Characterization of an Alkaline Alginate Lyase with pH-Stable and Thermo-Tolerance Property
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
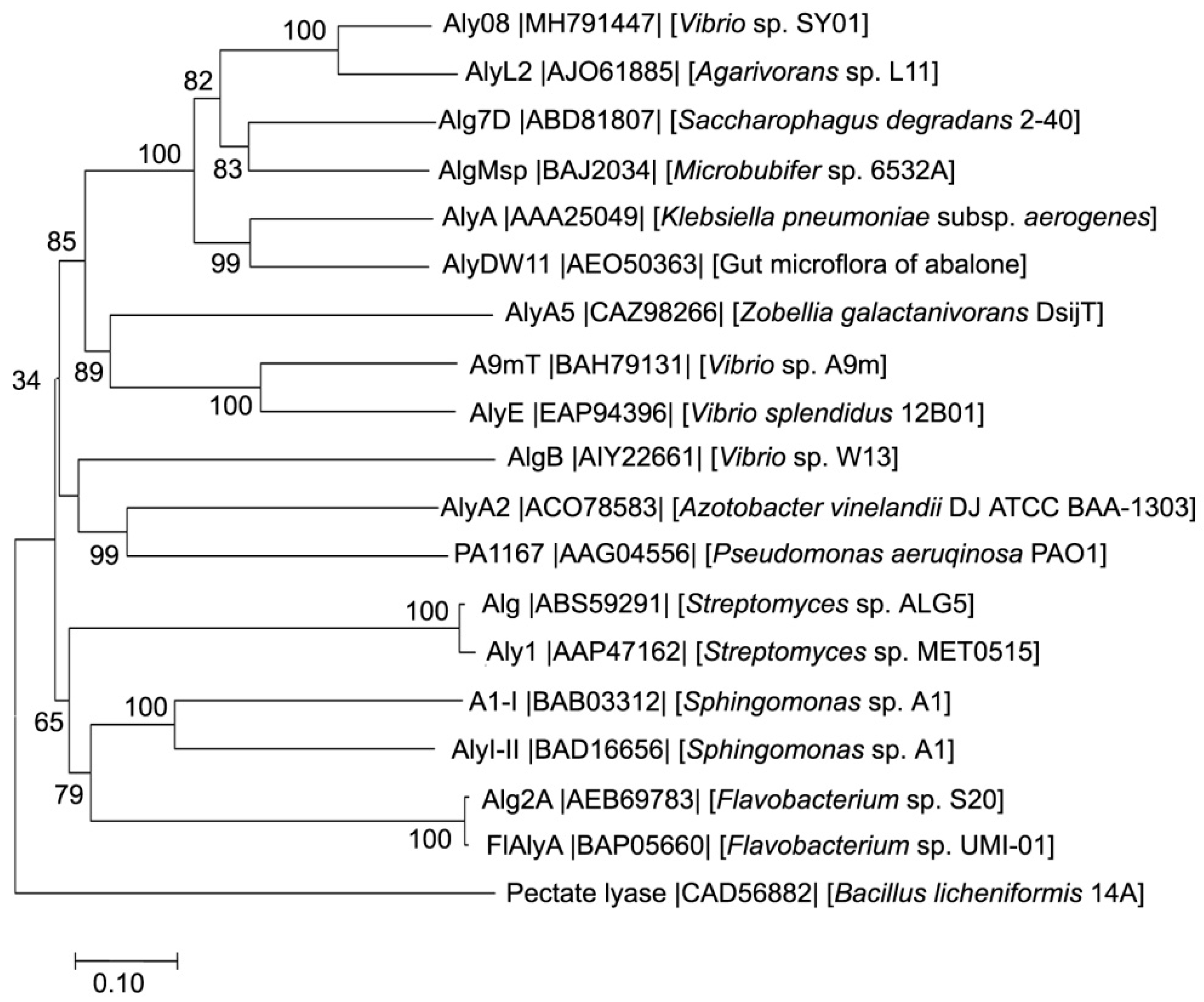
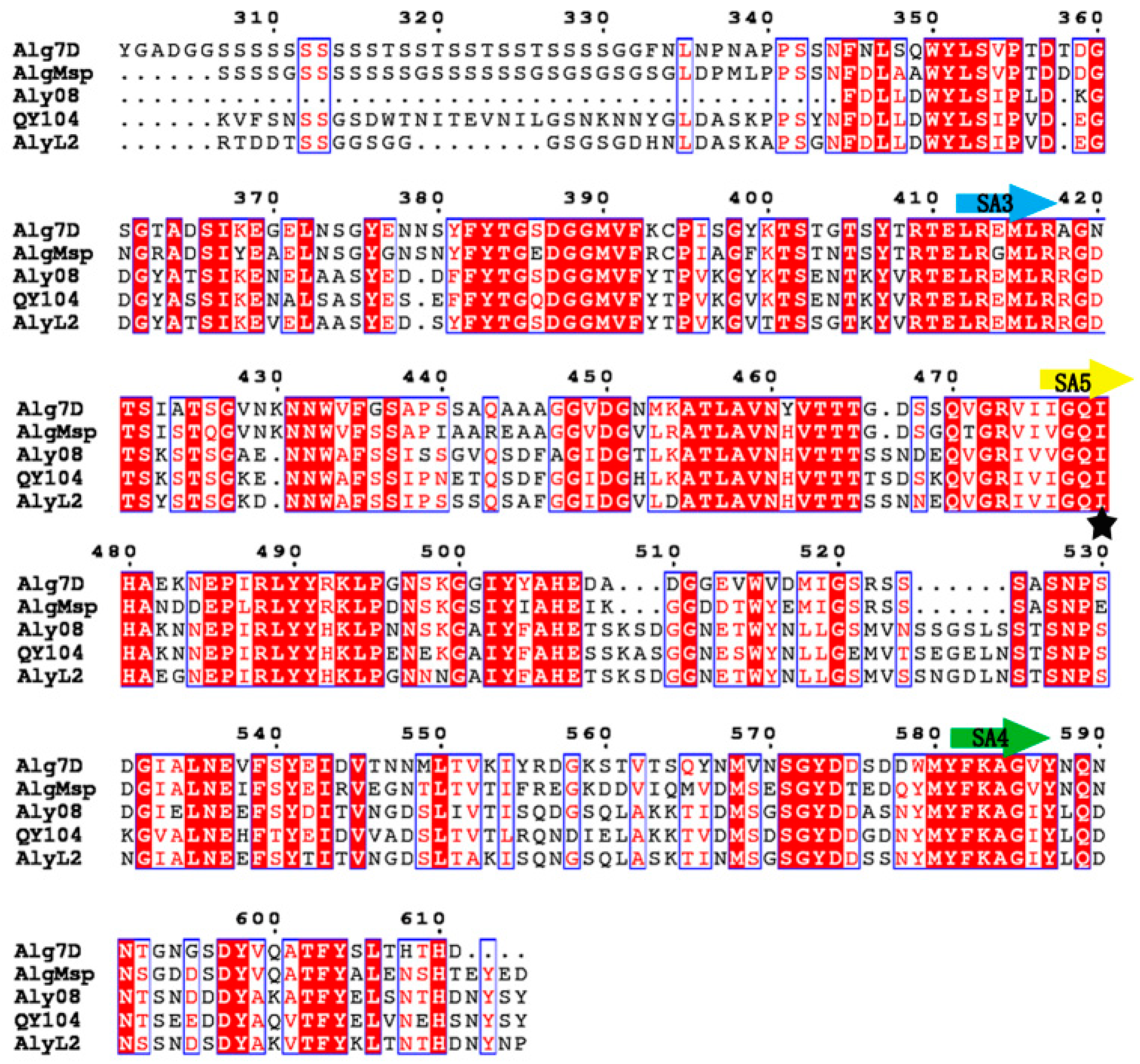
2.1. Sequence Analysis of Aly08
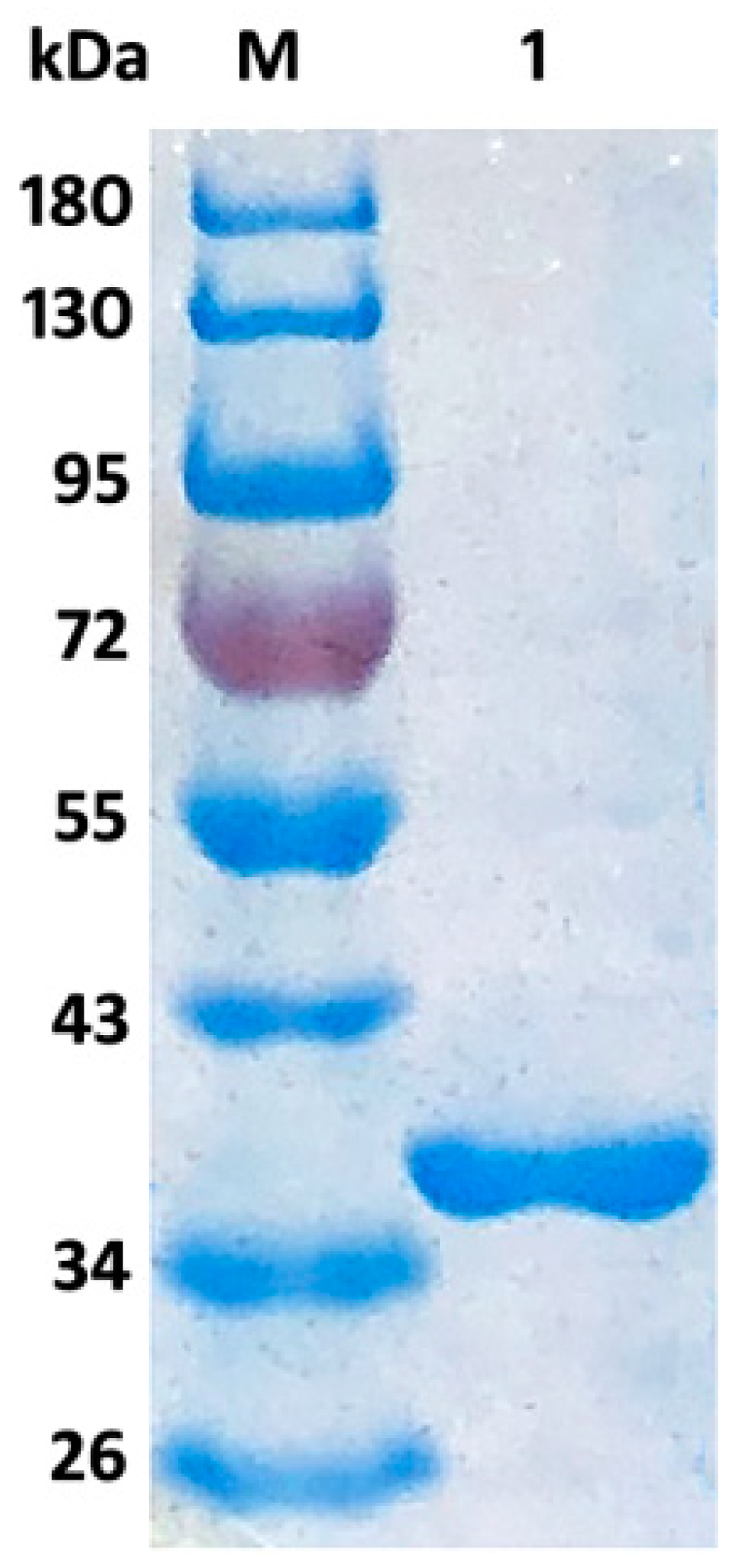
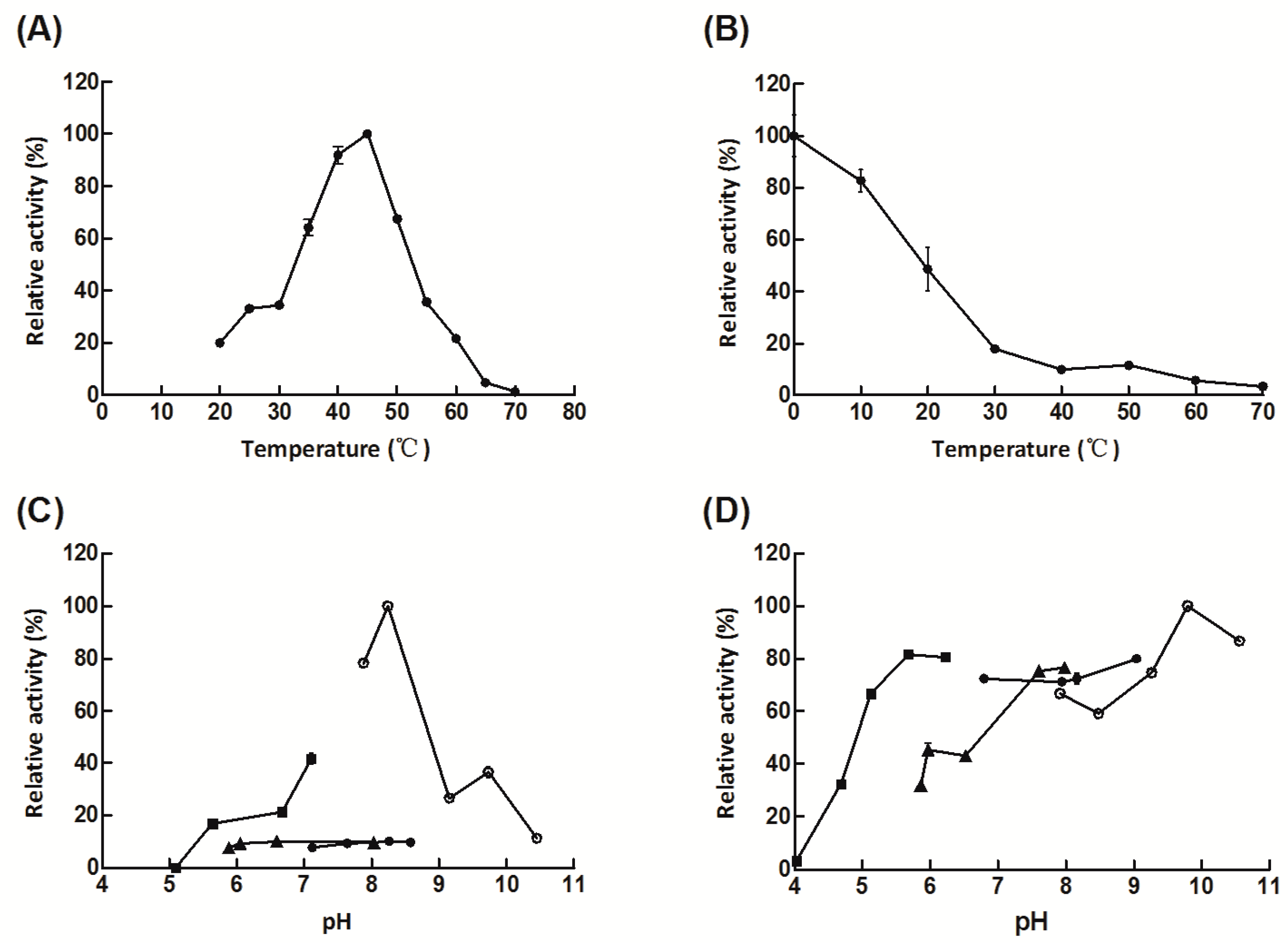
2.2. Expression, Purification, and Characterization of Aly08
2.3. Thermo-Tolerance and Heat Recovery of Aly08
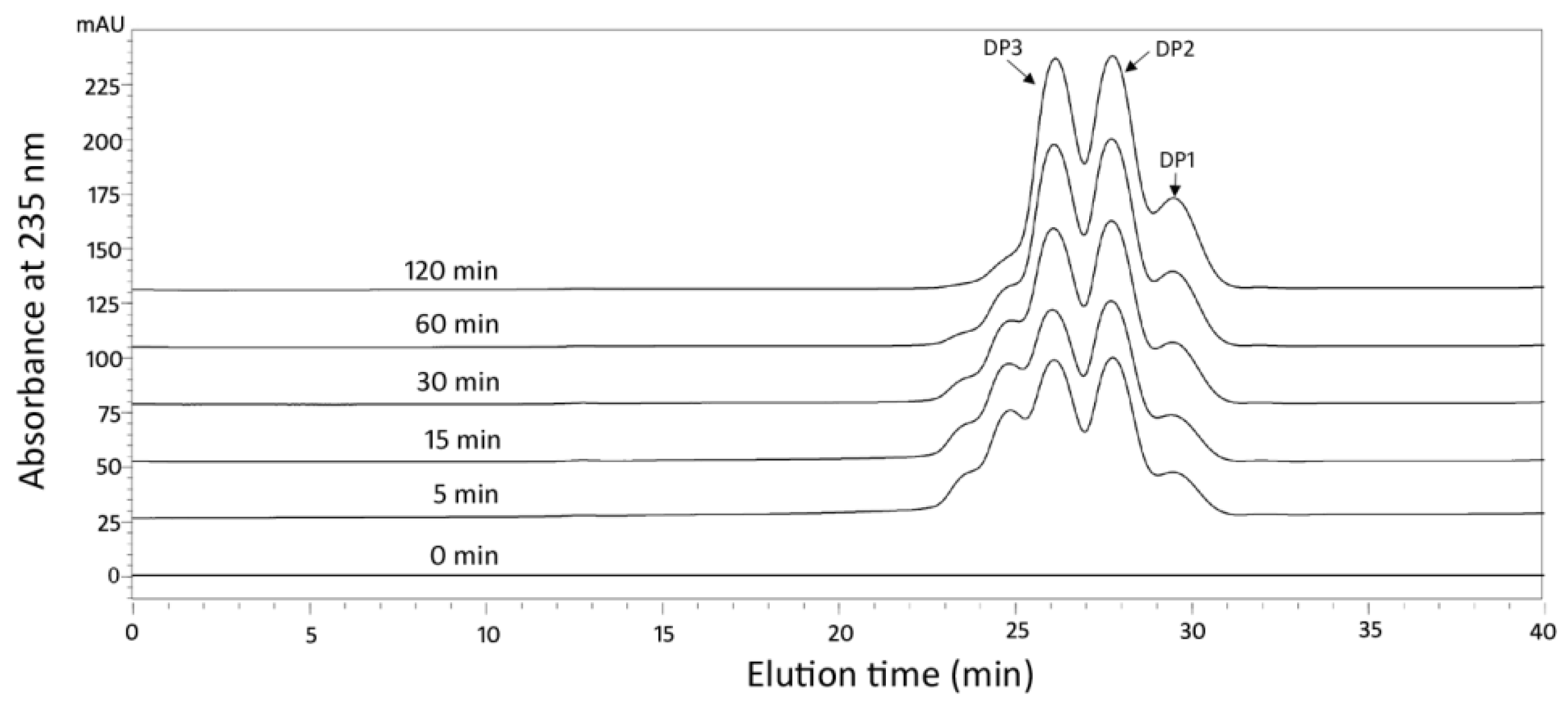
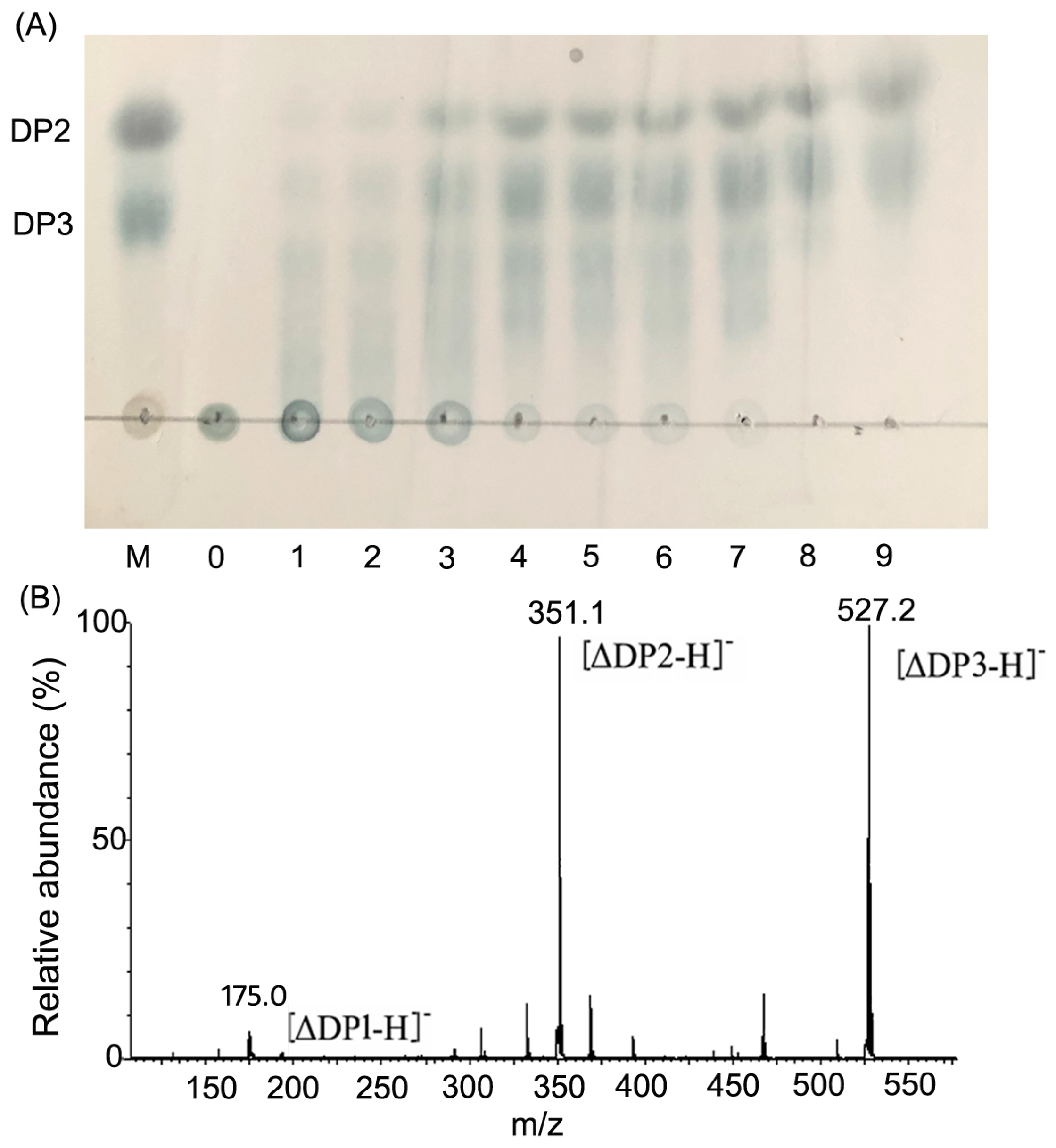
2.4. Action Pattern and Final Product Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Strains and Nucleotides
3.3. Sequence Analysis
3.4. Heterologous Expression and Purification of Recombinant Aly08
3.5. Alginate Lyase Activity Assay
3.6. Biochemical Characterization of the Recombinant Enzyme
3.7. Thermo-Tolerance Properties of Aly08
3.8. Analysis of Reaction Products and Hydrolytic Pattern
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scieszka, S.; Klewicka, E. Algae in food: A general review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senturk Parreidt, T.; Muller, K.; Schmid, M. Alginate-based edible films and coatings for food packaging applications. Foods 2018, 7, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wargacki, A.J.; Leonard, E.; Win, M.N.; Regitsky, D.D.; Santos, C.N.; Kim, P.B.; Cooper, S.R.; Raisner, R.M.; Herman, A.; Sivitz, A.B.; et al. An engineered microbial platform for direct biofuel production from brown macroalgae. Science 2012, 335, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, S.N.; Edgar, K.J. Alginate derivatization: A review of chemistry, properties and applications. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3279–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Moriwaki, S.; Miyake, O.; Hashimoto, W.; Murata, K.; Mikami, B. Structure and function of a hypothetical Pseudomonas aeruginosa protein PA1167 classified into family PL-7: A novel alginate lyase with a beta-sandwich fold. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31863–31872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertesvag, H. Alginate-modifying enzymes: Biological roles and biotechnological uses. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 523. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, T.Y.; Preston, L.A.; Schiller, N.L. Alginate lyase: Review of major sources and enzyme characteristics, structure-function analysis, biological roles, and applications. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 289–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Wang, Z.P.; Wang, L.N.; Peng, J.X.; Wang, Y.N.; Han, Y.T.; Zhao, S.F. Combined enzymatic hydrolysis and selective fermentation for green production of alginate oligosaccharides from Laminaria japonica. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Horn, S.J. Enzymatic saccharification of brown seaweed for production of fermentable sugars. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 213, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Chung, J.H.; Wang, D.; Lee, J.; Woo, H.C.; Choi, I.G.; Kim, K.H. Depolymerization of alginate into a monomeric sugar acid using Alg17C, an exo-oligoalginate lyase cloned from Saccharophagus degradans 2-40. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Dong, F.; Wang, P.; Cao, H.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Li, P.Y.; Pang, X.H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Chen, X.L. Novel molecular insights into the catalytic mechanism of marine bacterial alginate lyase AlyGC from polysaccharide lyase Family 6. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4457–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garron, M.L.; Cygler, M. Uronic polysaccharide degrading enzymes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2014, 28, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kam, N.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, E.Y.; Kim, H.S. Molecular identification of a polyM-specific alginate lyase from Pseudomonas sp. strain KS-408 for degradation of glycosidic linkages between two mannuronates or mannuronate and guluronate in alginate. Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Yu, Y.; Yang, S.; Shi, X.; Mou, H.; Li, L. Expression and characterization of a new PolyG-specific alginate lyase from marine bacterium Microbulbifer sp. Q7. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.L.; Dong, S.; Xu, F.; Dong, F.; Li, P.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhou, B.C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Xie, B.B. Characterization of a new cold-adapted and salt-activated polysaccharide lyase family 7 alginate lyase from Pseudoalteromonas sp. SM0524. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Anraku, M.; Nakagawa, S.; Ojima, T. Discovery of a novel alginate lyase from Nitratiruptor sp. SB155-2 thriving at deep-sea hydrothermal vents and identification of the residues responsible for its heat stability. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 15551–15563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S.S.; Hehemann, J.H.; Polz, M.F.; Lee, J.K.; Zhao, H. Comparative biochemical characterization of three exolytic oligoalginate lyases from Vibrio splendidus reveals complementary substrate scope, temperature, and pH adaptations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4207–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonugli-Santos, R.C.; Dos Santos Vasconcelos, M.R.; Passarini, M.R.; Vieira, G.A.; Lopes, V.C.; Mainardi, P.H.; Dos Santos, J.A.; de Azevedo Duarte, L.; Otero, I.V.; da Silva Yoshida, A.M.; et al. Marine-derived fungi: Diversity of enzymes and biotechnological applications. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Yang, X.M.; Bao, M.M.; Wu, Y.; Yu, W.G.; Han, F. Family 13 carbohydrate-binding module of alginate lyase from Agarivorans sp. L11 enhances its catalytic efficiency and thermostability, and alters its substrate preference and product distribution. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.W.; Sun, Y.; Ni, F.; Ning, L.M.; Yao, Z. Characterization of a new endo-type alginate lyase from Vibrio sp. NJU-03. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, K.; Yamasaki, M.; Mikami, B.; Hashimoto, W.; Murata, K. Substrate recognition by family 7 alginate lyase from Sphingomonas sp. A1. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 380, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, N.L.; Monday, S.R.; Boyd, C.M.; Keen, N.T.; Ohman, D.E. Characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate lyase gene (algL): Cloning, sequencing, and expression in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 4780–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.; Lundqvist, L.C.; Jam, M.; Jeudy, A.; Barbeyron, T.; Sandstrom, C.; Michel, G.; Czjzek, M. Comparative characterization of two marine alginate lyases from Zobellia galactanivorans reveals distinct modes of action and exquisite adaptation to their natural substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23021–23037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, S.M.; Hudgens, J.W.; Heselpoth, R.D.; Bales, P.M.; Nelson, D.C. Characterization of AlgMsp, an alginate lyase from Microbulbifer sp. 6532A. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.J.; Hashimoto, W.; Miyake, O.; Okamoto, M.; Mikami, B.; Murata, K. Overexpression in Escherichia coli, purification, and characterization of Sphingomonas sp. A1 alginate lyases. Protein Expr. Purif. 2000, 19, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.S.; Zhou, J.G.; Li, X.; Peng, Q.; Lu, H.; Du, Y.G. Characterization of a new alginate lyase from newly isolated Flavobacterium sp. S20. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchimura, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Nogi, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Horikoshi, K. Cloning and sequencing of alginate lyase genes from deep-sea strains of Vibrio and Agarivorans and characterization of a new Vibrio enzyme. Mar. Biotechnol. 2010, 12, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.J.; Zhang, K.K.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, W.Z.; Lyu, Q.Q.; Ji, A.G. Characterization of a novel polyM-preferred alginate lyase from marine Vibrio splendidus OU02. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, O.; Ochiai, A.; Hashimoto, W.; Murata, K. Origin and diversity of alginate lyases of families PL-5 and -7 in Sphingomonas sp. strain A1. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 2891–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.N.; Wang, Q.B.; Lu, D.R.; Han, W.J.; Li, F.C. A novel bifunctional endolytic alginate lyase with variable alginate-degrading modes and versatile monosaccharide-producing properties. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.F.; Han, F.; Yu, W.G. Cloning, sequence analysis, and expression of gene alyPI encoding an alginate lyase from marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. CY24. Can. J. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.J.; Preston, J.F.; Ingram, L.O. Cloning of alginate lyase gene (alxM) and expression in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 1870–1872. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Uchimura, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Nogi, Y.; Horikoshi, K. A new high-alkaline alginate lyase from a deep-sea bacterium Agarivorans sp. Extremophiles 2009, 13, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, A.; Takadono, K.; Nishiyama, R.; Tajima, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Ojima, T. Characterization of an alginate lyase, FlAlyA, from Flavobacterium sp. strain UMI-01 and its expression in Escherichia coli. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4693–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Shi, H.; Zhou, J.; Tan, Z.B.; Yuan, M.D.; Yao, P.; Liu, X.Y. Characterization of a novel alginate lyase from marine bacterium Vibrio furnissii H1. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.W.; Ni, F.; Ning, L.M.; Sun, Y.; Yao, Z. Cloning and characterization of a new pH-stable alginate lyase with high salt tolerance from marine Vibrio sp. NJ-04. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.Y.; Wang, Q.Z.; Lu, M.Q.; Xu, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, R.C.; Liao, W.; Huang, S.S. AlgM4: A new salt-activated alginate lyase of the PL7 family with endolytic activity. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.W.; Ni, F.; Ning, L.M.; Yao, Z. Elucidation of degrading pattern and substrate recognition of a novel bifunctional alginate lyase from Flammeovirga sp. NJ-04 and its use for preparation alginate oligosaccharides. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.H.; Bang, M.A.; Jang, C.H.; Jo, G.H.; Jung, S.K.; Ki, S.H. Alginate oligosaccharide enhances LDL uptake via regulation of LDLR and PCSK9 expression. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkeborg, M.; Cheong, L.Z.; Gianfico, C.; Sztukiel, K.M.; Kristensen, K.; Glasius, M.; Xu, X.; Guo, Z. Alginate oligosaccharides: Enzymatic preparation and antioxidant property evaluation. Food Chem. 2014, 164, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Yin, H.; Zhao, X.M.; Wang, W.X.; Du, Y.G.; He, A.; Sun, K.G. The promoting effects of alginate oligosaccharides on root development in Oryza sativa L. mediated by auxin signaling. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhou, H.H.; Kang, M.Y.; Dong, R.P.; Zhao, J.W. Oligosaccharide nanomedicine of alginate sodium improves therapeutic results of posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cages for degenerative lumbar disease in osteoporosis patients by downregulating serum miR-155. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 8459–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.M.; Miyakawa, T.; Inoue, A.; Nishiyama, R.; Nakamura, A.; Asano, A.; Ojima, T.; Tanokura, M. Structural basis for controlling the enzymatic properties of polymannuronate preferred alginate lyase FlAlyA from the PL-7 family. Chem Commun. (Camb) 2018, 54, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Tokura, Y.; Mori, Y.; Mori, K.; Asakura, Y.; Usuda, Y.; Fukuda, H.; Chinen, A. Identification of enzymes responsible for extracellular alginate depolymerization and alginate metabolism in Vibrio algivorus. Appl. Microbial. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Wang, L.N.; Hao, J.H.; Xing, M.X.; Sun, J.J.; Sun, M. Purification and characterization of a new alginate lyase from marine bacterium Vibrio sp. SY08. Mar. Drugs 2016, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zhu, Y.M.; Men, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, Y.X. Purification and characterization of a novel alginate lyase from the marine bacterium Bacillus sp. Alg07. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Protein Name | Optimal pH/Temperature (°C) | Conserved Region QIH/QVH | Substrate Specificity | Products (DP) | Source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aly08 | 8.35/45 | QIH | PolyG | 2,3 | Vibrio sp. SY01 | This study |
| AlgNJU-03 | 7.0/30 | QIH | PolyG, polyM,alginate | 2,3,4 | Vibrio sp. NJU-03 | [20] |
| AlgMsp | 8.0/40 | QIH | PolyG | 2–5 | Microbulbifer sp. 6532A | [24] |
| A1-II’ | 7.5/40 | QIH | polyG,polyM | 3,4 | Sphingomonas sp.A1 | [29] |
| Aly2 | 6.0/40 | QIH | polyG | 2,3,4 | Flammeovirga sp. strain MY04 | [30] |
| AlyPI | 7.0/40 | QIH | polyG,polyM | - | Pseudoalteromonas sp. CY24. | [31] |
| Alg2A | 8.3/40 | QIH | polyG | 5,6,7 | Flavobacterium sp. S20 | [26] |
| AlxM | - | QVH | polyM | - | Photobacterium sp. ATCC 43367 | [32] |
| A1m | 9.0/30 | QIH | polyG | - | Agarivorans sp. JAM-A1m | [33] |
| A9mT | 7.5/30 | QVH | polyM | - | Vibrio sp. A9m | [27] |
| FlAlyA | 7.7/55 | QIH | polyM, polyG | 2–5 | Flavobacterium sp. strain UMI-01 | [34] |
| AlyH1 | 7.5/40 | QIH | polyG, alginate | 2,3,4 | Vibrio furnissii H1 | [35] |
| Reagent Added | Concentration (mM) | Relative Activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| None | - | 100.00 ± 0.24 |
| 10 | 382.22 ± 2.64 | |
| NaCl | 50 | 580.89 ± 4.36 |
| 300 | 865.96 ± 26.46 | |
| 800 | 647.33 ± 11.25 | |
| 3000 | 361.97 ± 10.74 | |
| SDS | 1 | 50.00 ± 3.32 |
| EDTA | 1 | 55.88 ± 8.60 |
| Al2(SO4)3 | 1 | 85.33 ± 10.63 |
| KCl | 1 | 99.67 ± 0.86 |
| KCl | 100 | 103.54 ± 0.16 |
| NiCl2 | 1 | 97.24 ± 2.20 |
| (NH4)2SO4 | 1 | 105.56 ± 1.37 |
| MnSO4 | 1 | 100.64 ± 1.78 |
| Li2SO4 | 1 | 103.91 ± 0.93 |
| ZnCl2 | 1 | 114.27 ± 2.48 |
| BaCl2 | 1 | 120.74 ± 17.14 |
| CoCl2 | 1 | 130.86 ± 4.03 |
| MnCl2 | 1 | 166.39 ± 5.47 |
| CaCl2 | 1 | 281.18 ± 29.18 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Bi, X.; Ren, Y.; Han, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Han, Y.; Yao, R.; Li, S. Characterization of an Alkaline Alginate Lyase with pH-Stable and Thermo-Tolerance Property. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050308
Wang Y, Chen X, Bi X, Ren Y, Han Q, Zhou Y, Han Y, Yao R, Li S. Characterization of an Alkaline Alginate Lyase with pH-Stable and Thermo-Tolerance Property. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(5):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050308
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yanan, Xuehong Chen, Xiaolin Bi, Yining Ren, Qi Han, Yu Zhou, Yantao Han, Ruyong Yao, and Shangyong Li. 2019. "Characterization of an Alkaline Alginate Lyase with pH-Stable and Thermo-Tolerance Property" Marine Drugs 17, no. 5: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050308
APA StyleWang, Y., Chen, X., Bi, X., Ren, Y., Han, Q., Zhou, Y., Han, Y., Yao, R., & Li, S. (2019). Characterization of an Alkaline Alginate Lyase with pH-Stable and Thermo-Tolerance Property. Marine Drugs, 17(5), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050308




