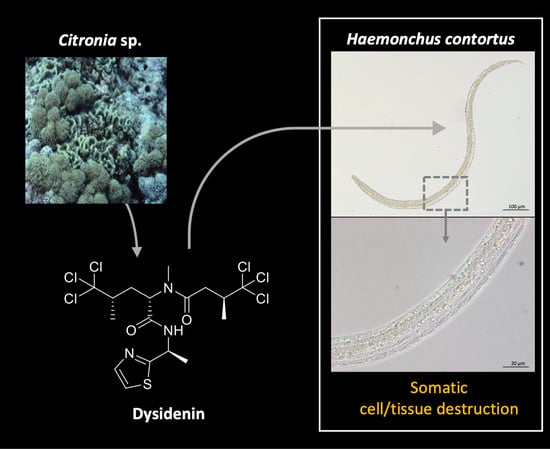
Dysidenin from the Marine Sponge Citronia sp. Affects the Motility and Morphology of Haemonchus contortus Larvae In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Bioassay-Guided Fractionation of the Citronia Extract
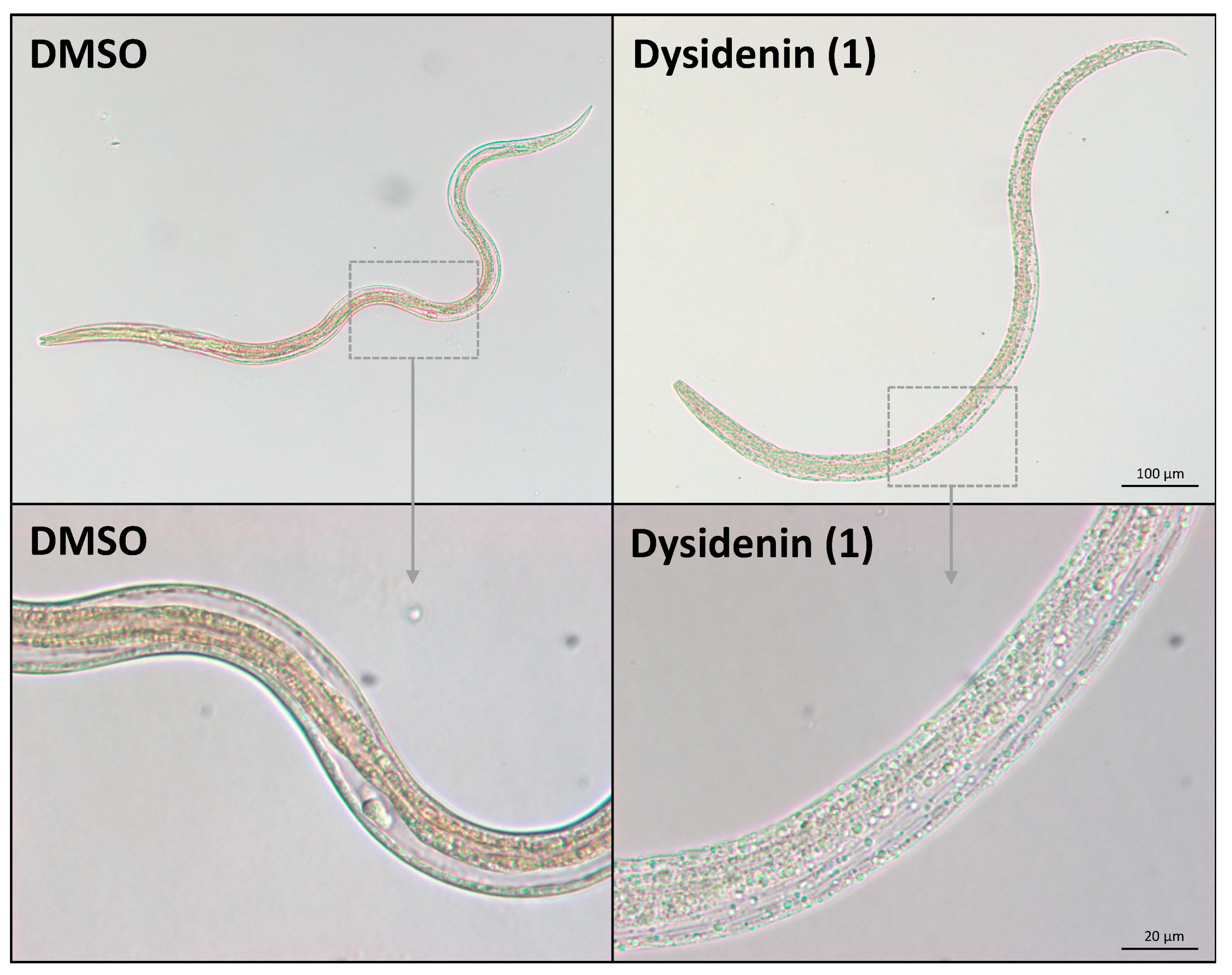
2.2. Biological Evaluation of Dysidenin (1) and Dysideathiazole (2) Purified from Citronia
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry Procedures
3.2. Collection of Sponge Material
3.3. Fractionation of the Citronia Extract
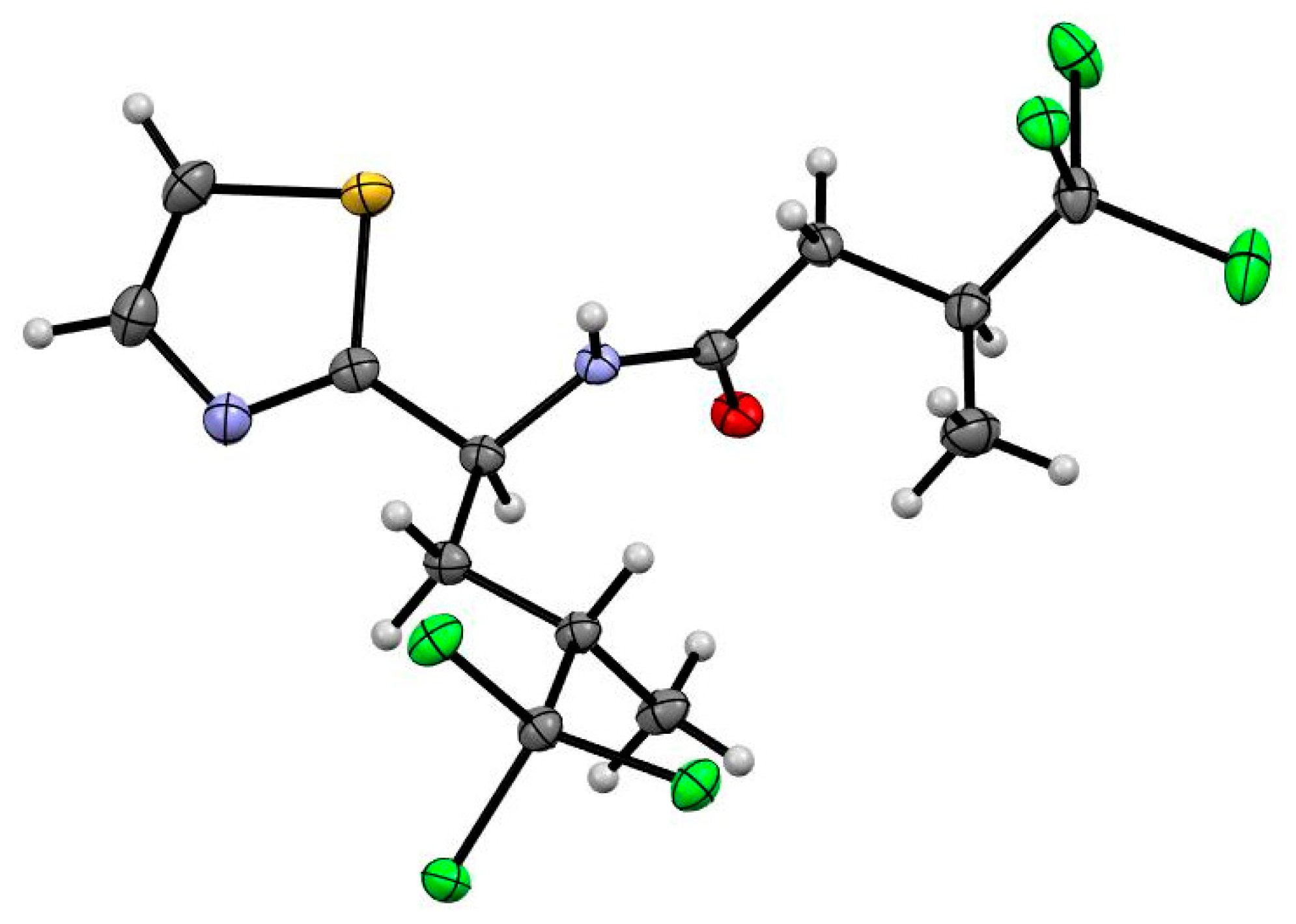
3.4. X-ray Crystallography Analysis of Dysideathiazole
3.5. Preparation of Parasitic Nematode Larvae for Bioassays
3.6. Bioassay for the Assessment of Anthelmintic Activity of Citronia Extract-Fractions
3.7. Bioassay for the Evaluation of Anthelmintic Activity of Purified Compounds
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roeber, F.; Jex, A.R.; Gasser, R.B. Impact of gastrointestinal parasitic nematodes of sheep, and the role of advanced molecular tools for exploring epidemiology and drug resistance—an Australian perspective. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beveridge, I.; Emery, D. Australian Animal Parasites—Inside and Out; The Australian Society for Parasitology Inc.: Smithfield, Australia, 2014; ISBN 9780646935607. [Google Scholar]
- Kotze, A.C.; Prichard, R.K. Anthelmintic resistance in Haemonchus contortus: History, mechanisms and diagnosis. Adv. Parasitol. 2016, 93, 397–428. [Google Scholar]
- Besier, R.B.; Kahn, L.P.; Sargison, N.D.; Van Wyk, J.A. Diagnosis, treatment and management of Haemonchus contortus in small ruminants. Adv. Parasitol. 2016, 93, 181–238. [Google Scholar]
- Herath, H.M.P.D.; Taki, A.C.; Sleebs, B.E.; Hofmann, A.; Nguyen, N.; Preston, S.; Davis, R.A.; Jabbar, A.; Gasser, R.B. Advances in the discovery and development of anthelmintics by harnessing natural product scaffolds. Adv. Parasitol. 2021, 111, 203–251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Preston, S.; Hofmann, A.; Taki, A.C.; Baell, J.B.; Chang, B.C.H.; Jabbar, A.; Gasser, R.B. A perspective on the discovery of selected compounds with anthelmintic activity against the barber’s pole worm—Where to from here? Adv. Parasitol. 2020, 108, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taki, A.C.; Byrne, J.J.; Jabbar, A.; Lum, K.Y.; Hayes, S.; Addison, R.S.; Ramage, K.S.; Hofmann, A.; Ekins, M.G.; Wang, T.; et al. High Throughput Screening of the NatureBank ‘Marine Collection’ in a Haemonchus Bioassay Identifies Anthelmintic Activity in Extracts from a Range of Sponges from Australian Waters. Molecules 2021, 26, 5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Pierens, G.K.; Fechner, G.; de Almeida Leone, P.; Ngo, A.; Simpson, M.; Hyde, E.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Boström, S.-L.; Musil, D.; et al. Dysinosin A: A Novel Inhibitor of Factor VIIa and Thrombin from a New Genus and Species of Australian Sponge of the Family Dysideidae. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13340–13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Duffy, S.; Avery, V.M. Citronamides A and B, Tetrapeptides from the Australian Sponge Citronia astra. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, H.; Preston, S.; Jabbar, A.; García-Bustos, J.; Taki, A.; Addison, R.; Hayes, S.; Beattie, K.; McGee, S.; Martin, S.; et al. Identification of fromiamycalin and halaminol A from Australian marine sponge extracts with anthelmintic activity against Haemonchus contortus. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, A.C.; Byrne, J.J.; Wang, T.; Sleebs, B.E.; Nguyen, N.; Hall, R.S.; Korhonen, P.K.; Chang, B.C.H.; Jackson, P.; Jabbar, A.; et al. High-throughput phenotypic assay to screen for anthelmintic activity on Haemonchus contortus. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unson, M.D.; Rose, C.B.; Faulkner, D.J.; Brinen, L.S.; Steiner, J.R.; Clardy, J. New polychlorinated amino acid derivatives from the marine sponge Dysidea herbacea. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 6336–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazlauskas, R.; Lidgard, R.; Wells, R.; Vetter, W. A novel hexachloro-metabolite from the sponge Dysidea herbacea. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 18, 3183–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biskupiak, J.E.; Ireland, C.M. Revised absolute configuration of dysidenin and isodysidenin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 2935–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, A.C.; Brkljača, R.; Wang, T.; Koehler, A.V.; Ma, G.; Danne, J.; Ellis, S.; Hofmann, A.; Chang, B.C.H.; Jabbar, A.; et al. Natural compounds from the marine brown alga Caulocystis cephalornithos with potent in vitro-activity against the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Sande, J.; Deneubourg, F.; Beauwens, R.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Dumont, J.E. Inhibition of iodide transport in thyroid cells by dysidenin, a marine toxin, and some of its analogs. Mol. Pharmacol. 1990, 37, 583–589. [Google Scholar]
- Van Sande, J.; Massart, C.; Beauwens, R.; Schoutens, A.; Costagliola, S.; Dumont, J.; Wolff, J. Anion selectivity by the sodium iodide symporter. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroye, L.; Beauwens, R.; Van Sande, J.; Daloze, D.; Braekman, J.; Golstein, P. The Na+-I– cotransporter of the thyroid: Characterisation of new inhibitors. Pflüg. Arch. 1997, 435, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenthal, S.; Lecat-Guillet, N.; Ondo-Mendez, A.; Ambroise, Y.; Rousseau, B.; Pourcher, T. Characterization of small-molecule inhibitors of the sodium iodide symporter. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 200, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, J.D.; Gautschi, J.T.; Whitman, S.; Johnson, T.A.; Gassner, N.C.; Crews, P.; Holman, T.R. Discovery of platelet-type 12-human lipoxygenase selective inhibitors by high-throughput screening of structurally diverse libraries. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 6900–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamazaki, H.; Ohte, S.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Sumilat, D.A.; Abdjul, D.B.; Maarisit, W.; Kapojos, M.M.; Namikoshi, M.; Katagiri, T.; et al. Screening for small molecule inhibitors of BMP-induced osteoblastic differentiation from Indonesian marine invertebrates. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, C.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Tursch, B.; Karlsson, R. Isodysidenin, a further hexachlorinated metabolite from the sponge Dysidea herbacea. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 17, 1519–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C.F.; Bruno, I.J.; Chisholm, J.A.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Rodriguez-Monge, L.; Taylor, R.; Van De Streek, J.; Wood, P. A, Mercury CSD 20—New features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, L. WinGX suite for small-molecule single-crystal crystallography. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1999, 32, 837–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, S.; Flack, H.D.; Wagner, T. Use of intensity quotients and differences in absolute structure refinement. Acta Crystallogr. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 2013, 69, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, S.; Jabbar, A.; Nowell, C.; Joachim, A.; Ruttkowski, B.; Baell, J.; Cardno, T.; Korhonen, P.K.; Piedrafita, D.; Ansell, B.R.; et al. Low cost whole-organism screening of compounds for anthelmintic activity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.G.; Kundu, A.; Ghoshal, A.; Nguyen, N.H.; Preston, S.; Jiao, Y.; Ruan, B.; Xue, L.; Huang, F.; Keiser, J.; et al. Optimization of novel 1-methyl-1 h -pyrazole-5-carboxamides leads to high potency larval development inhibitors of the barber’s pole worm. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10875–10894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| xL3s | In Vitro-Raised L4s | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motility Inhibition (72 h) | Development Inhibition (168 h) | Abnormal Phenotype(s) Detected (168 h) | Motility Inhibition (72 h) | Abnormal Phenotype Detected (72 h) | |
| Dysidenin (1) | nd | 58% | Cur (43%), Evi (14%), Ski (8%) | 61% | Ski (50%) |
| Dysideathiazole (2) | nd | nd | nd | 25% | Ski (28%) |
| Monepantel | 81% | 100% | Coi (90%) | 70% | Ski (78%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramage, K.S.; Taki, A.C.; Lum, K.Y.; Hayes, S.; Byrne, J.J.; Wang, T.; Hofmann, A.; Ekins, M.G.; White, J.M.; Jabbar, A.; et al. Dysidenin from the Marine Sponge Citronia sp. Affects the Motility and Morphology of Haemonchus contortus Larvae In Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120698
Ramage KS, Taki AC, Lum KY, Hayes S, Byrne JJ, Wang T, Hofmann A, Ekins MG, White JM, Jabbar A, et al. Dysidenin from the Marine Sponge Citronia sp. Affects the Motility and Morphology of Haemonchus contortus Larvae In Vitro. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(12):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120698
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamage, Kelsey S., Aya C. Taki, Kah Yean Lum, Sasha Hayes, Joseph J. Byrne, Tao Wang, Andreas Hofmann, Merrick G. Ekins, Jonathan M. White, Abdul Jabbar, and et al. 2021. "Dysidenin from the Marine Sponge Citronia sp. Affects the Motility and Morphology of Haemonchus contortus Larvae In Vitro" Marine Drugs 19, no. 12: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120698
APA StyleRamage, K. S., Taki, A. C., Lum, K. Y., Hayes, S., Byrne, J. J., Wang, T., Hofmann, A., Ekins, M. G., White, J. M., Jabbar, A., Davis, R. A., & Gasser, R. B. (2021). Dysidenin from the Marine Sponge Citronia sp. Affects the Motility and Morphology of Haemonchus contortus Larvae In Vitro. Marine Drugs, 19(12), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120698