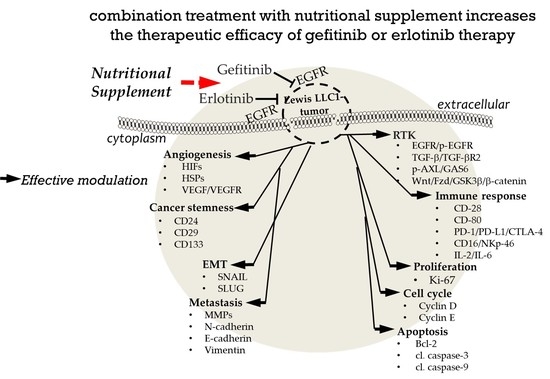
Targeting EGFR in Combination with Nutritional Supplements on Antitumor Efficacy in a Lung Cancer Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Inhibition of LLC1 Lung Cells Growth by EGFR-TKI (Gefitinib or Erlotinib)
2.2. Effects of Combination Treatment on Body Weight, Organ Weight, and Subcutaneous Tumor Size of LLC1 Tumor-Bearing Mice
2.3. Effects of Combination Treatment on Survival and Serum IL-6 Levels of LLC1 Tumor-Bearing Mice
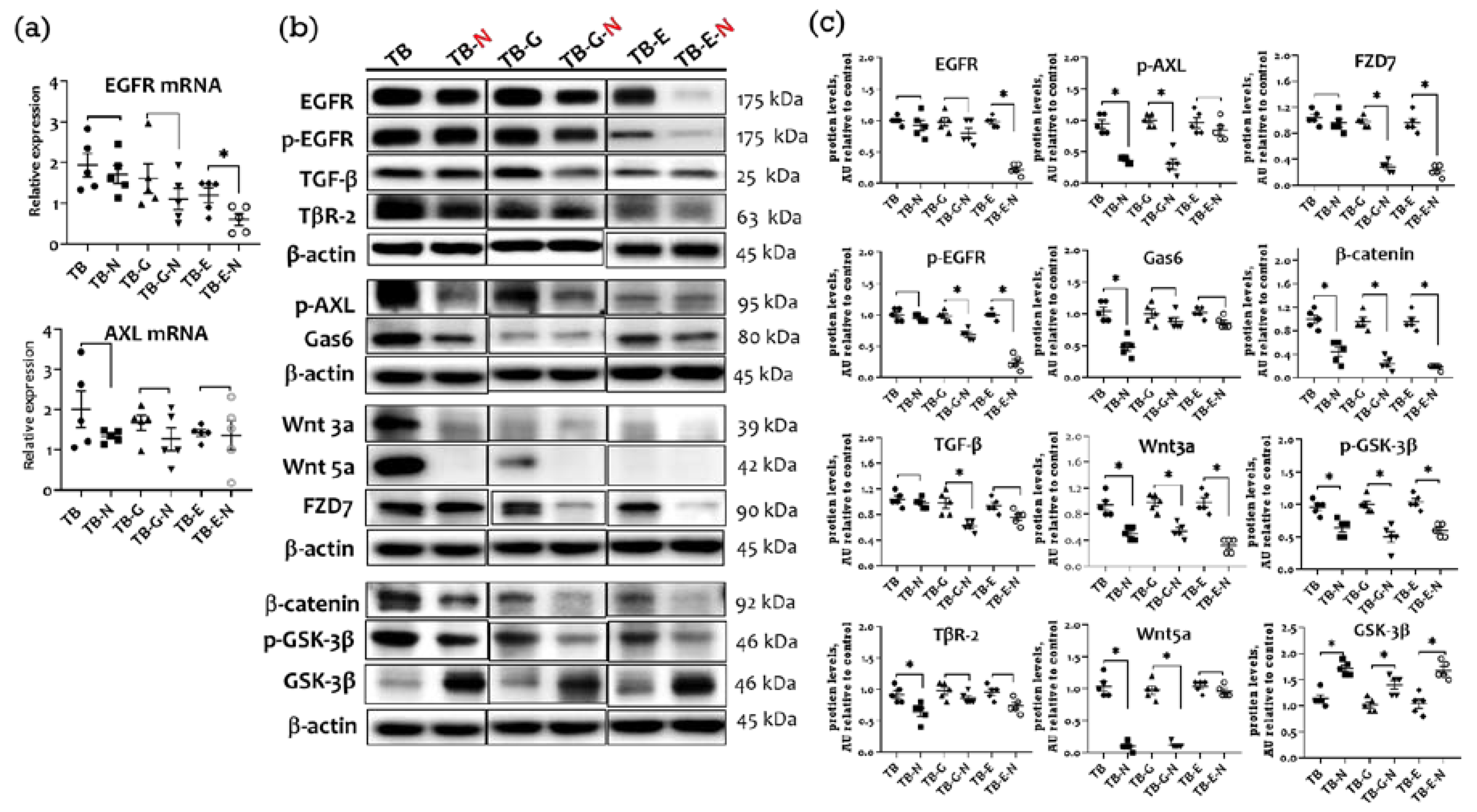
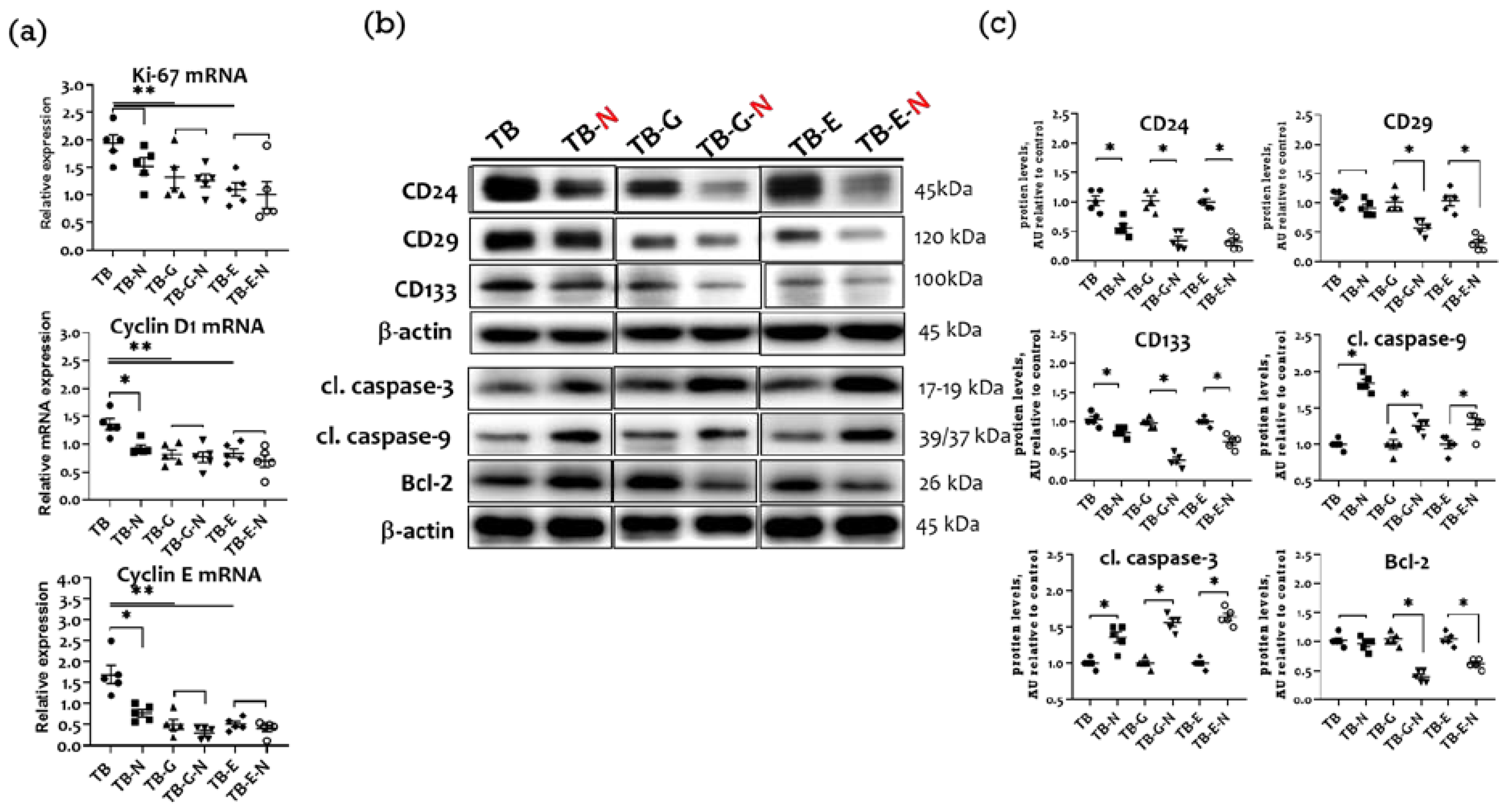
2.4. Effects of Combination Treatment on Tumor Transmembrane Receptors, β-Catenin, and GSK-3β Levels
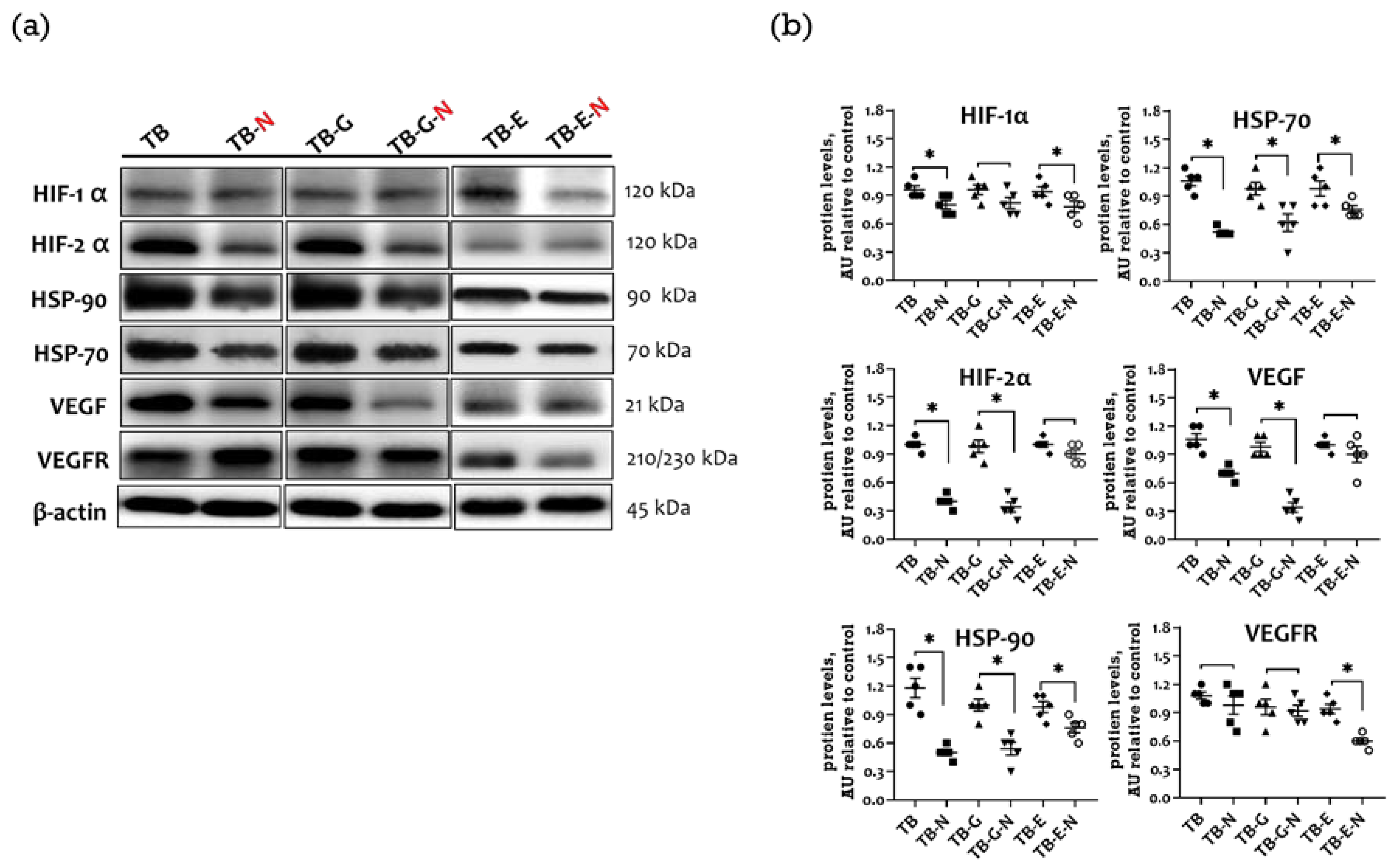
2.5. Effects of Combination Treatment on Expression of Tumor Angiogenic Markers
2.6. Effects of Combination Treatment on Tumor EMT Markers and Metastasis
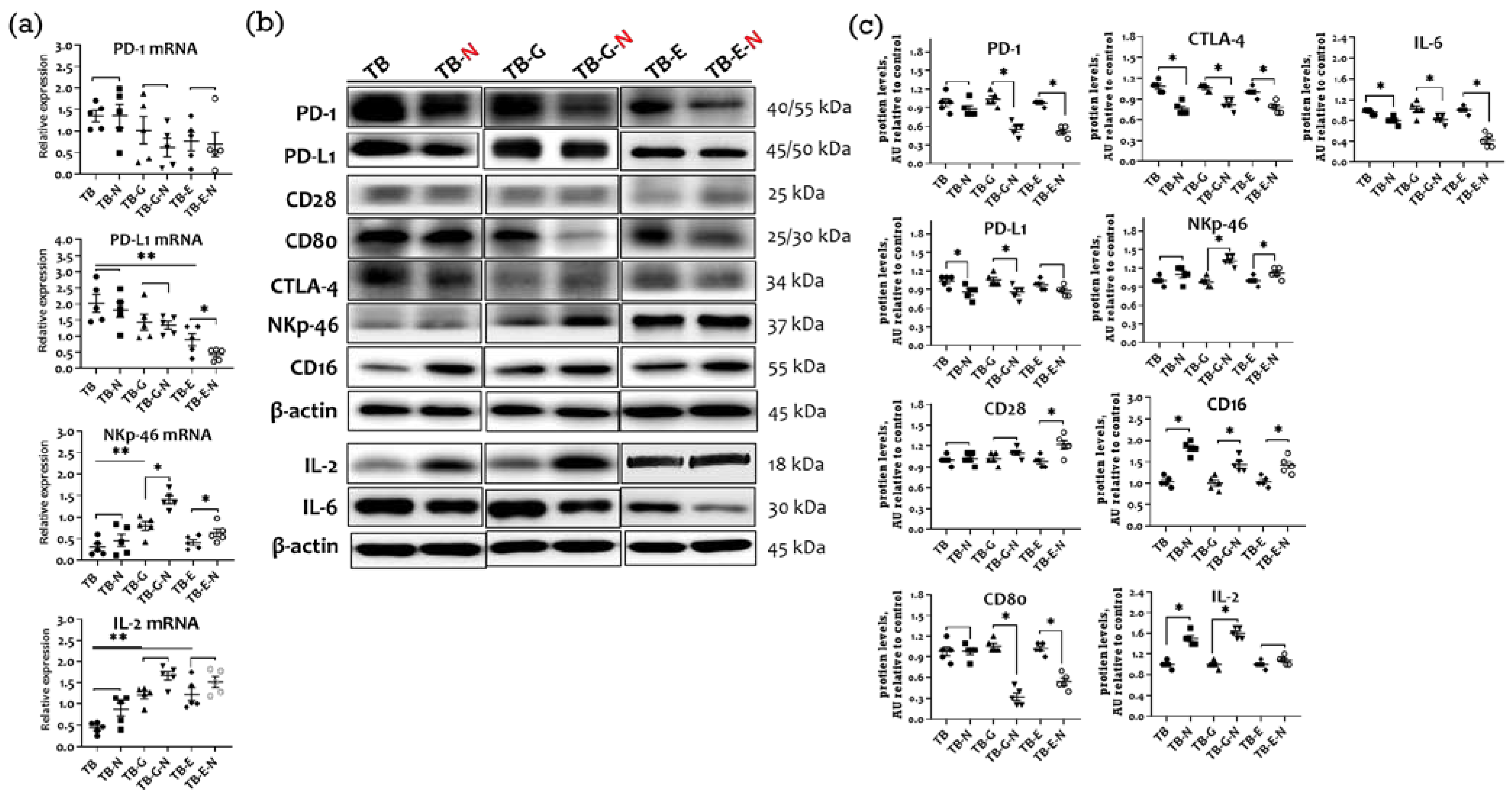
2.7. Effects of Combination Treatment on Immune Checkpoint Molecules Expression
2.8. Effects of Combination Treatment on Tumor Proliferation, Cell Cycle Proteins, and Apoptosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Anti-Cancer Agents and Nutritional Supplements
4.2. Cell Culture and Animal Experiments
4.3. Determination of Serum IL-6
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. RNA Isolation and Real-Time qPCR Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uhlig, J.; Case, M.D.; Blasberg, J.D.; Boffa, D.J.; Chiang, A.; Gettinger, S.N.; Kim, H.S. Comparison of survival rates after a combination of local treatment and systemic therapy vs. systemic therapy alone for treatment of stage IV non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e199702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Duan, J.; An, T.; Zhao, J.; Bai, H.; Wang, J. Phosphorylated EGFR expression may predict outcome of EGFR-TKIs therapy for the advanced NSCLC patients with wild-type EGFR. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eser, P.Ö.; Jänne, P.A. TGFβ pathway inhibition in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 184, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Cui, W. Function of Axl receptor tyrosine kinase in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 2726–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tian, R.; Ji, W.; Zhang, F.; Niu, R. TGF-β transactivates EGFR and facilitates breast cancer migration and invasion through canonical Smad3 and ERK/Sp1 signaling pathways. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Niu, X. EMT-mediated acquired EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC: Mechanisms and strategies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, A.; Bivona, T.G. Targeting AXL in NSCLC. Lung Cancer Auckl 2021, 12, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, A.; Yoshida, R.; Yamaguchi, R.; Yamauchi, M.; Tamada, Y.; Fujita, A.; Shimamura, T.; Imoto, S.; Higuchi, T.; Nomura, M.; et al. Elevated beta-catenin pathway as a novel target for patients with resistance to EGF receptor targeting drugs. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.Y.; Mohan, C.D.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Sethi, G.; Rangappa, K.S.; Ahn, K.S. Euphorbiasteroid abrogates EGFR and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer cells to impart anticancer activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Bach, D.H.; Fan, Y.H.; Luu, T.T.; Hong, J.Y.; Park, H.J.; Lee, S.K. AXL degradation in combination with EGFR-TKI can delay and overcome acquired resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, H.; Liao, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Sun, F.; Lin, H.W. Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin pathway reverses multi-drug resistance and EMT in Oct4+/Nanog+ NSCLC cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zeng, Y.; Du, W.; Zhu, J.; Shen, D.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.A. The EGFR pathway is involved in the regulation of PD-L1 expression via the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.H.; Hsia, S.; Hsiung, D.Y.; Chen, P.C. Supplementation with selenium yeast on the prooxidant-antioxidant activities and anti-tumor effects in breast tumor xenograft-bearing mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1568–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miccadei, S.; Masella, R.; Mileo, A.M.; Gessani, S. ω3 polyunsaturated fatty acids as immunomodulators in colorectal cancer: New potential role in adjuvant therapies. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razaghi, A.; Poorebrahim, M.; Sarhan, D.; Björnstedt, M. Selenium stimulates the antitumour immunity: Insights to future research. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 155, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hua, L.; Zhao, M.; Xu, T.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhu, B. Functionalized selenium nanoparticles for targeted delivery of doxorubicin to improve non-small-cell lung cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 6929–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, R.H.; Lai, G.M.; Chow, J.M.; Liao, C.H.; Zheng, Y.M.; Tsai, W.L.; Hsia, S.; Lai, I.C.; Lee, H.L.; Chuang, S.E.; et al. Opposite regulation of CHOP and GRP78 and synergistic apoptosis induction by selenium yeast and fish oil via AMPK activation in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Nutrients 2020, 15, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, I.C.; Liao, C.H.; Hu, M.H.; Chang, C.L.; Lai, G.M.; Chiou, T.J.; Hsia, S.; Tsai, W.L.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chuang, S.E.; et al. Selenium yeast and fish oil combination diminishes cancer stem cell traits and reverses cisplatin resistance in A549 sphere cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.H.; Tzeng, Y.T.; Lai, G.M.; Chang, C.L.; Hu, M.H.; Tsai, W.L.; Liu, Y.R.; Hsia, S.; Chuang, S.E.; Chiou, T.J.; et al. Omega-3 fatty acid-enriched fish oil and selenium combination modulates endoplasmic reticulum stress response elements and reverses acquired gefitinib resistance in HCC827 lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Zhang, J.Q.; Liang, G.K.; He, Q.J.; Ding, L.; Yang, B. Gefitinib inhibits M2-like polarization of tumor-associated macrophages in Lewis lung cancer by targeting the STAT6 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, Y.; Tsai, C.L.; Hou, W.H.; Chiang, Y.; Hsu, F.M.; Tsai, Y.C.; Cheng, J.C. Targeting human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 enhances radiosensitivity and reduces the metastatic potential of Lewis lung carcinoma cells. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Jin, H.; Zhao, W.; Chang, Z.; Wu, H. Effect of erlotinib combined with cisplatin on IL-6 and IL-12 in mice with Lewis lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, E.H.; Yang, I.A.; Wood-Baker, R.; Bowman, R.V.; Fong, K.M. Gefitinib for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 1, CD006847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hsia, S.; Wu, T.H.; Wu, C.J. Fish oil, Se yeast, and micronutrient-enriched nutrition as adjuvant treatment during target therapy in a murine model of lung cancer. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Chan, Y.L.; Wu, T.H.; Li, T.L.; Hsia, S.; Chiu, Y.H.; Wu, C.J. Antitumor, inhibition of metastasis and radiosensitizing effects of total nutrition formula on Lewis tumor-bearing mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Wu, T.H.; Chiu, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Li, T.L.; Hsia, S.; Chan, Y.L.; Wu, C.J. Positive effects of preventive nutrition supplement on anticancer radiotherapy in lung cancer bearing mice. Cancers 2020, 12, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.H.; Hsia, S.; Chung, C.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Shih, M.Y.; Chen, P.C.; Hsu, G.W.; Fan, C.T.; Peng, C.L. Combination of fish oil and selenium enhances anticancer efficacy and targets multiple signaling pathways in anti-VEGF agent treated-TNBC tumor-bearing mice. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Shao, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, F.; Xiang, R.; Zhao, A.Z.; Pan, J. Inhibition of lung cancer growth and metastasis by DHA and its metabolite, RvD1, through miR-138-5p/FOXC1 pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, C.; Fortin, S. Docosahexaenoic acid monoglyceride increases carboplatin activity in lung cancer models by targeting EGFR. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6015–6023. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.A.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.H.; Feng, Z.; Shang, X.C.; Peng, Z.M. DHA increases the anti-tumor effect of gefitinib on non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR mutations in vitro. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 7647–7657. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.H.; Yoon, M.J.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Bae, S. Enhanced lung cancer cell killing by the combination of selenium and ionizing radiation. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ashmawy, N.E.; Khedr, E.G.; El-Bahrawy, H.A.; Al-Tantawy, S.M. Chemopreventive effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and atorvastatin in rats with bladder cancer. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317692254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbut, E.; Ptak-Belowska, A.; Brzozowski, T. Inhibitory effect of selenomethionine on carcinogenesis in the model of human colorectal cancer in vitro and its link to the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2018, 65, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.S.; Jing, K.; Kim, J.S.; Yun, E.J.; Shin, S.; Seo, K.S.; Park, J.H.; Heo, J.Y.; Kang, J.X.; Suh, K.S.; et al. Omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids suppress pancreatic cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo via downregulation of Wnt/Beta-catenin signaling. Pancreatology 2011, 11, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, S. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α/vascular endothelial growth factor signaling activation correlates with re-sponse to radiotherapy and its inhibition reduces hypoxia-induced angiogenesis in lung cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 7707–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.J.; Ouyang, C.; Yu, B.; Chen, C.; Xu, X.F.; Ye, X.Q. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α in lung cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, B.; Yang, S. Molecular mechanism and targeted therapy of Hsp90 involved in lung cancer: New discoveries and de-velopments (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouradian, M.; Kikawa, K.D.; Dranka, B.P.; Komas, S.M.; Kalyanaraman, B.; Pardini, R.S. Docosahexaenoic acid attenuates breast cancer cell metabolism and the Warburg phenotype by targeting bioenergetic function. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, C.; Rodríguez, E.; Blier, P.U.; Fortin, S. Potential application of eicosapentaenoic acid monoacylglyceride in the management of colorectal cancer. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, N.; Hara, M.; Shiga, K.; Yanagita, T.; Takasu, K.; Nakai, N.; Maeda, Y.; Hirokawa, T.; Takahashi, H.; Ishiguro, H.; et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid suppresses angiogenesis via reducing secretion of IL-6 and VEGF from colon cancer-associated fibroblasts. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintala, S.; Najrana, T.; Toth, K.; Cao, S.; Durrani, F.A.; Pili, R.; Rustum, Y.M. Prolyl hydroxylase 2 dependent and Von-Hippel-Lindau independent degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and 2 alpha by selenium in clear cell renal cell carcinoma leads to tumor growth inhibition. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordian, E.; Welsh, E.A.; Gimbrone, N.; Siegel, E.M.; Shibata, D.; Creelan, B.C.; Cress, W.D.; Eschrich, S.A.; Haura, E.B.; Muñoz-Antonia, T. Transforming growth factor β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal signature predicts metastasis-free survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 810–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Kim, J. Combination Effect of cilengitide with erlotinib on TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Eliseo, D.; Di Rocco, G.; Loria, R.; Soddu, S.; Santoni, A.; Velotti, F. Epitelial-to-mesenchimal transition and invasion are upmodulated by tumor-expressed granzyme B and inhibited by docosahexaenoic acid in human colorectal cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, S.; Shafique, M. Combination checkpoint inhibitors for treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: An update on dual anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapies. Drugs Context 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, L.H.; Smith, R.; Switzer, K.C.; Chapkin, R.S.; McMurray, D.N. Dietary eicosapentaenoic acid modulates CTLA-4 ex-pression in murine CD4+ T-cells. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2006, 74, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, T.; Du, W.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.A. The canonical TGF-β/Smad signalling pathway is involved in PD-L1-induced primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Han, C.; Girard, L.; Park, H.; Zhang, A.; Dong, C.; Ye, J.; et al. AXL targeting restores PD-1 blockade sensitivity of STK11/LKB1 mutant NSCLC through expansion of TCF1+ CD8 T cells. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, I.Y.; Yang, Y.E.; Yang, P.S.; Tsai, Y.J.; Tzeng, H.T.; Cheng, H.C.; Kuo, W.T.; Su, W.C.; Chang, C.P.; Wang, Y.C. Con-verged Rab37/IL-6 trafficking and STAT3/PD-1 transcription axes elicit an immunosuppressive lung tumor microenvironment. Theranostics 2021, 11, 7029–7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.; Rådestad, E.; Khalkar, P.; Diaz-Argelich, N.; Schröder, A.; Klynning, C.; Ungerstedt, J.; Uhlin, M.; Fernandes, A.P. Methylseleninic acid sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to T-Cell mediated killing by decreasing PDL1 and VEGF levels. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, N.; Maebayashi, T.; Aizawa, T.; Sakaguchi, M.; Nishimaki, H.; Masuda, S. Correlation between the Ki-67 pro-lif-eration index and response to radiation therapy in small cell lung cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Li, M.; Zhong, W.; Hu, C.; Gu, Q.; Xie, Y. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors show different anti-brain metastases efficacy in NSCLC: A direct comparative analysis of icotinib, gefitinib, and erlotinib in a nude mouse model. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 98771–98781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, C.J.; Kimler, B.F.; Phillips, T.A.; Nydegger, J.L.; Kreutzjans, A.L.; Carlson, S.E.; Hidaka, B.H.; Metheny, T.; Zalles, C.M.; Mills, G.B.; et al. Modulation of breast cancer risk biomarkers by high-dose omega-3 fatty acids: Phase II pilot study in postmenopausal women. Cancer Prev. Res. Phila. 2015, 8, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, W.W.; Liu, W.N.; Leung, K.N. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids trigger cell cycle arrest and induce apoptosis in human neuroblastoma LA-N-1 Cells. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6956–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo, F.; Witte, T.R.; Hardman, W.E.; Claudio, P.P. Omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid decreases CD133 colon cancer stem-like cell marker expression while increasing sensitivity to chemotherapy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Yu, Z.Y.; Li, J.; Ouyang, X.N. Gefitinib induces lung cancer cell autophagy and apoptosis via blockade of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Chao, T.T.; Chang, F.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Tsai, Y.T.; Lin, H.I.; Huang, Y.C.; Shiau, C.W.; Yu, C.J.; Chen, K.F. CIP2A mediates erlotinib-induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells without EGFR mutation. Lung Cancer 2014, 85, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarada, S.K.; Himadri, P.; Ruma, D.; Sharma, S.K.; Pauline, T.; Mrinalini. Selenium protects the hypoxia induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells through upregulation of Bcl-2. Brain Res. 2008, 1209, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Cartwright, C.; Chan, D.; Ding, J.; Felix, E.; Pan, Y.; Pang, J.; Rhea, P.; Block, K.; Fischer, S.M.; et al. Anticancer activity of fish oils against human lung cancer is associated with changes in formation of PGE2 and PGE3 and alteration of Akt phosphorylation. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, C.-H.; Li, W.-C.; Peng, C.-L.; Chen, P.-C.; Lee, S.-Y.; Hsia, S. Targeting EGFR in Combination with Nutritional Supplements on Antitumor Efficacy in a Lung Cancer Mouse Model. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120751
Guo C-H, Li W-C, Peng C-L, Chen P-C, Lee S-Y, Hsia S. Targeting EGFR in Combination with Nutritional Supplements on Antitumor Efficacy in a Lung Cancer Mouse Model. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(12):751. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120751
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Chih-Hung, Wen-Chin Li, Chia-Lin Peng, Pei-Chung Chen, Shih-Yu Lee, and Simon Hsia. 2022. "Targeting EGFR in Combination with Nutritional Supplements on Antitumor Efficacy in a Lung Cancer Mouse Model" Marine Drugs 20, no. 12: 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120751
APA StyleGuo, C.-H., Li, W.-C., Peng, C.-L., Chen, P.-C., Lee, S.-Y., & Hsia, S. (2022). Targeting EGFR in Combination with Nutritional Supplements on Antitumor Efficacy in a Lung Cancer Mouse Model. Marine Drugs, 20(12), 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120751