Abstract
Marine sponges are exceptionally prolific sources of natural products for the discovery and development of new drugs. Until now, sponges have contributed around 30% of all natural metabolites isolated from the marine environment. Family Latrunculiidae Topsent, 1922 (class Demospongiae Sollas, 1885, order Poecilosclerida Topsent, 1928) is a small sponge family comprising seven genera. Latrunculid sponges are recognized as the major reservoirs of diverse types of pyrroloiminoquinone-type alkaloids, with a myriad of biological activities, in particular, cytotoxicity, fuelling their exploration for anticancer drug discovery. Almost 100 pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids and their structurally related compounds have been reported from the family Latrunculiidae. The systematics of latrunculid sponges has had a complex history, however it is now well understood. The pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids have provided important chemotaxonomic characters for this sponge family. Latrunculid sponges have been reported to contain other types of metabolites, such as peptides (callipeltins), norditerpenes and norsesterpenes (trunculins) and macrolides (latrunculins), however, the sponges containing latrunculins and trunculins have been transferred to other sponge families. This review highlights a comprehensive literature survey spanning from the first chemical investigation of a New Zealand Latrunculia sp. in 1986 until August 2020, focusing on the chemical diversity and biological activities of secondary metabolites reported from the family Latrunculiidae. The biosynthetic (microbial) origin and the taxonomic significance of pyrroloiminoquinone related alkaloids are also discussed.
1. Introduction
Marine organisms have an extraordinary track record as an invaluable source of novel secondary metabolites with unique chemical structures and a wide range of pharmacological activities that hold the key for the development of novel drugs [1,2]. Marine natural product (MNP) research began with investigation on the Bahamian sponge Tectitethya crypta (de Laubenfels, 1949) in the 1950s, yielding the nucleosides spongothymidine and spongouridine [3,4,5]. These metabolites served as the leading structures for the synthesis of the first marine-derived anticancer agent cytarabine (Ara-CTM) and antiviral agent vidarabine (Ara-ATM). Marine sponges are among the most primitive multicellular animals that have existed for 700–800 million years, with approximately 8900 described species distributed worldwide today [6]. Being sessile, sponges lack behavioral defenses and have evolved numerous structural and chemical defense strategies to defend themselves, e.g., the accumulation of toxic and/or antifeedant molecules [7]. Sponge structural components such as spicules, spongin, and chitin fibers all exhibit high defensive efficiency [8,9]. Sponges also produce a vast array of secondary metabolites featuring unprecedented carbon skeletons and multiple ecological functions, such as chemical defenses, which often underly their pharmacological activities [10,11,12,13]. It is well known that sponges possess a very rich microbiome that also contributes to the production of bioactive secondary metabolites [7,14,15]. Marine sponges have received the greatest attention of all marine organisms, and are recognized as the most prolific sources of MNPs, contributing to nearly 30% of all MNPs reported so far [16,17]. Currently, three out of 14 approved marine-derived drugs on the market have their origin in marine sponges, namely Halaven® (eribulin mesylate), Vira-A® (Ara-A), and Cytosar-U® (Ara-C) [18]. Furthermore, the sponge-derived metabolite plocabulin, a new tubulin-binding agent originally obtained from the sponge Lithoplocamia lithiostoides, is currently undergoing phase II clinical trials for the treatment of solid tumors; eribulin, a synthetic analogue of halichondrin B, which originated from sponge Halichondria okadai, is undergoing phase I clinical trials for its new application as payloads of antibody–drug conjugates (ADC) [18].
Latrunculiidae Topsent, 1922 [19] is a well-known and well-defined family of demosponges (class Demospongiae Sollas) within the order Poecilsoclerida Topsent, with an unusual amphipolar distribution; the 83 valid species presently recognized are largely distributed between the cold and temperate coastal shallow and deep-sea environments of: (1) South Africa; (2) New Zealand and Antarctica; (3) South America [20]; (4) the North Pacific Ocean, around the British Columbia, Alaskan, and Aleutian Islands, and the Kurile Islands, Sea of Okhotsk, Russia [21]. A few species are found between these primary regions, including the Southern Ocean, South Australia, New Caledonia, Japan, and the eastern Philippines. Latrunculid sponges have been recorded from the shallow subtidal zone down to 2500 m (Bomba endeavourensis Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016) [21]. Sponges of the family Latrunculiidae are all very similar in general morphology and skeletal architecture, having a differentiated aquiferous system of raised dome- to mushroom-shaped porefields and raised volcano-shaped oscules, and ranging in shape from spheres, to massive hemispheres, to pedunculate, to encrusting (Figure 1). The colour in life is characteristically rich chocolate to liver brown, sage to emerald green, deep turquoise to (rarely) purple and pink (Figure 1). The family Latrunculiidae now contains seven genera: Latrunculia du Bocage, 1869 (and three subgenera); Sceptrella Schmidt, 1870; Strongylodesma Levi, 1960; Tsitsikamma Samaai & Kelly, 2002; Cyclacanthia Samaai & Kelly, 2004; Bomba Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016; Latrunclava Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016 [21,22,23,24,25,26]. Species in the seven genera (and subgenera) are differentiated primarily on the morphology and ornamentation of the diagnostic microsclere—the anisodiscorhabd (Figure 1).
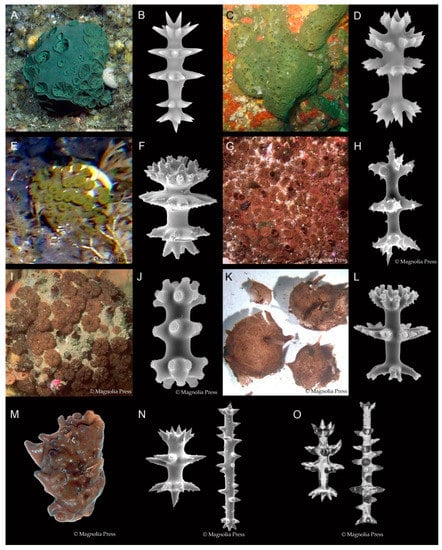
Figure 1.
Living Latrunculiidae sponges and their diagnostic spicules. Genus Strongylodesma Levi, 1969, is not represented here because they lack the diagnostic discorhabds. Species in subgenus Latrunculia (Latrunculia) have anisodiscorhabd microscleres with six visibly distinct substructures: (A) L. (L.) austini Samaai, Gibbons & Kelly, 2006, Gulf of Alaska (reproduced from reference [21], Figure 3F, with permission from copyright holder); (B) Typical anisodiscorhabd, undescribed species from the Chatham Islands, New Zealand. Species in subgenus Latrunculia (Biannulata) have anisodiscorhabd microscleres with two distinct substructures around the shaft, the median and subsidiary whorls, between an undifferentiated manubrium and basal whorl, and the undifferentiated apical whorl and apex: (C) L. (B.) kaakaariki Alvarez, Bergquist & Battershill, 2002, Three Kings Islands, New Zealand (reproduced with permission from Crispin Middleton); (D) Typical anisodiscorhabd from the same species. Species in subgenus Latrunculia (Uniannulata) have anisodiscorhabd microscleres with only a single substructure around the shaft, the median whorl, between the manubrium and basal whorl, and the apical whorl and apex: (E) L. (U.) oparinae Samaai & Krasokhin, 2002, Aleutian Islands, Alaska (reproduced with permission from Robert Stone; reproduced from reference [21], Figure 8A, with permission from copyright holder); (F) Typical anisodiscorhabd from the same species. Species in genus Cyclacanthia are Latrunculiidae with acanthose isospinodiscorhabd microscleres which have a shaft bearing identical apical and basal substructures: (G) Cyclacanthia bellae Samaai, Gibbons, Kelly & Davies-Coleman, 2003 (reproduced with permission from the Coral Reef Research Foundation, Palau, Micronesia; reproduced from reference [26], Figure 3A, with permission from copyright holder); (H) Typical isospinodiscorhabd (reproduced from reference [21], Figure 1D, with permission from copyright holder). Species in genus Tsitsikamma are Latrunculiidae with acanthose isospinodiscorhabd microscleres which have a shaft bearing identical apical and basal substructures: (I) Tsitsikamma favus Samaai & Kelly, 2002, Algoa Bay, South Africa (reproduced with permission from the Coral Reef Research Foundation, Palau, Micronesia; reproduced from reference [41], Figure 8E, with permission from copyright holder); (J) Typical isochiadiscorhabd from the same species (reproduced from reference [21], Figure 1E, with permission from copyright holder). Species in genus Bomba are Latrunculiidae with unusual anisodiscorhabds that have only three substructures: (K) Bomba endeavorensis Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016, Endeavour Ridge, British Columbia (reproduced from reference [21], Figure 11A, with permission from copyright holder); (L) Typical anisodiscorhabd from the same species. Species in genus Latrunclava are Latrunculiidae with two microsclere forms, an anisodiscorhabd and several longer anisoconicorhabds that have structurally different apical and basal whorls, unlike Sceptrella species which also have two microsclere forms, but the longer amphiclad sceptre has identical apical and basal whorls: (M) Latrunclava imago Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016, Aleutian Islands (reproduced from reference [21], Figure 13A, with permission from copyright holder); (N) Anisodiscorhabd and long anisoconicorhabd (reproduced from reference [21], Figure 1G, with permission from copyright holder); (O) Anisodiscorhabd and amphiclad sceptre from Sceptrella regalis Schmidt, 1870 (reproduced from reference [21], Figure 1F, with permission from copyright holder). All images are reproduced with permission from the original photographers or from Zootaxa.
The chemistry of latrunculid sponges is dominated by (bis)pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids (discorhabdins, tsitsikammamines) and structurally related derivatives (makaluvamines, batzellines, isobatzellines, etc.) that display various bioactivities; particularly anticancer, but also antimicrobial and antimalarial [27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. To date, almost 100 compounds belonging to this chemical family have been reported from latrunculid sponges, and their structure and activity relationships (SARs) and biosyntheses have been studied [30,34]. Taxonomic classification of this family has been complex. Chemical investigations on latrunculid sponges, especially the report of different (bis)pyrroloiminoquinone analogs, have provided significant chemotaxonomic evidence for phylogenetic revision of the family [21]. Pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids are responsible for the brownish or greenish coloration of latrunculid sponges and play an important role in the chemical defense of the sponge [28,35]. Pyrroloiminoquinones are not exclusive to latrunculid sponges and have been reported from other resources, such as ascidians, different sponge families (Acarnidae, Stelligeridae, and Halichondriidae) and terrestrial microbes (myxomycetes) [36,37,38,39]. Hence, a microbial origin is being hypothesized for pyrroloiminoquinone-related alkaloids and the debate on their biosynthetic origin is on-going [40].
Latrunculid sponges also produce cyclodepsipeptides, the so-called callipeltins, that are characterized by the presence of numerous unusual amino acids and promising in vitro bioactivities (cytotoxicity, antifungal and anti-HIV) [42,43,44]. Some norditerpene or norsesterterpene cyclic peroxides (trunculins) and prominent cytotoxic macrolides (latrunculin A and other latrunculins) were also reported from sponge specimens that were loosely grouped in the sponge family Latrunculiidae [45,46,47]. Subsequent phylogenetic revisions assisted by marine natural product chemistry studies have reidentified the source sponges as Dicarnus, Sigmaceptrella, or Negombata species belonging to the sponge family Podospongiidae Laubenfels, 1936 [21,48,49,50,51].
Numerous studies have shown the chemical uniqueness and bioactivity potential of the latrunculid sponges, hence, a systematic review on this family appeals to a broad scientific community working in the fields of, e.g., marine natural product chemistry, drug discovery, medicinal chemistry, pharmacology, oncology, and sponge taxonomy. This review covers all chemical and biological investigations performed on the members of the family Latrunculiidae from 1986 to August 2020, covering 110 natural metabolites reported from five latrunculid sponge genera (Latrunculia, Strongylodesma, Tsitsikamma, Sceptrella, Cyclacanthia). The review also encompasses highly relevant subjects, such as the biosynthetic (microbial) origin of the metabolites and the (chemo)taxonomy of the latrunculid sponges.
2. Systematics of Latrunculiidae Sponges
- Class Demospongiae Sollas, 1885 [52];
- Subclass Heteroscleromorpha Cárdenas, Perez and Boury-Esnault, 2012 [53];
- Order Poecilosclerida Topsent, 1928 [54];
- Family Latrunculiidae Topsent, 1922 [19].
The name of the subclass follows the classification proposal by Morrow and Cárdenas (2015) [55]. The systematics of Latrunculiidae follows Samaai and Kelly (2002) [25], Samaai et al. (2003, 2004, 2006, 2009, 2012) [26,50,56,57,58], and Kelly et al. (2016) [21]. Samaai et al. (2004) and Kelly et al. (2016) illustrate the diagnostic microscleres that define the Latrunculiidae genera [21,26]. The genus Strongylodesma lacks the diagnostic discorhabd microsclere; the first temperate Australian species described was from New South Wales [59]. The discovery of the pyrroloquinoline alkaloid damirone A in the holotype of S. australiense strongly supported the assignment of this new species to Strongylodesma, rather than to Batzella Topsent, 1893 [49,60].
3. Chemical Investigations of Marine Sponges from Family Latrunculiidae
3.1. Genus Latrunculia
Latrunculia du Bocage, 1869 represents the largest genus of the family Latrunculiidae. It comprises over 30 valid species that can be further divided into three subgenera; Biannulata, Latrunculia, and Uniannulata [21]. Latrunculia is the best studied subgenus in terms of chemical composition, and includes species of L. (L.) biformis Kirkpatrick, 1908 [61]; L. (L.) bocagei Ridley & Dendy, 1886 [62]; L. (L.) apicalis Ridley & Dendy, 1886 [62]; L. (L.) brevis Ridley & Dendy, 1886 [62]; L. (L.) triverticillata Alvarez, Bergquist & Battershill, 2002 [63]; L. (L.) fiordensis Alvarez, Bergquist & Battershill, 2002 [63]; L. (L.) austini Samaai, Gibbons & Kelly, 2006 [50]; L. (L.) hamanni Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016 [21]. Four species from the subgenus Biannulata, i.e., L. (B.) purpurea Carter, 1881 [64]; L. (B.) wellingtonensis Alvarez, Bergquist & Battershill, 2002 [63]; L. (B.) kaikoura Alvarez, Bergquist & Battershill, 2002 [63]; L. (B.) citharistae Vacelet, 1969 [65] (now accepted as Latrunculia incertae sedis and a possible species of Sceptrella by Kelly et al. 2016) [21] and only one species from the subgenus Uniannulata (L. (U.) oparinae Samaai & Krasokhin, 2002) [48] have reported chemistry.
Numerous studies on the chemical composition of Latrunculia spp. have yielded diverse pyrroloiminoquinone-type alkaloids with the trivial name of discorhabdin, which was originally named after the discorhabd spicules [27,30]. Bispyrroloiminoquinones (tsitsikammamines) and simple pyrroloquinoline-type alkaloids (e.g., makaluvamines and batzellines), which have been proved to be biosynthetic precursors of tsitsikammamines and discorhabdins, were also reported from this genus [30,66,67]. Apart from the aforementioned alkaloids, sponges of the genus Latrunculia were reported to produce cyclodepsipeptides, the so-called callipeltins. This section of the review will emphasize the origin, chemistry and bioactivity of different types of (bis)pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids and callipeltins deriving from the genus Latrunculia.
3.1.1. Discorhabdin Alkaloids Obtained from the Genus Latrunculia
Discorhabdins are pyrroloiminoquinone-type alkaloids possessing the characteristic tetracyclic pyrido[2,3-h]-pyrrolo-[4,3,2-de]quinoline core structure attached to an extra cyclohexanone ring via a carbocyclic spiro center C-6 (Figure 2), hence, forming a pentacyclic backbone [49,68]. Discorhabdins are reported from nature as monomers, dimers, and trimers, and mostly as trifluoroacetate (TFA) or formic acid (FA) salts with high or moderate polarity. Since the first report of discorhabdin C from an unidentified specimen of New Zealand Latrunculia [27], 35 monomeric and 11 dimeric/trimeric discorhabdins have been reported from the genus Latrunculia.
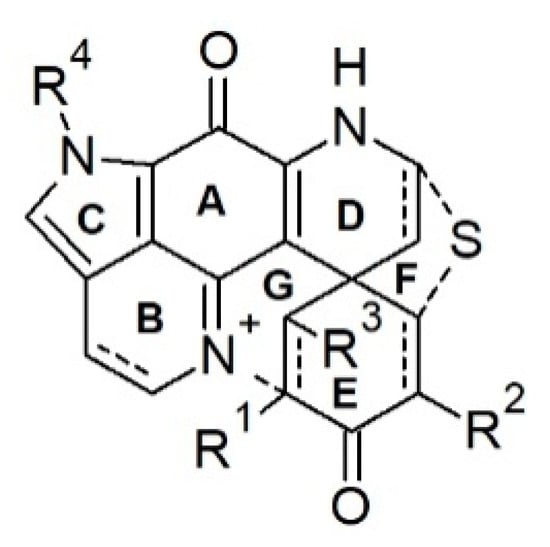
Figure 2.
Skeleton of monomeric discorhabdin-type alkaloids.
Chemical diversity of the monomeric discorhabdin alkaloids stems from various substitutions on their pentacyclic backbone, the stereochemistry of C-1, and their enantiomeric properties. A sulfide linkage between C-5 and C-8 (e.g., in discorhabdins B and Q) [69,70] is common, allowing the formation of hexacyclic discorhabdins. Some discorhabdins bear a heptacyclic backbone (as found in discorhabdins L and D) via a further intramolecular ring closure formed by a direct bond between the N-18 imino function and C-2 (Figure 2) [71,72]. With the formation of the sulfide bridge between C-5 and C-8, the relative geometry between rings D and E is locked, hence, the configurational relativity between C-6 and C-8 is fixed, i.e., bonds C6/C5 and C-8/S are always syn (Figure 2) [73]. In the case of heptacyclic discorhabdins, an extra direct bond between C-2 and N-18 further locks rings B and E, allowing only one relative configuration at C-2 (Figure 2) [73]. Halogenation (mainly bromine and chlorine) is a common substitution in discorhabdins, mostly at positions C-2/C-4/C-14 (e.g., discorhabdins A and C, 1-hydroxy-14-bromodiscorhabdin V) [27,30,69,71]. Several enantiomers of known discorhabdins were also reported from nature (e.g., (+)/(−)-discorhabdin B, L, and I), further increasing the chemical diversity of discorhabdins [74,75]. According to the ring number of the discorhabdin backbone, monomeric discorhabdins can be classified into three categories, namely, the pentacyclic discorhabdin C series (e.g., discorhabdins E and G), hexacyclic discorhabdin B series (e.g., discorhabdins Q, R, and I) and heptacyclic discorhabdin D series (e.g., discorhabdins L, N, and H) [68].
Dimeric discorhabdins linked by a disulfide or sulfide bridge between two discorhabdin units (e.g., discorhabdin W, discorhabdin B dimer) have also been reported from sponges of the genus Latrunculia [76,77]. Several discorhabdin dimers bearing a novel C1-N13 direct bond between two discorhabdin units have been newly reported [78,79]. The Antarctic Latrunculia biformis Kirkpatrick, 1908 is the source of the very first trimeric discorhabdin containing the same C1-N13 bond [79]. Different configurations of C-1 in discorhabdin oligomers were observed [78,79].
Structure elucidation of discorhabdins has been hampered by the presence of heteroatoms (N, O, S, Br, and Cl) and high degree of unsaturation in such highly fused ring systems. Structures of some discorhabdins (e.g., (+)-discorhabdin A and discorhabdin C) have been secured by X-ray analysis. Hence, interpretations of NMR spectroscopic data with analogy to discorhabdins A and C have assisted the structure elucidation of discorhabdins [27]. NOE data analysis has been used to assign the relative configurations. Biogenetic considerations and [α]D values have been used to propose the absolute configurations of discorhabdins, leading to inaccuracies. Since 2008, electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectroscopy in conjunction with the computationally assisted density-functional theory (DFT)-based calculations have become a more efficient and reliable method to confirm the absolute configurations of discorhabdins [74,75].
Discorhabdin Monomers
The story of pyrroloiminoquinone-type alkaloids began in 1986 with the discovery of discorhabdin C (1) from an unidentified specimen of a New Zealand Latrunculia sp. [27]. Bioactivity-guided fractionation of this cytotoxic Latrunculia sp. extract led to the purification of a toxic pigment named discorhabdin C (1) (Figure 3) [27]. The structure of 1 was secured by X-ray diffraction analysis, but its NMR spectrum was left unassigned because of the highly fused ring systems [27]. Discorhabdin C (1) showed significant activity against mouse lymphocytic leukemia cell line L1210 with an ED50 value below 100 ng/mL. Since then, a series of chemically related analogs have been reported from different Latrunculia species collected from diverse sites around the world. Continuous chemical investigations on three sponges of the genus Latrunculia collected from several locations in New Zealand [69,71] led to the isolation of (+)-discorhabdin A (2) and (−)546-discorhabdin D (4) from a specimen identified as L. (L.) brevis Ridley & Dendy, 1886, while (+)-discorhabdin B (3) and discorhabdin C (1) were reported from an undescribed Latrunculia specimen (Figure 3) [69,71,80]. Compounds 2 and 3 bear a hexacyclic backbone including a sulfide bridge between C-5 and C-8, while 4 is a heptacyclic compound with an extra ring closure through the formation of a direct bond bound between C-2 and N-18 imino function. This is very rare for a small molecule with only 18 carbons [71]. Although (−)546-discorhabdin D (4) possesses three stereogenic centers, it lacked optical activity under the common sodium D light (589 nm), while negative optical rotation values were observed under 578 and 546 nm [71]. This study assigned the 1H and 13C-NMR data of discorhabdin C for the first time, and the chemical structures of 2 and 3 were established by the comparison of the spectral data with those of discorhabdin C (1) [69]. The structure elucidation of (−)546-discorhabdin D (4) (Figure 3) was also based on a comparison of its NMR data with compounds 1–3 [71]. Unlike discorhabdin C (1), discorhabdins A, B, and D (2–4) are chiral molecules, and the relative configurations of their stereocenters were assigned by means of a 1D NOE difference experiment. The absolute configurations of (+)-discorhabdin B (3) and (−)546-discorhabdin D (4) were confirmed in 2008 and 2010, respectively, via direct comparison of their experimental and DFT-calculated ECD spectra [74,75].
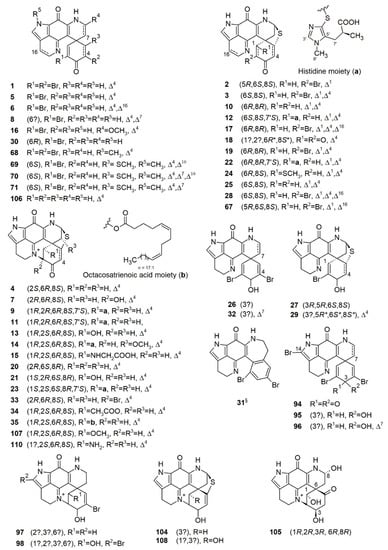
Figure 3.
Discorhabdin monomers reported from latrunculid sponges. ?: Unassigned stereochemistry; *: Relative configuration; §: Artifact.
Discorhabdin C (1), A (2), and B (3) exhibited in vitro cytotoxicity against P388 leukemia cells with ED50 values of 0.03, 0.05, and 0.1 μg/mL, respectively [69,71], but none of them had any significant in vivo activity in the P388 leukemia system in mice [69]. Notably, discorhabdin D (4) that was less active against P388 leukemia cells (ED50 value 6 μg/mL) showed in vivo activity at a dose of 20 mg/kg with a treatment-to-control ratio (T/C) of 132% in the P388 leukemia system in mice [71]. Discorhabdins A (2) and C (1) exerted significant antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and Candida albicans, while discorhabdin B (3) was active against E. coli and B. subtilis [69]. However, the MIC/IC50 values of the compounds were not presented.
In 1994, Copp et al. reported the isolation of a new 4-debromo derivative of discorhabdin C, named discorhabdin E (5), from a specimen identified as L. (L.) bocagei Ridley & Dendy, 1886 collected in the Auckland Islands, New Zealand (Figure 3) [80]. The elimination of the bromine atom generated a stereogenic center in 5, which was purified as a racemic mixture of its TFA salt. Compound 5 showed significant in vitro cytotoxicity against P388 murine leukemia cell lines (IC50 value 206 ng/mL) and antimicrobial activity against B. subtilis and E. coli (IC50 values not reported) [80]. Notably, the structures of discorhabdins E (5), F (6), and 2-hydroxydiscorhabdin D (7) were first presented by Blunt et al. in a review article [81], where the authors reported these three compounds from an unidentified New Zealand Latrunculia. However, the NMR data of compounds 5–7 were not reported therein.
Discovery of discorhabdin alkaloids from Latrunculia sp. continued with the report of (+)-discorhabdin G (8, Figure 3) together with discorhabdin C (1) from an Antarctic sponge identified as L. (L.) apicalis Ridley & Dendy, 1886 that showed significant antifeedant activity against the sea star Perknaster fuscus, the major predator of marine sponges in Antarctica [28]. This was also the first investigation of a Latrunculia specimen from a region other than New Zealand. (+)-Discorhabdin G (8) lacks the bromine atom at C-4 but bears the same pentacyclic core structure as discorhabdin C (1) with an additional double bond at C-7 [28]. (+)-Discorhabdin G (8) has a single stereogenic center (C-6) and exhibits a slightly positive [α]D value. However, its absolute configuration remained undetermined [28]. (+)-Discorhabdin G (8) demonstrated significant antifeedant activity against P. fuscus and antimicrobial activity against two common water column microorganisms (the IDs of microorganisms not mentioned) isolated from seawater surrounding the sponge. Hence, compound 8 was hypothesized to be involved in the chemical defense of the sponge [28]. The following study by Furrow et al. (2003) revealed that compound 8 was mainly distributed in the outermost layer of the sponge (2 mm) that has the highest chance of encountering predators, which further emphasized the ecological significance of (+)-discorhabdin G [29].
Discorhabdins H–O (9–16) were isolated from another Latrunculia sp. from New Zealand and their structures were presented by Munro et al. at the 37th Annual ASP Meeting in 1996, then listed in a review paper in 2000 [49,82]. In the review paper, the structure of discorhabdin H was omitted. The structures of some compounds published in this review contain some errors, i.e., the inadvertent omission of the ∆4 olefin in discorhabdins L and N; and the omission of the sulfide bridge between C-5 and C-8 in discorhabdins I and K [30,49,75,82]. The 1D NMR, [α]D, and CD data of all eight discorhabdins were inaccessible in the review, leading to some ambiguities in the nomenclature of newly discovered discorhabdins in the following studies.
In 1999, an orange solid was detected as the major component of cytotoxic extracts of three Australian sponges (Zyzzya massalis Dendy, 1922 [83] (accepted as Zyzzya fuliginosa Carter, 1879) [84], Zyzzya. sp., and L. (B.) purpurea Carter, 1881) and a Fijian sponge Z. fuliginosa Carter, 1879 [70,84]. The orange pigment was identified as 16,17-dehydrodiscorhabdin B with the trivial name (−)-discorhabdin Q (17) (Figure 3) because discorhabdin P has been reported from a Caribbean sponge of the genus Batzella (revised as Strongylodesma) [70,85]. (−)-Discorhabdin Q (17) bears the same core structure as discorhabdin B (3) and due to the olefinic bond at C-16, the tetracyclic pyrido[2,3-h]-pyrrolo-[4,3,2-de]quinoline portion of compound 17 is fully aromatic. (−)-Discorhabdin Q (17) exhibited a negative [α]D value (−452.4). Based on biogenetic considerations, the absolute configuration of 17 was originally proposed to be 6S,8S [70], however, it was revised into 6R,8R in 2010, based on the assignment of a 6S,8S configuration to (+)-discorhabdin Q (28) obtained from a New Zealand-sourced Latrunculia sp. [75]. Compound 17 exhibited moderate cytotoxicity in the NCI 60 cell line antitumor screen (mean panel GI50 = 0.5 μg/mL) [70].
Ford and Capon (2000) reported another sulfur-containing compound (+)-discorhabdin R (18) from an Antarctic Latrunculia sp. (Figure 3) [86]. The gross structure of (+)-discorhabdin R (18) was elucidated as a debromo epoxy analog of the co-occurring discorhabdin B (3). The stereochemistry of all the other chiral centers except C-1 and C-2 were established via biosynthetic considerations and further confirmed by comparison of its NMR data with those of (+)-discorhabdin B (3). The orientation of the epoxy function to the rest of the molecule could not be confirmed due to the lack of decisive NOE correlations [86]. The bioactivity of the pure compounds was not tested in this study, but the EtOH extract of the source sponge exhibited antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (the IC50 or MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) values were not mentioned in the publication).
Two new members of the discorhabdin family, namely (−)-discorhabdin I (10) and (−)546-discorhabdin L (13) were reported by Reyes et al. (2004) from the deep-sea Argentinian sponge L. (L.) brevis Ridley & Dendy, 1886 (Figure 3) [72]. At almost the same time, (−)-discorhabdin I (10) was also obtained from another South African latrunculid sponge (Latrunculia bellae Samaai & Kelly, 2003 (accepted as Cyclacanthia bellae Samaai & Kelly, 2003 [56])) and referred to as discorhabdin G* [30]. Discorhabdin G*/I (10) is a debromo analogue of discorhabdin B (3) and exhibited a negative [α]D value. Discorhabdin L (13) is a heptacyclic compound bearing the same skeleton as discorhabdin D (4) with the only difference being the presence of a hydroxy group at C-1 in 13. Although discorhabdin L (13) possesses four stereogenic centers, it was optically inactive at sodium D light (589 nm) but showed negative [α]D values under 578 and 546 nm, a phenomenon previously observed with discorhabdin D (4) [72,74]. The absolute configurations of 10 and 13 were confirmed only in 2008 by ECD spectroscopy [74]. Compounds 10 and 13 were tested against 14 different cancer cell lines, where they showed the best potency against the colon cancer cell line HT-29 with GI50 values of 0.35 and 0.12 μM, respectively [72].
Discorhabdins I (10), B (19), D (20), and L (21) were reisolated from a Latrunculia sp. collected from Milford Sound, New Zealand [76]. In a subsequent study, Grkovic et al. (2008) assigned the optical rotation and absolute configurations of these compounds as (−)-discorhabdin G*/I (10), (−)-discorhabdin B (19), (+)546-discorhabdin D (20) and (+)546-discorhabdin L (21) [74]. All four compounds exhibited promising in vitro cytotoxicity against P388 lymphocytic leukemia cells, with 19 being the most potent (GI50 value 0.087 μM). Compounds 10, 20, and 21 showed relatively weak activity, with IC50 values ranging from 0.51 to 1.6 μM [76].
Between 2008 and 2010, the Copp research group explored the chemical composition of Latrunculia sponges collected from different locations in New Zealand [74,75,87]. They reported three new monomeric discorhabdin analogs, i.e., (−)-discorhabdin K2 (22), (+)-discorhabdin H2 (23), and (+)-1-thiomethyldiscorhabdin G*/I (24); three new enantiomers of known discorhabdins, i.e., (−)-discorhabdins B (19), (+)546-discorhabdin L (21), and (+)-discorhabdin-G*/I (25); and numerous known discorhabdins, some of which have never been reported, from the genus Latrunculia, e.g., (−)-3-dihydrodiscorhabdin C (26, originated from Tsitsikamma pedunculata Samaai & Kelly, 2003 [56]) and (+)-3-dihydrodiscorhabdin A (27, originated from Higginsia sp.) (Table 1; Figure 3) [30,74,75,87]. The absolute configurations of several known discorhabdins, e.g., (−)-discorhabdin H (9), (+)-discorhabdin K (12), (−)546-discorhabdin L (13) were also confirmed in this series of studies [74,75,87]. Both discorhabdins H (9), H2 (23) bear a thiomethylhistidine fragment connected to a discorhabdin l-type core structure at C-1 via a sulfide bridge (Figure 3). The absolute configuration of the thiomethylhistidine substituent in (−)-discorhabdin H (9) has been established as 7’S by Antunes et al. (2004) through degradative techniques where compound 9 was purified from a South African sponge Strongylodesma algoaensis Samaai & Kelly, 2003 [30,56], but the absolute configuration of the stereocenters in the core discorhabdin structure was not assigned [30]. Grkovic et al. (2010) confirmed the absolute configuration of (−)-discorhabdin H (9) as 1R,2R,6R,8S,7′S by comparing its experimental ECD spectrum with the model compound (−)546-(1R,2R,6R,8S)-discorhabdin L (13) [75]. Compared to (−)-discorhabdin H (9), (+)-discorhabdin H2 (23) exhibited essentially equal and opposite experimental ECD spectra, and hence established the absolute configuration of (+)-discorhabdin H2 (23) as 1S,2S,6S,8R,7′S. The authors concluded that the induced circular dichroism properties of (−)-discorhabdin H (9) and (+)-discorhabdin H2 (23) were due to the core discorhabdin structure only [75]. The absolute configurations of (+)-discorhabdin K (12) and (−)-discorhabdin K2 (22) were established by the strategy used for discorhabdins H (9) and H2 (23) [75].

Table 1.
Discorhabdin enantiomers obtained from geographically distinct Latrunculia sponges collected from New Zealand (summarized from references [74,75,87]).
DFT calculations of ECD spectra were used, for the first time, in stereochemical assignments of discorhabdin analogs allowing the stereochemical revision of (+)-3-dihydrodiscorhabdin A (27) (from 3S,5R,6S,8S to 3R,5R,6S,8S), the establishment of absolute configurations for (−)546-discorhabdin D (4), (+)-2-hydroxydiscorhabdin D (7), (−)-discorhabdin H (9), (+)-discorhabdin K (12), (−)-discorhabdin N (15), (−)-discorhabdin K2 (22), (+)-discorhabdin H2 (23), and (+)-discorhabdin Q (28) [74,75,87]. Since then, DFT-based ECD calculations have become one of the most reliable and effective strategies to confirm the absolute configuration of discorhabdin-type alkaloids. Six sponges of the genus Latrunculia collected from four different sites of New Zealand (Table 1) were studied to investigate the relationships between sponge phenotypes and their production of discorhabdin enantiomers [74,75,87]. The results revealed that Milford/Doubtful Sound-sourced sponges of the genus Latrunculia produced discorhabdins with an α-orientated C-6/C-5 bond when their skeleton was drawn as Figure 3, e.g., (−)-discorhabdin B (19), (−)-discorhabdin-G*/I (10), and (+)546-discorhabdin L (21) (Table 1), while Wellington Harbor/Kaikoura Coast-sourced sponges of the genus Latrunculia yielded the corresponding enantiomeric discorhabdins, i.e., (+)-discorhabdin B (3), (+)-discorhabdin G/I (25), and (−)546-discorhabdin L (13) (Table 1) [74,75,87]. This series of studies highlight the enantiomeric specificity in the biosynthesis of thioether-containing discorhabdins, but the relationship with the collection sites is still not clear due to the limited dataset [74,75,87].
The new compounds (−)-discorhabdin K2 (22), (+)-discorhabdin H2 (23), and (+)-1-thiomethyldiscorhabdin G*/I (24); enantiomeric pairs of known discorhabdins, i.e., (−)-discorhabdin B (19), (+)546-discorhabdin L (21), and (+)-discorhabdin-G*/I (25) together with compounds (−)-discorhabdin-H (9), (+)-discorhabdin-K (12), (+)-3-dihydrodiscorhabdin A (27) and its semi-synthetic 3-epimer (+)-(3S)-3-dihydrodiscorhabdin A were tested on P388 murine leukemia cell lines to investigate their cytotoxicity and structure–activity relationships (SARs). The enantiomeric pairs of discorhabdins B ((+)/(−)-B, 3/19), I ((+)/(−)-I, 25/10), and L ((+)/(−)-L, 21/13)) displayed similar cytotoxicity, with IC50 values ranging from 0.17 to 1.08 μM, while (−)-discorhabdin-H (9), (+)-discorhabdin-K (12), (−)-discorhabdin K2 (22) and (+)-discorhabdin H2 (23) were weaker with IC50 values higher than 8.2 μM [74,75,87], suggesting that the C-1 substituation is detrimental to the anticancer activity of discorhabdins.
Since 2010, several Latrunculia sponges from the North Pacific Ocean have been studied for their chemical composition, yielding many new discorhabdin alkaloids [32,66,88,89,90]. An unidentified specimen of Latrunculia from the Aleutian Islands (Bering Sea, −230 m depth), now known as L. (L.) hamanni Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016, afforded the new alkaloids, 3-dihydrodiscorhabdin B (29) and (+)-discorhabdin Y (30), which is the 4-debromo derivative of discorhabdin C, and six known metabolites (+)-discorhabdin A (2), discorhabdin C (1), E (5), and L (13), 3-dihydrodiscorhabdin C (26), and the benzene derivative of discorhabdin C (31) (Figure 3) [32]. The latter compound (31), which was synthesized by Copp et al. (1994) via chemical modification of discorhabdin C was deemed to be an artifact of the isolation process [32,80]. Compound 29, 3-dihydrodiscorhabdin B, was unstable and decomposed rapidly before [α]D measurements. Discorhabdin Y (30) showed good stability and its absolute configuration was confirmed as (+)-(6R)-discorhabdin Y (30) based on its [α]D data and computationally-assisted ECD calculations [32]. This study investigated, for the first time, the in vitro antiviral and antimalarial activity of discorhabdin C (1), (+)-discorhabdin A (2), and 3-dihydrodiscorhabdin C (26). All compounds were active in the HCV (hepatitis C virus) Huh-7 replicon assay with EC90 values below 10 μM [32]. Compounds 1, 2, and 26 displayed antiplasmodial activity against both the chloroquine-susceptible P. falciparum D6 clone (IC50s 2.8, 0.053 and 0.17 μM, respectively), and the chloroquine-resistant W2 clone (IC50s 2.0, 0.053, and 0.13 μM, respectively) [32]. When evaluated for general toxicity toward the monkey kidney fibroblasts (Vero) cells, (+)-discorhabdin A (2), showed the highest selectivity index (SI = 130) followed by 3-dihydrodiscorhabdin C (26) (SI = 58) and discorhabdin C (1) (SI = 1). During in vivo studies of compounds 2 and 26 in a P. berghei mouse malaria model at a dose of 10 mg/kg, animals treated with 3-dihydrodiscorhabdin C (26) died due to toxicity on day 4 before the examination for parasitemia, whereas the animals treated with (+)-discorhabdin A (2) had to be euthanized because of significant weight loss (>25%) and severe signs of toxicosis despite the significant (approx. 50%) suppression of parasitemia [32]. In addition, discorhabdin C (1), (+)-discorhabdin A (2), and 3-dihydrodiscorhabdin C (26) also showed significant antimicrobial activity against MRSA, Mycobacterium intracellulare and M. tuberculosis with IC50 values ranging from 0.13 to 13 μM [32].
Latrunculia (U.) oparinae Samaai & Krasokhin, 2002, collected near the shores of Kuril Islands, Sea of Okhotsk (Russia), afforded the ethanol solvate of discorhabdin A (2) [88] with an opposite [α]D value (−449) to the Okinawan Strongylodesma sp. sourced discorhabdin A ([α]D +400) [69,91], although they have the same absolute configuration. This was due to the unique crystal structure of EtOH solvated discorhabdin A, whose [α]D value turned positive after three days of storage in MeOH [88]. This compound showed potent cytotoxicity against murine Ehrlich carcinoma cells (ED50 = 0.055 μg/mL).
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) is a subunit of hypoxia-inducible factors that is overexpressed in many human tumors [92]. Inhibition of HIF-1α by disrupting its binding to the transcriptional coactivator protein p300 is a validated target in cancer drug discovery [93,94,95]. (+)-Discorhabdin B (3), 3-dihydrodiscorhabdin C (26), and (+)-discorhabdin G*/I (25) (Figure 3) [77] isolated from an Australian Latrunculia sp. as well as five previously isolated discorhabdins namely, (+)-discorhabdin A (2), (−)546-discorhabdin D (4), (−)-discorhabdin-H (9), (−)546-discorhabdin L (13), and (−)-discorhabdin N (15) from a New Zealand-sourced Latrunculia sp. were tested for their inhibitory potential for HIF-1α/p300 interaction [77]. Compounds 3, 13, 9, and 26 were the most potent HIF-1α/p300 inhibitors, with IC50 values ranging from 0.73 to 35.2 μM. All four compounds demonstrated in vitro cytotoxicity under normoxic conditions [30], therefore the authors concluded that oxygen could mediate the cytotoxicity of pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids [77]. In the following in vivo anticancer activity study on (−)-discorhabdin-H (9) and (−)546-discorhabdin L (13) in a prostate cancer (LNCaP) xenograft model, only compound 13 showed significant inhibition of LNCaP tumor growth and no reduction in body weight of LNCaP-bearing mice after four weeks of treatment at a dose of 5 mg/kg [96]. This study shed some light on the anticancer mechanism of discorhabdins.
Botic et al. [33] studied the methanolic extracts of two Antarctic deep-water specimens, identified as L. (L.) biformis Kirkpatrick, 1908 and L. (L.) bocagei Ridley & Dendy, 1886, to obtain (+)-discorhabdin G (8) and (−)-3-dihydro-7,8-dehydrodiscorhabdin C (32) (from L. (L.) biformis Kirkpatrick, 1908) and (+)-discorhabdin B (3) and (−)546-discorhabdin L (13) (from L. (L.) bocagei Ridley & Dendy, 1886) (Figure 3) [33]. (+)-Discorhabdin G (8) appeared as the most potent competitive reversible inhibitor of electric eel acetylcholinesterase (EeAChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) enzymes, whereas compound 3 was the most potent competitive reversible inhibitor of human acetylcholinesterase (hAChE). In docking studies, (+)-discorhabdin G (8) showed the lowest value of binding energy and the highest number of hydrophobic interactions with EeAChE. Similarly, the observed activity of (+)-discorhabdin B (3) against hAChE was supported by a series of hydrophobic interactions and three relevant H-bonds in the complex formed with the enzyme. Furthermore, (+)-discorhabdin G (8) did not show undesirable side effects as EeAChE and BChE inhibitors, pointing out the potential of the discorhabdin scaffold as a new class of potent cholinesterase inhibitors with minimal side effects [33].
Our research group investigated the Antarctic deep-sea sponge L. (L.) biformis Kirkpatrick, 1908 that exhibited activity against multiple cancer cell lines. Molecular networking (MN)-based untargeted metabolomics analyses of the methanol soluble portion of the crude extract was found to be dominated by polar, monomeric discorhabdins (e.g., known discorhabdins A, D, G, and L) and some putatively new derivatives. Targeted isolation studies furnished three new compounds, (−)-2-bromodiscorhabdin D (33), (−)-1-acetyldiscorhabdin L (34), and (+)-1-octacosatrienoyldiscorhabdin L (35) along with the known discorhabdins, namely, (−)-discorhabdins L (13), (+)-discorhabdin Q (28) and (+)-discorhabdin A (2) (Figure 3) [73]. Their absolute configurations were assigned by comparison of the experimental CD spectra with that of the standard compound (−)546-discorhabdin L (13). This study reported the first discorhabdin alkyl esters (34 and 35) from nature. Compound 35 is an ester of (−)546-discorhabdin L (13) with an unbranched octacosatrienoic acid (C28:3) that has never been reported from any Latrunculia species before [73]. Upon testing against HCT-116 colon cancer cells in vitro, (−)546-discorhabdins L (13), (−)-1-acetyldiscorhabdin L (34), and (+)-1-octacosatrienoyldiscorhabdin L (35) demonstrated activities with IC50 values of 0.94 μM (13), 2.71 μM (34), and 34.0 μM (35), respectively, suggesting that a substitution at C-1, especially the presence of a long chain fatty acid, was detrimental to the anticancer activity of discorhabdins [73]. A molecular modeling study using two known anticancer targets (topoisomerase I/II, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1)) suggested these proteins as potential anticancer targets of discorhabdins. The partly aromatic pyrroloiminoquinone core was proven to be necessary for the cytotoxicity of discorhabdins, which formed an aromatic π-π stacking interaction with the targets [73]. Compound 35 did not show plausible binding modes against any of these target proteins, owing to the large side chain at C-1 [73]. Both (−)546-discorhabdins L (13) and its enantiomer (21) yielded plausible binding affinity instead against all the targeted proteins, indicating that discorhabdins are non-specific ligands and that the stereochemistry is not crucial for their anticancer action [73].
Discorhabdin C (1) has been reisolated from the purple-colored fractions of the New Zealand sponge L. (L.) triverticillata Alvarez, Bergquist & Battershill, 2002 [78]. Discorhabdin C (1) and eight known monomeric discorhabdins, (+)-discorhabdin B (3), 3-dihydrodiscorhabdin C (26), (−)546-discorhabdin D (4), (−)-discorhabdin H (9), (+)-discorhabdin H2 (23), (−)546-discorhabdin L (13), (−)-discorhabdin Q (17), and discorhabdin U (71, originating from Strongylodesma purpurea Samaai & Kelly, 2009 [57]) were evaluated for their antiparasitic activities and general toxicity on L6 rat myoblast cell line [78]. All tested compounds showed some degree of antimalarial activity towards Plasmodium falciparum K1 dual drug-resistant strain (Pf K1), with (−)546-discorhabdin L (13) being the most potent with an IC50 value of 30 nM and a SI of 19. (−)546-Discorhabdin L (13) inhibited the growth of the African trypanosome Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense with an IC50 value of 0.4 μM [78].
Discorhabdin Oligomers
Compared to monomeric discorhabdins, dimeric and trimeric discorhabdins are relatively rare in nature. Ten dimeric discorhabdins and only one trimeric discorhabdin have so far been reported. Depending on the atom(s) linking the monomeric units, discorhabdin oligomers can be divided into three categories: (a) those with a disulfide bridge as observed in (+)/(−)-discorhabdins W (36/37) and (+)/(−)-16a,17a-dehydrodiscorhabdins W (38/39); (b) those with a sulfide bridge as observed in discorhabdin B dimers (40–43); and (c) those with a direct C-1/N-13 bond as observed in didiscorhabdin, tridiscorhabdin, and discorhabdin C dimer (44–46) (Figure 4).
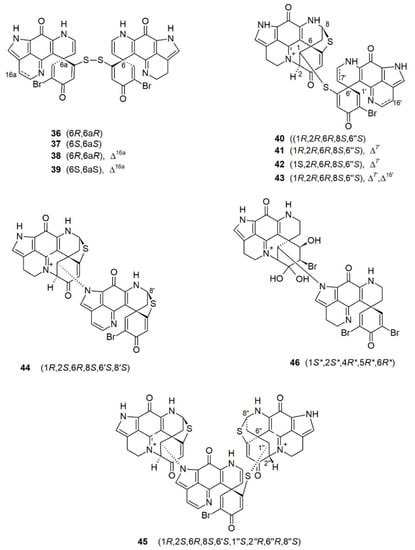
Figure 4.
Discorhabdin oligomers reported from latrunculid sponges. *: Relative configuration.
(+)-Discorhabdin W (36) is the very first dimeric discorhabdin sourced from a New Zealand Latrunculia sp. collected from Milford Sound (Figure 4) [76]. It is a symmetrical compound with two identical discorhabdin B-type units connected through a disulfide bridge as established by NMR spectroscopy and chemical means [76]. Chemical reduction of 36 with dithiothreitol (DTT) yielded the co-occurring metabolite discorhabdin B, while irradiation of discorhabdin B under sunlight further promoted its dimerization into (+)-discorhabdin W (36) [76]. Hence, the absolute configuration of (+)-discorhabdin W (36) was considered to be the same as the co-occurring metabolites, e.g., (−)-discorhabdin G*/I (10), (−)-discorhabdin B (19), (+)546-discorhabdin D (20), and (+)546-discorhabdin L (21) (Figure 4). Both (+)-discorhabdin W (36) and (−)-discorhabdin B (19) exert equal anticancer potency against P388 lymphocytic leukemia cells (IC50 values 0.084 and 0.087 μM, respectively) [76], while compounds 10, 20, and 21 had lower activity with IC50 values of 1.6, 0.51 and 1.1 μM, respectively [76].
Grkovic et al. reported two pairs of enantiomeric discorhabdin dimers, (+)/(−)-discorhabdin W (36 and 37) and (+)/(−)-16a,17a-dehydrodiscorhabdin W (38 and 39) (Figure 4) from sponges of the genus Latrunculia collected from different sites in New Zealand [74,75,87]. The dimers displayed potent cytotoxicity against P388 murine leukemia cell lines in a similar magnitude to the “parent” monomeric discorhabdins with IC50 values of 0.10 and 0.13 μM for (+) and (−)-discorhabdin W (36 and 37), respectively, and 0.45 μM for both enantiomeric pairs of 16a,17a-dehydrodiscorhabdin W (38 and 39) [74,87].
Dimeric discorhabdin B (40) and (−)-discorhabdin W (37) were isolated from an Australian Latrunculia sp. that showed activity in the HIF-1α/p300 interaction in a cell-free protein−protein assay (Figure 4) [77]. Compound 40 was deemed to have the same structure as the previously reported artifact (−)-discorhabdin B dimer (41), which formed after long-term storage of discorhabdin B [97]. However, from the observed NMR data and the structure shown in the article, compound 40 should be a new 7’,8’-dihydro derivative of compound 41 [77,97]. Compound 40 inhibited the HIF-1α/p300 interaction with an IC50 value of 2.4 μM, and compound 37 was inactive (IC50 value > 100 μM) [77]. However, 40 demonstrated no cytotoxicity against HCT-116 and LNCaP cell lines under hypoxic conditions [77].
Molecular networking-based metabolomics strategy revealed the presence of several putatively new dimeric and trimeric discorhabdins in the n-hexane subextract of the Antarctic deep-sea sponge L. (L.) biformis Kirkpatrick, 1908 [79,98]. Targeted isolation efforts yielded three new dimeric discorhabdins, namely, (−)-1-epi-discorhabdin B dimer (42), (−)-16′,17′-dehydrodiscorhabdin B dimer (43), and didiscorhabdin (44), the known (−)-discorhabdin B dimer (41) and a trimeric molecule tridiscorhabdin (45) (Figure 4) [79,98]. Their absolute configurations were assigned by comparison of the experimental and the DFT-calculated ECD spectra. The dimeric discorhabdins comprised a discorhabdin L- and a discorhabdin Q-type unit, while tridiscorhabdin (45) contained two discorhabdin L- and a discorhabdin Q-type units. Compounds 41–43 bear a sulfide linkage between two discorhabdin monomers, whereas didiscorhabdin (44) and tridiscorhabdin (45) represent the first examples of discorhabdin oligomers linked with a direct C1–N13 bond [79,98]. Furthermore, tridiscorhabdin (45) is the first trimeric discorhabdin oligomer ever reported from nature. Compounds 41, 42, and 45 all exhibited strong in vitro cytotoxicity against human colon cancer cell line HCT-116, but were also toxic to the noncancerous human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT with IC50 values of 0.16 and 0.56 μM (41), 2.01 and 4.69 μM (42) and 0.31 and 0.94 μM (45), respectively, indicating their low selectivity.
Shortly after the report of didiscorhabdin (44) and tridiscorhabdin (45) in 2020, the Copp group have published another C1-N13-linked discorhabdin C dimer (46) from the New Zealand sponge L. (L.) trivetricillata Alvarez, Bergquist & Battershill, 2002 (Figure 4) [78]. Discorhabdin C dimer (46) is the first tribrominated discorhabdin which is composed of two discorhabdin C-type units. Compound 46 was isolated as a racemate, because no specific rotation nor circular dichroism Cotton effects were observed at any wavelengths. Compounds 46 and 41 showed antimalarial (Pf K1 clone, IC50 values 6.4 and 0.08 μM, respectively) and antitrypanosomal activity against T. brucei rhodesiense (IC50 values 0.71 and 0.33 μM, respectively) [78]. Discorhabdin B dimer (41) was the least toxic against non-cancerous L6 rat skeletal myoblast cell lines (IC50 = 41 μM) with a very high selectivity (SI = 510), while compound 46 showed no selectivity (IC50 = 2.1 μM against L6 cells, SI = 0.3) [78].
3.1.2. Tsitsikammamines
Tsitsikammamines are a small bispyrroloiminoquinone subclass that bear a very similar backbone and close biosynthetic relationships with discorhabdins [82]. Tsitsikammamines possess the same pyrrolo[4,3,2-de]quinoline ring system as discorhabdins and a characteristic C-6 p-oxybenzyl group that differs from discorhabdins (Figure 5). This chemical subfamily (Figure 5) is represented by only six compounds, i.e., tsitsikammamines A, B, and C, 16,17-dehydrotsitsikammamine A, and the N-oxime analogs of tsitsikammamines A and B [30,67,99,100].
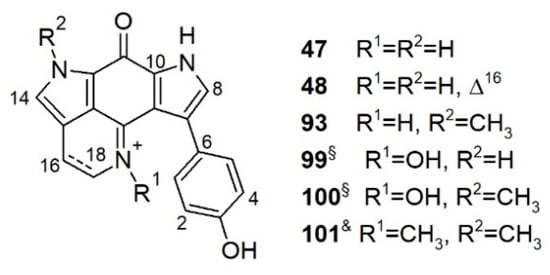
Figure 5.
Tsitsikammamines reported from latrunculid sponges. §: Artifact; &: Reported from Zyzzya sp.
Tsitsikammamines are rare alkaloids, and so far, have only been reported from another latrunculid, genus Tsitsikamma, and genus Zyzzya de Laubenfels, 1936 (order Poecilosclerida, family Acarnidae Dendy, 1922) [67]. However, a comprehensive MN-based untargeted metabolome study carried out by our research group on Antarctic L. (L.) biformis Kirkpatrick, 1908 indicated the presence of a small tsitsikammamine cluster (together with many discorhabdin analogs) in this sponge extract. Mass spectrometry-based targeted isolation of this cluster afforded tsitsikammamine A (47), and its new derivative 16,17-dehydrotsitsikammamine A (48) (Figure 5) [67]. This is the very first report of tsitsikammamines from the genus Latrunculia. Molecular docking of 47 and 48 into the active sites of topoisomerase-I and II as well as indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1) enzymes revealed plausible binding modes of both compounds. The aromatic pyrroloiminoquinone core structure that formed a π-π interaction with the target proteins was found to be essential for the cytotoxicity of tsitsikammamines 47 and 48. Docking study against IDO1 revealed that an olefinic bond at ∆16 can diminish the in vitro cytotoxicity of tsitsikammamines [67].
3.1.3. Rearranged Pyrroloiminoquinone-Type Alkaloids
The Hamann group reported an unusual alkaloid atkamine (49) (Figure 6) from a deep-water sponge, L. (L.) austini Samaai, Gibbons & Kelly, 2006, from the Aleutian Islands, Alaska [89]. Atkamine (49) has a unique rearranged pyrroloiminoquinone scaffold with a highly fused ring system joined with several heteroatoms and a mono-unsaturated alkyl chain of 20 carbons. The position of the double bond was confirmed by fragmentation using an olefin metathesis. The absolute configuration of atkamine (49) was assigned using ECD spectroscopy combined with DFT calculations. The discovery of atkamine (49) prompted a re-collection of another sponge specimen L. (L.) hamanni Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016, during an NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) deep ocean survey in Alaska [90]. MN-based targeted isolation studies afforded a new alkaloid, aleutianamine (50) (Figure 6) that possesses a highly strained heptacyclic ring system where a seven-membered azaheterocycle is formed via the rearrangement of rings D and F in a typical discorhabdin skeleton, plus a characteristic thioether bridge between C-5 and C-8 together with a direct bond between N-18 and C-3, which is different from the other heptacyclic discorhabdins (Figure 6) [90]. The structure of aleutianamine (50) was confirmed by DFT calculations of its 1D NMR and ECD data, plus the calculation of interproton distances between all non-exchangeable protons that were compared to the experimental ROE correlations. Aleutianamine (50) exhibited significant in vitro cytotoxicity toward pancreatic (PANC-1) and colon cancer (HCT-116) cell lines (IC50 values 25 nM and 1μM, respectively).
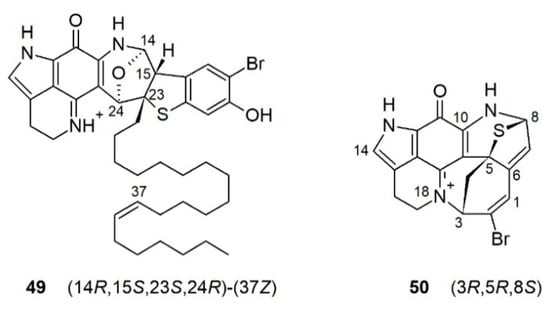
Figure 6.
Chemical structure of atkamine and aleutianamine.
3.1.4. Citharoxazole, Batzelline, and Makaluvamine
Some simple cyclized pyrroloiminoquinone-related alkaloids were also reported from latrunculid sponges, e.g., makaluvamines, makaluvone, citharoxazole, makaluvic acids, batzellines, isobatzellines, and glycosylated analogues (Figure 7), out of which three compounds were reported from Latrunculia sp., namely, citharoxazole (51), batzelline C (52), and (−)-makaluvamine F (53) (Figure 7). All these alkaloids bear the same aminoquinonline ring system as discorhabdins and tsitsikammamines (Figure 7). These simple cyclic alkaloids have been proposed as important precursors in the biosynthesis of more complex pyrroloiminoquinones such as discorhabdins and tsitsikammamines [82].
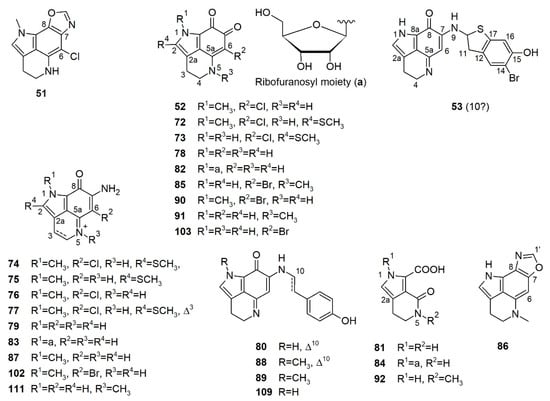
Figure 7.
Citharoxazole, batzelline, and makaluvamine reported from the genus Latrunculia. ?: Unassigned stereochemistry.
In 2011, a French group investigated the metabolome of a sponge identified as L. (B.) citharistae Vacelet, 1969 (now accepted as Latrunculia incertae sedis and a possible species of Sceptrella by Kelly et al. 2016) [21], the only described latrunculid sponge from the Mediterranean Sea (103 m depth) [66], and reported a new discorhabdin-related alkaloid, citharoxazole (51), and the known compound batzelline C (52) (Figure 7). Both 51 and 52 bear a chlorine atom at C-6, and 51 is a highly unsaturated compound possessing an unusual oxazole ring attached to C-7 and C-8. The positions of the nitrogen and oxygen atoms of the oxazole ring were established through the coupling constant differences between 3JH1’-C7 and 3JH1’-C8 [66]. No bioactivity was reported for compounds 51 or 52.
Makaluvamine F, a sulfur-containing alkaloid originally reported from a Fijian sponge, Zyzzya massalis Dendy, 1922 (now accepted as Zyzzya fuliginosa Carter, 1879 [37]) bears the typical pyrrolo[4,3,2-de]quinoline ring system (Figure 7) similar to discorhabdins and tsitsikammamines. It is regarded as the direct biosynthetic precursor of sulfur-containing discorhabdins (see Section 5) [82]. (−)-Makaluvamine F (53) was reported only from a New Zealand sponge identified as Latrunculia sp. in 2016 and shown to be a promising inhibitor of the HIF-1α/p300 protein–protein interactions (IC50 value 8.3 μM). It also exhibits moderate in vitro cytotoxicity against the HCT-116 cell line (IC50 value 7.2 μM) under hypoxic conditions [77].
3.1.5. Callipeltins
Callipeltins are a small family of marine peptides comprising 17 members (callipeltins A–Q), 13 of which (callipeltins A–M) originate from an unidentified Latrunculia sp., collected in Vanuatu, Oceania (Figure 8) [42,43,44,101]. Structurally, callipeltins are characterized by the presence of several non-proteinogenic units. For instance, the cyclic decapeptide callipeltin A (54) contains three unusual amino acid residues, β-methoxytyrosine (β-OMeTyr), (2R,3R,4S)-4-amino-7-guanidino-2,3-dihydroxyheptanoic acid (AGDHE), and (3S,4R)-3,4-dimethyl-l-glutamine (diMeGln) [42]. Some other unusual amino acids are represented by the 3,4-dimethyl-l-pyroglutamic acid (the N-terminus unit) in callipeltin B (55); d-arginine in callipeltin F (59); l-N-methylglutamine in callipeltins J (63) and K (64) [44].
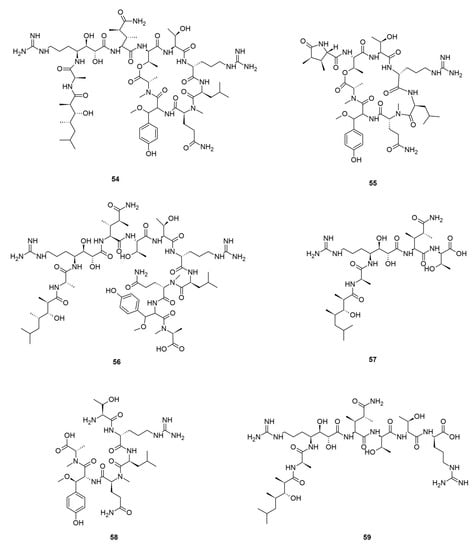
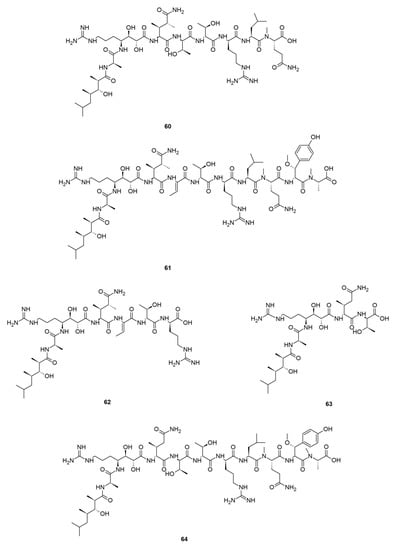
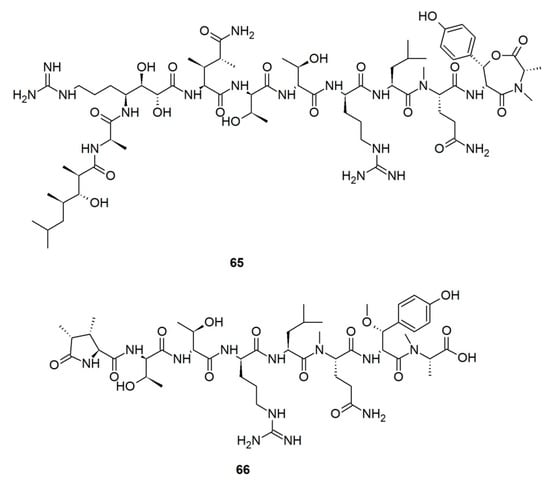
Figure 8.
Callipeltins reported from the genus Latrunculia.
Callipeltin A (54) was originally isolated from a New Caledonian Callipelta sp. (now accepted as an unidentified specimen of Sollasipelta Van Soest & Hooper, 2020 [102] (family Neopeltidae Sollas, 1888 [103], order Tetractinellida Marshall, 1876 [104]). D’Auria group reported callipeltins A–C (54–56) together with two new acyclic peptides, callipeltins D (57) and E (58) (Figure 8), from a Latrunculia sp. from Vanuatu [42]. Marfey’s reagent was used to establish the absolute stereochemistry of the new compounds and for the structural revision of callipeltin A (54). Callipeltin A (54) and B (55) appeared to exert strong cytotoxicity against multiple cell lines, including human bronchopulmonary non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC-N6); human renal carcinoma (E39), murine leukemia (P388), and human melanoma (M96), by showing IC50 values ranging from 1.1 to 10 μg/mL, while callipeltin C (56) was only moderately cytotoxic against NSCLC-N6 and E39 cells (IC50 values 53.5 and 36.1 μg/mL, respectively). Callipeltins A (54) and B (55) exhibited in vitro antifungal activity against C. albicans on a disc diffusion assay. Callipeltin A (54) also showed in vitro anti-HIV activity (SI = 29) [105,106] and is a selective and significant inhibitor of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger and a positive inotropic agent [107]. Further investigations on the same sponge yielded callipeltins F–M, (59–66) [43,44]. Callipeltins F–K (59–64) were found to display antifungal activity towards C. albicans (MIC values of ca. 10−4 M) but lacked anti-HIV activity [43,44]. Until now, this is the only Latrunculia sp. that has been reported to contain these unique marine peptides.
3.1.6. Other Types of Compounds
A few other classes of MNPs were reported from sponges that were originally loosely grouped in the genus Latrunculia. Between 1985 and 1998, the Capon group studied several Australian sponges initially identified as Latrunculia sp. and reported a suite of norditerpene or norsesterterpene cyclic peroxides with the trivial names of trunculins and conulosins [46,47,108,109,110,111]. Further taxonomic revisions have reidentified the sponge specimens as species of Sigmosceptrella Dendy, 1922 (family Podospongiidae de Laubenfels, 1936) [49,50,83]. He et al. (1991) also reported three new trunculins in their methyl ester form from an Australian specimen of Latrunculia [112]. Based on its sampling site (Jervis Bay, Australia) and chemical composition, this sponge could potentially be a specimen of either Diacarnus Burton, 1934 [113] or Sigmosceptrella. Cheenpracha et al. (2010) investigated an Indo-West Pacific specimen identified as Latrunculia sp., which yielded seven norsesterterpene peroxides (epimuqubilin A, muqubilone B, unnamed cyclic peroxide ester, epimuqubilin B, sigmosceptrellin A methyl ester, sigmosceptrellin A, sigmosceptrellin B methyl ester, and an unnamed cyclic peroxide ester) [114]. Although no taxonomic investigation has been carried out, this sponge appears to be misidentified based on the chemical composition. Kelly-Borges and Vacelet (1995) described seven species of Diacarnus from the Indo-West and Central Pacific [115], and a species of this genus (or Sigmosceptrella) most likely to be the correct identity. Currently, trunculins or conulosins are regarded as biochemical markers important for chemotaxonomy of the sponge genera Diacarnus and Sigmosceptrella [50].
Latrunculins are a group of marine toxins belonging to the polyketide macrolide family previously reported from the Red Sea sponge Latrunculia magnifica Keller, 1889 [116], which is now accepted as the podospongid Negombata magnifica Keller, 1889 [45,117,118,119].
3.2. Genus Strongylodesma
With nine reported species so far, Strongylodesma represents the second-largest genus of the family Latrunculiidae. Although they lack the diagnostic anisodiscorhabds that differentiate species of other latrunculid genera, the possession of smooth or terminally spined strongyle megascleres, in a single, broad size category, many of which have characteristic “shepherd’s crook” modifications, serve to distinguish Strongylodesma species from each other and from other latrunculid sponge genera and their species [57]. The strongyles form an irregular, large-meshed reticulation of heavy or loose tracts, that are somewhat reminiscent of the honeycomb structures in species of Tsitsikamma. The description of the first species from Australian waters, Strongylodesma australiense Kelly & Goudie, 2020 [59], from New South Wales, is significant, because it is the first record of Strongylodesma in the Southwest Pacific, providing a bridge between the disparate tropical Western and south Atlantic Ocean, and the western Pacific Ocean locations of other species (Kelly & Goudie 2020) [59]. Strongylodesma species are found both in shallow water (e.g., intertidal pools) and the deep-sea (exceeding −100 m) [25,57,120] and their morphology and coloration is very similar to that of other Latrunculiidae [57]. The genus Strongylodesma is another very prolific source of discorhabdin-type alkaloids and all known Strongylodesma species produce pyrroloiminoquinone (discorhabdins) and their structurally related alkaloids.
Between 1987 and 1991, Kobayashi group reported four sulfur-containing pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids, prianosins A–D (2, 67, 7, and 4, Figure 3) from an Okinawan sponge identified as Prianos melanos de Laubenfels, 1954 [91,121,122] on account of the possession of strongyles with shepherd’s crook modifications. However, this sponge was revised as Strongylodesma melanos by Samaai et al. in 2009 [57,91,121,122]. The structure of (+)-prianosin A was unambiguously determined by X-ray diffraction analysis [91]. The report of discorhabdins with the same NMR data from New Zealand Latrunculia sp. around the same period with prianosins [69,71] pointed out that (+)-prianosin A/(+)-discorhabdin A (2), (+)-prianosin C/(+)-2-hydroxydiscorhabdin D (7), and (+)-prianosin D/(−)546-discorhabdin D (4) are chemically identical compounds [91,121,122]. (+)-Prianosin B (16,17-dehydrodiscorhabdin A, 67), however, has never been reported from any other latrunculid sponge. Prianosins A–D show strong in vitro anticancer potency against mouse lymphocytic leukemia (L1210) and murine leukemic lymphoblast (L5178Y) cell lines with IC50 values of 0.037 and 0.014 μg/mL (prianosin A, 2), 2.0 and 1.8 μg/mL (prianosin B, 67), 0.15 and 0.024 μg/mL (prianosin C, 7) and 0.18 and 0.048 μg/mL (prianosin D, 4) [91,121,122]. Prianosins C (7) and D (4) were also cytotoxic against human epidermoid carcinoma (KB) cells (IC50s 0.57 and 0.46 μg/mL, respectively) while prianosins A (2) and D (4) significantly induced Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum [91,121,122].
Two Caribbean species, identified as species of Batzella (−141 m depth) from which new discorhabdins P (68), S–U (69–71) (Figure 3) were obtained [85,123] were revised as S. purpurea in 2009 [57]. Discorhabdin P (68) is an N-13 methylated derivative of discorhabdin C, while discorhabdins S–U (69–71) are chiral molecules with one stereocenter at C-6 and bear an additional S-methyl group at C-5 (Figure 3) [123]. This study did not report the [α]D values of the compounds. The absolute configurations of compounds 69–71 were only determined in 2010 as 6S via semisynthesis [75]. Discorhabdins P, S–U (68–71) were evaluated for their in vitro cytotoxicity against various cell lines, i.e., murine P-388, human lung carcinoma (A-549) cell line and human pancreatic cancer cell (PANC-1). As shown in Table 2, discorhabdins P (68) and U (71) are the most potent [123]. Discorhabdin P (68) is an inhibitor of calcineurin (CaN) and caspase-3 (CPP32) enzymes (IC50 values 1.15 and 0.77 μM), suggesting the great potency of discorhabdin P in preventing the pathological damage induced by caspase-mediated apoptotic events [85].

Table 2.
Cytotoxicity of discorhabdins P (68), S–U (69–71). IC50 values in μM.
The Davies-Coleman group reported known discorhabdin alkaloids (+)-discorhabdin A (2), (−)546-discorhabdin D (4), 3-dihydrodiscorhabdin C (26), and (−)-discorhabdin H (9) as major components of the South African sponge S. algoaensis Samaai & Kelly, 2003 (Figure 3) [30]. This was the first report of the fully assigned 1D NMR data of discorhabdin H (9). Compound 9 bears the typical heptacyclic discorhabdin d-skeleton substituted with an unusual histidine moiety at C-1 and the absolute configuration of the histidine moiety was assigned by chiral GC-MS analysis of the acylated ozonolysis products of discorhabdin H (9) [30]. When tested against human colon tumor cell line HCT-116, compound 2 was found to be the most potent molecule (IC50 value of 7.0 nM).
3.2.1. Batzellines and Isobatzellines
Sakemi et al. (1989) reported batzellines A (72), B (73), and C (52) from a deep-sea Caribbean sponge Batzella sp. collected at a depth of 120 m (Figure 7) [124]. A second collection of Batzella sp. (1990) from the same region yielded isobatzellines A–D (74–77) (Figure 7) [125]. In 2009, both sponge specimens were reidentified as S. nigra Samaai & Kelly, 2009 by Samaai et al. [57]. The structure of batzelline A (72) was ascertained by X-ray analysis. Isobatzellines have very similar backbone to batzellines with a further amination at C-7, hence, forming the characteristic pyrrolo[4,3,2-de]quinoline ring system for discorhabdins [68,125]. All batzellines and isobatzellines, except for isobatzelline B (75) reported in this study are chlorinated compounds. Interestingly, all batzellines and isobatzellines bear an S-methyl on C-2 and/or an N-methyl on N-1, which are uncommon for (bis)pyrroloiminoquinones and their analogs [125]. Isobatzellines (74–77) but not batzellines A–C (72, 73, and 52), were found to exert cytotoxic and antifungal activities [124,125], however, their IC50 or MIC values were not reported.
3.2.2. Makaluvamines, Damirones, Makaluvic Acids, and Tsitsikammamines
Polar extracts of a new South African sponge, S. aliwaliensis Samaai, 2004 [120] yielded the known alkaloids damirone C (78), makaluvamines I (79) and M (80), and four new compounds: makaluvic acid C (81), N-1-β-d-ribofuranosyldamirone C (82), N-1-β-d-ribofuranosylmakaluvamine I (83), and N-1-β-d-ribofuranosylmakaluvic acid C (84) (Figure 7) [126,127]. The sugar residues were confirmed by GC-MS analysis of the peracetylated aldononitrile derivatives of free sugars obtained by hydrolysis of compounds 82–84 and comparison with that of four aldopentoses pretreated with the same derivatization. Compounds 82–84 are also the first and the only glycosylated alkaloids reported from latrunculid sponges so far. Compounds 80 and 82 displayed sub-micromolar activity against the esophageal cancer cell line WHCO-1 (IC50 values 0.7 and 1.6 μM, respectively), whereas 78, 81, and 84 were marginally active (IC50 values 56, 38, 61 μM, respectively) [126,127].
An investigation on S. tongaensis Samaai & Kelly, 2009 [57] afforded the new alkaloids 6-bromodamirone B (85) and makaluvamine W (86), plus eight known compounds, makaluvamines A (87), E (88), F (53), and K (89), makaluvone (90), damirone B (91), makaluvic acid A (92) and tsitsikammamine B (93) (Figure 5 and Figure 7) [128]. Similar to citharoxazole (51) [66], makaluvamine W (86) bears an oxazole function on the aromatic ring. Compound 86 represents the first makaluvamine-type alkaloid with a nitrogen substitution at C-8. All compounds were tested against the human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL-60. Compounds 53, 89, 90, and 93 were the most active, with IC50 values of 3.0, 4.5, 2.6, and 1.6 μM, respectively, while 87 and 89 had much lower activity (IC50 values 30.4 and 20.3 μM, respectively) [128].
3.3. Genus Tsitsikamma
Tsitsikamma is a small genus of latrunculid sponges, endemic to South Africa, the name Tsitsikamma having been derived from the type locality, the marine protected area (MPA) of The Garden Route National Park named Tsitsikamma [129]. The genus currently comprises eight species, with the addition of three new species in two new subgenera (Tsitsikamma Samaai and Kelly, 2002 and Clavicaulis Samaai, Payne and Ngwakum, 2020) [41]. Members of the genus Tsitsikamma are mainly found in shallow water down to 25 m depth [25]. The genus Tsitsikamma has been regarded as a morphological intermediate between Latrunculia and Zyzzya [25]. Species of Tsitsikamma exhibit a similar morphology to other latrunculid sponges, especially the aquiferous structures, but they have a tough and leathery texture due to the sponge’s huge internal spicule tracts, which promote a purse- or honeycomb-like architecture [25]. Sponges of this genus are prolific sources of discorhabdins and makaluvamines.
3.3.1. Discorhabdins
Tsitsikamma (Tsitsikamma) favus Samaai & Kelly, 2002 [25] yielded the first examples of discorhabdins with a C-14 substituent, i.e., 14-bromodiscorhabdin C (94) and 14-bromo-3-dihydrodiscorhabdin C (95) (Figure 3) [99]. The configuration of the stereogenic center at C-3 remains unknown and its [α]D data were not recorded. Both compounds 94 and 95 were reported to exhibit antimicrobial activity against B. subtilis without reported MIC or IC50 values [99].
The examination of the organic extracts of two South African Tsitsikamma species, Tsitsikamma (Clavicaulis) pedunculata Samaai & Kelly 2003 [56] and T. (T.) favus Samaai & Kelly, 2002, yielded three known and four new discorhabdin C-and discorhabdin V-type alkaloids [30]. Known discorhabdin C analogs 94, 95, and 26 and the new analogs 3-dihydro-7,8-dehydrodiscorhabdin C (32), 14-bromo-3-dihydro-7,8-dehydrodiscorhabdin C (96), discorhabdin V (97), and 14-bromo-1-hydroxydiscorhabdin V (98) were sourced from T. (C.) pedunculata Samaai & Kelly 2003 (Figure 3). The T. (T.) favus Samaai & Kelly 2003 specimen produced the known compound 95 and the new metabolites 32 and 98 (Figure 3) [30]. The new discorhabdins contain one or more stereocenter(s), however, their configuration was not assigned. When tested against the human colon cancer cell line HCT-116, 14-bromodiscorhabdin C (94) appeared as the most potent molecule (IC50 value 77 nM), while 14-bromo-1-hydroxydiscorhabdin V (98) was the weakest (IC50 value 12.5 μM).
Kalinski et al. reported the reisolation of 14-bromo-3-dihydro-7,8-dehydrodiscorhabdin C (96) from T. (T.) favus Samaai & Kelly, 2002 [40]. The authors also demonstrated topoisomerase I inhibition, DNA intercalation and moderate in vitro anticancer and cytotoxic potential of 96 against human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK 293) and HeLa cells [40].
3.3.2. Tsitsikammamines, Makaluvamines and Makaluvone
The first members of the tsitsikammamine family, tsitsikammamines A (47) and B (93) were reported from a South African sponge T. (T.) favus Samaai & Kelly, 2002 collected from the Tsitsikamma Marine Reserve [99]. In vitro bioactivity tests revealed antimicrobial activity of these two compounds against B. subtilis. Tsitsikammamines were considered as strong chemotaxonomic markers for Tsitsikamma species until the report of tsitsikammamine C (101) from an Australian Zyzzya sp. and the absence of tsitsikammamines in the South African sponge, T. (C.) pedunculata Samaai & Kelly 2003 [30,100]. As chemotaxonomic markers for the genus Tsitsikamma, a critical role was placed to 14-brominated discorhabdin analogs which are present in all studied Tsitsikamma spp. so far [30,49]. Antunes et al. examined the chemical profile of two South African Tsitsikamma species. Tsitsikammamines A (47) and B (93), and their respective N-oxime analogs 99 and 100, were obtained from T. (T.) favus Samaai & Kelly, 2002 while T. (C.) pedunculata Samaai & Kelly 2003 only contained discorhabdin-type alkaloids (Figure 5, See Section 3.3.1) [30]. The N-oxime analogs 99 and 100 were deemed as isolation artifacts of the naturally occurring tsitsikammamines A (47) and B (93) N-oxides [30]. Both tsitsikammamines A (47), B (93) and their N-oxime analogs 99 and 100 exhibited similar topoisomerase I inhibitory activity and intercalated DNA with Ks values (the micromolar concentration that decreases DNA-bound ethidium bromide fluorescence by 50%) of 15, 45, 20, and 30 μM, respectively [30]. Against HCT-116 cells, tsitsikammamines A (47) and B (93) exerted promising cytotoxicity with IC50 values of 1.4 and 2.4 μM, respectively, while the N-oximes 99 and 100 were weaker (IC50s 128.2 and 16.5 μM, respectively).
In 2019, Kalinski et al. studied the secondary metabolite profile of seven South African T. (T.) favus Samaai & Kelly, 2002 specimens [40]. HR-ESI-LC-MS/MS-based MN studies revealed the presence of two chemotypes; chemical composition of chemotype I was predominated by discorhabdins and tsitsikammamines, while specimens of chemotype II produced mainly halogenated makaluvamines and trace levels of tsitsikammamines [40]. Chemical work-up of a chemotype I sponge T. (T.) favus Samaai & Kelly, 2002 sponge yielded tsitsikammamine B (93) and a chemotype II T. (T.) favus Samaai & Kelly, 2002 yielded the new compound makaluvamine Q (102) together with four known metabolites, namely, makaluvamines A (87), I (79), and O (103) and makaluvone (90) (Figure 7) [40]. Makaluvamine Q (102) represents the first and the only example of an N-methylated makaluvamine with a bromination on C-6. This study reported the presence of makaluvamines in the genus Tsitsikamma for the first time. All seven compounds showed some topoisomerase I inhibitory and DNA intercalation activities. Makaluvamine O (103) and makaluvone (90) appeared as the most effective topoisomerase I inhibitors and the weakest DNA intercalators [40], and they exerted the weakest activity against human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK 293) and HeLa cells. Makaluvamine Q (102) exhibited the highest DNA affinity and also showed the strongest in vitro activity against HEK 293 and HeLa cells and their IC50 values were not recorded [40]. This study suggested that DNA intercalation, instead of topoisomerase I, might be the anticancer targets of the planar molecules makaluvamines (79, 87, 102, and 103) and makaluvone (90) [40].
3.4. Genus Sceptrella
The genus Sceptrella is restricted to three species: the type species, S. regalis Schmidt, 1870 [23]; S. biannulata Topsent, 1892 [130] and S. insignis Topsent, 1890 [131], all from the Atlantic Ocean, specifically Floridian waters, and the Azores archipelago [25,132]. Sceptrella was compared to the monospecific Aleutian Islands genus, Latrunculava Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016, also with a second spicule form, the “sceptre”, in addition to the anisodiscorhabd first recorded from the Oamaru Diatomite (Eocene) of New Zealand [21]. Species of Sceptrella are morphologically similar to Latrunculia and Strongylodesma species, with a cakey, dense and compressible texture, and a hemispherical or spherical body shape [132]. Sceptrella species are deep-sea organisms, having been recorded from a depth of 2460 m in some regions (e.g., the north coast of Norway) [25]. Biochemical studies on sponges of the genus Sceptrella yielded only pyrroloiminoquinones (discorhabdins) and structurally related alkaloids (makaluvamines). To date, there has only been one chemical study from a sponge purported to be a species of Sceptrella, from Korea (potentially a species of Latrunclava), that yielded two new discorhabdin alkaloids, (−)-3-dihydrodiscorhabdin D (104) and (−)-discorhabdin Z (105) together with 12 previously reported pyrroloiminoquinones and related alkaloids namely, discorhabdin C (1), didebromodiscorhabdin C (106), 3-dihydrodiscorhabdin C (26), (+)-discorhabdin E (5), (+)-discorhabdin B (3), (+)-discorhabdin G*/I (25), (−)546-discorhabdin D (4), (+)-1-methoxydiscorhabdin D (107), (−)546-discorhabdin L (13), (−)-dihydrodiscorhabdin L (108), makaluvamine D (109) and (−)-makaluvamine F (53) (Figure 3 and Figure 7) [133]. The 2D structures of the new compounds were established by conventional spectroscopic methods, while the absolute configuration was then assigned by their [α]D values and ECD spectra in conjunction with DFT-calculations [133]. Most of the isolated metabolites exhibited cytotoxicity and antimicrobial activity. The strongest antibacterial activity was shown by (+)-discorhabdin B (3) against Proteus vulgaris (MIC 3.13 μg/mL) and the strongest cytotoxicity was exerted by (+)-discorhabdin E (5) (IC50 values 1.3 μM) [133]. (−)-Discorhabdin Z (105) inhibited the sortase A enzyme, an antibacterial drug target, with an IC50 value (6.5 μM) that was almost 20 times lower than the positive control p-(hydroxymercury)benzoic acid (IC50 110.9 μM) [133].
3.5. Genus Cyclacanthia
The genus Cyclacanthia is also endemic to South African waters and is represented by four species: Cyclacanthia mzimayiensis Samaai & Kelly, 2004 and C. cloverlyae Samaai & Kelly, 2004 [26] were reported from the subtropical east coast of South Africa, and the type species C. bellae Samaai & Kelly, 2003 was described from the temperate Algoa Bay [26,56]. A fourth species, C. rethahofmeyri Samaai, Payne and Ngwakum & Kelly is reported from South Africa [41]. To date, there has been only one report on the chemical constituents of the genus Cyclacanthia. New discorhabdins 1-methoxydiscorhabdin D (107) and 1-aminodiscorhabdin D (110) together with five known metabolites discorhabdins N (15) and I (25), damirone B (91), makaluvic acid A (92), and makaluvamine C (111) were obtained (Figure 3 and Figure 7) [30] from Latrunculia bellae Samaai & Kelly, 2003 (now accepted as Cyclacanthia bellae Samaai & Kelly, 2003) [26]. A re-examination of this sponge extract by Grkovic et al. in 2008 yielded another known compound (−)546-discorhabdin L (13) [74]. Compounds 15, 107, and 110 bear the same heptacyclic skeleton as discorhabdin D (4) but vary from each other with different substitutions at C-1. The relative configuration of C-1, absolute configurations and optical rotations of the molecules were not reported. Compounds 107, 110, 25 were clearly the most cytotoxic against human colon tumor cell line (HCT-116) with IC50 values 0.23, 0.12, and 0.33 μM, respectively. Compounds 15, 91, and 111 exhibited moderate cytotoxicity against HCT-116 cells with IC50 values ranging from 1.1 to 3.1 μM, while 92 had modest activity (IC50 value 28.4 μM) [30]
3.6. Other Genera
Apart from the five genera Latrunculia, Strongylodesma, Tsitsikamma, Sceptrella, and Cyclacanthia, the family Latrunculiidae includes several new genera established in 2016: Bomba Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016 and Latrunclava Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016 [21]. Genus Bomba comprises two species: the type species B. tricincta Hentschel, 1929 (initially identified as Latrunculia tricincta Hentschel, 1929) [134] reported from northern Norway, and the species B. endeavourensis Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016 [21] discovered in deep waters on Endeavour Ridge, British Columbia, Canada. Genus Latrunclava, discussed above in a comparison with genus Sceptrella, was established with only one species, Latrunclava imago Kelly, Reiswig & Samaai, 2016 [21], which was collected from Amchitka Pass, in the central Aleutian Islands. So far, no chemical investigation has been carried out on any of the new latrunculid sponge genera Bomba and Latrunclava because they are monospecific and restricted to small holotype species.
4. Biosynthetic Origin of Latrunculid Sponge Metabolites
Marine sponges are holobionts, comprising the sponge host cells and a dense microbiome. Sponge-associated microorganisms account for a large proportion of the sponge biomass, varying from 30% to 60% in total [135,136,137]. Significant physiological and ecological roles have been ascribed to sponge-associated microorganisms, including nutritional enhancements, stabilization of the sponge skeleton, and most importantly, production of secondary metabolites [138,139,140]. Hence, the true natural origin of sponge-derived metabolites is one of the key areas of sponge natural product research.
The debate on the origin of latrunculid sponge-derived pyrroloiminoquinone and bispyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids started shortly after the first report of discorhabdin C from an unidentified New Zealand species of Latrunculia [27], and still continues [40]. In 1991, Copp et al. reported the isolation of a new alkaloid wakayin from the colonial ascidian Clavelina sp. [36]. Wakayin belongs to the bispyrroloiminoquinone family and bears the same pyrrolo[4,3,2-de]quinoline ring system as latrunculid sponge metabolites, isobatzellines A–D, makaluvamines and discorhabdins [27,69,71,125]. Biosynthetically, isobatzellines, discorhabdins, and wakayin were proposed to be derived from the same precursor tryptophan [34,40]. The report of wakayin from a phylogenetically distinct ascidian indicated that bis-pyrroloiminoquinone-type alkaloids are not confined to the phylum Porifera. The report of wakayin also raised the question as to whether bispyrroloiminoquinone-type alkaloids originated from the sponge hosts or the associated microbes [36].
In 1995, Lill et al. carried out a preliminary investigation on the production of discorhabdin B using slices and unfractionated dispersed cells of the sponge Latrunculia sp. [34]. A putative biosynthetic pathway was proposed based on the perceived chemotaxonomic relationships between various groups of (bis)pyrroloiminoquinones found in different marine organisms. In this biogenesis, decarboxylation of tryptophan formed tryptamine, from which the pyrroloquinoline backbone (A) was generated after appropriate functionalization and oxidation (Scheme 1). The parent pyrroloquinoline (A) is considered to be the direct precursor of simple discorhabdin-related alkaloids, e.g., damirones, batzellines, and isobatzellines (Scheme 1). Via the incorporation of tyramine or a functionalized tyramine derivative, the parent pyrroloquinoline (A) then led directly to more complex pyrroloiminoquinone and their analogs, including discorhabdins and makaluvamine D series alkaloids (Scheme 1). To verify the proposed biosynthetic pathway, thin slices of a discorhabdin B-producing Latrunculia specimen were incubated with isotopically labeled phenylalanine ([U-14C]-l-phenylalanine). The de novo synthesis of discorhabdin B utilizing [U-14C]-l-phenylalanine was clearly observed by the detection of 14C via radiochemical analysis in the purified discorhabdin B, hence further confirming the biosynthetic pathway proposed by Lill et al. Aubart et al. (1999) advanced the putative biosynthetic pathway suggested by Lill et al. based on their successful syntheses of discorhabdins C and E and dethiadiscorhabdin D via a biomimetic approach [141]. In this advanced biosynthesis, the discorhabdin C skeleton was formed by an intramolecular Michael addition of makaluvamine D followed by auto-oxidation back to the quinone, and the discorhabdin D skeleton was formed by nucleophilic displacement of a C2 bromide to generate the C2–N18 bond, following the 1,5-hydride addition of discorhabdin B (Scheme 1) [141]. The wakayin skeleton was formed by a further substitution of tryptamine on the pyrroloquinoline backbone (A) and the tsitsikammamine skeleton was formed by an alternative cyclization of makaluvamine D (Scheme 1) [82]. Batzellines and isobatzellines are convertible via amination and hydrolyzation (Scheme 1) [40]. Through the modified biogenetic proposal raised by Lill, Aubart, Urban, and Kalinski, the whole suite of known monomeric discorhabdins and structurally related metabolites could be generated (Scheme 1).
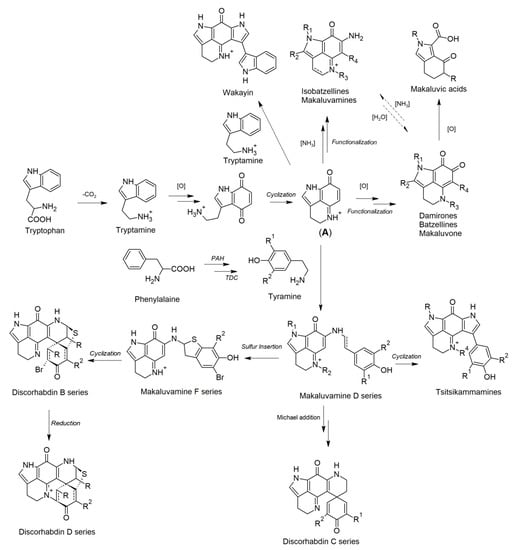
Scheme 1.
Proposed biosynthetic pathway of discorhabdins and structurally related metabolites (adapted from references [34,40,49,82,141]).
In order to address the question of whether the biosynthesis of pyrroloiminoquinones is restricted to the sponge cells or sponge-associated microbes alone, or requires the cooperation of commensal microorganism in its production, Lill et al. (1995) cultured slices of discorhabdin B-producing sponge (Latrunculia sp.) tissue with [U-14C]-l-phenylalanine under three different conditions: (A) the sponge tissue slices were presoaked with a broad-spectrum antibiotic mixture and then incubated in an artificial medium; (B) presoaked sponge tissue slices were incubated with broad-spectrum antibiotics; and (C) sponge tissue slices were not subjected to any antibiotic treatment [34]. The results revealed that the 14C-incorporation into discorhabdin B in both groups A and B was similar to that in group C, indicating that the production of discorhabdin B does not require the presence of sponge-associated bacteria [34]. This is the first and the only in vivo study referring to the natural origin of discorhabdins. Interestingly, in 1996, Hooper et al. reported the isolation of two bispyrroloiminoquinones (tsitsikammamines A and B) from a South African latrunculid sponge (Tsitsikamma sp.), while Ishibasha et al. (2001) reported a structurally related compound makaluvamine A from a laboratory cultured myxomycete Didymium bahiense [38,99]. Both tsitsikammamines and makaluvamine A bear the identical pyrrolo[4,3,2-de]quinoline ring system as wakayin does. The wide distribution of pyrroloiminoquinone and their structural related alkaloids in taxonomically unrelated organisms such as Porifera, tunicate, and myxomycete, suggest a possible symbiont origin for this type of compounds (especially to tsitsikammamines) although the production of discorhabdin B in sponge cells has been proved by Lill and coworkers [34].
A culture-independent study by Walmsley et al. investigated the diversity of bacterial communities associated with three T. (T.) favus Samaai & Kelly, 2002 specimens from South Africa [142]. An NMR-based metabolomics study revealed the major compound to be tsitsikammamine B for all three samples. The dominating bacterial species of these three samples was identified to be a unique Betaproteobacterium using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) together with clonal and deep amplicon sequencing of the microbial 16S rRNA gene. This is the first report of β-proteobacteria as the dominant taxon in a sponge holobiont, however, whether this β-proteobacterial community is responsible for the production of tsitsikammamines remains undetermined [142]. A subsequent study by Matcher et al. (2016) investigated whether the β-proteobacterium operational taxonomic unit (OTU0.03) dominates the bacterial community in other sponge species which produce (bis)pyrroloiminoquinones [143]. Hence, the microbial composition of nine sponges represented by eight latrunculid sponge specimens (three T. (T.) favus Samaai & Kelly, 2002 specimens, three unidentified Tsitsikamma specimens, one L. (B.) algoaensis Samaai, Janson & Kelly, 2012, and one Cyclacanthia bellae Samaai & Kelly, 2003) and one Mycale sp. specimen (found encrusting on one of the Tsitsikamma specimens) was investigated [143]. They observed the conservation of a single, dominant β-proteobacterium OTU within the microbiome of all eight latrunculid sponges (also at low levels in the seawater but not in the sediment) [143]. The microbial community of the Mycale sp. was dominated by a different β-proteobacterium species. The phylogeny of all these β-proteobacterial OTUs closely resembles that of their host sponges, suggesting that these Gram-negative bacteria may have coevolved with their hosts. The β-proteobacterial OTUs are numerically dominant and metabolically active in both T. (T.) favus Samaai & Kelly, 2002 and C. bellae Samaai & Kelly, 2003. Sequence analysis (BLAST) of the 16S rRNA genes from these β-proteobacterial strains identified them to be Nitrosomonadaceae bacteria, which have been proven to be lithoautotrophic ammonia oxidizers [144]. Furthermore, a significant proportion of Spirochaetae bacteria are also present in all nine sponges except for the Mycale sp. and L. (B.) algoaensis Samaai, Janson & Kelly, 2012 specimens [143]. The Spirochaetae bacteria found in sponges of the genera Tsitsikamma and Cyclacanthia were dominated by a single OTU(0.03) that have a close phylogenetic relationship with each other and a distant relationship to Spirochaetae bacteria found in other sponge families. Hence, the authors speculated the involvement of these Spirochaetae OTUs in the pyrroloiminoquinone production of sponges of the genera Tsitsikamma and Cyclacanthia [143].
Although the latrunculid sponge genera Tsitsikamma, Cyclacanthia, and Latrunculia share a similar bacterial community, tsitsikammamines have never been reported from a sponge of the genus Latrunculia until our report in 2018. Therein, a comprehensive MN-based metabolomic study of an Antarctic Latrunculia sp. revealed tsitsikammamines as the major component of the sponge [67]. The presence of tsitsikammamines in a species of Latrunculia lends support for the potential microbial origin of tsitsikammamines and contributes to discussions on the biosynthetic origin of (bis)pyrroloiminoquinones. A microbial community profiling of ten South African sponges of the genus Tsitsikamma revealed the conservation of a dominant, single β-proteobacterium OTU0.03 and a second dominant Spirochetes OTU0.03 within all the sponge specimens [40]. The authors hypothesized that the production of (bis)pyrroloiminoquinones was a combined effort of the sponge host and its selected associated microbes; after the production of makaluvamines and parent pyrroloquinoline backbone by the microbes (A, Scheme 1), the sponge hosts convert these simple precursors to more complex metabolites, i.e., discorhabdins and tsitsikammamines [56]. The debate on the biosynthetic origin of (bis)pyrroloiminoquinones is still ongoing, and it is tenuous to make a definitive conclusion.
5. The Significance of Pyrroloiminoquinone-Type Alkaloids in the Chemotaxonomy and Phylogeny of Latrunculid Sponges
The distribution of norsesterterpene cyclic peroxides and pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids across genera previously considered to be of latrunculid origin facilitated the separation of norsesterterpene cyclic peroxide-containing genera Sigmosceptrella, Diacarnus and Negombata Laubenfels, 1936 [51], from pyrroloiminoquinone-containing genera Latrunculia, Sceptrella and related taxa, into separate families within the order Poecilosclerida. This scheme was initially hypothesized by Kelly in Urban et al. (2000) [82], and formalized by the resurrection of the family Podospongiidae by Kelly and Samaai (2002) [145], to receive norsesterterpene cyclic peroxide-containing genera, resulting in a monophyletic group well separated from family Latrunculiidae.
The process undertaken provides a good example of the power of marine natural products to strengthen our understanding of the phylogeny of specific sponge groups. The thorough taxonomic investigation and full identification and description of all host and source sponges, by experts, underpins and facilitates such research. The process is of inestimable value to marine natural product studies; taxonomy underpins and smooths the biodiscovery process, allowing accurate drug discovery predictions and dereplication of samples, saving time and precious funding.
The need for good taxonomy is illustrated in the discovery that shepherd’s crook modifications of strongyles are diagnostic for latrunculid Strongylodesma and Batzella Topsent, 1893 (order Poecilosclerida, family Chondropsidae) only (see Kelly and Goudie, 2020) [59], but not for species of Prianos Gray, 1867 [146] (order Haplosclerida Topsent, 1928, family Chalinidae). Prianos (now accepted as Haliclona (Reniera) Schmidt, 1862) [147] is a genus to which many latrunculid species had been mistakenly assigned, resulting in serious confusion of species in the literature and confusion in the nomenclature of discorhabdins.
The full taxonomic process is exemplified by studies within the Hamann Group: (1) the identification of a new species of Latrunculia from Alaska amongst several other congeners and other species, and the isolation of two new, and six known pyrroloiminoquinones that exhibited anti-HCV, antimalarial and selective antimicrobial activities [21,32]; (2) the identification of L. (L.) austini Samaai, Kelly & Gibbons, 2006, from the Aleutian Islands, and differentiation from congeners in the region, facilitated the discovery of a new class of pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids (aleutianamines) that exhibited selective bioactivity against pancreatic cancer cell lines. The molecule was identified and structurally elucidated with the guidance of mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance, and molecular ion networking (MoIN) analysis of data collected from the injection of both various discorhabdin standards and new extracts of Pacific Latrunculia species identified and dereplicated within this study [90].
Two examples of non-latrunculid genera further illustrate the importance of the general taxonomic process: (1) the dereplication of numerous deep-water sponge specimens and the discovery of several new species of Monanchora Carter, 1883 (order Poecilosclerida, family Crambeidae Lévi, 1963) [148] from the Aleutian Islands, separating these from the northeastern Pacific species, Monanchora pulchra Lambe, 1894 [149], facilitated the discovery of three metabolites that exhibited potential antiproliferative activity against two CRT-positive colon cancer cell lines [150]; (2) the elucidation of morphological and colour variation in Acanthostrongylophora ingens Thiele, 1899 [151] (order Haplosclerida, family Petrosiidae Van Soest, 1980) [152] and revision of the classification of the numerous specimens that have yielded manzamines and related compounds in the literature, over many years [152] facilitated the discovery of a sponge-associated bacterium that produces the manzamine class of antimalarials in A. ingens Thiele, 1899 [152].
While the discovery of potential microbial biosynthetic origins for many of the compounds in latrunculid and podospongid genera weakens their chemotaxonomic diagnostic value somewhat, by adding “noise”, the biosynthetic pathways, intermediary and end-products remain strong markers of the phylogeny of these sponges. Future research to increase our understanding of sponge phylogeny, of the role microorganisms play in sponge evolution, and the intricacies of production of interesting bioactive metabolites derived from both must include a comparison with the biosynthetic pathways, and their intermediary and end-products. As exemplified in Kerr and Kelly-Borges [153], we can use cladistic analysis to explore the congruence of sponge and microbiome phylogeny and the metabolic origins and biosynthetic pathways of the target compounds as a hypothesis to test phylogenetic relationships between these sponges.
6. Conclusions
This systematic review has clearly highlighted the evidence that marine sponges of the family Latrunculiidae are prolific sources of numerous secondary metabolites that are structurally unique and exhibit a broad spectrum of biological activities. A comprehensive literature survey covering the chemical and biological investigations on the secondary metabolites isolated from marine sponges belonging to the family Latrunculiidae throughout 1986–2020 presented 110 naturally occurring metabolites that are categorized into two main groups. Additionally, the chemotaxonomic remarks, a brief insight of the proposed biogenetic pathway and the biosynthetic origin of the (bis)pyrroloiminoquinones are also discussed.
While the systematics of the Latrunculiidae and related genera has presented multiple challenges, we now consider the systematics of this group to be one of the better known in the Porifera. Numerous studies have resolved issues with the use of chemotaxonomy and comparisons of living and fossil material from the South Pacific. Latrunculid sponges have very similar morphologies, but the key to identification is full characterization of the anisodiscorhabd spicule (ornamentation and dimensions). The discovery of new latrunculid sponges is still ongoing, particularly in New Zealand and South Africa. Discorhabdins are the most important chemical family reported from latrunculid sponges. However, there is some confusion as to the nomenclature of discorhabdins due to the great chemical diversity of this type of compounds. Structure elucidation of discorhabdins is challenging, given the fact that compounds from this chemical family commonly contain several heteroatoms in highly unsaturated polycyclic ring systems, hence, there have been some revisions on the 3D structures of discorhabdins. ECD spectroscopy coupled with computational methods has become an efficient strategy to determine the absolute configurations of discorhabdins. The broad spectrum in vitro bioactivities of discorhabdins, especially their anticancer activity, is another driving force for studying the chemistry of latrunculid sponges. However, many studies, particularly the earlier research, did not report in vitro potency (IC50 or MIC values) of latrunculid sponge metabolites towards cancer cell lines. Similarly, many studies mostly omitted general toxicity assessments against non-cancerous cell lines, hence it is difficult to judge on the selectivity of some bioactive pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids. With the growing number of new and potent natural products from the marine environment, pre-clinical and pharmacokinetic studies on sponge-derived molecules are increasing [154]. To the best of our knowledge, however, no pharmacokinetic investigation has been carried out on any latrunculid sponge metabolite.
The natural origin of (bis)pyrroloiminoquinone-type alkaloids is still in debate. A proposed microbial origin has promoted a series of culture-independent studies on the microbial community of latrunculid sponges, and the predominated Spirochaetae bacteria have been proposed to be responsible for the production of (bis)pyrroloiminoquinone-type alkaloids. However, culture-dependent studies of these Spirochaetae bacteria are still needed to verify the assumption, which could possibly solve the supply issue of (bis)pyrroloiminoquinones. Although facing significant headwinds for further drug development in different therapeutic areas, e.g., the supply issue, the predominated cytotoxicity, and the highly fused structure-property that challenges their total or semisynthesis, latrunculid metabolites, especially discorhabdin-related alkaloids, remain to be interesting targets for drug developments and new discoveries from marine sponges of family Latrunculiidae Topsent, 1922 to continue apace.
Author Contributions
Design and elaboration of the work, D.T. and F.L.; taxonomy and chemotaxonomy of Latrunculiidae, M.K.; writing, F.L. and D.T. with support of M.K.; supervision, D.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge financial support by Land Schleswig-Holstein within the funding program Open Access Publikationsfonds.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, G.; Yu, J.; Zhu, X.; Lin, Y.; Chen, S.; Yuan, J. Statistical research on the bioactivity of new marine natural products discovered during the 28 years from 1985 to 2012. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C. Marine natural products in medicinal chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, W.; Feeney, R.J. Contributions to the study of marine products. XXXII. The nucleosides of sponges. I. J. Org. Chem. 1951, 16, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, W.; Burke, D.C. Contributions to the study of marine products. XXXIX. The nucleosides of sponges. III. Spongothymidine and spongouridine. J. Org. Chem. 1955, 20, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laubenfels, M.W. Sponges of the Western Bahamas. American Museum Novitates; American Museum of Natural History: New York, NY, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- El-Demerdash, A.; Tammam, M.A.; Atanasov, A.G.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Al-Mourabit, A.; Kijjoa, A. Chemistry and biological activities of the marine sponges of the genera Mycale (Arenochalina), Biemna and Clathria. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, P.; Putz, A.; Ortlepp, S.; Kjer, J.; Bayer, M. Bioactive natural products from marine sponges and fungal endophytes. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, J.N.; Van Soest, R.W.M. Systema Porifera. A guide to the classification of sponges. In Systema Porifera; Hooper, J.N.A., Van Soest, R.W.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Brunner, E.; Ehrlich, H.; Schupp, P.; Hedrich, R.; Hunoldt, S.; Kammer, M.; Machill, S.; Paasch, S.; Bazhenov, V.; Kurek, D. Chitin-based scaffolds are an integral part of the skeleton of the marine demosponge Ianthella basta. J. Struct. Biol. 2009, 168, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancheeva, E.; El-Neketi, M.; Song, W.G.; Lin, W.H.; Daletos, G.; Ebrahim, W.; Proksch, P. Structurally unprecedented metabolites from marine sponges. Curr. Org. Chem. 2017, 21, 426–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik, J.R.; Chanas, B.; Toonen, R.J.; Fenical, W. Defenses of Caribbean sponges against predatory reef fish. I. Chemical deterrency. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 127, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2000, 17, 7–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, V.J.; Arthur, K.E.; Ritson-Williams, R.; Ross, C.; Sharp, K. Chemical defenses: From compounds to communities. Biol. Bull. 2007, 213, 226–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radjasa, O.K.; Vaske, Y.M.; Navarro, G.; Vervoort, H.C.; Tenney, K.; Linington, R.G.; Crews, P. Highlights of marine invertebrate-derived biosynthetic products: Their biomedical potential and possible production by microbial associants. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6658–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, J.; Ohlendorf, B.; Blümel, M.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Phylogenetic identification of fungi isolated from the marine sponge Tethya aurantium and identification of their secondary metabolites. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 561–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehbub, M.F.; Perkins, M.V.; Zhang, W.; Franco, C.M. New marine natural products from sponges (Porifera) of the order Dictyoceratida (2001 to 2012); a promising source for drug discovery, exploration and future prospects. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 473–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.H.; Wang, J.M.; Zhou, X.Y.; Wu, W.H.; Guo, R.H. Recent advances on marine alkaloids from sponges. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Pipeline. Available online: https://www.midwestern.edu/departments/marinepharmacology/clinical-pipeline.xml (accessed on 17 November 2020).
- Topsent, É. Les mégasclères polytylotes des Monaxonides et la parenté des Latrunculiines. Bull. Inst. Océanogr. (Monaco) 1922, 415, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hajdu, E.; Desqueyroux-Faundez, R.; Carvalho, M.D.S.; Lobo-Hajdu, G.; Willenz, P. Twelve new Demospongiae (Porifera) from Chilean fjords, with remarks upon sponge-derived biogeographic compartments in the SE Pacific. Zootaxa 2013, 3744, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kelly, M.; Sim-Smith, C.; Stone, R.; Samaai, T.; Reiswig, H.; Austin, W. New taxa and arrangements within the family Latrunculiidae (Demospongiae, Poecilosclerida). Zootaxa 2016, 4121, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza Du Bocage, J. Éponges siliceuses nouvelles du Portugal et de l’île Saint-Iago (Archipel de Cap-Vert). J. Sci. Mat. Phys. nal. Lisbonne 1869, 2, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, E.O. Grundzüge Einer Spongien-Fauna des Atlantischen Gebietes; Wilhelm Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1870. [Google Scholar]
- Lévi, C. Spongiaires du Vema Seamount (Atlantique Sud). Bull. Mus. Natl. Hist. Nat. 1969, 41, 952–973. [Google Scholar]
- Samaai, T.; Kelly, M. Family Latrunculiidae Topsent, 1922. In Systema Porifera; Hooper, J.N.A., Van Soest, R.W.M., Willenz, P., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 708–719. [Google Scholar]
- Samaai, T.; Govender, V.; Kelly, M. Cyclacanthia n.g. (Demospongiae: Poecilosclerida: Latrunculiidae incertea sedis), a new genus of marine sponges from South African waters, and description of two new species. Zootaxa 2004, 725, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Mccombs, J.D.; Munro, M.H.G. Discorhabdin-C, a highly cytotoxic pigment from a sponge of the genus Latrunculia. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 5476–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.M.; Baker, B.J.; Grimwade, J.; Leonard, A.; McClintock, J.B. Discorhabdin alkaloids from the Antarctic sponge Latrunculia apicalis. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furrow, F.B.; Amsler, C.D.; McClintock, J.B.; Baker, B.J. Surface sequestration of chemical feeding deterrents in the Antarctic sponge Latrunculia apicalis as an optimal defense against sea star spongivory. Mar. Biol. 2003, 143, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, E.M.; Beukes, D.R.; Kelly, M.; Samaai, T.; Barrows, L.R.; Marshall, K.M.; Sincich, C.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Cytotoxic pyrroloiminoquinones from four new species of South African latrunculid sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, M.K.; Schinazi, R.F.; Kelly, M.; Stone, R.; Hamann, M.T. Anti-infective pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids from a deep-water Alaskan sponge of the genus Latrunculia. Planta. Med. 2008, 74, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, M.K.; Ding, Y.Q.; Wang, B.; Tekwani, B.L.; Schinazi, R.F.; Franzblau, S.; Kelly, M.; Stone, R.; Li, X.C.; Ferreira, D.; et al. Anti-infective discorhabdins from a deep-water Alaskan sponge of the genus Latrunculia. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botic, T.; Defant, A.; Zanini, P.; Zuzek, M.C.; Frangez, R.; Janussen, D.; Kersken, D.; Knez, Z.; Mancini, I.; Sepcic, K. Discorhabdin alkaloids from Antarctic Latrunculia spp. sponges as a new class of cholinesterase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lill, R.E.; Major, D.A.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G.; Battershill, C.N.; Mclean, M.G.; Baxter, R.L. Studies on the biosynthesis of discorhabdin-B in the New-Zealand sponge Latrunculia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.; Alvarez, B.; Battershill, C.; Northcote, P.; Parthasarathy, H. Genetic, morphological, and chemical divergence in the sponge genus Latrunculia (Porifera: Demospongiae) from New Zealand. Mar. Biol. 2001, 139, 235–250. [Google Scholar]
- Copp, B.R.; Ireland, C.M.; Barrows, L.R. Wakayin-a novel cytotoxic pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloid from the ascidian Clavelina species. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 4596–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radisky, D.C.; Radisky, E.S.; Barrows, L.R.; Copp, B.R.; Kramer, R.A.; Ireland, C.M. Novel cytotoxic topoisomerase-II inhibiting pyrroloiminoquinones from Fijian sponges of the genus Zyzzya. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Iwasaki, T.; Imai, S.; Sakamoto, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ito, A. Laboratory culture of the myxomycetes: Formation of fruiting bodies of Didymium bahiense and its plasmodial production of makaluvamine A. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, M.; Capon, R.J. Discorhabdins revisited: Cytotoxic alkaloids from southern Australian marine sponges of the genera Higginsia and Spongosorites. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinski, J.C.J.; Waterworth, S.C.; Noundou, X.S.; Jiwaji, M.; Parker-Nance, S.; Krause, R.W.M.; McPhail, K.L.; Dorrington, R.A. Molecular networking reveals two distinct chemotypes in pyrroloiminoquinone-producing Tsitsikamma favus sponges. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaai, T.; Ngwakum, B.; Payne, R.; Teske, P.R.; Janson, L.; Kerwath, S.; Parker, D.; Kelly, M.; Gibbons, M.J. New Latrunculiidae (Demospongiae, Poecilosclerida) from the Agulhas ecoregion of temperate southern Africa. Zootaxa 2020, 4896, 409–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampella, A.; Randazzo, A.; Borbone, N.; Luciani, S.; Trevisi, L.; Debitus, U.; D'Auria, M.V. Isolation of callipeltins A-C and of two new open-chain derivatives of callipeltin A from the marine sponge Latrunculia sp. and a revision of the stereostructure of callipeltins. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 6163–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; D'Orsi, R.; Borbone, N.; D'Auria, M.V.; Bifulco, G.; Monti, M.C.; Catania, A.; Zampella, A. Callipeltins F-I: New antifungal peptides from the marine sponge Latrunculia sp. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Auria, M.V.; Sepe, V.; D'Orsi, R.; Bellotta, F.; Debitus, C.; Zampella, A. Isolation and structural elucidation of callipeltins J-M: Antifungal peptides from the marine sponge Latrunculia sp. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashman, Y.; Groweiss, A.; Lidor, R.; Blasberger, D.; Carmely, S. Latrunculins: NMR study, two new toxins and a synthetic approach. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.S.; Capon, R.J. Trunculin F and contrunculin A and contrunculin B: Novel oxygenated norterpenes from a southern Australian marine sponge, Latrunculia conulosa. Aust. J. Chem. 1993, 46, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovenden, S.P.B.; Capon, R.J. Trunculins G-I: New norsesterterpene cyclic peroxides from a southern Australian marine sponge, Latrunculia sp. Aust. J. Chem. 1998, 51, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaai, T.; Krasokhin, V. Latrunculia oparinae n. sp. (Demospongiae, Poecilosclerida, Latrunculiidae) from the Kurile Islands, Sea of Okhotsk, Russia. Beaufortia 2002, 52, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, E.M.; Copp, B.R.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Samaai, T. Pyrroloiminoquinone and related metabolites from marine sponges. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaai, T.; Gibbons, M.J.; Kelly, M. Revision of the genus Latrunculia du Bocage, 1869 (Porifera: Demospongiae: Latrunculiidae) with descriptions of new species from New Caledonia and the Northeastern Pacific. Zootaxa 2006, 1127, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubenfels, M. A discussion of the sponge fauna of the Dry Tortugas in particular, and the West Indies in general, with materials for a revision of the families and orders of the Porifera.- Pap. Tortugas Lab. 1936, 467, 1–225. [Google Scholar]
- Sollas, W.J. A Classification of the Sponges. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1885, 16, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, P.; Perez, T.; Boury-Esnault, N. Sponge systematics facing new challenges. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2012, 61, 79–209. [Google Scholar]
- Topsent, É.; I, A. Spongiaires de l'Atlantique et de la Méditerranée, provenant des croisières du Prince Albert 1er de Monaco. Imprimerie de Monaco 1928, 74, 1–376. [Google Scholar]
- Morrow, C.; Cárdenas, P. Proposal for a revised classification of the Demospongiae (Porifera). Front. Zool. 2015, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaai, T.; Gibbons, M.J.; Kelly, M.; Davies-Coleman, M. South African Latrunculiidae (Porifera: Demospongiae: Poecilosclerida): Descriptions of new species of Latrunculia du Bocage, Strongylodesma Levi, and Tsitsikamma Samaai & Kelly. Zootaxa 2003, 371, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Samaai, T.; Gibbons, M.J.; Kelly, M. A revision of the genus Strongylodesma Levi (Porifera: Demospongiae: Latrunculiidae) with descriptions of four new species. J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. UK 2009, 89, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaai, T.; Janson, L.; Kelly, M. New species of Latrunculia from the Agulhas shelf, South Africa, with designation of a type species for subgenus Biannulata (Demospongiae, Poecilosclerida, Latrunculiidae). Zootaxa 2012, 3395, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.; Goudie, L. Bridging the gap: First record of sponge genus Strongylodesma in Australian waters. Zootaxa 2020, 4808, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topsent, E. Nouvelle série de diagnoses d’éponges de Roscoff et de Banyuls. Arch. Zool. Exp. Gen. 1893, 3, 33–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, R. Porifera (sponges). II. Tetraxonida, Dendy. Natl. Antarct. Exped. Nat. Hist. 1908, 4, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ridley, S.O.; Dendy, A. XXXIV.—Preliminary Report on the Monaxonida collected by HMS ‘Challenger’. J. Nat Hist. 1886, 18, 325–351. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, B.; Bergquist, P.R.; Battershill, C.N. Taxonomic revision of the genus Latrunculia Du Bocage (Porifera: Demospongiae: Latrunculiidae) in New Zealand. New Zeal. J. Mar. Fresh 2002, 36, 151–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, H. XXXVI.—Supplementary report on specimens dredged up from the Gulf Manaar, together with others from the sea in the vicinity of the Basse Rocks and from Bass's Straits respectively, presented to the Liverpool Free Museum by Capt. H. Cawne Warren. J. Nat Hist. 1881, 7, 361–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacelet, J. Eponges de la roche du large et de l'étage bathyal de Méditerranée: Récoltes de la soucoupe plongeante Cousteau et dragages. Memoir. Mus. Natl. Hist. 1969, 59, 145–219. [Google Scholar]
- Genta-Jouve, G.; Francezon, N.; Puissant, A.; Auberger, P.; Vacelet, J.; Perez, T.; Fontana, A.; Al Mourabit, A.; Thomas, O.P. Structure elucidation of the new citharoxazole from the Mediterranean deep-sea sponge Latrunculia (Biannulata) citharistae. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.J.; Janussen, D.; Peifer, C.; Perez-Victoria, I.; Tasdemir, D. Targeted isolation of tsitsikammamines from the Antarctic deep-sea sponge Latrunculia biformis by molecular networking and anticancer activity. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.F.; Fan, H.; Xiong, J.; Wu, S.B. Discorhabdins and pyrroloiminoquinone-related alkaloids. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5465–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G. Cytotoxic pigments from New Zealand sponges of the genus Latrunculia–discorhabdin A, discorhabdin B and discorhabdin C. Tetrahedron 1988, 44, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijoux, M.G.; Gamble, W.R.; Hallock, Y.F.; Cardellina, J.H.; van Soest, R.; Boyd, M.R. A new discorhabdin from two sponge genera. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 636–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G.; Higa, T.; Sakai, R. Discorhabdin D, an antitumor alkaloid from the sponges Latrunculia brevis and Prianos sp. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 4127–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, F.; Martin, R.; Rueda, A.; Fernandez, R.; Montalvo, D.; Gomez, C.; Sanchez-Puelles, J.M. Discorhabdins I and L, cytotoxic alkaloids from the sponge Latrunculia brevis. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.J.; Peifer, C.; Janussen, D.; Tasdemir, D. New discorhabdin alkaloids from the Antarctic deep-sea sponge Latrunculia biformis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovic, T.; Ding, Y.Q.; Li, X.C.; Webb, V.L.; Ferreira, D.; Copp, B.R. Enantiomeric discorhabdin alkaloids and establishment of their absolute configurations using theoretical calculations of electronic circular dichroism spectra. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 9133–9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovic, T.; Pearce, A.N.; Munro, M.H.G.; Blunt, J.W.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Copp, B.R. Isolation and characterization of diastereomers of discorhabdins H and K and assignment of absolute configuration to discorhabdins D, N, Q, S, T, and U. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, G.; Pinkert, A.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G. Discorhabdin W, the first dimeric discorhabdin. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1796–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goey, A.K.L.; Chau, C.H.; Sissung, T.M.; Cook, K.M.; Venzon, D.J.; Castro, A.; Ransom, T.R.; Henrich, C.J.; McKee, T.C.; McMahon, J.B.; et al. Screening and biological effects of marine pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids: Potential inhibitors of the HIF-1α/p300 interaction. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.F.; Cadelis, M.M.; Copp, B.R. Exploration of the electrophilic reactivity of the cytotoxic marine alkaloid discorhabdin C and subsequent discovery of a new dimeric C-1/N-13-linked discorhabdin natural product. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.J.; Pandey, P.; Janussen, D.; Chittiboyina, A.G.; Ferreira, D.; Tasdemir, D. Tridiscorhabdin and didiscorhabdin, the first discorhabdin oligomers linked with a direct C–N bridge from the sponge Latrunculia biformis collected from the deep sea in Antarctica. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copp, B.R.; Fulton, K.F.; Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G. Natural and synthetic derivatives of discorhabdin-C, a cytotoxic pigment from the New-Zealand sponge Latrunculia cf Bocagei. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 8233–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.; Munro, M.G.; Battershill, C.; Copp, B.; McCombs, J. From the antarctic to the antipodes: 45°of marine chemistry. New. J. Chem. 1990, 14, 761–775. [Google Scholar]
- Urban, S.; Hickford, S.; Blunt, J.; Munro, M. Bioactive marine alkaloids. Curr. Org. Chem. 2000, 4, 765–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendy, A. Report on the Sigmatotetraxonida collected by HMS “Sealark” in the Indian Ocean. Trans. Linn. Soc. Lond. Zool. (2nd) 1922, 18, 1–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, H. XXXIII.—Contributions to our knowledge of the Spongida. J. Nat. Hist. 1879, 3, 284–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; McCarthy, P.J.; Longley, R.E.; Pomponi, S.A.; Wright, A.E.; Lobkovsky, E.; Clardy, J. Discorhabdin P, a new enzyme inhibitor from a deep-water Caribbean sponge of the genus Batzella. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.; Capon, R.J. Discorhabdin R: A new antibacterial Pyrroloiminoquinone from two latrunculiid marine sponges, Latrunculia sp and Negombata sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1527–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grkovic, T.; Copp, B.R. New natural products in the discorhabdin A-and B-series from New Zealanlsourced Latrunculia spp. sponges. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 6335–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makar'eva, T.N.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Guzii, A.G.; Stonik, V.A. Strong ethanol solvate of discorhabdin A isolated from the far-east sponge Latruculia oparinae. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2010, 46, 152–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.K.; Hamann, M.T. Atkamine: A new pyrroloiminoquinone scaffold from the cold water Aleutian Islands Latrunculia sponge. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.K.; Wang, X.J.; Sims, J.; Wang, B.; Pandey, P.; Welsh, C.L.; Stone, R.P.; Avery, M.A.; Doerksen, R.J.; Ferreira, D.; et al. Computationally assisted discovery and assignment of a highly strained and PANC-1 selective alkaloid from Alaska's deep ocean. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4338–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.I.; Cheng, J.F.; Ishibashi, M.; Nakamura, H.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Lu, H.; Clardy, J. Prianosin A, a novel antileukemic alkaloid from the Okinawan marine sponge Prianos melanos. Tetrahedron Lett. 1987, 28, 4939–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; De Marzo, A.M.; Laughner, E.; Lim, M.; Hilton, D.A.; Zagzag, D.; Buechler, P.; Isaacs, W.B.; Semenza, G.L.; Simons, J.W. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5830–5835. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, H.S.; Kim, D.-R.; Yang, E.G.; Park, Y.K.; Ahn, H.C.; Min, S.J.; Ahn, D.R. Inhibition of VEGF transcription through blockade of the hypoxia inducible factor 1α-p300 interaction by a small molecule. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 5249–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burslem, G.M.; Kyle, H.F.; Breeze, A.L.; Edwards, T.A.; Nelson, A.; Warriner, S.L.; Wilson, A.J. Small-molecule proteomimetic inhibitors of the HIF-1α–p300 protein–protein interaction. Chembiochem 2014, 15, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, K.M.; Richardson, E.D.; Cook, K.M.; Campbell, T.J.; Pisle, S.T.; Holly, A.J.; Venzon, D.J.; Liewehr, D.J.; Chau, C.H.; Price, D.K. Epidithiodiketopiperazines (ETPs) exhibit in vitro antiangiogenic and in vivo antitumor activity by disrupting the HIF-1α/p300 complex in a preclinical model of prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, E.M.; Strope, J.D.; Beedie, S.L.; Huang, P.A.; Goey, A.K.L.; Cook, K.M.; Schofield, C.J.; Chau, C.H.; Cadelis, M.M.; Copp, B.R.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of discorhabdins in antiangiogenic and antitumor models. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.F.C.; Grkovic, T.; Pearce, A.N.; Copp, B.R. Investigation of the electrophilic reactivity of the cytotoxic marine alkaloid discorhabdin B. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 3092–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.J.; Janussen, D.; Tasdemir, D. New discorhabdin B dimers with anticancer activity from the Antarctic deep-sea sponge Latrunculia biformis. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, G.J.; DaviesColeman, M.T.; KellyBorges, M.; Coetzee, P.S. New alkaloids from a South African latrunculid sponge. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7135–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A.; Buchanan, M.S.; Duffy, S.; Avery, V.M.; Charman, S.A.; Charman, W.N.; White, K.L.; Shackleford, D.M.; Edstein, M.D.; Andrews, K.T.; et al. Antimalarial activity of pyrroloiminoquinones from the Australian marine sponge Zyzzya sp. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 5851–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierhof, M.; Hansen, K.Ø.; Sharma, M.; Feussner, K.; Subko, K.; Díaz-Rullo, F.F.; Isaksson, J.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Clarke, D.; Hansen, E. New cytotoxic callipeltins from the Solomon Island marine sponge Asteropus sp. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 6929–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, R.W.; Hooper, J.N.; Butler, P.J. Every sponge own its name: Removing Porifera homonyms. Zootaxa 2020, 4745, 1–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sollas, W.J. Report on the Tetractinellida collected by HMS Challenger during the years 1873-1876. Rept. Sci. Res. HMS Chall. 1888, 25, 1–458. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, W. Ideen über die Verwandtschaftsverhältnisse der Hexactinelliden. Z. Wiss. Zool. 1876, 27, 113–136. [Google Scholar]
- D'Auria, M.V.; Zampella, A.; Paloma, L.G.; Minale, L.; Debitus, C.; Roussakis, C.; Le Bert, V. Callipeltins B and C: Bioactive peptides from a marine Lithistida sponge Callipelta sp. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 9589–9596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampella, A.; D'Auria, M.V.; Paloma, L.G.; Casapullo, A.; Minale, L.; Debitus, C.; Henin, Y. Callipeltin A, an anti-HIV cyclic depsipeptide from the New Caledonian Lithistida sponge Callipelta sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 6202–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisi, L.; Bova, S.; Cargnelli, G.; Danieli-Betto, D.; Floreani, M.; Germinario, E.; D'Auria, M.; Luciani, S. Callipeltin A, a cyclic depsipeptide inhibitor of the cardiac sodium–calcium exchanger and positive inotropic agent. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 279, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, R.J.; Macleod, J.K. Structural and stereochemical studies on marine norterpene cyclic peroxides. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 3391–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Macleod, J.K.; Willis, A.C. Trunculin A and trunculin B, norsesterterpene cyclic peroxides from a marine sponge, Latrunculia brevis. J. Org. Chem. 1987, 52, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.S.; Capon, R.J. Norterpene dienes from an Australian marine sponge Latrunculia brevis. Aust. J. Chem. 1991, 44, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.S.; Capon, R.J. Conulosins (A and B): Novel norsesterterpene acids from an Australian marine sponge, Latrunculia conulosa. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1992, 1, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.Y.; Faulkner, D.J.; Lu, H.S.; Clardy, J. Norsesterterpene peroxides from the sponge Latrunculia sp. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 2112–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, M. Sponges. Sci. Rep. Gt. Barrier Reef Exped 1928-29 1934, 4, 513–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheenpracha, S.; Park, E.J.; Rostama, B.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Chang, L.C. Inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells by the norsesterterpene peroxide, epimuqubilin A. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly-Borges, M.; Vacelet, J. A revision of Diacamus Burton and Negombata de Laubenfels (Demospongiae: Latrunculiidae) with descriptions of new species from the west central Pacific and the Red Sea. Mem. Queensl. Mus. 1995, 38, 477–504. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, C. Die Spongienfauna des Rothen Meeres. Z. Wiss Zool. 1889, 48, 311–405. [Google Scholar]
- Kashman, Y.; Groweiss, A.; Shmueli, U. Latrunculin, a new 2-thiazolidinone macrolide from the marine sponge Latrunculia magnifica. Tetrahedron Lett. 1980, 21, 3629–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groweiss, A.; Shmueli, U.; Kashman, Y. Marine toxins of Latrunculia magnifica. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 3512–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasberger, D.; Carmely, S.; Cojocaru, M.; Spector, I.; Shochet, N.R. On the chemistry of latrunculins A and B. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1989, 12, 1171–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaai, T.; Keyzers, R.; Davies-Coleman, M. A new species of Strongylodesma Levi, 1969 (Porifera; Demospongiae; Poecilosclerida; Latrunculiidae) from Aliwal Shoal on the east coast of South Africa. Zootaxa 2004, 584, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.F.; Ohizumi, Y.; Walchli, M.R.; Nakamura, H.; Hirata, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Prianosins B, C, and D, novel sulfur-containing alkaloids with potent antineoplastic activity from the Okinawan marine sponge Prianos melanos. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 4621–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.I.; Cheng, J.F.; Yamamura, S.; Ishibashi, M. Revised structures of prianosins C and D, antineoplastic alkaloids from the Okinawan marine sponge Prianos melanos. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 1227–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; Zuleta, I.A.; Longley, R.E.; Wright, A.E.; Pomponi, S.A. Discorhabdins S, T, and U, new cytotoxic pyrroloiminoquinones from a deep-water Caribbean sponge of the genus Batzella. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1615–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakemi, S.; Sun, H.H.; Jefford, C.W.; Bernardinelli, G. Batzellines A, B, and C: Novel pyrroloquinoline alkaloids from the sponge Batzella sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 2517–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.H.; Sakemi, S.; Burres, N.; McCarthy, P. Isobatzellines A, B, C, and D: Cytotoxic and antifungal pyrroloquinoline alkaloids from the marine sponge Batzella sp. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 4964–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyzers, R.A.; Samaai, T.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Novel pyrroloquinoline ribosides from the South African latrunculid sponge Strongylodesma aliwaliensis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 9415–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyzers, R.A.; Arendse, C.E.; Hendricks, D.T.; Samaai, T.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Makaluvic acids from the South African latrunculid sponge Strongylodesma aliwaliensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taufa, T.; Gordon, R.M.A.; Hashmi, M.A.; Hira, K.; Miller, J.H.; Lein, M.; Fromont, J.; Northcote, P.T.; Keyzers, R.A. Pyrroloquinoline derivatives from a Tongan specimen of the marine sponge Strongylodesma tongaensis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 60, 1825–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker-Nance, S.; Hilliar, S.; Waterworth, S.; Walmsley, T.; Dorrington, R. New species in the sponge genus Tsitsikamma (Poecilosclerida, Latrunculiidae) from South Africa. ZooKeys 2019, 874, 101–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topsent, E. Contribution à l'étude des Spongiaires de l'Atlantique Nord (Golfe de Gascogne, Terre-Neuve, Açores). Résultats des campagnes scientifiques accomplies par le Prince Albert I. Monaco 1892, 2, 1–165. [Google Scholar]
- Topsent, E. Notice préliminaire sur les spongiaires recueillis durant les campagnes de l'Hirondelle. Bull. Soc. Zool. Fr. 1890, 15, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Antunes, E.M.; Beukes, D.R.; Samaai, T. Colourful chemistry of South African latrunculid sponges. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2019, 115, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.E.; Na, Z.; Jung, M.; Lee, H.S.; Sim, C.J.; Nahm, K.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Discorhabdins from the Korean marine sponge Sceptrella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, E. Die Kiesel-und Hornschwämme des Nördlichen Eismeers. Fauna Arct. 1929, 5, 859–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, C. Microbial associations in sponges. I. Ecology, physiology and microbial populations of coral reef sponges. Mar. Biol. 1978, 49, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C. Microbial associations in sponges. II. Numerical analysis of sponge and water bacterial populations. Mar. Biol. 1978, 49, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C. Microbial associations in sponges. III. Ultrastructure of the in-situ associations in coral reef sponges. Mar. Biol. 1978, 49, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.R.; Nowak, M.; Austin, B.; Colwell, R.R. Specificity of bacterial symbionts in Mediterranean and Great Barrier Reef sponges. Microb. Ecol. 1981, 7, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacelet, J.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Fiala-Medioni, A.; Fisher, C. A methanotrophic carnivorous sponge. Nature 1995, 377, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.; Obraztsova, A.; Davidson, S.; Faulkner, D.; Haygood, M. Identification of the antifungal peptide-containing symbiont of the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei as a novel δ-proteobacterium, “Candidatus Entotheonella palauensis”. Mar. Biol. 2000, 136, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubart, K.M.; Heathcock, C.H. A biomimetic approach to the discorhabdin alkaloids: Total syntheses of discorhabdins C and E and dethiadiscorhabdin D. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walmsley, T.A.; Matcher, G.F.; Zhang, F.; Hill, R.T.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Dorrington, R.A. Diversity of bacterial communities associated with the Indian Ocean sponge Tsitsikamma favus that contains the bioactive pyrroloiminoquinones, tsitsikammamine A and B. Mar. Biotechnol. 2012, 14, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matcher, G.F.; Waterworth, S.C.; Walmsley, T.A.; Matsatsa, T.; Parker-Nance, S.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Dorrington, R.A. Keeping it in the family: Coevolution of latrunculid sponges and their dominant bacterial symbionts. Microbiologyopen 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, J.I.; Head, I.M.; Stein, L.Y. The family nitrosomonadaceae. In The Prokaryotes: Alphaproteobacteria and Betaproteobacteria; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer Berlin/Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 901–918. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M.; Samaai, T. Family Podospongiidae de Laubenfels, 1936. In Systema Porifera; Hooper, J.N.A., Van Soest, R.W.M., Willenz, P., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 694–702. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, J. Notes on the arrangement of sponges, with the descriptions of some new genera. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1867, 2, 492–558. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, O. Die Spongien des Adriatischen Meeres, 1st ed.; Wilhelm Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1862. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, H. XLVII.—New genus of sponges. J. Nat. Hist. 1883, 11, 369–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambe, L.M. Sponges from the western coast of North America. Proc. Trans. R. Soc. Can. 1894, 12, 113–138. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.B.; Tuan, N.Q.; Oh, J.; Son, Y.; Hamann, M.T.; Stone, R.; Kelly, M.; Oh, S.; Na, M. Sesterterpenoid and steroid metabolites from a deep-water Alaska sponge inhibit Wnt/β-catenin signaling in colon cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, J. Studien über pazifische Spongien. Zoologica 1899, 24, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, A.L.; Peraud, O.; Kasanah, N.; Sims, J.W.; Kothalawala, N.; Anderson, M.A.; Abbas, S.H.; Rao, K.V.; Jupally, V.R.; Kelly, M. An analysis of the sponge Acanthostrongylophora igens' microbiome yields an actinomycete that produces the natural product manzamine A. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, R.; Kelly-Borges, M. Biochemical and morphological heterogeneity in the Caribbean sponge Xestospongia muta (Petrosida: Petrosiidae). In Sponges in Time and Space; Van Soest, R.W.M., VanKempen, T.M.G., Braekman, J.C., Eds.; Balkema: Rotterdam, Netherlands, 1994; pp. 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Shikov, A.N.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N. Pharmacokinetics of marine-derived drugs. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).