Promotion of Wound Healing and Prevention of Frostbite Injury in Rat Skin by Exopolysaccharide from the Arctic Marine Bacterium Polaribacter sp. SM1127
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
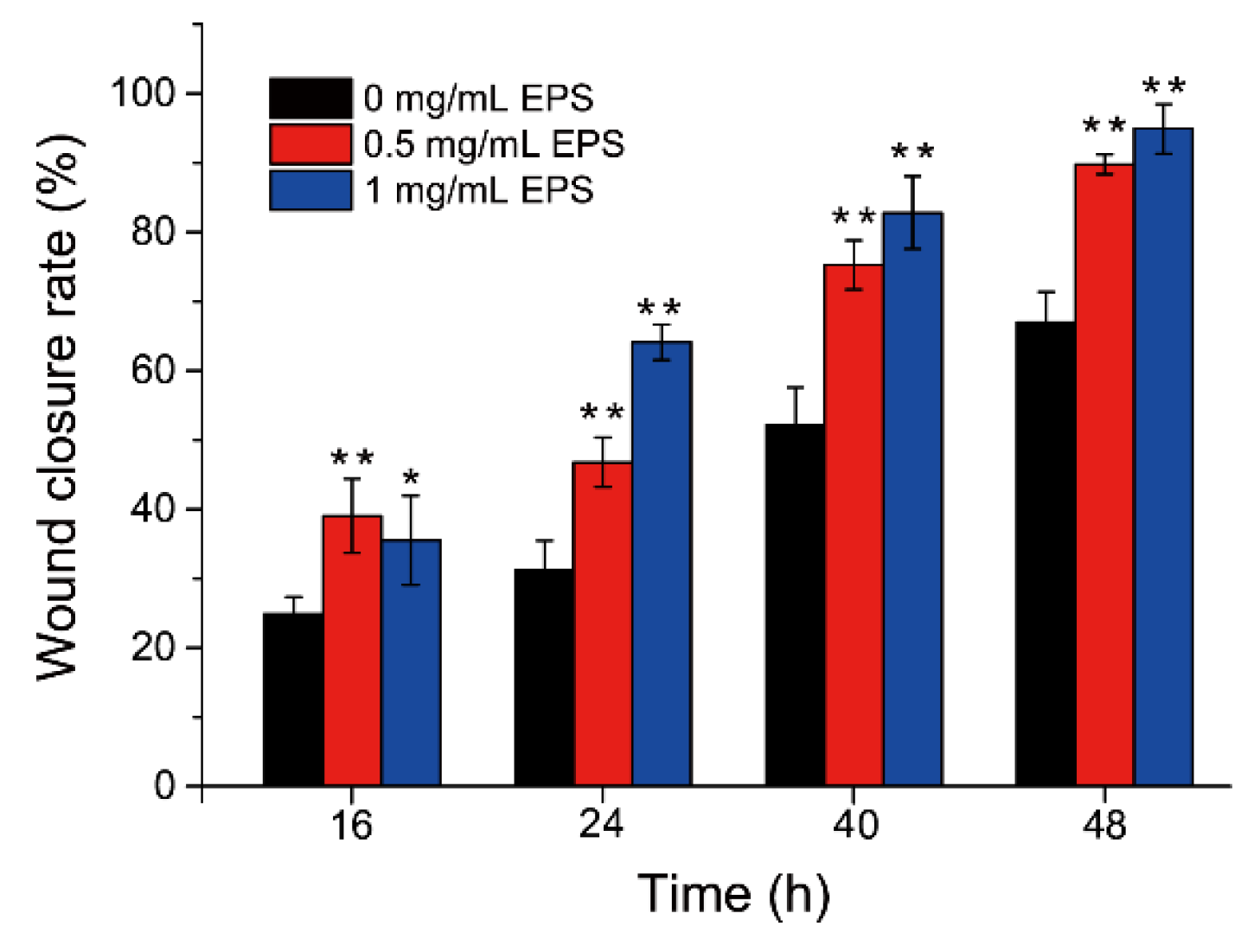
2.1. SM1127 EPS Promotes HDFs Migration In Vitro
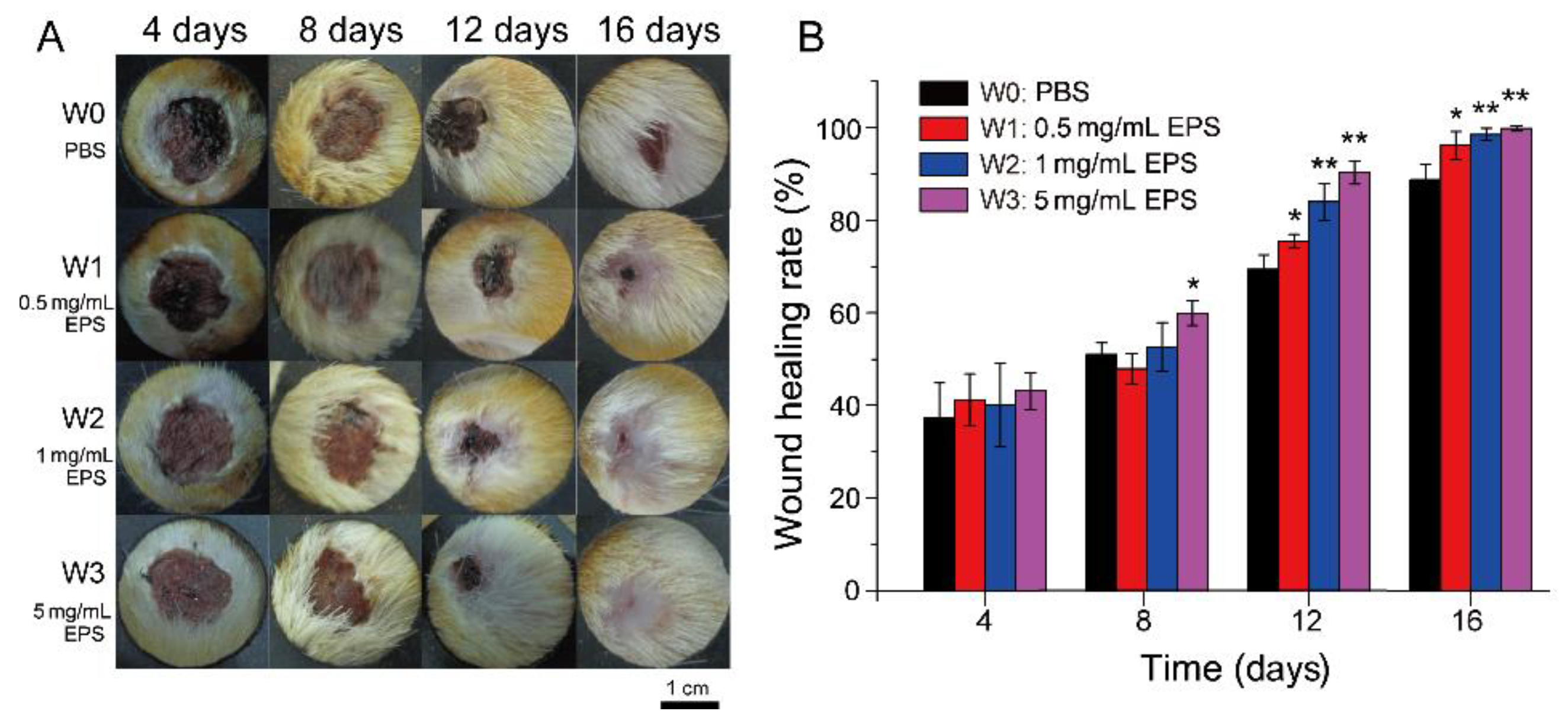
2.2. SM1127 EPS Increases the Healing Rate of Full-Thickness Cutaneous Wound
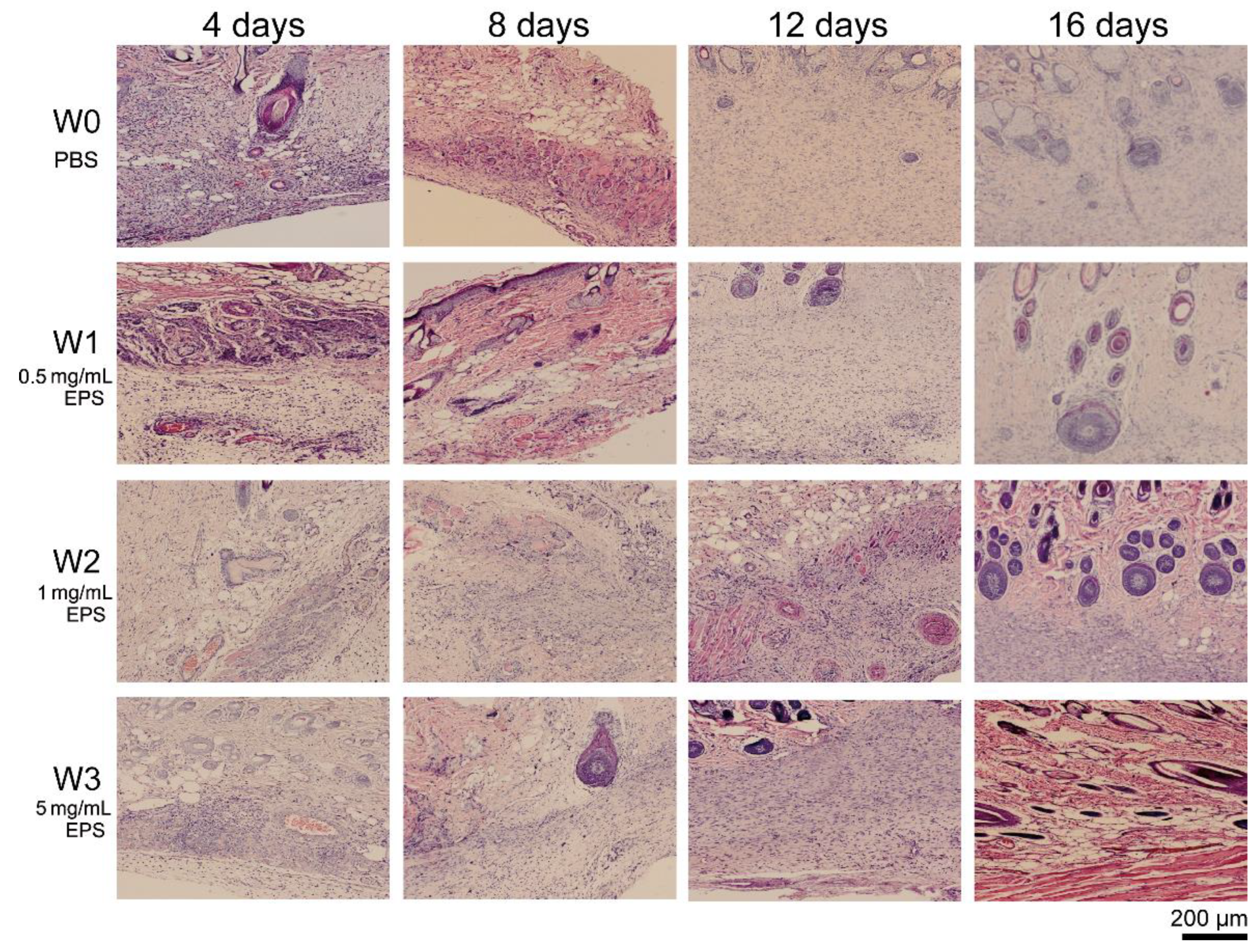
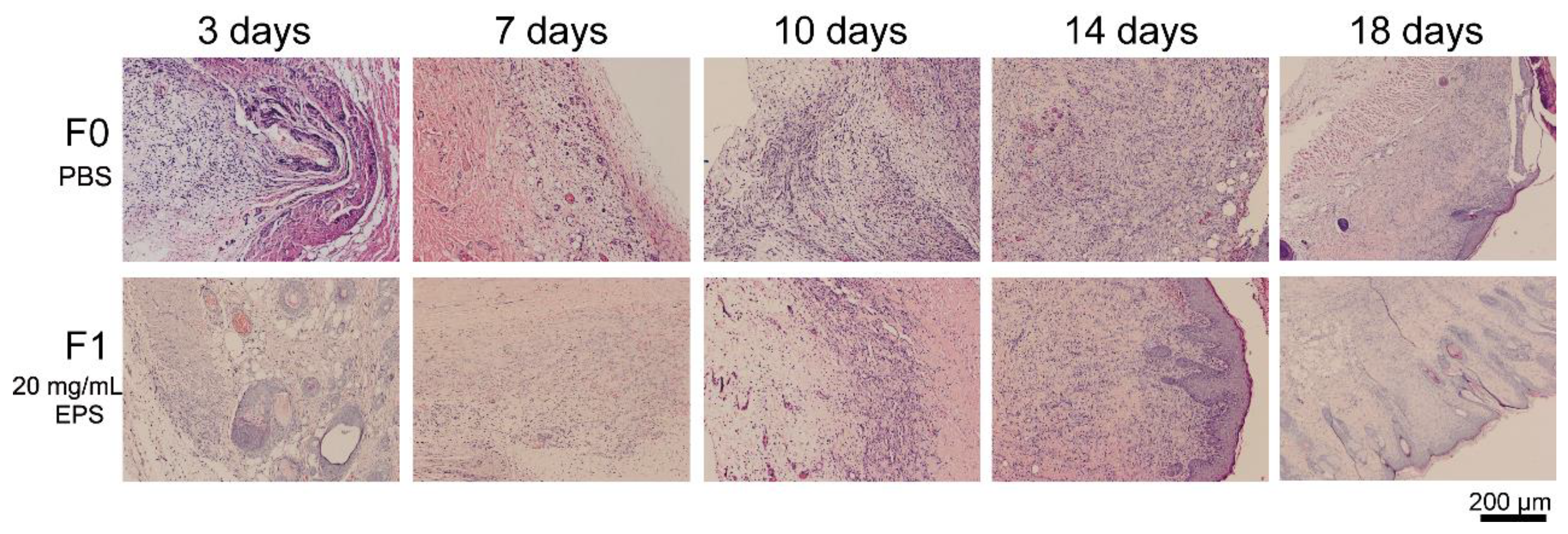
2.3. SM1127 EPS Accelerates Tissue Regeneration of Full-Thickness Cutaneous Wound in Histological Examination
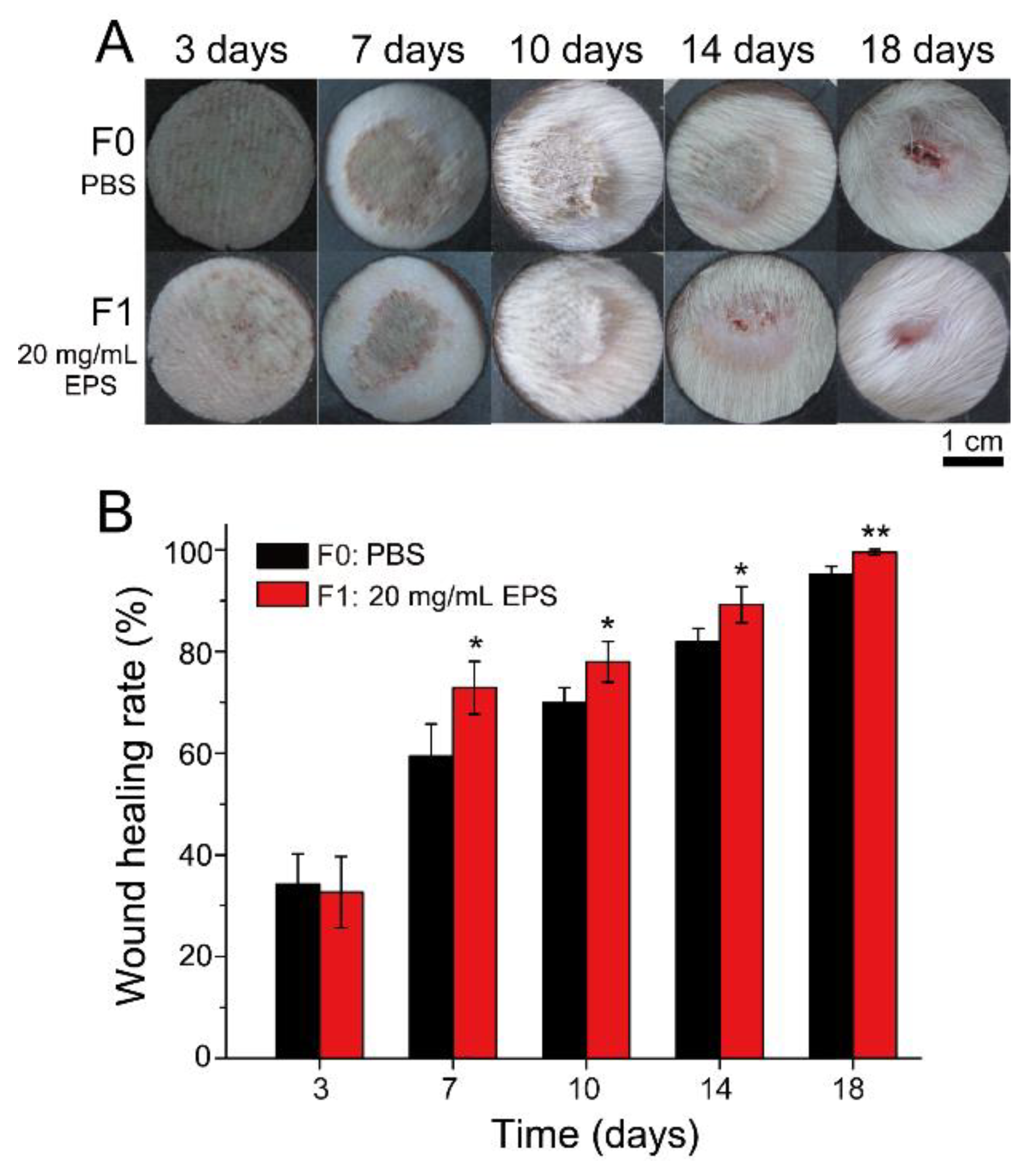
2.4. SM1127 EPS Pretreatment Increases Wound Healing Rate of the Frostbitten Skin
2.5. SM1127 EPS Pretreatment Facilitates Tissue Repair of the Frostbitten Skin in Histological Examination
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of SM1127 EPS
4.2. In Vitro Migration of HDFs
4.3. Animals
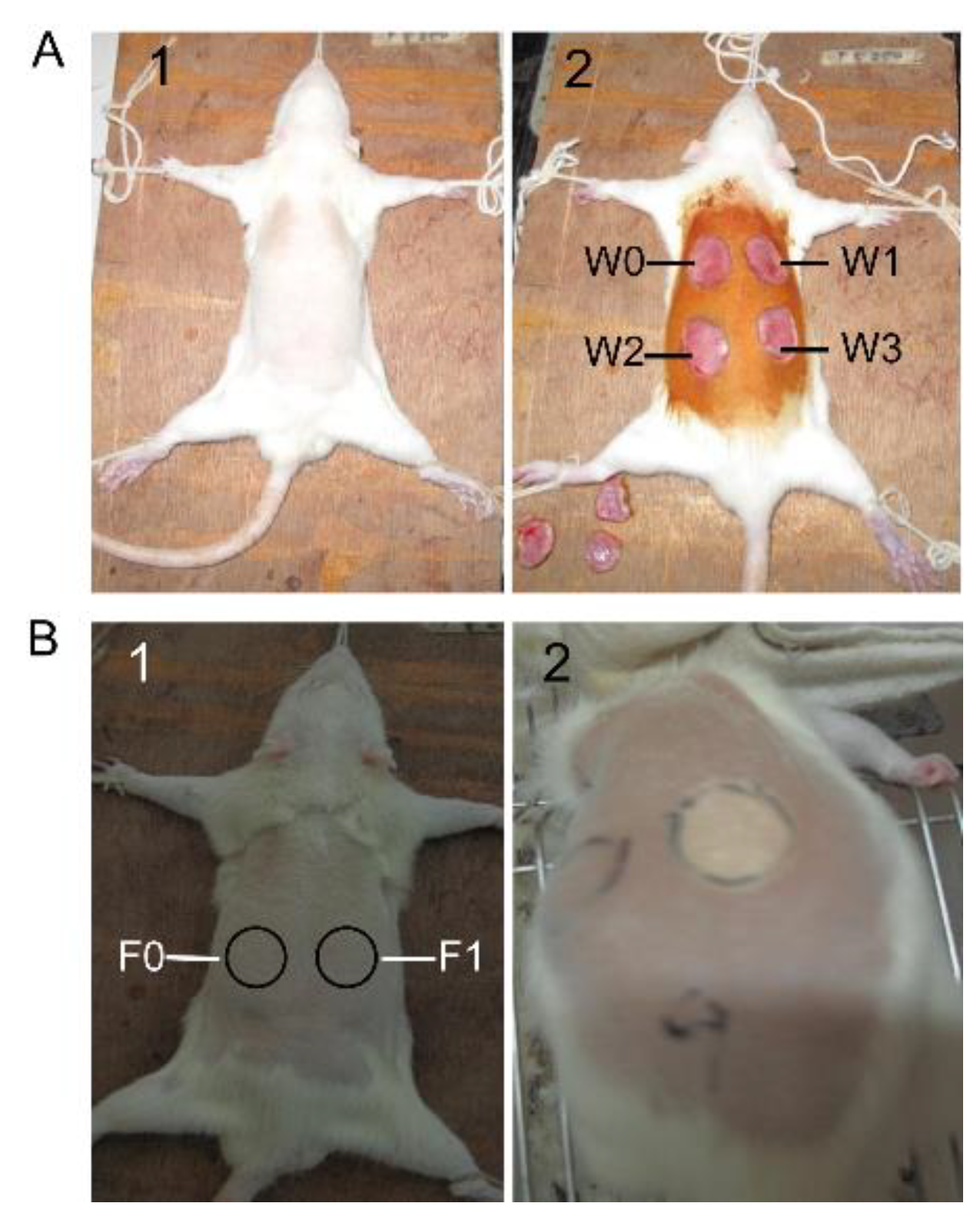
4.4. Full-Thickness Cutaneous Wound Model and SM1127 EPS Treatment
4.5. Frostbite Injury Model and SM1127 EPS Pretreatment
4.6. Measurement of Wound Healing Rate
4.7. Histological Examination
4.8. Statistics analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poli, A.; Anzelmo, G.; Nicolaus, B. Bacterial Exopolysaccharides from Extreme Marine Habitats: Production, Characterization and Biological Activities. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1779–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Zia, K.M.; Tabasum, S.; Noreen, A.; Ali, M.; Iqbal, R.; Zuber, M. Blends and composites of exopolysaccharides; properties and applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delattre, C.; Pierre, G.; Laroche, C.; Michaud, P. Production, extraction and characterization of microalgal and cyanobacterial exopolysaccharides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1159–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurienzo, P. Marine polysaccharides in pharmaceutical applications: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2435–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.S.; Mody, K.; Jha, B. Bacterial exopolysaccharides—A perception. J. Basic Microbiol. 2007, 47, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-B.; Qiao, L.-P.; He, H.-L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhou, W.-Z.; Zhou, B.-C.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Optimization of fermentation conditions and rheological properties of exopolysaccharide produced by deep-sea bacterium Zunongwangia profunda SM-A87. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, C.; Rizzo, C.; Mangano, S.; Poli, A.; Di Donato, P.; Nicolaus, B.; Di Marco, G.; Michaud, L.; Lo Giudice, A. Extracellular polymeric substances with metal adsorption capacity produced by Pseudoalteromonas sp. MER144 from Antarctic seawater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 4667–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, E.J.; Busch, K.; Weiner, R.M. Spatial and Temporal Deposition of Adhesive Extracellular Polysaccharide Capsule and Fimbriae by Hyphomonas Strain MHS-3. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotlikar, N.P.; Damare, S.R.; Meena, R.M.; Linsy, P.; Mascarenhas, B. Potential of Marine-Derived Fungi to Remove Hexavalent Chromium Pollutant from Culture Broth. Indian J. Microbiol. 2018, 58, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Yamori, T.; Naitoh, M.; Okutani, K. Structural Revision of Sulfated Polysaccharide B-1 Isolated from a Marine Pseudomonas Species and Its Cytotoxic Activity Against Human Cancer Cell Lines. Mar. Biotechnol. 2003, 5, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliec-Jouault, S.; Zanchetta, P.; Helley, D.; Ratiskol, J.; Sinquin, C.; Fischer, A.M.; Guezennec, J. Les polysaccharides microbiens d’origine marine et leur potentiel en thérapeutique humaine. Pathol. Biol. 2004, 52, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Shan, C.-Y.; Gao, X.-D.; Tan, R.-X. Protection of PC12 cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced injury by EPS2, an exopolysaccharide from a marine filamentous fungus Keissleriella sp. YS4108. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 115, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Liu, G.; Jin, W.; Xiu, P.; Sun, C. Antibiofilm and Anti-Infection of a Marine Bacterial Exopolysaccharide Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Ning, K.; Ling, B.; Chen, X.; Cheng, H.; Lu, B.; Gao, Z.; Xu, J. Multiple injections of autologous adipose-derived stem cells accelerate the burn wound healing process and promote blood vessel regeneration in a rat model. Stem. Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, S.; Chou, C.F.; Dinda, A.K.; Potdar, P.D.; Mishra, N.C. Surface modification of nanofibrous polycaprolactone/gelatin composite scaffold by collagen type I grafting for skin tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 34, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florian, G.; Monika, H.; Martina, H.; Svenja, H.; Katja, S.L. Skin tissue engineering—in vivo and in vitro applications. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2011, 39, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonguzhali, R.; Basha, S.K.; Kumari, V.S. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-PVP-nanocellulose composites for In-vitro wound dressing application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Chen, X.; Shen, X.; He, Y.; Chen, W.; Luo, Q.; Ge, W.; Yuan, W.; Tang, X.; Hou, D.; et al. Preparation of chitosan-collagen-alginate composite dressing and its promoting effects on wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Shitiz, K.; Singh, A. Chitin and chitosan: Biopolymers for wound management. Int. Wound J. 2017, 14, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-W.; Sun, J.-S.; Wu, H.-C.; Tsuang, Y.-H.; Wang, W.-H.; Lin, F.-H. The effect of gelatin-chondroitin sulfate-hyaluronic acid skin substitute on wound healing in SCID mice. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5689–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guly, H.R. Frostbite and Other Cold Injuries in the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2012, 23, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, S.E.; Opacic, M.; Freer, L.; Grissom, C.K.; Auerbach, P.S.; Rodway, G.W.; Cochran, A.; Giesbrecht, G.G.; McDevitt, M.; Imray, C.H.; et al. Wilderness Medical Society Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Frostbite: 2014 Update. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2014, 25, S43–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auerbach, L.J.; De Clerk, B.K.; Fathman, C.G.; Gurtner, G.C.; Auerbach, P.S. Poly-l-Arginine Topical Lotion Tested in a Mouse Model for Frostbite Injury. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2014, 25, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.-L.; Zhao, F.; Shi, M.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhou, B.-C.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Chen, X.-L. Characterization and Biotechnological Potential Analysis of a New Exopolysaccharide from the Arctic Marine Bacterium Polaribacter sp. SM1127. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Shi, M.; Song, X.-Y.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Cultivable alginate lyase-excreting bacteria associated with the Arctic brown alga Laminaria. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2481–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitto, J.; Mauviel, A.; Mc Grath, J. The Dermal-Epidermal Basement Membrane Zone in Cutaneous Wound Healing. In The Molecular and Cellular Biology of Wound Repair; Clark, R.A.F., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1988; pp. 513–560. ISBN 978-1-4899-0185-9. [Google Scholar]
- Rosińczuk, J.; Taradaj, J.; Dymarek, R.; Sopel, M. Mechanoregulation of Wound Healing and Skin Homeostasis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, A.D.; Ferguson, M.W. Tissue engineering of replacement skin: The crossroads of biomaterials, wound healing, embryonic development, stem cells and regeneration. J. R. Soc. Interface 2007, 4, 413–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Park, B.S.; Sung, J.H.; Yang, J.M.; Park, S.B.; Kwak, S.J.; Park, J.S. Wound healing effect of adipose-derived stem cells: A critical role of secretory factors on human dermal fibroblasts. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 48, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.H.; Nam, M.J. Effects of human epidermal growth factor gene-transfected mesenchymal stem cells on fibroblast migration and proliferation. Cell Prolif. 2013, 46, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampugnani, M.G. Cell migration into a wounded area in vitro. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 96, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarrow, J.C.; Perlman, Z.E.; Westwood, N.J.; Mitchison, T.J. A high-throughput cell migration assay using scratch wound healing, a comparison of image-based readout methods. BMC Biotechnol. 2004, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, F.; Yue, Z.; Zhang, T.; Deng, H.; Huselstein, C.; Anderson, D.P.; Chang, P.R.; et al. Accelerated skin wound healing by soy protein isolate-modified hydroxypropyl chitosan composite films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.-M.; Min, S.; Lee, H.; Kwon, Y.; Jung, M.; Shin, H. Spirulina-PCL Nanofiber Wound Dressing to Improve Cutaneous Wound Healing by Enhancing Antioxidative Mechanism. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decho, A.W. Microbial exopolymer secretions in ocean environments: Their role(s) in food webs and marine processes. In Oceanography Marine Biology Annual Review; Barnes, M., Ed.; Aberdeen University Press: Aberdeen, UK, 1990; Volume 28, pp. 73–153. ISBN 0078-3218. [Google Scholar]
- Krembs, C.; Eicken, H.; Junge, K.; Deming, J.W. High concentrations of exopolymeric substances in Arctic winter sea ice: Implications for the polar ocean carbon cycle and cryoprotection of diatoms. Deep Sea Res. Pt. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 2163–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Yim, J.H. Cryoprotective Properties of Exopolysaccharide (P-21653) Produced by the Antarctic Bacterium, Pseudoalteromonas arctica KOPRI 21653. J. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-B.; Chen, X.-L.; He, H.-L.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Xie, B.-B.; Yu, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhou, B.-C.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Structure and ecological roles of a novel exopolysaccharide from the arctic sea ice bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. Strain SM20310. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, C.; Rizzo, C.; Mangano, S.; Poli, A.; Di Donato, P.; Finore, I.; Nicolaus, B.; Di Marco, G.; Michaud, L.; Lo Giudice, A. Production and Biotechnological Potential of Extracellular Polymeric Substances from Sponge-Associated Antarctic Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01624-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, D.; Tamés, R.S.; Revilla, M.A. Cryopreservation of in vitro-grown shoot-tips of hop (Humulus lupulus L.) using encapsulation/dehydration. Plant. Cell Rep. 1999, 19, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, L.G.; Wu, X.; Guan, J.-L. Wound-healing assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 294, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Ma, D.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y. Expansion and delivery of human fibroblasts on micronized acellular dermal matrix for skin regeneration. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2666–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, L.J.; Galvez, M.G.; De Clerck, B.K.; Glotzbach, J.; Wehner, M.R.; Chang, E.I.; Gurtner, G.C.; Auerbach, P.S. A Novel Mouse Model for Frostbite Injury. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2013, 24, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.-L.; Zhao, F.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Song, X.-Y.; Sun, C.-Y.; Yang, J. Promotion of Wound Healing and Prevention of Frostbite Injury in Rat Skin by Exopolysaccharide from the Arctic Marine Bacterium Polaribacter sp. SM1127. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010048
Sun M-L, Zhao F, Chen X-L, Zhang X-Y, Zhang Y-Z, Song X-Y, Sun C-Y, Yang J. Promotion of Wound Healing and Prevention of Frostbite Injury in Rat Skin by Exopolysaccharide from the Arctic Marine Bacterium Polaribacter sp. SM1127. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010048
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Mei-Ling, Fang Zhao, Xiu-Lan Chen, Xi-Ying Zhang, Yu-Zhong Zhang, Xiao-Yan Song, Cai-Yun Sun, and Jie Yang. 2020. "Promotion of Wound Healing and Prevention of Frostbite Injury in Rat Skin by Exopolysaccharide from the Arctic Marine Bacterium Polaribacter sp. SM1127" Marine Drugs 18, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010048
APA StyleSun, M.-L., Zhao, F., Chen, X.-L., Zhang, X.-Y., Zhang, Y.-Z., Song, X.-Y., Sun, C.-Y., & Yang, J. (2020). Promotion of Wound Healing and Prevention of Frostbite Injury in Rat Skin by Exopolysaccharide from the Arctic Marine Bacterium Polaribacter sp. SM1127. Marine Drugs, 18(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010048




