Light-Mediated Toxicity of Porphyrin-Like Pigments from a Marine Polychaeta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemical Characterization of Pigments
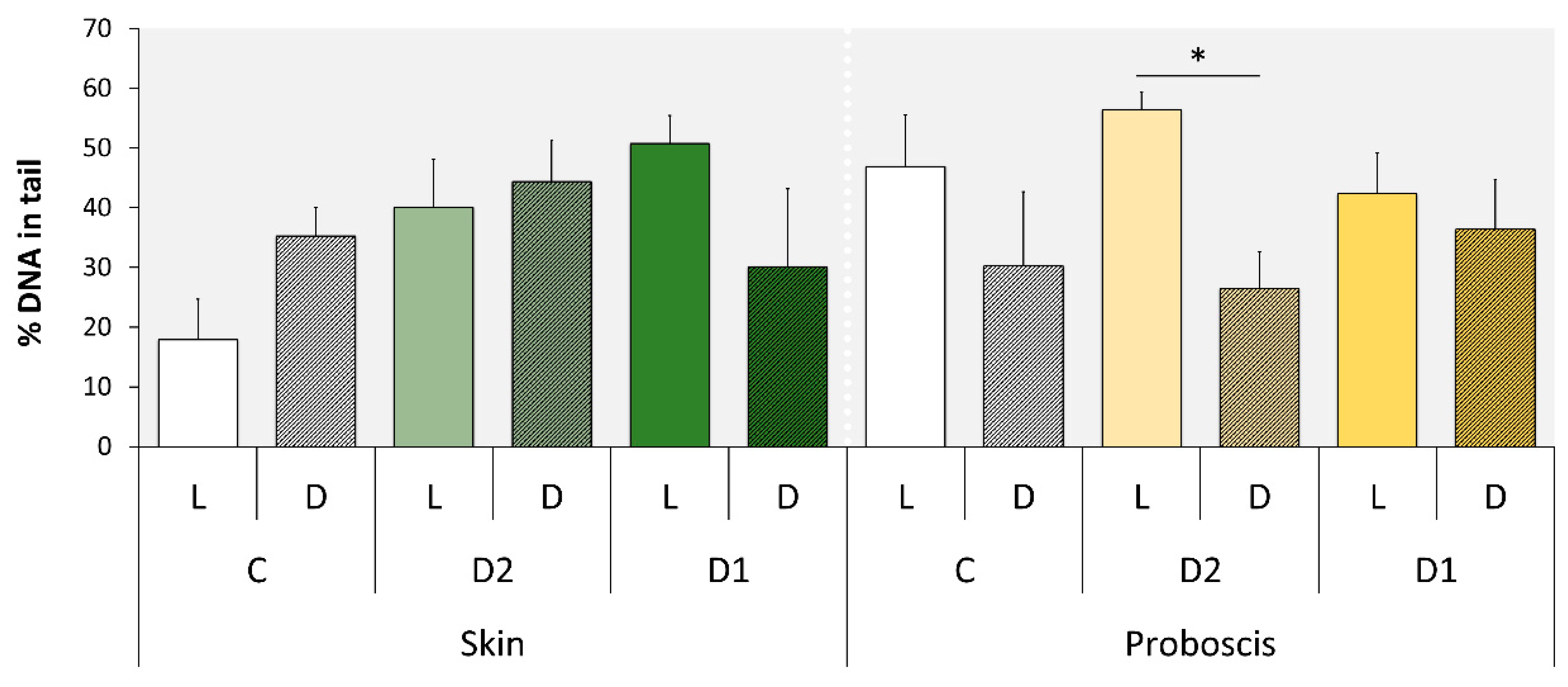
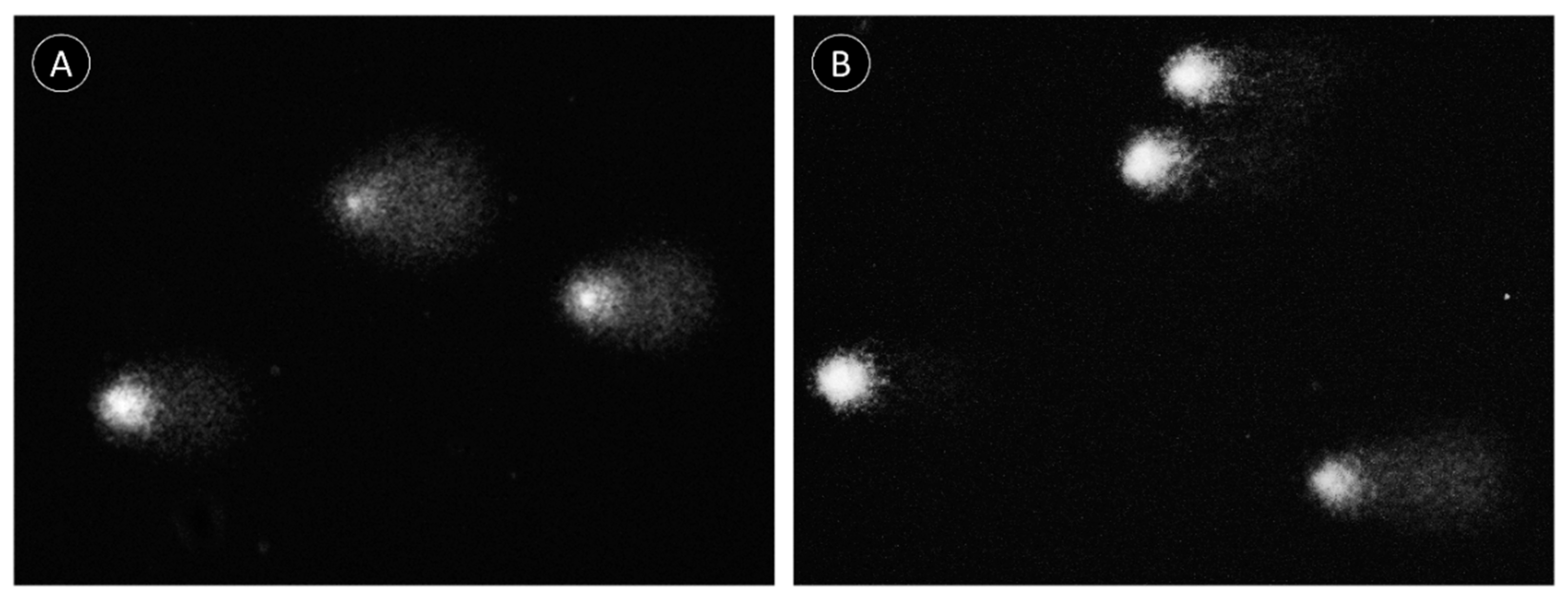
2.2. Comet Assay
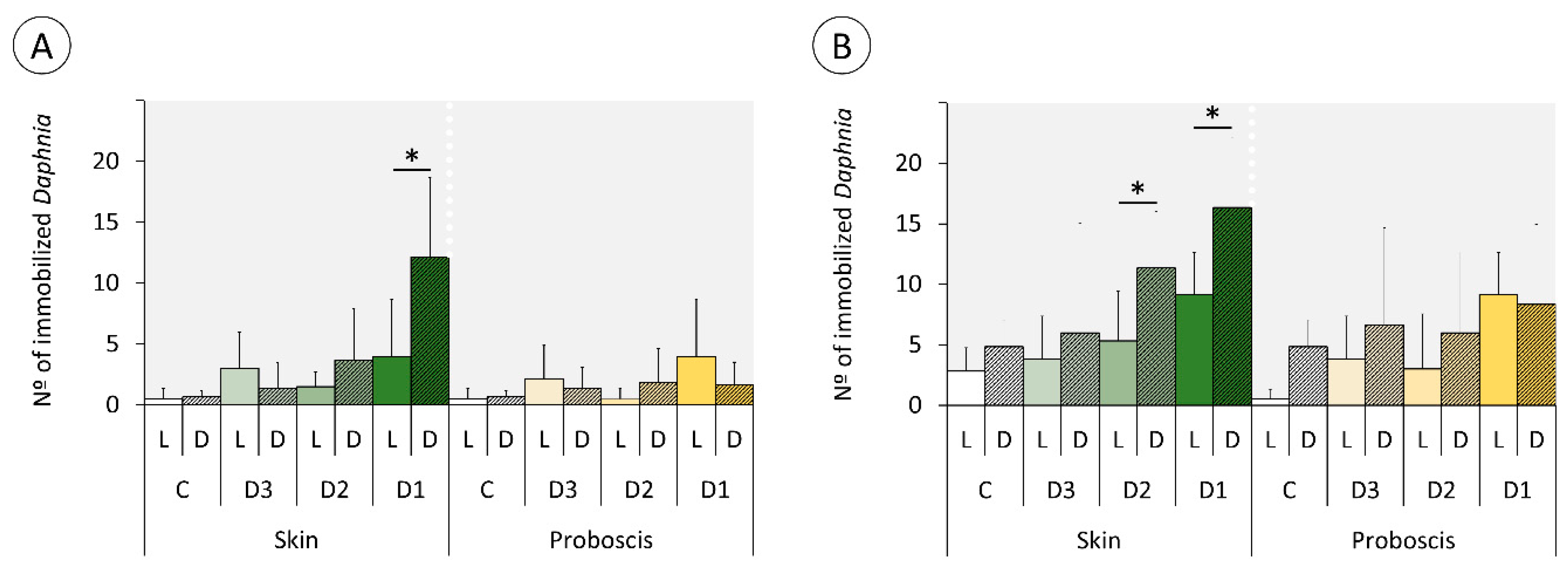
2.3. Daphnia Immobilization Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Pigment Extraction
4.3. Chemical Characterization of Pigments
4.4. Experimental Design
4.4.1. Assays with Mytilus sp. Gills
4.4.2. Comet Assay
4.4.3. Acute Toxicity Assay with Daphnia pulex
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diamond, J. Concealing Coloration in Animals; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; 288p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, A.E. The Significance of Zoochromes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1974; 429p. [Google Scholar]
- Milgrom, L.R. The Colours of Life. An introduction to the Chemistry of Porphyrins and Related Compounds; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997; 256p. [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto, J.Y.; Chang, C.T.; Chen, D.; Hinton, G. Heme-derived bilins. Isr. J. Chem. 2019, 59, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandaranayake, W.M. The nature and role of pigments of marine invertebrates. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 223–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulmer, A.C.; Ried, K.; Blanchfield, J.T.; Wagner, K.H. The anti-mutagenic properties of bile pigments. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2008, 658, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnett, R.; Berenbaum, M. Porphyrins as photosensitizers. Ciba Found. Symp. 1989, 146, 40–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaut, L.G. Design of porphyrin-based photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 63, 187–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.M.; Sibrian-Vazquez, M.; Vicente, M.G.H. Design and synthesis of photosensitizer-peptide conjugates for PDT. In Handbook of Photodynamic Therapy Updates on Recent Applications of Porphyrin-Based Compounds; Pandey, R.K., Kessel, D., Dougherty, T.J., Eds.; World Scientific: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 45–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-O.; Ha, K.-S. New insights into the mechanisms for photodynamic therapy-induced cancer cell death. In International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology; Jeon, K.W., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 295, pp. 139–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Amor, T.; Jori, G. Sunlight-activated insecticides: Historical background and mechanisms of phototoxic activity. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 30, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozja, J.; Sherrill, J.; Michielsen, S.; Stojiljkovic, I. Porphyrin-based, light-activated antimicrobial materials. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2003, 41, 2297–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, S.; Fossi, M.C.; Leonzio, C.; Renzoni, A. Porphyrins as biomarkers for hazard assessment of bird populations: Destructive and non-destructive use. Ecotoxicology 2003, 12, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schembri, P.J.; Jaccarini, V. Evidence of a chemical defence mechanism in the echiuran worm Bonellia viridis Rolando (Echiura: Bonelliidae). Mar. Behav. Physiol. 1979, 6, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelter, A.; Ballantine, J.A.; Ferrito, V.; Jaccariki, V.; Psaila, A.F.; Schembr, P.J. Bonellin, a most Unusual Chlorin. J. Chem. Soc. 1976, 999–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dales, R.P.; Kennedy, G.Y. On the diverse colours of Nereis diversicolor. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK 1954, 33, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.M.; Carrapiço, F.; Alves de Matos, A.P.; Costa, M.H. A microscopical study of the “chlorophylloid” pigment cells of the marine polychaete Eulalia viridis (L.). Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, A.P.; Costa, M.H.; Alves De Matos, A.P.; Carrapiço, F.; Costa, P.M. A Study on the digestive physiology of a marine polychaete (Eulalia viridis) through microanatomical changes of epithelia during the digestive cycle. Microsc. Microanal. 2015, 21, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, A.P.; Martins, C.; Costa, M.H.; Alves de Matos, A.P.; Costa, P.M. A morphoanatomical approach to the adaptive features of the epidermis and proboscis of a marine Polychaeta: Eulalia viridis (Phyllodocida: Phyllodocidae). J. Anat. 2018, 233, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Rodrigo, A.P.; Cabrita, L.; Henriques, P.; Parola, A.J.; Costa, P.M. The complexity of porphyrin-like pigments in a marine annelid sheds new light on haem metabolism in aquatic invertebrates. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, N.; Martins, M.; Rodrigo, A.P.; Martins, C.; Costa, P.M. Explorations on the ecological role of toxin secretion and delivery in jawless predatory Polychaeta. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malatesti, N.; Munitic, I.; Jurak, I. Porphyrin-based cationic amphiphilic photosensitisers as potential anticancer, antimicrobial and immunosuppressive agents. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisch, T.; Baier, J.; Franz, B.; Maier, M.; Landthaler, M.; Szeimies, R.M.; Bäumler, W. The role of singlet oxygen and oxygen concentration in photodynamic inactivation of bacteria. PNAS 2007, 104, 7223–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanat, J.L.; Sauvaigo, S.; Caillat, S.; Martinez, G.R.; Medeiros, M.H.G.; Di Mascio, P.; Favier, A.; Cadet, J. Singlet oxygen-mediated damage to cellular DNA determined by the comet assay associated with DNA repair enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 385, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, M.G.H.; Nurco, D.J.; Shetty, S.J.; Osterloh, J.; Ventre, E.; Hedge, V.; Deutsch, W.A. Synthesis, dark toxicity and induction of in vitro DNA photodamage by a tetra(4-nido-carboranylphenyl)porphyrin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2002, 68, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckl, D.B.; Dengler, L.; Nemmert, M.; Eichner, A.; Bäumler, W.; Huber, H. A closer look at dark toxicity of the photosensitizer TMPyP in bacteria. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamkemeyer, T.; Zeis, B.; Decker, H.; Jaenicke, E.; Waschbüsch, D.; Gebauer, J.; Meissner, U.; Rousselot, M.; Zal, F.; Nicholson, G.J.; et al. Molecular mass of macromolecules and subunits and the quaternary structure of hemoglobin from the microcrustacean Daphnia magna. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 3393–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabris, C.; Soncin, M.; Jori, G.; Hablueetzel, A.; Lucantoni, L.; Sawadogo, S.; Guidolin, L.; Coppellotti, O. Effects of a new photoactivatable cationic porphyrin on ciliated protozoa and branchiopod crustaceans, potential components of freshwater ecosystems polluted by pathogenic agents and their vectors. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2012, 11, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangum, C.P.; Phillips Dales, R. Products of haem synthesis in polychaetes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1965, 15, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegri, V.; Gorbi, G.; Buschini, A. Comet assay on Daphnia magna in eco-genotoxicity testing. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 155, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, V.S.V.; Silveira, E.; Pereira, B.B. Ecotoxicological assessment of synthetic and biogenic surfactants using freshwater cladoceran species. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, J.S.; Simmonds, P.L. HPLC Methods for analysis of porphyrins in biological media. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2001, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; McCoy, M.T.; Tice, R.R.; Schneider, E.L. A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1988, 175, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimundo, J.; Costa, P.M.; Vale, C.; Costa, M.H.; Moura, I. DNA damage and metal accumulation in four tissues of feral Octopus vulgaris from two coastal areas in Portugal. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1543–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Costa, P.M. Technical updates to the Comet assay in vivo for assessing DNA damage in zebrafish embryos from fresh and frozen cell suspensions. Zebrafish 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.F.; Steinert, S. Use of the single cell gel electrophoresis/comet assay for detecting DNA damage in aquatic (marine and freshwater) animals. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2003, 544, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adema, D.M.M. Daphnia magna as a test animal in acute and chronic toxicity tests. Hydrobiologia 1978, 59, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persoone, G.; Baudo, R.; Cotman, M.; Blaise, C.; Thompson, K.C.; Vollat, B.; Törökne, A.; Han, T. Review on the acute Daphnia magna toxicity test—Evaluation of the sensitivity and the precision of assays performed with organisms from laboratory cultures or hatched from dormant eggs. Knowl. Managt. Aquatic Ecosyst. 2009, 393, 01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Ecological Effects Test Guidelines OCSPP 850.1010: Aquatic Invertebrate Acute Toxicity Test, Freshwater Daphnids; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Ihaka, R.; Gentleman, R.R. A Language for Data Analysis and Graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
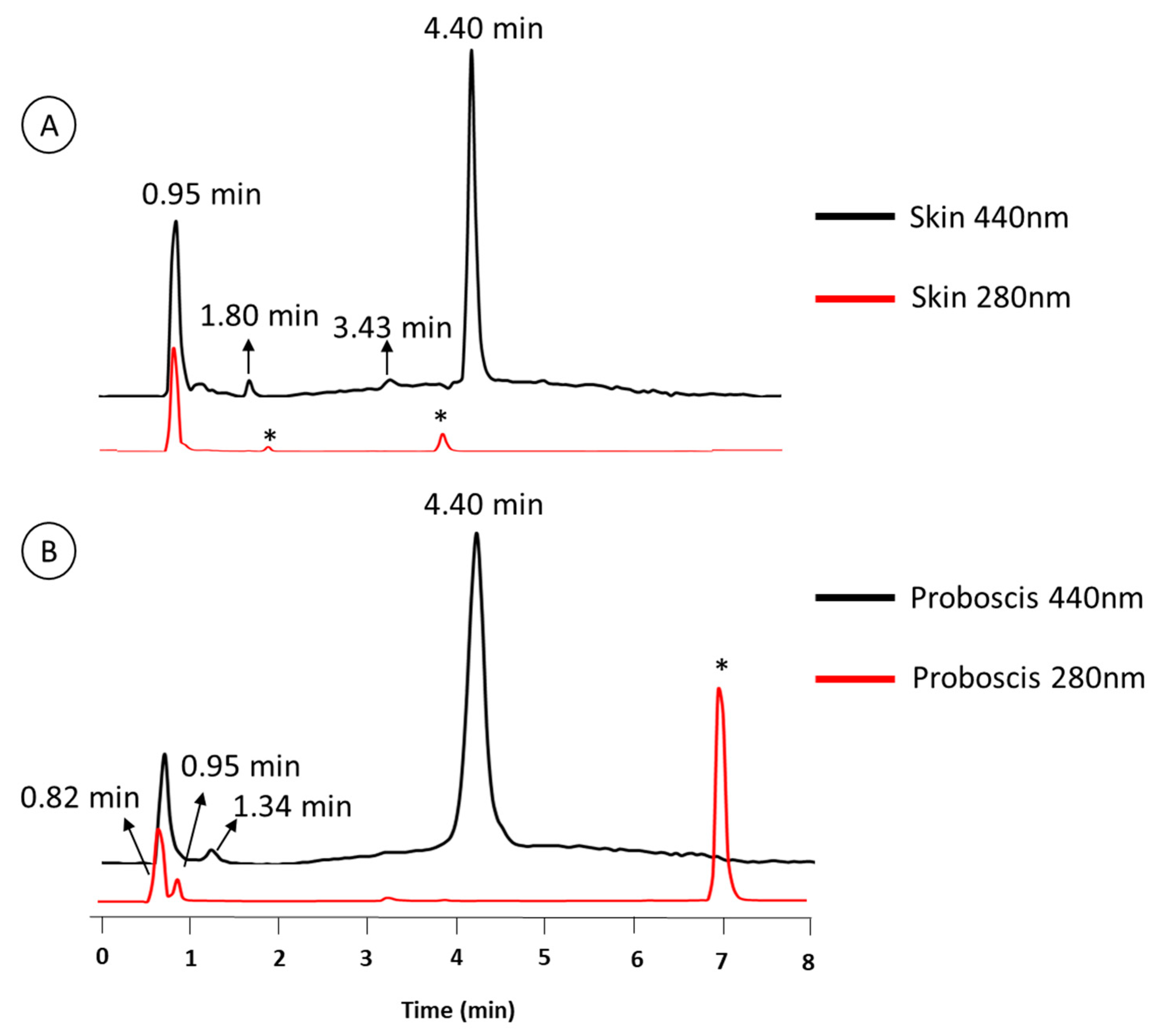

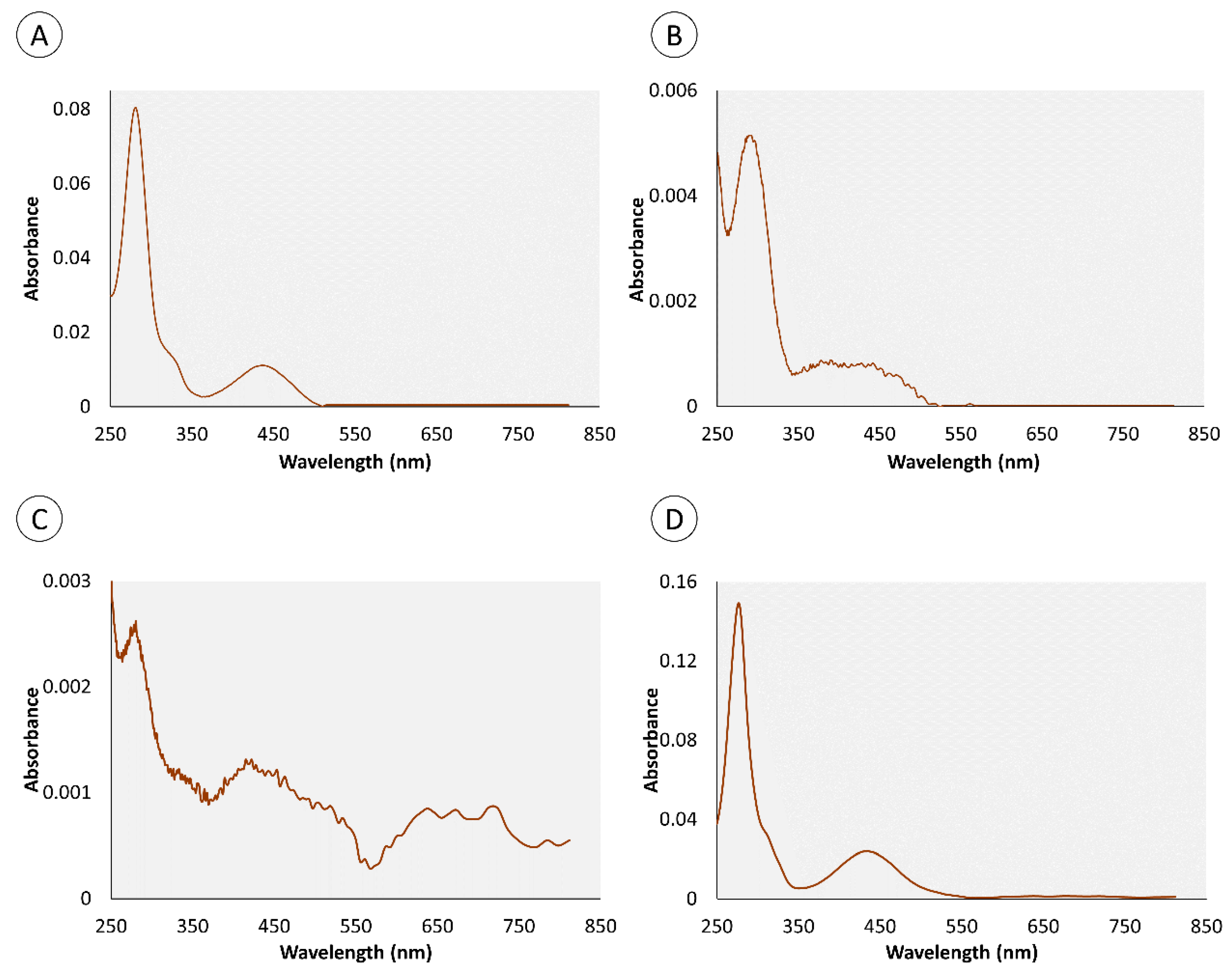

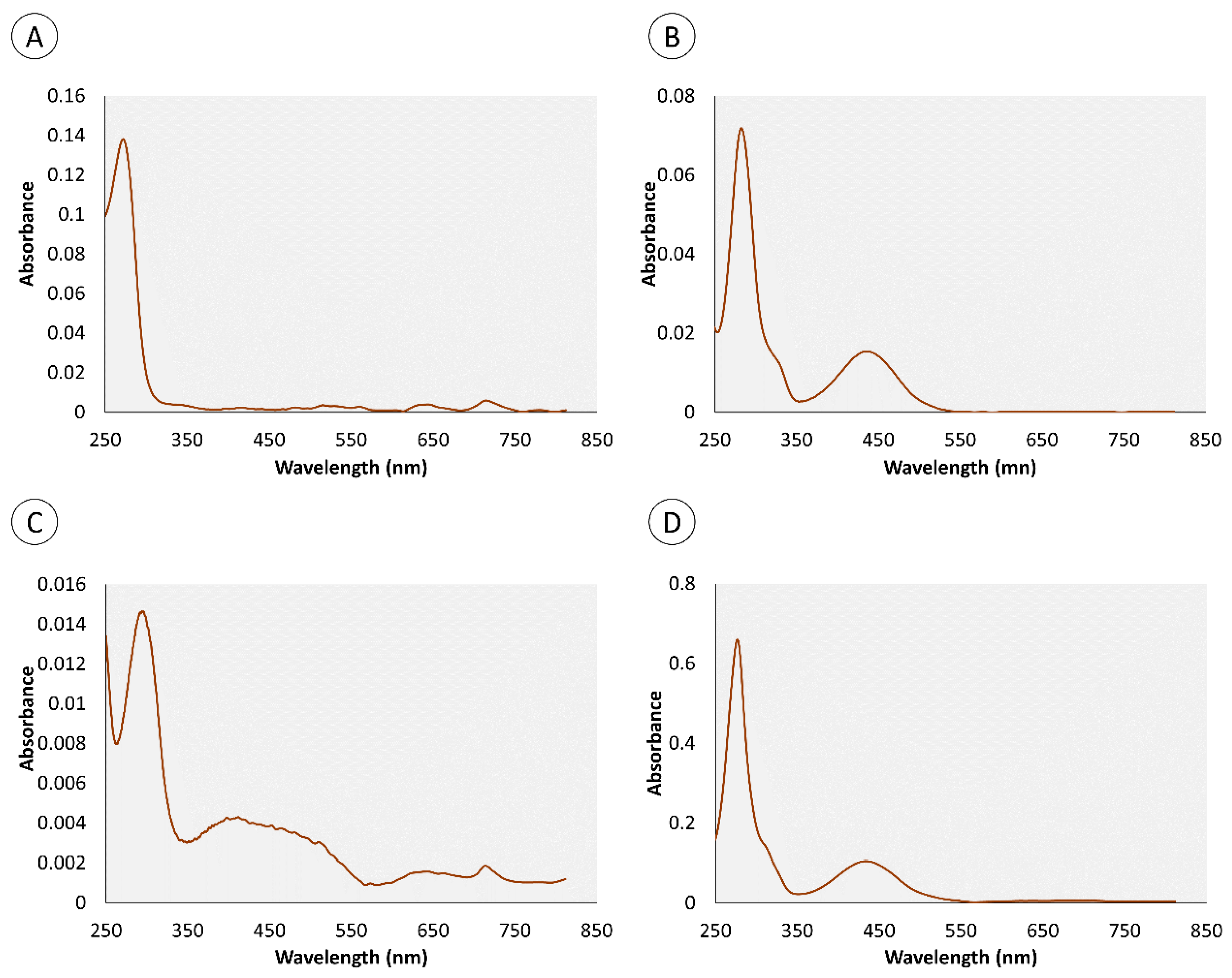
| Retention Time (min) | Organ | Color | Absorbance Maximum (nm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin | Proboscis | Green | Yellow | Skin | Proboscis | |
| 0.95 | • | • | • | 280 nm | 282 nm | |
| 4.4 | • | • | • | 276 nm | 286 nm | |
| 0.82 | – | • | • | – | 272 nm | |
| 1.34 | – | • | • | – | 257 nm | |
| 1.8 | • | – | • | 288 nm | – | |
| 3.43 | • | – | • | 288 nm | – | |
| Variable | df | Deviance Residuals | df | Residual Deviance | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 1 | 0.44403 | 46 | 5.0954 | 0.02629 1 |
| Pigment | 1 | 0.20322 | 45 | 4.8922 | 0.13280 |
| Dilution | 2 | 0.13029 | 43 | 4.7619 | 0.48465 |
| Variable | df | Deviance Residuals | df | Residual Deviance | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 1 | 36.461 | 190 | 862.43 | 1.558 × 10−9 1 |
| Pigment | 1 | 31.388 | 189 | 795.04 | 2.113 × 10−8 1 |
| Exposure time | 1 | 143.122 | 188 | 651.92 | <2 × 10−16 1 |
| Dilution | 3 | 160.977 | 185 | 490.94 | <2 × 10−16 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Ambrosio, M.; Santos, A.C.; Alejo-Armijo, A.; Parola, A.J.; Costa, P.M. Light-Mediated Toxicity of Porphyrin-Like Pigments from a Marine Polychaeta. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060302
D’Ambrosio M, Santos AC, Alejo-Armijo A, Parola AJ, Costa PM. Light-Mediated Toxicity of Porphyrin-Like Pigments from a Marine Polychaeta. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(6):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060302
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Ambrosio, Mariaelena, Ana Catarina Santos, Alfonso Alejo-Armijo, A. Jorge Parola, and Pedro M. Costa. 2020. "Light-Mediated Toxicity of Porphyrin-Like Pigments from a Marine Polychaeta" Marine Drugs 18, no. 6: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060302
APA StyleD’Ambrosio, M., Santos, A. C., Alejo-Armijo, A., Parola, A. J., & Costa, P. M. (2020). Light-Mediated Toxicity of Porphyrin-Like Pigments from a Marine Polychaeta. Marine Drugs, 18(6), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060302







