactyloquinone C (12) [25], polyfibrospongol A (14) [26], dictyoceratin A (15) [27], dictyoceratin B (16) [27], dictyoceratin C (17) [28], dactyloquinone A (18) [29], dactyloquinone B (19) [29], ilimaquinone (20) [30], epi-ilimaquinone (21) [31], dactyloquinone D (22) [25], and dactyloquinone E (23) [25], by comparing their NMR data and optical rotation values with those reported in the literature.
Compound 6 was obtained as a stable yellow oil. Its molecular formula, C24H34O4, was established by HRESIMS (m/z 409.2357 [M + Na]+, calcd 409.2349). Its UV (λmax 286 and 204 nm) and IR (νmax 3414, 1709, 1609 cm−1) showed typical absorptions for hydroxyl, carbonyl group and aromatic ring, of which, the 1,2,3,5-tetrasubstituted pattern could be easily recognized by its 1H NMR data (Table 1), in particular meta-coupling between two aromatic protons of δH 7.41 (d, J = 1.9 Hz) and 7.52 (d, J = 1.9 Hz). Further, a polyene linear substituent assignable to a farnesyl (3,7,11-trimethyl-2,6,10-dodecatrienyl) moiety [5.32 (t, J = 7.4 Hz), 5.11 (t, J = 5.6 Hz), 5.07 (t, J = 5.6 Hz), 1.73 (s), 1.67 (s), 1.58 (2 s), 137.0 (C), 135.2 (C), 131.4 (C), 124.6 (CH), 124.3 (CH), 121.6 (CH), 25.8 (CH3), 17.7 (CH3), 16.4 (CH3), 16.1 (CH3)] was identified by the extensive analysis of 1H-1H COSY and HMBC spectrum (Figure 2). There are three 1H-1H COSY spin systems by clear correlations of H-4 (δH 5.11)/H2-5 (δH 2.09, 2.09)/H2-6 (δH 2.04, 1.95), H-9 (δH 5.07)/H2-10 (δH 2.04, 2.04)/H2-11 (δH 2.04, 1.95), and H-14 (δH 5.32)/H2-15 (δH 3.37, 3.37); these fragments were connected by the well-resolved HMBC correlations as shown in Figure 2. The hydroquinone part was located at C-15 (δC 28.1) by the HMBC correlations from H2-15 to C-16 (δC 127.4), C-17(δC 147.9) and C-21 (δC 124.6). A literature survey revealed that compound 6 showed great similarities with the model compound 10, a sesquiterpene hydroquinone recently isolated from the fungus Aspergillus flavipes [32]. An overall comparison of the NMR data of 6 (Table 1; Table 2) and 10 revealed that the only difference between them happened at C-20 (the former carbomethoxy, the latter carboxylic acid), according to 14 mass units’ difference between their molecular weights. Compound 6 is simply a C-20 carboxyl methylation derivative of 10 and named xishaeleganin A.

Table 1.
1H NMR Data for compounds 6–9.
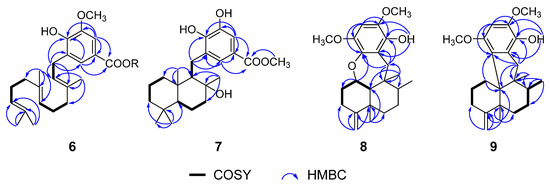
Figure 2.
Selected key 1H-1H COSY and HMBC correlations of 6–9.

Table 2.
13C NMR Data for compounds 6–9.
Compound 7 was isolated as a stable, violet, amorphous solid. Its molecular formula of C23H34O5 was deduced by HRESIMS (m/z 413.2302 [M + Na]+, calcd 413.2298), implying seven degrees of unsaturation. The IR absorptions of νmax 3401, 1687, 1595 cm−1, like those of 6, indicated the presence of an aromatic ring and an ester carbonyl in the structure of 7. Further, the diagnostic meta-coupling between two aromatic protons of δH 7.43 (d, J = 2.1 Hz) and 7.40 (d, J = 2.1 Hz) in the 1H NMR spectrum of 7 (Table 1) clearly suggested the presence of the same tetrasubstituted aromatic ring as that of co-occurring 15. The one carbonyl carbon and an aromatic ring accounted for five out of the seven degrees of unsaturation, suggesting the presence of two rings in the remaining part of 7. 1H NMR spectrum of 7 showed, bearing in mind the abovementioned two aromatic protons, five methyl signals (δH 3.85, s; 1.35, s; 0.94, s; 0.83, s; 0.79, s). The 13C NMR spectrum displayed resonances for one ester carbonyl carbon (δC 167.4), six aromatic carbons (δC 147.0, 145.1, 128.7, 125.2, 121.2, 113.7), three quaternary carbons (δC 40.1, 33.3 and an oxygenated one at δC 77.1), two methine carbons (δC 60.4, 56.0), six methylene carbons (δC 43.9, 41.7, 40.2, 27.5, 20.6, 18.3), and five methyl carbons (δC 33.4, 24.9, 21.5, 15.4 and an oxygenated one at δC 51.9).
Subtraction of the already elaborated partial structure C from the molecular formula of 7 indicated the chemical composition of the remaining unassigned part of 7 is C15H27O, which must be of a bicyclic sesquiterpene nature, probably a drimane-type sesquiterpene. To confirm the hypothesis, we carefully studied the literature, finding that the 1H and 13C NMR data of 7 showed high similarity to those of model compound 11 (ent-yahazunol), a merosesquiterpene isolated from the sponge of the genus Dysidea collected in the Gulf of California [33]. In fact, 7 differs from 11 only at ring C, where the former is a 1,2,3,5-tetrasubstituted hydroquinone, while the latter is a 1,2,4-trisubstituted hydroquinone. In addition, the carbon signals at δC 128.7, 147.0, and 125.2 were located at the neighboring C-16, C-17, and C-21 positions by the HMBC correlations (Figure 2) from H2-15 to C-16 (δC 128.7)/C-17 (δC 147.0)/C-21 (δC 125.2). At the same time, both aromatic hydrogen protons displayed HMBC correlations with the methoxy carbonyl group (δC 167.4 and 51.9) which attached to the quaternary carbon (δC 121.2), allowing the carbon signals at δC 113.7, 121.2, and 125.2 to be assignable to C-19, C-20, and C-21 positions. In light of these observations, the planar structure of 7 was established as shown in Figure 2. Analogously to 11, the relative configuration of 7 was elucidated to be the same as that of 11 by comparison of 13C NMR data of 7 with those of 11, and confirmed by NOESY experiment as shown in Figure 3. Finally, considering the fact that all drimane sesquiterpenoids isolated from sponges possess the same absolute stereochemistry, and because the observed chemical shifts and coupling pattern of sesquiterpene moiety in 7 are similar to those of 11, the absolute configuration (AC) of 7 is presumed to be identical to that of 11.
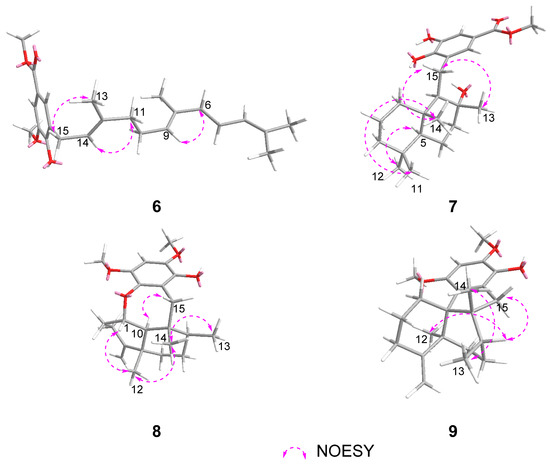
Figure 3.
Selected key NOE correlations of 6–9.
The compounds 8 and 9 showed NMR data characteristic for a multisubstituted aromatic moiety, like that of co-occurring 6 and 7. In particular, Compounds 8 and 9 not only shared a common pentasubstituted aromatic ring, but also possessed the same 4,9-friedodrimane skeleton, like that of co-occurring known sesquiterpene hydroquinones (14–17) as evidenced by a typical exo-cyclic olefin (δH 4.57, s; 4.57, s; δC 158.5, 103.4 in 8. δH 4.67, s; 4.54, s; δC 157.9, 106.0 in 9) and three high-field methyl signals (δH 0.93, s; 1.03, d, J = 6.6 Hz; 0.61, s; δC 21.8, 16.7, 15.4 in 8. δH 0.81, s; 1.15, d, J = 7.3 Hz; 1.03, s; δC 24.3, 17.9, 24.8 in 9). The structure elucidation of these new metabolites is described as follows.
Compound 8 was obtained as a violet amorphous solid. Its molecular formula, C23H32O4, was established by HRESIMS at m/z 373.2384 ([M + H]+; calcd 373.2373), suggesting eight degrees of unsaturation. Considering the already elaborated pentasubstituted aromatic ring and 4,9-friedodrimane motif, the remaining task is to assign the location of the substituents on the aromatic ring and the linking manner with the sesquiterpene unit. In fact, the 1H and 13C NMR data of 8 (Table 1; Table 2) were similar to those of co-occurring compound 12 (dactyloquinone C) except for the benzene portion, indicating the sesquiterpene moiety is connected to hydroquinone to form a seven-membered ring with an ether linkage between C-1 and C-17. Further, the key HMBC cross peaks from H-19 to C-17 (δC 142.0)/C-18 (δC 144.2)/C-20 (δC 142.2)/C-21 (δC 137.9), H2-15 to C-9 (δC 38.7)/C-16 (δC 122.9)/C-17 (δC 142.0)/C-21 (δC 137.9), and OH-21 to C-16 (δC 122.9)/C-20 (δC 142.2)/C-21 (δC 137.9) allowed the assignment of two methoxy groups at C-18 and C-20, and hydroxyl at C-21, completing the planar structure of 8.
The relative configuration of 8 was deduced to be the same as those of 12 based on the biogenetic consideration, and supported by the NOESY correlations from H-1 to H3-12, from H3-14 to H3-12 and H3-13, and from H-10 to H2-15 as shown in Figure 3. Because the observed chemical shifts and coupling pattern of 8 are similar to those of 12, the stereochemistry of 8 is presumed to be identical to that of 12. The AC of 8 may consequently be considered to be 1S,5S,8S,9R,10S assuming 14 to be its precursor. To secure this assignment, the TDDFT-ECD method, which has proven to be a powerful and reliable method for the elucidation of the AC of natural products [34], was applied. As shown in Figure 4, the Boltzmann-averaged ECD spectrum of 1S,5S,8S,9R,10S-8 was matched well to the experimental one of 8. Consequently, the AC of compound 8 was determined as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 4.
Experimental and calculated ECD spectra of 8.
Compound 9 was also obtained as a violet amorphous solid. Its molecular formula, C23H32O3, was established by HREIMS at m/z 356.2346 (calcd 356.2346), 16 mass units less than that of 8. Careful comparison of the 13C NMR data of 9 and 8 revealed the main differences between them happened at sesquiterpene moiety. In particular, the disappearance of the oxymethine carbon at δC 78.1 and methine carbon at δC 61.2 in 8, accompanying the appearance of a methylene carbon at δC 32.1 and a quaternary carbon at δC 58.3 in 9, indicated the sesquiterpene is connected to benzene moiety by a direct carbon-carbon linkage between the A/B ring junction C-10 and C-17 according to the degree of unsaturations inherent in its mass data.
To confirm the deduced structure of 9, 2D NMR spectra of 9 were analyzed in detail. A combination of HSQC and 1H−1H COSY data revealed two linear spin systems of shielded protons for 9 (Figure 1). Subsequently, extensive HMBC analysis, including the correlations of the conspicuous H2-11 exo-methylenes, the H3-13 and H3-14 methyls, and the H2-15 methylenes with neighboring carbons, supported a rearranged drimane sesquiterpene moiety identical to 14–17. In this way, a nonprotonated carbon at δC 58.3 in the 13C NMR spectrum was assigned at the C-10 ring junction through its HMBC correlations with H2-1, H3-12 and H2-15. Due to the significant shifts of the hydroquinone carbons in the 13C NMR data from the other compounds, both the structure determination and NMR assignments of this portion of 9 were accomplished through HMBC analysis (Table 2). The long-range correlations with H2-15 were used to place the nonprotonated carbons δC 130.3, 131.3, and 135.3 at the neighboring C-16, C-17, and C-21 positions (Figure 1). An additional long-range correlation with H2-1 not only secured the signal at δC 131.3 at C-17 of the hydroquinone unit, but also directly linked this carbon at C-10 of the sesquiterpene moiety, thus constructing a five-membered ring corresponding to an additional degree of unsaturation (Figure 1). Accordingly, the other carbons at δC 130.3 and 135.3 were placed at C-16 and C-21, respectively. The HMBC correlations of the methine proton at δH 6.31 (δC 95.7) with C-17 C-18, C-20, and C-21, with no HMBC correlations with C-16 (δC 130.3), secured the remaining carbons signals δC 150.2, 95.7, and 144.8 at C-18, C-19, and C-20, respectively, fully assigning a pentasubstituted-hydroquinone moiety as depicted in Figure 2. A literature survey revealed that the spectroscopic data of 9 were reminiscent of those of model compound 13, a sesquiterpene quinone previously reported from a Dysidea sp. sponge [34]. Overall comparison of the 1H and 13C NMR data of 9 and 13 revealed the significant differences occurred only in the hydroquinone portion (Table 1; Table 2) indicating the ACs at C-5, C-8, C-9, and C-10 in 9 should be the same as those of 13 [34]. Once again, by analog to 8, the TDDFT-ECD approach was employed. The experimental ECD spectrum of 9 matched well with the calculated ECD spectrum of 5S,8S,9R,10R-9 (Figure 5) and further supported its absolute configuration.
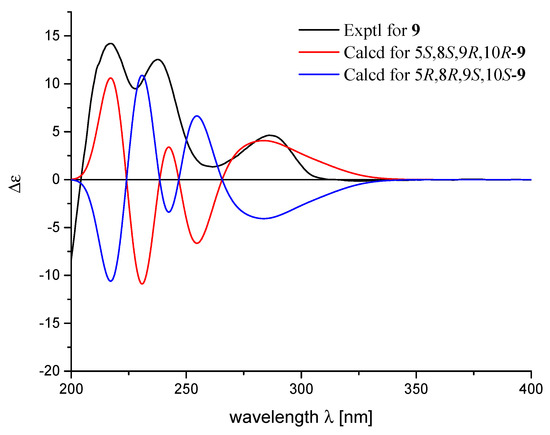
Figure 5.
Experimental and calculated ECD spectra of 9.
A literature survey revealed that the sesquiterpene quinones/hydroquinones show interesting antibacterial activity [9]; consequently, all the isolated compounds were tested for antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Enterococcus faecium (Table 3). Compounds 7, 15, 20, and 21 showed maximum antibacterial activity against S. aureus (MIC: 1.5, 2.9, 5.6, and 5.6 µg/mL), comparable with that obtained for the positive control vancomycin (MIC: 1.0 µg/mL). As for S. pyogenes, compounds 7, 8, 12, 15, 16, 20, and 21 showed significant antibacterial activity with the MIC 1.5, 5.6, 2.8, 2.9, 1.5, 2.8, and 2.8 µg/mL, respectively. At the same time, compounds 7, 8, 12, 15, and 16 showed significant antibacterial activity against E. faecium with the MIC 3.0, 5.6, 5.6, 1.4, and 3.0 µg/mL, respectively. These results highly suggested that the sesquiterpene hydroquinones/quinones such as compounds 7 and 15 have the potential to be the new lead compounds of antibiotics.

Table 3.
Antibacterial activities of compounds 7–23 (MIC µg/mL).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
IR spectrum was recorded on a Nicolet 6700 spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Optical rotation was measured on a PerkinElmer 241 MC polarimeter (PerkinElmer, Fremont, CA, USA). 1H and 13C NMR spectra were acquired on a Bruker DRX-500 spectrometer (Bruker Biospin AG, Fällanden, Germany). Chemical shifts (δ) are reported in ppm with reference to the solvent signals, and coupling constants (J) are in Hz. ESIMS spectra were recorded on a Finngan-MAT-95 mass spectrometer and HRESIMS spectra were recorded on an Agilent 1290–6545 UHPLC-QTOF mass spectrometer. Commercial silica gel (Qingdao Haiyang Chemical Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China, 200–300 and 300–400 mesh) and Sephadex LH-20 gel (Amersham Biosciences, Little Chalfont, UK) were used for column chromatography (CC). Precoated silica gel GF-254 plates (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Shanghai, China) were used for analytical TLC. Reversed-phase (RP) HPLC was performed on an Agilent 1260 series liquid chromatograph equipped with a DAD G1315D detector at 210 nm (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). An Agilent semipreparative XDB-C18 column (5 μm, 250 × 9.4 mm) was employed for the purification. All solvents used for CC and HPLC were of analytical grade (Shanghai Chemical Reagents Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and chromatographic grade (Dikma Technologies Inc., Lake Forest, CA, USA), respectively.
3.2. Biological Material
The sponges of D. elegans was collected from the coast of Xisha Island, Hainan Province, China, in 2019, and identified by Dr. L.G. Yao (Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China). A voucher specimen (No. 19-XS-39) is available for inspection at the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, CAS.
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
The frozen animals (275 g, dry weight) were cut into pieces and extracted exhaustively with acetone at room temperature (4 × 3.5 L). The organic extract was evaporated to give a brown residue, which was then partitioned between Et2O and H2O. The upper layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a Et2O portion (10.7 g). The Et2O extract was separated into eleven fractions (A–K) by gradient silica-gel column chromatography. The resulting fractions were then fractionated into sub-fractions by Sephadex LH-20. Fraction EA was separated by semi-preparative HPLC (90% acetonitrile), yielding compound 6 (0.6 mg). Fraction DC was separated by semi-preparative HPLC (95% acetonitrile), yielding compound 8 (4.0 mg). Fraction FC was separated by semi-preparative HPLC (95% methanol), yielding compound 20 (2.4 mg) and 21 (5.8 mg). Fraction GC was separated by semi-preparative HPLC (95% methanol), yielding compounds 9 (0.4 mg) and 14 (3.4 mg). Fraction HB was separated by semi-preparative HPLC (95% methanol), yielding compounds 7 (0.9 mg), 16 (8.7 mg), and 17 (4.1 mg). Fraction JB was separated by semi-preparative HPLC (88% acetonitrile), yielding compounds 12 (1.6 mg), 18 (1.8 mg), and 19 (2,9 mg). Fraction JD was separated by silica gel column eluting with petroleum ether (PE)/Et2O (4:1, v/v) to give compound 15 (15.4 mg). Fraction KA was separated by semi-preparative HPLC (100% methanol) to give compound 22 (3.2 mg) and 23 (0.8 mg).
3.4. Spectroscopic Data of Compounds
Xishaeleganin A (6): yellow oil; [α] −3.6 (c 0.06, CH3OH); IR (KBr): νmax 3414, 2926, 2864, 1709, 1609, 1438, 1379, 1304, 1217, 1086, 1018, 803 cm−1; For 1H NMR (CDCl3, 500 MHz) and 13C NMR (CDCl3, 125 MHz) spectral data, see Table 1 and Table 2; HRESIMS m/z 409.2357 ([M + Na]+; calcd 409.2349).
Xishaeleganin B (7): violet amorphous solid; [α] −32.8 (c 0.09, CH3OH); IR (KBr): νmax 3401, 2921, 2847, 1687, 1595, 1431, 1310, 1210, 1185, 1024, 1005, 768 cm−1; For 1H NMR (CDCl3, 500 MHz) and 13C NMR (CDCl3, 125 MHz) spectral data, see Table 1 and Table 2; HRESIMS m/z 413.2302 ([M + Na]+; calcd 413.2298).
Xishaeleganin C (8): violet amorphous solid; [α] −16.4 (c 0.40, CH3OH); IR (KBr): νmax 3446, 2924, 2866, 1604, 1492, 1454, 1345, 1249, 1207, 1098, 1031, 973, 938, 890 cm−1; For 1H NMR (CDCl3, 500 MHz) and 13C NMR (CDCl3, 125 MHz) spectral data, see Table 1 and Table 2; HRESIMS m/z 373.2384 ([M + H]+; calcd 373.2373).
Xishaeleganin D (9): violet amorphous solid; [α] +174.6 (c 0.04, CH3OH); IR (KBr): νmax 3452, 2953, 2924, 2860, 1627, 1591, 1498, 1460, 1377, 1338, 1293, 1092, 973, 887, 845 cm−1; For 1H NMR (CDCl3, 500 MHz) and 13C NMR (CDCl3, 125 MHz) spectral data, see Table 1 and Table 2; HREIMS m/z 356.2346 (calcd 356.2346).
3.5. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Determination
The MIC values for all antimicrobial agents were measured by 96-well micro-dilution method. Mueller–Hinton II broth (cation-adjusted, BD 212322) was used for MIC value determination. Generally, compounds were dissolved with DMSO to 20 mM as stock solutions. All samples were diluted with culture broth to 500 μM as the initial concentration. Further 1:2 serial dilutions were performed by addition of culture broth to reach concentrations ranging from 500 μM to 0.24 μM or lower. 100 µL of each dilution was distributed in 96-well plates, as well as sterile controls, growth controls (containing culture broth plus DMSO, without compounds), and positive controls (containing culture broth plus control antibiotics such as vancomycin). Each test and growth control well was inoculated with 5 µL of an exponential-phase bacterial suspension (about 105 CFU/well). The 96-well plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. MIC values of these compounds were defined as the lowest concentration to inhibit the bacterial growth completely. All MIC values were interpreted according to recommendations of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI).
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, although the chemical studies on the South China Sea sponges D. elegans have been well documented in literature [5,21,22,23], the chemical reinvestigation of the same species collected from the same water area has still provided additional interesting and innovative results. The notable contribution towards the advance of meroterpenoid chemistry is the discovery of four new chemically diverse sesquiterpene hydroquinones, namely xishaeleganins A–D (6–9). It is interesting to note that although the structures of 6–9 are formally quite different, they are actually biogenetically related. It is obvious that compound 6 should be the common precursor for all sesquiterpene hydroquinones/quinones [35]. As outlined in Scheme 1, a plausible biogenetic pathway could be proposed to explain the biosynthesis of drimane skeleton of 7. Thus, the cyclization of farnesyl in 6 takes place by an initial electrophilic attack at the head position of 6, giving rise to a concerted process leading to a bicyclic carbocationic intermediate 6i, which underwent further hydroxylation at C-8 to generate a drimane skeleton of 7. Alternatively, starting from 6i, other 4,9-friedodrimane-type sesquiterpene hydroquinones (e.g., 8, 9) are formed through concerted processes including 1,2 hydride shift accompanying the migration of methyls of C-4 and C-10. It is noteworthy that acyclic sesquiterpene quinones/hydroquinones are relatively rare, and to the best of our knowledge, until now, fewer than ten of this kind of metabolite were reported from sponges [35,36,37]. Last but not least, the recent report about the discovery of 10 from a fungus associated with mangrove Acanthus ilicifolius strongly suggests the microorganisms, which may be symbiotic, endophytic, or associated with the host sponge, could be the true producer of the sesquiterpene hydroquinones/quinones. Further study should be conducted to gain insight into the microorganisms responsible for producing sesquiterpene hydroquinones/quinones, and in particular to figure out the enzymatic mechanisms to biosynthesize these sponge metabolites.
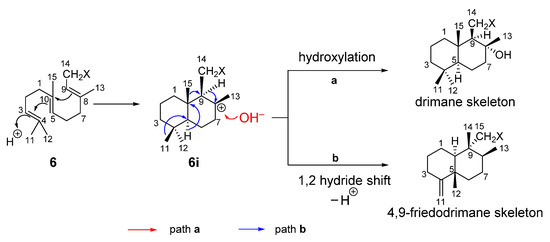
Scheme 1.
Plausible biosynthetic pathway proposed for drimane skeleton formation or rearranged drimane skeleton.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/md20020118/s1, Figures S1−S4: 1D, 2D NMR, MS and IR spectra of compounds 6–9; Figure S5: 1H and 13C NMR spectra of Compound 12 and 14–23.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.-W.G., C.-Y.W. and L.L.; methodology, Y.-W.G., C.-Y.W. and L.L.; software, Y.-W.G. and L.L.; validation, Y.-W.G., L.L., Q.Z. and B.C.; formal analysis, Y.-W.G. and B.C.; investigation, B.C. and Q.Z.; resources, Y.-W.G. and C.-Y.W.; data curation, B.C. and Q.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.-W.G. and B.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.-W.G. and B.C.; visualization, Y.-W.G. and B.C.; supervision, Y.-W.G., C.-Y.W., L.L. and Y.-C.G.; project administration, Y.-W.G. and C.-Y.W.; funding acquisition, Y.-W.G. and C.-Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81991521, 41830535), the SKLDR/SIMM Project (No. SIMM2103ZZ-06), and the Taishan Scholars Program.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article or Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
B. Chen is thankful for the financial support of Syngenta-OUC-PhD Studentship Project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Carte, B.; Rose, C.B.; Faulkner, D.J. 5-epi-ilimaquinone, a metabolite of the sponge Fenestraspongia sp. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 2785–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Marrero, A.R.; Austin, P.; Van Soest, R.; Matainaho, T.; Roskelley, C.D.; Roberge, A.M.; Andersen, R.J. Avinosol, a meroterpenoid-nucleoside conjugate with antiinvasion activity isolated from the marine sponge Dysidea sp. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 3749–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkina, N.K.; Denisenko, V.A.; Scholokova, O.V.; Virovaya, M.V.; Prokof’Eva, N.G. Cyclosmenospongine, a new sesquiterpenoid aminoquinone from an Australian marine sponge Spongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piña, I.C.; Sanders, M.L.; Crews, P. Puupehenone Congeners from an Indo-Pacific Hyrtios sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-B.; Yin, Z.-F.; Gu, B.-B.; Zhang, J.-P.; Wang, S.-P.; Yang, F.; Lin, H.-W. Cytotoxic meroterpenoids from the marine sponge Dactylospongia elegans. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 1620–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musman, M.; Ohtani, I.I.; Nagaoka, D.; Tanaka, A.J.; Higa, T. Hipposulfates A and B, new sesterterpene sulfates from an Okinawan sponge, Hippospongia cf. metachromia. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.M. A new sesquiterpenoid hydroquinone from the marine sponge Dysidea arenaria. Molecules 2008, 13, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, D.; Yamori, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Duan, H. Antiproliferative and antiangiogenic activities of smenospongine, a marine sponge sesquiterpene aminoquinone. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, H.-Y.; Huang, A.-M.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Cao, P.-Y.; Yang, P.-M. Antibacterial meroterpenoids from the South China Sea sponge Dysidea sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arai, M.; Kawachi, T.; Sato, H.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. Marine spongian sesquiterpene phenols, dictyoceratin-C and smenospondiol, display hypoxia-selective growth inhibition against cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3155–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, C.E.; Larsen, L.; Perry, N.B.; Harper, J.L.; Berridge, M.V.; Chia, E.W.; Kelly, M.; Webb, V.L. Anti-inflammatory Sesquiterpene-quinones from the New Zealand sponge Dysidea cf. cristagalli. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1431–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, S.; Kong, D.; Matsui, K.; Kobayashi, M. Smenospongine, a spongean sesquiterpene aminoquinone, induces erythroid differentiation in K562 cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2004, 15, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minale, L.; Riccio, R.; Sodano, G. Avarol a novel sesquiterpenoid hydroquinone with a rearranged drimane skeleton from the sponge Disidea avara. Tetrahedron Lett. 1974, 15, 3401–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.C.; Sarin, P.S.; Rottmann, M.; Wenger, R.; Maidhof, A.; Renneisen, K.; Müller, W.E.G. Differential modulation of host cell and HIV gene expression by combinations of avarol and AZT in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1988, 37, 3947–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, P.S.; Sun, D.; Thornton, A.; Müller, W.E.G. Inhibition of replication of the etiologic agent of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (human T-lymphotropic retrovirus/lymphadenopathy-associated virus) by avarol and avarone2. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1987, 78, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loya, S.; Hizi, A. The inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase by avarol and avarone derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1990, 269, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loya, S.S.; Hizi, A. The interaction of illimaquinone, a selective inhibitor of the RNase H activity, with the reverse transcriptases of human immunodeficiency and murine leukemia retroviruses. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 9323–9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Huan, X.-J.; Miao, Z.-H.; de Voogd, N.J.; Gu, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-Y.; Guo, Y.-W.; Li, X. Uncommon bis-quinolizidine alkaloids from the Hainan sponge Neopetrosia chaliniformis. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, S.-W.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Hu, P.; Zhang, H.; Luo, C.; Chen, K.-X.; Nay, B.; Guo, Y.-W.; et al. Complex polypropionates from a South China Sea photosynthetic mollusk: Isolation and biomimetic synthesis highlighting novel rearrangements. Angew. Chem. 2020, 59, 12203–12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, W.-S.; Gu, Y.-C.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, C.-Y.; Guo, Y.-W.; Li, X.-W. New formamidobisabolene-type sesquiterpenoids from a Hainan sponge Halichondria sp. Tetrahedron 2021, 96, 132396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, W.; Yang, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.-P.; Jiao, W.-H.; Xu, S.-H.; Lin, H.-W. Popolohuanones G–I, dimeric sesquiterpene quinones with IL-6 inhibitory activity from the marine sponge Dactylospongia elegans. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1800078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-B.; Gu, B.-B.; Iwasaki, A.; Jiang, W.-L.; Ecker, A.; Wang, S.-P.; Yang, F.; Lin, H.-W. Dactylospenes A–E, sesterterpenes from the marine sponge Dactylospongia elegans. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Jiao, W.-H.; Lin, H.-W.; Xu, S.-H. Two new steroids with cytotoxicity from the marine sponge Dactylospongia elegans collected from the South China Sea. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1340–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-B.; Gu, B.-B.; Wang, S.-P.; Cheng, C.-W.; Yang, F.; Lin, H.-W. New diterpenoids from the marine sponge Dactylospongia elegans. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 6657–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitome, H.; Nagasawa, T.; Miyaoka, H.; Yamada, Y.; Soest, R.W.M.V. Dactyloquinones C, D and E novel sesquiterpenoid quinones, from the Okinawan marine sponge, Dactylospongia elegans. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 1693–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-C.; Hsieh, P.-W. New sesquiterpene hydroquinones from a Taiwanese marine sponge Polyfibrospongia australis. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Deng, S.; Kobayashi, J.I.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, Y. Dictyoceratin-A and -B, novel antimicrobial terpenoids from the Okinawan marine sponge Hipposponqia sp. Tetrahedron 1986, 42, 4197–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Schmitz, F.J.; Kelly, M. Sesquiterpene quinols/quinones from the Micronesian sponge Petrosaspongia metachromia. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitome, H.; Nagasawa, T.; Miyaoka, H.; Yamada, Y.; Soest, R.W.M.V. Dactyloquinones A and B, new sesquiterpenoid quinones from the Okinawan marine sponge Dactylospongia elegans. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1506–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luibrand, R.T.; Erdman, T.R.; Vollmer, J.J.; Scheuer, P.J.; Finer, J.; Clardy, J. Ilimaquinone, a sesquiterpenoid quinone from a marine sponge. Tetrahedron 1979, 35, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Quinoa, E.; Riguera, R.; Peters, B.M.; Abrell, L.M.; Crews, P. The structures and stereochemistry of cytotoxic sesquiterpene quinones from Dactylospongia elegans. Tetrahedron 1992, 48, 6667–6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Bai, Z.Q.; Lin, X.P.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.F.; Liu, Y.H. Chemical constituents of an endophytic fungus Aspergillus flavipes AIL8 obtained from mangrove Acanthus ilicifolius. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2016, 28, 860–863. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-García, E.; Zubía, E.; Ortega, M.J.; Carballo, J.L. Merosesquiterpenes from two sponges of the genus Dysidea. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.-K.; Woo, J.-K.; Kim, S.-H.; Cho, E.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-S.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, D.-C.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J. Meroterpenoids from a tropical Dysidea sp. sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2814–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonny, M.L.; Capon, R.J. A sesquiterpene quinone and hydroquinone from the southern Australian marine sponge, Thorecta choanoides. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 539–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göthel, Q.; Köck, M. New sesquiterpene hydroquinones from the Caribbean sponge Aka coralliphagum. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiso, A.; Kittiwisut, S.; Chantakul, R.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Putchakarn, S.; Schäberle, T.F.; Temkitthaworn, P.; Ingkaninan, K.; Chaithirayanon, K.; Plubrukarn, A. Quintaquinone, a merosesquiterpene from the yellow sponge Verongula cf. rigida Esper. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).