A Novel Marine Natural Product Derived Pyrroloiminoquinone with Potent Activity against Skin Cancer Cells
Abstract
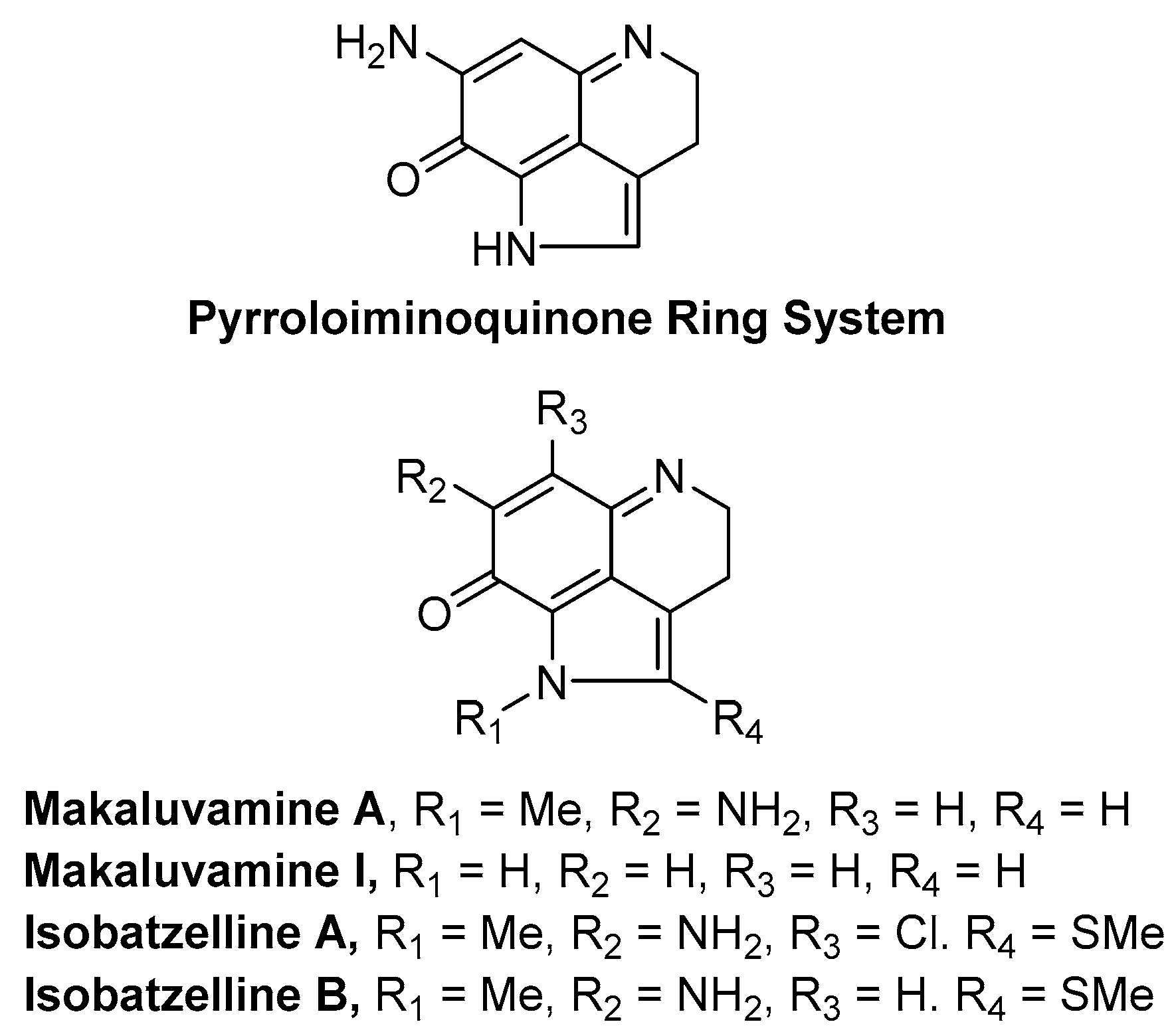
1. Introduction
2. Results
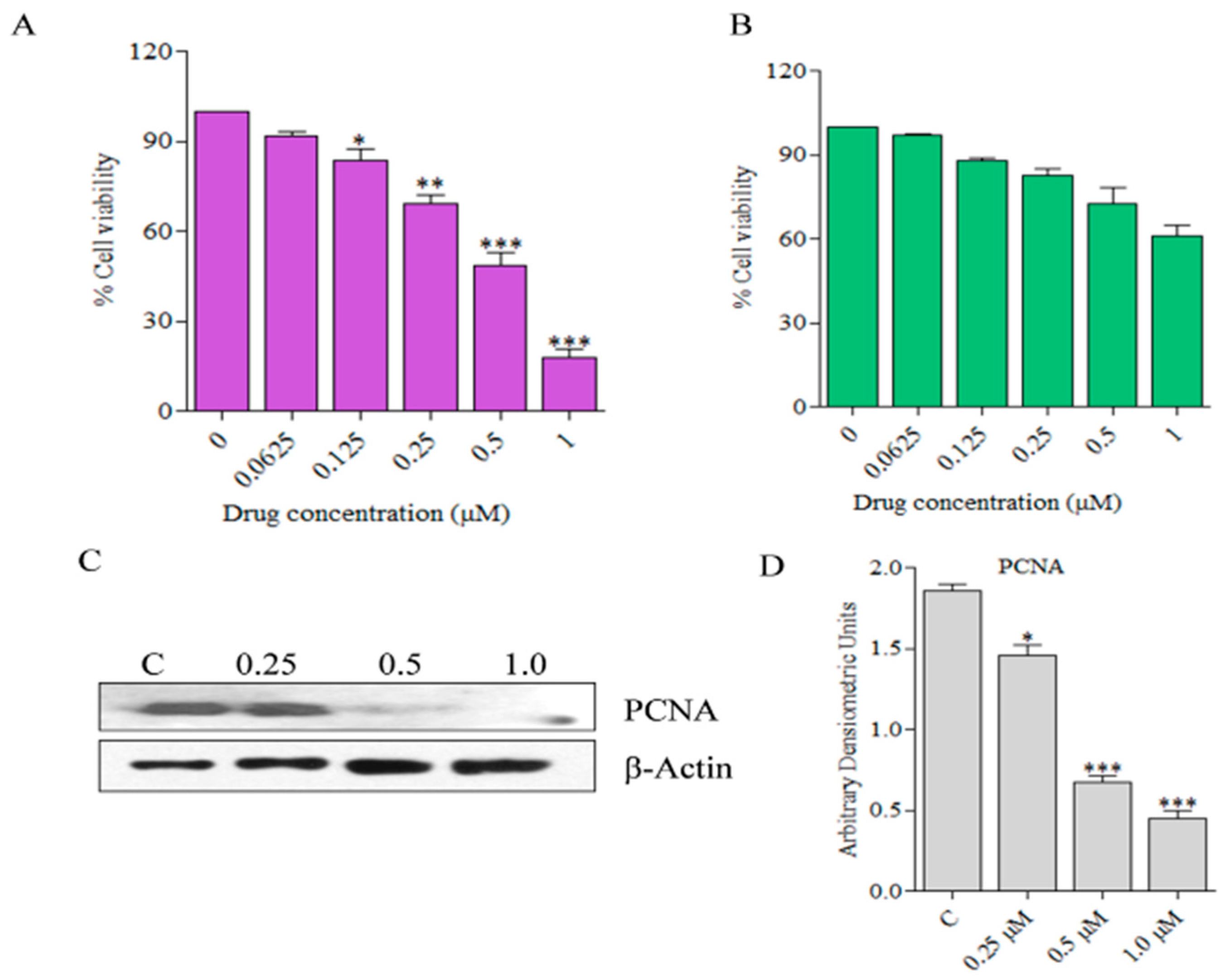
2.1. Alkaloid Analogs Induce Killing of Human Skin Cancer Cells in a Dose-Dependent Manner
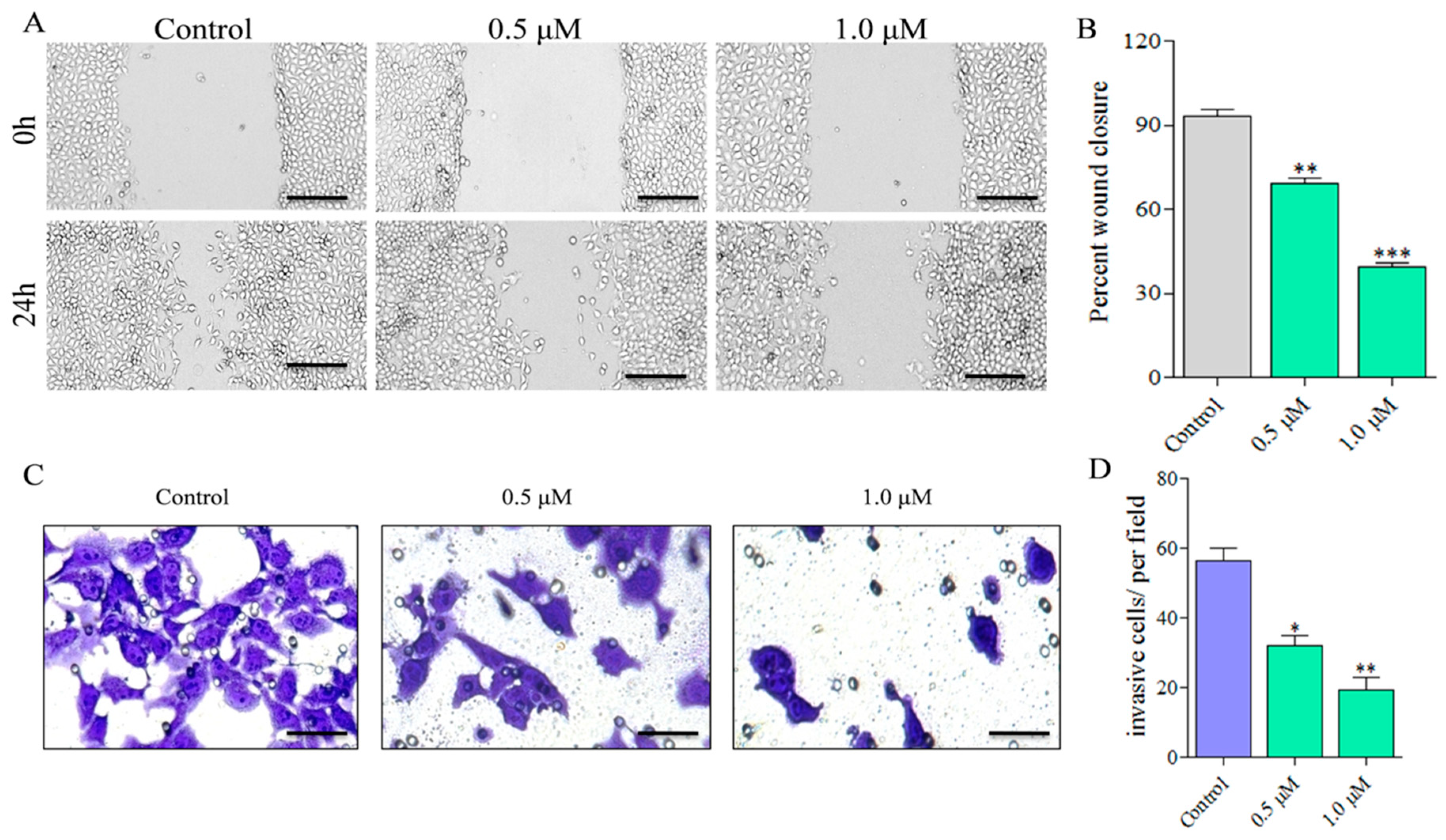
2.2. Compound C278 Treatment Restrains Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion in a Dose-Dependent Manner
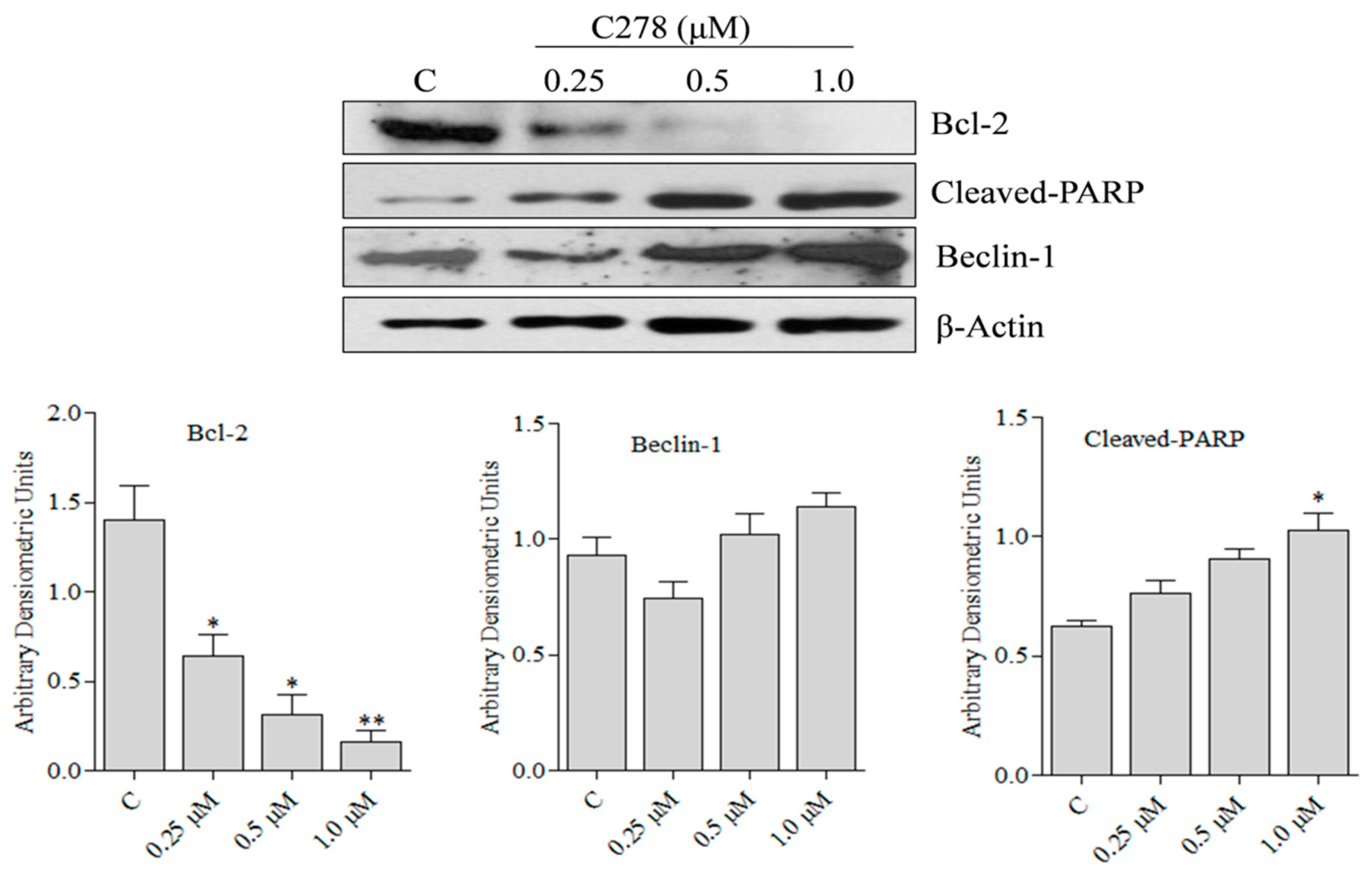
2.3. Compound C278 Induced Killing of SCC13 Cells Is Associated with the Modulation of Apoptosis and Autophagy Related Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Test Compounds
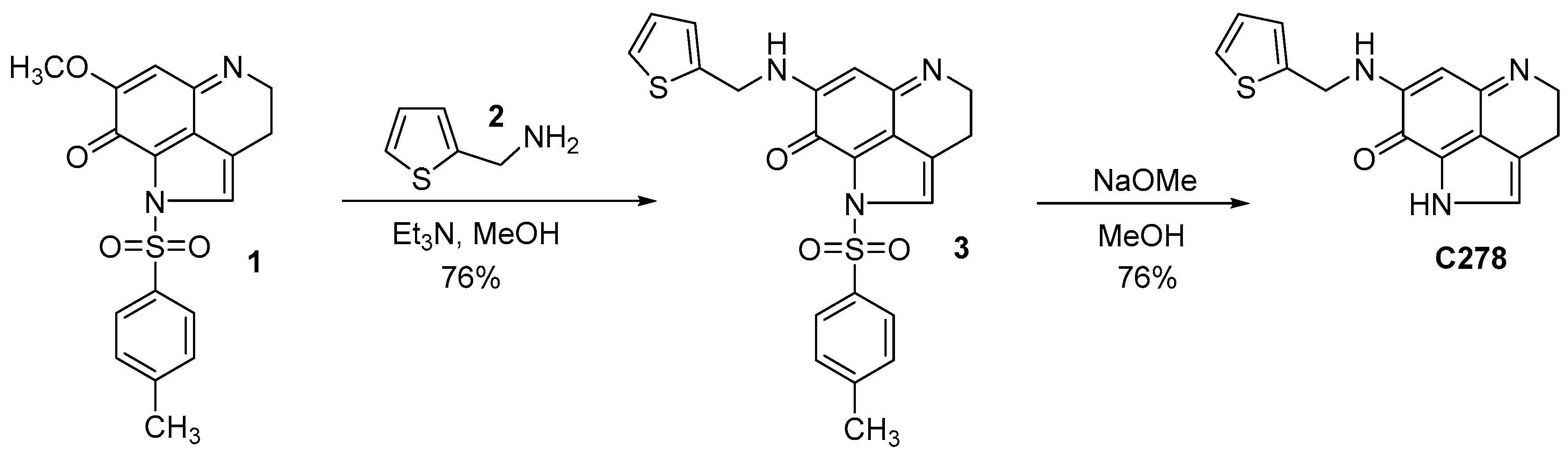
4.2. Synthesis of the Lead Compound C278
4.3. Amination of the Pyrroloiminoquinone Intermediate 1
4.4. Removal of the P-Toluene Sulfonyl Group from Compound 3 to Obtain C278
4.5. Chemicals and Reagents
4.6. Cell Line and Culture Conditions
4.7. MTT Assay for Cell Viability
4.8. Wound Healing Assay
4.9. Cell Invasion Assay
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. Statistical Calculations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linares, M.A.; Zakaria, A.; Nizran, P. Skin Cancer. Prim. Care 2015, 42, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomas, A.; Leonardi-Bee, J.; Bath-Hextall, F. A systematic review of worldwide incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, B.K.; Kricker, A. The epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2001, 63, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, J.; Jarrett, S.; Amaro-Ortiz, A.; Scott, T. UV radiation and the skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12222–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrocini, G.; Triassi, M.; Mauriello, M.C.; Torre, G.; Annunziata, M.C.; De Vita, V.; Pastore, F.; D’Arco, V.; Monfrecola, G. Epidemiology of skin cancer: Role of some environmental factors. Cancers 2010, 2, 1980–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoes, M.C.F.; Sousa, J.J.S.; Pais, A. Skin cancer and new treatment perspectives: A review. Cancer Lett. 2015, 357, 8–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, L.T.; Abdul Hamid, R.; Saiful Yazan, L.; Khaza’ai, H.; Mohtarrudin, N. Low dose triterpene-quinone fraction from Ardisia crispa root precludes chemical-induced mouse skin tumor promotion. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chinembiri, T.N.; du Plessis, L.H.; Gerber, M.; Hamman, J.H.; du Plessis, J. Review of natural compounds for potential skin cancer treatment. Molecules 2014, 19, 11679–11721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, L.T.; Hamid, R.A.; Yazan, L.S.; Khaza’ai, H. Isolation of a quinone-rich fraction from Ardisia crispa roots and its attenuating effects on murine skin tumorigenesis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 2301–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, L.M.; Kleemann, B.; Kacerovska, D.; Pizinger, K.; Kidson, S.H. Hypericin phototoxicity induces different modes of cell death in melanoma and human skin cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2008, 91, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, B.A.; Kleiner, H.E.; Ryan, E.A.; Dulik, D.M.; Monks, T.J.; Lau, S.S. Identification of multi-S-substituted conjugates of hydroquinone by HPLC-coulometric electrode array analysis and mass spectroscopy. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1993, 6, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yi, J. Cancer cell killing via ROS: To increase or decrease, that is the question. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 15–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 26–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haefner, B. Drugs from the deep: Marine natural products as drug candidates. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, P.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R. Drugs from the seas—Current status and microbiological implications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Antunes, E.M.; Copp, B.R.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Samaai, T. Pyrroloiminoquinone and related metabolites from marine sponges. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002, 19, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Radisky, D.C.; Radisky, E.S.; Barrows, L.R.; Copp, B.R.; Kramer, R.A.; Ireland, C.M. Novel cytotoxic topoisomerase II inhibiting pyrroloiminoquinones from Fijian sponges of the genus Zyzzya. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, J.R.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Makaluvamine G, a cytotoxic pigment from an an Indonesian Sponge Histodermella sp. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 8483–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Ng, P.L.; Schmitz, F.J.; Hossain, M.B.; van der Helm, D.; Kelly-Borges, M. Makaluvic Acids A and B: Novel Alkaloids from the Marine Sponge Zyzzya fuliginosus. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1104–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkina, N.K.; Makarchenko, A.E.; Denisenko, V.A. Zyzzyanones B-D, dipyrroloquinones from the marine sponge Zyzzya fuliginosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1424–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkina, N.K.; Makarchenko, A.E.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S. Zyzzyanone A, a novel pyrrolo[3,2-f]indole alkaloid from the Australian marine sponge Zyzzya fuliginosa. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 7491–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.F.; Schetz, J.A.; Kelly, M.; Peng, J.N.; Ang, K.K.; Flotow, H.; Leong, C.Y.; Ng, S.B.; Buss, A.D.; Wilkins, S.P.; et al. New antiinfective and human 5-HT2 receptor binding natural and semisynthetic compounds from the Jamaican sponge Smenospongia aurea. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkre, B.A.; Raisch, K.P.; Fan, L.; Velu, S.E. Analogs of the marine alkaloid makaluvamines: Synthesis, topoisomerase II inhibition, and anticancer activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 2890–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkre, B.A.; Raisch, K.P.; Fan, L.; Velu, S.E. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of benzyl and phenethyl analogs of makaluvamines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 2541–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Ezell, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Rayburn, E.R.; Nadkarni, D.H.; Murugesan, S.; Velu, S.E.; Zhang, R. FBA-TPQ, a novel marine-derived compound as experimental therapy for prostate cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2010, 28, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, Z.; Wu, C.; Li, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhou, R.; Shi, K.; Guo, J.; Li, N.; Liu, J.; et al. Evaluation of the anticancer and anti-metastasis effects of novel synthetic sodium channel blockers in prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Prostate 2019, 79, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qin, J.J.; Voruganti, S.; Nijampatnam, B.; Velu, S.E.; Ruan, K.H.; Hu, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, R. Discovery and Characterization of Dual Inhibitors of MDM2 and NFAT1 for Pancreatic Cancer Therapy. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5656–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Rayburn, E.R.; Velu, S.E.; Chen, D.; Nadkarni, D.H.; Murugesan, S.; Chen, D.; Zhang, R. A novel synthetic iminoquinone, BA-TPQ, as an anti-breast cancer agent: In vitro and in vivo activity and mechanisms of action. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 123, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Rayburn, E.R.; Velu, S.E.; Nadkarni, D.H.; Murugesan, S.; Zhang, R. In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of novel synthetic makaluvamine analogues. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3511–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Wang, W.; Qin, J.J.; Nijampatnam, B.; Murugesan, S.; Kozlovskaya, V.; Zhang, R.; Velu, S.E.; Kharlampieva, E. Highly efficient delivery of potent anticancer iminoquinone derivative by multilayer hydrogel cubes. Acta Biomater. 2017, 58, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, E.; Nakada, N.; Hikichi, T.; Kobayashi, J.; Nakanishi, I. EGF and beta1 integrin convergently regulate migration of A431 carcinoma cell through MAP kinase activation. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 272, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Krakhmal, N.V.; Zavyalova, M.V.; Denisov, E.V.; Vtorushin, S.V.; Perelmuter, V.M. Cancer Invasion: Patterns and Mechanisms. Acta Naturae 2015, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malliri, A.; Symons, M.; Hennigan, R.F.; Hurlstone, A.F.; Lamb, R.F.; Wheeler, T.; Ozanne, B.W. The transcription factor AP-1 is required for EGF-induced activation of rho-like GTPases, cytoskeletal rearrangements, motility, and in vitro invasion of A431 cells. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, L.G.; Wu, X.; Guan, J.L. Wound-healing assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 294, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Justus, C.R.; Leffler, N.; Ruiz-Echevarria, M.; Yang, L.V. In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, e51046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J. Transwell(®) invasion assays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 769, 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Hata, A.N.; Engelman, J.A.; Faber, A.C. The BCL2 Family: Key Mediators of the Apoptotic Response to Targeted Anticancer Therapeutics. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begleiter, A. Studies on the mechanism of action of quinone antitumor agents. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1985, 34, 2629–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.J.; Bao, J.L.; Wu, G.S.; Xu, W.S.; Huang, M.Q.; Chen, X.P.; Wang, Y.T. Quinones derived from plant secondary metabolites as anti-cancer agents. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 456–463. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, R.; Jin, X.; Hu, L.; You, C. Pyrroloquinoline quinone induces chondrosarcoma cell apoptosis by increasing intracellular reactive oxygen species. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7184–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzuto, G.; Ruggieri, P.; Molinari, A. Molecular aspects of tumor cell migration and invasion. Annali Dell'Istituto Superiore Sanitã 2010, 46, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, Y. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in apoptosis: Apoptosomes or mitochondria? Genes Cells 1998, 3, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.H.; Jackson, S.; Seaman, M.; Brown, K.; Kempkes, B.; Hibshoosh, H.; Levine, B. Induction of autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature 1999, 402, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadkarni, D.H.; Wang, F.; Wang, W.; Rayburn, E.R.; Ezell, S.J.; Murugesan, S.; Velu, S.E.; Zhang, R. Synthesis and in vitro anti-lung cancer activity of novel 1, 3, 4, 8-tetrahydropyrrolo [4, 3, 2-de]quinolin-8(1H)-one alkaloid analogs. Med. Chem. 2009, 5, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadanandan, E.V.; Pillai, S.K.; Lakshmikantham, M.V.; Billimoria, A.D.; Culpepper, J.S.; Cava, M.P. Efficient Syntheses of the Marine Alkaloids Makaluvamine D and Discorhabdin C: The 4,6,7-Trimethoxyindole Approach. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 1800–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, A.L.; Rice, R.H. Differential regulation by retinoic acid and calcium of transglutaminases in cultured neoplastic and normal human keratinocytes. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 2356–2361. [Google Scholar]
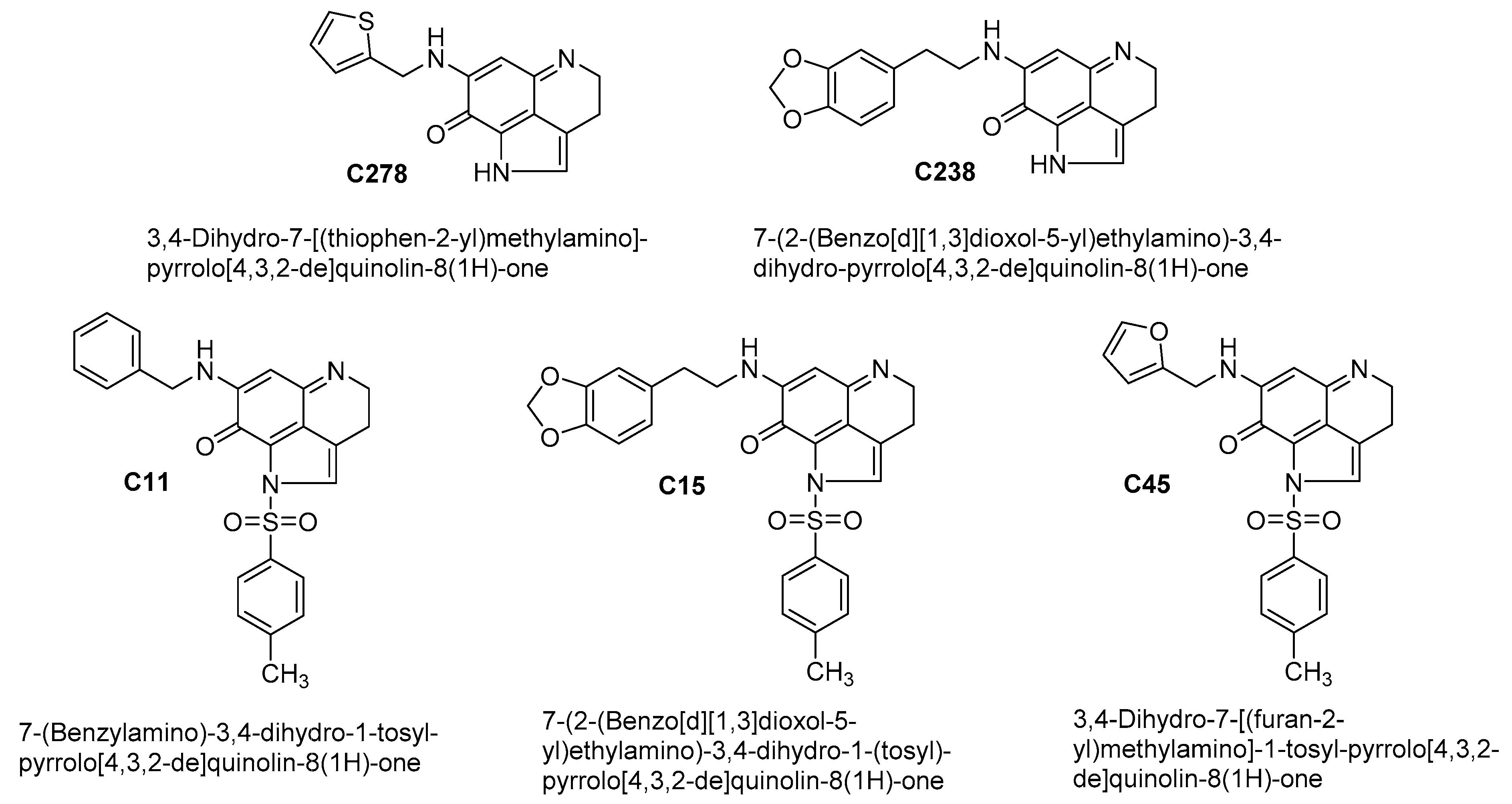
| Compd | SSC13 Cells | HaCaT Cells | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 ± SD (μM) | IC90 ± SD (μM) | IC50 ± SD (μM) | IC90 ± SD (μM) | |
| C238 | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 1.48 ± 0.04 | 2.35 ± 0.21 | 4.23 ± 0.36 |
| C278 | 0.50 ± 0.11 | 0.90 ± 0.21 | 1.15 ± 0.21 | 2.07 ± 0.37 |
| C11 | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 0.92 ± 0.06 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 0.87 ± 0.03 |
| C15 | 5.31 ± 0.19 | 9.56 ± 0.35 | 0.73 ± 0.09 | 1.32 ± 0.16 |
| C45 | 2.58 ± 0.23 | 4.65 ± 0.42 | 5.24 ± 0.08 | 9.43 ± 0.15 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cowan, J.; Shadab, M.; Nadkarni, D.H.; KC, K.; Velu, S.E.; Yusuf, N. A Novel Marine Natural Product Derived Pyrroloiminoquinone with Potent Activity against Skin Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080443
Cowan J, Shadab M, Nadkarni DH, KC K, Velu SE, Yusuf N. A Novel Marine Natural Product Derived Pyrroloiminoquinone with Potent Activity against Skin Cancer Cells. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(8):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080443
Chicago/Turabian StyleCowan, Jaden, Mohammad Shadab, Dwayaja H. Nadkarni, Kailash KC, Sadanandan E. Velu, and Nabiha Yusuf. 2019. "A Novel Marine Natural Product Derived Pyrroloiminoquinone with Potent Activity against Skin Cancer Cells" Marine Drugs 17, no. 8: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080443
APA StyleCowan, J., Shadab, M., Nadkarni, D. H., KC, K., Velu, S. E., & Yusuf, N. (2019). A Novel Marine Natural Product Derived Pyrroloiminoquinone with Potent Activity against Skin Cancer Cells. Marine Drugs, 17(8), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080443






