Padina pavonica Extract Promotes In Vitro Differentiation and Functionality of Human Primary Osteoblasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
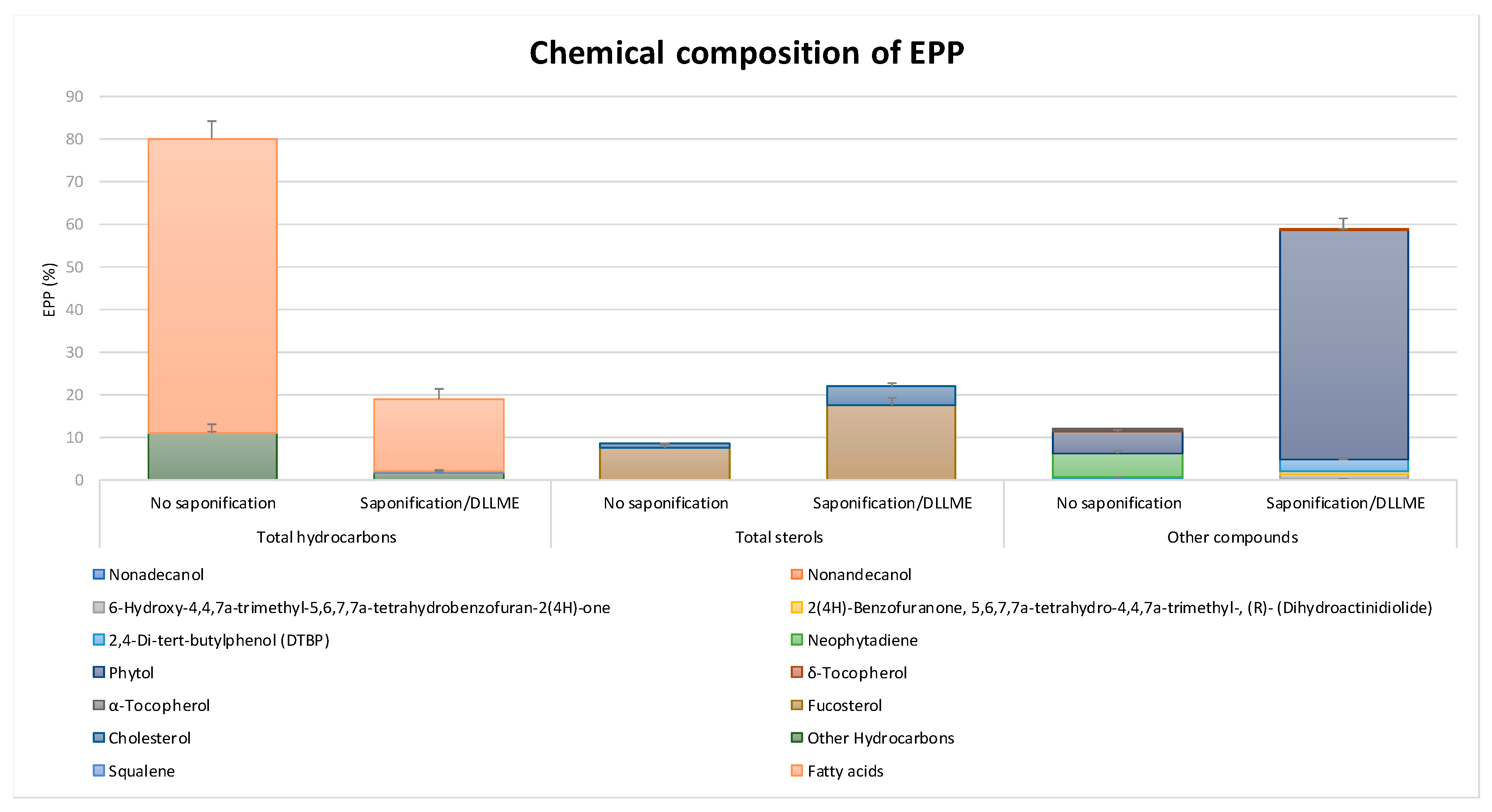
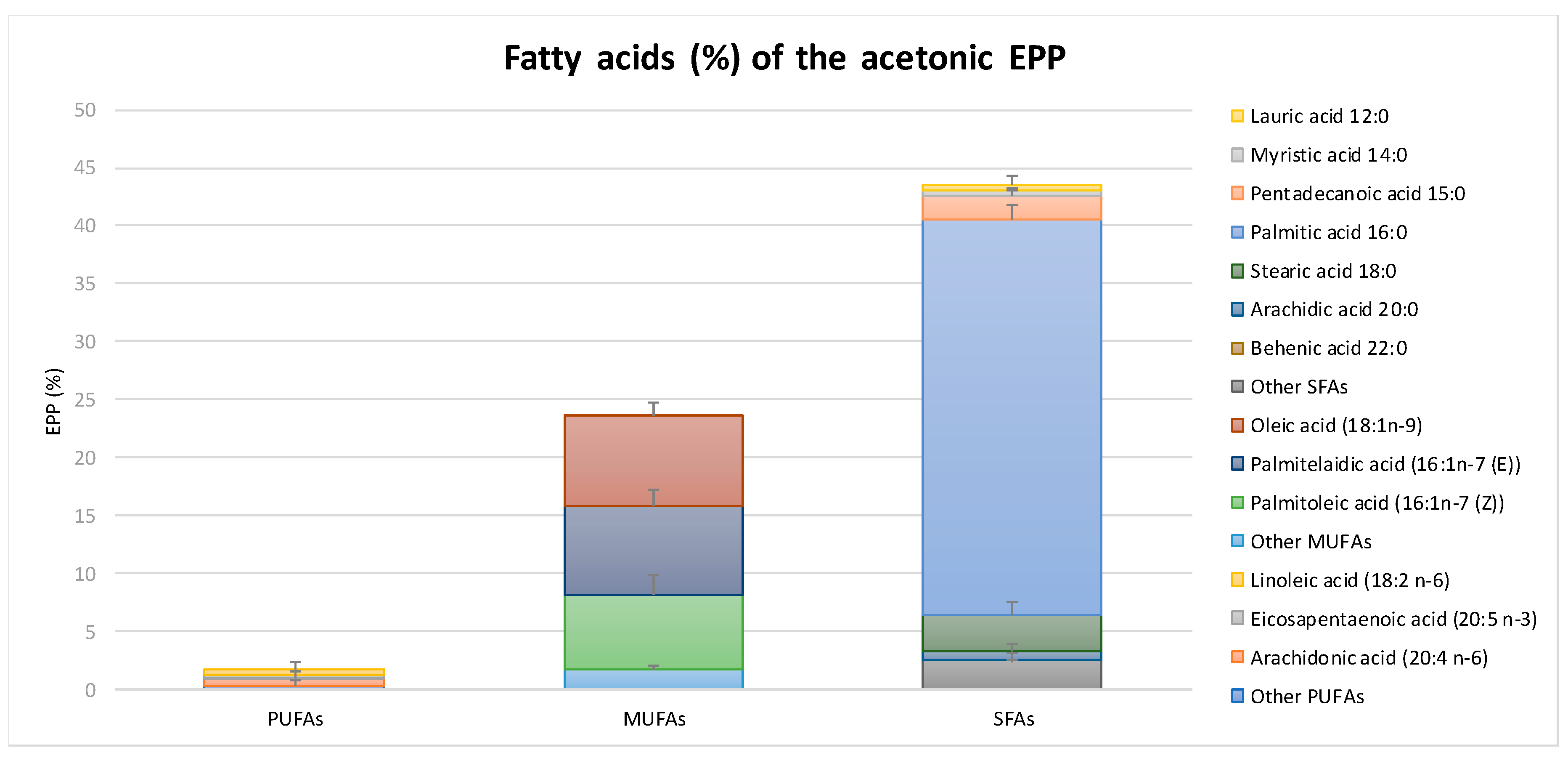
2.1. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Capacity of EPP
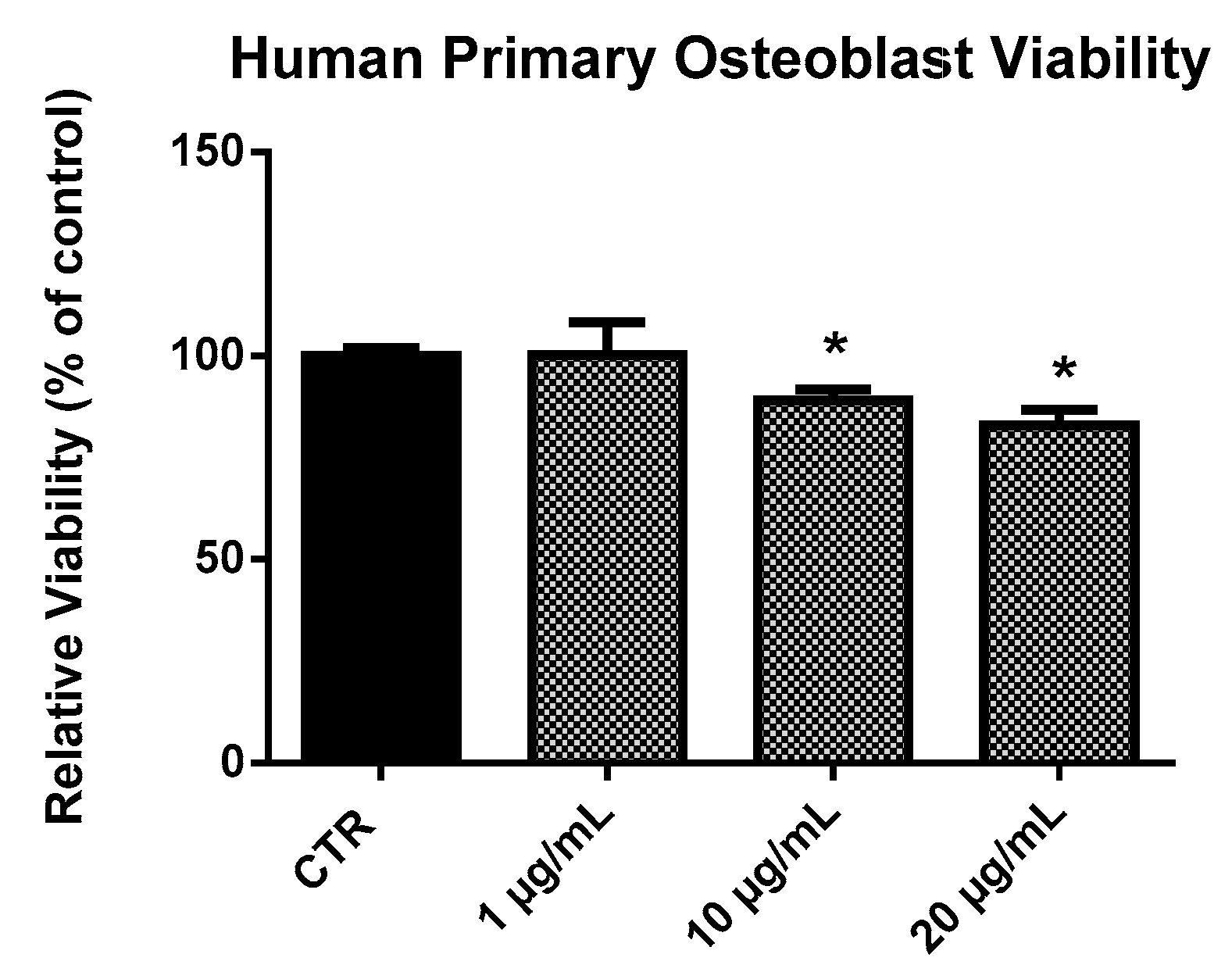
2.2. EPP Effects on HOb Viability
2.3. Expression Analysis of Bone Differentiation Markers
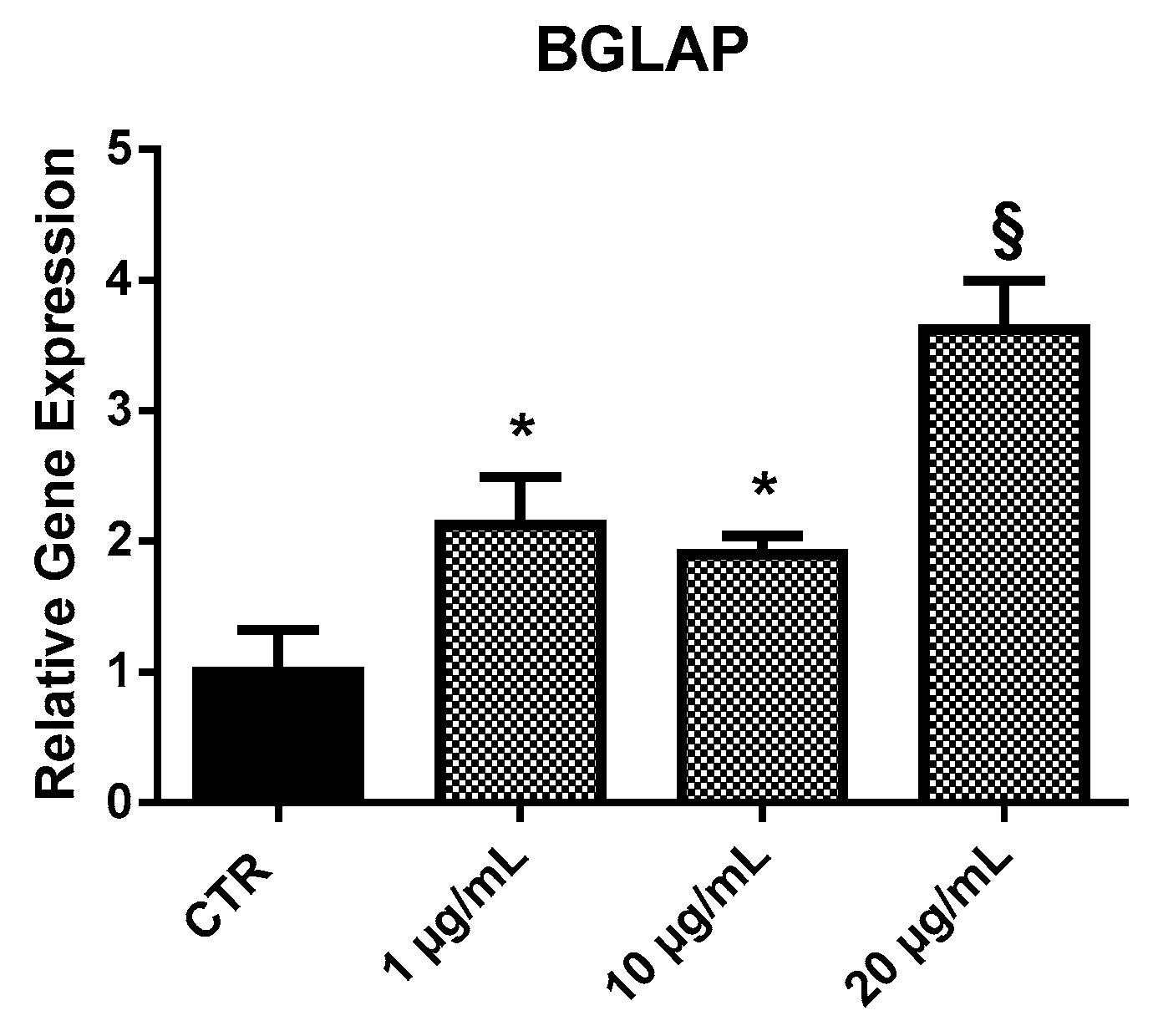
2.3.1. BGLAP
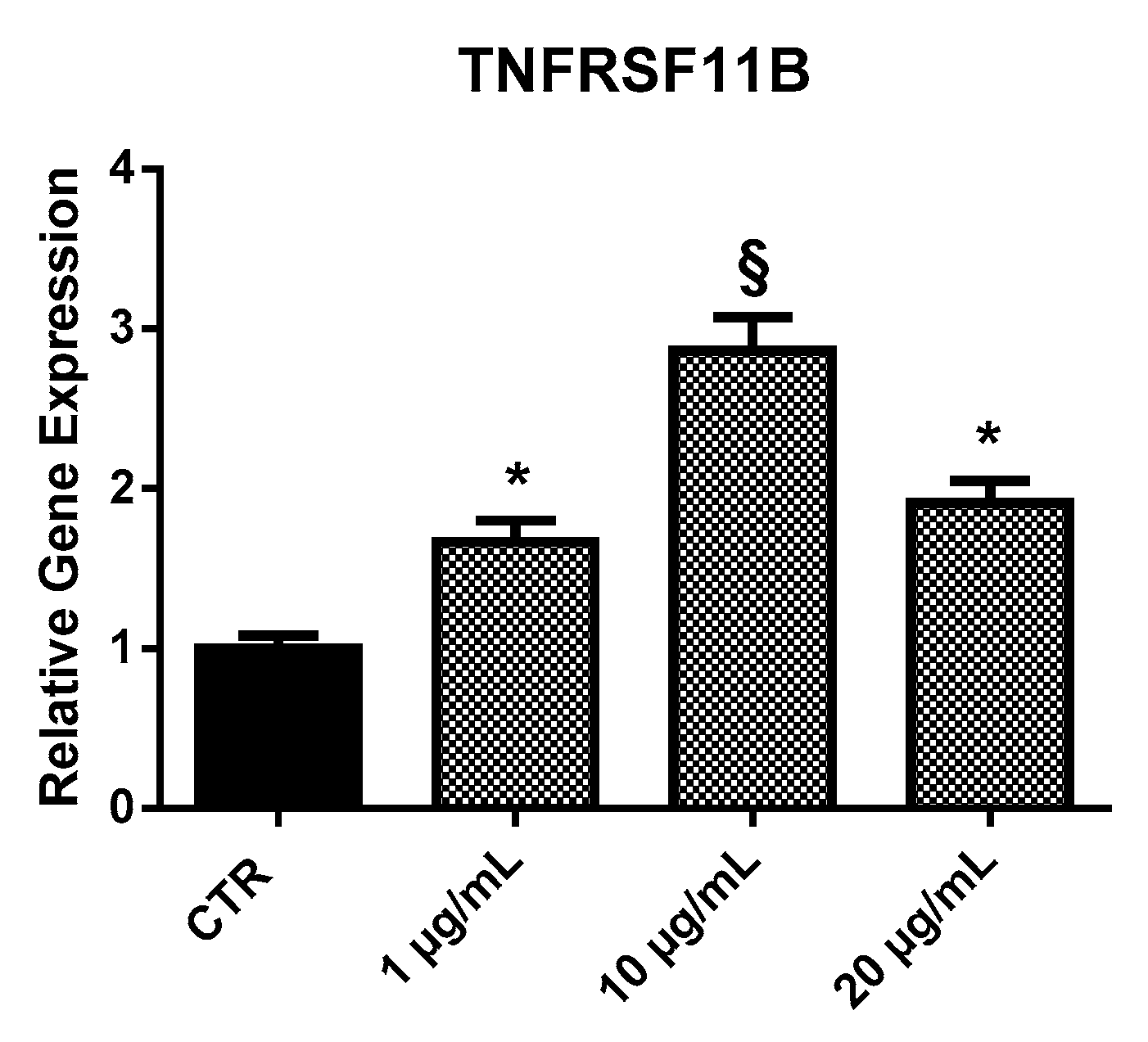
2.3.2. TNFRSF11B
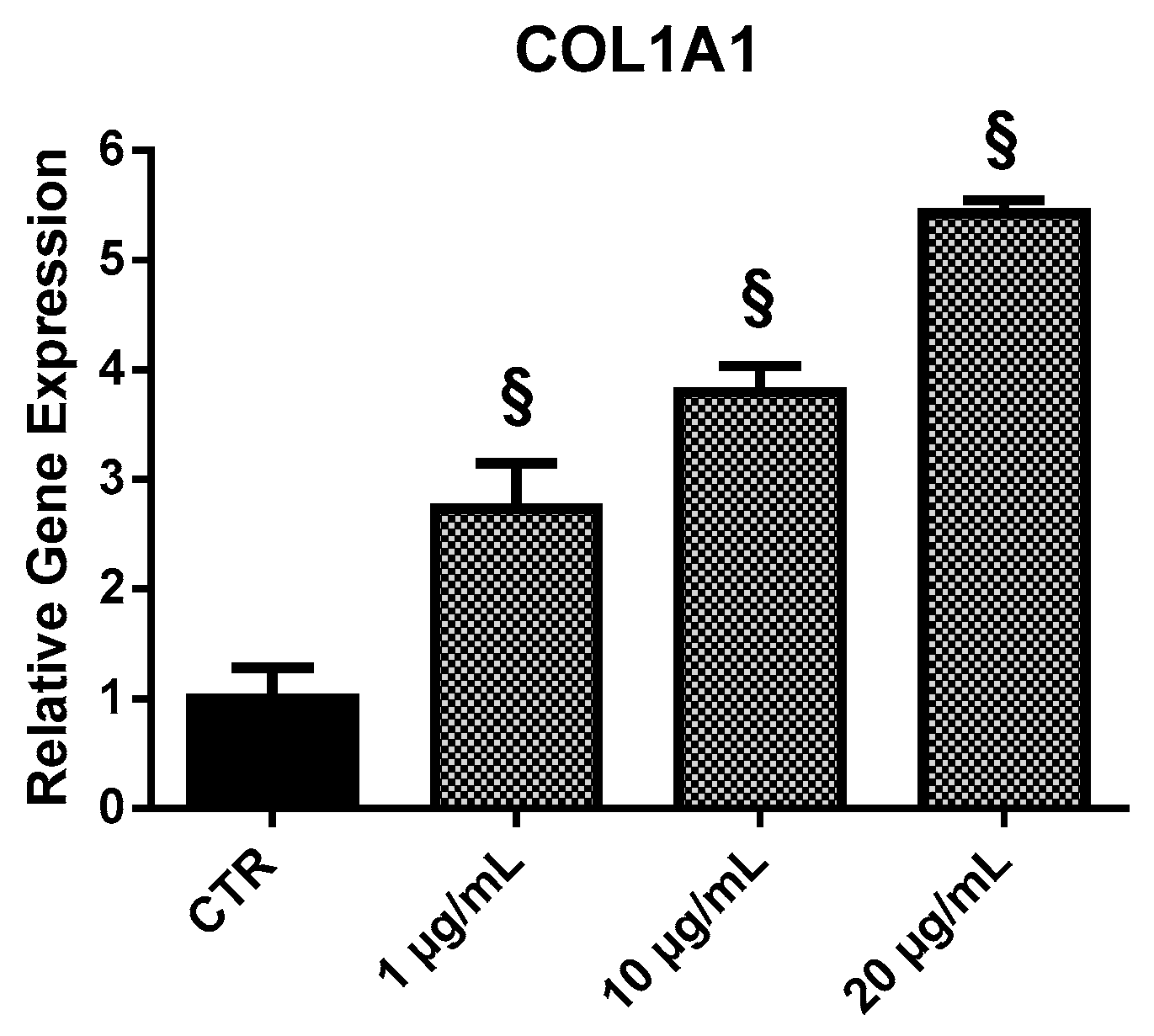
2.3.3. COL1A1
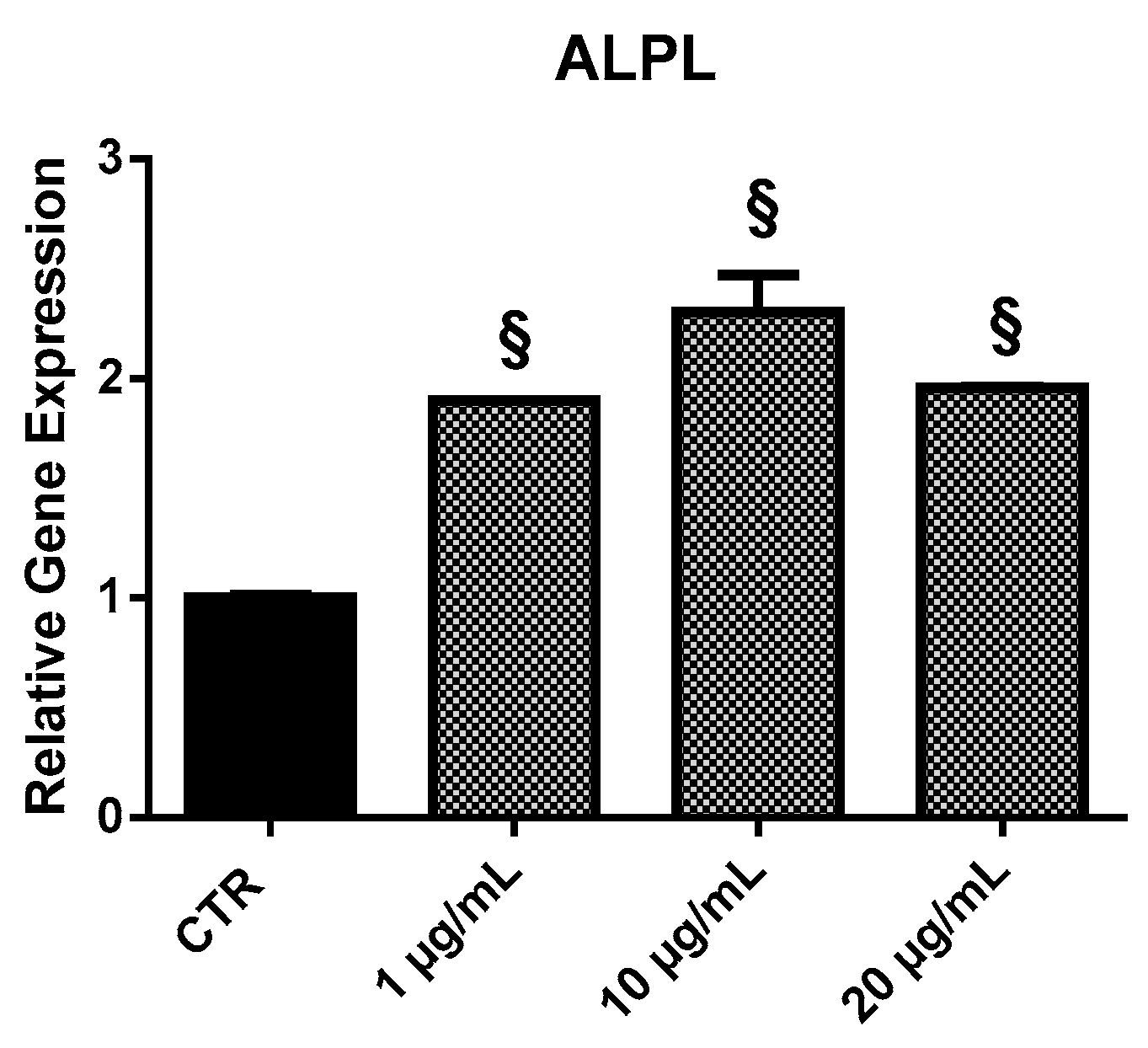
2.3.4. ALPL
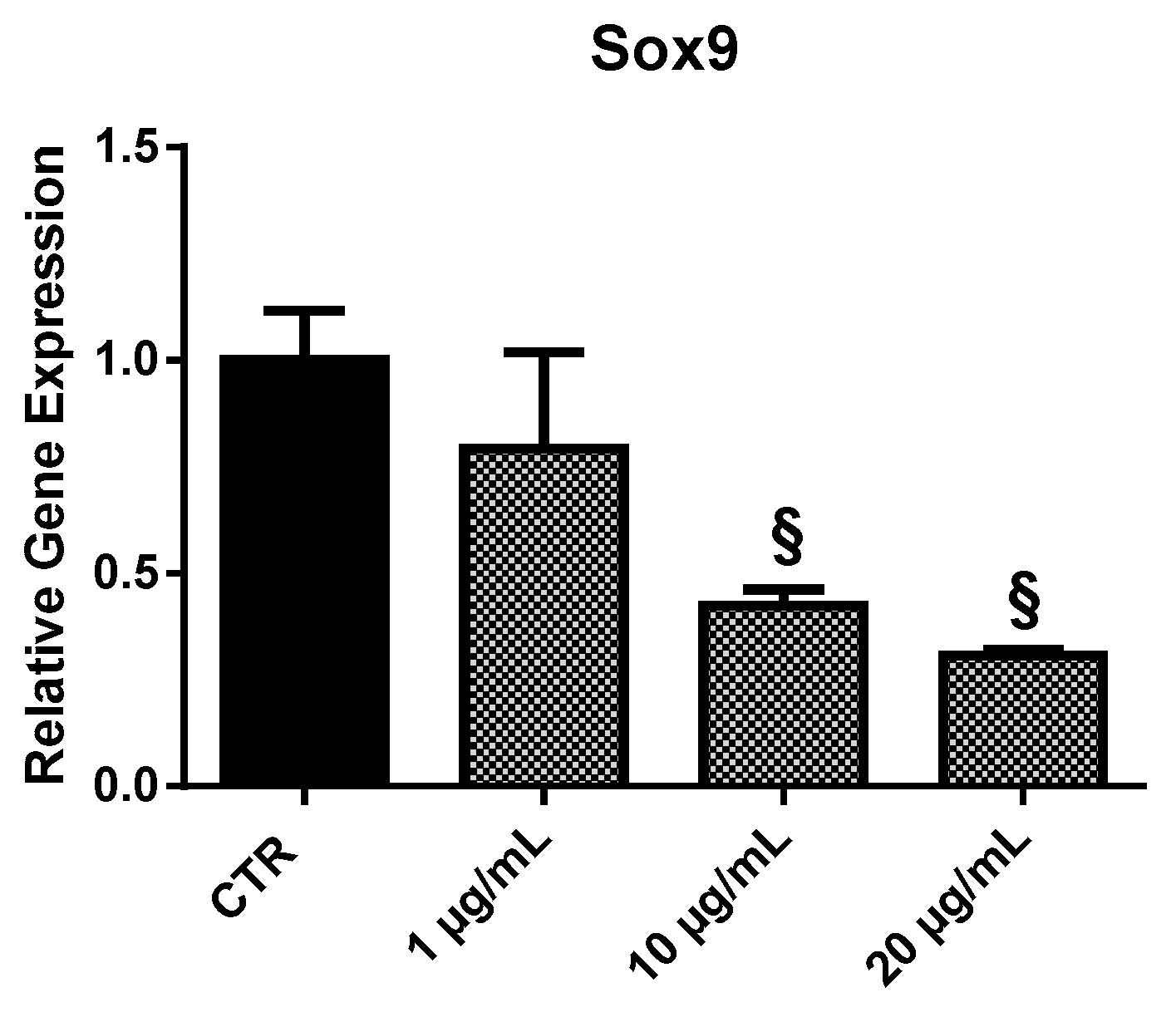
2.3.5. Sox9
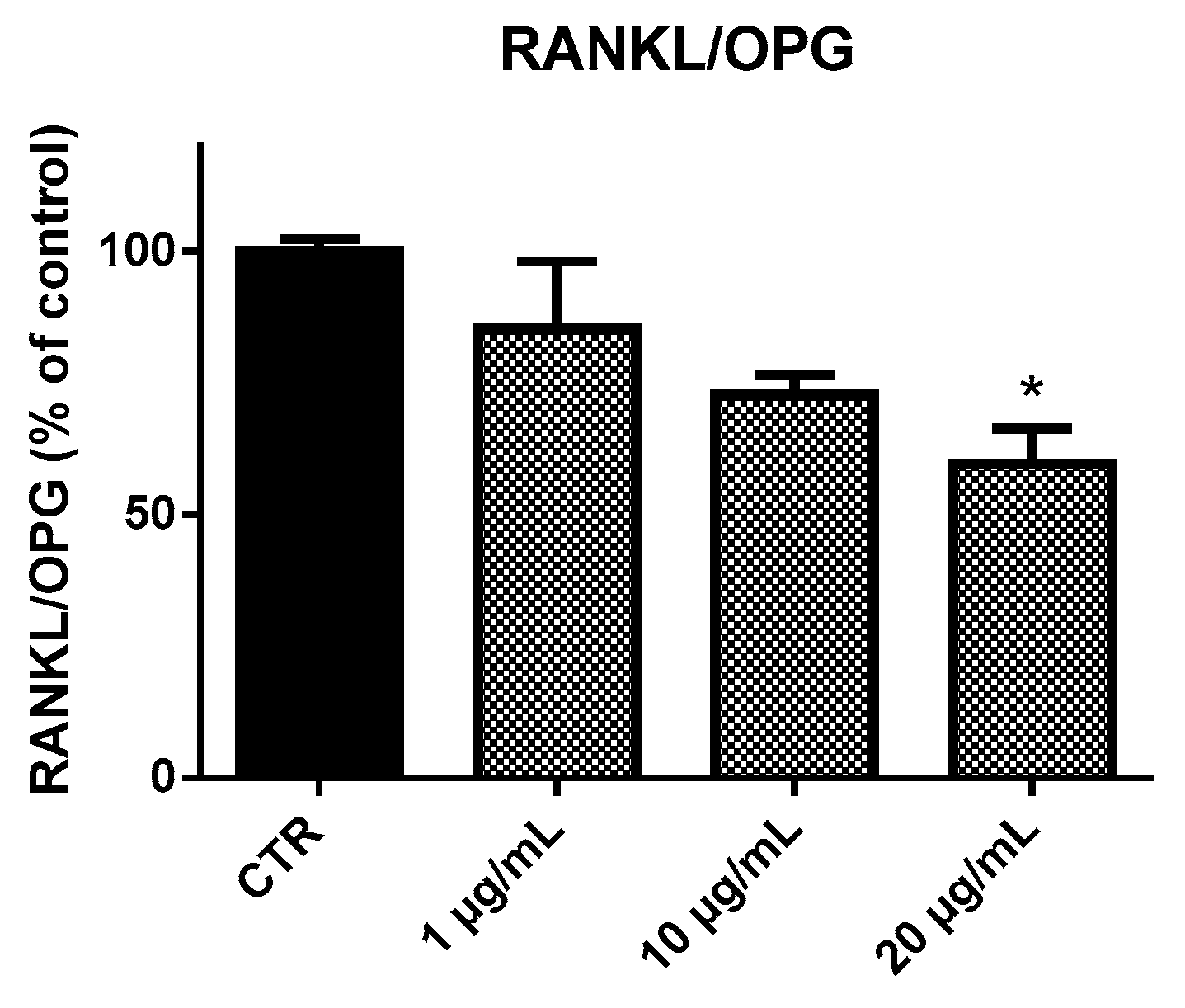
2.4. Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand (RANKL) and Osteoprotegerin (OPG) Ratio (RANKL/OPG Ratio)
2.5. Alkaline Phosphatase (ALPL) Activity
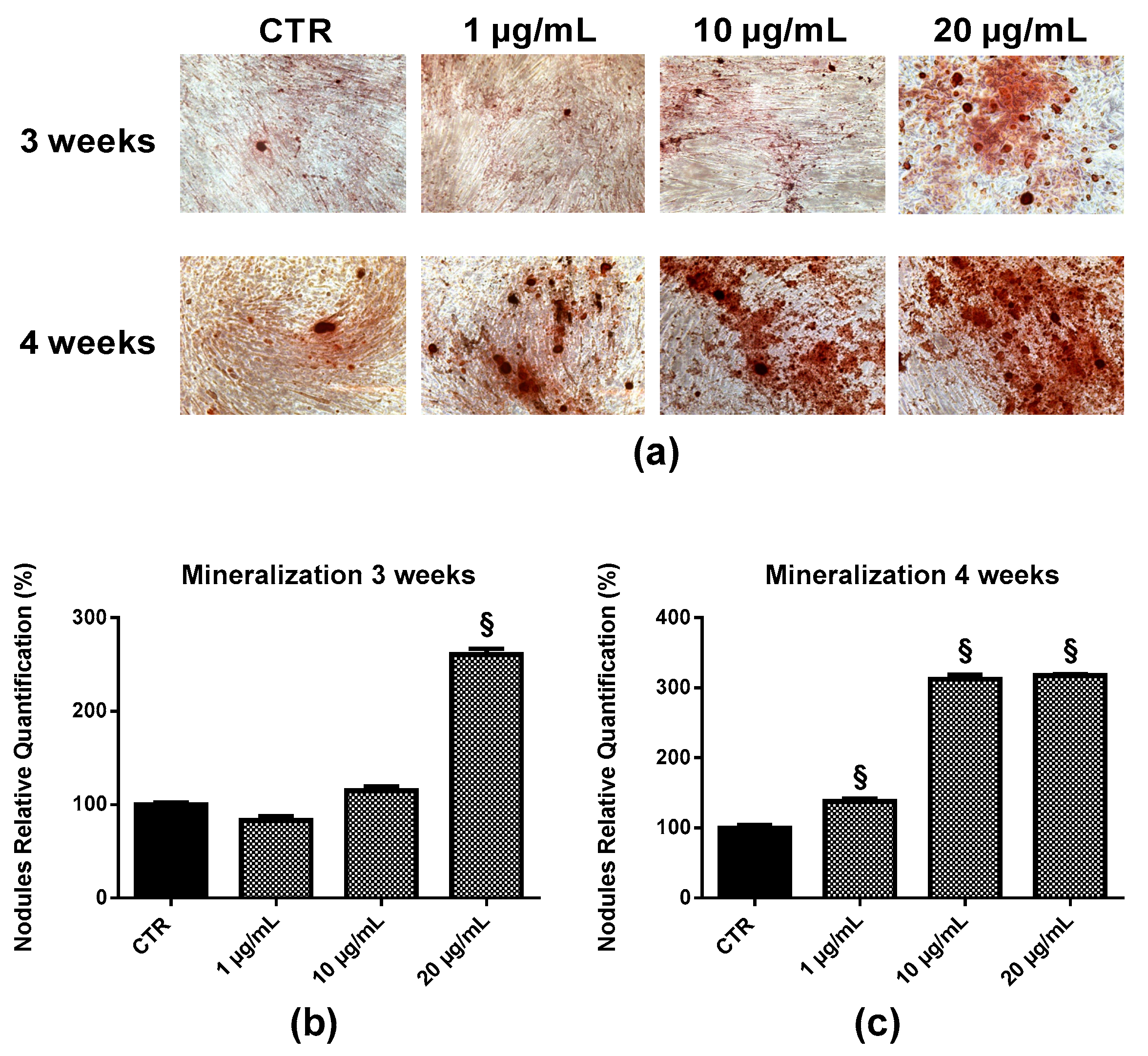
2.6. Bone Nodule Formation and Mineralization
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Composition of EPP
4.2. Isolation and Culture of HOb
4.3. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.4. MTT Assay
4.5. RT-qPCR
4.6. ALPL Assay
4.7. Quantitative Detection of RANKL and OPG
4.8. Nodules Formation and Mineralization Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, B.J.; Koh, J.M. Coupling factors involved in preserving bone balance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardini, G.; Braconi, D.; Spreafico, A.; Santucci, A. Post-genomics of bone metabolic dysfunctions and neoplasias. Proteomics 2012, 12, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, M.A.; Clarke, S.A. Bioactive Compounds from Marine Organisms: Potential for Bone Growth and Healing. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.S.; Jung, W.-K.; Kim, J.-A.; Choi, I.-W.; Kim, S.-J. Beneficial effects of fucoidan on osteoblastic MG63 cell differentiation. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, I.; Özogul, F.; Özogul, Y.; Regenstein, J.M. Marine Bioactive Compounds and Their Health Benefits: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 446–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, G.; Minetti, M.; Polizzotto, G.; Biazzo, M.; Santucci, A. Pro-Apoptotic Activity of French Polynesian Padina pavonica Extract on Human Osteosarcoma Cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cikoš, A.M.; Jokić, S.; Šubarić, D.; Jerković, I. Overview on the Application of Modern Methods for the Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Marine Macroalgae. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, H.M.; Fernandes, F.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; Malcata, F.X.; Guedes, A.C. Effect of Solvent System on Extractability of Lipidic Components of Scenedesmus obliquus (M2-1) and Gloeothece sp. on Antioxidant Scavenging Capacity Thereof. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6453–6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Reddy, C.R.; Jha, B. Comparative evaluation and selection of a method for lipid and fatty acid extraction from macroalgae. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 415, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando-Bonaca, M.; Lipej, L.; Orfanidis, S. Benthic macrophytes as a tool for delineating, monitoring and assessing ecological status: The case of Slovenian coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofer, R.; Yerachmiel, A.; Shmuel, Y. Marine macroalgae as biosorbents for cadmium and nickel in water. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behmer, S.T.; Olszewski, N.; Sebastiani, J.; Palka, S.; Sparacino, G.; Sciarrno, E.; Grebenok, R.J. Plant phloem sterol content: Forms, putative functions, and implications for phloem-feeding insects. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, G. Compositions of Padina Algae or Their Extracts, and Their Pharmaceutical, Food Compositions, or Use for the Culture of Molluscs or Arthropods. European Patent EP 655250, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Zheng, Q.; Engin, F.; Munivez, E.; Chen, Y.; Sebald, E.; Krakow, D.; Lee, B. Dominance of SOX9 function over RUNX2 during skeletogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19004–19009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrado, A.; Neve, A.; Macchiarola, A.; Gaudio, A.; Marucci, A.; Cantatore, F.P. RANKL/OPG Ratio and DKK-1 Expression in Primary Osteoblastic Cultures from Osteoarthritic and Osteoporotic Subjects. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaugule, S.; Indap, M.; Chiplunkar, S. Marine Natural Products: New Avenue in Treatment of Osteoporosis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumara, K.; Venkatesana, J.; Kim, S.K. Marine derived natural products for osteoporosis. Biomed. Prev. Nutr. 2014, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuru, P.; D’Auria, M.V.; Muller, C.D.; Tammela, P.; Vuorela, H.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J. Exploring marine resources for bioactive compounds. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskin, E.; Caki, Z.; Ozturk, M. Assessment of in vitro antitumoral and antimicrobial activities of marine algae harvested from the eastern Mediterranean sea. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 4272–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devery, R.; Miller, A.; Stanton, C. Conjugated linoleic acid and oxidative behavior in cancer cells. Biochem. Soc. Transact. 2001, 29, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojković, T.P.; Šavikin, K.; Zdunić, G.; Kljajić, Z.; Grozdanić, N.; Antić, J. In vitro antitumoral Activities of Padina pavonia on human cervix and breast cancer cell Lines. J. Med. Plant Res. 2013, 7, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.K. Osteoporosis treatment: Marine algal compounds. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 64, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Hokari, Y.; Hashizume, M.; Yamaguchi, M. Effect of Sargassum horneri extract on circulating bone metabolic markers: Supplemental intake has an effect in healthy humans. J. Health Sci. 2008, 54, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Hachiya, S.; Hiratuka, S.; Suzuki, T. Effect of marine algae extract on bone calcification in the femoral-metaphyseal tissues of rats: Anabolic effect of Sargassum horneri. J. Health Sci. 2001, 47, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ryu, B.; Li, Y.; Qian, Z.-J.; Kim, M.-M.; Kim, S.-K. Differentiation of human osteosarcoma cells by isolated phlorotannins is subtly linked to COX-2, iNOS, MMPs, and MAPK signaling: Implication for chronic articular disease. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 179, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkovskiy, A.; Stensløkken, K.-O.; Vaage, I.-J. Osteoblast Differentiation at a Glance. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2016, 22, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, P.; Dy, P.; Mitra, S.; Lefebvre, V. Sox5 and Sox6 are needed to develop and maintain source, columnar, and hypertrophic chondrocytes in the cartilage growth plate. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 164, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, L.; Abu-Awwad, H.A.M.; Dixon, J.E. Osteogenic Programming of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Highly Efficient Intracellular Delivery of RUNX2. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 2146–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofbauer, L.C.; Schoppet, M. Clinical implications of the osteoprotegerin/RANKL/RANK system for bone and vascular diseases. JAMA 2004, 292, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.H.; Jung, W.K.; Kim, S.K. Marine algae possess therapeutic potential for Ca-mineralization via osteoblastic differentiation. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 64, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreafico, A.; Frediani, B.; Capperucci, C.; Chellini, F.; Paffetti, A.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Bernardini, G.; Mini, R.; Collodel, G.; Scaloni, A.; et al. A proteomic study on human osteoblastic cells proliferation and differentiation. Proteomics 2006, 6, 3520–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.-W.; Liou, H.-M.; Lin, C.-J.; Kuo, K.-L.; Hung, Y.-S.; Weng, R.-C.; Hsu, F.-Y. MG63 Osteoblast-Like Cells Exhibit Different Behavior when Grown on Electrospun Collagen Matrix versus Electrospun Gelatin Matrix. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laschi, M.; Bernardini, G.; Geminiani, M.; Ghezzi, L.; Amato, L.; Braconi, D.; Millucci, L.; Frediani, B.; Spreafico, A.; Franchi, A.; et al. Establishment of Four New Human Primary Cell Cultures from Chemo-Naïve Italian Osteosarcoma Patients. J. Cell Physiol. 2015, 230, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minetti, M.; Bernardini, G.; Biazzo, M.; Gutierrez, G.; Geminiani, M.; Petrucci, T.; Santucci, A. Padina pavonica Extract Promotes In Vitro Differentiation and Functionality of Human Primary Osteoblasts. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080473
Minetti M, Bernardini G, Biazzo M, Gutierrez G, Geminiani M, Petrucci T, Santucci A. Padina pavonica Extract Promotes In Vitro Differentiation and Functionality of Human Primary Osteoblasts. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(8):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080473
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinetti, Mariagiulia, Giulia Bernardini, Manuele Biazzo, Gilles Gutierrez, Michela Geminiani, Teresa Petrucci, and Annalisa Santucci. 2019. "Padina pavonica Extract Promotes In Vitro Differentiation and Functionality of Human Primary Osteoblasts" Marine Drugs 17, no. 8: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080473
APA StyleMinetti, M., Bernardini, G., Biazzo, M., Gutierrez, G., Geminiani, M., Petrucci, T., & Santucci, A. (2019). Padina pavonica Extract Promotes In Vitro Differentiation and Functionality of Human Primary Osteoblasts. Marine Drugs, 17(8), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080473





