Two New Piperazine-Triones from a Marine-Derived Streptomycetes sp. Strain SMS636
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
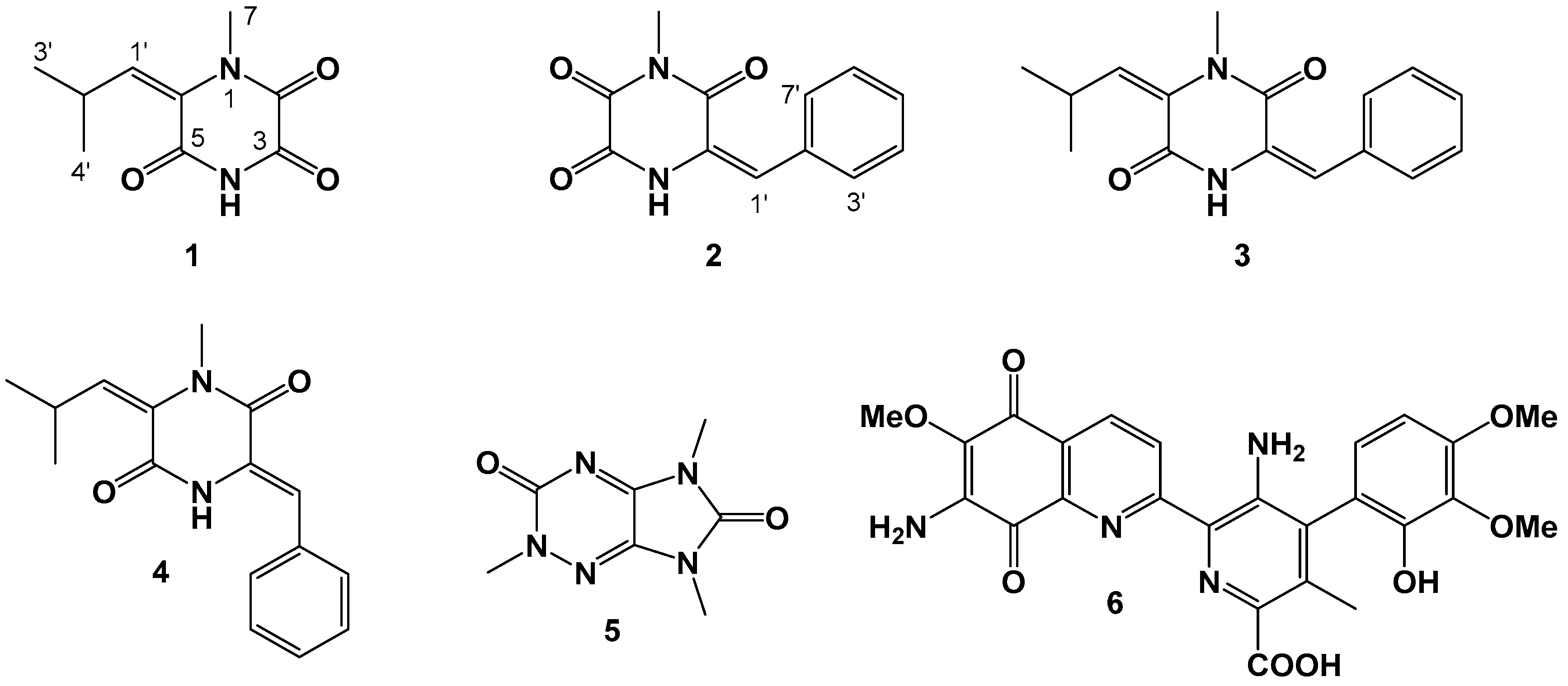
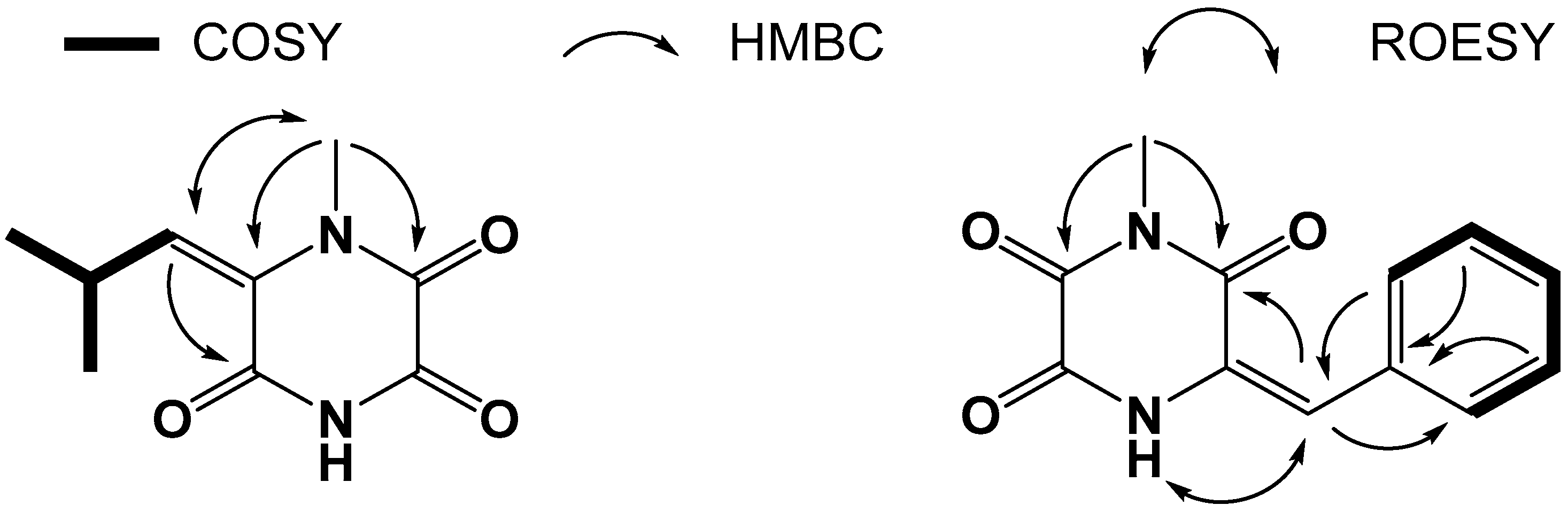
2.1. Structure Elucidation
2.2. Biological Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Microbial Material
3.3. Fermentation and Extraction
3.4. Isolation and Purification
3.4.1. Lansai E (1)
3.4.2. Lansai F (2)
3.5. Antimicrobial Assays
3.6. Anti-Bacillus Calmette Guérin (BCG) Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooike, M.; Nozawa, K.; Kawai, K.I. An epitetrathiodioxopiperazine related to emestrin from Emericella foveolata. Photochemistry 1997, 46, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seya, H.; Nozawa, K.; Udagawa, S.; Nakajima, S.; Kawai, K. Studies on fungal products. IX.: Dethiosecoemestrin, a new metabolite related to emestrin, from Emericella striata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 2411–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.J.; Li, X.M.; Li, C.S.; Wang, B.G. Alkaloid and anthraquinone derivatives produced by the marine-derived endophytic fungus Eurotium rubrum. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2012, 95, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usami, Y.; Yamaguchi, J.; Numata, A. Gliocladins A–C and Glioperazine; cytotoxic dioxo- or trioxopiperazine metabolites from a Gliocladium Sp. deparated from a sea hare. Heterocycles 2004, 63, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Jiang, N.; Mei, Y.N.; Chu, Y.L.; Ge, H.M.; Song, Y.C.; Ng, S.W.; Tan, R.X. An antibacterial metabolite from Lasiodiplodia pseudotheobromae F2. Phytochemistry 2014, 100, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, H.; Hasegawa, A.; Tsumagari, N.; Nakai, R.; Ogawa, T.; Kanda, Y. MPC1001 and its analogues: New antitumor agents from the fungus Cladorrhinum species. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 4101–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Si, L.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, D.; Lin, W. Neoechinulin B and its analogues as potential entry inhibitors of influenza viruses, targeting viral hemagglutinin. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 93, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbetta, M.; Casnati, G.; Pochini, A.; Selva, A. Neoechinuline: a new indole metabolite from Aspergillus amstelodami. Tetrahedron Lett. 1969, 10, 4457–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Lu, Z.Y.; Tao, H.W.; Zhu, T.J.; Fang, Y.C.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhu, W.M. Isoechinulin-type alkaloids, Variecolorins A–L, from Halotolerant Aspergillus variecolor. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Hua, H.; Bai, J.; Pei, Y.H. 1H and 13C NMR assignments of two new iperazine-trione from the fungus Penicillium crustosum YN-HT-15. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2015, 53, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamjam, M.; Sivalingam, P.; Deng, Z.; Hong, K. Deep sea actinomycetes and their secondary metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procópio, R.E.; Silva, I.R.; Martins, M.K.; Azevedo, J.L.; Araújo, J.M. Antibiotics produced by Streptomyces. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Ding, T.; Li, J. Medicinal purposes: Bioactive metabolites from marine-derived organisms. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuntiwachwuttikul, P.; Taechowisan, T.; Wanbanjob, A.; Thadanitia, S.; Taylor, W.C. Lansai A–D, secondary metabolites from Streptomyces sp. SUC1. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 7583–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, D.J.; Sefton, M.A. 1-N-methyl-(6E)-(2-methylpropylidene)-(3Z)-3-(phenylmethylene)-2,5-piperazinedione, a metabolite from Streptomyces albus. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lim, K.L.; Yeo, S.L.; Xu, X.; Sim, M.M.; Ting, A.E.; Wang, Y.; Yee, S.; Tan, Y.H.; Pallen, C.J. Isolation of a novel protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor, 2-methyl-fervenulone, and its precursors from Streptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lown, J.W.; Beglieiter, A. Studies relating to aziridine antitumor antibiotics. part II 13C and lH nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of mitomycin C and structurally related streptonigrin. Can. J. Chem. 1974, 52, 2331–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Song, F.; Xiao, X.; Huang, P.; Li, L.; Monte, A.; Abdel-Mageed, W.M.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; He, W.; et al. Abyssomicins from the South China Sea deep-sea sediment Verrucosispora sp.: Natural thioether Michael addition adducts as antitubercular prodrugs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 1231–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.R.; Lawrence, C.H.; Embleton, J.; Calhoun, L.A. More chemistry of the thaxtomin phytotoxins. Phytochemistry 2003, 64, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, G.; Reichert, M.; Hemberger, Y. The absolute configuration of streptonigrin. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Position | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH, mult (J in Hz) | δC | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δC | |
| 2 | 152.4 | 158.7 | ||
| 3 | 155.6 | 125.9 | ||
| 4 | 12.01, brs | 11.44, s | ||
| 5 | 160.2 | 151.6 | ||
| 6 | 127.8 | 156.7 | ||
| 7 | 3.17, s | 30.4 | 3.07, s | 26.8 |
| 1′ | 5.81, d (9.0) | 136.6 | 6.77, s | 124.3 |
| 2′ | 3.94, m | 26.3 | 133.7 | |
| 3′ | 1.05, d (6.6) | 22.7 | 7.53, d (7.8) | 130.1 |
| 4′ | 1.05, d (6.6) | 22.7 | 7.34, dd (7.8, 7.8) | 127.7 |
| 5′ | 7.31, dd (7.8, 7.8) | 128.3 | ||
| 6′ | 7.34, dd (7.8, 7.8) | 127.7 | ||
| 7′ | 7.53, d (7.8) | 130.1 | ||
| Compounds | S. aureusa | MRSA a | E. colib | P. aeruginosab | BCGc | C. albicansd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >40 | >100 |
| 2 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >40 | >100 |
| 3 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >40 | >100 |
| 4 | 12.5 | 25 | >100 | >100 | >40 | >100 |
| 5 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >40 | >100 |
| 6 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 100 | 100 | 1.25 | >100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Han, J.; Lin, R.; Polyak, S.W.; Song, F. Two New Piperazine-Triones from a Marine-Derived Streptomycetes sp. Strain SMS636. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17030186
Xu X, Han J, Lin R, Polyak SW, Song F. Two New Piperazine-Triones from a Marine-Derived Streptomycetes sp. Strain SMS636. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(3):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17030186
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiuli, Jiahui Han, Rui Lin, Steven W. Polyak, and Fuhang Song. 2019. "Two New Piperazine-Triones from a Marine-Derived Streptomycetes sp. Strain SMS636" Marine Drugs 17, no. 3: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17030186
APA StyleXu, X., Han, J., Lin, R., Polyak, S. W., & Song, F. (2019). Two New Piperazine-Triones from a Marine-Derived Streptomycetes sp. Strain SMS636. Marine Drugs, 17(3), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17030186





