Microalgae and Cyanobacteria Strains as Producers of Lipids with Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Microalgae and Cyanobacteria Strains Selection
2.2. Antibiotic Activity of Fractions and Sub-fractions
2.3. Antibiofilm Activity of Fractions and Sub-Fractions
2.4. HRESIMS and NMR Results
2.5. Antibiotic and Antibiofilm Activity of α-Linolenic Acid (ALA) and 1-Palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (C16:0 LPC)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microalgae and Cyanobacteria Strains
4.2. Microbial Strains
4.3. Antibiotic Analysis
4.4. Antibiofilm Analysis
4.5. Solid Phase Extraction Methods for Methanolic and Ethyl Acetate Extracts
4.6. Bioassay-Guided HPLC-DAD Purification
4.7. HPLC-HRESIMS Analyses
4.8. NMR Assays
4.9. Reagents and Biochemicals
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U.; et al. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojas, V.; Rivas, L.; Cárdenas, C.; Guzmán, F. Cyanobacteria and eukaryotic microalgae as emerging sources of antibacterial peptides. Molecules 2020, 25, 5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzkar, N.; Jahromi, S.T.; Poorsaheli, H.B.; Vianello, F. Metabolites from marine microorganisms, micro, and macroalgae: Immense scope for pharmacology. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maschek, J.A.; Baker, B.J. The chemistry of algal secondary metabolism. In Algal Chemical Ecology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, V.M.C.; Castelo-Branco, R.; Leão, P.N.; Martins, J.; Carvalhal-Gomes, S.; Sobrinho da Silva, F.; Mendonça Filho, J.G.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Cyanobacterial diversity in microbial mats from the hypersaline lagoon system of Araruama, Brazil: An in-depth polyphasic study. Front Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borowitzka, M.A. Microalgae in medicine and human health. In Microalgae in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 652, pp. 195–210. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-del-Río, I.; Brugerolle de Fraissinette, N.; Castelo-Branco, R.; Oliveira, F.; Morais, J.; Redondo-Blanco, S.; Villar, C.J.; Iglesias, M.J.; Soengas, R.; Cepas, V.; et al. Chlorosphaerolactylates A–D: Natural lactylates of chlorinated fatty acids isolated from the cyanobacterium Sphaerospermopsis sp. LEGE 00249. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1885–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepas, V.; López, Y.; Gabasa, Y.; Martins, C.B.; Ferreira, J.D.; Correia, M.J.; Santos, L.M.A.; Oliveira, F.; Ramos, V.; Reis, M.; et al. Inhibition of bacterial and fungal biofilm formation by 675 extracts from microalgae and cyanobacteria. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, F.; Antunes, J.T.; Ribeiro, T.; Azevedo, J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Leão, P.N. Cyanobacterial allelochemicals but not cyanobacterial cells markedly reduce microbial community diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thormar, H. Lipids and Essential Oils as Antimicrobial Agents; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 2010; ISBN 9780470976623. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, B.; Jackman, J.; Valle-González, E.; Cho, N.-J. Antibacterial free fatty acids and monoglycerides: Biological activities, experimental testing, and therapeutic applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casillas-Vargas, G.; Ocasio-Malavé, C.; Medina, S.; Morales-Guzmán, C.; Del Valle, R.G.; Carballeira, N.M.; Sanabria-Ríos, D.J. Antibacterial fatty acids: An update of possible mechanisms of action and implications in the development of the next-generation of antibacterial agents. Prog. Lipid Res. 2021, 82, 101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbois, A.P. Potential applications of antimicrobial fatty acids in medicine, agriculture and other industries. Recent Pat. AntiInfect. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabara, J.J.; Swieczkowski, D.M.; Conley, A.J.; Truant, J.P. Fatty acids and derivatives as antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1972, 2, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenar, J.A.; Moser, B.R.; List, G.R. Naturally occurring fatty acids: Source, chemistry, and uses. In Fatty Acids. Chemistry, Synthesis and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 23–82. [Google Scholar]
- Coraça-Huber, D.C.; Steixner, S.; Wurm, A.; Nogler, M. Antibacterial and anti-biofilm activity of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids against periprosthetic joint infections-isolated multi-drug resistant strains. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Lee, J.H.; Beyenal, H.; Lee, J. Fatty acids as antibiofilm and antivirulence agents. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbois, A.P.; Smith, V.J. Antibacterial free fatty acids: Activities, mechanisms of action and biotechnological potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jüttner, F. Liberation of 5,8,11,14,17-eicosapentaenoic acid and other polyunsaturated fatty acids from lipids as a grazer defense reaction in epilithic diatom biofilms. J. Phycol. 2001, 37, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, H.; Miller, T.B. Physicochemical effects of long chain fatty acids on bacterial cells and their protoplasts. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1973, 36, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.J.; Yoo, J.-S.; Lee, T.-G.; Cho, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, W.-G. Fatty acid synthesis is a target for antibacterial activity of unsaturated fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5157–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sado-Kamdem, S.L.; Vannini, L.; Guerzoni, M.E. Effect of α-linolenic, capric and lauric acid on the fatty acid biosynthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 129, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, E.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Antibacterial Derivatives of Marine Algae: An overview of pharmacological mechanisms and applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratzer, R.; Murkovic, M. Food Ingredients and nutraceuticals from microalgae: Main product classes and biotechnological production. Foods 2021, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, R.; Daniels, T.C.; Eiler, J.J.; Gunnison, J.B.; Kumler, W.D.; Oneto, J.F.; Strait, L.A.; Spoehr, H.A.; Hardin, G.J.; Milner, H.W.; et al. Chlorellin, an antibacterial substance from chlorella. Science 1944, 99, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falaise, C.; François, C.; Travers, M.; Morga, B.; Haure, J.; Tremblay, R.; Turcotte, F.; Pasetto, P.; Gastineau, R.; Hardivillier, Y.; et al. Antimicrobial compounds from eukaryotic microalgae against human pathogens and diseases in aquaculture. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mudimu, O.; Rybalka, N.; Bauersachs, T.; Born, J.; Friedl, T.; Schulz, R. Biotechnological screening of microalgal and cyanobacterial strains for biogas production and antibacterial and antifungal effects. Metabolites 2014, 4, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ördög, V.; Stirk, W.A.; Lenobel, R.; Bancířová, M.; Strnad, M.; van Staden, J.; Szigeti, J.; Németh, L. Screening microalgae for some potentially useful agricultural and pharmaceutical secondary metabolites. J. Appl. Phycol. 2004, 16, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Ohta, S.; Ikegami, N.; Miyata, H. Antibiotic substances produced by a marine green alga, Dunaliella primolecta. Bioresour. Technol. 1993, 44, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasakumar, K.P.; Rajashekhar, M. In vitro studies on bactericidal activity and sensitivity pattern of isolated marine microalgae against selective human bacterial pathogens. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2009, 2, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannell, R.J.P.; Owsianka, A.M.; Walker, J.M. Results of a large-scale screening programme to detect antibacterial activity from freshwater algae. Br. Phycol. J. 2007, 23, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoyo, S.; Rodríguez-Meizoso, I.; Cifuentes, A.; Jaime, L.; García-Blairsy Reina, G.; Señorans, F.J.; Ibáñez, E. Green processes based on the extraction with pressurized fluids to obtain potent antimicrobials from Haematococcus pluvialis microalgae. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, A.C.; Barbosa, C.R.; Amaro, H.M.; Pereira, C.I.; Malcata, F.X. Microalgal and cyanobacterial cell extracts for use as natural antibacterial additives against food pathogens. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S.; Shiomi, Y.; Kawashima, A.; Aozasa, O.; Nakao, T.; Nagate, T.; Kitamura, K.; Miyata, H. Antibiotic effect of linolenic acid from Chlorococcum strain HS-101 and Dunaliella primolecta on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Appl. Phycol. 1995, 7, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbois, A.P.; Lebl, T.; Yan, L.; Smith, V.J. Isolation and structural characterisation of two antibacterial free fatty acids from the marine diatom, Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 81, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbois, A.P.; Mearns-Spragg, A.; Smith, V.J. A fatty acid from the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum is antibacterial against diverse bacteria including multi-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiola, J.A.; Torres, C.F.; Toré, A.; Martín-Álvarez, P.J.; Santoyo, S.; Arredondo, B.O.; Señoráns, F.J.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E. Use of supercritical CO2 to obtain extracts with antimicrobial activity from Chaetoceros muelleri microalga. A correlation with their lipidic content. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006, 224, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Yu, G.; Guan, H. Total synthesis and structure-activity relationship of glycoglycerolipids from marine organisms. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3634–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Costa, E.; Silva, J.; Mendonça, S.H.; Abreu, M.H.; Domingues, M.R. Lipidomic approaches towards deciphering glycolipids from microalgae as a reservoir of bioactive lipids. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, E.; Dias, M.; Lopes, D.; Almeida, A.; Domingues, M.d.R.; Rey, F. Antimicrobial lipids from plants and marine organisms: An overview of the current state-of-the-art and future prospects. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, I.C.; Falaise, C.; Hellio, C.; Bourgougnon, N.; Mouget, J.-L. Anticancer, antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal properties in microalgae. In Microalgae in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 235–261. [Google Scholar]
- Plouguerné, E.; da Gama, B.A.P.; Pereira, R.C.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Glycolipids from seaweeds and their potential biotechnological applications. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüninger, J.; Delavault, A.; Ochsenreither, K. Enzymatic glycolipid surfactant synthesis from renewables. Process Biochem. 2019, 87, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Baky, H.H.; El Baz, F.K.; El Baroty, G.S.; Asker, M.M.S.; Ibrahim, E.A. Phospholipids of some marine microalgae: Identification, antivirus, anticancer and antimicrobial bioactivities. Der Pharma Chem. 2014, 6, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Smani, Y.; Domínguez-Herrera, J.; Ibáñez-Martínez, J.; Pachón, J. Therapeutic efficacy of lysophosphatidylcholine in severe infections caused by Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 3920–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Logvinov, S.; Gerasimenko, N.; Esipov, A.; Denisenko, V.A. Examination of the structures of several glycerolipids from marine macroalgae by NMR and GC-MS. J. Phycol. 2015, 51, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keusgen, M.; Curtis, J.M.; Thibault, P.; Walter, J.A.; Windust, A.; Ayer, S.W. Sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerols from the alga Heterosigma carterae. Lipids 1997, 32, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aursand, M.; Grasdalen, H. Interpretation of the 13C-NMR spectra of omega-3 fatty acids and lipid extracted from the white muscle of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Chem. Phys. Lipids 1992, 62, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamsjah, M.A.; Hirao, S.; Ishibashi, F.; Fujita, Y. Isolation and structure determination of algicidal compounds from Ulva fasciata. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murakami, N.; Morimoto, T.; Imamura, H.; Nagatsu, A.; Sakakibara, J. Enzymatic transformation of glyceroglycolipids into sn-1 and sn-2 lysoglyceroglycolipids by use of Rhizopus arrhizus lipase. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edzes, H.T.; Teerlink, T.; Van Der Knaap, M.S.; Valk, J. Analysis of phospholipids in brain tissue by 31P NMR at different compositions of the solvent system chloroform-methanol-water. Magn. Reson. Med. 1992, 26, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaffarnik, S.; Ehlers, I.; Gröbner, G.; Schleucher, J.; Vetter, W. Two-Dimensional 31P, 1H NMR spectroscopic profiling of phospholipids in cheese and fish. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7061–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimeno, M.L.; Valverde, S.; Błaszczak, W.; Fornal, J.; Amarowicz, R. 13C and 1H NMR study of lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) isolated from the surface of wheat starch granules. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2002, 8, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banskota, A.H.; Stefanova, R.; Sperker, S.; McGinn, P.J. New diacylglyceryltrimethylhomoserines from the marine microalga Nannochloropsis granulata and their nitric oxide inhibitory activity. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 5, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolganyuk, V.; Belova, D.; Babich, O.; Prosekov, A.; Ivanova, S.; Katserov, D.; Patyukov, N.; Sukhikh, S. Microalgae: A promising source of valuable bioproducts. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhunov, A.A.; Gusakova, S.D.; Taubaev, T.T.; Umarov, A.U. Isolation and antibiotic properties of cis-hexadeca-4,7,10,13-tetraenoic acid from the alga Scenedesmus obliquus UA-2-6. Chem. Nat. Compd. 1978, 14, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, M.J.; Soengas, R.; Probert, I.; Guilloud, E.; Gourvil, P.; Mehiri, M.; López, Y.; Cepas, V.; Gutiérrez-del-Río, I.; Redondo-Blanco, S.; et al. NMR characterization and evaluation of antibacterial and antiobiofilm activity of organic extracts from stationary phase batch cultures of five marine microalgae (Dunaliella sp., D. salina, Chaetoceros calcitrans, C. gracilis and Tisochrysis lutea). Phytochemistry 2019, 164, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supardy, N.A.; Ibrahim, D.; Nor, S.R.M.; Noordin, W.N.M. Bioactive compounds of Pseudoalteromonas sp. IBRL PD4.8 inhibit growth of fouling bacteria and attenuate biofilms of Vibrio alginolyticus FB3. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Shin, D.-H. Antimicrobial synergistic effect of linolenic acid and monoglyceride against Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2193–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galbraith, H.; Miller, T.B.; Paton, A.M.; Thompson, J.K. Antibacterial activity of long chain fatty acids and the reversal with calcium, magnesium, ergocalciferol and cholesterol. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1971, 34, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Johnson, E.A. Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes by fatty acids and monoglycerides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.Q.; O’Connor, C.J.; Roberton, A.M. Antibacterial actions of fatty acids and monoglycerides against Helicobacter pylori. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 36, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, C.; Frank, M.W.; Batte, J.L.; Whaley, S.G.; Rock, C.O. Oleate hydratase from Staphylococcus aureus protects against palmitoleic acid, the major antimicrobial fatty acid produced by mammalian skin. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 9285–9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butt, U.; ElShaer, A.; Snyder, L.A.S.; Chaidemenou, A.; Alany, R.G. Fatty acid microemulsion for the treatment of neonatal conjunctivitis: Quantification, characterisation and evaluation of antimicrobial activity. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2016, 6, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergsson, G.; Arnfinnsson, J.; Steingrímsson, O.; Thormar, H. Killing of Gram-positive cocci by fatty acids and monoglycerides. APMIS 2001, 109, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsson, G.; Steingrímsson, O.; Thormar, H. In vitro susceptibilities of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to fatty acids and monoglycerides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 2790–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicol, M.; Alexandre, S.; Luizet, J.-B.; Skogman, M.; Jouenne, T.; Salcedo, S.; Dé, E. Unsaturated fatty acids affect quorum sensing communication system and inhibit motility and biofilm formation of Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plaza, M.; Santoyo, S.; Jaime, L.; García-Blairsy Reina, G.; Herrero, M.; Señoráns, F.J.; Ibáñez, E. Screening for bioactive compounds from algae. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, J.B.; Yao, J.; Frank, M.W.; Jackson, P.; Rock, C.O. Membrane disruption by antimicrobial fatty acids releases low-molecular-weight proteins from Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 5294–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Treyvaud Amiguet, V.; Jewell, L.E.; Mao, H.; Sharma, M.; Hudson, J.B.; Durst, T.; Allard, M.; Rochefort, G.; Arnason, J.T. Antibacterial properties of a glycolipid-rich extract and active principle from Nunavik collections of the macroalgae Fucus evanescens C. Agardh (Fucaceae). Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plouguerné, E.; de Souza, L.M.; Sassaki, G.L.; Hellio, C.; Trepos, R.; da Gama, B.A.P.; Pereira, R.C.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Glycoglycerolipids from Sargassum vulgare as potential antifouling agents. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parveez Ahamed, A.A.; Rasheed, M.U.; Peer Muhamed Noorani, K.; Reehana, N.; Santhoshkumar, S.; Mohamed Imran, Y.M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Arunachalam, C.; Alharbi, S.A.; Akbarsha, M.A.; et al. In vitro antibacterial activity of MGDG-palmitoyl from Oscillatoria acuminata NTAPC05 against extended-spectrum β-lactamase producers. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadhli, A.A.; Wahidulla, S.; D’Souza, L. Glycolipids from the red alga Chondria armata (Kutz.) Okamura. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Baz, F.K.; El Baroty, G.S.; Abd El Baky, H.H.; Abd El-Salam, O.I.; Ibrahim, E.A. Structural characterization and biological activity of sulfolipids from selected marine algae. Grasas y Aceites 2013, 64, 561–571. [Google Scholar]
- Yuyama, K.T.; Rohde, M.; Molinari, G.; Stadler, M.; Abraham, W.R. Unsaturated fatty acids control biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus and other gram-positive bacteria. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasath, K.G.; Tharani, H.; Kumar, M.S.; Pandian, S.K. Palmitic acid inhibits the virulence factors of Candida tropicalis: Biofilms, cell surface hydrophobicity, ergosterol biosynthesis, and enzymatic activity. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 864–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LewisOscar, F.; Nithya, C.; Alharbi, S.A.; Alharbi, N.S.; Thajuddin, N. Microfouling inhibition of human nosocomial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa using marine cyanobacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.G.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.G.; Lee, J. Inhibition of Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus biofilms by centipede oil and linoleic acid. Biofouling 2020, 36, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.E.; Pandit, S.; Jeon, J.G. Identification of linoleic acid, a main component of the n-hexane fraction from Dryopteris crassirhizoma, as an anti-Streptococcus mutans biofilm agent. Biofouling. 2014, 30, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanda, W.; Joseph, T.P.; Padhiar, A.A.; Guo, X.; Min, L.; Wang, W.; Lolokote, S.; Ning, A.; Cao, J.; Huang, M.; et al. Combined effect of linolenic acid and tobramycin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and quorum sensing. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 4328–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, J. Inhibition of polymicrobial biofilm formation by saw palmetto oil, lauric acid and myristic acid. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalbæk, B.; Jensen, L.K.; Jensen, H.E.; Olsen, J.E.; Christensen, H. Whole-genome sequence of Staphylococcus aureus S54F9 isolated from a chronic disseminated porcine lung abscess and used in human infection models. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e01207-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pannanusorn, S.; Ramírez-Zavala, B.; Lünsdorf, H.; Agerberth, B.; Morschhäuser, J.; Römling, U. Characterization of biofilm formation and the role of bcr1 in clinical isolates of Candida parapsilosis. Eukaryot. Cell 2014, 13, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CLSI document M100-S20. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 26th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, M.J.; Soengas, R.; Martins, C.B.; Correira, M.J.; Ferreira, J.D.; Santos, L.M.A.; López-Ortiz, F. Chemotaxonomic profiling trough NMR. J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
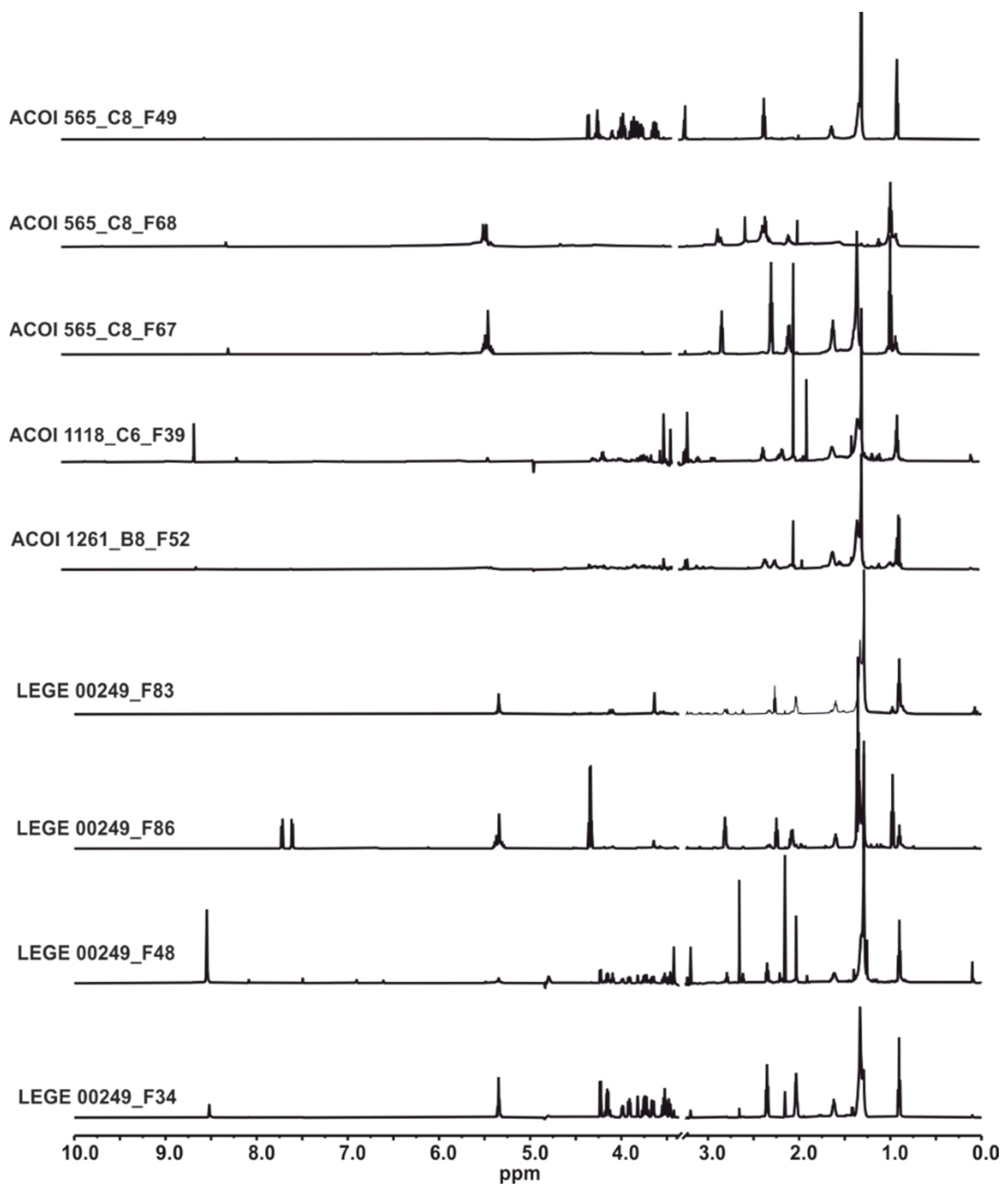


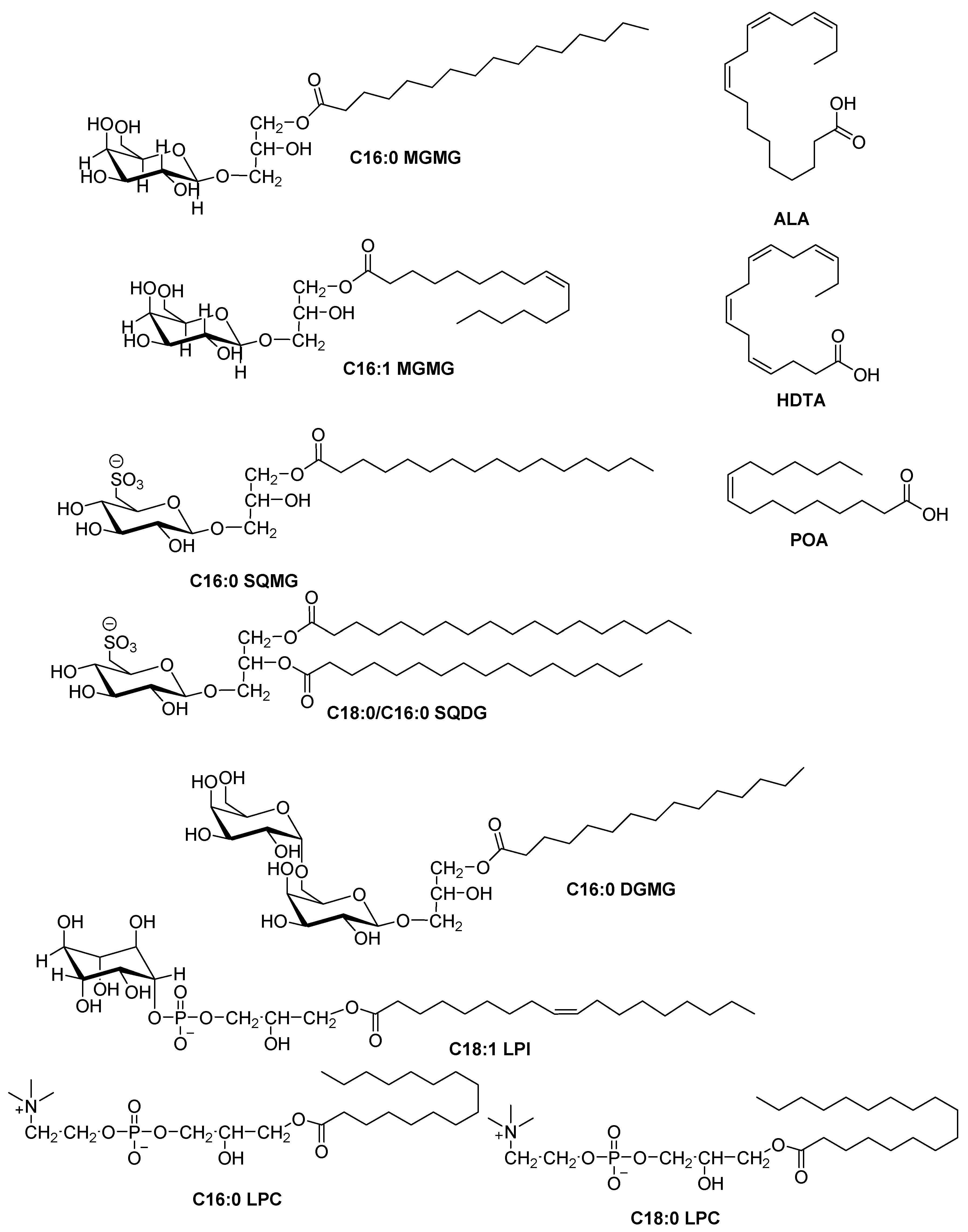
| Microalgae/Cyanobacteria Strain | SPE-Fraction | HPLC Sub-Fraction | Molecules Detected | Microorganism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACOI 1261 | B8 | F52 | C16:0 MGMG, C18:0/C16:0 SQDG | S. aureus |
| ACOI 118 | C6 | F39 | C16:0 SQMG | S. aureus |
| ACOI 565 | C8 | F67 | ALA | S. aureus |
| C4 | F68 | HDTA | S. aureus | |
| LEGE 00249 | - | F34 (from Group A F69-F76 refractionation) | C16:1 MGMG | S. aureus |
| - | F48 (from Group A F69-F76 refractionation) | C16:0 MGMG | S. aureus | |
| - | F83 | ALA, C16:0/C18:0 SQDG | S. aureus | |
| - | F86 | POA | S. aureus |
| Microalgae/Cyanobacteria Strain | SPE-Fraction | HPLC Sub-Fraction | Molecules Detected | Microorganism | % of Biofilm Inhibition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACOI 1261 | B8 | F26-27 | C16:0 MGMG, C18:0/C16:0 SQDG | CoNS | 80% |
| F28-29 | C16:0 MGMG, C18:0/C16:0 SQDG | CoNS C. parapsilosis | 40% 40% | ||
| F47-51 | C16:0 MGMG, C18:0/C16:0 SQDG | E. coli CoNS | 80% 40% | ||
| F59-66 | C16:0 MGMG, C18:0/C16:0 SQDG | E. coli C. parapsilosis | 40% 40% | ||
| ACOI 118 | C6 | F36-38 | C16:0 SQMG | CoNS | 34% |
| ACOI 565 | C8 | F48-49 | C16:0 DGMG C18:0 LPC, C16:0 LPC, C18:1 LPI C16:0 SQMG | CoNS E. coli C. albicans | 60% 60% 60% |
| LEGE 00249 | - | F34 (from Group A F69-F76 refractionation) | C16:1 MGMG | CoNS | 61% |
| F48 (from Group A F69-F76 refractionation) | C16:0 MGMG | CoNS | 70% |
| Microbial Strain | MIC (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| E. coli | >250 |
| S. aureus | 15.6 |
| C. parapsilosis | 125 |
| 50% Biofilm Inhibition | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microbial Strain | ALA (mg/L) | ALA 1: C16:0 LPC 1 (mg/L) | ALA 1: C16:0 LPC 0.5 (mg/L) | ALA 0.5: C16:0 LPC 1 (mg/L) | C16:0 LPC (mg/L) |
| K. pneumoniae | >128 | >128 | >128 | 2 | 32 |
| P. aeruginosa | 32 | 64 | 32 | 16 | >128 |
| E. coli | >128 | >128 | 128 | 64 | 32 |
| E. cloacae | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 |
| CoNS | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 |
| S. epidermidis | 128 | 128 | 128 | 64 | 64 |
| S. aureus | 64 | 128 | 128 | 64 | >128 |
| C. parapsilosis | 128 | 128 | 64 | 64 | 64 |
| C. albicans | 1 | 8 | 64 | >128 | 128 |
| Microalgae Strain | Hexane (mg) | Ethyl Acetate (mg) | Methanol (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACOI 1261 | 136 | 69 | 1109 |
| ACOI 118 | 301 | 214 | 821 |
| ACOI 565 | 292 | 143 | 1316 |
| Cyanobacterium Strain | Hexane (mg) | Ethyl Acetate (mg) | Methanol (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LEGE 00249 | 66.07 | 352.88 | 949.65 |
| Microalgae/Cyanobacteria Strain | SPE-Fraction | HPLC Sub-Fraction |
|---|---|---|
| ACOI 1261 | B8 (4.3 mg) | F52 (0.7 mg) |
| F26–27 (0.5 mg) | ||
| F28–29 (0.7 mg) | ||
| F47–51 (0.9 mg) | ||
| F59–66 (1.1 mg) | ||
| ACOI 118 | C6 (9 mg) | F39 (0.3 mg) |
| F36–38 (0.4 mg) | ||
| ACOI 565 | C8 (129.1 mg) | F67 (5.4 mg) |
| F48–49 (2.4 mg) | ||
| C4 (27.9 mg) | F68 (0.5 mg) | |
| LEGE 00249 | - | F34 (0.4 mg) |
| F48 (0.4 mg) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cepas, V.; Gutiérrez-Del-Río, I.; López, Y.; Redondo-Blanco, S.; Gabasa, Y.; Iglesias, M.J.; Soengas, R.; Fernández-Lorenzo, A.; López-Ibáñez, S.; Villar, C.J.; et al. Microalgae and Cyanobacteria Strains as Producers of Lipids with Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120675
Cepas V, Gutiérrez-Del-Río I, López Y, Redondo-Blanco S, Gabasa Y, Iglesias MJ, Soengas R, Fernández-Lorenzo A, López-Ibáñez S, Villar CJ, et al. Microalgae and Cyanobacteria Strains as Producers of Lipids with Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(12):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120675
Chicago/Turabian StyleCepas, Virginio, Ignacio Gutiérrez-Del-Río, Yuly López, Saúl Redondo-Blanco, Yaiza Gabasa, María José Iglesias, Raquel Soengas, Andrés Fernández-Lorenzo, Sara López-Ibáñez, Claudio J. Villar, and et al. 2021. "Microalgae and Cyanobacteria Strains as Producers of Lipids with Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity" Marine Drugs 19, no. 12: 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120675
APA StyleCepas, V., Gutiérrez-Del-Río, I., López, Y., Redondo-Blanco, S., Gabasa, Y., Iglesias, M. J., Soengas, R., Fernández-Lorenzo, A., López-Ibáñez, S., Villar, C. J., Martins, C. B., Ferreira, J. D., Assunção, M. F. G., Santos, L. M. A., Morais, J., Castelo-Branco, R., Reis, M. A., Vasconcelos, V., López-Ortiz, F., ... Soto, S. M. (2021). Microalgae and Cyanobacteria Strains as Producers of Lipids with Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity. Marine Drugs, 19(12), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120675










