Efficacy of Compounds Isolated from Streptomyces olivaceus against the Morphogenesis and Virulence of Candida albicans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
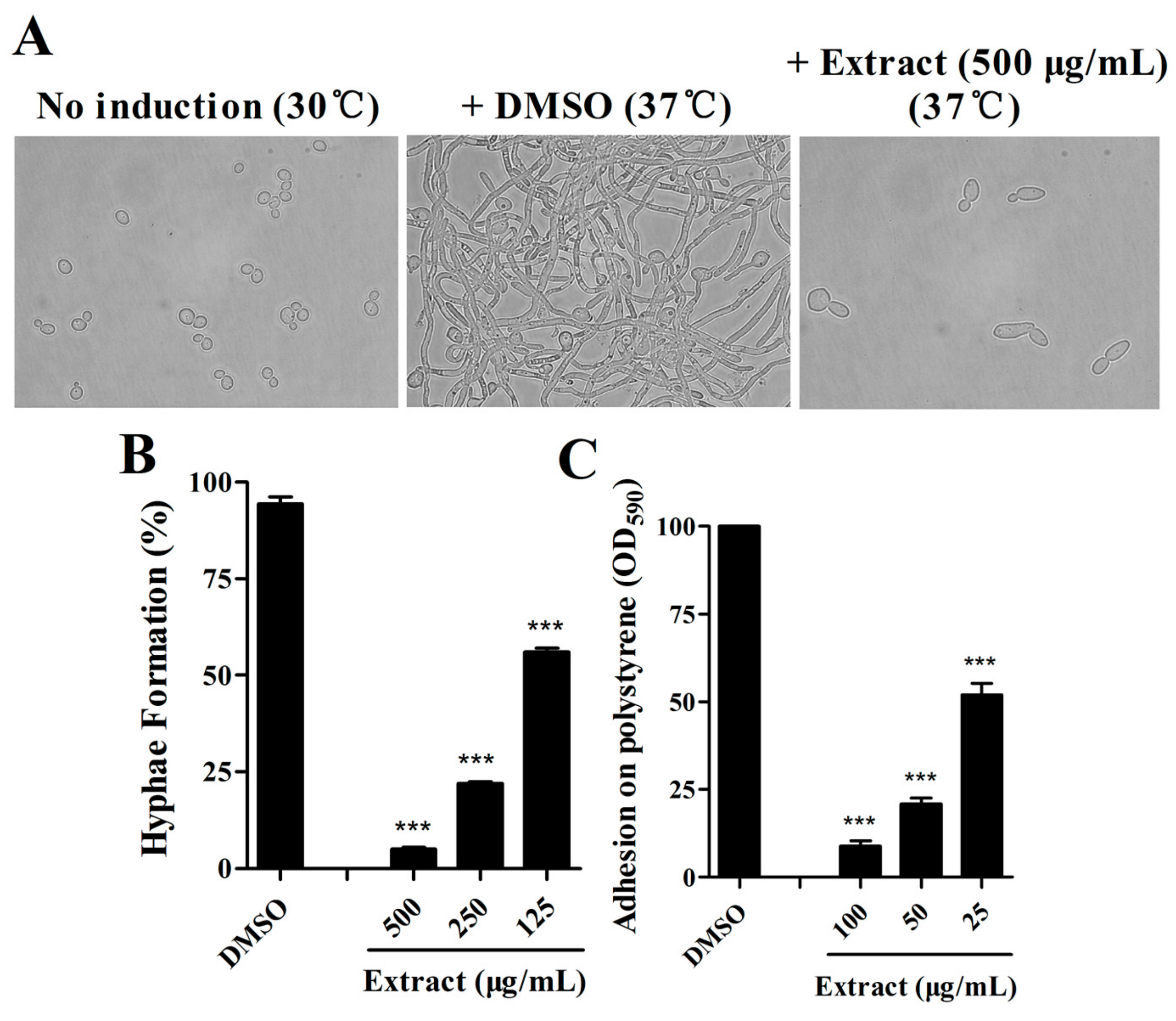
2.1. Extract of S. olivaceus SCSIO T05 ΔrsdK2/ΔxmcP Inhibits Hypha Formation and Adhesion of C. albicans
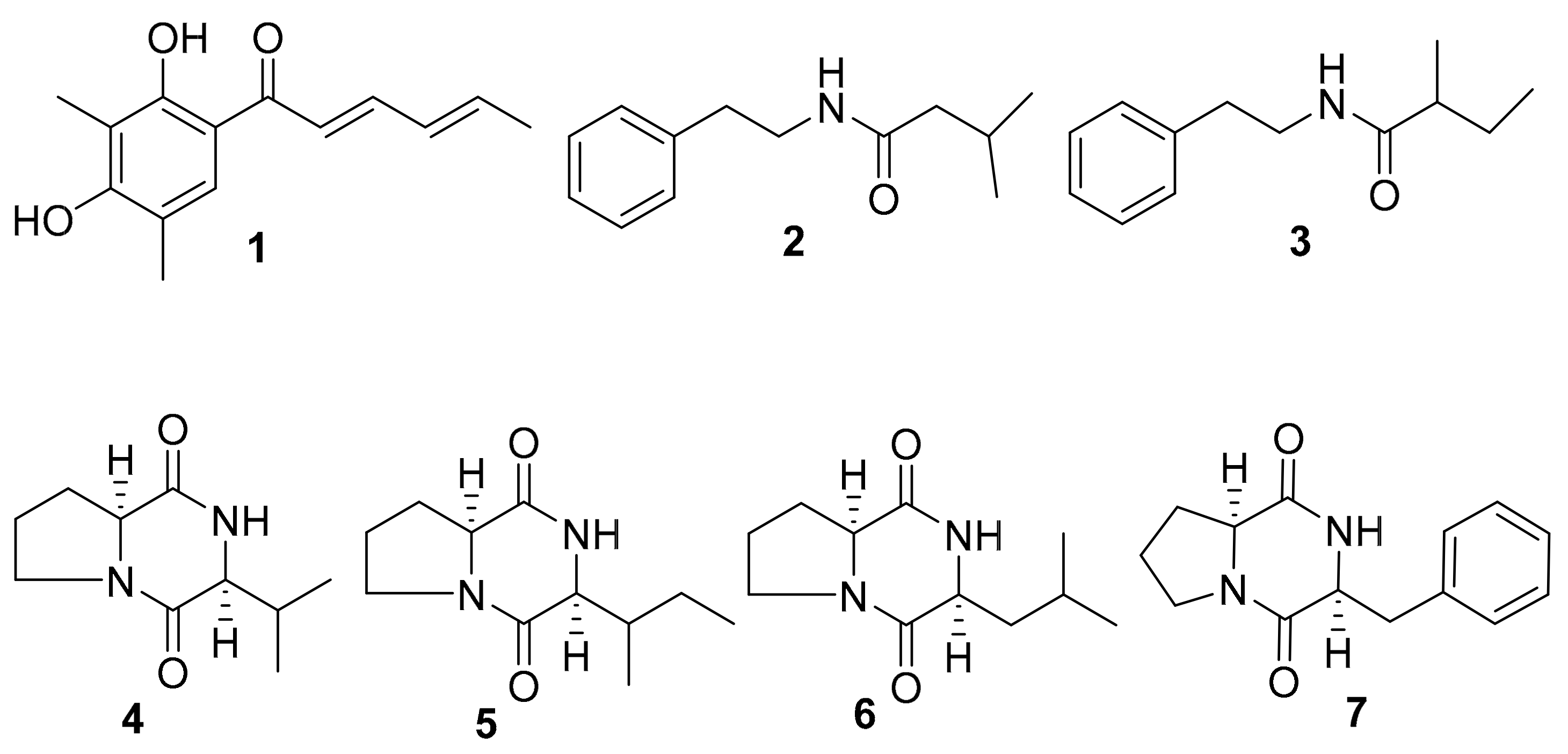
2.2. Isolation of Active Compounds from the Extract
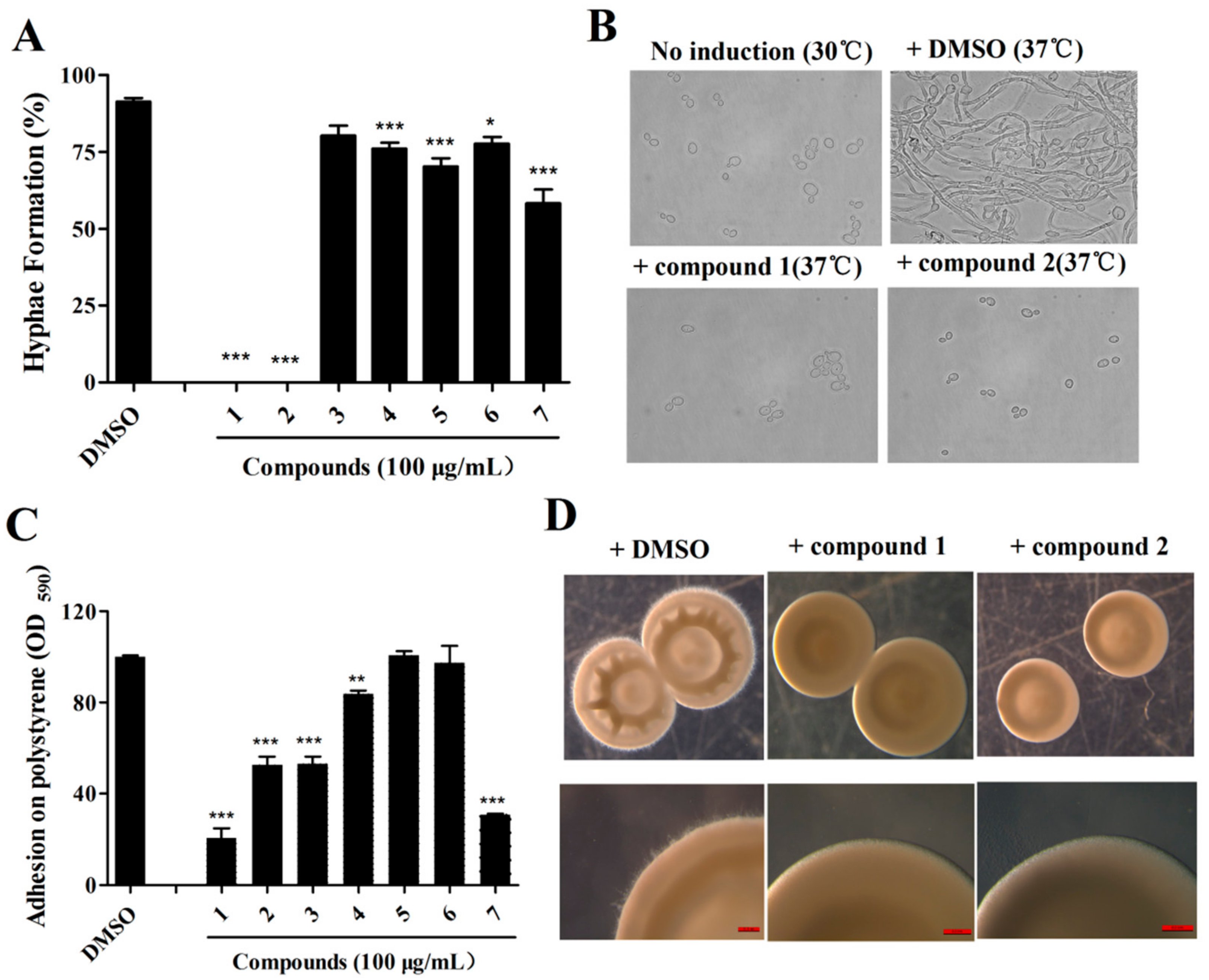
2.3. Effects of Isolated Compounds on the Cytotoxicity of C. albicans
2.4. The Effects of Compound 1 and 2 on C. albicans Are Dose-Dependent
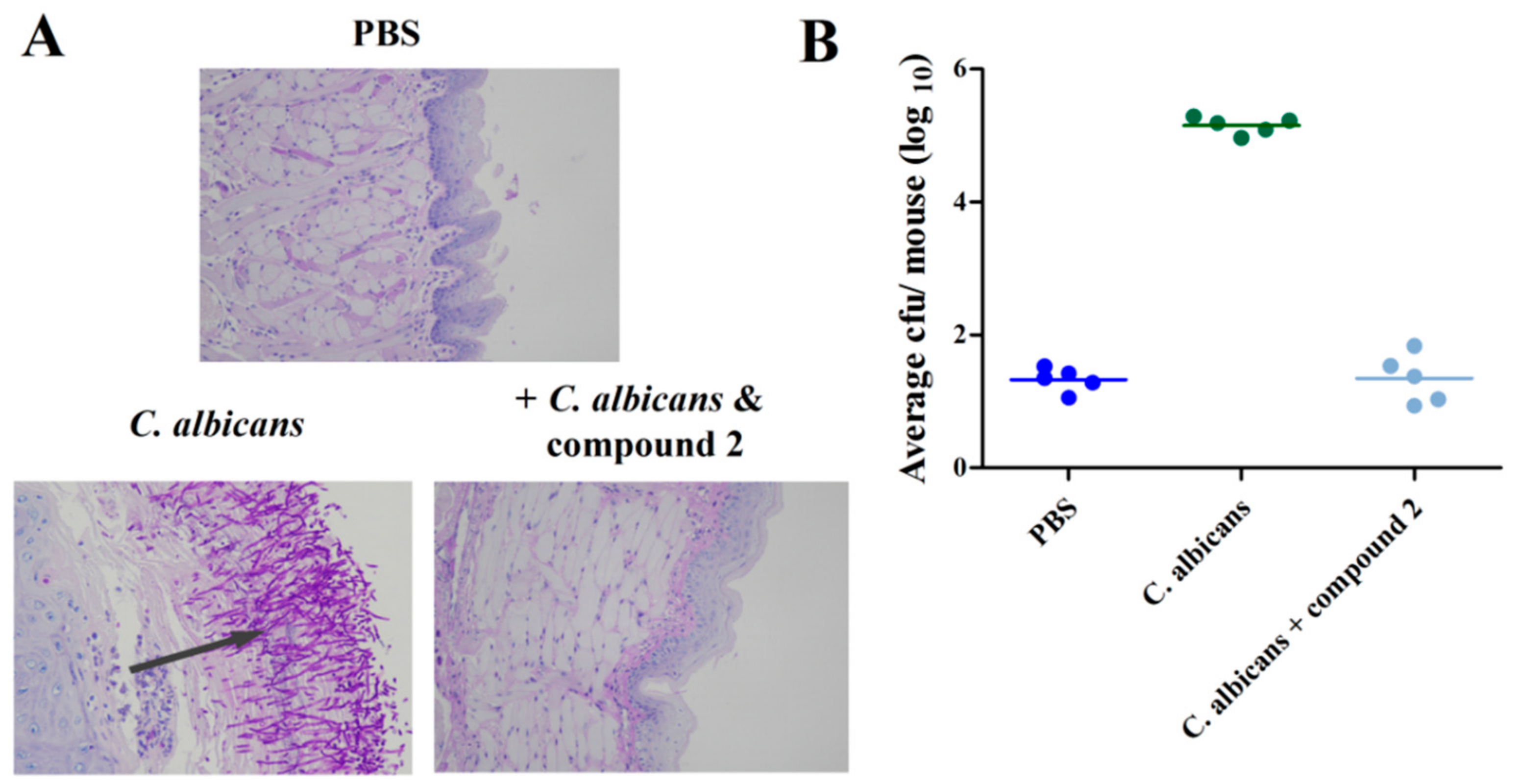
2.5. Compound 2 Reduced C. albicans Infection in the Mouse Oral Mucosal Infection Model
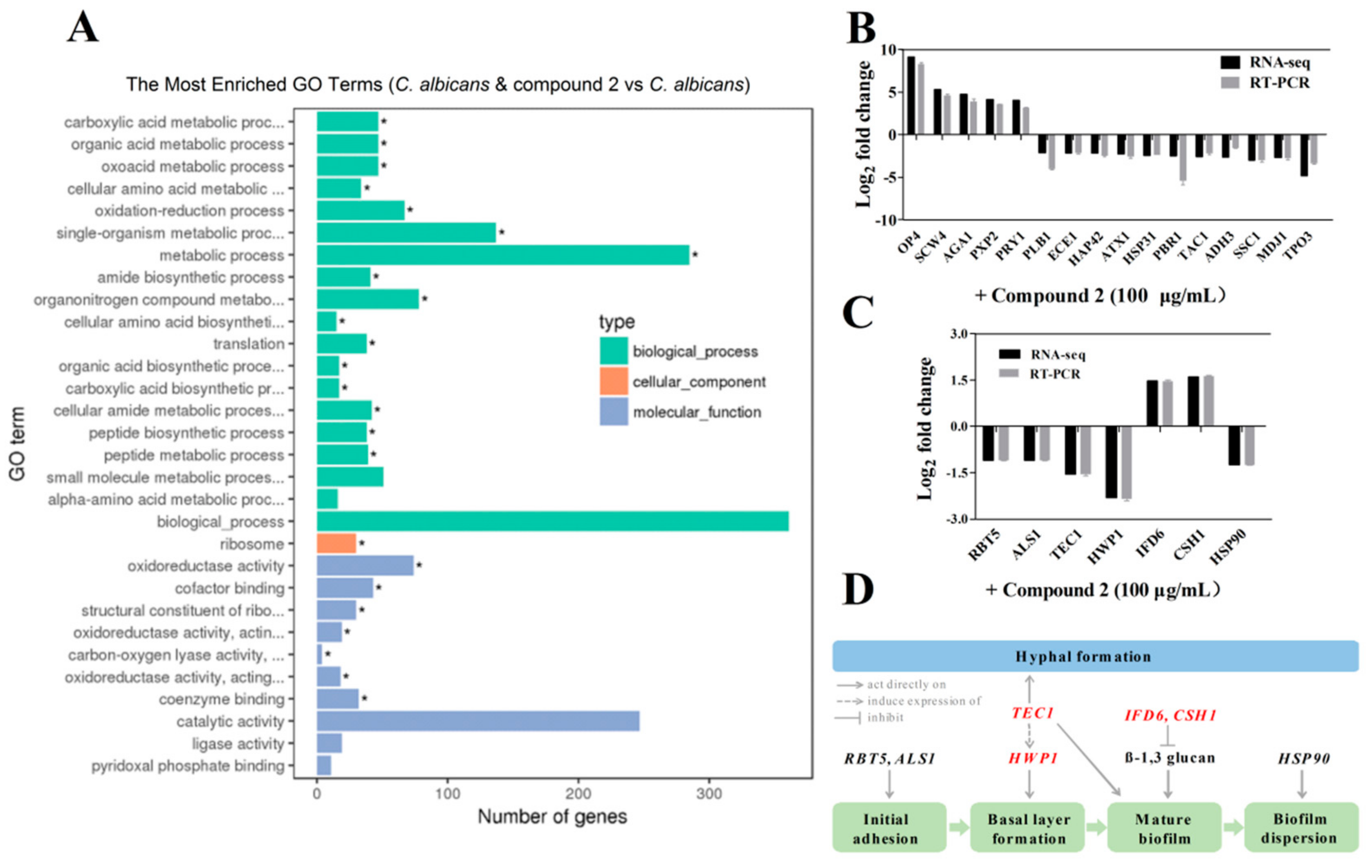
2.6. Compound 2 Affected the Expression Levels of a Wide Range of Genes in C. albicans
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Strains and Reagents
4.3. Fermentation and Isolation
4.4. Adhesion Assays
4.5. Cell Binding Assays
4.6. Hypha Formation Assays
4.7. Colony Morphology Assays
4.8. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.9. Cell Growth Analysis
4.10. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.11. Mouse Oral Mucosal Assays
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pfaller, M.A.; Diekema, D.J. Epidemiology of invasive candidiasis: A persistent public health problem. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 133–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boral, H.; Metin, B.; Döğen, A.; Seyedmousavi, S.; Ilkit, M. Overview of selected virulence attributes in Aspergillus fumigatus, Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, Trichophyton rubrum, and Exophiala dermatitidis. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2018, 111, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, K. Virulence in Candida species. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudbery, P.; Gow, N.; Berman, J. The distinct morphogenic states of Candida albicans. Trends Microbiol. 2004, 12, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazly, A.; Jain, C.; Dehner, A.C.; Issi, L.; Lilly, E.A.; Ali, A.; Cao, H.; Fidel, P.L., Jr.; Rao, R.P.; Kaufman, P.D. Chemical screening identifies filastatin, a small molecule inhibitor of Candida albicans adhesion, morphogenesis, and pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13594–13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saville, S.P.; Lazzell, A.L.; Monteagudo, C.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L. Engineered control of cell morphology in vivo reveals distinct roles for yeast and filamentous forms of Candida albicans during infection. Eukaryot. Cell 2003, 2, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.J.; Köhler, J.R.; DiDomenico, B.; Loebenberg, D.; Cacciapuoti, A.; Fink, G.R. Nonfilamentous C. albicans mutants are avirulent. Cell 1997, 90, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, F.L.; Wilson, D.; Hube, B. Candida albicans pathogenicity mechanisms. Virulence 2013, 4, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumamoto, C.A. Candida biofilms. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ribot, J.L. Candida albicans biofilms: More than filamentation. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, G.; Saville, S.P.; Thomas, D.P.; López-Ribot, J.L. Candida biofilms: An update. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojic, E.M.; Darouiche, R.O. Candida infections of medical devices. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.L.; Cannon, R.D.; Villas-Bôas, S.G. The metabolic basis of Candida albicans morphogenesis and quorum sensing. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2011, 48, 747–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmioglu, S.; Ilkit, M.; Badak, Z. Comparison of 12 liquid media for germ tube production of Candida albicans and C. tropicalis. Mycoses 2007, 50, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkey, L.L.; McNemar, M.D.; Saporito-Irwin, S.M.; Sypherd, P.S.; Fonzi, W.A. HWP1 functions in the morphological development of Candida albicans downstream of EFG1, TUP1, and RBF1. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 5273–5279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Padovan, A.C.; Chaves, G.M.; Colombo, A.L.; Briones, M.R. A novel allele of HWP1, isolated from a clinical strain of Candida albicans with defective hyphal growth and biofilm formation, has deletions of Gln/Pro and Ser/Thr repeats involved in cellular adhesion. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoldt, V.R.; Sonneborn, A.; Leuker, C.E.; Ernst, J.F. Efg1p, an essential regulator of morphogenesis of the human pathogen Candida albicans, is a member of a conserved class of bHLH proteins regulating morphogenetic processes in fungi. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1982–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputo, S.; Kumar, A.; Krysan, D.J. Efg1 directly regulates ACE2 expression to mediate cross talk between the cAMP/PKA and RAM pathways during Candida albicans morphogenesis. Eukaryot. Cell 2014, 13, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.; Birse, C.; Zhou, S.; Matson, R.; Liu, H. DNA array studies demonstrate convergent regulation of virulence factors by Cph1, Cph2, and Efg1 in Candida albicans. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 48988–48996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, D.; Henriques, M.; Silva, S. Portrait of Candida species biofilm regulatory network genes. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, L.L.; Cota, E. Candida albicans agglutinin-like sequence (Als) family vignettes: A review of Als protein structure and function. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, C.; Huang, H.; Gui, C.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Ju, J. Biosynthetic baeyer-villiger chemistry enables access to two anthracene scaffolds from a single gene cluster in deep-sea-derived Streptomyces olivaceus SCSIO T05. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, C.; Qin, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q.; Ju, J. Genome mining of Streptomyces olivaceus SCSIO T05: Discovery of olimycins A and B and assignment of absolute configurations. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.J.; Li, G.H.; Shen, Y.M. New Chemical Constituents from the Endophyte Streptomyces Species LR4612 Cultivated on Maytenus hookeri. Chem. Biodivers. 2006, 3, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tang, J.; Gao, H.; Lin, H.; Hong, K.; Yao, X. Study of anti-MRSA bioactive constituents from a marine actinomycetes Micromonospora sp. (No. 69). Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2010, 29, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, S.M.; French, S.; Kohn, L.A.; Chen, V.; Johnson, A.D. Systematic screens of a Candida albicans homozygous deletion library decouple morphogenetic switching and pathogenicity. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, M.; Nobile, C.J. Candida albicans biofilms: Development, regulation, and molecular mechanisms. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinney, D.C.; Anthony, J. How were new medicines discovered? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Chávez, F.; Salo, O.; Nygård, Y.; Lankhorst, P.P.; Bovenberg, R.A.L.; Driessen, A.J.M. Mechanism and regulation of sorbicillin biosynthesis by Penicillium chrysogenum. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassegoda, A.; Ivanova, K.; Ramon, E.; Tzanov, T. Strategies to prevent the occurrence of resistance against antibiotics by using advanced materials. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 2075–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzariai, A.; Hafidi, M.; Khadra, A.; Aemig, Q.; El Fels, L.; Barret, M.; Merlina, G.; Patureau, D.; Pinelli, E. Human and veterinary antibiotics during composting of sludge or manure: Global perspectives on persistence, degradation, and resistance genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monroy-Pérez, E.; Sáinz-Espuñes, T.; Paniagua-Contreras, G.; Negrete-Abascal, E.; Rodríguez-Moctezuma, J.R.; Vaca, S. Frequency and expression of ALS and HWP1 genotypes in Candida albicans strains isolated from Mexican patients suffering from vaginal candidosis. Mycoses 2012, 55, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staab, J.F.; Ferrer, C.A.; Sundstrom, P. Developmental expression of a tandemly repeated, proline- and glutamine-rich amino acid motif on hyphal surfaces of Candida albicans. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 6298–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ene, I.V.; Bennett, R.J. Hwp1 and related adhesins contribute to both mating and biofilm formation in Candida albicans. Eukaryot. Cell 2009, 8, 1909–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staab, J.F.; Bradway, S.D.; Fidel, P.L.; Sundstrom, P. Role of Tec1 in the development, architecture, and integrity of sexual biofilms of Candida albicans. Eukaryot. Cell 2015, 14, 228–240. [Google Scholar]
- Sahni, N.; Yi, S.; Daniels, K.J.; Huang, G.; Srikantha, T.; Soll, D.R. Tec1 mediates the pheromone response of the white phenotype of Candida albicans: Insights into the evolution of new signal transduction pathways. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobile, C.J.; Nett, J.E.; Hernday, A.D.; Homann, O.R.; Deneault, J.S.; Nantel, A.; Andes, D.R.; Johnson, A.D.; Mitchell, A.P. Biofilm matrix regulation by Candida albicans Zap1. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, M.E.; Liu, J.; Wallace, J.; Akhlaghi, F.; Rowley, D.C. Secondary metabolites produced by the marine bacterium Halobacillus salinus that inhibit quorum sensing-controlled phenotypes in gram-negative bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, T.B.; Fink, G.R. Bakers’ yeast, a model for fungal biofilm formation. Science 2001, 291, 878–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Dias, A.; Miranda, I.; Branco, J.; Monteiro-Soares, M.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Rodrigues, A.G. Adhesion, biofilm formation, cell surface hydrophobicity, and antifungal planktonic susceptibility: Relationship among Candida spp. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, M.; Fournier, H.; de Repentigny, L.; Belhumeur, P. Characterization of CaGSP1, the Candida albicans RAN/GSP1 homologue. Gene 2000, 250, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xiu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, G.; Shang, X. Transcriptional responses of Candida albicans to antimicrobial peptide MAF-1A. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis, N.V.; Filler, S.G. Mouse model of oropharyngeal candidiasis. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtappels, M.; Swinnen, E.; De Groef, L.; Wuyts, J.; Moons, L.; Lagrou, K.; Van Dijck, P.; Kucharíková, S. Antifungal activity of oleylphosphocholine on in vitro and in vivo Candida albicans biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 62, e01767–e01817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, L.; Sun, C.; Zhang, C.; Song, S.; Sun, X.; Ju, J.; Deng, Y. Efficacy of Compounds Isolated from Streptomyces olivaceus against the Morphogenesis and Virulence of Candida albicans. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080442
Meng L, Sun C, Zhang C, Song S, Sun X, Ju J, Deng Y. Efficacy of Compounds Isolated from Streptomyces olivaceus against the Morphogenesis and Virulence of Candida albicans. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(8):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080442
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Lili, Changli Sun, Chunyan Zhang, Shihao Song, Xiuyun Sun, Jianhua Ju, and Yinyue Deng. 2019. "Efficacy of Compounds Isolated from Streptomyces olivaceus against the Morphogenesis and Virulence of Candida albicans" Marine Drugs 17, no. 8: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080442
APA StyleMeng, L., Sun, C., Zhang, C., Song, S., Sun, X., Ju, J., & Deng, Y. (2019). Efficacy of Compounds Isolated from Streptomyces olivaceus against the Morphogenesis and Virulence of Candida albicans. Marine Drugs, 17(8), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080442





