Characterization of Two Toxin-Antitoxin Systems in Deep-Sea Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 02999
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
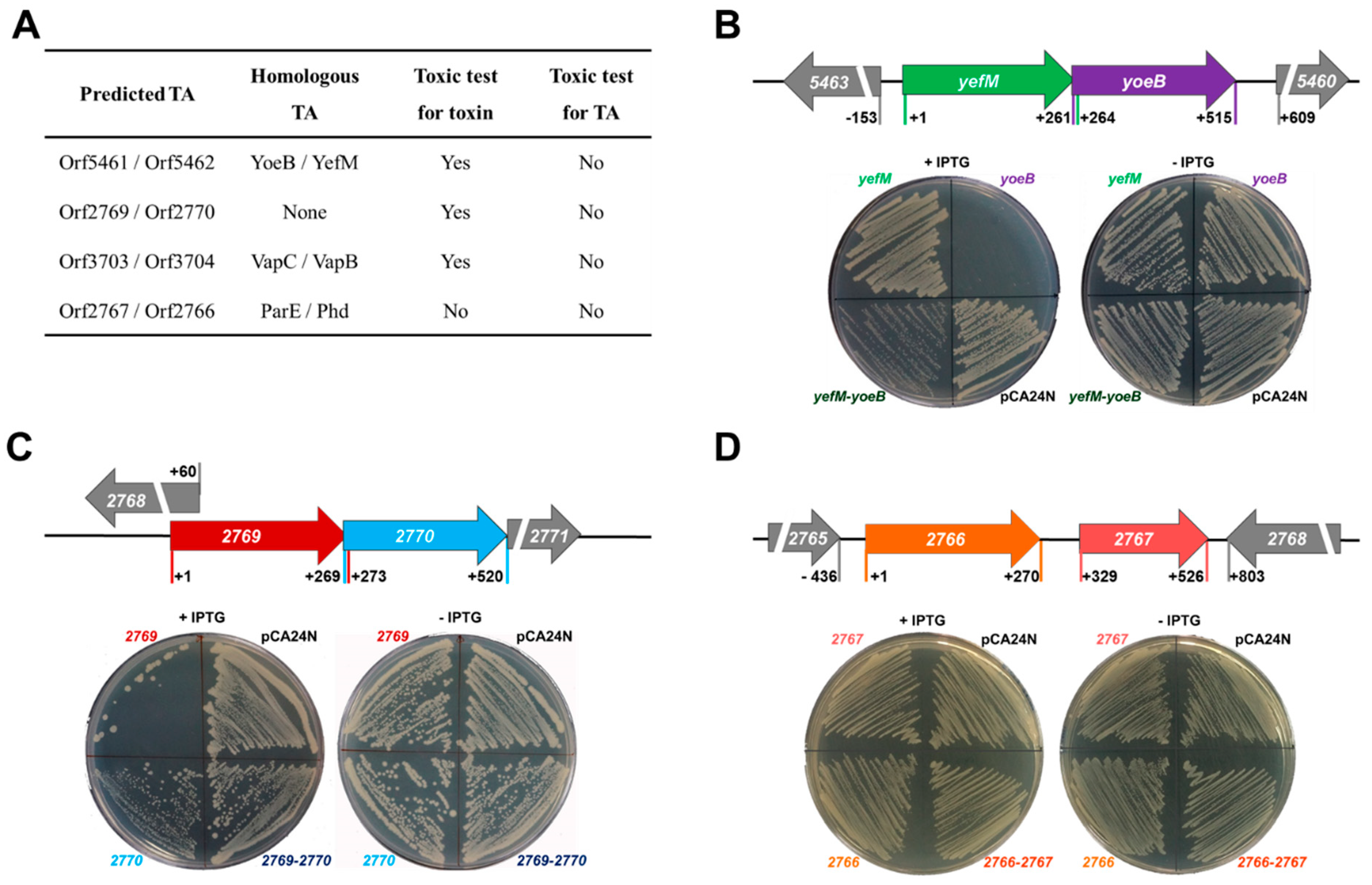
2.1. Identification of Two TA Pairs in Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 02999
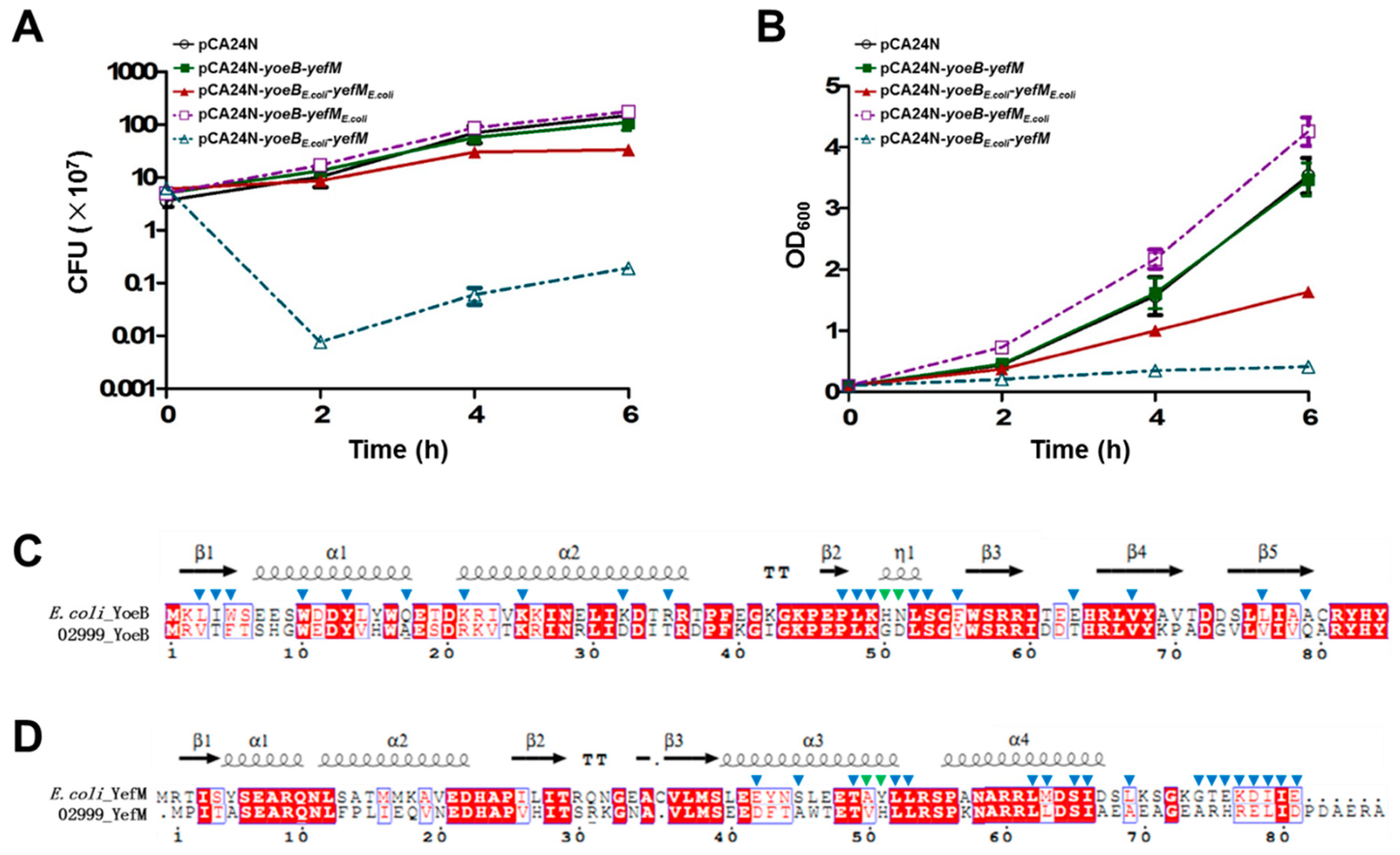
2.2. Characterization of the Type-II TA Pair YoeB/YefM
2.3. Cross-Complementation of YoeB/YefM from E. coli and Streptomyces sp.
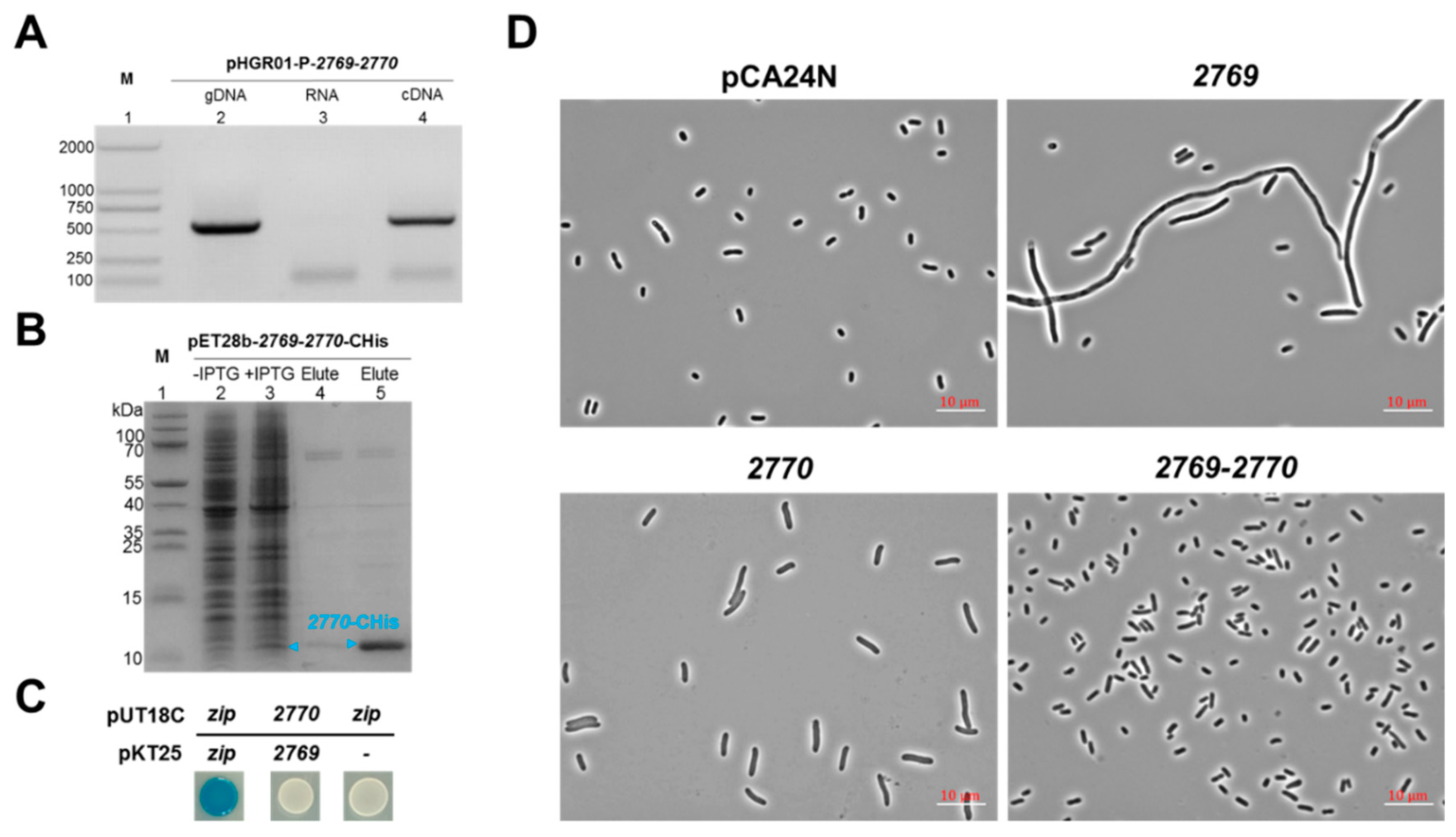
2.4. Characterization of a Novel TA Pair Orf2769/Orf2770
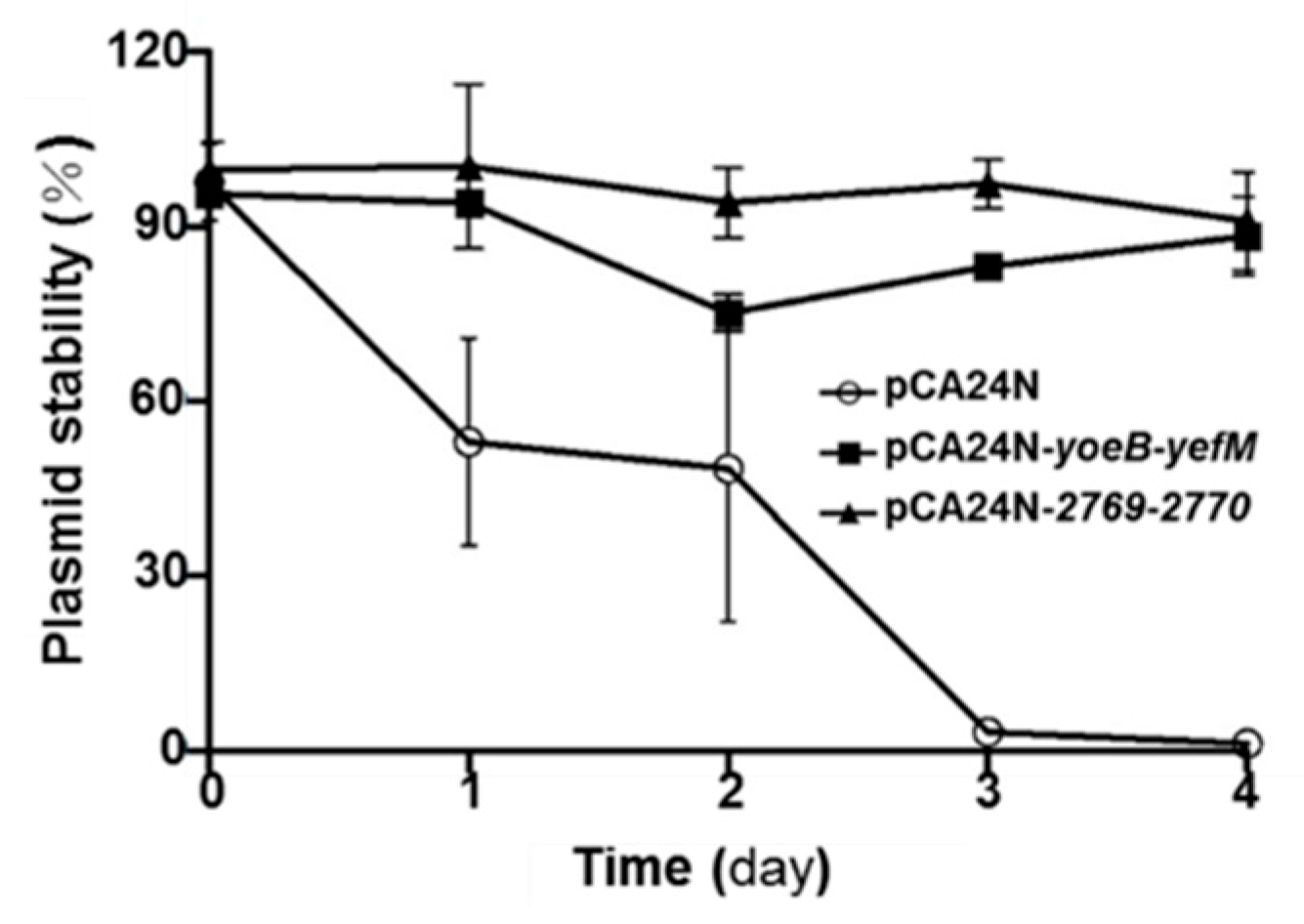
2.5. YoeB/YefM and Orf2769/Orf2770 Both Stabilize Plasmids in E. coli
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Procedures
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids and Growth Conditions
4.2. Construction of Expression Plasmids
4.3. Protein Expression and Purification
4.4. RNA Isolation, RT-PCR and qRT-PCR
4.5. Live/Dead Staining
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. BACTH Assay
4.8. Plasmid Stability Test
4.9. Sequence Alignment
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harms, A.; Brodersen, D.E.; Mitarai, N.; Gerdes, K. Toxins, targets, and triggers: An overview of toxin-antitoxin biology. Mol. Cell 2018, 70, 768–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, F.; Van Melderen, L. Toxins-antitoxins: Diversity, evolution and function. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. 2011, 46, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.M.; Gollan, B.; Helaine, S. Toxin-antitoxin systems: Reversible toxicity. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 36, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, R.; Peti, W. Toxin-antitoxin systems in bacterial growth arrest and persistence. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.T.; Moreno-Cordoba, I.; Yeo, C.C.; Espinosa, M. Toxin-antitoxin genes of the Gram-positive pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae: So few and yet so many. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2012, 76, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaychikova, M.V.; Zakharevich, N.V.; Sagaidak, M.O.; Bogolubova, N.A.; Smirnova, T.G.; Andreevskaya, S.N.; Larionova, E.E.; Alekseeva, M.G.; Chernousova, L.N.; Danilenko, V.N. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Type II toxin-antitoxin systems: Genetic polymorphisms and functional properties and the possibility of their use for genotyping. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato-Marquez, D.; Moreno-Cordoba, I.; Figueroa, V.; Diaz-Orejas, R.; Garcia-del Portillo, F. Distinct type I and type II toxin-antitoxin modules control Salmonella lifestyle inside eukaryotic cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, T.L.; Wood, T.K. The HigB/HigA toxin/antitoxin system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa influences the virulence factors pyochelin, pyocyanin, and biofilm formation. Microbiol. Open 2016, 5, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shen, M.; Lu, S.; Le, S.; Tan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Shen, W.; Guo, K.; Yang, Y.; et al. Identification and characterization of the HicAB toxin-antitoxin system in the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Toxins 2016, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, M.; White, J.C.; Murphy, T.; Ames, J.R.; Bourne, C.R. The toxin from a ParDE toxin-antitoxin system found in Pseudomonas aeruginosa offers protection to cells challenged with anti-gyrase antibiotics. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 111, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fineran, P.C.; Blower, T.R.; Foulds, I.J.; Humphreys, D.P.; Lilley, K.S.; Salmond, G.P. The phage abortive infection system, ToxIN, functions as a protein-RNA toxin-antitoxin pair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, F.; Short, F.L.; Voss, J.E.; Blower, T.R.; Orme, A.L.; Whittaker, T.E.; Luisi, B.F.; Salmond, G.P. Co-evolution of quaternary organization and novel RNA tertiary interactions revealed in the crystal structure of a bacterial protein-RNA toxin-antitoxin system. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 9529–9540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakre, C.D.; Phung, T.N.; Huang, D.; Laub, M.T. A bacterial toxin inhibits DNA replication elongation through a direct interaction with the beta sliding clamp. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piscotta, F.J.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Link, A.J. ParST is a widespread toxin-antitoxin module that targets nucleotide metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankevicius, G.; Ariza, A.; Ahel, M.; Ahel, I. The toxin-antitoxin system DarTG catalyzes reversible ADP-ribosylation of DNA. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurenas, D.; Chatterjee, S.; Konijnenberg, A.; Sobott, F.; Droogmans, L.; Garcia-Pino, A.; Van Melderen, L. AtaT blocks translation initiation by N-acetylation of the initiator tRNA(fMet). Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurenas, D.; Van Melderen, L.; Garcia-Pino, A. Mechanism of regulation and neutralization of the AtaR-AtaT toxin-antitoxin system. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsan, D.; Place, A.; Fucich, D.; Chen, F. Toxin-antitoxin systems in estuarine Synechococcus strain CB0101 and their transcriptomic responses to environmental stressors. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Behiels, E.; Felix, J.; Elegheert, J.; Vergauwen, B.; Devreese, B.; Savvides, S.N. The bacterial antitoxin HipB establishes a ternary complex with operator DNA and phosphorylated toxin HipA to regulate bacterial persistence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 10134–10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, X.; Shi, F.; Wang, X. Identification and characterization of a HEPN-MNT family type II toxin-antitoxin in Shewanella oneidensis. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 8, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, P.; Zeng, Z.; Li, B.; Tang, K.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Type II toxin/antitoxin system ParESO /CopASO stabilizes prophage CP4So in Shewanella oneidensis. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 1224–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schippers, A.; Neretin, L.N.; Kallmeyer, J.; Ferdelman, T.G.; Cragg, B.A.; Parkes, R.J.; Jorgensen, B.B. Prokaryotic cells of the deep sub-seafloor biosphere identified as living bacteria. Nature 2005, 433, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Yao, J.; Sun, C.; Wen, Z.; Wang, X. Characterization of the deep-sea Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 02999 derived VapC/VapB toxin-antitoxin system in Escherichia coli. Toxins 2016, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.T.; Chen, I.T.; Yang, Y.T.; Ko, T.P.; Huang, Y.T.; Huang, J.Y.; Huang, M.F.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, S.S.; et al. The opportunistic marine pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus becomes virulent by acquiring a plasmid that expresses a deadly toxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10798–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.B.; Mandi, A.; Li, S.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Zhang, W.J.; Tian, X.P.; Zhang, H.B.; Li, H.X.; Zhang, W.M.; Zhang, S.; et al. N-N-coupled indolo-sesquiterpene atropo-diastereomers from a marine-derived actinomycete. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5256–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; et al. Activation and characterization of a cryptic gene cluster reveals a cyclization cascade for polycyclic tetramate macrolactams. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Yu, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.M.; Shen, Y.; Tian, C.; et al. Characterization of the flavoenzyme XiaK as an N-hydroxylase and implications in indolosesquiterpene diversification. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 5067–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, B.; Zheng, L.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C. Genome mining and activation of a silent PKS/NRPS gene cluster direct the production of totopotensamides. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 5697–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Tian, X.; Zhang, S.; Ju, J.; Zhang, C. Identification and characterization of xiamycin A and oxiamycin gene cluster reveals an oxidative cyclization strategy tailoring indolosesquiterpene biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8996–9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevin, E.W.; Barloy-Hubler, F. RASTA-Bacteria: A web-based tool for identifying toxin-antitoxin loci in prokaryotes. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, K.; Hanaoka, F. Conformational change in the catalytic site of the ribonuclease YoeB toxin by YefM antitoxin. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.C.; Helinski, D.R. Definition of a minimal plasmid stabilization system from the broad-host-range plasmid RK2. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 8119–8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazit, E.; Sauer, R.T. Stability and DNA binding of the phd protein of the phage P1 plasmid addiction system. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 2652–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.L.; Wood, T.K.; Peti, W.; Page, R. Structure of the Escherichia coli antitoxin MqsA (YgiT/b3021) bound to its gene promoter reveals extensive domain rearrangements and the specificity of transcriptional regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, C.; Cherny, I.; Khoo, S.K.; de Lacoba, M.G.; Chan, W.T.; Yeo, C.C.; Gazit, E.; Espinosa, M. The yefM-yoeB toxin-antitoxin systems of Escherichia coli and Streptococcus pneumoniae: Functional and structural correlation. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Xu, J.; Ren, S.; Li, J.; Xia, M.; Chen, H.; Bei, W. Identification and characterization of the chromosomal yefM-yoeB toxin-antitoxin system of Streptococcus suis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibb, M.J. Understanding and manipulating antibiotic production in actinomycetes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrancken, K.; Anne, J. Secretory production of recombinant proteins by Streptomyces. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anne, J.; Maldonado, B.; Van Impe, J.; Van Mellaert, L.; Bernaerts, K. Recombinant protein production and streptomycetes. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 158, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Ding, M.Z.; Luo, H.; Gao, F.; Yuan, Y.J. Complete genome sequencing and antibiotics biosynthesis pathways analysis of Streptomyces lydicus 103. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevillano, L.; Diaz, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Inouye, M.; Santamaria, R.I. Identification of the first functional toxin-antitoxin system in Streptomyces. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tai, C.; Deng, Z.X.; Gan, J.H.; Oggioni, M.R.; Ou, H.Y. Identification and characterization of chromosomal relBE toxin-antitoxin locus in Streptomyces cattleya DSM46488. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevillano, L.; Diaz, M.; Santamaria, R.I. Development of an antibiotic marker-free platform for heterologous protein production in Streptomyces. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevillano, L.; Diaz, M.; Santamaria, R.I. Stable expression plasmids for Streptomyces based on a toxin-antitoxin system. Microb. Cell Fact. 2013, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Quiroga, C.; Chen, Q.; McAnulty, M.J.; Benedik, M.J.; Wood, T.K.; Wang, X. RalR (a DNase) and RalA (a small RNA) form a type I toxin-antitoxin system in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 6448–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brielle, R.; Pinel-Marie, M.L.; Felden, B. Linking bacterial type I toxins with their actions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 30, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.K.; Gerdes, K. RelE toxins from Bacteria and Archaea cleave mRNAs on translating ribosomes, which are rescued by tmRNA. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcus, V.L.; McKenzie, J.L.; Robson, J.; Cook, G.M. The PIN-domain ribonucleases and the prokaryotic VapBC toxin-antitoxin array. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2011, 24, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schifano, J.M.; Cruz, J.W.; Vvedenskaya, I.O.; Edifor, R.; Ouyang, M.; Husson, R.N.; Nickels, B.E.; Woychik, N.A. tRNA is a new target for cleavage by a MazF toxin. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 1256–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.; Dewan, P.C.; Barua, B.; Varadarajan, R. Additional role for the ccd operon of F-plasmid as a transmissible persistence factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12497–12502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, E.; Castro-Roa, D.; Zenkin, N.; Gerdes, K. Molecular mechanism of bacterial persistence by HipA. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Ara, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Takai, Y.; Okumura, Y.; Baba, M.; Datsenko, K.A.; Tomita, M.; Wanner, B.L.; Mori, H. Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: The Keio collection. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladant, D.; Ullmann, A. Bordatella pertussis adenylate cyclase: A toxin with multiple talents. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, M.; Ara, T.; Arifuzzaman, M.; Ioka-Nakamichi, T.; Inamoto, E.; Toyonaga, H.; Mori, H. Complete set of ORF clones of Escherichia coli ASKA library (a complete set of E. coli K-12 ORF archive): Unique resources for biological research. DNA Res. 2005, 12, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Jin, M.; Ju, L.; Mao, Y.; Gao, H. Evidence for function overlapping of CymA and the cytochrome bc1 complex in the Shewanella oneidensis nitrate and nitrite respiration. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 3181–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimova, G.; Pidoux, J.; Ullmann, A.; Ladant, D. A bacterial two-hybrid system based on a reconstituted signal transduction pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5752–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Bacterial Strains/Plasmids | Genotype or Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 02999 | ||
| wild-type | A marine-derived Streptomyces sp., cultured in AM6 medium | [29] |
| E. coli strains | ||
| K-12 BW25113 | lacIqrrnBT14 ΔlacZWJ16 hsdR514 ΔaraBADAH33 ΔrhaBADLD78 rph-1 | [52] |
| K-12 BW25113∆lon | ∆lon ∆kmR | [52] |
| K-12 BW25113∆clpP | ∆clpP ∆kmR | [52] |
| K-12 BW25113∆clpX | ∆clpX ∆kmR | [52] |
| BL21(DE3) | F-ompT hsdSB(rB-mB-) gal dcm λ(DE3) Ω PtacUV5::T7 polymerase | Novagen |
| WM3064 | thrB1004 pro thi rpsL hsdS lacZΔM15 RP4-1360) Δ(araBAD)567 ΔdapA1341::[erm pir(wt)] | W. Metcalf, UIUC |
| Rosetta (DE3) | F- ompT hsdSB(rB- mB-) gal dcm (DE3) pRARE(argU, argW, ilex, glyT, leuW, proL)(CmR) | Novagen |
| BTH101 | F-,cya-99,araD139,galE15,galK16,rpsL1(StrR),hsdR2,mcrA1,mcrB1 | [53] |
| Plasmids | ||
| pCA24N | CmR; lacIq, IPTG inducible expression vector q q | [54] |
| pCA24N-2769 | CmR; lacIq, PT5-lac::2769 q, PT5-lac::vapB q, PT5-lac::vapB | this study |
| pCA24N-2770 | CmR; lacIq, PT5-lac::2770 | this study |
| pCA24N-2769-2770 | CmR; lacIq, PT5-lac::2769-2770 | this study |
| pCA24N-yoeB | CmR; lacIq, PT5-lac::yoeB | this study |
| pCA24N-yefM | CmR; lacIq, PT5-lac::yefM | this study |
| pCA24N-yoeB-yefM | CmR; lacIq, PT5-lac::yoeB-yefM | this study |
| pCA24N-yoeBE.coli-yefME.coli | CmR; lacIq, PT5-lac::yoeBE.coli-yefME.coli | this study |
| pCA24N-yoeB-yefME.coli | CmR; lacIq, PT5-lac::yoeB-yefME.coli | this study |
| pCA24N-yoeBE.coli-yefM | CmR; lacIq, PT5-lac::yoeBE.coli-yefM | this study |
| pCA24N-yoeBE.coli | CmR; lacIq, PT5-lac::yoeBE.coli | [54] |
| pCA24N-ghoT | CmR; lacIq, PT5-lac:: ghoT | [54] |
| pHGR01 | KmR; R6K ori, promoterless lacZ reporter vector | [55] |
| pHGR01-P-2769-2770 | KmR; R6K ori, fused 2769-2770 promoter in pHGR01 | this study |
| pHGR01-P-yoeB-yefM | KmR; R6K ori, fused yoeB-yefM promoter in pHGR01 | this study |
| pET28b | KmR; lacIq, IPTG inducible expression vector | Novagen |
| pET28b-NHis-yefM-yoeB | KmR; lacIq, pET28b PT7-lac:: yoeB-yefM with N-terminal His-tagged | this study |
| pET28b-yefM-yoeB | KmR; lacIq, pET28b PT7-lac:: yoeB-yefM without His-tagged | this study |
| pET28b-2769-2770-CHis | KmR; lacIq, pET28b PT7-lac:: 2769-2770 with C-terminal His-tagged | this study |
| pKT25 | KmR; encoding T25 fragment | [56] |
| pKT25-2769 | KmR; 2769 was fused to the C termini of adenylate cyclase in pKT25 | this study |
| pUT18C | AmpR; encoding T18 fragment | [56] |
| pUT18C-2770 | AmpR; 2770 was fused to the C termini of adenylate cyclase in pUT18C | this study |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, W.; Yao, J.; Tang, K.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. Characterization of Two Toxin-Antitoxin Systems in Deep-Sea Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 02999. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040211
Zhan W, Yao J, Tang K, Li Y, Guo Y, Wang X. Characterization of Two Toxin-Antitoxin Systems in Deep-Sea Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 02999. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(4):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040211
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Waner, Jianyun Yao, Kaihao Tang, Yangmei Li, Yunxue Guo, and Xiaoxue Wang. 2019. "Characterization of Two Toxin-Antitoxin Systems in Deep-Sea Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 02999" Marine Drugs 17, no. 4: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040211
APA StyleZhan, W., Yao, J., Tang, K., Li, Y., Guo, Y., & Wang, X. (2019). Characterization of Two Toxin-Antitoxin Systems in Deep-Sea Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 02999. Marine Drugs, 17(4), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040211





